Submitted:
01 August 2023
Posted:
02 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
2.3. Antimicrobial Compounds
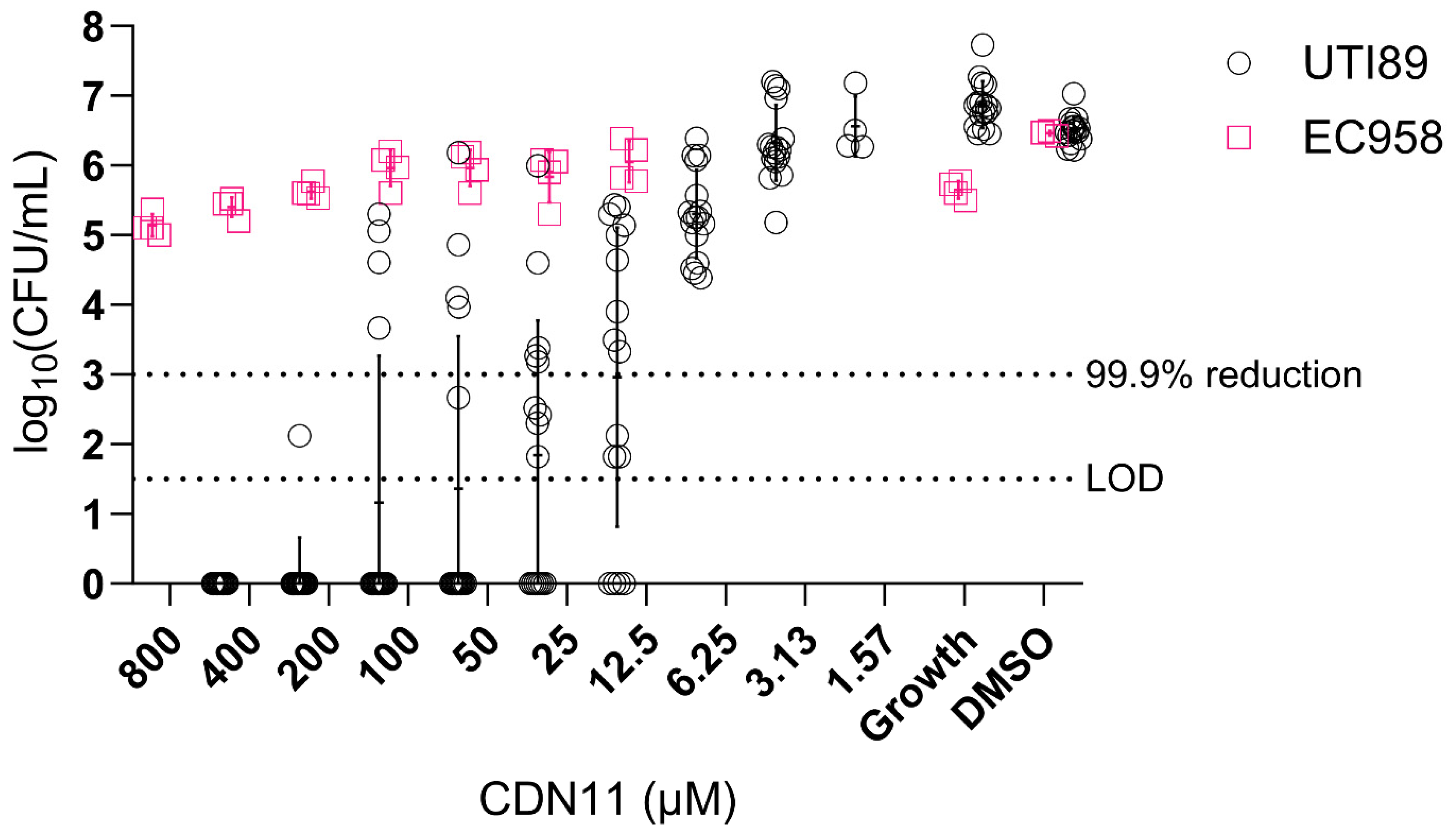
2.4. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Assay
2.5. Minimum Biofilm Eradication Concentration (MBEC) Assay
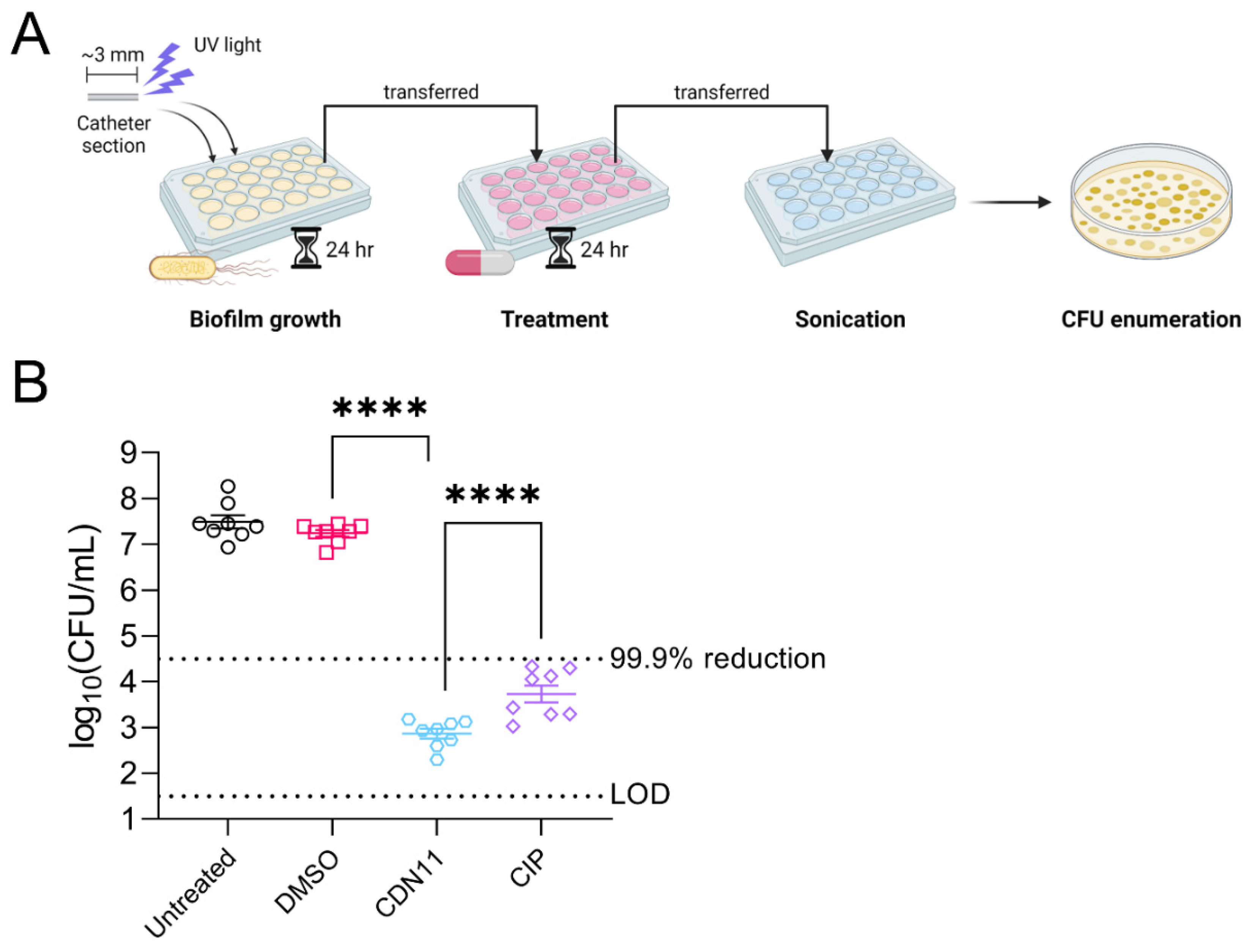
2.6. Catheter Biofilm Model
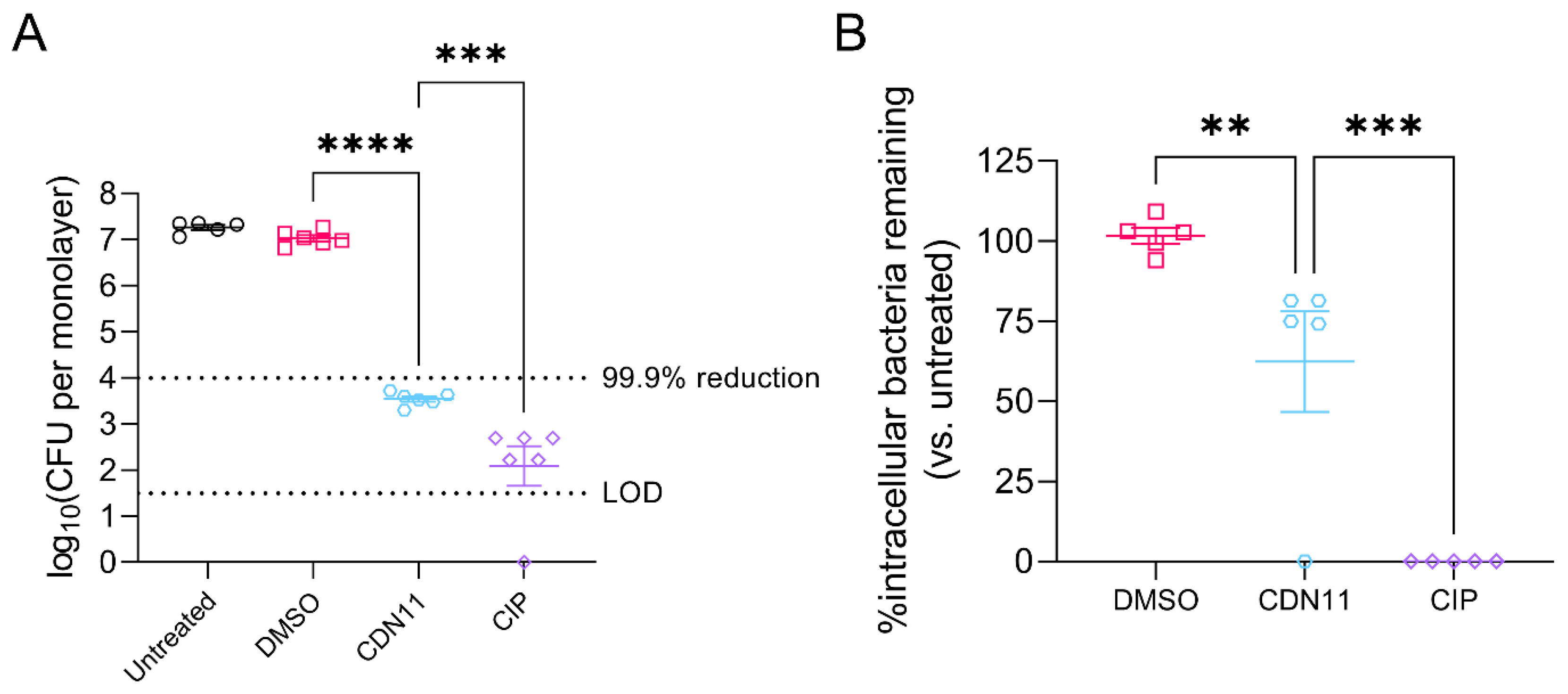
2.7. Human Cell Infection Assays
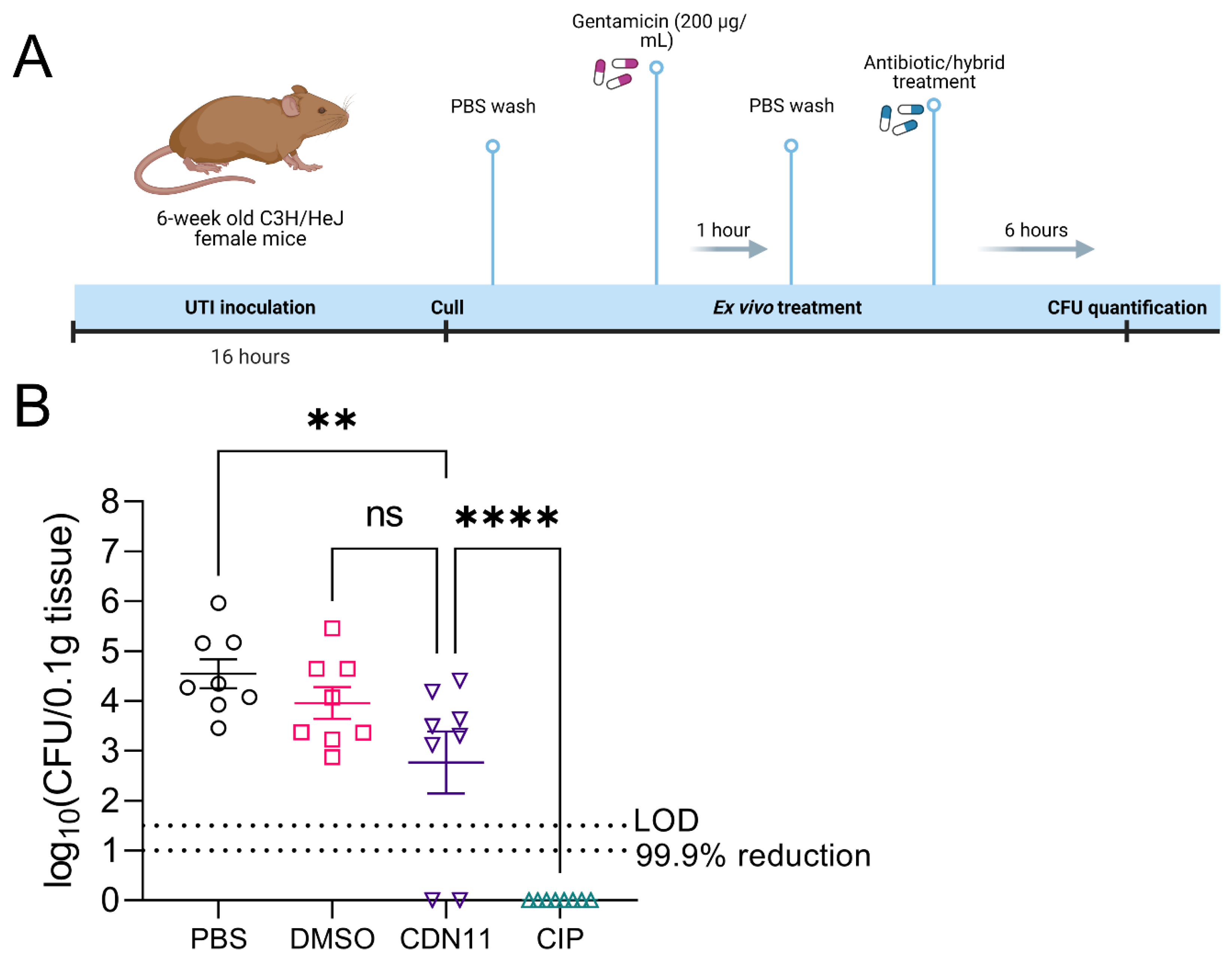
2.8. In Vivo UTI Mouse Model and Ex Vivo Bladder Antibiotic Treatment
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. CDN11 Eradicates UPEC Biofilms Formed on Urinary Catheters In Vitro
3.2. In Vitro Treatment of Infected Human Bladder Cells with CDN11 Reduces Extracellular and Intracellular UPEC Titers
3.3. Ex Vivo Treatment of Infected Mouse Bladders with CDN11 Reduces Intracellular UPEC Reservoirs
3.4. CDN11 Displays Activity against Biofilms by fluoroquinolone-Sensitive not Fluoroquinolone Resistant UPEC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tamadonfar, K.O.; Omattage, N.S.; Spaulding, C.N.; Hultgren, S.J. Reaching the End of the Line: Urinary Tract Infections. Microbiol Spectr 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Mireles, A.; Hreha, T.N.; Hunstad, D.A. Pathophysiology, Treatment, and Prevention of Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection. Top Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil 2019, 25, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, R.D.; Hultgren, S.J. Urinary tract infections: microbial pathogenesis, host-pathogen interactions and new treatment strategies. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justice, S.S.; Hung, C.; Theriot, J.A.; Fletcher, D.A.; Anderson, G.G.; Footer, M.J.; Hultgren, S.J. Differentiation and developmental pathways of uropathogenic Escherichia coli in urinary tract pathogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004, 101, 1333–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiton, P.S.; Hung, C.S.; Hancock, L.E.; Caparon, M.G.; Hultgren, S.J. Enterococcal biofilm formation and virulence in an optimized murine model of foreign body-associated urinary tract infections. