Submitted:
28 August 2023
Posted:
29 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
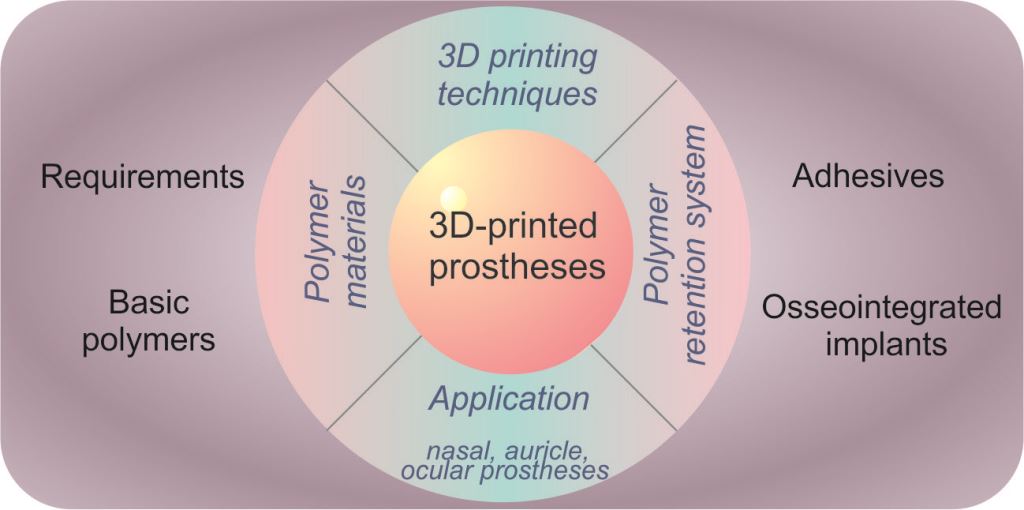
Keywords:
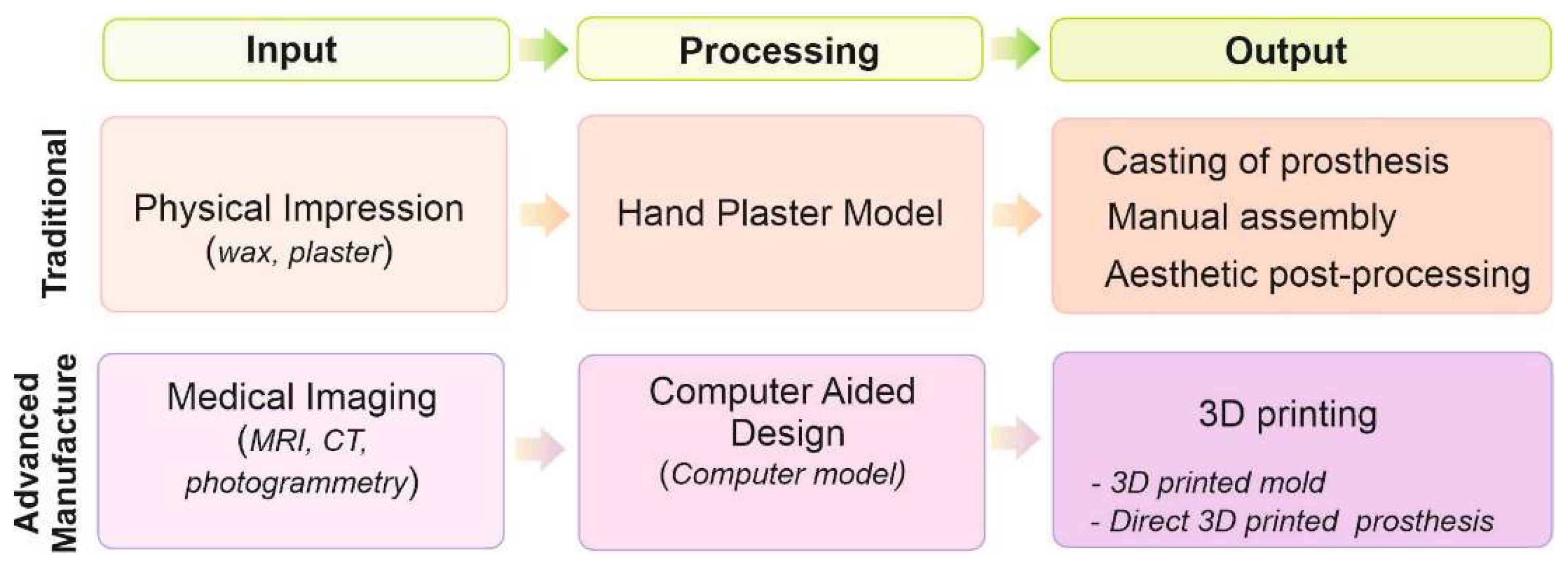
1. Introduction
2. 3D printing technology
2.1. Background
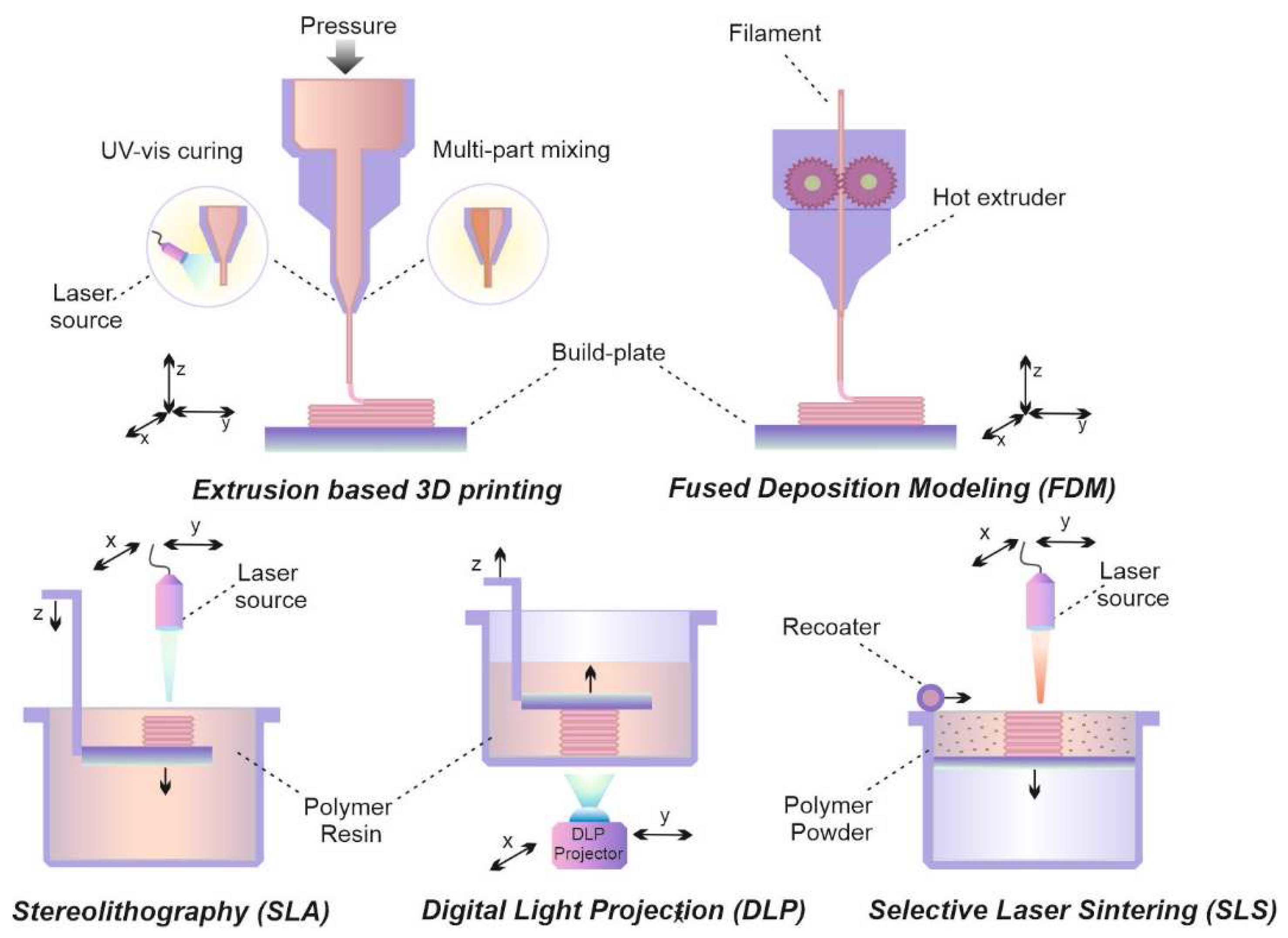
2.2. Extrusion-based 3D printing
2.3. Lithography-based 3D printing
3. Polymers for 3D printing of prostheses
3.1. Relevant characteristics of prostheses
3.2. Basic polymers
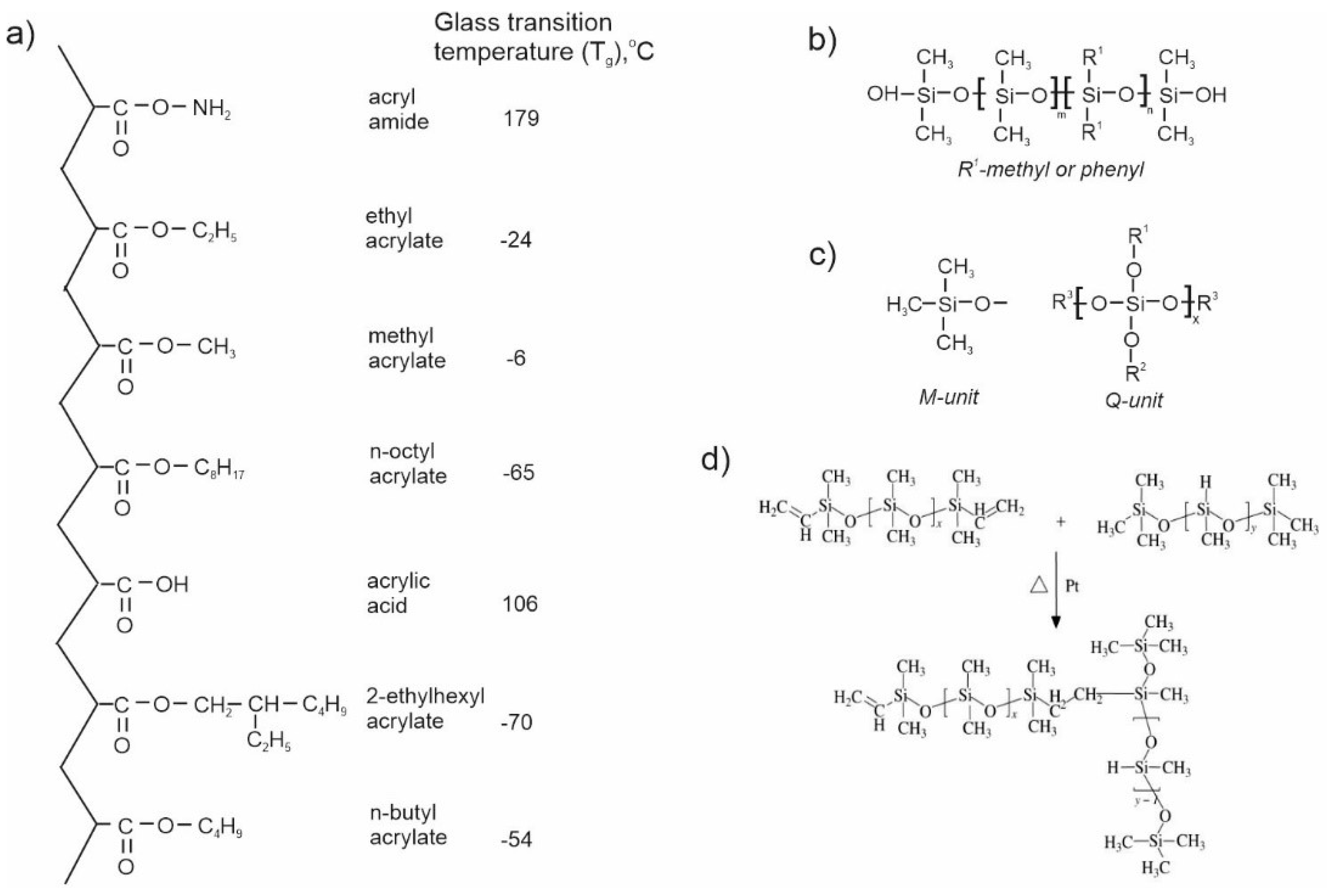
3.2.1. Acrylic polymers (resins)
3.2.2. Polyurethane Elastomer (Thermoset)
3.2.3. Polyesters
3.2.4. Styrene-based polymers
3.2.5. Silicones
4. Polymers in retention systems
4.1. Adhesives
- -
- hold the prosthesis in place for at least 12 h a day;
- -
- do not cause tissue irritation;
- -
- do not damage tissue when adhesive peels off the skin;
- -
- dry quickly after application
4.2. Implants
5. Special features of polymers
6. Application of 3D-printed prostheses
6.1. Nasal prostheses
6.2. Auricular prostheses
6.3. Ocular prostheses
7. Conclusions and Future Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dewan:, M.C.; Rattani, A.; Gupta, S.; Baticulon, R.E.; Hung, Y.-C.; Punchak, M.; Agrawal, A.; Adeleye, A.O.; Shrime, M.G.; Rubiano, A.M.; et al. Estimating the global incidence of traumatic brain injury. Journal of Neurosurgery 2019, 130, 1080–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, A.I.R.; Menon, D.K.; Adelson, P.D.; Andelic, N.; Bell, M.J.; Belli, A.; Bragge, P.; Brazinova, A.; Büki, A.; Chesnut, R.M.; et al. Traumatic brain injury: integrated approaches to improve prevention, clinical care, and research. The Lancet Neurology 2017, 16, 987–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyberg, E.L.; Farris, A.L.; Hung, B.P.; Dias, M.; Garcia, J.R.; Dorafshar, A.H.; Grayson, W.L. 3D-Printing Technologies for Craniofacial Rehabilitation, Reconstruction, and Regeneration. Annals of Biomedical Engineering 2017, 45, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, B.; Owen, R.; Bahmaee, H.; Wally, Z.; Sreenivasa Rao, P.; Reilly, G.C. Composite porous scaffold of PEG/PLA support improved bone matrix deposition in vitro compared to PLA-only scaffolds. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A 2018, 106, 1334–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, K. Poly(trimethylene carbonate)-based polymers engineered for biodegradable functional biomaterials. Biomaterials Science 2016, 4, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finch, J. The ancient origins of prosthetic medicine. The Lancet 2011, 377, 548–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.H.; Hodges, J.S. Effects of processing parameters on physical properties of the silicone maxillofacial prosthetic materials. Dental Materials 1999, 15, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer-Glover, A.M.; Shellock, F.G. Pre-MRI Procedure Screening: Recommendations and Safety Considerations for Biomedical Implants and Devices. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging 2000, 12, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ring, M. Special Topic: PDF Only The History of Maxillofacial Prosthetics. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 1991, 87, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jindal, S.K.; Sherriff, M.; Waters, M.G.; Smay, J.E.; Coward, T.J. Development of a 3D printable maxillofacial silicone: Part II. Optimization of moderator and thixotropic agent. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry 2018, 119, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liravi, F.; Toyserkani, E. A hybrid additive manufacturing method for the fabrication of silicone bio-structures: 3D printing optimization and surface characterization. Materials & Design 2018, 138, 46–61. [Google Scholar]
