1. Introduction
Fluid management during anesthesia is necessary to control vascular tone, maintain the circulating volume, and improve cardiac output. Hypovolemia and hypervolemia can increase perioperative complications, including pulmonary edema, electrolytes, hemodilution coagulopathy, tissue hypoperfusion, and acid-base derangements. Optimizing perioperative fluid treatment often improves postoperative outcomes, reduces perioperative complications, and shortens hospitalization [
1,
2]. Therefore, assessing volume status and responsiveness is essential for fluid management in patients undergoing surgery and with critical illnesses.
The earliest static indices (central venous and pulmonary arterial wedge pressure ) used clinically could not accurately assess volume status [
3,
4]. Dynamic indices (stoke volume variation and pulse pressure variation) are derived from cardiopulmonary interactions during mechanical ventilation and may guide fluid management. Although functional hemodynamic parameters have been shown to reliably predict fluid responsiveness, factors such as pulmonary compliance, cardiac function, and mechanical ventilation may limit their broad clinical application [
5,
6]. The ideal hemodynamic monitoring technique should be less invasive, continuously dynamic, simple to operate, and less expensive. Due to their noninvasive nature and easy access, bedside ultrasound techniques have gained widespread application and are commonly used for fluid management in perioperative and critical care units. In addition, carotid corrected flow time (FTc) measured in the common carotid artery is considered a reliable method for predicting fluid reactivity [
7,
8,
9]. Previous studies have found that ΔFTc induced by the recruitment maneuver or the passive leg raise test could effectively identify “fluid responsive” patients with increased stroke volume after adequate fluid resuscitation [
10,
11].
The main aim of our study was to assess the ability of point-of-care FTc and ΔFTc induced by volume expansion to predict the responsiveness of fluid in patients undergoing robot-assisted gynecological surgery in a modified head-down lithotomy position.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Chongqing University Cancer Hospital (approval number: CZLS2021041-A) and registered in the Chinese Clinical Trial Register (CHiCTR2200060573). Written informed consent was obtained from all the patients. This prospective study included 52 American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) class I–III patients scheduled to undergo robot-assisted gynecological surgery in a modified head-down lithotomy position. Exclusion criteria were body mass index >30 or <15 kg/m2, arrhythmia, decreased cardiac function (moderate or severe valve regurgitation, left ventricular ejection fraction < 50 %, right ventricular dysfunction), a history of carotid artery stenosis of 50%, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic kidney disease, pregnancy, or unwillingness to participate in the study.
2.2. Anesthesia technique
The patients were placed supine in the operating room and underwent standard monitoring, including electrocardiography, heart rate (HR), pulse oxygen saturation, and noninvasive blood pressure. Anesthesia induction using propofol (2–3 mg/kg), sufentanil (0.3–0.5 µg/kg), midazolam (1–2 mg), and tracheal intubation was facilitated with rocuronium (0.8 mg/kg). Intraoperative anesthesia was maintained with continuous infusion of propofol (1.5–3 mg/kg/h), remifentanil (0.02–0.2 μg/kg/min), and sevoflurane (1.5–2.5 vol%). Neuromuscular blockade was maintained by rocuronium (0.15 mg/kg) administered at 30–40 minute intervals. The radial artery was catheterized after the induction of anesthesia. The tidal volume was set at 6 mL/kg of predicted body weight in volume-controlled mechanical ventilation mode using a WATO EX-65 anesthesia machine (Mindray Medical Systems, Shenzhen, China), and the positive end-expiratory pressure was set at 5 cmH2O. An end-tidal carbon dioxide concentration of 35–45 mmHg was maintained by controlling the ventilation frequency parameters. Pneumoperitoneum was achieved by continuous carbon dioxide inflation while maintaining an intra-abdominal pressure of 12 mmHg. During the study procedure, all patients were placed in the modified head-down lithotomy position, and intraoperative maintenance fluids were administered with Ringer’s solution at a rate of 4 mL/kg/h.
