1. Introduction
Plant-based foods such as teas, coffee, spices, fruits and others have been extensively studied for their potential health benefits [
1]. Leaves from tea (
Camellia sinensis) are used to make the second most widely consumed beverage in the world after water, and is a good example of a beverage associated to health [
2]. In China, infusions of
Camellia. sinensis leaves have been known for their traditional benefits [
3]. Daily tea consumption by generally healthy adults has been associated in a dose-dependent manner with lower risk of mortality [
4]. The bioactive components of the leaves and the teas brewed from them are the subject of intensive research for phytochemical content characterization [
5,
6,
7]. The molecular mechanisms of tea’s health function in the context of chronic diseases have been reported to include their alkaloids and catechins, epicatechin and their metabolites [
4,
5,
6,
7] (
Figure 1). For some diseases, a therapeutic approach has been achieved with traditional medicinal plants with the Ginkgo biloba Extract (EGb) 761 [
8]. However, the use of plant-based foods for prevention of these human chronic diseases in the healthy population is not always possible as the evidence provided is insufficient to establish a scientifically-based substantiation needed for a therapeutic claim related to a food and/or its constituents [
9,
10,
11].
In 2006, the European Union (EU) adopted a regulation on the use of nutrition and health claims for foods (the Nutrition and Health Claims Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006) [
11,
12,
13]. However, EU health claims (health either in relation to a function of the body (Article 13 claims) for botanicals remain as an « on hold» health claims [
14,
15].
We have developed the innovative method afforded by the ABC (in English, Bio Concentrate Assets®) patent. The ABC process is an exclusive method of enriching organic infusion leaves with organic dry and concentrated extracts using organic acacia gum and its application of this method has provided us with 9 new beverages, the first one being Qi cha tea®. Since some steps of ABC process could alter the biological activities of the new tea beverage, there is adsorbtion of the active ingredients with the use of the hydroalcoholic solution with acacia gum and then evaporation of ethanol solution by drying. No information on the use of these processes with teas has been reported, to the best of our knowledge. This article aims to evaluate qualitatively and quantitatively the major constituents of the first beverage produced with the ABC process i.e. Qi cha tea® by comparing with commercially available chemicals. Antioxidant activity of Camellia sinensis is related to its phenolic compounds. The preservation of the water soluble phenolic compounds are essential for Camellia sinensis and for infusions issued from the ABC process. Therefore, we evaluated the content of gallic acid, tea catechins and caffeine using high-performance liquid chromatography with diode-array detection (HPLC-DAD). We also evaluated these constituents in two extracts obtained by water infusion (WI) and pressurized liquid extraction (PLE). As well we determined in vitro antioxidant and cytotoxic activities in two cell lines by 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) assay and 3-(4,5-Dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2 ,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay, respectively. These two targets were chosen to evaluate the antioxidant potential of the extracts, which expresses the beneficial effect on health, and the anti-cancer potential against two lines of colon cancer, which is directly related to food consumption.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
All chemicals used were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich-Fluka (Saint-Quentin France) and stored under optimum conditions as indicated by the manufacturer.
2.2. Preparation of Qi Cha Tea® by the ABC Method
A predetermined quantity of plant fragments or whole plants was introduced in a 2 L balloon as a carrier. These plants were then homogenized by rotation (using a rotavapor at room temperature). Then the desired quantity of dry extracts was introduced and these solids were mixed by rotating the flask for at least 10 min. At the same time, a 3% acacia gum hydroalcoholic solution was prepared: water, 100% ethanol and acacia gum were added to a beaker fitted with a magnetic rod. The solution was mixed for about 1 hour until the acacia gum was perfectly dissolved. Part of the hydro-alcoholic solution thus obtained was removed and the various liquid flavors were introduced into the remaining solution. The solution was then thoroughly mixed. Part of the 3% acacia gum hydroalcoholic solution, containing the flavorings, was then introduced drop by drop (or sprayed) onto the initial carrier preparation contained in the 2 L flask. The solution was stirred by rotation as it was wetted. The introduction and mixing operation was repeated until all the 3% acacia gum hydroalcoholic solution was introduced. The dry extract powder then adhered to the plant fragment support by the sticky effect of acacia gum. Part of the water and all the ethanol were then removed by drying to regain a standard moisture content for this type of infusion. Ethanol is also used to accelerate the drying process by a surface tension gradient. Drying was carried out by blowing of dry air through the preparation by homogenizing every half hour, i.e. in the oven at 40 °C with continuous stirring.
