1. Introduction
Postural control relies on integrated processing of multisensory afferent information by the vestibular, proprioceptive, and visual system. These are integrated in the cerebellum and basal ganglia and result in output to the brainstem and spinal cord for the execution of postural reflexes aimed at maintaining balance [
1]. These mechanisms are deranged in the advanced stages of Parkinson’s disease (PD), which are often characterized by postural instability (PI). Abnormal balance control in PD patients may manifest either during stance, where abnormal posture may be observed, or in dynamic conditions, characterized by poor automatic postural reactions and festination [
2]. PI exposes PD patients to an increased risk of falls (RF), which often leads to a dramatic worsening of the patient’s clinical status [
3]. In PD, PI recognizes a multifactorial origin that includes muscle stiffness, abnormal visual, vestibular and proprioceptive processing, as well as cognitive deficits [
4]. These abnormalities result in a mismatch between the center of mass (COM) and the center of pressure (COP), with consequent increase in RF [
5]. While the efficacy of deep brain stimulation (DBS) of the subthalamic nucleus (STN) in improving appendicular symptoms in PD is widely accepted, its effect on axial symptoms is still not clear [
6]. Limited evidence suggested postural improvement after DBS [
7,
8], whereas other work reported either worsening [
9] or no effect [
10]. We hypothesized that these inconsistencies could be due, at least in part, to the fact that possible interactions between DBS and dopaminergic medications were not fully considered. Therefore, the aim of our study was to systematically evaluate the effects of DBS, dopaminergic therapy and their interaction on PI and RF parameters assessed by a stabilometric platform. Understanding which DBS/medication combinations result in greater postural stability may lead to new strategies aimed at improving axial symptoms in PD.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
We enrolled six consecutive patients with PD from the Parkinson’s disease center of the IRCCS Neuromed Institute (Pozzilli, Italy). Inclusion criteria included a diagnosis of PD based on international clinical criteria [
11], disease duration longer than 6 years, bilateral STN DBS performed more than 1 year before the evaluation, confirmed STN leads position. Exclusion criteria were a history of neurological conditions other than PD, significant disorders of visual acuity vestibular or proprioceptive dysfunction, major orthopedics conditions, diabetes mellitus, Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) score < 24. The study was performed according to the Declaration of Helsinki. Patients signed an informed consent form prior to examination and the study was approved by the local ethics committee.
2.2. Clinical Assessment
Clinical evaluation included collection of patients’ demographics, disease duration, Levodopa equivalent daily dose (LEDDs), Unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale (UPDRS) part III, MMSE. LEDD is a conversion factor that allows to estimate the global amount of dopaminergic treatment by converting each antiparkinsonian drug dosage into levodopa equivalent. UPDRS part III provides an objective estimation of motor symptoms severity in PD based on the evaluation of the examiner.
2.3. Stabilometric platform
We assessed PI and RF using the Biodex Stability System (BSS) (Biodex, Inc., Shirley, NY), a standardized system that allows objective and reliable quantification of postural control in static and dynamic conditions [
12,
13]. The BSS consists of a circular platform that is free to move in the anterior-posterior and medial-lateral axes with 12 levels of stability. The system provides the degree and velocity of platform tilt and, given the subject’s height, it can measure the COM displacement. Digitized COM and platform tilt are transmitted to a dedicated software for objective quantification of PI and RF (Version 1.08, Biodex Inc.).
2.4. PI and RF assessment
PI and RF were assessed using standardized tests provided by the system dedicated software [
12,
13]. At the beginning of the test session, the patient was asked to stand on the platform in a stable position. The feet position was marked to ensure a consistent starting position across conditions, thus excluding confounding due to a different base of support. PI was assessed by measuring patients’ COM sway during stance with a stable platform. To assess RF, patients were instructed to maintain a stable posture while the platform became progressively more unstable. RF was described as patients’ ability to control the platform angle and was quantified as degree variance over time. Participants performed three consecutive trials for each test and in each experimental condition. PI and RF were scored from 0 to 18, each score representing the mean of the three measurements. Higher scores corresponded to poorer performance. One training trial for each test was performed at the beginning of the experimental session and its value discarded. Two examiners were ready to support the patient in the event of a fall; in this case, a score of 18 was attributed.