2.3. Hemodynamic monitoring
Following arterial insertion, the arterial pressure signal was simultaneously transmitted to the operating room IntelliVue MP40 monitor (Philips Medizin Systeme Boblingen GmbH, Boeblingen, Germany) and the MostCare device (Vygon, Vytech, Padova, Italy) using a Y-cable. The patient was positioned for surgery, and the arterial signal was calibrated to zero. MostCare, a multiparameter hemodynamic monitoring tool, utilizes pressure recording analysis methods to estimate cardiac output without requiring calibration. By analyzing the arterial waveform signal sampled at a high rate of 1000 Hz, MostCare accurately identifies the dicrotic notch’s position and calculates the area under the arterial pressure waveform and systemic vascular impedance to determine the stroke volume [
12,
13]. Notably, the square-wave test was performed to ensure the normalcy of the arterial waveform after connecting the monitor, effectively excluding any under-or-overdamping of the pressure signal [
14].
2.4. Study procedures
The study protocol was conducted at least 45 min after the intra-abdominal pressure was maintained at 12 mmHg while the patient was hemodynamically stable (i.e., the change in mean arterial pressure and heart rate was less than 10% over 5 minutes). Vasoactive medications were not administered during the study period. Upon program initiation, baseline hemodynamic variables (HR, mean arterial pressure [MAP], PPV, and stroke volume index [SVI]) were obtained, and carotid FTc was measured (T
0). Subsequently, a 250 mL infusion of Ringer's solution was administered for 10 min. Hemodynamic variables were re-recorded 5 min after fluid expansion (T1) completion. FTc was calculated as follows: ΔFTc = FTc
T1 – FTc
T0. Fluid responsiveness was defined as an SVI increase of ≥10% after fluid administration [
11].
2.5. Carotid ultrasonography
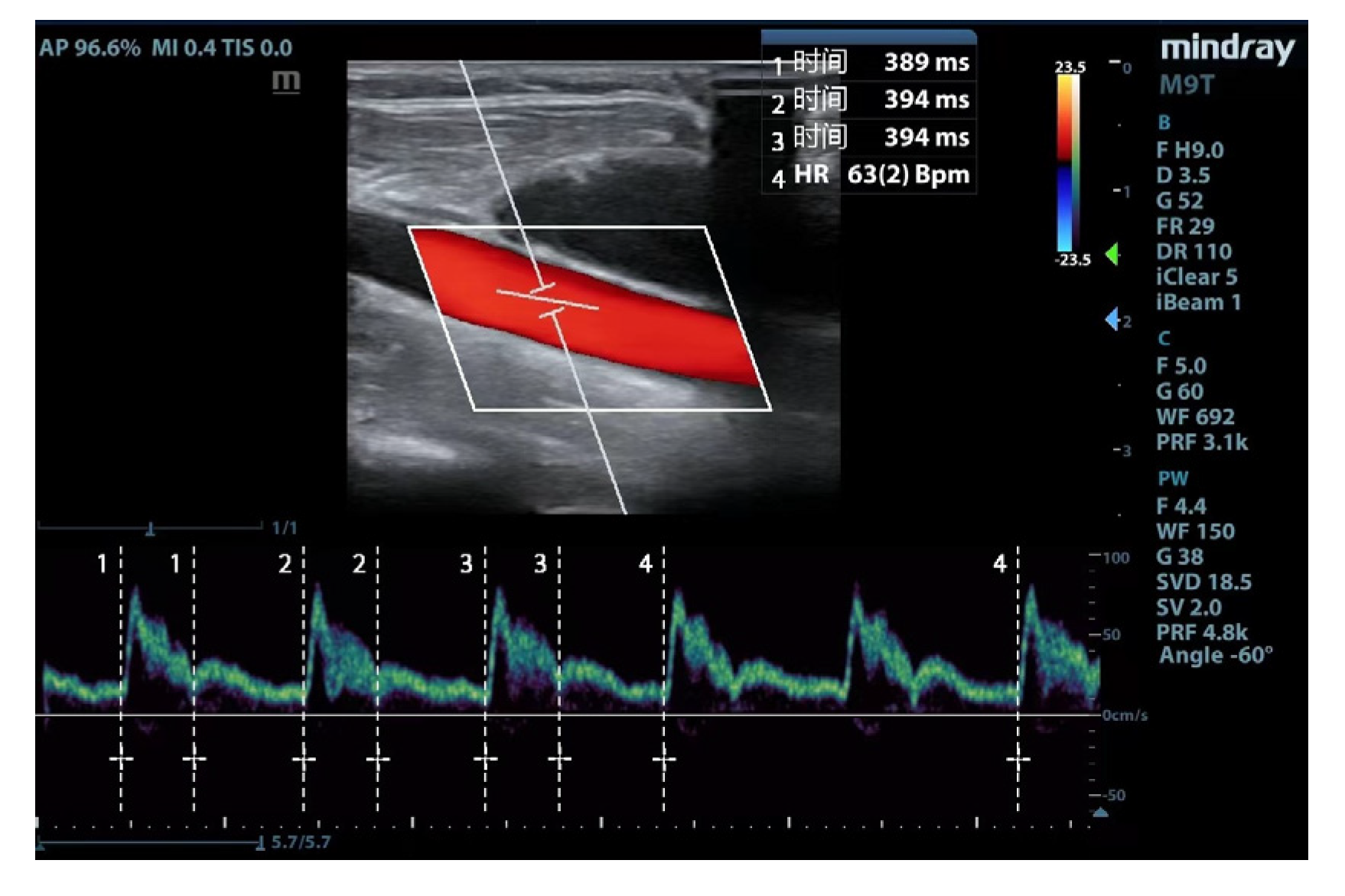
The ultrasonic parameters were measured using a portable ultrasound device (Mindray Medical Systems, Shenzhen, China). The following scanning protocol acquired images of the common carotid artery: (1) a high-frequency line array transducer was placed transversely at the lower border of the thyroid cartilage, ensuring the common carotid artery was centered on the screen; (2) the long axis B-mode image of the common carotid artery was obtained with the probe marker pointing towards the patient’s head; (3) the sample volume was placed at the center of the arterial vessel, and the cursor angle was adjusted parallel to the direction of blood flow, with an insonation angle of ≤60°, approximately 2 cm proximal to the carotid bifurcation; (4) a satisfactory spectrum is displayed and frozen