Organic white tea, dried parts (Elderflower, Orange peel, Tulsi, Echinacea dry extract, and Lemongrass), and natural aromas of Bergamot and Orange were obtained from Thé de la Pagode, Paris, France.
Application of the ABC method to white tea with 5 organic phytochemicals and natural aromas provided us with Qi cha tea®.
The composition of Qi cha tea
® is showed in the
Table 1.
2.3. Preparation of Water Infusion Products (WIP) and Pressurized Liquid Extraction Products (PLEP)
100 mL of boiled water were added to 10 g of each sample (Qi cha tea® or botanicals), and infused for 30 min. The mixture was filtered through a filter paper. The resulting filtrate was evaporated using a rotary evaporator to provide WIP. The solid mass was weighed to estimate the extraction yield.
PLE was performed by the Dionex extraction system (ASE 100, CA, USA). The extraction cell was filled with 10 g of the sample using water. The extraction conditions were 80°C and 110 bar. The solvent was evaporated using a rotary evaporator under a vacuum at 35°C (IKA, Staufen Germany).
2.4. HPLC-DAD Analysis
Analytical HPLC gradient elution methods were used for Qi cha tea
® or botanicals [
28]. Standard solution named G-016 (Sigma Aldrich, France) contained: caffeine, EGCG, EC, ECG, GC, GCG, CG, EGC and GA. The dried extracts were injected at a concentration of 20 µg/mL of acetonitrile and water (20:80 v/v) and the contents in the samples were determined by HPLC-DAD (Thermo Scientific Dionex Ultimate 3000). Standard solutions were separately prepared at concentrations of 50, 20, 10, 5, and 1 µg/mL using a (20:80 v/v) acetonitrile/water.
2.5. Free Radical Scavenging Activity: DPPH Test
Antioxidant scavenging activity was studied using the 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl free radical (DPPH) with some modifications [
16]. About 20 µL of various dilutions (water) of each sample was mixed with a 0.2 mM methanolic DPPH solution. After 30 min of incubation at 25°C, the absorbance at 524 nm was recorded as A (sample). For the A (blank), the same experimentation was applied for a solution devoid of the test material and then, the absorbance was recorded. Then, for each solution the free radical scavenging activity was calculated as percent inhibition as the following equation:
The IC50 is the concentration required for the test material to cause a 50% decrease in DPPH concentration. Ascorbic acid was used as reference. All the measurements were performed in triplicate.
2.6. Cell Viability Evaluation
The cell viability was evaluated by MTT (3-(4, 5-dimethyl thiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide) assay. Briefly, MTT is a yellow tetrazolium salt. In the biological system, the succinate deshydrogenase, a mitochondrial enzyme of the viable cells, reduces the tetrazolium to dark blue formazan precipitate as previously described [
16]. The quantity of this product is proportional to the quantity of active cells. The cell viability (cytotoxic activity) of each compound was determined in the Caco-2 and human HCT-116 cell lines (American Type Culture Collection, Manassas, VA, USA). In a 96-well microplate, cells were distributed at 13 × 103 cells/well for HCT116 and 12 × 103 cells/well for Caco-2 in 100 µL. After 24 h of incubation at 37 ◦C, 100 µL of each extract diluted in the medium after being solubilized in DMSO was added to 100 µL of the corresponding culture medium; RPMI (RPMI 1640, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Illkirch France) for HCT-116, or DMEM (Advanced DMEM, Thermo Fisher Scientific). The plate was then incubated for 48 h at 37 ◦C and the cytotoxic potential of the tested samples was evaluated by the MTT assay. After removing the supernatant, cells were treated with 50 µL of MTT solution, and the plate was incubated for 40 min at 37 ◦C; then MTT was eliminated and 80 µL of DMSO was added. The absorbance was measured at 605 nm using a microplate reader (Multiskan Go, F1-01620, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Vantaa, Finland). The mitochondrial reduction of MTT to formazan was used to determine the cytotoxic effect of those compounds. Tested samples were suspended in the dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and then diluted, so the concentration of DMSO does not exceed 1% in the mixture. Tamoxifen was used as a positive control. The test was performed in triplicate.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
All data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation of duplicate measurements.