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 4166–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Bonillo, C.; Texidó, R.; Reyes-Carmenaty, G.; Gilabert-Porres, J.; Borrós, S. Study of the Human Albumin Role in the Formation of a Bacterial Biofilm on Urinary Devices Using QCM-D. ACS Appl Bio Mater 2020, 3, 3354–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K. Multidrug tolerance of biofilms and persister cells. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2008, 322, 107–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Bassler, B.L. Surviving as a Community: Antibiotic Tolerance and Persistence in Bacterial Biofilms. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, M.J.; Da Cunda, P.; Notejane, M.; Zunino, P.; Scavone, P.; Robino, L. Fosfomycin tromethamine activity on biofilm and intracellular bacterial communities produced by uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from patients with urinary tract infection. Pathog Dis 2019, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.; Zhou, Y.; Pinkner, J.S.; Dodson, K.W.; Crowley, J.R.; Heuser, J.; Chapman, M.R.; Hadjifrangiskou, M.; Henderson, J.P.; Hultgren, S.J. Escherichia coli biofilms have an organized and complex extracellular matrix structure. mBio 2013, 4, e00645–00613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.G.; Goller, C.C.; Justice, S.; Hultgren, S.J.; Seed, P.C. Polysaccharide capsule and sialic acid-mediated regulation promote biofilm-like intracellular bacterial communities during cystitis. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 963–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, K.J.; Seed, P.C.; Hultgren, S.J. Development of intracellular bacterial communities of uropathogenic Escherichia coli depends on type 1 pili. Cell. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2230–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totsika, M.; Kostakioti, M.; Hannan, T.J.; Upton, M.; Beatson, S.A.; Janetka, J.W.; Hultgren, S.J.; Schembri, M.A. A FimH inhibitor prevents acute bladder infection and treats chronic cystitis caused by multidrug-resistant uropathogenic Escherichia coli ST131. J Infect Dis 2013, 208, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mysorekar, I.U.; Hultgren, S.J. Mechanisms of uropathogenic Escherichia coli persistence and eradication from the urinary tract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006, 103, 14170–14175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannan, T.J.; Mysorekar, I.U.; Hung, C.S.; Isaacson-Schmid, M.L.; Hultgren, S.J. Early severe inflammatory responses to uropathogenic E. coli predispose to chronic and recurrent urinary tract infection. PLoS Pathog 2010, 6, e1001042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.J.; Fong, C.; La Bella, A.A.; Molina, J.J.; Molesan, A.; Champion, M.M.; Howell, C.; Flores-Mireles, A.L. Inhibiting host-protein deposition on urinary catheters reduces associated urinary tract infections. Elife 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barraud, N.; Kelso, M.J.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S. Nitric oxide: a key mediator of biofilm dispersal with applications in infectious diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawas, S.; Verderosa, A.D.; Totsika, M. Combination Therapies for Biofilm Inhibition and Eradication: A Comparative Review of Laboratory and Preclinical Studies. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poh, W.H.; Rice, S.A. Recent Developments in Nitric Oxide Donors and Delivery for Antimicrobial and Anti-Biofilm Applications. In Molecules, 2022; Vol. 27. [CrossRef]