by adjusting the optimal sampling volume and angle, then measurement was performed by the caliper function on the machine. Flow time (FT) was measured from the beginning of the systolic upstroke to the dicrotic notch. HR was obtained by measuring the interval between the beginning of two consecutive Doppler flow upstrokes. The average of three consecutive cycles was recorded once stability was achieved and the quality reached an acceptable level (
Figure 1). FTc was calculated using the Wodey formula: FTc = FT + [1.29 × (HR - 60)] [
15].
2.6. Sample size calculation and statistical analysis
PASS ver.15.0 (IBM Corp, Armonk, NY, USA) was used to calculate the sample size. A previous study reported that the area under the curve (AUC) was 0.82 for the descending aorta FTc to predict fluid responsiveness. We hypothesized that the carotid FTc might have a low predictive capacity of 0.75. [
9] We compared this value with the null hypothesis (AUC = 0.50, ratio of sample sizes in the negative/positive groups = 1) and generated a sample size of 50 patients (type I error = 0.05, power = 0.90). With an expected dropout rate of 10%, 55 patients were included.
Normality was tested for all quantitative data using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Data are presented as the mean (standard deviation), median (interquartile range), and absolute numbers or percentages (%). Continuous variables of patient characteristics were compared between responders and non-responders using an independent-sample t-test or Mann–Whitney U test and the chi-square test for categorical data. Hemodynamic parameters before and after volume expansion (VE) were assessed using the paired t-test or Wilcoxon signed-rank sum test. In contrast, between-group comparisons were performed using the t-test or Mann–Whitney U test.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was performed to assess the predictive ability of FTc and FTc, and the AUC values were compared using the DeLong method [
16]. The optimal cut-off value was determined using the maximum Youden index (sensitivity + specificity - 1) [
17]. We applied a gray-zone approach to describe an inconclusive range, considering threshold values corresponding to a sensitivity and specificity of 90% [
18]. Pearson correlation coefficient was used to investigate the association between carotid ultrasound variables and percentage changes in SVI after VE.
Statistical analyses were performed using the MedCalc ver. 20.1.0 (MedCalc Software, Ostend, Belgium), GraphPad Prism ver. 9.4.0 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA), and SPSS ver. 27.0 (IBM Corp, Armonk, NY, USA). A P value <0.05 was regarded as statistically significant.