2.5. Experimental conditions
In a single session, patients were tested for PI and RF first in OFF-medication (OFF) and then in pharmacological ON-medication (ON). In each pharmacological condition, patients were tested in four STN-DBS conditions: DBS of the more affected side (DBS-more), DBS of the less affected side (DBS-less), bilateral DBS (DBS-bilateral), and off DBS (DBS-off). More and less affected sides DBS were defined respectively as DBS contralateral and ipsilateral to limbs showing higher scores in the UPDRS part III. The ON-medication recordings were performed one hour after the intake of each subject’s usual dose of levodopa. DBS conditions were set apart by 20 minutes, and their order was randomized for each participant to exclude a possible bias due to motor learning.
2.6. Statistical analysis
PI, RF, and UPDRS values were tested for normality by the Shapiro-Wilk’s test on the studentized residuals. Three two-way repeated-measures ANOVAs (rmANOVAs) with “medication” (on, off), and “stimulation” (DBS-more, DBS-less, DBS-bilateral, DBS-off) were performed on UPDRS-III, PI and RF scores. Post hoc analysis were carried out with paired T-tests. Type I errors in testing of multiple pairwise comparisons were controlled for with the false discovery rate (FDR) correction (maximum acceptable FDR 0.05). P values < 0.05 were considered significant. Sphericity in data distribution was verified by Mauchly’s tests and the Greenhouse-Geisser correction was applied when necessary. Statistical analysis was performed with SPSS Version 25.0.
3. Results
Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation unless otherwise specified.
Table 1 shows patients’ group characteristics.
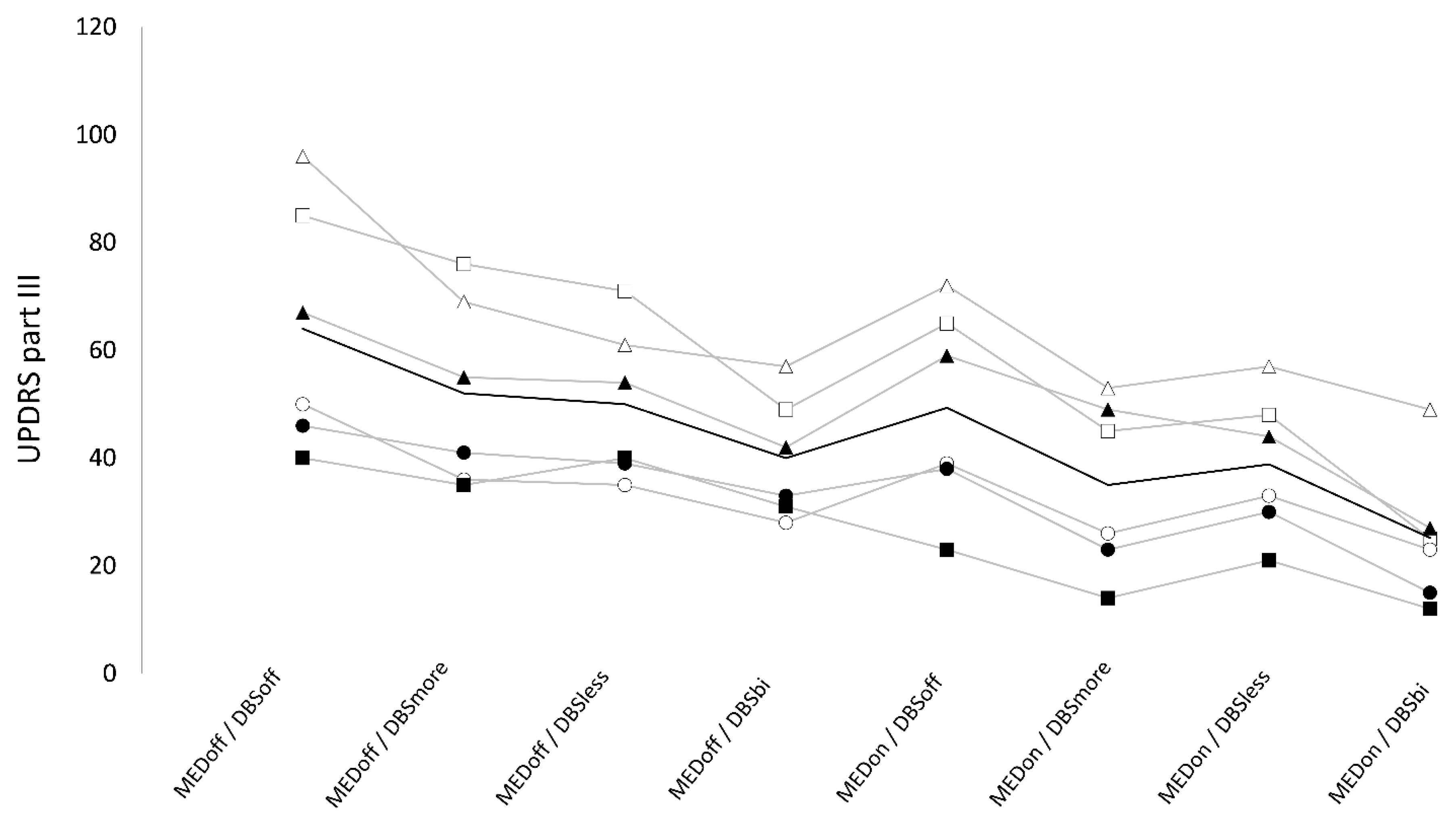
3.1. UPDRS part III
We found a non-significant “stimulation×medication” interaction on UPDRS part-III (F
3,5 = 1.33, p = 0.3), but a significant effect of “medication” (F
1,5 = 30.74, p < 0.005) and stimulation (F
3,15 = 22.54, p < 0.01). UPDRS part-III was significantly higher in OFF (51.5 ± 6.6) compared to ON-medication (37.1 ± 6.1, t = 5.5, p < 0.01, q < 0.01). Also, UPDRS part-III was significantly higher in DBS-off condition (56.8 ± 20.4) compared with DBS-more (43.7 ± 16.2, t = 5.9, p = 0.01), DBS-less (44.7 ± 13.1, t = 3.7, p = 0.02), and DBS-bilateral (32.8 ± 11.6, t = 5.8, p < 0.01). UPDRS-III score was significantly lower in DBS-bilateral compared to DBS-more (t = 3.3, p = 0.03), and DBS-less (t = 4.7, p < 0.01), whereas it was not significantly different when comparing DBS-more and DBS-less (t = 0.7, p = 0.5) (
