Submitted:
06 August 2023
Posted:
07 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
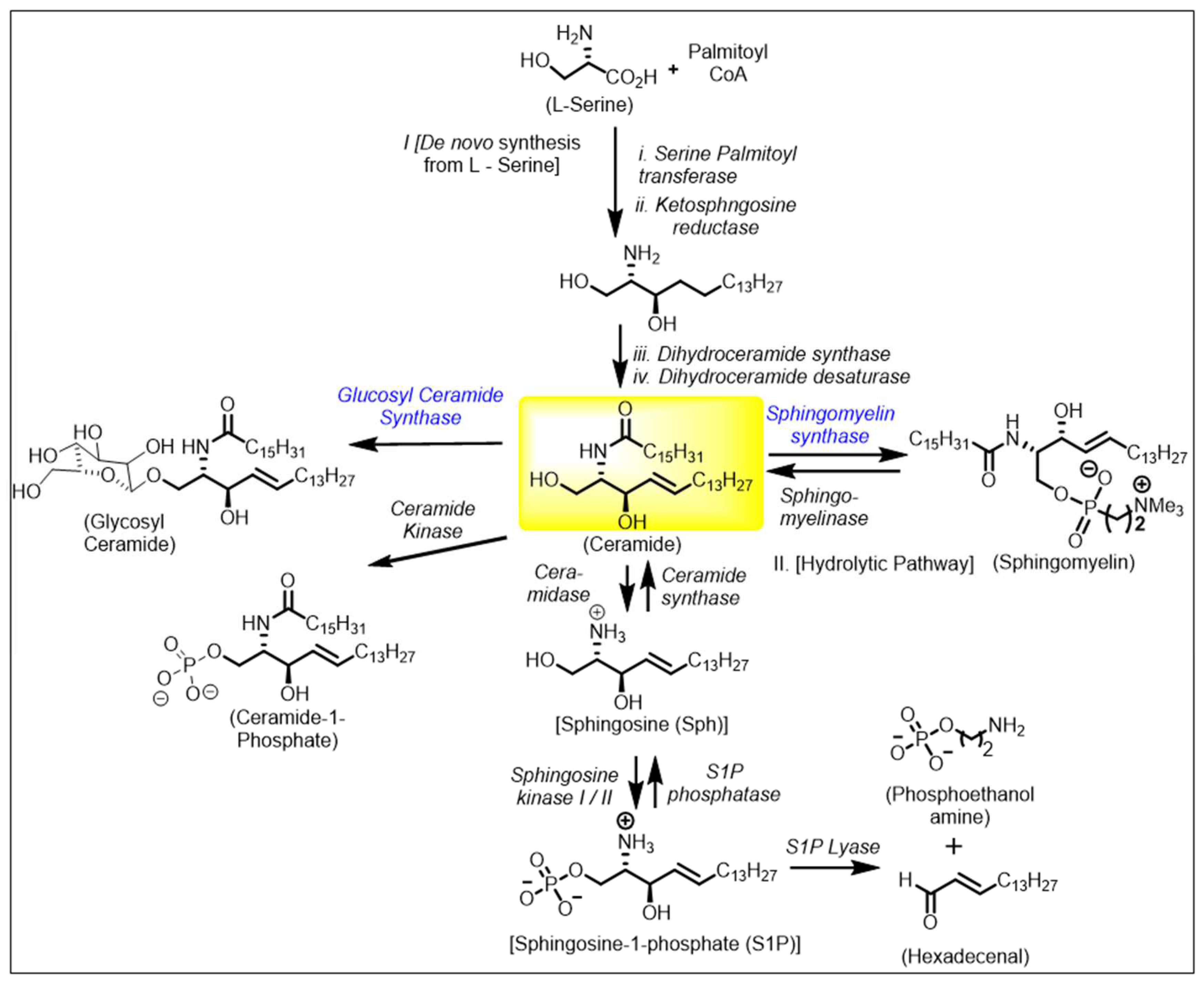
2. Ceramide biosynthesis pathway
3. Ceramidase
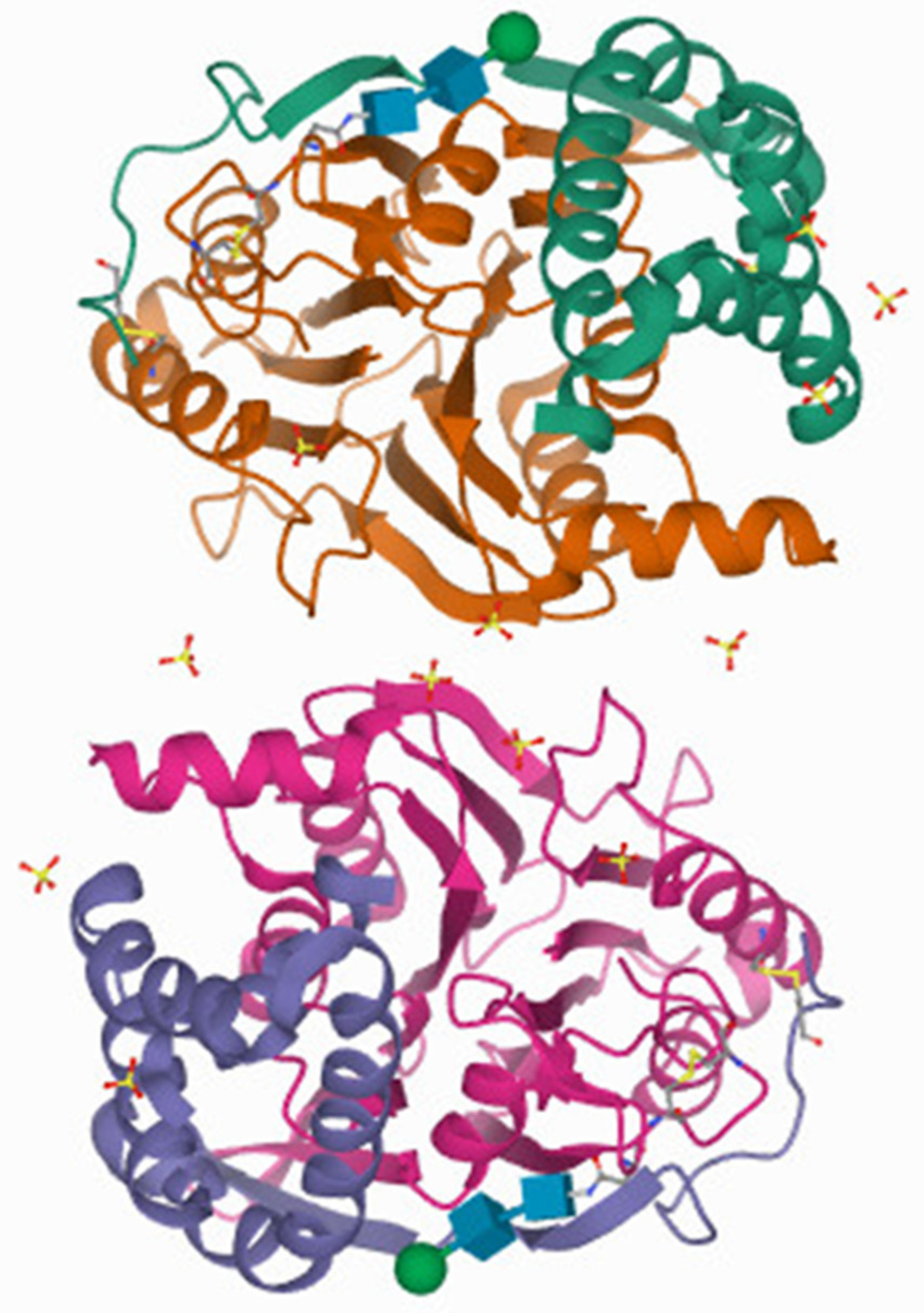
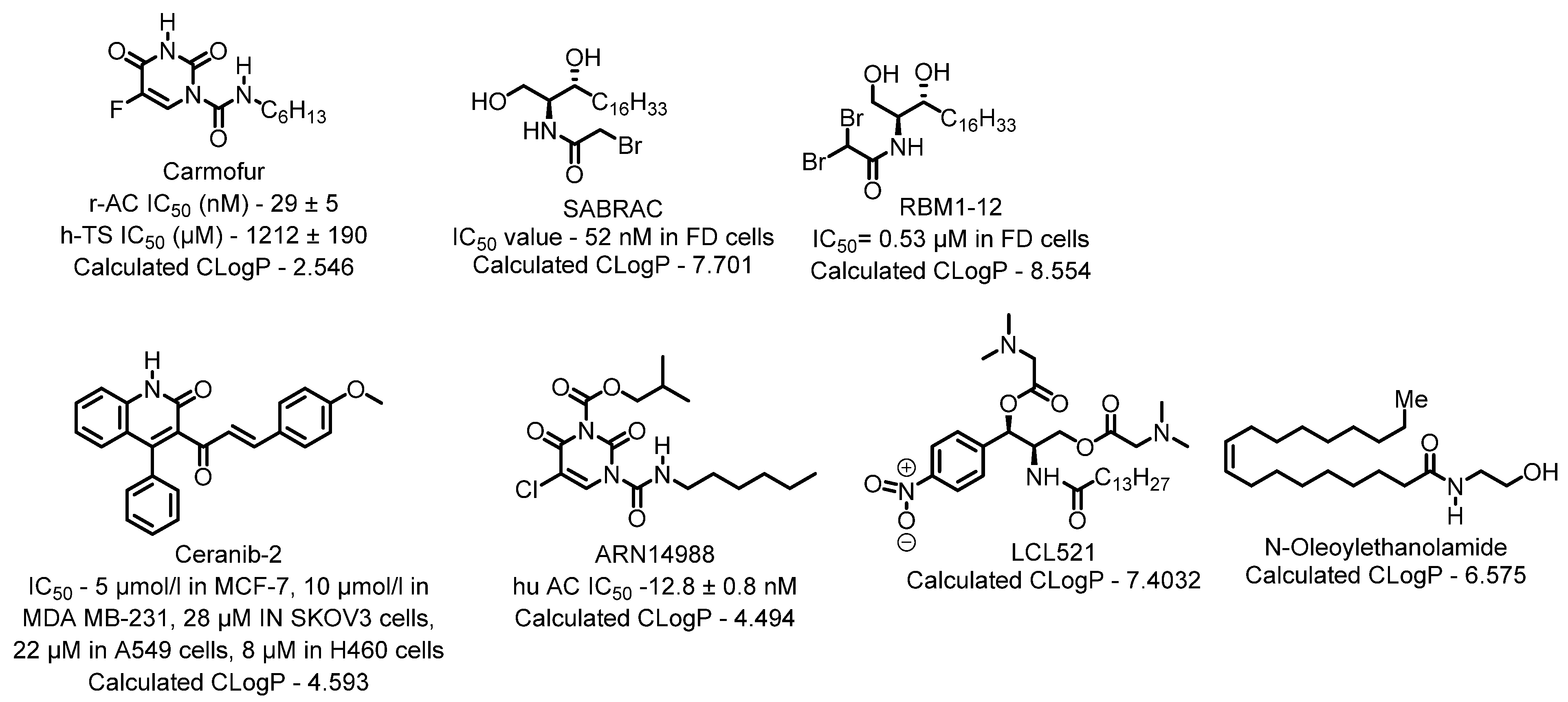
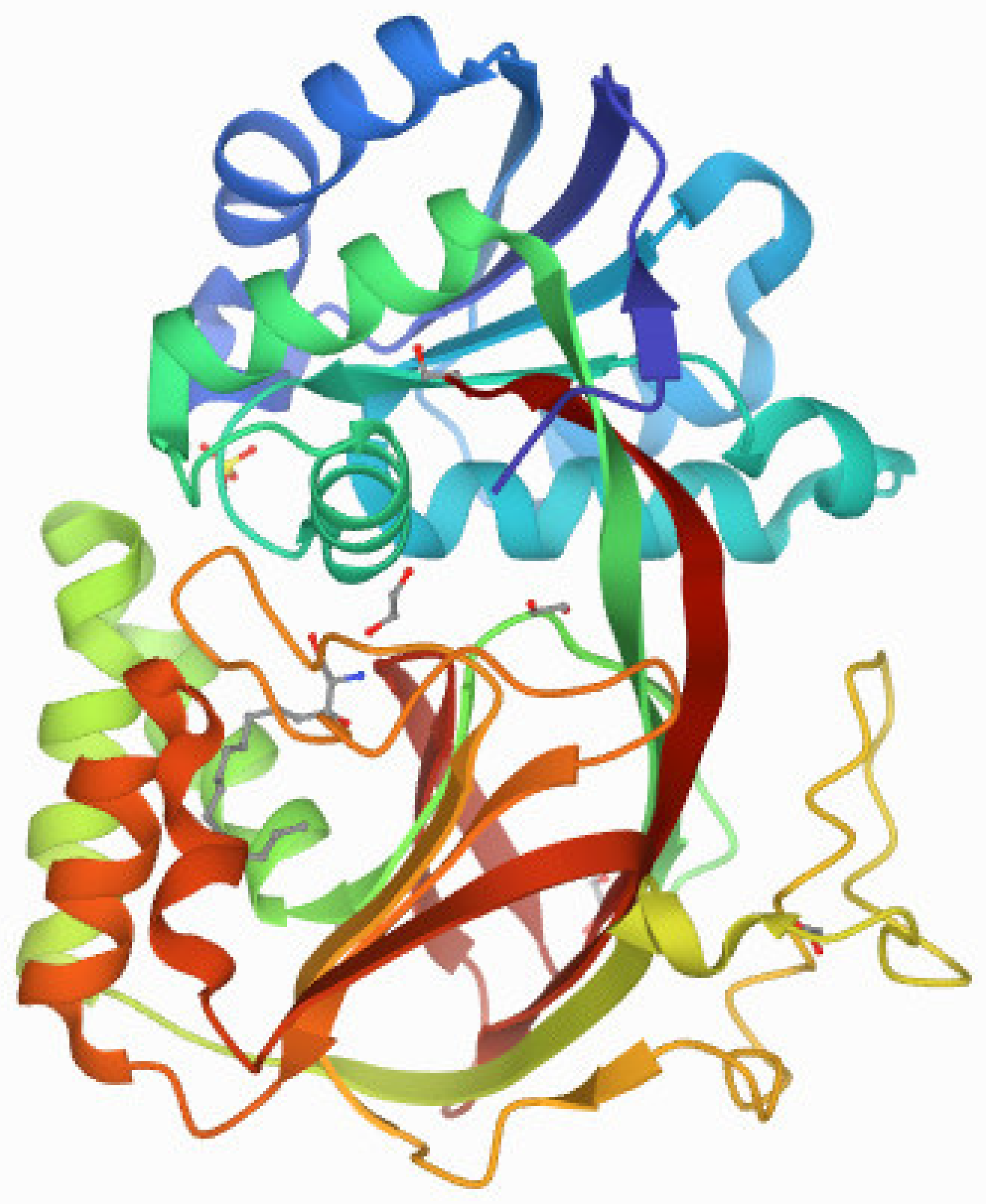
3.1. Acid Ceramidase
3.2. Role of AC in Pathological Conditions
3.2.1. Prostate Cancer (PC)
3.2.2. Head and Neck Cancer (HNC)
3.2.3. Melanoma
3.2.4. Myeloid Leukemia
3.2.5. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
3.2.6. Breast Cancer
3.2.7. Ovarian Cancer (OC)
3.2.8. Hepatobiliary Cancers
3.2.9. Colon Cancer
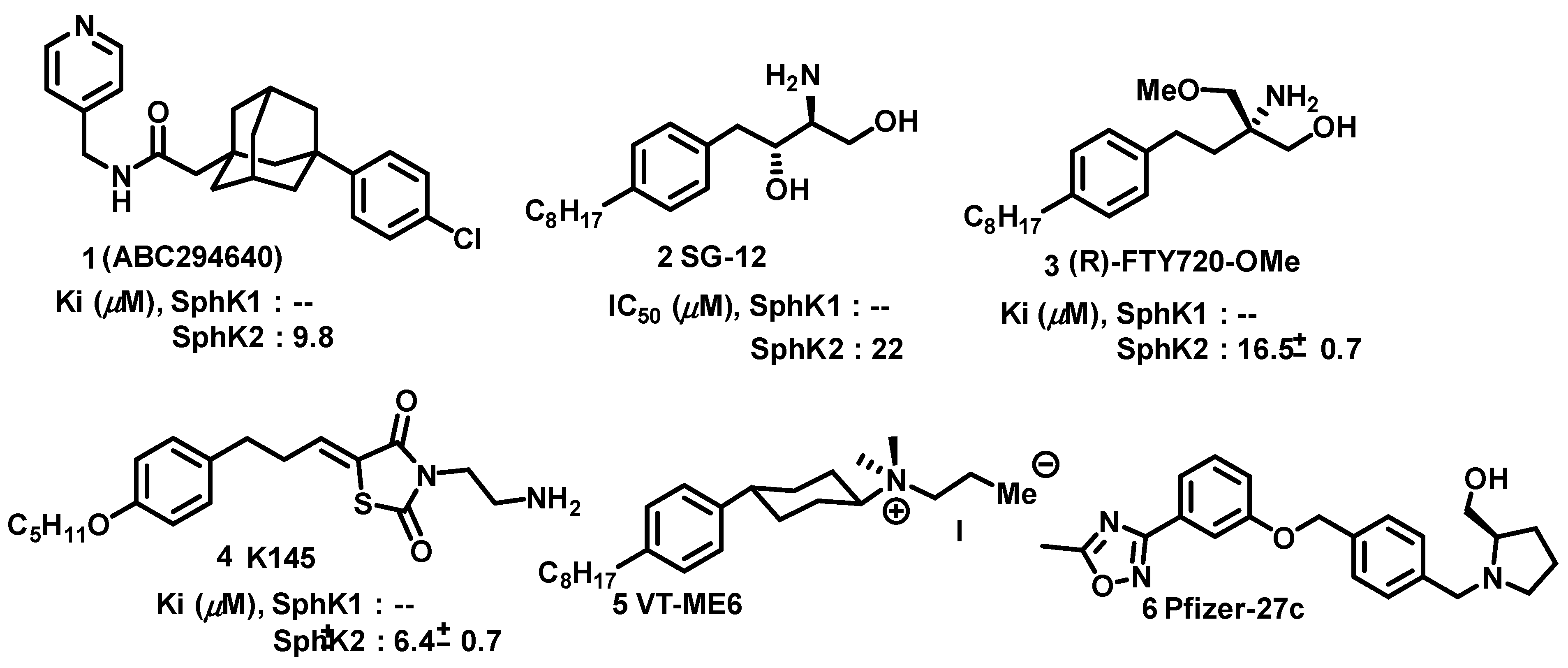
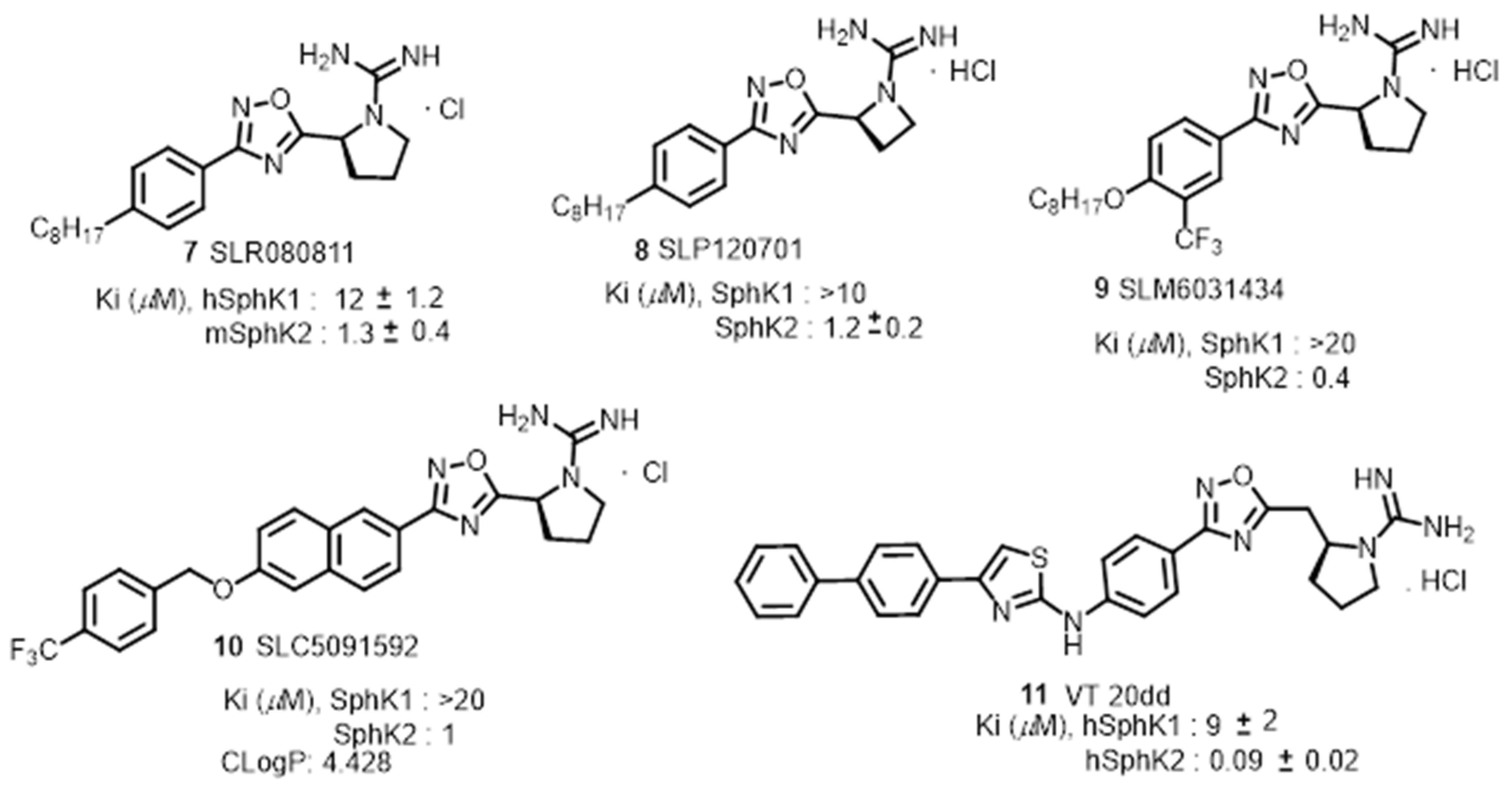
4. Sphingosine Kinase
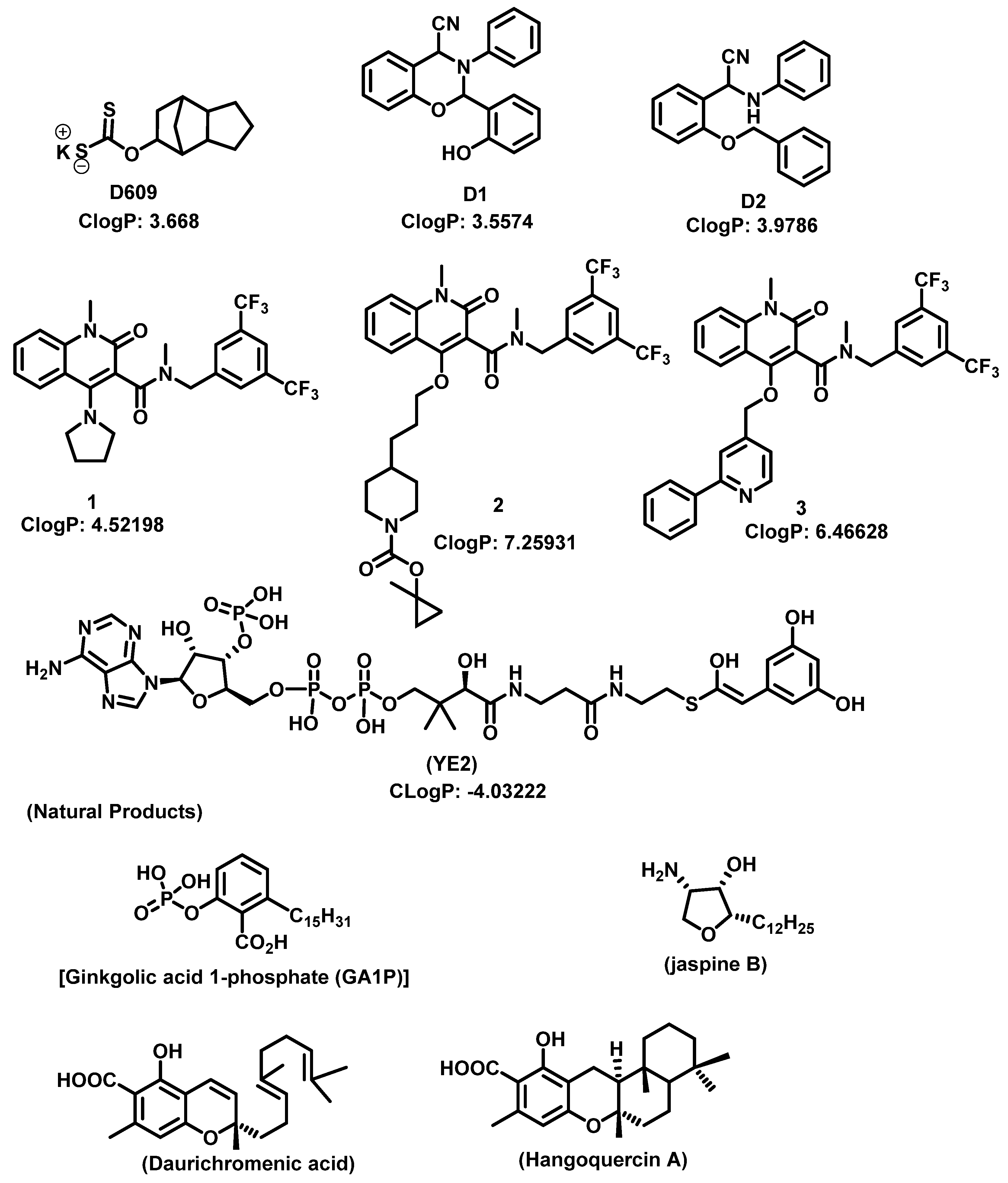
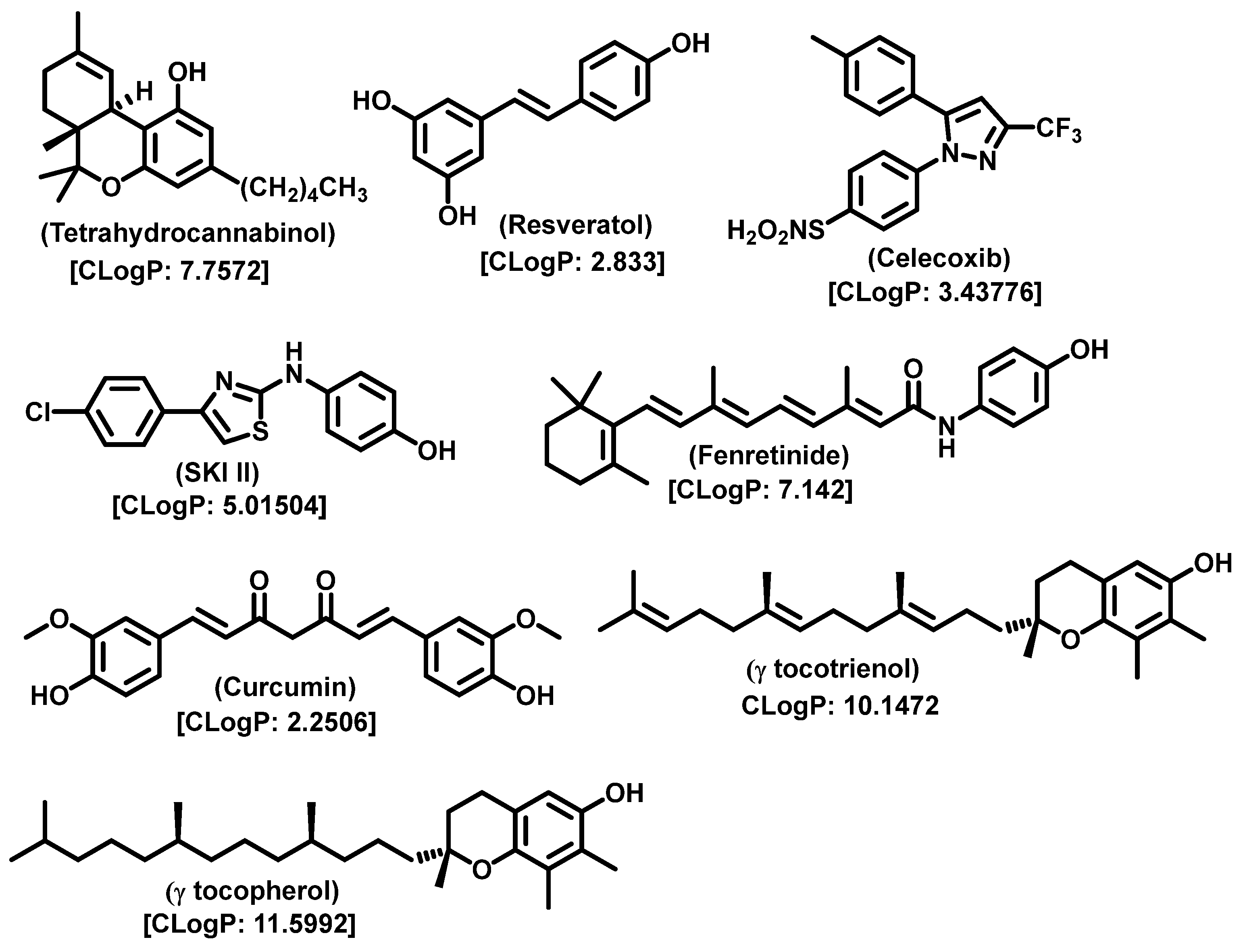
5. Sphingomyelin Synthase
5.1. Biological Significance of Sphingomyelin Synthase
6. 3-Ketosphinganine Reductase
7. Dihydroceramide Desaturase
7.1. Role of Dihydroceramides in various disease
7.1.1. DhCer in Brain Diseases
7.1.2. DhCer in Cardiovascular Disease
7.1.3. DhCer in Cancer Therapy
8. (Dihydro)ceramide Synthase
9. Ceramide Synthases
9.1. Ceramide Synthase 1
9.2. Ceramide Synthase 2
9.3. Ceramide Synthase 3
9.4. Ceramide Synthase 4
9.5. Ceramide Synthase 5
9.6. Ceramide Synthase 6
10. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SL | Sphingolipid |
| S1P | Sphingosine-1-phosphate |
| CDases | Ceramidases |
| AC | Acid ceramidase |
| AML | Acute myeloid leukemia |
| HNC | Head and Neck Cancer |
| SMS | Sphingomyelin synthase |
| DES | Dihydroceramide desaturase |
| DHSph | Dihydrosphingosine |
| CerS | Ceramide synthase |
References
- Adada, M.; Luberto, C.; Canals, D. Inhibitors of the sphingomyelin cycle: Sphingomyelin synthases and sphingomyelinases. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2016, 197, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogretmen, B.; Hannun, Y.A. Biologically active sphingolipids in cancer pathogenesis and treatment. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 604–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckham, T.H.; Elojeimy, S.; Cheng, J.C.; Turner, L.S.; Hoffman, S.R.; Norris, J.S.; Liu, X. Targeting sphingolipid metabolism in head and neck cancer: rational therapeutic potentials. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2010, 14, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Sun, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Q. Short-chain C6 ceramide sensitizes AT406-induced anti-pancreatic cancer cell activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 479, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckham, T.H.; Lu, P.; Jones, E.E.; Marrison, T.; Lewis, C.S.; Cheng, J.C.; Ramshesh, V.K.; Beeson, G.; Beeson, C.C.; Drake, R.R.; et al. LCL124, a Cationic Analog of Ceramide, Selectively Induces Pancreatic Cancer Cell Death by Accumulating in Mitochondria. Experiment 2012, 344, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, G.; van der Wilt, C.; van Moorsel, C.; Kroep, J.; Bergman, A.; Ackland, S. Basis for effective combination cancer chemotherapy with antimetabolites. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 87, 227–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modrak, D.E.; Leon, E.; Goldenberg, D.M.; Gold, D.V. Ceramide Regulates Gemcitabine-Induced Senescence and Apoptosis in Human Pancreatic Cancer Cell Lines. Mol. Cancer Res. 2009, 7, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, B.M.; Prieto, M.; Silva, L.C. Ceramide: A simple sphingolipid with unique biophysical properties. Prog. Lipid Res. 2014, 54, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edvardson, S.; Yi, J.K.; Jalas, C.; Xu, R.; Webb, B.D.; Snider, J.; Fedick, A.; Kleinman, E.; Treff, N.R.; Mao, C.; et al. Deficiency of the alkaline ceramidase ACER3 manifests in early childhood by progressive leukodystrophy. J. Med Genet. 2016, 53, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannun, Y.A. and L.M. Obeid, Many ceramides. J Biol Chem, 2011. 286(32): p. 27855-62.
- Schulze, H.; Schepers, U.; Sandhoff, K. Overexpression and mass spectrometry analysis of mature human acid ceramidase. Biol. Chem. 2007, 388, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, C.; Obeid, L.M. Ceramidases: regulators of cellular responses mediated by ceramide, sphingosine, and sphingosine-1-phosphate. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2008, 1781, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatt, S. Enzymatic hydrolysis of sphingolipids. I. Hydrolysis and synthesis of ceramides by an enzyme from rat brain. J. Biol. Chem. 1966, 241, 3724–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-M.; Park, J.-H.; He, X.; Levy, B.; Chen, F.; Arai, K.; Adler, D.A.; Disteche, C.M.; Koch, J.; Sandhoff, K.; et al. The Human Acid Ceramidase Gene (ASAH): Structure, Chromosomal Location, Mutation Analysis, and Expression. Genomics 1999, 62, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X. , et al., Purification and characterization of recombinant, human acid ceramidase. Catalytic reactions and interactions with acid sphingomyelinase. J Biol Chem, 2003. 278(35): p. 32978-86.