3. Results
Of the 59 initially screened patients, 55 were enrolled in the study. Three patients were excluded due to high airway pressure (n = 1), severe hypotension (n = 1), or unexpected cardiac arrhythmia (n = 1). Ultimately 52 patients were included in this study.
The final analysis divided the responders and non-responders in half (
Figure 2). The demographics of the participants are shown in
Table 1. There were no significant differences in patient characteristics between responders and non-responders.
The hemodynamic, ventilatory, and ultrasound parameters before and after VE are presented in
Table 2. Higher MAP was observed in non-responders than responders at each time point, but there was no difference before and after rehydration. The baseline PPV, SVI, and FTc were comparable between the two groups, and PPV significantly decreased in both groups after VE, whereas FTc significantly increased. In contrast, SVI after VE showed significant changes only in the responders.
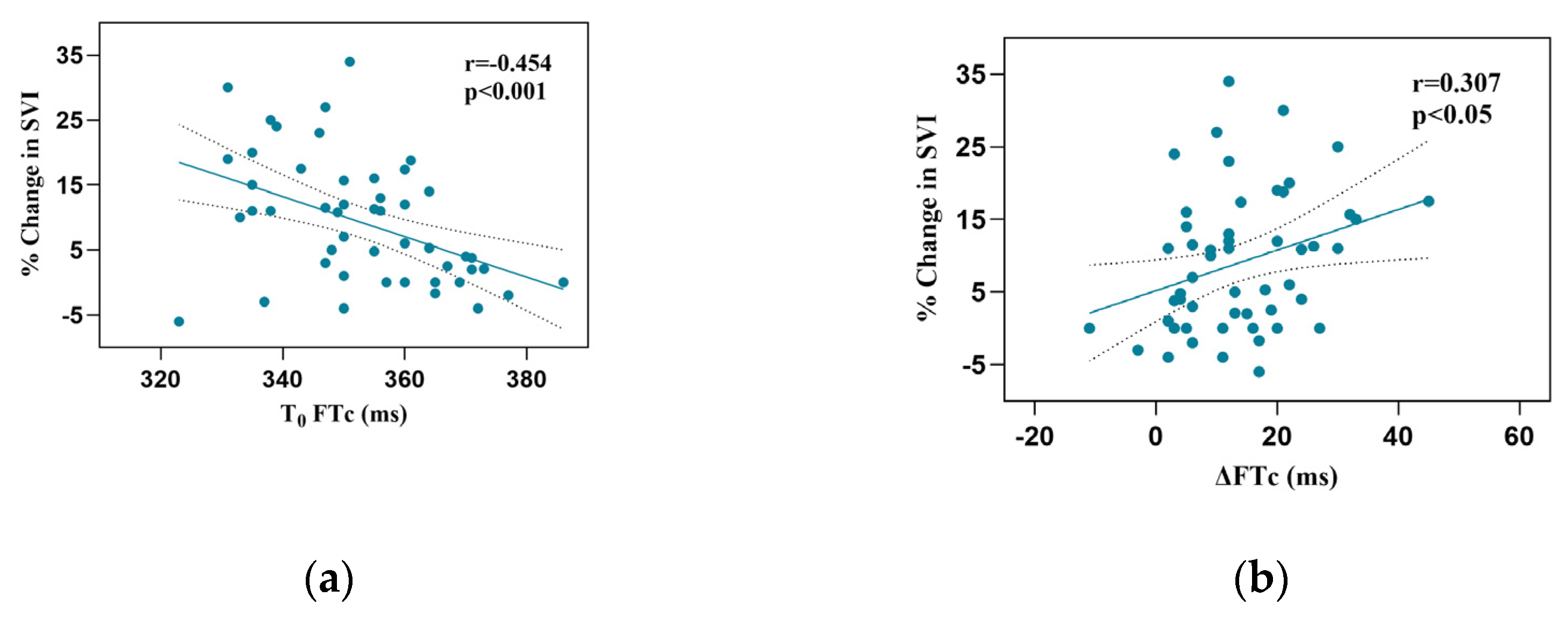
Responder patients had a more significant increase in FTc after VE than non-responders (17.2±10.9 vs 10.4±9.0 ms, P < 0.05). Baseline FTc and FTc correlated with the percentage change in SVI after VE (r = -0.454, 95% confidence interval [CI]: -0.647–0.207, P < 0.001; r = 0.307, 95% CI:0.371–0.535], P < 0.05, respectively;
Figure 3).