- Lanzara, D.R.; Viswambaran, D.M.; Kumar, D.D. Maxillofacial prosthetic materials: current status and recent advances: A comprehensive review. International Journal of Applied Dental Sciences 2021, 7, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, S.K.; Cruz, R.L.J.; Ross, M.T.; Woodruff, M.A. Past, Present, and Future of Soft-Tissue Prosthetics: Advanced Polymers and Advanced Manufacturing. Advanced Materials 2020, 32, 2001122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, G.K.; Jain, D.; Goel, D.; Juneja, P. Rehabilitation after Surgical Treatment for Retinoblastoma: Ocular Prosthesis for a 6-Month-Old Child. Journal of Prosthodontics 2012, 21, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemon, J.C.; Chambers, M.S.; Wesley, P.J.; Martin, J.W. Technique for fabricating a mirror-image prosthetic ear. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry 1996, 75, 292–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, R.L.J.; Ross, M.T.; Powell, S.K.; Woodruff, M.A. Advancements in Soft-Tissue Prosthetics Part A: The Art of Imitating Life. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritham, C.H. Fundamentals of Facial Prosthetics. JPO Journal of Prosthetics and Orthotics 1995, 7, 22A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.H.; Castleberry, D.J. An assessment of recent advances in external maxillofacial materials. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry 1980, 43, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murtezani, I.; Sharma, N.; Thieringer, F.M. Medical 3D printing with a focus on Point-of-Care in Cranio- and Maxillofacial Surgery. A systematic review of literature. Annals of 3D Printed Medicine 2022, 6, 100059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, C.; van Langeveld, M.C.; Donoso, L.A. Innovations in 3D printing: a 3D overview from optics to organs. British Journal of Ophthalmology 2014, 98, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadad, H.; Boos Lima, F.B.; Shirinbak, I.; Porto, T.S.; Chen, J.E.; Guastaldi, F.P. The impact of 3D printing on oral and maxillofacial surgery. Journal of 3D Printing in Medicine 2023, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazayeri, H.E.; Kang, S.; Masri, R.M.; Kuhn, L.; Fahimipour, F.; Vanevenhoven, R.; Thompson, G.; Gheisarifar, M.; Tahriri, M.; Tayebi, L. Advancements in craniofacial prosthesis fabrication: A narrative review of holistic treatment. The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics 2018, 10, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitemeier, B.; Notni, G.; Heinze, M.; Schöne, C.; Schmidt, A.; Fichtner, D. Optical modeling of extraoral defects. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry 2004, 91, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, S.; Zhou, B.; Bi, Y.; Wu, G. Computer-assisted technique for the design and manufacture of realistic facial prostheses. British Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 2010, 48, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorsandi, D.; Fahimipour, A.; Abasian, P.; Saber, S.S.; Seyedi, M.; Ghanavati, S.; Ahmad, A.; De Stephanis, A.A.; Taghavinezhaddilami, F.; Leonova, A.; et al. 3D and 4D printing in dentistry and maxillofacial surgery: Printing techniques, materials, and applications. Acta Biomaterialia 2021, 122, 26–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Generalova, A. N.; Demina, P.A.; Akasov, R.A.; Khaydukov, E.V. Photopolymerization in 3D printing of tissue-engineered constructs for regenerative medicine. Russian Chemical Reviews 2023, 92, RCR5068. [Google Scholar]