- Azuma, N.; Obrien, J.; Moser, H.; Kishimoto, Y. Stimulation of Acid Ceramidase Activity by Saposin D. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1994, 311, 354–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.P.S.; Amintas, S.; Levade, T.; Medin, J.A. Acid ceramidase deficiency: Farber disease and SMA-PME. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2018, 13, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.M. , et al., Insertional mutagenesis of the mouse acid ceramidase gene leads to early embryonic lethality in homozygotes and progressive lipid storage disease in heterozygotes. Genomics, 2002. 79(2): p. 218-24.
- Mahdy, A.E.; Cheng, J.C.; Li, J.; Elojeimy, S.; Meacham, W.D.; Turner, L.S.; Bai, A.; Gault, C.R.; McPherson, A.S.; Garcia, N.; et al. Acid Ceramidase Upregulation in Prostate Cancer Cells Confers Resistance to Radiation: AC Inhibition, a Potential Radiosensitizer. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.C.; Bai, A.; Beckham, T.H.; Marrison, S.T.; Yount, C.L.; Young, K.; Lu, P.; Bartlett, A.M.; Wu, B.X.; Keane, B.J.; et al. Radiation-induced acid ceramidase confers prostate cancer resistance and tumor relapse. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 4344–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, L. , et al., Acid ceramidase as a therapeutic target in metastatic prostate cancer[S]. Journal of Lipid Research, 2013. 54(5): p. 1207-1220.
- Holman, D.H.; Turner, L.S.; El-Zawahry, A.; Elojeimy, S.; Liu, X.; Bielawski, J.; Szulc, Z.M.; Norris, K.; Zeidan, Y.H.; Hannun, Y.A.; et al. Lysosomotropic acid ceramidase inhibitor induces apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2007, 61, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouazé-Andersson, V.; Flowers, M.; Karimi, R.; Fabriás, G.; Delgado, A.; Casas, J.; Cabot, M.C. Inhibition of acid ceramidase by a 2-substituted aminoethanol amide synergistically sensitizes prostate cancer cells to N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide. Prostate 2010, 71, 1064–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, L.S.; Cheng, J.C.; Beckham, T.H.; E Keane, T.; Norris, J.S.; Liu, X. Autophagy is increased in prostate cancer cells overexpressing acid ceramidase and enhances resistance to C6 ceramide. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2010, 14, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, J.-L.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, E.H.; Jang, H.J. Targeting acid ceramidase sensitises head and neck cancer to cisplatin. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 52, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korbelik, M.; Banáth, J.; Zhang, W.; Saw, K.M.; Szulc, Z.M.; Bielawska, A.; Separovic, D. Interaction of acid ceramidase inhibitor LCL521 with tumor response to photodynamic therapy and photodynamic therapy-generated vaccine. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 1372–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Separovic, D.; Breen, P.; Boppana, N.B.; VAN Buren, E.; Joseph, N.; Kraveka, J.M.; Rahmaniyan, M.; Li, L.; Gudz, T.I.; Bielawska, A.; et al. Increased killing of SCCVII squamous cell carcinoma cells after the combination of Pc 4 photodynamic therapy and dasatinib is associated with enhanced caspase-3 activity and ceramide synthase 1 upregulation. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 43, 2064–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elojeimy, S.; Liu, X.; Mckillop, J.C.; El-Zawahry, A.M.; Holman, D.H.; Cheng, J.Y.; Meacham, W.D.; Mahdy, A.E.; Saad, A.F.; Turner, L.S.; et al. Role of Acid Ceramidase in Resistance to FasL: Therapeutic Approaches Based on Acid Ceramidase Inhibitors and FasL Gene Therapy. Mol. Ther. 2007, 15, 1259–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Realini, N. , et al., Acid Ceramidase in Melanoma: expression, localization, and effects of pharmacological inhibition*. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2016. 291(5): p. 2422-2434.
- Bedia, C.; Casas, J.; Andrieu-Abadie, N.; Fabriàs, G.; Levade, T. Acid Ceramidase Expression Modulates the Sensitivity of A375 Melanoma Cells to Dacarbazine. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 28200–28209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, M.; Realini, N.; La Ferla, M.; Passalacqua, I.; Matteoli, G.; Ganesan, A.; Pistello, M.; Mazzanti, C.M.; Piomelli, D. Complete Acid Ceramidase ablation prevents cancer-initiating cell formation in melanoma cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.-F.; Liu, X.; Fox, T.E.; Barth, B.M.; Sharma, A.; Turner, S.D.; Awwad, A.; Dewey, A.; Doi, K.; Spitzer, B.; et al. Acid ceramidase is upregulated in AML and represents a novel therapeutic target. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 83208–83222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Yang, D.; Zimmerman, M.; Liu, F.; Yang, J.; Kannan, S.; Burchert, A.; Szulc, Z.; Bielawska, A.; Ozato, K.; et al. IRF8 Regulates Acid Ceramidase Expression to Mediate Apoptosis and Suppresses Myelogeneous Leukemia. Cancer Res 2011, 71, 2882–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, A.R.d. , et al., Acid Ceramidase as a Chemotherapeutic Target to Overcome Resistance to the Antitumoral Effect of Choline Kinase α Inhibition. Current Cancer Drug Targets, 2012. 12(6): p. 617-624.
