Submitted:
03 August 2023
Posted:
04 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
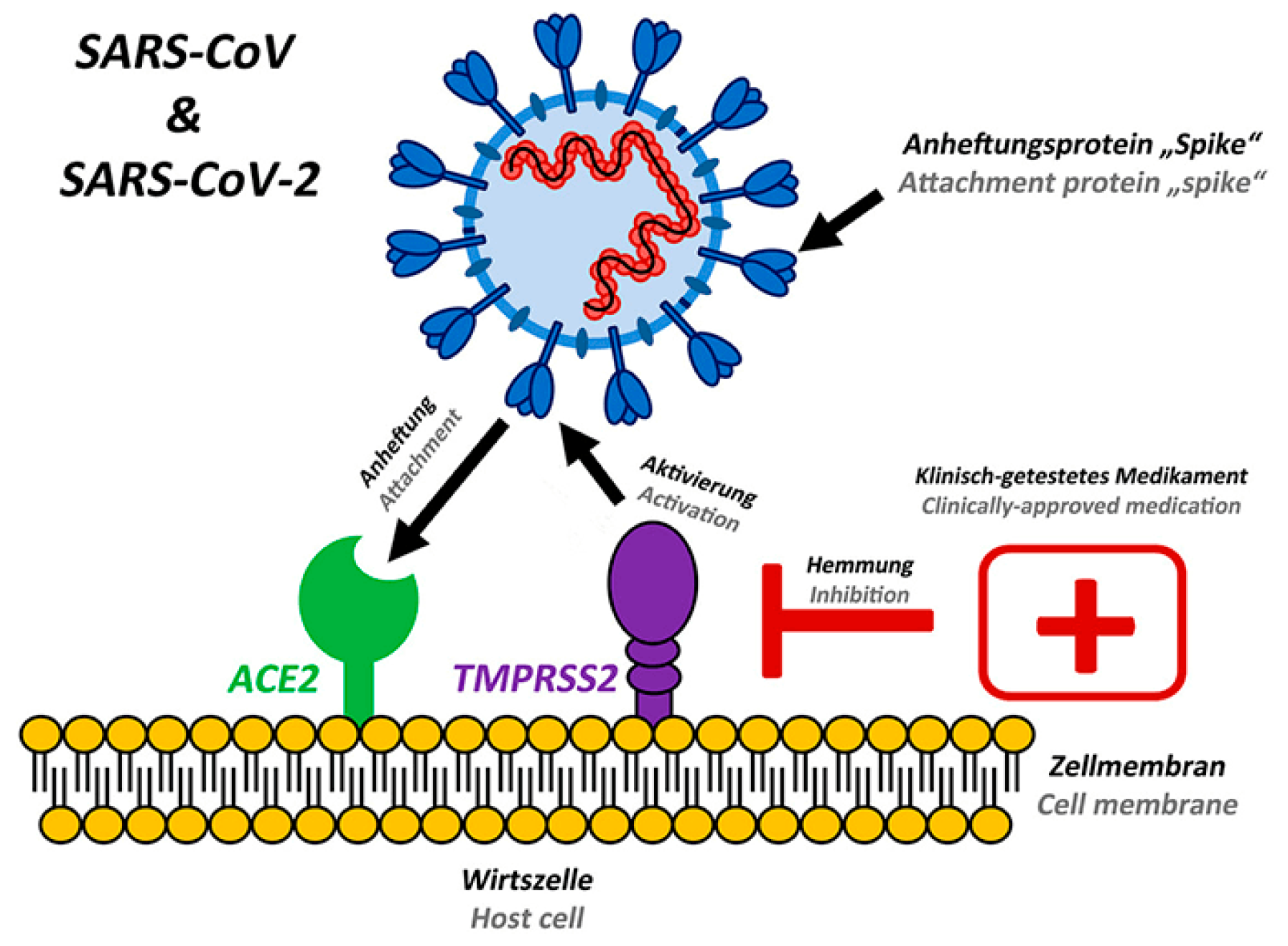
2. SARS-CoV-2 Receptors
2.1. Overview of the Receptors that SARS-CoV-2 Interacts with, Such as ACE2, TMPRSS2, and Others
2.2. The role of each receptor in the viral entry process
2.3. Significance of targeting these receptors for drug discovery
2.4. Significance of receptors in SARS-CoV-2 infection