- Phogat, A.; Chhabra, D.; Sindhu, V.; Ahlawat, A. Analysis of wear assessment of FDM printed specimens with PLA, multi-material and ABS via hybrid algorithms. Materials Today: Proceedings 2022, 62, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbolat, I.T.; Hospodiuk, M. Current advances and future perspectives in extrusion-based bioprinting. Biomaterials 2016, 76, 321–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, R.; Mehrotra, D. 3D bioprinting and craniofacial regeneration. Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research 2020, 10, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baca, D.; Ahmad, R. The impact on the mechanical properties of multi-material polymers fabricated with a single mixing nozzle and multi-nozzle systems via fused deposition modeling. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 2020, 106, 4509–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhou, Z.; Gou, J.; Hui, D. 3D printing of polymer matrix composites: A review and prospective. Composites Part B: Engineering 2017, 110, 442–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, N.; Wei, W.; Hu, X.; Tan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Bi, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H. Assessing the dynamic extrusion-based 3D printing process for power-law fluid using numerical simulation. Journal of Food Engineering 2020, 275, 109861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savelyev, A.G.; Sochilina, A. V.; Akasov, R.A.; Mironov, A. V.; Kapitannikova, A.Y.; Borodina, T.N.; Sholina, N. V.; Khaydukov, K. V.; Zvyagin, A. V.; Generalova, A.N.; et al. Facile Cell-Friendly Hollow-Core Fiber Diffusion-Limited Photofabrication. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, T.D.; Kashani, A.; Imbalzano, G.; Nguyen, K.T.Q.; Hui, D. Additive manufacturing (3D printing): A review of materials, methods, applications and challenges. Composites Part B: Engineering 2018, 143, 172–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, S.; Jessop, Z.M.; Al-Sabah, A.; Whitaker, I.S. Biofabrication: ‘Printability’’ of Candidate Biomaterials for Extrusion Based 3D Printing: State-of-the-Art (Adv. Healthcare Mater. 16/2017).’ Advanced Healthcare Materials 2017, 6.
- Ozbolat, I.T.; Hospodiuk, M. Current advances and future perspectives in extrusion-based bioprinting. Biomaterials 2016, 76, 321–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovsianikov, A.; Schlie, S.; Ngezahayo, A.; Haverich, A.; Chichkov, B.N. Two-photon polymerization technique for microfabrication of CAD-designed 3D scaffolds from commercially available photosensitive materials. Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine 2007, 1, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, X.; Roach, D.J.; Wu, J.; Hamel, C.M.; Ding, Z.; Wang, T.; Dunn, M.L.; Qi, H.J. Advances in 4D Printing: Materials and Applications. Advanced Functional Materials 2019, 29, 1805290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, F.; Mehdi, M.; Hassani, N.S.; Liu, X.; Ni, J. A review of 4D printing. Materials & Design 2017, 122, 42–79. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzoli, A. Selective laser sintering in biomedical engineering. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing 2013, 51, 245–256. [Google Scholar]
- Dwivedi, R.; Mehrotra, D. 3D bioprinting and craniofacial regeneration. Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research 2020, 10, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaee, M.; Crane, N.B. Binder jetting: A review of process, materials, and methods. Additive Manufacturing 2019, 28, 781–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billiet, T.; Vandenhaute, M.; Schelfhout, J.; Van Vlierberghe, S.; Dubruel, P. A review of trends and limitations in hydrogel-rapid prototyping for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6020–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahzad, K.; Deckers, J.; Zhang, Z.; Kruth, J.-P.; Vleugels, J. Additive manufacturing of zirconia parts by indirect selective laser sintering. Journal of the European Ceramic Society 2014, 34, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, W.C. Apparatus for Production of Three-Dimensional Objects by Stereolithography 1984.