Figure 1).
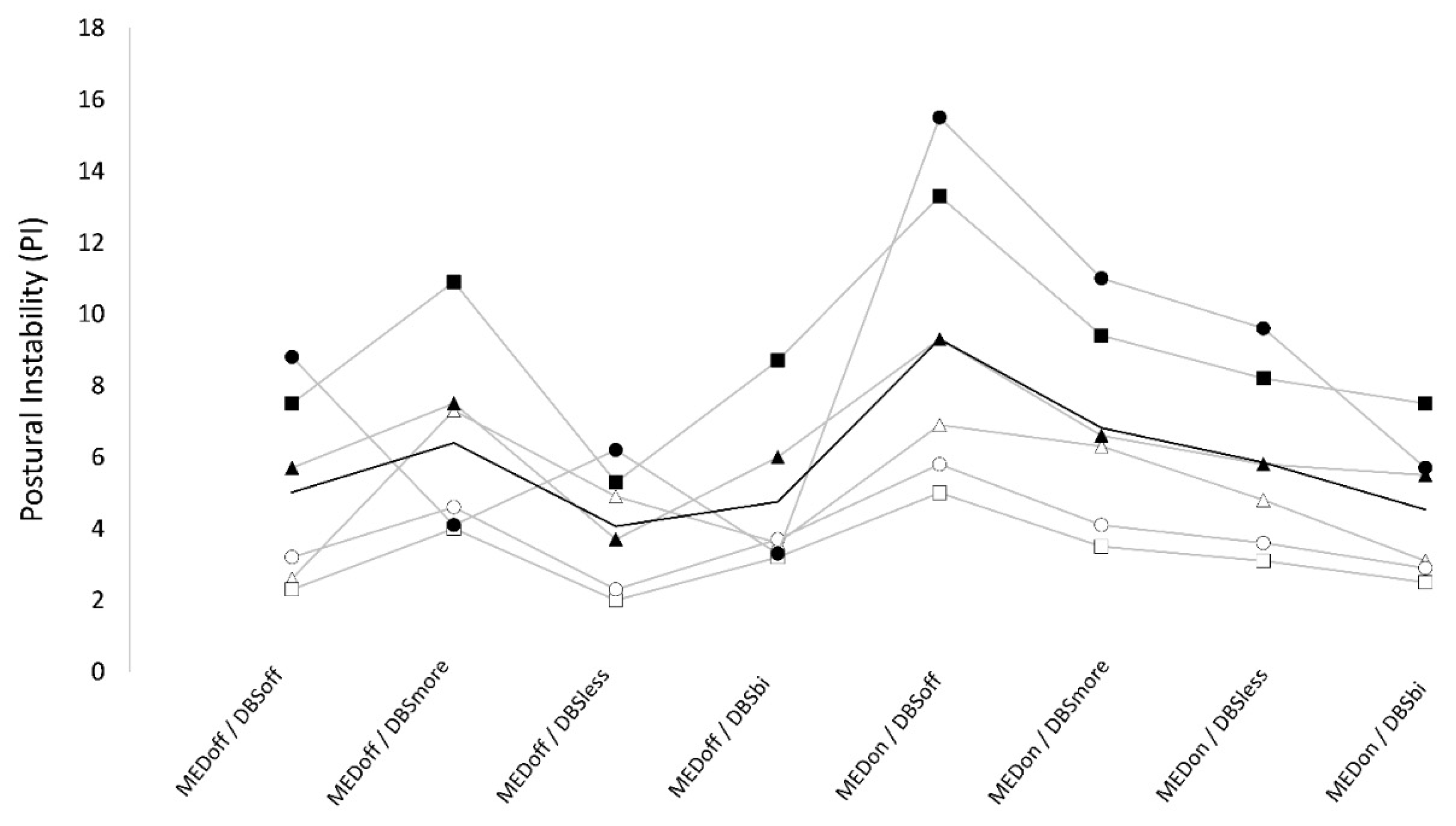
3.2. Postural instability
Numeric results are reported in
Table 2. We found a significant “stimulation×medication” interaction on PI. In OFF-medication, PI values were not significantly different between conditions. In ON-medication, PI was significantly higher in DBS-off (9.3 ± 4.3) compared to DBS-bilateral (4.5 ± 2.0), DBS-more (6.8 ± 2.9), and DBS-less (5.9 ± 2.6). Also, when ON-medication, there was a trend for lower values in DBS-bilateral than DBS more and DBS-less. Finally, when ON- medication, PI was significantly higher in DBS-more compared to DBS-less. When testing for the effect of medication, we found that PI was not significantly different between OFF and ON medication in DBS-bilateral (4.8 ± 2.2 vs 4.5 ± 2.0), and in DBS-more condition (6.4 ± 2.7 vs 6.8 ± 2.9). However, PI was significantly lower in OFF compared to ON medication in DBS-off (5.0 ± 2.6 v.s. 9.3 ± 4.3) condition and there was a trend for lower values in OFF than ON in DBS-less (4.1 ± 1.7 v.s. 5.9 ± 2.6) condition. (
Table 2) (
Figure 2).