2.5. Types of receptors involved
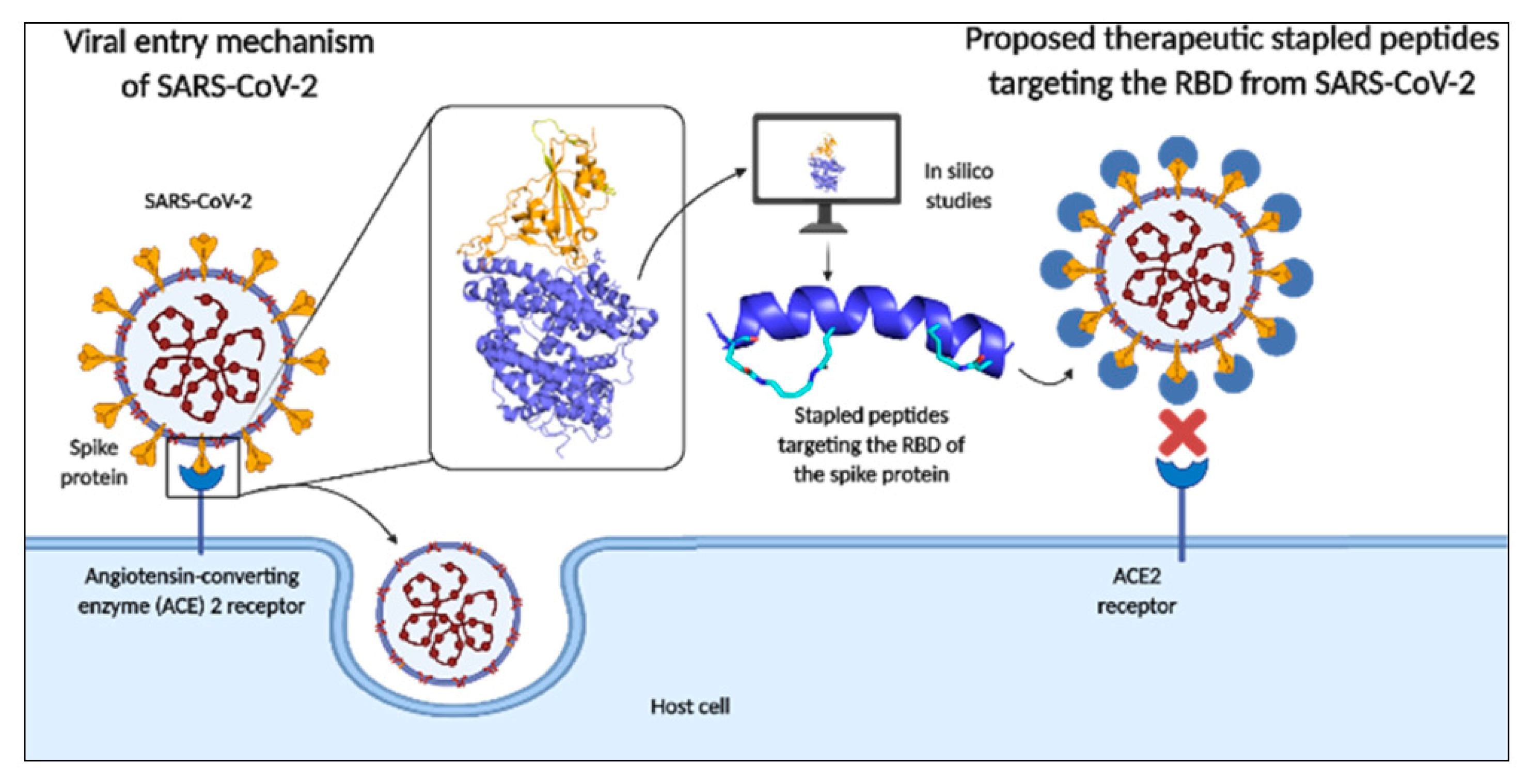
3. In Silico Studies for Drug Discovery
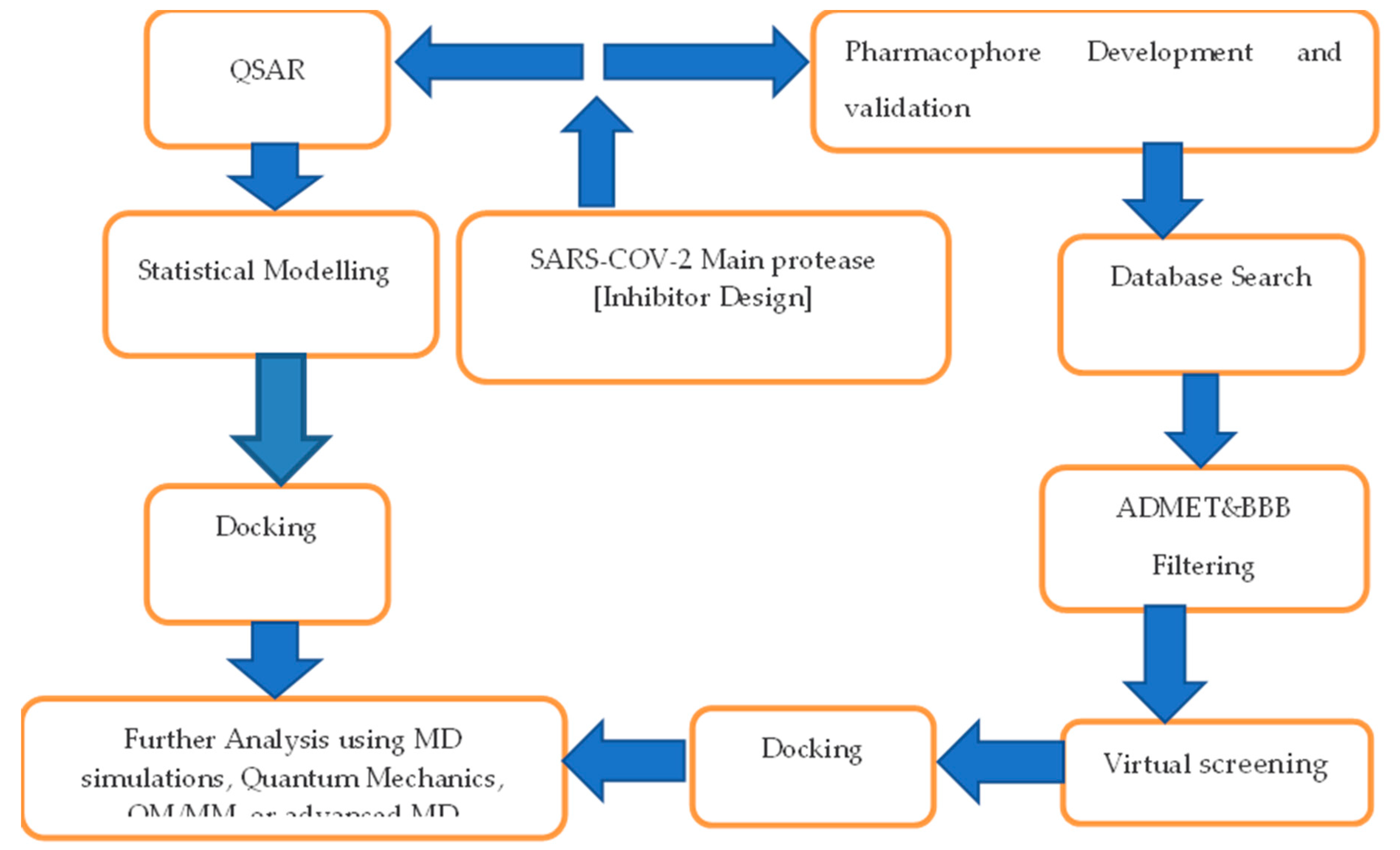
3.1. SARS-CoV-2 In silico studies and how they are used for drug discovery
3.2. SARS-CoV-2 in silico methods that can be used to study drug-receptor interactions, such as molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulations, and virtual screening