- Levato, R.; Lim, K.S.; Li, W.; Asua, A.U.; Peña, L.B.; Wang, M.; Falandt, M.; Bernal, P.N.; Gawlitta, D.; Zhang, Y.S.; et al. High-resolution lithographic biofabrication of hydrogels with complex microchannels from low-temperature-soluble gelatin bioresins. Materials Today Bio 2021, 12, 100162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, B.E.; Bhattacharya, I.; Heidari, H.; Shusteff, M.; Spadaccini, C.M.; Taylor, H.K. Volumetric additive manufacturing via tomographic reconstruction. Science 2019, 363, 1075–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumbleston, J.R.; Shirvanyants, D.; Ermoshkin, N.; Janusziewicz, R.; Johnson, A.R.; Kelly, D.; Chen, K.; Pinschmidt, R.; Rolland, J.P.; Ermoshkin, A.; et al. Continuous liquid interface production of 3D objects. Science 2015, 347, 1349–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgersen, J.; Qin, X.-H.; Li, Z.; Ovsianikov, A.; Liska, R.; Stampfl, J. Hydrogels for Two-Photon Polymerization: A Toolbox for Mimicking the Extracellular Matrix. Advanced Functional Materials 2013, 23, 4542–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrubudin, N.; Koshy, P.; Alipal, J.; Kadir, M.H.A.; Lee, T.C. Challenges of 3D printing technology for manufacturing biomedical products: A case study of Malaysian manufacturing firms. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, A.; Bose, S.; Narayan, R. Translation of 3D printed materials for medical applications. MRS Bulletin 2022, 47, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanveer, W.; Ridwan-Pramana, A.; Molinero-Mourelle, P.; Koolstra, J.H.; Forouzanfar, T. Systematic Review of Clinical Applications of CAD/CAM Technology for Craniofacial Implants Placement and Manufacturing of Nasal Prostheses. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2021, 18, 3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3D Printing in Plastic Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery; Di Rosa, L., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2022. ISBN 978-3-031-10557-9.
- Zhou, L.; Fu, J.; He, Y. A Review of 3D Printing Technologies for Soft Polymer Materials. Advanced Functional Materials 2020, 30, 2000187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, T.; Waters, M.; Jagger, R. Analysis of the properties of silicone rubber maxillofacial prosthetic materials. Journal of Dentistry 2003, 31, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Harbi, F.A.; Ayad, N.M.; Saber, M.A.; ArRejaie, A.S.; Morgano, S.M. Mechanical behavior and color change of facial prosthetic elastomers after outdoor weathering in a hot and humid climate. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry 2015, 113, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younis, I.; Gault, D.; Sabbagh, W.; Kang, N. V. Patient satisfaction and aesthetic outcomes after ear reconstruction with a Branemark-type, bone-anchored, ear prosthesis: A 16 year review. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery 2010, 63, 1650–1655. [Google Scholar]
- Frade, J.P.; Arthington-Skaggs, B.A. Effect of serum and surface characteristics on Candida albicans biofilm formation. Mycoses 2011, 54, e154–e162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantini, M.; De Crescenzio, F.; Ciocca, L. Design and Rapid Manufacturing of anatomical prosthesis for facial rehabilitation. International Journal on Interactive Design and Manufacturing (IJIDeM) 2013, 7, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, Jr.; Kumar, Bm.; Ahila, S.; Rajendiran, S. Materials in maxillo-facial prosthesis. Journal of Indian Academy of Dental Specialist Researchers 2015, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanohkan, S.; Kukiattrakoon, B.; Peampring, C. Tensile bond strength of facial silicone and acrylic resin using different primers. Journal of Orofacial Sciences 2017, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Fu, J.; He, Y. A Review of 3D Printing Technologies for Soft Polymer Materials. Advanced Functional Materials 2020, 30, 2000187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, S.M.; Sonawane, R.Y.; More, A.P. Thermoplastic polyurethane for three-dimensional printing applications: A review. Polymers for Advanced Technologies 2023, 34, 2061–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemon, J.C.; Kiat-amnuay, S.; Gettleman, L.; Martin, J.W.; Chambers, M.S. Facial prosthetic rehabilitation: preprosthetic surgical techniques and biomaterials. Current Opinion in Otolaryngology & Head and Neck Surgery 2005, 13, 255–262. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.R.; Kim, S.H.; Ko, J.; Baek, S.W.; Park, Y.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Yoon, J.S. A Pilot Clinical Study of Ocular Prosthesis Fabricated by Three-dimensional Printing and Sublimation Technique. Korean Journal of Ophthalmology 2021, 35, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guevara, C.; Matouk, M. In-office 3D printed guide for rhinoplasty. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 2021, 50, 1563–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuseir, A.; Hatamleh, M.M.; Alnazzawi, A.; Al-Rabab’ah, M.; Kamel, B.; Jaradat, E. Direct 3D Printing of Flexible Nasal Prosthesis: Optimized Digital Workflow from Scan to Fit. Journal of Prosthodontics 2019, 28, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diken Türksayar, A.; Saglam, S.; Bulut, A. Retention systems used in maxillofacial prostheses: A review. Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice 2019, 22, 1629. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y. Application of the three-dimensionally printed biodegradable polycaprolactone (PCL) mesh in repair of orbital wall fractures. Journal of Cranio-Maxillofacial Surgery 2019, 47, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.H.; Shim, J.-H.; Lee, H.; Kim, B.Y.; Lee, J.-S.; Jung, J.W.; Yun, W.-S.; Baek, C.H.; Rhie, J.-W.; Cho, D.-W. Reconstruction of Complex Maxillary Defects Using Patient-specific 3D-printed Biodegradable Scaffolds. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery - Global Open 2018, 6, e1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witek, L.; Khouri, K.S.; Coelho, P.G.; Flores, R.L. Patient-specific 3D Models for Autogenous Ear Reconstruction. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery - Global Open 2016, 4, e1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berens, A.M.; Newman, S.; Bhrany, A.D.; Murakami, C.; Sie, K.C.Y.; Zopf, D.A. Computer-Aided Design and 3D Printing to Produce a Costal Cartilage Model for Simulation of Auricular Reconstruction. Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery 2016, 155, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, A.B.; Campbell, A.A.; Petris, C.; Kazim, M. Low-Cost 3D Printing Orbital Implant Templates in Secondary Orbital Reconstructions. Ophthalmic Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery 2017, 33, 376–380. [Google Scholar]
- Borghi, A.; Ruggiero, F.; Tenhagen, M.; Schievano, S.; Ponniah, A.; Dunaway, D.; O’Hara, J.; Ong, J.; Britto, J.A. Design and manufacturing of a patient-specific nasal implant for congenital arhinia: Case report. JPRAS Open 2019, 21, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhitya, M.; Sunarso, S.; Muis, A. Comparison of Popular Three-Dimensional Printing Materials for Oral and Maxillofacial Surgical Guidance Model Oral and Maxillofacial Surgical Guidance Model. Journal of Dentistry Indonesia 2020, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.D.; Kim, Y.; Park, E. Patient-Specific Augmentation Rhinoplasty Using a Three-Dimensional Simulation Program and Three-Dimensional Printing. Aesthetic Surgery Journal 2017, 37, 988–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimoto, S.; Sotsuka, Y.; Kawai, K.; Fujita, K.; Kakibuchi, M. Three-Dimensional Mock-Up Model for Chondral Framework in Auricular Reconstruction, Built with a Personal Three-Dimensional Printer. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 2014, 134, 180e–181e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unkovskiy, A.; Spintzyk, S.; Brom, J.; Huettig, F.; Keutel, C. Direct 3D printing of silicone facial prostheses: A preliminary experience in digital workflow. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry 2018, 120, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unkovskiy, A.; Wahl, E.; Huettig, F.; Keutel, C.; Spintzyk, S. Multimaterial 3D printing of a definitive silicone auricular prosthesis: An improved technique. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry 2021, 125, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denour, E.; Woo, A.S.; Crozier, J.; Van Dongen, C. The Use of Three-Dimensional Photography and Printing in the Fabrication of a Nasal Prosthesis. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery 2020, Publish Ah.