- Sänger, N.; Ruckhäberle, E.; Györffy, B.; Engels, K.; Heinrich, T.; Fehm, T.; Graf, A.; Holtrich, U.; Becker, S.; Karn, T. Acid ceramidase is associated with an improved prognosis in both DCIS and invasive breast cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 9, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowers, M.; Fabriás, G.; Delgado, A.; Casas, J.; Abad, J.L.; Cabot, M.C. C6-Ceramide and targeted inhibition of acid ceramidase induce synergistic decreases in breast cancer cell growth. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 133, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vethakanraj, H.S.; Sesurajan, B.P.; Padmanaban, V.P.; Jayaprakasam, M.; Murali, S.; Sekar, A.K. Anticancer effect of acid ceramidase inhibitor ceranib-2 in human breast cancer cell lines MCF-7, MDA MB-231 by the activation of SAPK/JNK, p38 MAPK apoptotic pathways, inhibition of the Akt pathway, downregulation of ERα. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2018, 29, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kus, G.; Kabadere, S.; Uyar, R.; Kutlu, H.M. Induction of apoptosis in prostate cancer cells by the novel ceramidase inhibitor ceranib-2. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. - Anim. 2015, 51, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanker, L.C.M.; Karn, T.M.; Holtrich, U.M.; Gätje, R.; Rody, A.; Heinrich, T.M.; Ruckhäberle, E.M.; Engels, K.M. Acid Ceramidase (AC)—A Key Enzyme of Sphingolipid Metabolism—Correlates With Better Prognosis in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. 2013, 32, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, A.; París, R.; Villanueva, A.; Llacuna, L.; García-Ruiz, C.; Fernández-Checa, J.C. Pharmacological inhibition or small interfering RNA targeting acid ceramidase sensitizes hepatoma cells to chemotherapy and reduces tumor growth in vivo. Oncogene 2006, 26, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannetti, E.; Leon, L.G.; Bertini, S.; Macchia, M.; Minutolo, F.; Funel, N.; Alecci, C.; Giancola, F.; Danesi, R.; Peters, G.J. Study of Apoptosis Induction and Deoxycytidine Kinase/Cytidine Deaminase Modulation in the Synergistic Interaction of a Novel Ceramide Analog and Gemcitabine in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Nucleosides, Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2010, 29, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klobučar, M.; Grbčić, P.; Pavelić, S.K.; Jonjić, N.; Visentin, S.; Sedić, M. Acid ceramidase inhibition sensitizes human colon cancer cells to oxaliplatin through downregulation of transglutaminase 2 and β1 integrin/FAK−mediated signalling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baspinar, M.; Ozyurt, R.; Kus, G.; Kutlay, O.; Ozkurt, M.; Erkasap, N.; Kabadere, S.; Yasar, N.F.; Erkasap, S. Effects of ceranib-2 on cell survival and TNF-alpha in colon cancer cell line. Bratisl. Med J. 2017, 118, 391–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hait, N.C.; Allegood, J.; Maceyka, M.; Strub, G.M.; Harikumar, K.B.; Singh, S.K.; Luo, C.; Marmorstein, R.; Kordula, T.; Milstien, S.; et al. Regulation of Histone Acetylation in the Nucleus by Sphingosine-1-Phosphate. Science 2009, 325, 1254–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiegel, S.; Milstien, S. The outs and the ins of sphingosine-1-phosphate in immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkel, G.T.; Maceyka, M.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Targeting the sphingosine-1-phosphate axis in cancer, inflammation and beyond. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 688–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truman, J.-P.; García-Barros, M.; Obeid, L.M.; Hannun, Y.A. Evolving concepts in cancer therapy through targeting sphingolipid metabolism. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2013, 1841, 1174–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemaire, M. , WANTED: Natural-Born Sickler. Science Translational Medicine, 2014. 6(240): p. 240ec101.
- Heeney, M.; Renella, R.; Y, Z.; V, B.; A, S.; K, S.; W, W.; W, Z.; C, N.; C, L.; et al. Faculty Opinions recommendation of Elevated sphingosine-1-phosphate promotes sickling and sickle cell disease progression. . 2014, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakumar, P.; Kaur, T.; Singh, M. Potential target sites to modulate vascular endothelial dysfunction: Current perspectives and future directions. Toxicology 2008, 245, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, T.; Hamaya, Y.; Izumi, S.; Hamaya, Y.; Iizuka, K.; Igarashi, Y.; Minami, M.; Levi, R.; Hirafuji, M. Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Inhibits Nitric Oxide Production Induced by Interleukin-1β in Rat Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Experiment 2008, 325, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorrentino, R.; Bertolino, A.; Terlizzi, M.; Iacono, V.M.; Maiolino, P.; Cirino, G.; Roviezzo, F.; Pinto, A. B Cell Depletion Increases Sphingosine-1-Phosphate–Dependent Airway Inflammation in Mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 52, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.M.; Oskeritzian, C.A.; Falanga, Y.T.; Harikumar, K.B.; Allegood, J.C.; Alvarez, S.E.; Conrad, D.; Ryan, J.J.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. A specific sphingosine kinase 1 inhibitor attenuates airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation in a mast cell–dependent murine model of allergic asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 131, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyne, N.J. G. Dubois, and S. Pyne, Role of sphingosine 1-phosphate and lysophosphatidic acid in fibrosis. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids, 2013. 1831(1): p. 228-238.
- Maceyka, M.; Sankala, H.; Hait, N.C.; Le Stunff, H.; Liu, H.; Toman, R.; Collier, C.; Zhang, M.; Satin, L.S.; Merrill, A.H.; et al. SphK1 and SphK2, Sphingosine Kinase Isoenzymes with Opposing Functions in Sphingolipid Metabolism. PEDIATRICS 2005, 280, 37118–37129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neubauer, H.A.; Pitson, S.M. Roles, regulation and inhibitors of sphingosine kinase 2. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 5317–5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizugishi, K.; Yamashita, T.; Olivera, A.; Miller, G.F.; Spiegel, S.; Proia, R.L. Essential Role for Sphingosine Kinases in Neural and Vascular Development. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 11113–11121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, K.J.; Zhuang, Y.; Maines, L.W.; Gao, P.; Wang, W.; Beljanski, V.; Upson, J.J.; Green, C.L.; Keller, S.N.; Smith, C.D. Pharmacology and Antitumor Activity of ABC294640, a Selective Inhibitor of Sphingosine Kinase-2. Experiment 2010, 333, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maines, L.W.; Fitzpatrick, L.R.; French, K.J.; Zhuang, Y.; Xia, Z.; Keller, S.N.; Upson, J.J.; Smith, C.D. Suppression of Ulcerative Colitis in Mice by Orally Available Inhibitors of Sphingosine Kinase. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2007, 53, 997–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maines, L.W.; Fitzpatrick, L.R.; Green, C.L.; Zhuang, Y.; Smith, C.D. Efficacy of a novel sphingosine kinase inhibitor in experimental Crohn’s disease. Inflammopharmacology 2010, 18, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Rehman, H.; Ramshesh, V.K.; Schwartz, J.; Liu, Q.; Krishnasamy, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lemasters, J.J.; Smith, C.D.; Zhong, Z. Sphingosine kinase-2 inhibition improves mitochondrial function and survival after hepatic ischemia–reperfusion. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumanevich, A.A.; Poudyal, D.; Cui, X.; Davis, T.; Wood, P.A.; Smith, C.D.; Hofseth, L.J. Suppression of colitis-driven colon cancer in mice by a novel small molecule inhibitor of sphingosine kinase. Carcinog. 2010, 31, 1787–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, C.; Chen, M.-B.; Qi, L.; Tie-Ning, Z.; Peng, X.; Ning, L.; Zhi-Xiao, C.; Li-Wei, W. Targeting sphingosine kinase 2 (SphK2) by ABC294640 inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 34, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoon, J.W.; White, M.D.; Meacham, W.D.; Slaughter, E.M.; Muir, S.E.; Elliott, S.; Rhodes, L.V.; Ashe, H.B.; Wiese, T.E.; Smith, C.D.; et al. Antiestrogenic Effects of the Novel Sphingosine Kinase-2 Inhibitor ABC294640. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 5124–5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara-Yokoyama, M.; Terasawa, K.; Ichinose, S.; Watanabe, A.; Podyma-Inoue, K.A.; Akiyoshi, K.; Igarashi, Y.; Yanagishita, M. Sphingosine kinase 2 inhibitor SG-12 induces apoptosis via phosphorylation by sphingosine kinase 2. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 2220–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.G.; Sun, C.; Bittman, R.; Pyne, N.J.; Pyne, S. (R)-FTY720 methyl ether is a specific sphingosine kinase 2 inhibitor: Effect on sphingosine kinase 2 expression in HEK 293 cells and actin rearrangement and survival of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Cell. Signal. 2011, 23, 1590–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Guo, T.L.; Hait, N.C.; Allegood, J.; Parikh, H.I.; Xu, W.; Kellogg, G.E.; Grant, S.; Spiegel, S.; Zhang, S. Biological Characterization of 3-(2-amino-ethyl)-5-[3-(4-butoxyl-phenyl)-propylidene]-thiazolidine-2,4-dione (K145) as a Selective Sphingosine Kinase-2 Inhibitor and Anticancer Agent. PLOS ONE 2013, 8, e56471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raje, M.R.; Knott, K.; Kharel, Y.; Bissel, P.; Lynch, K.R.; Santos, W.L. Design, synthesis and biological activity of sphingosine kinase 2 selective inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2011, 20, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Childress, E.S.; Kharel, Y.; Brown, A.M.; Bevan, D.R.; Lynch, K.R.; Santos, W.L. Transforming Sphingosine Kinase 1 Inhibitors into Dual and Sphingosine Kinase 2 Selective Inhibitors: Design, Synthesis, and in Vivo Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 3933–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnute, M.E.; McReynolds, M.D.; Carroll, J.; Chrencik, J.; Highkin, M.K.; Iyanar, K.; Jerome, G.; Rains, J.W.; Saabye, M.; Scholten, J.A.; et al. Discovery of a Potent and Selective Sphingosine Kinase 1 Inhibitor through the Molecular Combination of Chemotype-Distinct Screening Hits. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 2562–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharel, Y.; Raje, M.; Gao, M.; Gellett, A.M.; Tomsig, J.L.; Lynch, K.R.; Santos, W.L. Sphingosine kinase type 2 inhibition elevates circulating sphingosine 1-phosphate. Biochem. J. 2012, 447, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patwardhan, N.N.; Morris, E.A.; Kharel, Y.; Raje, M.R.; Gao, M.; Tomsig, J.L.; Lynch, K.R.; Santos, W.L. Structure−Activity Relationship Studies and in Vivo Activity of Guanidine-Based Sphingosine Kinase Inhibitors: Discovery of SphK1- and SphK2-Selective Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 1879–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharel, Y.; Morris, E.A.; Congdon, M.D.; Thorpe, S.B.; Tomsig, J.L.; Santos, W.L.; Lynch, K.R. Sphingosine Kinase 2 Inhibition and Blood Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Levels. Experiment 2015, 355, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congdon, M.D.; Kharel, Y.; Brown, A.M.; Lewis, S.N.; Bevan, D.R.; Lynch, K.R.; Santos, W.L. Structure–Activity Relationship Studies and Molecular Modeling of Naphthalene-Based Sphingosine Kinase 2 Inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futerman, A.H.; Stieger, B.; Hubbard, A.L.; E Pagano, R. Sphingomyelin synthesis in rat liver occurs predominantly at the cis and medial cisternae of the Golgi apparatus. PEDIATRICS 1990, 265, 8650–8657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huitema, K.; van den Dikkenberg, J.; Brouwers, J.F.H.M.; Holthuis, J.C.M. Identification of a family of animal sphingomyelin synthases. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albi, E.; Lazzarini, R.; Magni, M.V. Reverse sphingomyelin-synthase in rat liver chromatin. FEBS Lett. 2003, 549, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M. and T. Okazaki, The role of sphingomyelin and sphingomyelin synthases in cell death, proliferation and migration-from cell and animal models to human disorders. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2014. 1841(5): p. 692-703.