One way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used for the significance calculation using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) 20.1 (Version IBM. 20.0. 2004, San Francisco, CA, USA).
Statistical differences between the solvents used in the study were estimated using Tukey's test. The confidence limits were set at p ≤ 0.05.
3. Results
All the raw materials as well as the final tea were used to prepare extracts. These latter extracts were evaporated to dryness to estimate the yields, perform the chromatographic analyzes by HPLC-DAD and evaluate the antioxidant and cytotoxic activities.
3.1. Efficacy for Preparing WI Products (WIP)and PLE Products (PLEP)
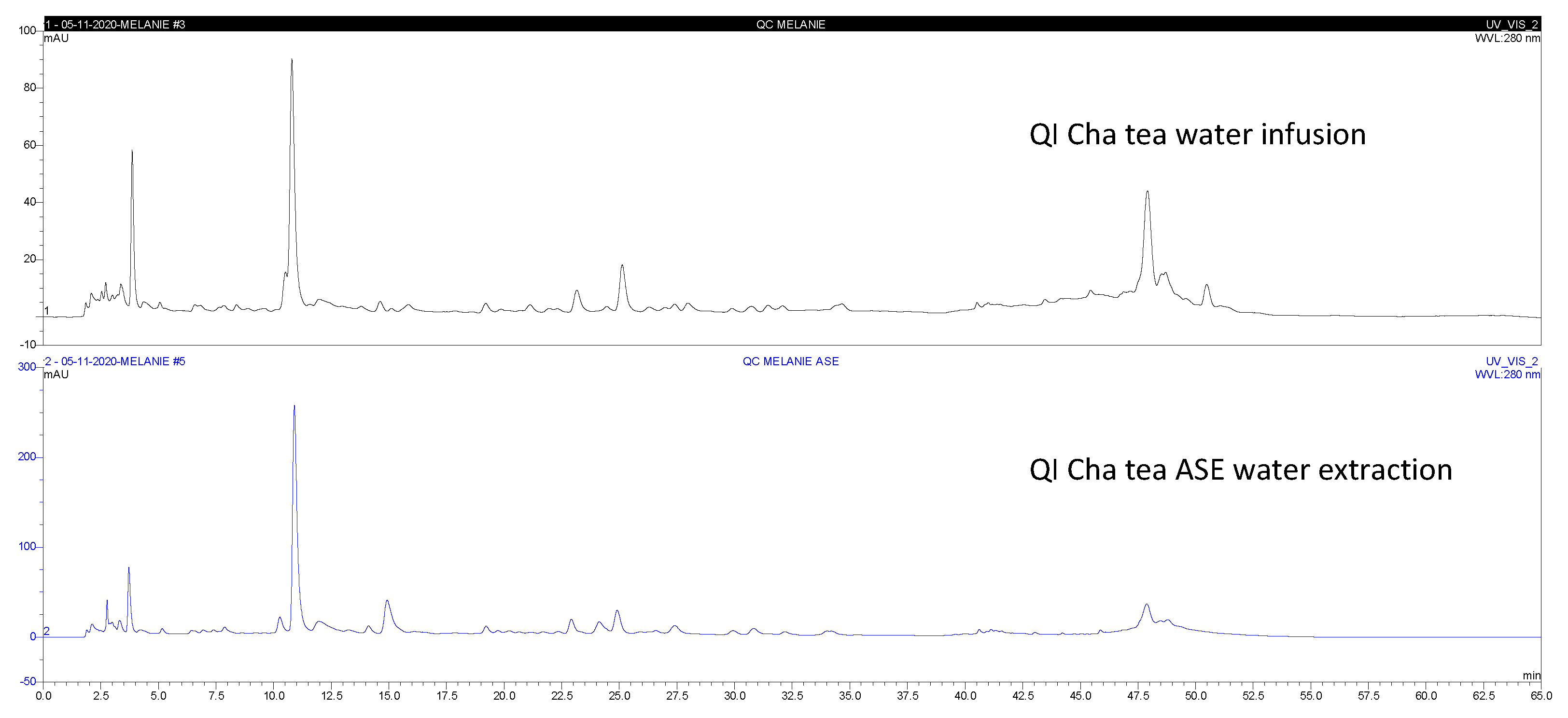
The typical chromatograms of Qi cha tea
® water extract obtained by the both methods (water infusion WI or PLE water extraction) are shown in the
Figure 2. Extract yields from Qi cha tea
®and botanicals to prepare WIP and PLEP are listed in the
Table 1. As compared to WIP, PLEP showed the improved extraction yields in the case of Elderberry, Tulsi, white tea and Lemongrass samples. For Echinacea, the extraction yield was about 100% because the sample was already a dried extract. The yields of WIP from Qi cha Tea
® and Orange peel are higher than those of PLEP. This result may be due to the presence of terpenes from essential oils, for example, which are recovered in the infusion at the surface of the water phase (essential oil extraction principle) whereas the PLEP preparation method does not allow extract of them under the effect of pressure given the large difference in polarity.