- Moore, D.J.; Glaser, Z.R.; Tabacco, M.J.; Linebaugh, M.G. Evaluation of polymeric materials for maxillofacial prosthetics. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry 1977, 38, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stansbury, J.W.; Idacavage, M.J. 3D printing with polymers: Challenges among expanding options and opportunities. Dental Materials 2016, 32, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goiato, M.; Freitas, E.; dos Santos, D.; de Medeiros, R.; Sonego, M. Acrylic Resin Cytotoxicity for Denture Base: Literature Review. Advances in Clinical and Experimental Medicine 2015, 24, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiaschi, P.; Pavanello, M.; Imperato, A.; Dallolio, V.; Accogli, A.; Capra, V.; Consales, A.; Cama, A.; Piatelli, G. Surgical results of cranioplasty with a polymethylmethacrylate customized cranial implant in pediatric patients: a single-center experience. Journal of Neurosurgery: Pediatrics 2016, 17, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goiato, M.; Freitas, E.; dos Santos, D.; de Medeiros, R.; Sonego, M. Acrylic Resin Cytotoxicity for Denture Base: Literature Review. Advances in Clinical and Experimental Medicine 2015, 24, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espalin, D.; Arcaute, K.; Rodriguez, D.; Medina, F.; Posner, M.; Wicker, R. Fused deposition modeling of patient-specific polymethylmethacrylate implants. Rapid Prototyping Journal 2010, 16, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.S.; Sugavaneswaran, M.; Arumaikkannu, G.; Mukherjee, B. An innovative method of ocular prosthesis fabrication by bio-CAD and rapid 3-D printing technology: A pilot study. Orbit 2017, 36, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, C.C.; Nguyen, T.T.; Kim, S.; Kim, J. Effects of 3D Printing-Line Directions for Stretchable Sensor Performances. Materials 2021, 14, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, K.; Zhang, H.; Guo, S. Study on the forming and sensing properties of laser-sintered TPU/CNT composites for plantar pressure sensors. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 2021, 112, 2211–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wei, Y.; Li, Y. 3D printing of shape memory polymer for functional part fabrication. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 2016, 84, 2079–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanei, S.H.R.; Popescu, D. 3D-Printed Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites: A Systematic Review. Journal of Composites Science 2020, 4, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covolan, V.L.; Di Ponzio, R.; Chiellini, F.; Grillo Fernandes, E.; Solaro, R.; Chiellini, E. Polyurethane Based Materials for the Production of Biomedical Materials. Macromolecular Symposia 2001, 169, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touchet, T.J.; Cosgriff-Hernandez, E.M. Advances in Polyurethane Biomaterials. In; Cooper, S.L., Guan, J., Eds.; Elsevier, New York, 2016; pp. 3–22.
- Xiao, J.; Gao, Y. The manufacture of 3D printing of medical grade TPU. Progress in Additive Manufacturing 2017, 2, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, Z.C.; Christ, J.F. Printing polymer blends through in situ active mixing during fused filament fabrication. Additive Manufacturing 2020, 36, 101233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmatabadi, D.; Ghasemi, I.; Baniassadi, M.; Abrinia, K.; Baghani, M. 3D printing of PLA-TPU with different component ratios: Fracture toughness, mechanical properties, and morphology. Journal of Materials Research and Technology 2022, 21, 3970–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, S.M.; Sonawane, R.Y.; More, A.P. Thermoplastic polyurethane for three-dimensional printing applications: A review. Polymers for Advanced Technologies 2023, 34, 2061–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, D.; Griffith, M.; Venkatraman, S.S. Polycaprolactone-based biomaterials for tissue engineering and drug delivery: Current scenario and challenges. International Journal of Polymeric Materials and Polymeric Biomaterials 2016, 65, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; Wan, Q. The Application of Polycaprolactone in Three-Dimensional Printing Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. Polymers 2021, 13, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, A.; Hollister, S.J.; Dalton, P.D. Additive manufacturing of polymer melts for implantable medical devices and scaffolds. Biofabrication 2017, 9, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyberg, E.; Rindone, A.; Dorafshar, A.; Grayson, W.L. Comparison of 3D-Printed Poly-ɛ-Caprolactone Scaffolds Functionalized with Tricalcium Phosphate, Hydroxyapatite, Bio-Oss, or Decellularized Bone Matrix. Tissue Engineering Part A 2017, 23, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, G.; Jiang, S.; Xu, X.; Ke, Y. Electrospun aligned PLLA/PCL/HA composite fibrous membranes and their in vitro degradation behaviors. Materials Letters 2012, 82, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Hochleitner, G.; Woodfield, T.; Groll, J.; Dalton, P.D.; Amsden, B.G. Additive Manufacturing of a Photo-Cross-Linkable Polymer via Direct Melt Electrospinning Writing for Producing High Strength Structures. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stichler, S.; Böck, T.; Paxton, N.; Bertlein, S.; Levato, R.; Schill, V.; Smolan, W.; Malda, J.; Teßmar, J.; Blunk, T.; et al. Double printing of hyaluronic acid/poly(glycidol) hybrid hydrogels with poly( ε -caprolactone) for MSC chondrogenesis. Biofabrication 2017, 9, 044108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pretula, J.; Slomkowski, S.; Penczek, S. Polylactides—Methods of synthesis and characterization. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2016, 107, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, S.; Anderson, D.G.; Langer, R. Physical and mechanical properties of PLA, and their functions in widespread applications — A comprehensive review. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2016, 107, 367–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito Corcione, C.; Gervaso, F.; Scalera, F.; Padmanabhan, S.K.; Madaghiele, M.; Montagna, F.; Sannino, A.; Licciulli, A.; Maffezzoli, A. Highly loaded hydroxyapatite microsphere/ PLA porous scaffolds obtained by fused deposition modelling. Ceramics International 2019, 45, 2803–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritz, U.; Gerke, R.; Götz, H.; Stein, S.; Rommens, P.M. A New Bone Substitute Developed from 3D-Prints of Polylactide (PLA) Loaded with Collagen I: An In Vitro Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2017, 18, 2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchewka, J.; Laska, J. Processing of poly-l-lactide and poly(l-lactide-co-trimethylene carbonate) blends by fused filament fabrication and fused granulate fabrication using RepRap 3D printer. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 2020, 106, 4933–4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.M.; Devine, J.N. PEEK biomaterials in trauma, orthopedic, and spinal implants. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 4845–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekin, S.; Cangül, S.; Adıgüzel, Ö.; Değer, Y. Areas for use of PEEK material in dentistry. International Dental Research 2018, 8, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylläri, V.; Ruoko, T.-P.; Järvelä, P. The effects of UV irradiation to polyetheretherketone fibres – Characterization by different techniques. Polymer Degradation and Stability 2014, 109, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, J. Enthalpic relaxation in semi-crystalline PEEK. Polymer 2002, 43, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Termoplasti, Z.; Modeliranje, N. Processing poly (ether etherketone) on a 3D printer for thermoplastic modelling, Materiali in Tehnologije 2013, 47, 715–721. [Google Scholar]
- Cicala, G.; Latteri, A.; Del Curto, B.; Lo Russo, A.; Recca, G.; Farè, S. Engineering Thermoplastics for Additive Manufacturing: A Critical Perspective with Experimental Evidence to Support Functional Applications. Journal of Applied Biomaterials & Functional Materials 2017, 15, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaoyong, S.; Liangcheng, C.; Honglin, M.; Peng, G.; Zhanwei, B.; Cheng, L. Experimental Analysis of High Temperature PEEK Materials on 3D Printing Test. In Proceedings of the 2017 9th International Conference on Measuring Technology and Mechatronics Automation (ICMTMA); IEEE, 2017; pp. 13–16.