3.3. Advantages and limitations of using in silico studies for drug discovery for SARS-CoV-2
4. Using in Silico Studies to Discover Drug Candidates for SARS-COV-2
4.1. Summary of the existing in silico studies that have been conducted to discover drug candidates for SARS-CoV-2
4.2. Highlight of the most promising drug candidates that have been identified using in silico studies.
| Drug Candidate [structure] | Identified through | Target Protein | Mechanism of Action | Potential Use | Current Status | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Remdesivir | Molecular docking | RNA Polymerase | Inhibits viral replication | Antiviral | Approved for emergency use in several countries | Elfiky, A.A., 2020. |
| Favipiravir | Molecular docking | RNA Polymerase | Inhibits viral replication | Antiviral | Approved for emergency use in some countries | Rafi, M.O., Bhattacharje, G., Al-Khafaji, K., et al., 2022. |
| Ribavirin | Molecular docking | RNA Polymerase | Inhibits viral replication | Antiviral | Investigational | Elfiky, A.A., 2020. |
| Ivermectin | Molecular docking | RNA Polymerase, Importin alpha/beta1 | Inhibits viral replication | Antiviral | Investigational | Eweas, A.F., Alhossary, A.A. and Abdel-Moneim, A.S., 2021. |
| Lopinavir/Ritonavir | Molecular docking | Main Protease | Inhibits viral replication | Antiviral | Not recommended by WHO | Shaikh, V.S., Shaikh, Y.I. and Ahmed, K., 2020. |
| Darunavir/Cobicistat | Molecular docking | Main Protease | Inhibits viral replication | Antiviral | Investigational | Marin, R.C., Behl, T., Negrut, N. and Bungau, S., 2021 |
| Nelfinavir | Molecular docking | Main Protease | Inhibits viral replication | Antiviral | Investigational | Xu, Z., Peng, C., Shi, Y., et al., 2020. |
| Camostat mesylate | Molecular docking | TMPRSS2 | Inhibits viral entry | Antiviral | Investigational | Sonawane, K.D., Barale, S.S., Dhanavade, M.J., et al., 2021. |
| Ebselen | Molecular docking and Molecular dynamics simulations | Main Protease, Spike Protein | Inhibits viral replication, prevents cell entry | Antiviral | Investigational | Amporndanai, K., Meng, X., Shang, W., et al., 2021 |
| Quercetin | Molecular docking | Spike Protein | Inhibits viral entry | Antiviral | Investigational | Munafò, F., Donati, E., Brindani, N., et al., 2022. |
| Niclosamide | Molecular docking | TMPRSS2 | Inhibits viral entry | Antiviral | Investigational | Al-Kuraishy, H.M., Al-Gareeb, A.I., Alzahrani, K.J., et al., 2021. |
| Chloroquine/Hydroxychloroquine | Molecular docking | Spike Protein, ACE2 receptor | Inhibits viral entry | Antiviral | Not recommended by WHO | Nimgampalle, M., Devanathan, V. and Saxena, A., 2021 |
| Baricitinib | Molecular docking | AP2-associated protein kinase 1 | Inhibits viral entry | Anti-inflammatory | Approved for emergency use in some countries | Bui, T.Q., Hai, N.T.T., My, T.T.A., et al., 2022. |
| Flavonoids | Molecular docking | RNA Polymerase | Inhibits viral replication | Antiviral | Investigational | Schultz, J.V., Tonel, M.Z., Martins, M.O. and Fagan, S.B., 2023. |
| Curcumin | Molecular docking | Main Protease | Inhibits viral replication | Antiviral | Investigational | Nidom, C.A., Ansori, A.N., et al., 2023. |
| Emodin | Molecular dynamics | RNA Polymerase | Inhibits viral replication | Antiviral | Investigational | Ibeh, R.C., Ikechukwu, G.C., Ukweni, C.J., et al., 2023. |
| Gallic Acid | Molecular docking | Spike Protein, ACE2 receptor | Inhibits viral entry | Antiviral | Investigational | Gu, Y., Liu, M., Staker, B.L., et al., 2023. |
| Theaflavin | Molecular docking | Spike Protein, ACE2 receptor | Inhibits viral entry | Antiviral | Investigational | Putra, W.E., Hidayatullah, A., Heikal, M.F., et al., 2023. |
| Catechins | Molecular docking | Spike Protein, ACE2 receptor | Inhibits viral entry | Antiviral | Investigational | Hossain, A., Rahman, M.E., Rahman, M.S., et al., 2023. |
| Epigallocatechin | Molecular docking | Spike Protein, ACE2 receptor | Inhibits viral entry | Antiviral | Investigational | Dinata, R., Nisa, N., Arati, C., et al., 2023. |
4.3. In silico analysis of drug candidates’ interaction with SARS-CoV-2 receptors
| Drug Candidate | Target Receptor | In Silico Analysis | Result | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Remdesivir | Viral RNA Polymerase | Molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulations | Strong binding affinity, stable complex formation | Shahabadi, N., Zendehcheshm, S., Mahdavi, M. and Khademi, F., 2023. |
| Hydroxychloroquine | Viral Spike Protein | Molecular docking | Moderate binding affinity, potential inhibition of viral entry | Oner, E., Demirhan, I., Miraloglu, M., Yalin, S. and Kurutas, E.B., 2023 |
| Camostat Mesylate | Human ACE2 Receptor | Molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulations | Strong binding affinity, potential inhibition of viral entry | Wang, C., Ye, X., Ding, C., Zhou, M., et al., 2023 |
| Ivermectin | Viral NSP14 Protein | Molecular docking | Moderate binding affinity, potential inhibition of viral replication | Kumar, S. and Choudhary, M., 2023. |
| Favipiravir | Viral RNA Polymerase | Molecular docking | Moderate binding affinity, potential inhibition of viral replication | Nath, A., Rani, M., Rahim, A., et al., 2023. |
| Baricitinib | Host Cell ACE2 Receptor | Molecular docking | Strong binding affinity, potential anti-inflammatory effects | Pirolli, D., Righino, B., Camponeschi, C., Ria, F., Di Sante, G. and De Rosa, M.C., 2023. |
| Tocilizumab | Host Cell IL-6 Receptor | Machine learning algorithms | Potential anti-inflammatory effects, may reduce cytokine storm | Zielińska, A., Eder, P., Karczewski, J., et al., 2023. |
| Lopinavir | Viral Protease | Molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulations | Moderate binding affinity, potential inhibition of viral replication | Oner, E., Demirhan, I., Miraloglu, M., Yalin, S. and Kurutas, E.B., 2023 |
| Ritonavir | Viral Protease | Molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulations | Moderate binding affinity, potential inhibition of viral replication | Miatmoko, A., Sulistyowati, M.I., Setyawan, D. and Cahyani, D.M., 2023. |
| Nitazoxanide | Viral Protease | Molecular docking | Moderate binding affinity, potential inhibition of viral replication | Shoaib, S., Ansari, M.A., Kandasamy, G., et al., 2023. |
| Nelfinavir | Viral Protease | Molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulations | Moderate binding affinity, potential inhibition of viral replication | Ghasemlou, A., Uskoković, V. and Sefidbakht, Y., 2023. |
| Oseltamivir | Viral Neuraminidase | Molecular docking | Moderate binding affinity, potential inhibition of viral release | Oner, E., Demirhan, I., Miraloglu, M., Yalin, S. and Kurutas, E.B., 2023. |
| Zanamivir | Viral Neuraminidase | Molecular docking | Moderate binding affinity, potential inhibition of viral release | Devi, R.N., Pounraj, P., Kumar, S.B., et al., 2023. |
| Darunavir | Viral Protease | Molecular docking | Moderate binding affinity, potential inhibition of viral replication | Makhloufi, A., Ghemit, R., El Kolli, M. and Baitiche, M., 2023. |
| Sofosbuvir | Viral RNA Polymerase | Molecular docking | Moderate binding affinity, potential inhibition of viral replication | Mohamed, E.A., Abdel-Rahman, I.M., et al., 2023. |
| Ribavirin | Viral RNA Polymerase | Molecular docking | Moderate binding affinity, potential inhibition of viral replication | Oner, E., Demirhan, I., Miraloglu, M., Yalin, S. and Kurutas, E.B., 2023. |
| Tenofovir | Viral Reverse Transcriptase | Molecular docking | Moderate binding affinity, potential inhibition of viral replication | Mohandoss, S., Velu, K.S., Stalin, T., Ahmad, N., Alomar, S.Y. and Lee, Y.R., 2023. |
| Emtricitabine | Viral Reverse Transcriptase | Molecular docking | Moderate binding affinity, potential inhibition of viral replication | Oner, E., Demirhan, I., Miraloglu, M., Yalin, S. and Kurutas, E.B., 2023. |
| Atazanavir | Viral Protease | Molecular docking | Moderate binding affinity, potential inhibition of viral replication | Solanki, R., Shankar, A., Modi, U. and Patel, S., 2023. |