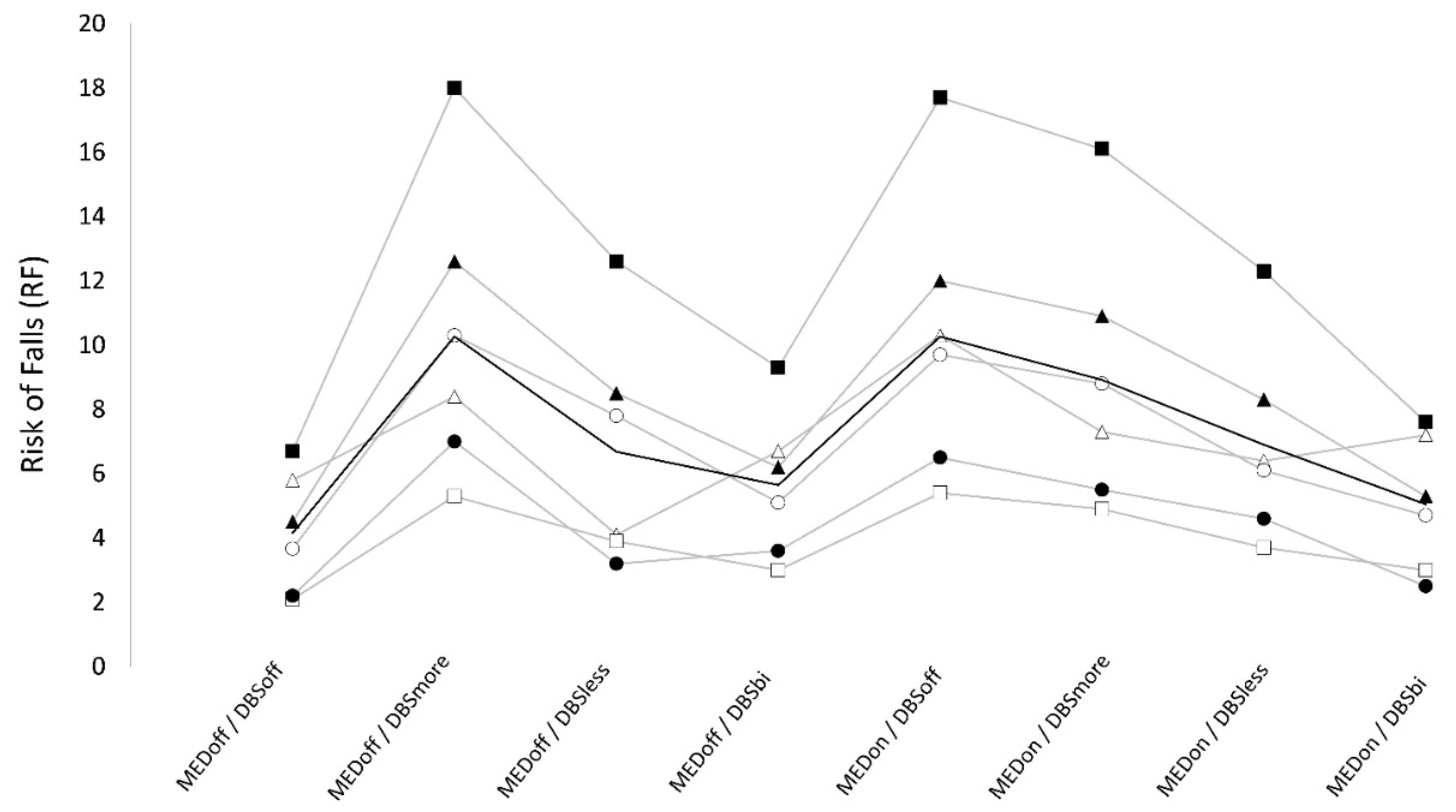
3.3. Risk of falls
Numeric results are reported in
Table 2. We found a significant “stimulation×medication” interaction on RF. When OFF-medication, lowest and highest RF values were observed respectively in DBS-off (4.2 ± 1.9), and DBS-more conditions (10.3 ± 4.5), and the difference between these conditions was significant. DBS-bilateral showed intermediate RF scores (5.6 ± 2.4) that were significantly higher than DBS-off and significantly lower than DBS-more, whereas no significant difference was observed when compared to DBS-less (6.7 ± 3.4). Finally, when OFF- medication, RF was significantly higher in DBS-more compared to DBS-less whereas only a trend was found for lower values in DBS-off than DBS-less. When ON-medication, RF was maximum in DBS-off (10.1±4.5) and was significantly higher compared to all ON DBS conditions (DBS-more: 8.9±4.2, DBS-less: 6.9 ± 3.2, DBS-bilateral: 5.1 ± 2.3). Also, when ON-medication, RF was significantly higher in DBS-more than DBS-less, and DBS-bilateral, and RF was higher in DBS-less compared to DBS-bilateral, but this difference did not reach statistical significance. When testing for the effect of medication, we found that RF was not significantly different between OFF and ON medication in DBS-bilateral conditions (5.6 ± 2.4 vs 5.0 ± 2.3), and in DBS-less condition (6.7 ± 3.4 vs 6.9 ± 3.2). However, RF was significantly higher in ON compared to OFF medication in DBS-off condition (10.1 ± 4.5 vs 4.2 ± 1.9), while it was significantly higher in OFF compared to ON medication in DBS-more condition (10.3 ± 4.5 vs 8.9 ± 4.2).(
Table 2) (
Figure 3).