- Vaezi, M.; Yang, S. Extrusion-based additive manufacturing of PEEK for biomedical applications. Virtual and Physical Prototyping 2015, 10, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Tian, X.; Li, D.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, F.; Shi, C. Influence of thermal processing conditions in 3D printing on the crystallinity and mechanical properties of PEEK material. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 2017, 248, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupin, S.; Lame, O.; Barrès, C.; Charmeau, J.-Y. Microstructural origin of physical and mechanical properties of polyamide 12 processed by laser sintering. European Polymer Journal 2012, 48, 1611–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong-Ji, W.; Xin-hua, L.; Qing-ding, W.; Lingling, W. Optimizing process parameters for selective laser sintering based on neural network and genetic algorithm. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 2009, 42, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, S.A.; Ashany, J.Z.; Aghchai, A.J.; Abolghasemi, A. Experimental investigation of process parameters on layer thickness and density in direct metal laser sintering: a response surface methodology approach. Virtual and Physical Prototyping 2017, 12, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Wu; Liu, X.; Guo; Wei Nano-TiO2/PEEK bioactive composite as a bone substitute material: in vitro and in vivo studies. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 2012; 1215. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monich, P.R.; Henriques, B.; Novaes de Oliveira, A.P.; Souza, J.C.M.; Fredel, M.C. Mechanical and biological behavior of biomedical PEEK matrix composites: A focused review. Materials Letters 2016, 185, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Teoh, J.E.M.; Suntornnond, R.; Chua, C.K. Design and 3D Printing of Scaffolds and Tissues. Engineering 2015, 1, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskies, M.; Jordan, J.O.; Fang, D.; Abdallah, M.-N.; Hier, M.P.; Mlynarek, A.; Tamimi, F.; Tran, S.D. Improving PEEK bioactivity for craniofacial reconstruction using a 3D printed scaffold embedded with mesenchymal stem cells. Journal of Biomaterials Applications 2016, 31, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHutchion, L.; Aalto, D. Simulation of tissue-prosthesis margin interface by using surface scanning and digital design for auricular prostheses. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry 2021, 125, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jockusch, J.; Ozcan, M. Additive manufacturing of dental polymers: An overview on processes, materials and applications. Dental Materials Journal 2020, 39, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Singh, R.; Farina, I. On the 3D printing of recycled ABS, PLA and HIPS thermoplastics for structural applications. PSU Research Review 2018, 2, 115–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaveh, M.; Badrossamay, M.; Foroozmehr, E.; Hemasian Etefagh, A. Optimization of the printing parameters affecting dimensional accuracy and internal cavity for HIPS material used in fused deposition modeling processes. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 2015, 226, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, M.; Potgieter, J.; Archer, R.; Arif, K.M. Effect of Material and Process Specific Factors on the Strength of Printed Parts in Fused Filament Fabrication: A Review of Recent Developments. Materials 2019, 12, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echte, A. Rubber-Toughened Styrene Polymers. In; 1989; pp. 15–64.
- Quan, H.; Zhang, T.; Xu, H.; Luo, S.; Nie, J.; Zhu, X. Photo-curing 3D printing technique and its challenges. Bioactive Materials 2020, 5, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, C.R.; Torrado Perez, A.R.; Roberson, D.A.; Shemelya, C.M.; MacDonald, E.; Wicker, R.B. Novel ABS-based binary and ternary polymer blends for material extrusion 3D printing. Journal of Materials Research 2014, 29, 1859–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzois, G.L. Evaluation of a New Silicone Elastomer for Maxillofacial Prostheses. Journal of Prosthodontics 1995, 4, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goiato, M.C.; Haddad, M.F.; Santos, D.M. dos; Pesqueira, A.A.; Moreno, A. Hardness evaluation of prosthetic silicones containing opacifiers following chemical disinfection and accelerated aging. Brazilian Oral Research 2010, 24, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, A. Maxillofacial Prosthetic Materials- An Inclination Towards Silicones. JOURNAL OF CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC RESEARCH 2014. [CrossRef]
- Chalian, V.A.; Phillips, R.W. Materials in maxillofacial prosthetics. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research 1974, 8, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakirov, A. V.; Krasheninnikov, S. V.; Shcherbina, M.A.; Meshkov, I.B.; Kalinina, A.A.; Gorodov, V. V.; Tatarinova, E.A.; Muzafarov, A.M.; Chvalun, S.N. True Molecular Composites: Unusual Structure and Properties of PDMS-MQ Resin Blends. Polymers 2022, 15, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, Z.; Mark, J.E. Biomimetic materials: recent developments in organic-inorganic hybrids. Materials Science and Engineering: C 1998, 6, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, M.; Ghomi, E.R.; Venkatraman, P.D.; Ramakrishna, S. Silicone-based biomaterials for biomedical applications: Antimicrobial strategies and 3D printing technologies. Journal of Applied Polymer Science 2021, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colas, A.; Curtis, J. Silicones. In Handbook of Polymer Applications in Medicine and Medical Devices; Elsevier, 2013; pp. 131–143.
- Muslov, S.A.; Polyakov, D.I.; Lotkov, A.I.; Stepanov, A.G.; Arutyunov, S.D. Measurement and Calculation of Mechanical Properties of Silicone Rubber. Russian Physics Journal 2021, 63, 1525–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santawisuk, W.; Kanchnavasita, W.; Sirisisna, C.; Harniattisai, C. Dynamic viscoelastic properties of experimental silicone soft lining materials. Dental Materials Journal 2010, 29, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Kiat-amnuay, S.; Powers, J.M.; Zhao, Y. Effect of nano-oxide concentration on the mechanical properties of a maxillofacial silicone elastomer. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry 2008, 100, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhao, H.; Gao, Q.; Xia, B.; Fu, J. Research on the printability of hydrogels in 3D bioprinting. Scientific Reports 2016, 6, 29977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekštytė, S.; Malinauskas, M.; Juodkazis, S. Three-dimensional laser micro-sculpturing of silicone: towards bio-compatible scaffolds. Optics Express 2013, 21, 17028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordeiro, P.G.; Disa, J.J. Challenges in midface reconstruction. Seminars in Surgical Oncology 2000, 19, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Serriah, M.M.; McGowan, D.A.; Moos, K.F.; Bagg, J. Extra-oral craniofacial endosseous implants and radiotherapy. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 2003, 32, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobein, M.V.; Coto, N.P.; Crivello Junior, O.; Lemos, J.B.D.; Vieira, L.M.; Pimentel, M.L.; Byrne, H.J.; Dias, R.B. Retention systems for extraoral maxillofacial prosthetic implants: a critical review. British Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 2017, 55, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldstein, M.M.; Dormidontova, E.E.; Khokhlov, A.R. Pressure sensitive adhesives based on interpolymer complexes. Progress in Polymer Science 2015, 42, 79–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applications of Pressure-Sensitive Products; Benedek, I., Feldstein, M.M., Eds.; CRC Press, 2008. ISBN 9780429150517.