3.2. HPLC-DAD Analysis
Analysis of Qicha tea
® and botanical samples using HPLC-DAD was conducted. All tests were performed in duplicate. The results for Qi cha tea
® and its constituents are shown in the
Table 2. The quantification of the following components (G1-G8): [caffeine (G1) - (-)–epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG, G2) - (+)-catechin (G3) - (-)-epicatechin (G4) - (-)-epicatechin-3-gallate (G5) - (-)-gallocatechin (G6) - (-)–gallocatechin-3-gallate (G7) - (-)–catechin-3-gallate (G8)], gallic acid (GA) and epigallocatechin (EGC) levels of the Qicha tea and botanicals, were compared. A significant variation of HPLC-DAD profile between WIP and PLEP Qi cha tea
® was observed (
Figure 2). In the analysed samples, it was observed that the extracts obtained by PLE showed an improvement of 113, 13, 1.7, 15, 4.6, and 3.6 times of GA, EGC, G1, G2, G4 and G6 for Qi cha tea
®. For other samples, the highest content of compounds from the catechin family were observed in samples of Qi cha tea
® and also in organic white tea, with amounts of 5173 mg/Kg for EGC and 9095 mg/Kg for G1 in Qi cha tea
®, and 4089 mg/Kg for compound G3 in organic white tea. Echinacea also contained important quantity of the component G4 (9653 mg/kg). The most important difference was observed in Qi cha tea
® extract PLEP. We quantified 7 molecules, and this is strong evidence that PLE enhances the extraction and isolation of molecules compared to the classic direct infusion method. The Qi cha tea
® analysis obtained with further PLE revealed high level of GA (1470 mg/kg), EGC (5173 mg/kg) and G1 (9095 mg/kg).
The comparison of Qi cha tea® WIP to the original WIP white tea polyphenols and caffeine showed that caffeine, catechin, and epicatechin composition was modified, resulting in less caffeine and gallic acid and the presence of EGCG (G2). The EGCG (G2) was not detected in the white tea that was used.
Gallic acid (GA), epigallocatechin (EGC), caffeine (G1) - (-)-epigallocatechin 3-gallate (G2) -(+)-catechin (G3)- (-)-epicatechin (G4) - (-)-epicatechin-3-gallate (G5) - (-)-gallocatechin (G6), (-)-gallocatechin 3-gallate (G7) and (-)-catechin 3-gallate (G8) levels in Qicha tea®, tea and botanicals using HPLC-DAD. ”-“: not determined.
3.3. Antioxidant Capacity and Cytotoxic Activity of Qi Cha Tea® and Its Components
3.3.1. Antioxidant Activity
Antioxidant properties as determined by the method using DPPH and cytotoxic activity of Qi cha tea® and botanicals in Caco-2 and human HCT-116 cell lines are shown in
Table 4.
Qi cha tea® inhibition strength was increased in PLEP and doubled the percentage from 32 to 61% as compared to Qi cha tea® WIP. This result indicates that the method to prepare PLEP enhances antioxidant activity and can ameliorate bioactive molecule isolation. The majority of Qi cha tea® and botanicals tested at the concentration 50 µg/mL showed measurable antioxidant activity, with the exception of Echinacea. The greatest activity was found in white tea PLEP (90% of inhibition at 50 µg/mL and an IC50 equal to 29 µg/mL). Tulsi PLEP was also considered to be a very potent antioxidant (82% of inhibition at 50 µg/mL).