| Remdesivir | Viral RNA Polymerase | Molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulations | Strong binding affinity, stable complex formation | Oner, E., Demirhan, I., Miraloglu, M., Yalin, S. and Kurutas, E.B., 2023. |
4.4. Challenges and limitations of using in silico studies to discover drug candidates for SARS-CoV-2
5. Conclusion and Authors Insight
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, H.J. , Zhang, Y.M., Yang, M. and Huang, X. Predictors of mortality for patients with COVID-19 pneumonia caused by SARS-CoV-2. European Respiratory Journal 2020, 56. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L. , Wang, Y., Ye, D. and Liu, Q. Review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) based on current evidence. International journal of antimicrobial agents 2020, 55, 105948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhavana, V. , Thakor, P., Singh, S.B. and Mehra, N.K. COVID-19: Pathophysiology, treatment options, nanotechnology approaches, and research agenda to combating the SARS-CoV2 pandemic. Life sciences 2020, 261, 118336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, E.A. , O'Connor, R.C., Perry, V.H., Tracey, I., Wessely, S., Arseneault, L., Ballard, C., Christensen, H., Silver, R.C., Everall, I. and Ford, T. Multidisciplinary research priorities for the COVID-19 pandemic: a call for action for mental health science. The Lancet Psychiatry 2020, 7, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudrapal, M. , Khairnar, S.J. and Jadhav, A.G. Drug repurposing (DR): an emerging approach in drug discovery. Drug repurposing-hypothesis, molecular aspects and therapeutic applications 2020, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Stanzione, F. , Giangreco, I. and Cole, J.C. Use of molecular docking computational tools in drug discovery. Progress in Medicinal Chemistry 2021, 60, 273–343. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pokhrel, S. , Bouback, T.A., Samad, A., Nur, S.M., Alam, R., Abdullah-Al-Mamun, M., Nain, Z., Imon, R.R., Talukder, M.E.K., Tareq, M.M.I. and Hossen, M.S. Spike protein recognizer receptor ACE2 targeted identification of potential natural antiviral drug candidates against SARS-CoV-2. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2021, 191, 1114–1125. [Google Scholar]
- Sohrab, S.S. , El-Kafrawy, S.A., Mirza, Z., Hassan, A.M., Alsaqaf, F. and Azhar, E.I. In silico prediction and experimental validation of siRNAs targeting ORF1ab of MERS-CoV in Vero cell line. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences 2021, 28, 1348–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhar, T. Virtual Screening based prediction of potential drugs for COVID-19. Combinatorial Chemistry & High Throughput Screening 2020, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Vamathevan, J. , Clark, D., Czodrowski, P., Dunham, I., Ferran, E., Lee, G., Li, B., Madabhushi, A., Shah, P., Spitzer, M. and Zhao, S. Applications of machine learning in drug discovery and development. Nature reviews Drug discovery 2019, 18, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, C. , Carriere, M., Fusco, L., Capua, I., Regla-Nava, J.A., Pasquali, M., Scott, J.A., Vitale, F., Unal, M.A., Mattevi, C. and Bedognetti, D. Toward nanotechnology-enabled approaches against the COVID-19 pandemic. ACS nano 2020, 14, 6383–6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capell, T. , Twyman, R.M., Armario-Najera, V., Ma, J.K.C., Schillberg, S. and Christou, P. Potential applications of plant biotechnology against SARS-CoV-2. Trends in plant science 2020, 25, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, W. , Yang, X., Yang, D., Bao, J., Li, R., Xiao, Y., Hou, C., Wang, H., Liu, J., Yang, D. and Xu, Y. Role of ACE2 in COVID-19. Critical Care 2020, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, M. , Kleine-Weber, H., Schroeder, S., Krüger, N., Herrler, T., Erichsen, S., Schiergens, T.S., Herrler, G., Wu, N.H., Nitsche, A. and Müller, M.A. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letko, M. , Marzi, A. and Munster, V. Functional assessment of cell entry and receptor usage for SARS-CoV-2 and other lineage B betacoronaviruses. Nature microbiology 2020, 5, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, H. , Choudhari, R., Nema, V. and Khan, A.A. ACE2 and TMPRSS2 polymorphisms in various diseases with special reference to its impact on COVID-19 disease. Microbial pathogenesis 2021, 150, 104621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Prior, P. Priming of SARS-CoV-2 S protein by several membrane-bound serine proteinases could explain enhanced viral infectivity and systemic COVID-19 infection. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2021, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdonin, P.P. , Rybakova, E.Y., Trufanov, S.K. and Avdonin, P.V. SARS-CoV-2 Receptors and Their Involvement in Cell Infection. Biochemistry (Moscow), Supplement Series A: Membrane and Cell Biology 2023, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z. , Fu, X., Zhao, Y., Li, X., Long, J. and Zhang, L. Molecular insights into the inhibition mechanism of harringtonine against essential proteins associated with SARS-CoV-2 entry. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2023, 124352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalejaiye, T.D. , Bhattacharya, R., Burt, M.A., Travieso, T., Okafor, A.E., Mou, X., Blasi, M. and Musah, S. SARS-CoV-2 employ BSG/CD147 and ACE2 receptors to directly infect human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived kidney podocytes. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegretti, M. , Cesta, M.C., Zippoli, M., Beccari, A., Talarico, C., Mantelli, F., Bucci, E.M., Scorzolini, L. and Nicastri, E. Repurposing the estrogen receptor modulator raloxifene to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cell Death & Differentiation 2022, 29, 156–166. [Google Scholar]
- Low, Z.Y. , Yip, A.J.W. and Lal, S.K. Repositioning Ivermectin for COVID-19 treatment: Molecular mechanisms of action against SARS-CoV-2 replication. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Basis of Disease 2022, 1868, 166294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, N. , Aghbash, P.S., Shamekh, A., Entezari-Maleki, T., Nahand, J.S., Sales, A.J. and Baghi, H.B. SARS-CoV-2: receptor and co-receptor Tropism Probability. Current Microbiology 2022, 79, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, C.B. , Farzan, M., Chen, B. and Choe, H. Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology 2022, 23, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettunen, P. , Lesnikova, A., Räsänen, N., Ojha, R., Palmunen, L., Laakso, M., Lehtonen, Š., Kuusisto, J., Pietiläinen, O., Saber, S.H. and Joensuu, M. SARS-CoV-2 Infection of Human Neurons Is TMPRSS2 Independent, Requires Endosomal Cell Entry, and Can Be Blocked by Inhibitors of Host Phosphoinositol-5 Kinase. Journal of Virology 2023, e00144-23. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, D. , Turelli, P., Beckert, B., Nazarov, S., Uchikawa, E., Myasnikov, A., Pojer, F., Trono, D., Stahlberg, H. and Lau, K. Cryo-EM structures and binding of mouse and human ACE2 to SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern indicate that mutations enabling immune escape could expand host range. PLoS pathogens 2023, 19, e1011206. [Google Scholar]