- Droesbeke, M.A.; Aksakal, R.; Simula, A.; Asua, J.M.; Du Prez, F.E. Biobased acrylic pressure-sensitive adhesives. Progress in Polymer Science 2021, 117, 101396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.B.; Durfee, L.D.; Ekeland, R.A.; McVie, J.; Schalau, G.K. Recent advances in silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology 2007, 21, 605–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiat-amnuay, S.; Gettleman, L.; Goldsmith, L.J. Effect of multi-adhesive layering on retention of extraoral maxillofacial silicone prostheses in vivo. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry 2004, 92, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goiato, M.C.; Delben, J.A.; Monteiro, D.R.; dos Santos, D.M. Retention Systems to Implant-Supported Craniofacial Prostheses. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery 2009, 20, 889–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrektsson, T.; Brånemark, P.-I.; Hansson, H.-A.; Lindström, J. Osseointegrated Titanium Implants: Requirements for Ensuring a Long-Lasting, Direct Bone-to-Implant Anchorage in Man. Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica 1981, 52, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjellström, A. Osseointegrated implants for replacement of absent or defective ears. Clinics in Plastic Surgery 1990, 17, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Arnaoutakis, D.; Kadakia, S.; Vest, A.; Sawhney, R.; Ducic, Y. Osseointegrated Implants and Prosthetic Reconstruction Following Skull Base Surgery. Seminars in Plastic Surgery 2017, 31, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu, J.A.; Boahene, K. Update of patient-specific maxillofacial implant. Current Opinion in Otolaryngology & Head and Neck Surgery 2015, 23, 261–264. [Google Scholar]
- Binder, W.J. Custom-Designed Facial Implants. Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America 2008, 16, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scolozzi, P. Maxillofacial Reconstruction Using Polyetheretherketone Patient-Specific Implants by “Mirroring” Computational Planning. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery 2012, 36, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.M.; Boahene, K.D.O.; Byrne, P.J. Use of Customized Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) Implants in the Reconstruction of Complex Maxillofacial Defects. Archives of Facial Plastic Surgery 2009, 11, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes da Silva, A.L.; Borba, A.M.; Simão, N.R.; Pedro, F.L.M.; Borges, A.H.; Miloro, M. Customized Polymethyl Methacrylate Implants for the Reconstruction of Craniofacial Osseous Defects. Case Reports in Surgery 2014, 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haug, S.P.; Richard, G.E.; Margiotti, E.; Winkler, M.M.; Moore, D.J. An In Vivo Evaluation of Adhesives Used in Extraoral Maxillofacial Prostheses. Journal of Prosthodontics 1995, 4, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatamleh, M.M.; Polyzois, G.L.; Nuseir, A.; Hatamleh, K.; Alnazzawi, A. Mechanical Properties and Simulated Aging of Silicone Maxillofacial Elastomers: Advancements in the Past 45 Years. Journal of Prosthodontics 2016, 25, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, D.M.; Goiato, M.C.; Sinhoreti, M.A.C.; Fernandes, A.Ú.R.; Ribeiro, P. do P.; Dekon, S.F. de C. Color Stability of Polymers for Facial Prosthesis. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery 2010, 21, 54–58.
- Bettencourt, A.F.; Neves, C.B.; de Almeida, M.S.; Pinheiro, L.M.; Oliveira, S.A. e; Lopes, L.P.; Castro, M.F. Biodegradation of acrylic based resins: A review. Dental Materials 2010, 26, e171–e180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleni, P.N.; Krokida, M.K.; Polyzois, G.L.; Charitidis, C.A.; Koumoulos, E.P.; Tsikourkitoudi, V.P.; Ziomas, I. Mechanical behaviour of a poydimethylsiloxane elastomer after outdoor weathering in two different weathering locations. Polymer Degradation and Stability 2011, 96, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.M.; Jamayet, N. Bin; Nizami, M.M.U.I.; Johari, Y.; Husein, A.; Alam, M.K. Effect of Aging and Weathering on the Physical Properties of Maxillofacial Silicone Elastomers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Prosthodontics 2019, 28, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleni, P.N.; Krokida, M.; Polyzois, G.; Gettleman, L.; Bisharat, G.I. Effects of outdoor weathering on facial prosthetic elastomers. Odontology 2011, 99, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleni, P.N.; Krokida, M.K.; Polyzois, G.L. Effects of Storage in Simulated Skin Secretions on Mechanical Behavior and Color of Polydimethylsiloxanes Elastomers. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery 2011, 22, 830–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariani, N.; Vissink, A.; van Oort, R.P.; Kusdhany, L.; Djais, A.; Rahardjo, T.B.W.; van der Mei, H.C.; Krom, B.P. Microbial biofilms on facial prostheses. Biofouling 2012, 28, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatamleh, M.M.; Polyzois, G.L.; Silikas, N.; Watts, D.C. Effect of Extraoral Aging Conditions on Mechanical Properties of Maxillofacial Silicone Elastomer. Journal of Prosthodontics 2011, 20, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleni, P.N.; Perivoliotis, D.; Dragatogiannis, D.A.; Krokida, M.K.; Polyzois, G.L.; Charitidis, C.A.; Ziomas, I.; Gettleman, L. Tensile and microindentation properties of maxillofacial elastomers after different disinfecting procedures. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials 2013, 28, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagay, B.E.; Goiato, M.C.; da Silva, E.V.F.; Andreotti, A.M.; Bitencourt, S.B.; Duque, C.; dos Santos, P.H.; dos Santos, D.M. Effect of photopolymerized glaze application on bacterial adhesion on ocular acrylic resin surfaces submitted to accelerated ageing. Letters in Applied Microbiology 2019, 68, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, D.M.; Goiato, M.C.; Moreno, A.; Pesqueira, A.A.; Haddad, M.F. Influence of Pigments and Opacifiers on Color Stability of an Artificially Aged Facial Silicone. Journal of Prosthodontics 2011, 20, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, C.; Powers, J.M.; Kiat-amnuay, S. Color stability of pigmented maxillofacial silicone elastomer: Effects of nano-oxides as opacifiers. Journal of Dentistry 2010, 38, e100–e105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Powers, J.M.; Kiat-amnuay, S. Effect of opacifiers and UV absorbers on pigmented maxillofacial silicone elastomer, part 1: Color stability after artificial aging. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry 2013, 109, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, M.E.T.A.; Bergsma, J. Problems and coping behaviour of facial cancer patients. Social Science & Medicine 1990, 30, 569–578. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, M.I.; Cadd, B.; Peart, G.; Gibson, I. Augmented patient-specific facial prosthesis production using medical imaging modelling and 3D printing technologies for improved patient outcomes. Virtual and Physical Prototyping 2018, 13, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, Y.L.; Tan, Y.S.E.; Tan, H.K.J.; Peh, Z.K.; Low, X.Y.; Yeong, W.Y.; Tan, C.S.H.; Laude, A. 3D printed bio-models for medical applications. Rapid Prototyping Journal 2017, 23, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, E.J.; Scholten, T.; Song, Y.; Verlinden, J.C.; Wolff, J.; Forouzanfar, T.; Helder, M.N.; van Zuijlen, P. Developing a parametric ear model for auricular reconstruction: A new step towards patient-specific implants. Journal of Cranio-Maxillofacial Surgery 2015, 43, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palousek, D.; Rosicky, J.; Koutny, D. Use of digital technologies for nasal prosthesis manufacturing. Prosthetics & Orthotics International 2014, 38, 171–175. [Google Scholar]