The antioxidant power of the Qi cha tea® (90% at 50 µg/mL for PLEP) was divided by approximately a factor of 2 (61% at 50 µg/mL for PLEP) which corresponds to the 48.3% (m/m) white tea content in the Qi cha tea®.
Orange peel and Echinacea antioxidant activities were low: 7, 14, 6, and 21% for WI and PLE, respectively. The Qi cha tea® presented an important antioxidant level towards DPPH. This was also observed for Tulsi and white tea. High antioxidant power is likely related to high level of molecules present in each sample. Cytotoxic effects evaluated on both on HCT-116 and Caco-2 cells for all PLE samples were always present (viability between 63-80%) and important only for lemongrass samples (viability at 49%). Lemongrass had a medium level of antioxidant action: 40% at 50 µg/mL
3.3.2. Cytotoxic Activity
The results for cytotoxic activity are shown in
Table 3 for PLEP. Qi cha tea® showed the lowest cytotoxic activity in the both cell lines used. The results demonstrated that the percentage of viability was high and varied from 63 to 80% at 50 µg/mL in the Caco-2 cell line for the first six samples tested (
Table 3). The viability of the lemongrass PLE in Caco-2 cells was about 49%. In HCT-116 colon cancer cells, cytotoxicity (100% viability) of tested PLE samples, including Qi cha tea®, varied from 12 to 28%.
4. Discussion
Many processes such as encapsulation, nanoparticles have been published for tea catechin preservation. We have prepared white tea formulation called Qi cha tea® using the new process termed as the ABC process (
Table 4) [
17].
Table 4.
The ABC method for preparation of Qi cha tea®.
Table 4.
The ABC method for preparation of Qi cha tea®.
| ABC process |
Components of Qi cha tea®
|
Amount (in %) |
| Support |
White tea |
48.3 |
| Tulsi |
12.5 |
| Edelberry |
10.0 |
| Lemongrass |
10.0 |
| Orange peel |
6.5 |
Active ingredient
(dry extract) |
Echinacea |
10.0 |
Hydroalcoholic solution with binder
Drying |
Organic acacia gum |
2.5 |
| Blowing dry air |
ND |
| Flavors |
Natural aromas of bergamot and orange |
0.2 |
The technological advantages of the ABC method (the ability to adsorb the active ingredients more uniformly due to the use of the hydroalcoholic solution with added acacia gum could have modify the new beverages in a way to reduce their biological activities and chemical composition. So, in this study, we analysed the chemical composition, the antioxidant activity and the cell viability or cytotoxicity activities of Qi cha tea
® and all botanical constituents of Qi cha tea
®. We used two methods of analysis. The data indicate that the PLE from Qi cha tea
® has high level of tea polyphenols and caffeine than Qi cha tea
® WI (
Table 2). Other compounds were present only in either WIP or PLEP. This difference can be explained by a competition between all the substances present in the plant matrix and their affinities with respect to the solvent on the one hand and the influence of the extraction parameters (agitation, temperature and extraction time for infusion pressure and temperature). Indeed, in addition to these tracked substances, there are other metabolites that are extracted. This competition generates variable extract yields and a risk of hydrolysis, oxidation or reduction under the effect of temperature.
Caffeine content is a major compound in tea [
18]. Caffeine content from white tea WIP was found one of the most abundant coumpound in our study according to previous study of Pan et al [
19]. The catechins EGCG, EC, ECG and EGC were the major polyphenols compounds according to Pan et al [
19]. EGCG was not detected in the white tea WIP but detected in the Qi cha tea
® WIP. The 6.5% of Orange peel content used for the process of Qi cha tea
® and detected only in PLEP could not explain the presence of EGCG in the Qi cha tea
® WIP. Our results with undetectable ECGC in the white tea WIP are similar to results of AlHafez et al [
20]. In conclusion, as the water infusion composition is close from that brewing tea beverages, the ABC process play a role in the polyphenols and caffeine contents of Qi cha tea
® in reducing caffeine content and increasing EGCG content.
EGC is present in Qi cha tea® (WIP or PLEP) and comes mainly from white tea (1054-1370 mg/Kg) or Tulsi (414-1027 mg/Kg) and to a lesser extent from Lemongrass (255 mg/Kg). Its PLE extraction is the highest (5173 mg/Kg). This high recovery of PLEP can be explained by the influence of parameters (higher temperature and pressure) in the PLE.