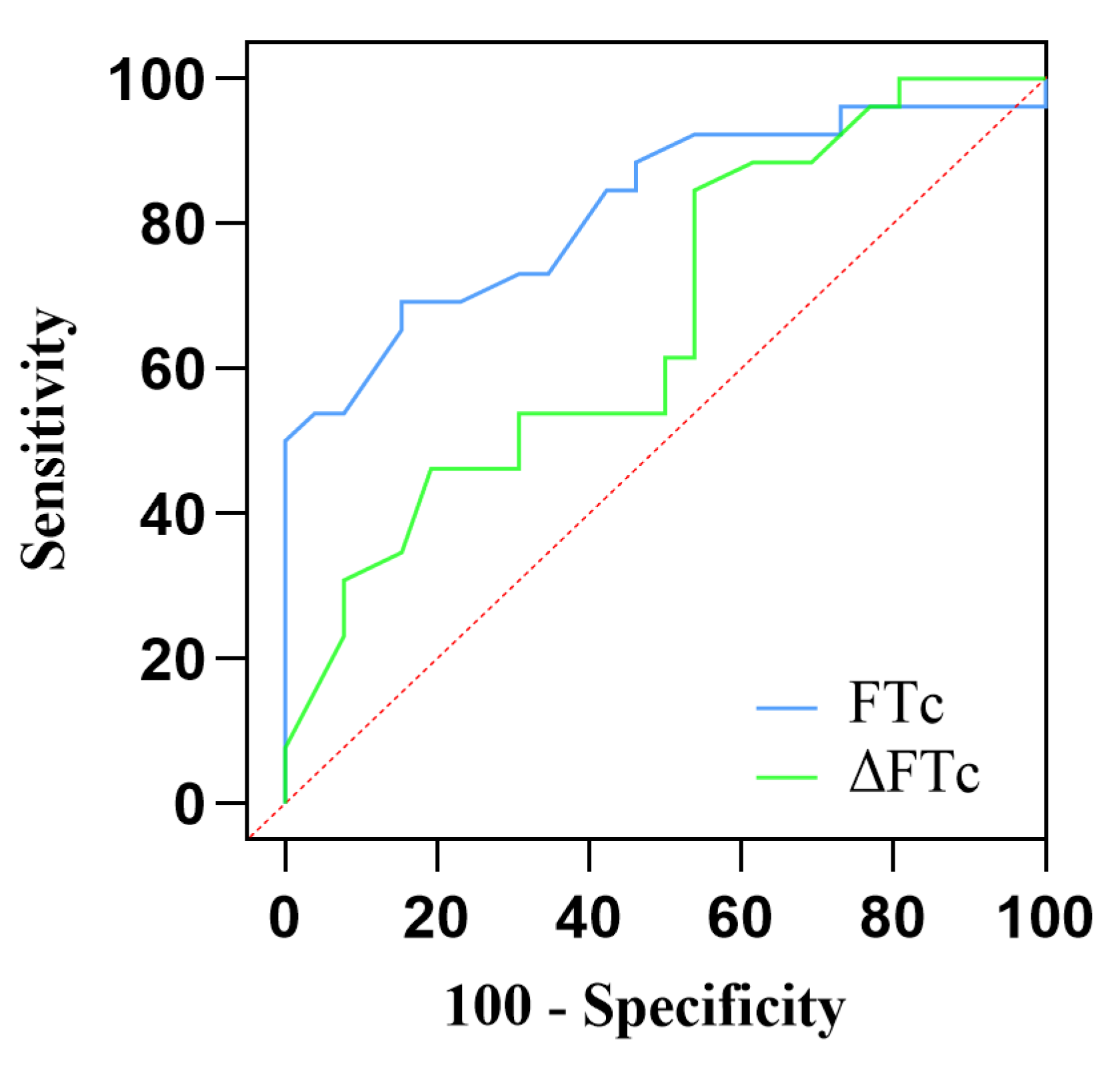
AUC values of FTc were 0.82 (95% CI:0.705–0.937; P < 0.0001), showing excellent predictive capability for fluid responsiveness. The optimal cut-off value of FTc was 356.5 ms, with a sensitivity of 69.2% and a specificity of 84.6%. In contrast, the ability of ΔFTc to predict fluid responsiveness with an AUC of 0.67 (95% CI:0.520–0.815; P < 0.05) indicates a lower accuracy. The optimal cutoff value of ΔFTc was 19.5 ms, with a sensitivity of 84.6% and specificity of 46.2%. However, the predictive accuracy for fluid responsiveness was not significantly different between the FTc and FTc groups (P = 0.12). The gray zone for FTc (347.1–359.9 ms) contained 14 patients (27 %). The grey zone for ΔFTc (4.7–22.2 ms) contained 33 (63%) patients (
Table 3,
Figure 4).