- Yamaoka, S.; Miyaji, M.; Kitano, T.; Umehara, H.; Okazaki, T. Expression Cloning of a Human cDNA Restoring Sphingomyelin Synthesis and Cell Growth in Sphingomyelin Synthase-defective Lymphoid Cells. Perspect. Surg. 2004, 279, 18688–18693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luberto, C. and Y.A. Hannun, Sphingomyelin Synthase, a Potential Regulator of Intracellular Levels of Ceramide and Diacylglycerol during SV40 Transformation: does sphingomyelin synthase account for the putative phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase c? *. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1998. 273(23): p. 14550-14559.
- Riboni, L. , et al., Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor-induced Proliferation of Primary Astrocytes: evidence for the involvement of sphingomyelin biosynthesis *. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2001. 276(16): p. 12797-12804.
- Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M. The Ceramide-centric Universe of Lipid-mediated Cell Regulation: Stress Encounters of the Lipid Kind. PEDIATRICS 2002, 277, 25847–25850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegmann, K.; Schütze, S.; Machleidt, T.; Witte, D.; Krönke, M. Functional dichotomy of neutral and acidic sphingomyelinases in tumor necrosis factor signaling. Cell 1994, 78, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam-Klages, S.; Adam, D.; Wiegmann, K.; Struve, S.; Kolanus, W.; Schneider-Mergener, J.; Krönke, M. FAN, a Novel WD-Repeat Protein, Couples the p55 TNF-Receptor to Neutral Sphingomyelinase. Cell 1996, 86, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiegel, S.; Milstien, S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate: an enigmatic signalling lipid. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holthuis, J.C.M.; Pomorski, T.; Raggers, R.J.; Sprong, H.; Van Meer, G.; Zheng, T.; Li, W.; Altura, B.T.; Shah, N.C.; Altura, B.M.; et al. The Organizing Potential of Sphingolipids in Intracellular Membrane Transport. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 1689–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, C.L.; Malhotra, V. Role of Diacylglycerol in PKD Recruitment to the TGN and Protein Transport to the Plasma Membrane. Science 2002, 295, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M. The Ceramide-centric Universe of Lipid-mediated Cell Regulation: Stress Encounters of the Lipid Kind. PEDIATRICS 2002, 277, 25847–25850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, R.Y.; Morand, O.H. Sphingomyelin Synthase and PKC Activation. Science 1989, 246, 1050–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ordóñez, Y.F.; González, J.; Bedia, C.; Casas, J.; Abad, J.L.; Delgado, A.; Fabrias, G. 3-Ketosphinganine provokes the accumulation of dihydroshingolipids and induces autophagy in cancer cells. Mol. Biosyst. 2016, 12, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadena, D.L.; Kurten, R.C.; Gill, G.N. The Product of the MLD Gene Is a Member of the Membrane Fatty Acid Desaturase Family: Overexpression of MLD Inhibits EGF Receptor Biosynthesis, Biochemistry 1997, 36, 6960–6967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geeraert, L.; Mannaerts, G.P.; VAN Veldhoven, P.P. Conversion of dihydroceramide into ceramide: involvement of a desaturase. Biochem. J. 1997, 327, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, C. , et al., Characterization of ceramide synthesis. A dihydroceramide desaturase introduces the 4,5-trans-double bond of sphingosine at the level of dihydroceramide. J Biol Chem, 1997. 272(36): p. 22432-7.
- Savile, C.K. G. Fabriàs, and P.H. Buist, Dihydroceramide delta(4) desaturase initiates substrate oxidation at C-4. J Am Chem Soc, 2001. 123(19): p. 4382-5.
- Beauchamp, E. , et al., Myristic acid increases the activity of dihydroceramide Delta4-desaturase 1 through its N-terminal myristoylation. Biochimie, 2007. 89(12): p. 1553-61.
- Ternes, P. , et al., Identification and characterization of a sphingolipid delta 4-desaturase family. J Biol Chem, 2002. 277(28): p. 25512-8.
- Casasampere, M.; Ordoñez, Y.F.; Pou, A.; Casas, J. Inhibitors of dihydroceramide desaturase 1: Therapeutic agents and pharmacological tools to decipher the role of dihydroceramides in cell biology. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2016, 197, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizutani, Y.; Kihara, A.; Igarashi, Y. Identification of the human sphingolipid C4-hydroxylase, hDES2, and its up-regulation during keratinocyte differentiation. FEBS Lett. 2004, 563, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.M.; Bikman, B.T.; Wang, L.; Ying, L.; Reinhardt, E.; Shui, G.; Wenk, M.R.; Summers, S.A. Ablation of Dihydroceramide Desaturase Confers Resistance to Etoposide-Induced Apoptosis In Vitro. PLOS ONE 2012, 7, e44042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, W.L.; Brozinick, J.T.; Wang, L.-P.; Hawkins, E.D.; Sargent, K.M.; Liu, Y.; Narra, K.; Hoehn, K.L.; Knotts, T.A.; Siesky, A.; et al. Inhibition of Ceramide Synthesis Ameliorates Glucocorticoid-, Saturated-Fat-, and Obesity-Induced Insulin Resistance. Cell Metab. 2007, 5, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M. Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: lessons from sphingolipids. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testai, F.D.; Kilkus, J.P.; Berdyshev, E.; Gorshkova, I.; Natarajan, V.; Dawson, G. Multiple sphingolipid abnormalities following cerebral microendothelial hypoxia. J. Neurochem. 2014, 131, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testai, F.D.; Xu, H.-L.; Kilkus, J.; Suryadevara, V.; Gorshkova, I.; Berdyshev, E.; Pelligrino, D.A.; Dawson, G. Changes in the metabolism of sphingolipids after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Neurosci. Res. 2015, 93, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielke, M.M.; Haughey, N.J.; Bandaru, V.V.R.; Weinberg, D.D.; Darby, E.; Zaidi, N.; Pavlik, V.; Doody, R.S.; Lyketsos, C.G. Plasma Sphingomyelins are Associated with Cognitive Progression in Alzheimer's Disease. J. Alzheimer's Dis. 2011, 27, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pardo, A.; Basit, A.; Armirotti, A.; Amico, E.; Castaldo, S.; Pepe, G.; Marracino, F.; Buttari, F.; Digilio, A.F.; Maglione, V. De novo Synthesis of Sphingolipids Is Defective in Experimental Models of Huntington's Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Peña, D.; Checa, A.; de Ancos, B.; Wheelock, C.E.; Sánchez-Moreno, C. New insights into the effects of onion consumption on lipid mediators using a diet-induced model of hypercholesterolemia. Redox Biol. 2017, 11, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeng, H.J. , et al., Celecoxib-mediated activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress induces de novo ceramide biosynthesis and apoptosis in hepatoma HepG2 cells mobilization. BMB Rep, 2017. 50(3): p. 144-149.