- Jaiswal, D. , Kumar, U., Gaur, V. and Salunke, D.M. Epitope-directed anti-SARS-CoV-2 scFv engineered against the key spike protein region could block membrane fusion. Protein Science 2023, 32, e4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. , Yuan, H., Li, X. and Wang, H. Spike protein mediated membrane fusion during SARS-CoV-2 infection. Journal of Medical Virology 2023, 95, e28212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipoor, S.D. and Mirsaeidi, M. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry beyond the ACE2 receptor. Molecular biology reports 2022, 49, 10715–10727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalpoor, H. , Akbari, A., Samei, A., Forghaniesfidvajani, R., Kamali, M., Afzalnia, A., Manshouri, S., Heidari, F., Pornour, M., Khoshmirsafa, M. and Aazami, H. The roles of Eph receptors, neuropilin-1, P2X7, and CD147 in COVID-19-associated neurodegenerative diseases: inflammasome and JaK inhibitors as potential promising therapies. Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters 2022, 27, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Kolarič, A. , Jukič, M. and Bren, U. Novel small-molecule inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein binding to neuropilin 1. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W. , Montano, M., Corley, M.J., Helmy, E., Kobayashi, H., Kinisu, M., Suryawanshi, R., Luo, X., Royer, L.A., Roan, N.R. and Ott, M. Neuropilin-1 mediates SARS-CoV-2 infection of astrocytes in brain organoids, inducing inflammation leading to dysfunction and death of neurons. MBio 2022, 13, e02308–22. [Google Scholar]
- Farahani, M. , Niknam, Z., Amirabad, L.M., Amiri-Dashatan, N., Koushki, M., Nemati, M., Pouya, F.D., Rezaei-Tavirani, M., Rasmi, Y. and Tayebi, L. Molecular pathways involved in COVID-19 and potential pathway-based therapeutic targets. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2022, 145, 112420. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, L. , Bento Cunha, R., Vassilevskaia, T., Viveiros, M. and Cunha, C. Drug repurposing for COVID-19: A review and a novel strategy to identify new targets and potential drug candidates. Molecules 2022, 27, 2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.H. , Hussen, N.H., Shakya, S., Jamalis, J., Pratama, M.R.F., Chander, S., Kharkwal, H. and Murugesan, S. In silico discovery of multi-targeting inhibitors for the COVID-19 treatment by molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulation studies, and ADMET predictions. Structural Chemistry 2022, 33, 1645–1665. [Google Scholar]
- Eslami, N. , Aghbash, P.S., Shamekh, A., Entezari-Maleki, T., Nahand, J.S., Sales, A.J. and Baghi, H.B. SARS-CoV-2: receptor and co-receptor Tropism Probability. Current Microbiology 2022, 79, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H. , Cherukupalli, S., Feng, D., Gao, S., Kang, D., Zhan, P. and Liu, X. SARS-CoV-2 Entry inhibitors targeting virus-ACE2 or virus-TMPRSS2 interactions. Current Medicinal Chemistry 2022, 29, 682–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.M. , Zhu, Y., Zhang, L., Zhong, G., Tai, L., Liu, S., Yin, G., Lu, J., He, Q., Li, M.J. and Zhao, R.X. Novel cleavage sites identified in SARS-CoV-2 spike protein reveal mechanism for cathepsin L-facilitated viral infection and treatment strategies. Cell Discovery 2022, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.H. , Jeong, K., Lee, J., Lee, H.J., Yim, J., Kim, J., Kim, S. and Park, S.B. Inhibition of ACE2-Spike Interaction by an ACE2 Binder Suppresses SARS-CoV-2 Entry. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2022, 61, e202115695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M. , Gohda, J., Kobayashi, A., Tomita, K., Hirayama, Y., Koshikawa, N., Seiki, M., Semba, K., Akiyama, T., Kawaguchi, Y. and Inoue, J.I. Metalloproteinase-dependent and TMPRSS2-independent cell surface entry pathway of SARS-CoV-2 requires the furin cleavage site and the S2 domain of spike protein. Mbio 2022, 13, e00519–22. [Google Scholar]
- Vardhan, S. and Sahoo, S.K. Virtual screening by targeting proteolytic sites of furin and TMPRSS2 to propose potential compounds obstructing the entry of SARS-CoV-2 virus into human host cells. Journal of traditional and complementary medicine 2022, 12, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantzourani, C. , Vasilakaki, S., Gerogianni, V.E. and Kokotos, G. The discovery and development of transmembrane serine protease 2 (TMPRSS2) inhibitors as candidate drugs for the treatment of COVID-19. Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery 2022, 17, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.E. , Chen, W., Zhang, Z., Deng, Y., Lian, J.Q., Du, P., Wei, D., Zhang, Y., Sun, X.X., Gong, L. and Yang, X. CD147-spike protein is a novel route for SARS-CoV-2 infection to host cells. Signal transduction and targeted therapy 2020, 5, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, T. , Kaur, I., Aleya, L., Sehgal, A., Singh, S., Sharma, N., Bhatia, S., Al-Harrasi, A. and Bungau, S. CD147-spike protein interaction in COVID-19: Get the ball rolling with a novel receptor and therapeutic target. Science of the Total Environment 2022, 808, 152072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siri, M. , Dastghaib, S., Zamani, M., Rahmani-Kukia, N., Geraylow, K.R., Fakher, S., Keshvarzi, F., Mehrbod, P., Ahmadi, M., Mokarram, P. and Coombs, K.M. Autophagy, unfolded protein response, and neuropilin-1 cross-talk in SARS-CoV-2 infection: What can be learned from other coronaviruses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2021, 22, 5992. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, N. , Wang, W., Liu, Z., Liang, C., Wang, W., Ye, F., Huang, B., Zhao, L., Wang, H., Zhou, W. and Deng, Y. Morphogenesis and cytopathic effect of SARS-CoV-2 infection in human airway epithelial cells. Nature communications 2020, 11, 3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, G. and Shin, H.W. SARS-CoV-2 infection of airway epithelial cells. Immune network 2021, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyran, M. , Takayama, K., Uversky, V.N., Lundstrom, K., Palù, G., Sherchan, S.P., Attrish, D., Rezaei, N., Aljabali, A.A., Ghosh, S. and Pizzol, D. The structural basis of accelerated host cell entry by SARS-CoV-2. The FEBS journal 2021, 288, 5010–5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. , Qiu, Z., Hou, Y., Deng, X., Xu, W., Zheng, T., Wu, P., Xie, S., Bian, W., Zhang, C. and Sun, Z. AXL is a candidate receptor for SARS-CoV-2 that promotes infection of pulmonary and bronchial epithelial cells. Cell research 2021, 31, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. and Xiang, Y. Spike glycoprotein-mediated entry of SARS coronaviruses. Viruses 2020, 12, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breining, P. , Frølund, A.L., Højen, J.F., Gunst, J.D., Staerke, N.B., Saedder, E., Cases-Thomas, M., Little, P., Nielsen, L.P., Søgaard, O.S. and Kjolby, M. Camostat mesylate against SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19—Rationale, dosing and safety. Basic & clinical pharmacology & toxicology 2021, 128, 204–212. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, C.B. , Farzan, M., Chen, B. and Choe, H. Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology 2022, 23, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyrou, I. , Randeva, H.S., Spandidos, D.A. and Karteris, E. Not only ACE2—the quest for additional host cell mediators of SARS-CoV-2 infection: Neuropilin-1 (NRP1) as a novel SARS-CoV-2 host cell entry mediator implicated in COVID-19. Signal transduction and targeted therapy 2021, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalpoor, H. , Shapourian, H., Akbari, A., Shahveh, S. and Haghshenas, L. Increased neuropilin-1 expression by COVID-19: a possible cause of long-term neurological complications and progression of primary brain tumors. Human Cell 2022, 35, 1301–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, A.M. , Wysocki, J. and Batlle, D. Interaction of SARS-CoV-2 and other coronavirus with ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme)-2 as their main receptor: therapeutic implications. Hypertension 2020, 76, 1339–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, J.A. , Tremblay, B.J., Mansfield, M.J., Woody, O., Lobb, B., Banerjee, A., Chandiramohan, A., Tiessen, N., Cao, Q., Dvorkin-Gheva, A. and Revill, S. Gene expression and in situ protein profiling of candidate SARS-CoV-2 receptors in human airway epithelial cells and lung tissue. European Respiratory Journal 2020, 56. [Google Scholar]