4. Discussion
Among gynecologic patients undergoing robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery in a modified head-down laparotomy position, the results of our study suggest that the carotid FTc assessed using Doppler ultrasound is an excellent predictor of fluid responsiveness. Although ΔFTc induced by VE also could predict fluid responsiveness, it showed only moderate predictive capability. Our results also showed that 63% of patients were in the gray zone of FTc, compared to 27% of patients in the gray zone of FTc, which is significantly lower. The grey zone was defined as the area where responders and non-responders were not well separated.
Perioperative fluid management is directly related to patient survival, and volume assessment is essential for guiding the individualization and accuracy of intraoperative fluid therapy. Monitoring has evolved from being static to dynamic. In recent years, researchers have focused on developing noninvasive techniques with significant accuracy and precision, thus avoiding the complications of invasive monitoring and analyzing the response to fluid therapy [
3,
4,
5,
6,
19]. Since then, portable ultrasound has been widely recommended for volume status assessment in critical care, emergency, and perioperative patients because of its convenient, non-invasive, easy-to-acquire, and reproducible characteristics.
Recent studies have increasingly identified a statistically significant correlation between changes in FTc and intravascular volume status [
7,
8,
20]. Accordingly, as intravascular volume decreases, FTc tends to decrease as well. In contrast, volume-deficient patients experience an increase in FTc following volume infusion. Patients with advanced renal failure had significantly lower FTc values after hemodialysis, and there was a statistically significant negative correlation between the volume of fluid excreted during hemodialysis and changes in FTc [
8]. Mackenzie et al. found that FTC decreases after acute blood loss and that passive leg raising restores FTc to predicted levels in acute hypovolemia [
20]. Assessing the correlation between changes in volume status and changes in carotid FTc, Blehar et al. reported that dehydrated patients receiving fluid resuscitation showed an increase in carotid FTc from a mean of 299 ms before injection to a mean of 340 ms after injection. Moreover, the carotid FTc responded more significantly to changes in intravascular volume than to negligible changes in HR and MAP [
7]. Similarly, our results showed an increase in FTc in both groups of patients after fluid injection, a more pronounced increase in responders, and no significant changes in HR or blood pressure.
A growing body of evidence highlights the significance of ultrasound measurement of carotid FTc in volume management. Kim et al. confirmed that FTc could accurately predict volume responsiveness in spontaneously breathing patients with an AUC of 0.84. [
9] Jung et al. considered carotid FTc as a reliable predictor to assess fluid responsiveness in patients with low tidal volume mechanical ventilation; a systematic review analysis revealed that the diagnostic characteristics of FTc varied, with sensitivity ranging from 60% to 73%, specificity from 82% to 92%, and an optimal cutoff of the area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) from 0.7526 to 0.8819 [
21]. The higher optimal cutoff value of 356.5 ms obtained in our study may be based on the patient’s positioning, potentially increasing venous return and affecting the FTc measurement.