- Edsfeldt, A.; Dunér, P.; Ståhlman, M.; Mollet, I.G.; Asciutto, G.; Grufman, H.; Nitulescu, M.; Persson, A.F.; Fisher, R.M.; Melander, O.; et al. Sphingolipids Contribute to Human Atherosclerotic Plaque Inflammation. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Mundra, P.A.; Fan, F.; Galvin, A.; Weir, J.M.; Wong, G.; Chin-Dusting, J.; Cicuttini, F.; Meikle, P.; Dart, A.M. Plasma lipidomic profiling in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.; Chang, J.Y.; Liao, X.; Zhang, X.; Kennel, P.; Castillero, E.; Brunjes, D.; Akashi, H.; Homma, S.; Goldberg, I.; et al. Abstract 17320: Inhibition of Ceramide Synthesis Preserves Cardiac Function and Increases Survival in Doxorubicin-induced Cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.A. , et al., Vorinostat and Sorafenib Increase CD95 Activation in Gastrointestinal Tumor Cells through a Ca2+-De novo Ceramide-PP2A-Reactive Oxygen Species–Dependent Signaling Pathway. Cancer Research, 2010. 70(15): p. 6313.
- Gencer, E.B.; Ural, A.U.; Avcu, F.; Baran, Y. A novel mechanism of dasatinib-induced apoptosis in chronic myeloid leukemia; ceramide synthase and ceramide clearance genes. Ann. Hematol. 2011, 90, 1265–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Kollmeyer, J.; Symolon, H.; Momin, A.; Munter, E.; Wang, E.; Kelly, S.; Allegood, J.C.; Liu, Y.; Peng, Q.; et al. Ceramides and other bioactive sphingolipid backbones in health and disease: Lipidomic analysis, metabolism and roles in membrane structure, dynamics, signaling and autophagy. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Biomembr. 2006, 1758, 1864–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casasampere, M.; Ordóñez, Y.F.; Casas, J.; Fabrias, G. Dihydroceramide desaturase inhibitors induce autophagy via dihydroceramide-dependent and independent mechanisms. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Signorelli, P.; Munoz-Olaya, J.M.; Gagliostro, V.; Casas, J.; Ghidoni, R.; Fabriàs, G. Dihydroceramide intracellular increase in response to resveratrol treatment mediates autophagy in gastric cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2009, 282, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenald, S.A.; Doyle, T.M.; Zhang, H.; Slosky, L.M.; Chen, Z.; Largent-Milnes, T.M.; Spiegel, S.; Vanderah, T.W.; Salvemini, D. Targeting the S1P/S1PR1 axis mitigates cancer-induced bone pain and neuroinflammation. Pain 2017, 158, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holliday, M.W. , et al., C22:0- and C24:0-dihydroceramides confer mixed cytotoxicity in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines. PLoS One, 2013. 8(9): p. e74768.
- Knapp, P.; Baranowski, M.; Knapp, M.; Zabielski, P.; Błachnio-Zabielska, A.U.; Górski, J. Altered sphingolipid metabolism in human endometrial cancer. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2010, 92, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Realini, N. , et al., Acid Ceramidase in Melanoma: expression, localization, and effects of pharmacological inhibition. J Biol Chem, 2016. 291(5): p. 2422-34.
- Illuzzi, G.; Bernacchioni, C.; Aureli, M.; Prioni, S.; Frera, G.; Donati, C.; Valsecchi, M.; Chigorno, V.; Bruni, P.; Sonnino, S.; et al. Sphingosine Kinase Mediates Resistance to the Synthetic Retinoid N-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)retinamide in Human Ovarian Cancer Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 18594–18602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noack, J.; Choi, J.; Richter, K.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; Régnier-Vigouroux, A. A sphingosine kinase inhibitor combined with temozolomide induces glioblastoma cell death through accumulation of dihydrosphingosine and dihydroceramide, endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1425–e1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsecchi, M.; Aureli, M.; Mauri, L.; Illuzzi, G.; Chigorno, V.; Prinetti, A.; Sonnino, S. Sphingolipidomics of A2780 human ovarian carcinoma cells treated with synthetic retinoids. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 1832–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Maurer, B.J.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Wang, E.; Allegood, J.C.; Kelly, S.; Symolon, H.; Liu, Y.; Merrill, A.H.; Gouazé-Andersson, V.; et al. N-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)retinamide increases dihydroceramide and synergizes with dimethylsphingosine to enhance cancer cell killing. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 2967–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idkowiak-Baldys, J.; Apraiz, A.; Li, L.; Rahmaniyan, M.; Clarke, C.J.; Kraveka, J.M.; Asumendi, A.; Hannun, Y.A. Dihydroceramide desaturase activity is modulated by oxidative stress. Biochem. J. 2010, 427, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venant, H.; Rahmaniyan, M.; Jones, E.E.; Lu, P.; Lilly, M.B.; Garrett-Mayer, E.; Drake, R.R.; Kraveka, J.M.; Smith, C.D.; Voelkel-Johnson, C. The Sphingosine Kinase 2 Inhibitor ABC294640 Reduces the Growth of Prostate Cancer Cells and Results in Accumulation of Dihydroceramides In Vitro and In Vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 2744–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Corbacho, M.J. , et al., Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNFα)-induced Ceramide Generation via Ceramide Synthases Regulates Loss of Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK) and Programmed Cell Death. J Biol Chem, 2015. 290(42): p. 25356-73.
- McNair, C.; Urbanucci, A.; Comstock, C.E.S.; A Augello, M.; Goodwin, J.F.; Launchbury, R.; Zhao, S.G.; Schiewer, M.J.; Ertel, A.; Karnes, J.; et al. Cell cycle-coupled expansion of AR activity promotes cancer progression. Oncogene 2016, 36, 1655–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Ye, X.-L.; Sun, Z.-J.; Ji, X.-D.; Chen, H.-X.; Xie, D. Overexpression of degenerative spermatocyte homolog 1 up-regulates the expression of cyclin D1 and enhances metastatic efficiency in esophageal carcinoma Eca109 cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2009, 48, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pewzner-Jung, Y. S. Ben-Dor, and A.H. Futerman, When do Lasses (longevity assurance genes) become CerS (ceramide synthases)?: Insights into the regulation of ceramide synthesis. J Biol Chem, 2006. 281(35): p. 25001-5.
- Lahiri, S. , et al., Kinetic characterization of mammalian ceramide synthases: determination of K(m) values towards sphinganine. FEBS Lett, 2007. 581(27): p. 5289-94.
- Venkataraman, K. , et al., Upstream of growth and differentiation factor 1 (uog1), a mammalian homolog of the yeast longevity assurance gene 1 (LAG1), regulates N-stearoyl-sphinganine (C18-(dihydro)ceramide) synthesis in a fumonisin B1-independent manner in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem, 2002. 277(38): p. 35642-9.
- Sridevi, P.; Alexander, H.; Laviad, E.L.; Pewzner-Jung, Y.; Hannink, M.; Futerman, A.H.; Alexander, S. Ceramide synthase 1 is regulated by proteasomal mediated turnover. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Mol. Cell Res. 2009, 1793, 1218–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, S.K.; Li, H.; Muñoz, S.S.; Knoch, B.; Batterham, M.; Murphy, K.E.; Halliday, G.M.; Garner, B. Altered ceramide acyl chain length and ceramide synthase gene expression in Parkinson's disease. Mov. Disord. 2013, 29, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielke, M.M.; Maetzler, W.; Haughey, N.J.; Bandaru, V.V.R.; Savica, R.; Deuschle, C.; Gasser, T.; Hauser, A.-K.; Gräber-Sultan, S.; Schleicher, E.; et al. Plasma Ceramide and Glucosylceramide Metabolism Is Altered in Sporadic Parkinson's Disease and Associated with Cognitive Impairment: A Pilot Study. PLOS ONE 2013, 8, e73094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberle, M.; Ebel, P.; Wegner, M.-S.; Männich, J.; Tafferner, N.; Ferreiros, N.; Birod, K.; Schreiber, Y.; Krishnamoorthy, G.; Willecke, K.; et al. Regulation of ceramide synthase 6 in a spontaneous experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model is sex dependent. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 92, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinar, R. , et al., Hepatic cannabinoid-1 receptors mediate diet-induced insulin resistance by increasing de novo synthesis of long-chain ceramides. Hepatology, 2014. 59(1): p. 143-53.
- Karahatay, S.; Thomas, K.; Koybasi, S.; Senkal, C.E.; ElOjeimy, S.; Liu, X.; Bielawski, J.; Day, T.A.; Gillespie, M.B.; Sinha, D.; et al. Clinical relevance of ceramide metabolism in the pathogenesis of human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC): Attenuation of C18-ceramide in HNSCC tumors correlates with lymphovascular invasion and nodal metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2007, 256, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, K.; Kawaguchi, T.; Tsuchida, J.; Gabriel, E.; Qi, Q.; Yan, L.; Wakai, T.; Takabe, K.; Nagahashi, M. Ceramide species are elevated in human breast cancer and are associated with less aggressiveness. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 19874–19890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Spassieva, S.D.; Jucius, T.J.; Shultz, L.D.; Shick, H.E.; Macklin, W.B.; Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M.; Ackerman, S.L. A Deficiency of Ceramide Biosynthesis Causes Cerebellar Purkinje Cell Neurodegeneration and Lipofuscin Accumulation. PLOS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanni, N.; Fruscione, F.; Ferlazzo, E.; Striano, P.; Robbiano, A.; Traverso, M.; Sander, T.; Falace, A.; Gazzerro, E.; Bramanti, P.; et al. Impairment of ceramide synthesis causes a novel progressive myoclonus epilepsy. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 76, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wen, L.; Zhu, F.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Q.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y. Overexpression of ceramide synthase 1 increases C18-ceramide and leads to lethal autophagy in human glioma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 104022–104036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laviad, E.L. , et al., Characterization of ceramide synthase 2: tissue distribution, substrate specificity, and inhibition by sphingosine 1-phosphate. J Biol Chem, 2008. 283(9): p. 5677-84.