Determination of the biochemical activity of Qi cha tea
® confirmed an important antioxidant level in the DPPH assay. This was also observed for Tulsi and white tea. High antioxidant power is likely related to high level of molecules present in each sample. Evaluation of cytotoxic effects on HCT-116 and Caco-2 cells was comparable between the Qi cha tea
® and the original sample extracts. The evaluation of biological activity of Qi cha tea® and its components are in good agreement with previous studies [
21,
22]. White tea and Echinacea showed comparable cytotoxicity activity (28%). Hajiaghaalipour et al [
23] cited that extract of white tea inhibited the proliferation of HT-29 cells with an IC
50 of 87 μg/mL. In another work, the IC
50 of white tea extract is 324 µg/mL against MFC-7 cell line [
24]. These results prove that our extracts are much more active against the two cell lines studied.
A previous study evaluated the anti-proliferative property of the white tea and demonstrated that white tea containing important quantity of EGC seems to have the better anti-cancer effect than other teas [
21]. It has been shown that one of the anti-cancer processes of growth inhibitory activity of tea may involve the catalytic regulation of the P450 enzymes and glucuronosyltransferase [
22].
In the literature, catechins (flavan-3-ols), which are considered low-cost applicable phytochemicals, are the major green tea polyphenols [
24]. EC, EGC, ECG and EGCG are major components in little fermented teas like white tea. EGCG from green teas is the most abundant and biologically active catechin [
25]. Based on decades of research, EGCG has received considerable attention for its inhibitory activities against cancer initiation, promotion and progression [
26]. Other catechins, such as ECG and EGC, have been shown to have similar, albeit lower, activities in numerous studies [
3,
4]. Concerning white teas, the levels were not considered to be very high in a previous study [
20]. In another study conducted on aqueous methanol (70%) extracts, DPPH radical scavenging activity and antiproliferative effects of white tea against colorectal cancer cell line HCT-116, were most likely due to its catechin content [
27,
28]. The determination of antioxidant and others biochemical properties of these food formulations may lead to explanations for others health claims [
14,
29].
Table 5 presents the formulation of Qi cha tea
®, and the function health claim wording for respiratory and immune systems (ID2466 and ID2366 respectively) with Tulsi, Elderberry and Echinacea respectively (15).
In this study, we presented the formulation of Qi cha tea®, its biological activities and the associated health claims that results from an original and organic tea beverage processed according to the patented ABC method innovation. According to the “on hold” european botanical heath claims, new health claims could be associated to botanical health claims. It will be of interest to explore its application to various botanicals from the european botanical list to improve of human healthcare with the ABC method.
5. Conclusions
The ABC method has many advantages and offers a real breakthrough in the production of teas and botanical infusions for health and wellness. Qi cha tea® is the white tea-based formulation produced by this innovative method. In conclusion, application of the patented ABC (Bio Concentrate Assets®) method to Qi cha tea® using various botanicals and dry extract with the acacia gum has allowed the development a new innovative functional health beverage which complies with European health claims.
6. Patents
European patent EP 3501291, PROCÉDÉ DE FABRICATION D'INFUSIONS OU DE THÉS CONTENANT DES ACTIFS D'ORIGINE VÉGÉTALE, ANIMALE OU MINERALE. Owner of the patent: Thés de la Pagode, 4 Avenue Bertie Albrecht, 75008, Paris, France
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.M.M. and J.M.Z.; methodology, J.M.Z., J.M.M., J.B.; analysis, M.B., O.P., J.B., J.M.M.; investigation, J.M.M.; M.B.; J.M.Z.; resources, J.M.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, J.M.M.; writing—review and editing, J.M.M.; M.B.; O.P.; E.T.; J.B. and J.M.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Thés de la Pagode (France).
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Pr Mamoru Isemura (School of Nutritional and Environmental Sciences, University of Shizuoka, Suruga-ku, Shizuoka, Japan for extensive revision and review, Dr Sandrine Pierre (Marshall Institute for Interdisciplinary Research, Huntington, West Virginia, USA) for providing insightful comments. We are also grateful to Dr. Susan Whiting (University of Saskatchewan) and Dr. Souad Sennoune and Raul Martinez-Zaguilan (Texas Tech University, Health Sciences center, Lubbock, Texas, USA) for their revisions. This work is also dedicated to Dr. Zijian Xie (Marshall Institute for Interdisciplinary Research, Huntington, West Virginia, USA) for discussion on teas.