However, the absolute value of FTc alone as a static indicator has limitations as it depends on left ventricular preload, cardiac inotropy, and systemic vascular resistance [
22]. Based on the above findings, researchers hypothesized that changes in FTc can be considered an indicator of fluid reactivity. Jalil et al. first attempted to determine whether passive leg raising induced increase in FTc can be used to predict fluid responsiveness in critically ill patients with a cardiac output monitor, ultimately concluding that an increase of ≥ 24.6% in the FTc in response to passive leg raising is a reasonable predictor of fluid responsiveness [
23]. In patients with early undifferentiated shock, Barjaktarevic et al. demonstrated through prospective experiments that not only changes in FTc evoked by a passive leg raising operation can determine fluid responsiveness but also a threshold of 7 ms as FTc to define fluid responsiveness with a specificity of 96% and sensitivity of 68% [
11]. While passive leg raising is a straightforward method to evaluate fluid responsiveness, its implementation during surgery is challenging. Consequently, alternative interventions are necessary. Therefore, the following experiment directly illustrated that the percentage change in FTc induced by the recruitment maneuver used to predict fluid responsiveness in supine patients under general anesthesia is feasible [
10]. Our study data gave a higher absolute value for change in FTc with a cutoff value of 19.5ms (sensitivity of 84.6% and specificity of 46.2%). Regardless of whether the threshold for a change in FTc with a fluid challenge varied from 7 ms to 30 ms or a 25% relative change, possible reasons for this difference include the following: first, our study object was in a head-down position, which would have increased venous return and cardiac preload; second, the hemodynamic effects of pneumoperitoneum were complex; and finally, we identified responders and non-responders by additional fluid supplementation [
24,
25]. Therefore, it is easy to note that ΔFTc increases significantly in patients who respond to fluids after intravenous infusion or passive leg raising.
This study has several limitations. We didn't utilize the gold standard for monitoring fluid responsiveness, replacing it with a less invasive continuous hemodynamic monitor. Although the MostCare monitor showed good agreement with echocardiographic measurements, potential errors may be unavoidable under the dual effects of pneumoperitoneum and head-down position. The impact of cerebrovascular tension on the common carotid artery cannot be excluded entirely, and brain autoregulatory mechanisms and blood carbon dioxide levels correlate with the former. Finally, the results cannot be generalized to other patients because of the specificity of the type of disease and the surgical approach, such as facial and cerebral surgery or open surgery.
5. Conclusions
The carotid FTc measured using Doppler ultrasound is a reasonable predictor of the modified head-down lithotomy position. This extensive gray zone may limit the clinical replication of FTc. We will continue to conduct additional clinical trials and offer additional reference points for perioperative volume management.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, XX.T and HL.L; methodology, JQ.L; software, Q.C; validation, TJ.Y, and HL.L; formal analysis, XX.T; investigation, JQ.L; resources, Q.C; data curation, TJ.Y; writing—original draft preparation, XX.T, JQ.L; writing—review and editing, TJ.Y, HL.L; supervision, HL.L; funding acquisition, JQ.L, Q.C.
Funding
This work was supported by the Laboratory Open Fund of Chongqing University Cancer Hospital (2021); Chongqing medical scientific research project (Joint project of Chongqing Health Commission and Science and Technology Bureau 2023MSXM125). Scientific and Technological Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission(KJQN202300117); Chongqing Shapingba District Technology Innovation and Application Development Project(2023116).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Chongqing University Cancer Hospital (approval number: CZLS2021041-A).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from all the patients.
Data Availability Statement
The data analyzed and preserved during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request via e-mail.