- Pan, H.; Qin, W.-X.; Huo, K.-K.; Wan, D.-F.; Yu, Y.; Xu, Z.-G.; Hu, Q.-D.; Gu, K.T.; Zhou, X.-M.; Jiang, H.-Q.; et al. Cloning, Mapping, and Characterization of a Human Homologue of the Yeast Longevity Assurance Gene LAG1. Genomics 2001, 77, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrache, I.; Kamocki, K.; Poirier, C.; Pewzner-Jung, Y.; Laviad, E.L.; Schweitzer, K.S.; Van Demark, M.; Justice, M.J.; Hubbard, W.C.; Futerman, A.H. Ceramide Synthases Expression and Role of Ceramide Synthase-2 in the Lung: Insight from Human Lung Cells and Mouse Models. PLOS ONE 2013, 8, e62968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffmann, S.; Sandner, J.; Birod, K.; Wobst, I.; Angioni, C.; Ruckhäberle, E.; Kaufmann, M.; Ackermann, H.; Lötsch, J.; Schmidt, H.; et al. Ceramide synthases and ceramide levels are increased in breast cancer tissue. Carcinog. 2009, 30, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laviad, E.L. , et al., Characterization of Ceramide Synthase 2: tissue distribution, substrate specificity, and inhibition by sphingosine 1-phosphate*. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2008. 283(9): p. 5677-5684.
- Barthelmes, J.; de Bazo, A.M.; Pewzner-Jung, Y.; Schmitz, K.; Mayer, C.A.; Foerch, C.; Eberle, M.; Tafferner, N.; Ferreirós, N.; Henke, M.; et al. Lack of ceramide synthase 2 suppresses the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by impairing the migratory capacity of neutrophils. Brain, Behav. Immun. 2015, 46, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Silva, J.; Dasgupta, S.; Bieberich, E. Long-chain ceramide is elevated in presenilin 1 (PS1M146V) mouse brain and induces apoptosis in PS1 astrocytes. Glia 2008, 56, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosbech, M.; Olsen, A.S.B.; Neess, D.; Ben-David, O.; Klitten, L.L.; Larsen, J.; Sabers, A.; Vissing, J.; Nielsen, J.E.; Hasholt, L.; et al. Reduced ceramide synthase 2 activity causes progressive myoclonic epilepsy. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2014, 1, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, H.; Wang, T.; Yang, C.; Jin, G.; Gu, D.; Deng, X.; Wang, C.; Qin, W.; Jin, H. Co-expression of LASS2 and TGF-β1 predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Niu, Y.; Tan, N.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; You, H.; Ke, R.; Song, J.; Shen, Q.; Wang, W.; et al. LASS2 enhances chemosensitivity of breast cancer by counteracting acidic tumor microenvironment through inhibiting activity of V-ATPase proton pump. Oncogene 2012, 32, 1682–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F. , et al., Overexpression of LASS2 inhibits proliferation and causes G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in papillary thyroid cancer. Cancer Cell International, 2018. 18(1): p. 151.
- Ke, R.-H.; Wang, Y.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, J. Decreased expression of LASS2 is associated with worse prognosis in meningiomas. J. Neuro-Oncology 2014, 118, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Zuo, Y.; Ding, M.; Yan, R.; Yang, D.; Ke, C. Expression and prognostic significance of a new tumor metastasis suppressor gene LASS2 in human bladder carcinoma. Med Oncol. 2011, 29, 1921–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Zuo, Y.; Ding, M.; Ke, C.; Yan, R.; Zhan, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, J. miR-9 promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis by targeting LASS2 in bladder cancer. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 9631–9640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Xiong, T.; Zou, R.; Tang, Z.; Wang, J. The role of LASS2 in regulating bladder cancer cell tumorigenicity in a nude mouse model. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 5149–5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X. J. You, and F. Pei, Silencing of a novel tumor metastasis suppressor gene LASS2/TMSG1 promotes invasion of prostate cancer cell in vitro through increase of vacuolar ATPase activity. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 2012. 113(7): p. 2356-2363.
- Xu, X. , et al., Silencing of LASS2/TMSG1 enhances invasion and metastasis capacity of prostate cancer cell. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 2014. 115(4): p. 731-743.
- Mizutani, Y.; Kihara, A.; Igarashi, Y. LASS3 (longevity assurance homologue 3) is a mainly testis-specific (dihydro)ceramide synthase with relatively broad substrate specificity. Biochem. J. 2006, 398, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.; Futerman, A.H. Mammalian ceramide synthases. IUBMB Life 2010, 62, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizutani, Y.; Kihara, A.; Chiba, H.; Tojo, H.; Igarashi, Y. 2-Hydroxy-ceramide synthesis by ceramide synthase family: enzymatic basis for the preference of FA chain length. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 2356–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.-F.; Tao, Z.; Yan, Z.-Q.; Yang, S.-L.; Gong, Y. Molecular cloning, characterisation and tissue-specific expression of human LAG3, a member of the novel Lag1 protein family. DNA Seq. 2003, 14, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckl, K.-M.; Tidhar, R.; Thiele, H.; Oji, V.; Hausser, I.; Brodesser, S.; Preil, M.-L.; Önal-Akan, A.; Stock, F.; Müller, D.; et al. Impaired Epidermal Ceramide Synthesis Causes Autosomal Recessive Congenital Ichthyosis and Reveals the Importance of Ceramide Acyl Chain Length. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 2202–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radner, F.P. , et al., Mutations in CERS3 cause autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis in humans. PLoS Genet, 2013. 9(6): p. e1003536.
- Marsching, C.; Rabionet, M.; Mathow, D.; Jennemann, R.; Kremser, C.; Porubsky, S.; Bolenz, C.; Willecke, K.; Gröne, H.-J.; Hopf, C.; et al. Renal sulfatides: sphingoid base-dependent localization and region-specific compensation of CerS2-dysfunction. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 2354–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, X.; Ma, D.; Liu, T.; Tian, P.; Wu, C. [Corrigendum] Ceramide synthase-4 orchestrates the cell proliferation and tumor growth of liver cancer in vitro and in vivo through the nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 1–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffmann, S.; Sandner, J.; Birod, K.; Wobst, I.; Angioni, C.; Ruckhäberle, E.; Kaufmann, M.; Ackermann, H.; Lötsch, J.; Schmidt, H.; et al. Ceramide synthases and ceramide levels are increased in breast cancer tissue. Carcinog. 2009, 30, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruckhäberle, E.; Rody, A.; Engels, K.; Gaetje, R.; von Minckwitz, G.; Schiffmann, S.; Grösch, S.; Geisslinger, G.; Holtrich, U.; Karn, T.; et al. Microarray analysis of altered sphingolipid metabolism reveals prognostic significance of sphingosine kinase 1 in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2007, 112, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riebeling, C. , et al., Two mammalian longevity assurance gene (LAG1) family members, trh1 and trh4, regulate dihydroceramide synthesis using different fatty acyl-CoA donors. J Biol Chem, 2003. 278(44): p. 43452-9.
- Chen, L.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Qiu, Y.; Ren, J. Endocannabinoid and ceramide levels are altered in patients with colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.W.; Park, W.; Min, H.; Kwon, T.K.; Baek, S.K.; Hwang, I.; Kim, S.; Park, J. Altered mRNA expression levels of the major components of sphingolipid metabolism, ceramide synthases and their clinical implication in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 3489–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijanka, G.; Hector, S.; Kay, E.W.; Murray, F.; Cummins, R.; Murphy, D.; MacCraith, B.D.; Prehn, J.H.M.; Kenny, D. Human IgG antibody profiles differentiate between symptomatic patients with and without colorectal cancer. Gut 2009, 59, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, S.; Sheehan, K.M.; Espina, V.; O'Grady, A.; Cummins, R.; Kenny, D.; Liotta, L.; O'Kennedy, R.; Kay, E.W.; Kijanka, G.S. High CerS5 expression levels associate with reduced patient survival and transition from apoptotic to autophagy signalling pathways in colorectal cancer. J. Pathol. Clin. Res. 2014, 1, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Li, F.; Han, Z.; Yuan, W.; Cao, L.; Deng, Y.; Peng, X.; Chen, F.; Fan, X.; Liu, X.; et al. LASS5 Interacts with SDHB and Synergistically Represses p53 and p21 Activity. Curr. Mol. Med. 2016, 16, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiffmann, S.; Ferreiros, N.; Birod, K.; Eberle, M.; Schreiber, Y.; Pfeilschifter, W.; Ziemann, U.; Pierre, S.; Scholich, K.; Grösch, S.; et al. Ceramide Synthase 6 Plays a Critical Role in the Development of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 5723–5733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erez-Roman, R.; Pienik, R.; Futerman, A.H. Increased ceramide synthase 2 and 6 mRNA levels in breast cancer tissues and correlation with sphingosine kinase expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 391, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makoukji, J.; Raad, M.; Genadry, K.; El-Sitt, S.; Makhoul, N.J.; Aldin, E.S.; Nohra, E.; Jabbour, M.; Sangaralingam, A.; Chelala, C.; et al. Association between CLN3 (Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis, CLN3 Type) Gene Expression and Clinical Characteristics of Breast Cancer Patients. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruckhäberle, E.; Holtrich, U.; Engels, K.; Hanker, L.; Gätje, R.; Metzler, D.; Karn, T.; Kaufmann, M.; Rody, A. Acid ceramidase 1 expression correlates with a better prognosis in ER-positive breast cancer. Climacteric 2009, 12, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uen, Y.-H. , et al., Ceramide synthase 6 predicts the prognosis of human gastric cancer: It functions as an oncoprotein by dysregulating the SOCS2/JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Molecular Carcinogenesis, 2018. 57(12): p. 1675-1689.
- Minamoto, S.; Ikegame, K.; Ueno, K.; Narazaki, M.; Naka, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Matsumoto, T.; Saito, H.; Hosoe, S.; Kishimoto, T. Cloning and Functional Analysis of New Members of STAT Induced STAT Inhibitor (SSI) Family: SSI-2 and SSI-3. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 237, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