- Sarker, J. , Das, P., Sarker, S., Roy, A.K. and Momen, A.R. A review on expression, pathological roles, and inhibition of TMPRSS2, the serine protease responsible for SARS-CoV-2 spike protein activation. Scientifica 2021, 2021, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, S.N. , S., Pratap, A.P. and Cruz, J.N. Molecular modeling approaches to investigate essential oils (volatile compounds) interacting with molecular targets. In Essential Oils: Applications and Trends in Food Science and Technology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2022; pp. 417–442. [Google Scholar]
- Daoui, O. , Nour, H., Abchir, O., Elkhattabi, S., Bakhouch, M. and Chtita, S. A computer-aided drug design approach to explore novel type II inhibitors of c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase for cancer therapy: QSAR, molecular docking, ADMET and molecular dynamics simulations. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics 2022, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Boufissiou, A. , Abdalla, M., Sharaf, M., Al-Resayes, S.I., Imededdine, K., Alam, M., Yagi, S., Azam, M. and Yousfi, M. In-silico investigation of phenolic compounds from leaves of Phillyrea angustifolia L. as a potential inhibitor against the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (MPro PDB ID: 5R83) using a virtual screening method. Journal of Saudi Chemical Society 2022, 26, 101473. [Google Scholar]
- Rudrapal, M. , Gogoi, N., Chetia, D., Khan, J., Banwas, S., Alshehri, B., Alaidarous, M.A., Laddha, U.D., Khairnar, S.J. and Walode, S.G. Repurposing of phytomedicine-derived bioactive compounds with promising anti-SARS-CoV-2 potential: Molecular docking, MD simulation and drug-likeness/ADMET studies. Saudi journal of biological sciences 2022, 29, 2432–2446. [Google Scholar]
- Adem, Ş. , Eyupoglu, V., Ibrahim, I.M., Sarfraz, I., Rasul, A., Ali, M. and Elfiky, A.A. Multidimensional in silico strategy for identification of natural polyphenols-based SARS-CoV-2 main protease (MPro) inhibitors to unveil a hope against COVID-19. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2022, 145, 105452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalasariya, H.S. , Patel, N.B., Gacem, A., Alsufyani, T., Reece, L.M., Yadav, V.K., Awwad, N.S., Ibrahium, H.A., Ahn, Y., Yadav, K.K. and Jeon, B.H. Marine Alga Ulva fasciata-Derived Molecules for the Potential Treatment of SARS-CoV-2: An In Silico Approach. Marine Drugs 2022, 20, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukhari, S.N.H. , Jain, A., Haq, E., Mehbodniya, A. and Webber, J. Machine learning techniques for the prediction of B-cell and T-cell epitopes as potential vaccine targets with a specific focus on SARS-CoV-2 pathogen: A review. Pathogens 2022, 11, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, K. , Sarma, P., Rana, S.V., Medhi, B. and Naithani, M. Emerging role of artificial intelligence in therapeutics for COVID-19: a systematic review. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics 2022, 40, 4750–4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C. and Yang, M. Newly Emerged Antiviral Strategies for SARS-CoV-2: From Deciphering Viral Protein Structural Function to the Development of Vaccines, Antibodies, and Small Molecules. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalrahman, T. and Checa, S. On the role of mechanical signals on sprouting angiogenesis through computer modeling approaches. Biomechanics and Modeling in Mechanobiology 2022, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Chopra, H. , Baig, A.A., Gautam, R.K. and Kamal, M.A. Application of Artificial intelligence in Drug Discovery. Current Pharmaceutical Design 2022, 28, 2690–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macip, G. , Garcia-Segura, P., Mestres-Truyol, J., Saldivar-Espinoza, B., Ojeda-Montes, M.J., Gimeno, A., Cereto-Massagué, A., Garcia-Vallvé, S. and Pujadas, G. Haste makes waste: A critical review of docking-based virtual screening in drug repurposing for SARS-CoV-2 main protease (M-pro) inhibition. Medicinal Research Reviews 2022, 42, 744–769. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q. , Wan, J. and Wang, G. A survey on computational methods in discovering protein inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2. Briefings in Bioinformatics 2022, 23, bbab416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More-Adate, P. , Lokhande, K.B., Swamy, K.V., Nagar, S. and Baheti, A. GC-MS profiling of Bauhinia variegata major phytoconstituents with computational identification of potential lead inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 MPro. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2022, 147, 105679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujwar, S. , Sun, L. and Fidan, O. In silico evaluation of food-derived carotenoids against SARS-CoV-2 drug targets: Crocin is a promising dietary supplement candidate for COVID-19. Journal of Food Biochemistry 2022, 46, e14219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y. , Liu, Y., Gupta, S., Paramo, M.I., Hou, Y., Mao, C., Luo, Y., Judd, J., Wierbowski, S., Bertolotti, M. and Nerkar, M. A comprehensive SARS-CoV-2–human protein–protein interactome reveals COVID-19 pathobiology and potential host therapeutic targets. Nature biotechnology 2023, 41, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazniewski, M. , Dermawan, D., Hidayat, S., Muchtaridi, M., Dawson, W.K. and Plewczynski, D. Drug repurposing for identification of potential spike inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 using molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations. Methods 2022, 203, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puthanveetil, P. Metabolic Activation of PARP as a SARS-CoV-2 Therapeutic Target—Is It a Bait for the Virus or the Best Deal We Could Ever Make with the Virus? Is AMBICA the Potential Cure? Biomolecules 2023, 13, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozdemir, E.S. , Le, H.H., Yildirim, A. and Ranganathan, S.V. In silico screening and testing of FDA-approved small molecules to block SARS-CoV-2 entry to the host cell by inhibiting spike protein cleavage. Viruses 2022, 14, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabzian-Molaei, F. , Nasiri Khalili, M.A., Sabzian-Molaei, M., Shahsavarani, H., Fattah Pour, A., Molaei Rad, A. and Hadi, A. Urtica dioica Agglutinin: A plant protein candidate for inhibition of SARS-COV-2 receptor-binding domain for control of Covid19 Infection. PLoS One 2022, 17, e0268156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P. , T., Mathpal, S., Tamta, S. and Chandra, S. Computational approaches for drug discovery against COVID-19. In Omics Approaches and Technologies in COVID-19; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 321–337. [Google Scholar]
- Panda, S. , L., Badwaik, H.R. and Shanmugarajan, D. Computational approaches for drug repositioning and repurposing to combat SARS-CoV-2 infection. In Computational Approaches for Novel Therapeutic and Diagnostic Designing to Mitigate SARS-CoV2 Infection; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 247–265. [Google Scholar]
- Parihar, A. , Sonia, Z.F., Akter, F., Ali, M.A., Hakim, F.T. and Hossain, M.S. Phytochemicals-based targeting RdRp and main protease of SARS-CoV-2 using docking and steered molecular dynamic simulation: A promising therapeutic approach for Tackling COVID-19. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2022, 145, 105468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R. , Bhardwaj, V.K., Das, P., Bhattacherjee, D., Zyryanov, G.V. and Purohit, R. Benchmarking the ability of novel compounds to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 main protease using steered molecular dynamics simulations. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2022, 146, 105572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumskiy, R.S. , Tumskaia, A.V., Klochkova, I.N. and Richardson, R.J. SARS-CoV-2 proteases MPro and PLpro: Design of inhibitors with predicted high potency and low mammalian toxicity using artificial neural networks, ligand-protein docking, molecular dynamics simulations, and ADMET calculations. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2023, 153, 106449. [Google Scholar]