3.4. Summary of results
UPDRS part III values were significantly lower in ON-medication compared to OFF-medication. Also, UPDRS part III values were significantly lower in DBS-bilateral compared to all other DBS conditions and were significantly higher in DBS-off compared to all other DBS conditions.
The best scores of PI and RF were observed when in off-medication, DBS-off condition. When in DBS-off condition, patients showed higher PI and RF in the ON-medication condition.
When OFF-medication, DBS did not affect postural instability, while all DBS-on conditions (i.e., bilateral, more and less affected side) worsened RF compared to DBS-off with highest RF in DBS-more and lowest in bilateral-DBS. When ON-medication, DBS improved PI and RF, with maximal improvement when in DBS-bilateral condition and minimal improvement in DBS-more condition. Finally, in ON and OFF-medication, DBS-less showed intermediate PI and RF values, with significantly lower values compared to DBS-more, and a trend for higher values compared to bilateral-DBS. The effects of DBS, medication, and their interaction on PI and RF values were independent from motor improvement as assessed by UPDRS part III.
4. Discussion
In the present study we investigated the effects of the interaction between pharmacological dopaminergic treatment and STN-DBS on balance control in advanced PD. We found that PD patients had best motor performance, as tested by UPDRS part III when ON-medication and DBS-bilateral. When in DBS-off, dopaminergic treatment worsened both PI and RF, and when OFF-medication, DBS did not change PI, but worsened RF. When ON-medication, PI and RF significantly improved after turning the DBS on, regardless the stimulation condition. However, no combination between pharmacological treatment and DBS was able to induce a significant improvement on postural control respect to the OFF- medication/DBS-off condition.
This is the first study that systematically assessed PI and RF in all medication and DBS conditions in PD in a single session. Previous studies reported conflicting results on the relationship between dopaminergic treatment and motor balance, showing either improvement [
14,
15], no affect [
16] or even worsening [
10,
17]. Our observation that dopaminergic medication improves motor performance, but worsen PI and RF, may be explained by a reduction in axial rigidity without associated improvement in postural control [
18]. This result also suggests that balance control in advanced PD cannot be due to dopaminergic deficit only, thus confirming previous observations [
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21].
Although several studies have investigated the effect of STN-DBS on balance control, producing conflicting results, few used objective posturometric measurements [
6,
22,
23]. While studies that compared DBS effects before and shortly after surgery may be biased by the surgical procedure itself [
24], studies that assessed the effect of DBS in a single session after surgery found an improvement of postural control consistent with our results [
15,
17]. However, these studies were limited by evaluation performed only in bilateral-DBS [
17], or in OFF- medication conditions [
15]. To the best of our knowledge, only one study investigated the effect of DBS on postural control while ON medication using the BSS and found a non-significant improvement of postural sway in bilateral-DBS compared to DBS-off [
25]. However, patients were tested with eyes closed, and since an abnormal visual control of balance is thought to contribute to postural instability in PD, performing the tests with the eyes closed may have limited the BSS sensitivity to probe postural control in this population [
26].
In line with previous studies, our results showed that, whereas STN-DBS improved PI and RF when ON-medication, dopaminergic medication alone had negative impact on both indices [
22,
27]. DBS associated reduction of PI and RF when ON-medication may in part account for balancing out the negative effect of dopaminergic medication on postural control. These observations hint that the effect of STN-DBS on postural control may recognize non-dopaminergic mechanisms. Supporting this hypothesis, several lines of evidence suggested that the subthalamo-nigro-pedunculopontine pathway plays a central role in determining balance control in humans, and STN-DBS might improve axial symptoms by modulating non-dopaminergic descending pathways directed at the pedunculopontine nucleus [
22,
28]. The observation that DBS-bilateral showed better PI and RF than monolateral DBS suggests that a balanced activity between the two STNs is important for postural control mechanisms in both static and dynamic conditions. However, how do we conciliate this hypothesis with the finding that less-affected side DBS produced better PI and RF than more-affected side DBS? If the effect of STN-DBS on PI and RF is mediated only by the silencing of a hyperactive STN, the more-affected side DBS should produce better balance than DBS of the less affected side. Instead, when off medication (i.e., when abnormal STN activity should be maximal), more-affected side DBS proved to worsen RF compared to DBS-off and other DBS conditions including less-affected side. The question remains unanswered and warrants further investigation with larger study samples.