Conflicts of Interest
None
References
- Fantoni, D.; Shih, A.C. Perioperative fluid therapy. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract 2017, 47, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellge, B.E.; Trepte, C.J.; Zöllner, C.; Izbicki, J.R.; Bockhorn, M. Perioperatives Volumenmanagement [Perioperative fluid management]. Chirurg 2020, 91, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marik, P.E.; Cavallazzi, R. Does the central venous pressure predict fluid responsiveness? An updated meta-analysis and a plea for some common sense. Crit Care Med 2013, 41, 1774–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, D.; Ridel, C.; Ray, P.; Monnet, X.; Anguel, N.; Richard, C.; Teboul, J.L. Cardiac filling pressures are not appropriate to predict hemodynamic response to volume challenge. Crit Care Med 2007, 35, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, C.K.; Cannesson, M. Monitoring fluid responsiveness. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan 2011, 49, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnet, X.; Marik, P.E.; Teboul, J.L. Prediction of fluid responsiveness: an update. Ann Intensive Care 2016, 6, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blehar, D.J.; Glazier, S.; Gaspari, R.J. Correlation of corrected flow time in the carotid artery with changes in intravascular volume status. J Crit Care 2014, 29, 486–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein-Nejad, H.; Mohammadinejad, P.; Lessan-Pezeshki, M.; Davarani, S.S.; Banaie, M. Carotid artery corrected flow time measurement via bedside ultrasonography in monitoring volume status. J Crit Care 2015, 30, 1199–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Shin, S.; Kim, N.; Choi, T.; Choi, S.H.; Choi, Y.S. Carotid ultrasound measurements for assessing fluid responsiveness in spontaneously breathing patients: corrected flow time and respirophasic variation in blood flow peak velocity. Br J Anaesth 2018, 121, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, A.; Suehiro, K.; Juri, T.; Tanaka, K.; Mori, T. Changes in corrected carotid flow time induced by recruitment maneuver predict fluid responsiveness in patients undergoing general anesthesia. J Clin Monit Comput 2022, 36, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barjaktarevic, I.; Toppen, W.E.; Hu, S.; Aquije Montoya, E.; Ong, S.; Buhr, R.; David, I.J.; Wang, T.; Rezayat, T.; Chang, S.Y.; et al. Ultrasound assessment of the change in carotid corrected flow time in fluid responsiveness in undifferentiated shock. Crit Care Med 2018, 46, e1040–e1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Critchley, L.A. Validation of the MostCare pulse contour cardiac output monitor: beyond the Bland and Altman Plot. Anesth Analg 2011, 113, 1292–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romagnoli, S.; Ricci, Z.; Romano, S.M.; Dimizio, F.; Bonicolini, E.; Quattrone, D.; De Gaudio, R. FloTrac/Vigileo(TM) (third generation) and MostCare(®)/PRAM versus echocardiography for cardiac output estimation in vascular surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 2013, 27, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, A.; Montagnini, C.; Cammarota, G.; Giuliani, F.; Muratore, L.; Baggiani, M.; Bennett, V.; Della Corte, F.; Navalesi, P.; Cecconi, M. Assessment of fluid responsiveness in prone neurosurgical patients undergoing protective ventilation: role of dynamic indices, tidal volume challenge, and end-expiratory occlusion test. Anesth Analg 2020, 130, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadinejad, P.; Hossein-Nejad, H. Calculation of corrected flow time: Wodey’s formula vs. Bazett’s formula. J Crit Care 2018, 44, 154–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLong, E.R.; DeLong, D.M.; Clarke-Pearson, D.L. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics 1988, 44, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youden, W.J. Index for rating diagnostic tests. Cancer 1950, 3, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coste, J.; Pouchot, J. A grey zone for quantitative diagnostic and screening tests. Int J Epidemiol 2003, 32, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheeren, T.W.L.; Ramsay, M.A.E. New developments in hemodynamic monitoring. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 2019, 33, Suppl 1–S67–S72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, D.C.; Khan, N.A.; Blehar, D.; Glazier, S.; Chang, Y.; Stowell, C.P.; Noble, V.E.; Liteplo, A.S. Carotid flow time changes with volume status in acute blood loss. Ann Emerg Med 2015, 66, 277–282.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, L.; Davis, J.; Esener, D.; Grant, C.; Fields, J.M. Carotid ultrasound to predict fluid responsiveness: A systematic review. J Ultrasound Med 2020, 39, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, M.; Allen, M.J.; Webb, A.R.; Bennett, E.D. Effects of alterations in left ventricular filling, contractility, and systemic vascular resistance on the ascending aortic blood velocity waveform of normal subjects. Crit Care Med 1991, 19, 1138–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalil, B.; Thompson, P.; Cavallazzi, R.; Marik, P.; Mann, J.; El-Kersh, K.; Guardiola, J.; Saad, M. Comparing changes in carotid flow time and stroke volume induced by passive leg raising. Am J Med Sci 2018, 355, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeuzem-Lampert, C.; Groene, P.; Brummer, V.; Hofmann-Kiefer, K. Kardiorespiratorische Effekte perioperativer Positionierungsmaßnahmen [Cardiorespiratory effects of perioperative positioning techniques]. Anaesthesist 2019, 68, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antiperovitch, P.; Iliescu, E.; Chan, B. Carotid systolic flow time with passive leg raise correlates with fluid status changes in patients undergoing dialysis. J Crit Care 2017, 39, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).