- Pawnikar, S. , Bhattarai, A., Wang, J. and Miao, Y. Binding Analysis Using Accelerated Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Future Perspectives. Advances and Applications in Bioinformatics and Chemistry 2022, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansori, A.N.M. , Kharisma, V.D., Parikesit, A.A., Dian, F.A., Probojati, R.T., Rebezov, M., Scherbakov, P., Burkov, P., Zhdanova, G., Mikhalev, A. and Antonius, Y. Bioactive compounds from mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana L.) as an antiviral agent via dual inhibitor mechanism against SARSCoV-2: an in silico approach. Pharmacognosy Journal 2022, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Jahantigh, H.R. , Ahmadi, N., Shahbazi, B., Lovreglio, P., Habibi, M., Stufano, A., Gouklani, H. and Ahmadi, K. Evaluation of the dual effects of antiviral drugs on SARS-CoV-2 receptors and the ACE2 receptor using structure-based virtual screening and molecular dynamics simulation. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics 2022, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Anuj, M. , Afzal, A., Sharma, M., Purna, D. and Singh, P. Interaction of surface glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern with potential drug candidates: A molecular docking study. F1000Research 2022, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Shahbazi, B. , Mafakher, L. and Teimoori-Toolabi, L. Different compounds against ACE2 receptor potentially containing the infectivity of SARS-CoV-2: an in silico study. Journal of molecular modeling 2022, 28, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahabadi, N. , Zendehcheshm, S., Mahdavi, M. and Khademi, F. Repurposing FDA-approved drugs cetilistat, abiraterone, diiodohydroxyquinoline, bexarotene, and Remdesivir as potential inhibitors against RNA dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2: A comparative in silico perspective. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked 2023, 36, 101147. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C. , Liu, Y., Yang, Y., Zhang, P., Zhong, W., Wang, Y., Wang, Q., Xu, Y., Li, M., Li, X. and Zheng, M. Analysis of therapeutic targets for SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of potential drugs by computational methods. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B 2020, 10, 766–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, N.A. , Pandian, C.J. and Jeyakanthan, J. Computational investigation on Andrographis paniculata phytochemicals to evaluate their potency against SARS-CoV-2 in comparison to known antiviral compounds in drug trials. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics 2021, 39, 4415–4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V. , Liu, H. and Wu, C. Drug repurposing against SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain using ensemble-based virtual screening and molecular dynamics simulations. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2021, 135, 104634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipitò, L. , Rujan, R.M., Reynolds, C.A. and Deganutti, G. Molecular dynamics studies reveal structural and functional features of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. BioEssays 2022, 44, 2200060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahammad, I. and Lira, S.S. Designing a novel mRNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2: An immunoinformatics approach. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2020, 162, 820–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotze, A.C. , Hunt, P.W., Skuce, P., von Samson-Himmelstjerna, G., Martin, R.J., Sager, H., Krücken, J., Hodgkinson, J., Lespine, A., Jex, A.R. and Gilleard, J.S. Recent advances in candidate-gene and whole-genome approaches to the discovery of anthelmintic resistance markers and the description of drug/receptor interactions. International Journal for Parasitology: Drugs and Drug Resistance 2014, 4, 164–184. [Google Scholar]
- Couto, M. and Cates, C. Laboratory guidelines for animal care. Vertebrate Embryogenesis: Embryological, Cellular, and Genetic Methods 2019, 407–430. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, R. , Perera, L. and Tillekeratne, L.V. Potential SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors. Drug Discovery Today 2021, 26, 804–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaker, B. , Ahmad, S., Lee, J., Jung, C. and Na, D. In silico methods and tools for drug discovery. Computers in biology and medicine 2021, 137, 104851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekins, S. , Mestres, J. and Testa, B. In silico pharmacology for drug discovery: methods for virtual ligand screening and profiling. British journal of pharmacology 2007, 152, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travassos, G.H.; Barros, M.O. Contributions of in virtuo and in silico experiments for the future of empirical studies in software engineering. In 2nd Workshop on empirical software engineering the future of empirical studies in software engineering; 2003; pp. 117–130. [Google Scholar]
- Park, B.K. , Boobis, A., Clarke, S., Goldring, C.E., Jones, D., Kenna, J.G., Lambert, C., Laverty, H.G., Naisbitt, D.J., Nelson, S. and Nicoll-Griffith, D.A. Managing the challenge of chemically reactive metabolites in drug development. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 2011, 10, 292–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N. and Villoutreix, B.O. Resources and computational strategies to advance small molecule SARS-CoV-2 discovery: Lessons from the pandemic and preparing for future health crises. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal 2021, 19, 2537–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghufran, M. , Ullah, M., Khan, H.A., Ghufran, S., Ayaz, M., Siddiq, M., Abbas, S.Q., Hassan, S.S.U. and Bungau, S. In-Silico Lead Druggable Compounds Identification against SARS COVID-19 Main Protease Target from In-House, Chembridge and Zinc Databases by Structure-Based Virtual Screening, Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 100. [Google Scholar]
- Azeem, M. , Mustafa, G. and Mahrosh, H.S. Virtual screening of phytochemicals by targeting multiple proteins of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2: Molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation studies. International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology 2022, 36, 03946320221142793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, M. , Muhammad, S., Bibi, S., Abbasi, S.W., Al-Sehemi, A.G., Chaudhary, A.R. and Bai, F.Q. Exploring the potential of novel phenolic compounds as potential therapeutic candidates against SARS-CoV-2, using quantum chemistry, molecular docking and dynamic studies. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 2021, 43, 128079. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S. , Sharma, P.P., Shankar, U., Kumar, D., Joshi, S.K., Pena, L., Durvasula, R., Kumar, A., Kempaiah, P., Poonam and Rathi, B. Discovery of new hydroxyethylamine analogs against 3CLpro protein target of SARS-CoV-2: Molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulation, and structure–activity relationship studies. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling 2020, 60, 5754–5770. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, R. , Chakraborty, A., Biswas, A. and Chowdhuri, S. Evaluation of green tea polyphenols as novel corona virus (SARS CoV-2) main protease (MPro) inhibitors–an in silico docking and molecular dynamics simulation study. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics 2021, 39, 4362–4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvez, M.S.A. , Karim, M.A., Hasan, M., Jaman, J., Karim, Z., Tahsin, T., Hasan, M.N. and Hosen, M.J. Prediction of potential inhibitors for RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2 using comprehensive drug repurposing and molecular docking approach. International journal of biological macromolecules 2020, 163, 1787–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.M. , Maruthi, K.R., Bajpe, S.N., Vyshali, V.M., Sushmitha, S., Akhila, C. and Ramu, R. Comparative molecular docking and simulation analysis of molnupiravir and Remdesivir with SARS-CoV-2 RNA dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). Bioinformation 2021, 17, 932. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y. , Wang, F., Tang, J., Nussinov, R. and Cheng, F. Artificial intelligence in COVID-19 drug repurposing. The Lancet Digital Health 2020, 2, e667–e676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, T. , Wang, H. and Luan, B. In silico exploration of the molecular mechanism of clinically oriented drugs for possibly inhibiting SARS-CoV-2’s main protease. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters 2020, 11, 4413–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A. , Das, N.C., Patra, R., Bhattacharya, M., Ghosh, P., Patra, B.C. and Mukherjee, S. Exploring the binding efficacy of ivermectin against the key proteins of SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis: an in silico approach. Future Virology 2021, 16, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braz, H.L.B. , de Moraes Silveira, J.A., Marinho, A.D., de Moraes, M.E.A., de Moraes Filho, M.O., Monteiro, H.S.A. and Jorge, R.J.B. In silico study of azithromycin, chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine and their potential mechanisms of action against SARS-CoV-2 infection. International journal of antimicrobial agents 2020, 56, 106119. [Google Scholar]
- Ghahremanian, S. , Rashidi, M.M., Raeisi, K. and Toghraie, D. Molecular dynamics simulation approach for discovering potential inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2: A structural review. Journal of Molecular Liquids 2022, 118901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallei, T.E. , Tumilaar, S.G., Niode, N.J., Kepel, B.J., Idroes, R., Effendi, Y., Sakib, S.A. and Emran, T.B. Potential of plant bioactive compounds as SARS-CoV-2 main protease (M pro) and spike (S) glycoprotein inhibitors: a molecular docking study. Scientifica 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdian, S. , Ebrahim-Habibi, A. and Zarrabi, M. Drug repurposing using computational methods to identify therapeutic options for COVID-19. Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders 2020, 19, 691–699. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, Arun Dev, and Inderjeet Kaur. Molecular docking studies on Jensenone from eucalyptus essential oil as a potential inhibitor of COVID 19 corona virus infection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.00217. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, Y. , Singh, H. and Patel, C.N. In silico prediction of potential inhibitors for the main protease of SARS-CoV-2 using molecular docking and dynamics simulation based drug-repurposing. Journal of infection and public health 2020, 13, 1210–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahanta S, Chowdhury P, Gogoi N, Goswami N, Borah D, Kumar R, Chetia D, Borah P, Buragohain AK, Gogoi B. Potential anti-viral activity of approved repurposed drug against main protease of SARS-CoV-2: an in silico based approach. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics 2021, 39, 3802–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, R.R. , Tiwari, A.P., Nyayanit, N. and Modak, M. In silico molecular docking analysis for repurposing therapeutics against multiple proteins from SARS-CoV-2. European journal of pharmacology 2020, 886, 173430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H. , Zhao, L., Gong, X., Hu, M. and Wang, H. Virtual screening FDA approved drugs against multiple targets of SARS-CoV-2. Clinical and translational science 2021, 14, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, K. and Singh, M.K. Drug repurposing in COVID-19: a review with past, present and future. Metabolism Open 2021, 12, 100121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheahan, T.P. , Sims, A.C., Zhou, S., Graham, R.L., Pruijssers, A.J., Agostini, M.L., Leist, S.R., Schäfer, A., Dinnon III, K.H., Stevens, L.J. and Chappell, J.D. An orally bioavailable broad-spectrum antiviral inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in human airway epithelial cell cultures and multiple coronaviruses in mice. Science translational medicine 2020, 12, eabb5883. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, M.K. , Shrivastava-Ranjan, P., Chatterjee, P., Flint, M., Beadle, J.R., Valiaeva, N., Murphy, J., Schooley, R.T., Hostetler, K.Y., Montgomery, J.M. and Spiropoulou, C.F. Broad-spectrum in vitro antiviral activity of ODBG-P-RVn: an orally-available, lipid-modified monophosphate prodrug of Remdesivir parent nucleoside (GS-441524). Microbiology Spectrum 2021, 9, e01537–21. [Google Scholar]
- Khater, S. , Kumar, P., Dasgupta, N., Das, G., Ray, S. and Prakash, A. Combining SARS-CoV-2 proofreading exonuclease and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitors as a strategy to combat COVID-19: a high-throughput in silico screening. Frontiers in Microbiology 2021, 12, 647693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S. , Attar, F., Bloukh, S.H., Sharifi, M., Nabi, F., Bai, Q., Khan, R.H. and Falahati, M. A review on the interaction of nucleoside analogues with SARS-CoV-2 RNA dependent RNA polymerase. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2021, 181, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. , Anirudhan, V., Du, R., Cui, Q. and Rong, L. RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2 as a therapeutic target. Journal of medical virology 2021, 93, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, I. , Erol, M. and Duzgun, Z. In silico evaluation of potential inhibitory activity of Remdesivir, favipiravir, ribavirin and galidesivir active forms on SARS-CoV-2 RNA polymerase. Molecular Diversity 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y. , Zeng, M., Jiang, B., Zhang, W., Wang, M., Jia, R., Zhu, D., Liu, M., Zhao, X., Yang, Q. and Wu, Y. Flavivirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase interacts with genome UTRs and viral proteins to facilitate flavivirus RNA replication. Viruses 2019, 11, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, R. , Chan, H., Kamath, G., Ramprasad, R., Cherukara, M.J. and Sankaranarayanan, S.K. Screening of therapeutic agents for COVID-19 using machine learning and ensemble docking studies. The journal of physical chemistry letters 2020, 11, 7058–7065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wilde, P. The gap between predicted and measured energy performance of buildings: A framework for investigation. Automation in construction 2014, 41, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L. Pharmacokinetics of monoclonal antibodies and Fc-fusion proteins. Protein & cell 2018, 9, 15–32. [Google Scholar]
- Bzówka, M. , Mitusińska, K., Raczyńska, A., Samol, A., Tuszyński, J.A. and Góra, A. Structural and evolutionary analysis indicate that the SARS-CoV-2 MPro is a challenging target for small-molecule inhibitor design. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2020, 21, 3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahtarin, R. , Islam, S., Islam, M.J., Ullah, M.O., Ali, M.A. and Halim, M.A. Structure and dynamics of membrane protein in SARS-CoV-2. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics 2022, 40, 4725–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cournia, Z. , Allen, B. and Sherman, W. Relative binding free energy calculations in drug discovery: recent advances and practical considerations. Journal of chemical information and modeling 2017, 57, 2911–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, G. , Bartels, J. and Vodovotz, Y. In silico augmentation of the drug development pipeline: examples from the study of acute inflammation. Drug development research 2011, 72, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodos, R.A. , Kidd, B.A., Shameer, K., Readhead, B.P. and Dudley, J.T. In silico methods for drug repurposing and pharmacology. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Systems Biology and Medicine 2016, 8, 186–210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