Conflicts of Interest
J.-M.Z. as Thés de la Pagode and funder. J.M.M., O.P., J.B., M.B. authors declare no conflict of interest J.M.Z. as funder had no role in the design of the analytical study and in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data.
Sample Availability
Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
References
- Li HY, Gan RY, Shang A, Mao QQ, Sun QC, Wu DT, Geng F, He XQ, Li HB. Plant-Based Foods and Their Bioactive Compounds on Fatty Liver Disease: Effects, Mechanisms, and Clinical Application. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2021, 1, 2021:6621644. [CrossRef]
- Chen Y, Zhou Y, Zeng L, Dong F, Tu Y, Yang Z. Occurrence of Functional Molecules in the Flowers of Tea (Camellia sinensis) Plants: Evidence for a Second Resource. Molecules, 2018, Mar 29;23(4):790. [CrossRef]
- Chung M, Zhao N, Wang D, Shams-White M, Karlsen M, Cassidy A, Ferruzzi M, Jacques PF, Johnson EJ, Wallace TC. Dose-Response Relation between Tea Consumption and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and All-Cause Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Population-Based Studies. Adv Nutr, 2020, Jul 1;11(4):790-814. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmaa010. PMID: 32073596; PMCID: PMC7360449. [CrossRef]
- Tang GY, Meng X, Gan RY, Zhao CN, Liu Q, Feng YB, Li S, Wei XL, Atanasov AG, Corke H, Li HB. Health Functions and Related Molecular Mechanisms of Tea Components: An Update Review. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(24):6196. [CrossRef]
- Liu JY, He D, Xing YF, Zeng W, Ren K, Zhang C, Lu Y, Yang S, Ou SJ, Wang Y, Xing XH. Effects of bioactive components of Pu-erh tea on gut microbiomes and health: A review. Food Chem, 2021, 3, 353:129439. [CrossRef]
- Braud L, Peyre L, de Sousa G, Rahmani R Maixent JM. Effect of brewing duration on the antioxidant and hepatoprotective abilities of tea phenolic and alkaloid compounds in a t-BHP oxidative stress-Induced rat hepatocyte model. Molecules 2015, 20:14985-15002. [CrossRef]
- Braud L, Battault S, Nascimento A, Gaillard S de Sousa G, Rahmnani R, Riva C, Armand M, Meyer G, Maixent JM, Reboul C. Antioxidant properties of tea blunt ROS-dependent lipogenesis: beneficial effect on hepatic steatosis in a high fat-sucrose diet NAFDL obese rat model. J Nut Biochem, 2017, 40:95-104.
- Pierre, S , Lesnik P , Duran MJ, Moreau, M, Paganelli, F, Chapman J, George F, Sampol J, Maixent JM. Oxidized LDLs alter Na,K-ATPase activity in human endothelial cells. Prevention by Ginkgo biloba Extract (EGb 761). Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand), 2008, 54, 1032-1042.
- Maixent, JM, Fares, M, François C. Safe plants infusion from traditional herbal remedies for insomnia and anxiety causes a dose-dependent increase of NO and has a protective effect on the renal cellular stress caused by hypoxia and reoxygenation. Can J Biotech, 2018, 2, 116-123.
- François C, Fares, M, Maixent JM. Safety of Desmodium adsencendens extract on hepatocyte and renal cells. Efficacy on oxidative stress. J Intercult Ethnopharmacol, 2015, 1, 1-5.
- Maixent JM. Opinion paper food supplements: the European regulation and its application in France. Thoughts on safety of food supplements. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand), 2012, 30, 720-17299.
- Battault S, Whiting SJ, Peltier SL, Sadrin S, Gerber G, Maixent JM. Vitamin D metabolism, functions and needs: from science to health claims. Eur J Nutr, 2013, 52, 429-441. [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 20 December 2006 on nutrition and health claims made on foods (OJ L 404, 30.12.2006, p.9).
- European Commission Evaluation (SWD (2020)95 Final-pt1) of the Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006 on Nutrition and Health Claims Made on Foods with Regard to Nutrient Profiles and Health Claims Made on Plants and Their Preparations and of the General Regulatory Framework for Their Use in Foods. European Commission; Brussels, Belgium: 2020.