The main limitation of our study is represented by the small sample size; this was due to the difficulty in recruiting patients with appropriate features, such as long disease duration, high disability, and DBS implantation. Therefore, albeit the effects were consistent across patients and were statistically significant, they need confirmation in future work. Since we used a cross-sectional design, we cannot draw any conclusions about the long-term effect of dopaminergic therapy and DBS on PI and RF. However, the cross-sectional design excluded bias produced by disease-progression and day-to-day variability of symptoms and allowed us to compare different medication and DBS setups, providing useful information to guide therapeutic management of PD patients.
In conclusion, improvement of motor performance produced by dopaminergic medication alone and DBS alone comes at the cost of reduced postural control. However, bilateral DBS seems to balance the negative effect of dopaminergic medication on postural control. Bilateral DBS, when ON-medication, proved to be the best option to obtain maximal improvement of motor performance at a minimal cost in terms of balance control. Finally, the consistency of our results between subjects suggests that the BSS, in addition to predicting falls in patients implanted with DBS [
29], may be a promising tool to assess the medication/stimulation combination that produces the best postural control in PD.
Author Contributions
conceptualization, G.L., N.M., A.C., L.R., G.F, D.B.; methodology, G.L., M.S., N.M., A.F., D.B.; validation, M.S.; formal analysis, G.L., M.I.D.B., A.F., L.R.; investigation, M.S., M.D.; data curation, M.S., N.M., M.D.; writing—original draft preparation, G.L., M.D., M.I.D.B.; writing—review and editing, A.F., A.C., L.R., G.F., D.B.; visualization, A.C., L.R., G.F., D.B.; supervision, N.M., A.C., L.R., G.F., D.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ivanenko, Y.; Gurfinkel, V.S. Human Postural Control. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 171. [CrossRef]
- Nonnekes, J.; Goselink, R.J.M.; Růžička, E.; Fasano, A.; Nutt, J.G.; Bloem, B.R. Neurological disorders of gait, balance and posture: A sign-based approach. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 183-189. [CrossRef]
- Fasano, A.; Plotnik, M.; Bove, F.; Berardelli, A. The neurobiology of falls. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 33, 1215-1223. [CrossRef]
- Schoneburg, B.; Mancini, M.; Horak, F.; Nutt, J.G. Framework for understanding balance dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 1474-1482. [CrossRef]
- Horak, F.B.; Dimitrova, D.; Nutt, J.G. Direction-specific postural instability in subjects with Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 193, 504-521. [CrossRef]
- Fasano, A.; Aquino, C.C.; Krauss, J.K.; Honey, C.R.; Bloem, B.R. Axial disability and deep brain stimulation in patients with Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 98-110. [CrossRef]
- Umemura, A.; Oka, Y.; Ohkita, K.; Yamawaki, T.; Yamada, K. Effect of subthalamic deep brain stimulation on postural abnormality in Parkinson disease. J. Neurosurg. 2010, 112, 1283-1288. [CrossRef]
- Artusi, C.A.; Zibetti, M.; Romagnolo, A.; Rizzone, M.G.; Merola, A.; Lopiano, L. Subthalamic deep brain stimulation and trunk posture in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2018, 137, 481-487. [CrossRef]
- St George, R.J.; Carlson-Kuhta, P.; Burchiel, K.J.; Hogarth, P.; Frank, N.; Horak, F.B. The effects of subthalamic and pallidal deep brain stimulation on postural responses in patients with Parkinson disease. J. Neurosurg. 2012, 116, 1347-1356. [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; McIntire, K.; Kim, S.H.; Zhang, J.; Dascalos, S.; Lyons, K.E.; Pahwa, R. Bilateral subthalamic stimulation improves gait initiation in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Gait Posture 2006, 23, 492-498. [CrossRef]
- Berardelli, A.; Wenning, G.K.; Antonini, A.; Berg, D.; Bloem, B.R.; Bonifati, V.; Brooks, D.; Burn, D.J.; Colosimo, C.; Fanciulli, A.; et al. EFNS/MDS-ES/ENS [corrected] recommendations for the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2013, 20, 16-34. [CrossRef]
- Arnold, B.L.; Schmitz, R.J. Examination of balance measures produced by the biodex stability system. Journal of athletic training 1998, 33, 323-327.