- Kincade, C.; McHutchion, L.; Wolfaardt, J. Digital design of patient-specific abutments for the retention of implant-retained facial prostheses. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry 2018, 120, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, D.J.; Singh, D. 3D printing for developing patient specific cosmetic prosthetics at the point of care. International Journal of Surgery 2020, 80, 241–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero Antón de Vez, H.; Herrero Jover, J.; Silva-Vergara, C. Personalized 3D Printed Surgical Tool for Guiding the Chisel during Hump Reduction in Rhinoplasty. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery - Global Open 2018, 6, e1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.W.; Kim, M.J.; Kang, M.K.; Kim, S.C.; Jeong, W.S.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, T.H.; Koh, K.S. Clinical Application of a Patient-Specific, Three-Dimensional Printing Guide Based on Computer Simulation for Rhinoplasty. Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery 2020, 145, 365–374. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, S.; Narayan, A.I.; Choudhry, A.; Balakrishnan, D. CAD/CAM-Assisted Auricular Prosthesis Fabrication for a Quick, Precise, and More Retentive Outcome: A Clinical Report. Journal of Prosthodontics 2017, 26, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unkovskiy, A.; Brom, J.; Huettig, F.; Keutel, C. Auricular Prostheses Produced by Means of Conventional and Digital Workflows: A Clinical Report on Esthetic Outcomes. The International Journal of Prosthodontics 2018, 31, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zopf, D.A.; Mitsak, A.G.; Flanagan, C.L.; Wheeler, M.; Green, G.E.; Hollister, S.J. Computer Aided–Designed, 3-Dimensionally Printed Porous Tissue Bioscaffolds for Craniofacial Soft Tissue Reconstruction. Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery 2015, 152, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, J.; Hatamleh, M.M. Complete integration of technology for improved reproduction of auricular prostheses. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry 2014, 111, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mussi, E.; Furferi, R.; Volpe, Y.; Facchini, F.; McGreevy, K.S.; Uccheddu, F. Ear Reconstruction Simulation: From Handcrafting to 3D Printing. Bioengineering 2019, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, B.; Lee, C.; Kim, M.; Choi, T.H.; Kim, S.; Kim, S. Fabrication of three-dimensional scan-to-print ear model for microtia reconstruction. Journal of Surgical Research 2016, 206, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, S. A New Method of Total Reconstruction of the Auricle for Microtia. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 1993, 92, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, M.; Geerling, G.; Spaniol, K.; Witt, J. Eye Socket Regeneration and Reconstruction. Current Eye Research 2020, 45, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puls, N.; Carluccio, D.; Batstone, M.D.; Novak, J.I. The rise of additive manufacturing for ocular and orbital prostheses: A systematic literature review. Annals of 3D Printed Medicine 2021, 4, 100036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavlekar, A.; Aras, M.; Chitre, V. An innovative and simple approach to fabricate a hollow ocular prosthesis with functional lubricant reservoir: A solution to artificial eye comfort. The Journal of Indian Prosthodontic Society 2017, 17, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dave, T.; Tiple, S.; Vempati, S.; Palo, M.; Ali, M.; Kaliki, S.; Naik, M. Low-cost three-dimensional printed orbital template-assisted patient-specific implants for the correction of spherical orbital implant migration. Indian Journal of Ophthalmology 2018, 66, 1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Bai, S.; Yu, X.; Zhao, Y. Combined use of a facial scanner and an intraoral scanner to acquire a digital scan for the fabrication of an orbital prosthesis. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry 2019, 121, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Mechanical and physical properties |
Goal | Units | |
|---|---|---|---|
| min | max | ||
| Tear strength | 0.005 | 0.018 | kN/mm |
| Tensile strength | 6900 | 13800 | kPa |
| Modulus at 100% elongation | 345 | 1720 | kPa |
| Elongation at break | 400 | 800 | % |
| Glass transition temperature | less 0 | °С | |
| Heat distortion temperature | above 120 | °С | |
| Critical surface tension | 30 | 45 | mN/m |
| Coefficient of friction | 0.4 | 0.6 | none |
| Hardness | 25 | 35 | Shore A scale |
| Water absorption | None | ||
| Polymer | Description | 3D printing | Advantages | Disadvantages | Application | Ref |
| PU | Thermoset, high elastic properties | FDM, SLS, casting in 3D-printed molds | Excellent flexibility, ability to external and internal staining, fine cosmetic results | Sensitivity to moisture, limited mechanical properties | Ocular prostheses, molds, skin-like coating | [63] [64] |
| Polyacrylates | ||||||
| PMMA | Thermoplast, easy to blend, copolymerization to improve properties | FDM, SLS, casting in 3D-printed molds | low cost, lightweight, transparency, easy to manipulation | Brittle, scratched, unstable in organic solvent, limited mechanical properties | Ocular prostheses, eyeballs, surface coating, implant-supports, molds | [16] [65] |
| Photocurable resins | Acryic-based copolymer, cured by light (λ ~365nm) e.g. FotoTec DLP.A, TangoPlus |
SLA, DLP, casting in 3D-printed molds | Easy to manipulation, diversity of samples with various properties | Shrinkage, distortion, side-product under curing, fracture | Auricular, nasal, ocular prostheses, implants, molds | [65] [66] [67] |
| Adhesives | Polyalkyl acrylates with soft and hard segments, viscoelastic | - | Diversity of samples, easy tuned adhesion-cohesion, low cost | Contain solvents, insufficient wetting strength | Attachment of prostheses | [68] |
| Polyesters | ||||||
| PCL | Thermoplast, easy to blend, high strength, elasticity. | FDM, SLS, casing in 3D-printed molds | Low melting point, biodegradable, mechanically strong, easy processing, tissue regeneration | Slow biodegradation with acid release, impossibility of thermal sterilization | Implant-supports of orbital prostheses, molds | [69] [70] |
| PLA | Thermoplast, easy to blend, high strength, permeability for gases and water | FDM, SLS, casting in 3D-printed molds | Low melting point, low shrinkage, mechanically strong, easy processing | Low heat resistance, brittleness, slow biodegradation with acid release | Implant-supports of auricular prostheses, molds, mock implants | [71] [72] [73] |
| PEEK | Thermoplast, exceptional mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties, capable of blending. | FDM, SLS, | High strength, stiffness, and toughness | High melting point, high melt viscosity, moderately resistant to UV radiation, processing affects mechanical properties. | Reinforcement of auricular prostheses | [74] |
| Polystyrenes | ||||||
| PS | Thermoplast, rigid, hard, easy to blend, copolymerization to improve properties. | FDM | High dimensional stability, good processing, low water uptake and shrinkage, chemically resistant | Brittle, limited chemical resistance to organic solvents | Molds | [75] |
| ABS | Thermoplast, rigid, hard, easy to blend | SLA, FDM,SLS , binder jetting | Chemically resistant, heat tolerance, high impact strength, rigidity, high resistance to stress cracking | Poor resistance to chlorinated solvents, UV-light | Molds, mock implants | [73] [76] [77] |
| Silicones | ||||||
| Silicone RTV | Elastomer, easy to blend | Casting in 3D-printed molds, extrusion, jetting, SLA, DLP | Skin-like flexibility, heat resistance, radically low viscosity-temperature coefficients, biocompatibility, and intrinsic transparency, easy processing | Poor mechanical properties, hydrophobicity, troubles with external staining, and impurities. | All types of facial prostheses | [76] [78] [72] |
| Silicone HTV | Elastomer, easy to blend | Casting in 3D-printed molds, extrusion, jetting, SLA, DLP | Transparent, odorless polycondensation samples, have relatively high tensile and tear strength, easy processing | Volatile residues, yellowing after curing, Pt-catalyzed have a strong odor, sticky to the touch | Auricular prostheses, molds | [79] |
| Adhesives | Elastomer, viscoelastic, formed MQ resins | - | Spread and rapid, intensive surface wetting, easy tuned adhesion- cohesion, low cost | Possible damage of skin, insufficient wetting strength | Attachment of prostheses | [80] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