- Silano V, Coppens P, Larrañaga-Guetaria A, Minghetti P, Roth-Ehrang R. Regulations applicable to plant food supplements and related products in the European Union. Food Funct, 2011, 2, 710-719. [CrossRef]
- Khelifi I, Hayouni EA, Cazaux S, Ksouri R, Bouajila J. Evaluation of in vitro biological activities: antioxidant; anti-inflammatory; anti-cholinesterase; anti- xanthine oxidase, anti-superoxyde dismutase, anti-α-glucosidase and cytotoxic of 19 bioflavonoids. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand), 2020, 66, 9-19. [CrossRef]
- Maixent JM, Zeil JM. ABC, a patented innovation in the infusion of teas and herbal plants: enrichment of Camellia sinensis leaves with dry extracts from herbal plants. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2019, 65, 76-78. [CrossRef]
- Ramalho SA, Nigam N, Oliveira GB, Pa O, Tom S, Santos AGP, Narain N. Effect of infusion time on phenolic compounds and caffeine content in black tea. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51: 155–161. [CrossRef]
- Pan J, Jiang Y, Lv Y, Li M, Zhang S, Liu J, Zhu Y, Zhang H. Comparison of the main compounds in Fuding white tea infusions from various tea types. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2018 May 23;27(5):1311-1318. [CrossRef]
- AlHafez M, Kheder F, AlJoubbeh M. Polyphenols, flavonoids and (-)- epigallocatechin gallate in tea leaves and in their infusions under various conditions. Nutr. Food Sci. 2014, 44: 455–463. [CrossRef]
- Östlund J, Zlabek V, Zamaratskaia G. In vitro inhibition of human CYP2E1 and CYP3A by quercetin and myricetin in hepatic microsomes is not gender dependent. Toxicology 2017, 381,10-18. [CrossRef]
- Yuan JM, Gao YT, Yang CS, Yu MC. Urinary biomarkers of tea polyphenols and risk of colorectal cancer in the shanghai cohort study. Int J Cancer, 2007, 120,1344-50. [CrossRef]
- Hajiaghaalipour F, Kanthimathi M.S., Sanus J, Rajarajeswaran J. White tea (Camellia sinensis) inhibits proliferation of the colon cancer cell line, HT-29, activates caspases and protects DNA of normal cells against oxidative damage, Food Chemistry, 2015, 169, 401-410. [CrossRef]
- Ronimara A. S, Andrade E.D.S., Monteiro M, Fialho E, Silva J.L., Daleprane J.B., Ferraz da Costa D.C.. Green tea (Camellia sinensis) extract induces p53-Mediated cytotoxicity and inhibits migration of breast cancer cells. Foods 2021, 10, 12: 3154. [CrossRef]
- Chen XQ , Du YL, Wu, JC, Xie XL, Chen, BB, Hu Q. Li. Effects of tea-polysaccharide conjugates and metal ions on precipitate formation by epigallocatechin gallate and caffeine, the key components of green tea infusion. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2019, 67, 3744-3751. [CrossRef]
- Shirakami, Y., & Shimizu, M. Possible mechanisms of green tea and its constituents against cancer. Molecules, 2018, 23(0), 2284. [CrossRef]
- Fereydoon B, Ebrahimi A, Mahjoubi F, Hervan EM, Gonbad RA. 2018. Evaluation of biochemical constituents and inhibitory effect of tea clone 100 on colorectal cancer cell line HCT-116. Tropical Journal Pharmaceutical Research. 2018, 17, 1033-1041. [CrossRef]
- Dawra, M, El Rayess, Y, El Beyrouthy, M, Nehme N, El Hage, R, Taillandier, P, Bouajila, J. Biological activities and chemical characterization of the Lebanese endemic plant Origanum ehrenbergii Boiss. Flavour Fragr J. 2021; 36: 339–351. [CrossRef]
- Qin C, Lian L, Xu W, Jiang Z, Wen M, Han Z, Zhang L. Comparison of the chemical composition and antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, α-amylase and α-glycosidase inhibitory activities of the supernatant and cream from black tea infusion. Food Funct. 2022,13(11):6139-6151. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).