- Melzer, I.; Benjuya, N.; Kaplanski, J. Postural stability in the elderly: A comparison between fallers and non-fallers. Age Ageing 2004, 33, 602-607. [CrossRef]
- Burleigh, A.; Horak, F.; Nutt, J.; Frank, J. Levodopa reduces muscle tone and lower extremity tremor in Parkinson’s disease. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 1995, 22, 280-285. [CrossRef]
- Crenna, P.; Carpinella, I.; Rabuffetti, M.; Rizzone, M.; Lopiano, L.; Lanotte, M.; Ferrarin, M. Impact of subthalamic nucleus stimulation on the initiation of gait in Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Brain Res. 2006, 172, 519-532. [CrossRef]
- Bloem, B.R.; Beckley, D.J.; van Dijk, J.G.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Remler, M.P.; Roos, R.A. Influence of dopaminergic medication on automatic postural responses and balance impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 1996, 11, 509-521. [CrossRef]
- Rocchi, L.; Chiari, L.; Cappello, A.; Gross, A.; Horak, F.B. Comparison between subthalamic nucleus and globus pallidus internus stimulation for postural performance in Parkinson’s disease. Gait Posture 2004, 19, 172-183. [CrossRef]
- Rocchi, L.; Palmerini, L.; Weiss, A.; Herman, T.; Hausdorff, J.M. Balance testing with inertial sensors in patients with Parkinson’s disease: Assessment of motor subtypes. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2014, 22, 1064-1071. [CrossRef]
- Grimbergen, Y.A.; Langston, J.W.; Roos, R.A.; Bloem, B.R. Postural instability in Parkinson’s disease: The adrenergic hypothesis and the locus coeruleus. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2009, 9, 279-290. [CrossRef]
- Bohnen, N.I.; Frey, K.A.; Studenski, S.; Kotagal, V.; Koeppe, R.A.; Scott, P.J.; Albin, R.L.; Müller, M.L. Gait speed in Parkinson disease correlates with cholinergic degeneration. Neurology 2013, 81, 1611-1616. [CrossRef]
- Pötter-Nerger, M.; Volkmann, J. Deep brain stimulation for gait and postural symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 1609-1615. [CrossRef]
- Collomb-Clerc, A.; Welter, M.L. Effects of deep brain stimulation on balance and gait in patients with Parkinson’s disease: A systematic neurophysiological review. Neurophysiol. Clin. 2015, 45, 371-388. [CrossRef]
- Crouse, J.J.; Phillips, J.R.; Jahanshahi, M.; Moustafa, A.A. Postural instability and falls in Parkinson’s disease. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 27, 549-555. [CrossRef]
- Nantel, J.; McDonald, J.C.; Bronte-Stewart, H. Effect of medication and STN-DBS on postural control in subjects with Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2012, 18, 285-289. [CrossRef]
- Brandmeir, N.J.; Brandmeir, C.L.; Carr, D.; Kuzma, K.; McInerney, J. Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson Disease Does not Worsen or Improve Postural Instability: A Prospective Cohort Trial. Neurosurgery 2018, 83, 1173-1182. [CrossRef]
- Weil, R.S.; Schrag, A.E.; Warren, J.D.; Crutch, S.J.; Lees, A.J.; Morris, H.R. Visual dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2016, 139, 2827-2843. [CrossRef]
- Bronte-Stewart, H.M.; Minn, A.Y.; Rodrigues, K.; Buckley, E.L.; Nashner, L.M. Postural instability in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: The role of medication and unilateral pallidotomy. Brain 2002, 125, 2100-2114. [CrossRef]
- Welter, M.L.; Demain, A.; Ewenczyk, C.; Czernecki, V.; Lau, B.; El Helou, A.; Belaid, H.; Yelnik, J.; François, C.; Bardinet, E.; et al. PPNa-DBS for gait and balance disorders in Parkinson’s disease: A double-blind, randomised study. J. Neurol. 2015, 262, 1515-1525. [CrossRef]
- Brandmeir, N.J.; Brandmeir, C.L.; Kuzma, K.; McInerney, J. A Prospective Evaluation of an Outpatient Assessment of Postural Instability to Predict Risk of Falls in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease Presenting for Deep Brain Stimulation. Movement disorders clinical practice 2016, 3, 151-155. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).