- Reffuveille, F.; Fuente-Nunez Cde, L.; Fairfull-Smith, K.E.; Hancock, R.E. Potentiation of ciprofloxacin action against Gram-negative bacterial biofilms by a nitroxide. Pathog Dis 2015, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verderosa, A.D.; Dhouib, R.; Fairfull-Smith, K.E.; Totsika, M. Nitroxide Functionalized Antibiotics Are Promising Eradication Agents against Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 64, e01685–01619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verderosa, A.D.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C.; Mansour, S.C.; Cao, J.; Lu, T.K.; Hancock, R.E.W.; Fairfull-Smith, K.E. Ciprofloxacin-nitroxide hybrids with potential for biofilm control. Eur J Med Chem 2017, 138, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verderosa, A.D.; Mansour, S.C.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C.; Hancock, R.E.; Fairfull-Smith, K.E. Synthesis and Evaluation of Ciprofloxacin-Nitroxide Conjugates as Anti-Biofilm Agents. Molecules 2016, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verderosa, A.D.; Harris, J.; Dhouib, R.; Totsika, M.; Fairfull-Smith, K.E. Eradicating uropathogenic Escherichia coli biofilms with a ciprofloxacin-dinitroxide conjugate. Medchemcomm 2019, 10, 699–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verderosa, A.D.; Dhouib, R.; Fairfull-Smith, K.E.; Totsika, M. Profluorescent Fluoroquinolone-Nitroxides for Investigating Antibiotic⁻Bacterial Interactions. Antibiotics (Basel) 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, D.; Rumbaugh, K. The Consequences of Biofilm Dispersal on the Host. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 10738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kot, B. Antibiotic Resistance Among Uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Pol J Microbiol 2019, 68, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manges, A.R.; Geum, H.M.; Guo, A.; Edens, T.J.; Fibke, C.D.; Pitout, J.D.D. Global Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli (ExPEC) Lineages. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totsika, M.; Moriel, D.G.; Idris, A.; Rogers, B.A.; Wurpel, D.J.; Phan, M.D.; Paterson, D.L.; Schembri, M.A. Uropathogenic Escherichia coli mediated urinary tract infection. Curr. Drug Targets 2012, 13, 1386–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultgren, S.J.; Schwan, W.R.; Schaeffer, A.J.; Duncan, J.L. Regulation of production of type 1 pili among urinary tract isolates of Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 1986, 54, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forde, B.M.; Ben Zakour, N.L.; Stanton-Cook, M.; Phan, M.D.; Totsika, M.; Peters, K.M.; Chan, K.G.; Schembri, M.A.; Upton, M.; Beatson, S.A. The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli EC958: a high quality reference sequence for the globally disseminated multidrug resistant E. coli O25b:H4-ST131 clone. PLoS One 2014, 9, e104400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). In Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 28th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, 950 West Valley Road, Suite 2500, Wayne, Pennsylvania 19087 USA, 2018.
- Berry, R.E.; Klumpp, D.J.; Schaeffer, A.J. Urothelial cultures support intracellular bacterial community formation by uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 2762–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannan, T.J.; Hunstad, D.A. A Murine Model for Escherichia coli Urinary Tract Infection. Methods Mol Biol 2016, 1333, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, B.O.; Flores, C.; Williams, C.; Flusberg, D.A.; Marr, E.E.; Kwiatkowska, K.M.; Charest, J.L.; Isenberg, B.C.; Rohn, J.L. Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection: A Mystery in Search of Better Model Systems. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2021, 11, 691210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totsika, M.; Beatson, S.A.; Sarkar, S.; Phan, M.D.; Petty, N.K.; Bachmann, N.; Szubert, M.; Sidjabat, H.E.; Paterson, D.L.; Upton, M. , et al. Insights into a multidrug resistant Escherichia coli pathogen of the globally disseminated ST131 lineage: genome analysis and virulence mechanisms. PLoS One 2011, 6, e26578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, M.D.; Peters, K.M.; Alvarez Fraga, L.; Wallis, S.C.; Hancock, S.J.; Nhu, N.T.K.; Forde, B.M.; Bauer, M.J.; Paterson, D.L.; Beatson, S.A. , et al. Plasmid-Mediated Ciprofloxacin Resistance Imparts a Selective Advantage on Escherichia coli ST131. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e0214621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werneburg, G.T. Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infections: Current Challenges and Future Prospects. Res Rep Urol 2022, 14, 109–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fuente-Nunez, C.; Reffuveille, F.; Fairfull-Smith, K.E.; Hancock, R.E. Effect of nitroxides on swarming motility and biofilm formation, multicellular behaviors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 4877–4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceri, H.; Olson, M.E.; Stremick, C.; Read, R.R.; Morck, D.; Buret, A. The Calgary Biofilm Device: new technology for rapid determination of antibiotic susceptibilities of bacterial biofilms. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 1771–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macia, M.D.; Rojo-Molinero, E.; Oliver, A. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing in biofilm-growing bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, A.; Sagar, F.; Latif, A.; Hassan, H.; Iftikhar, A.; Darouiche, R.O.; Mohajer, M.A. Does antimicrobial coating and impregnation of urinary catheters prevent catheter-associated urinary tract infection? A review of clinical and preclinical studies. Expert Rev Med Devices 2019, 16, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talja, M.; Korpela, A.; Järvi, K. Comparison of urethral reaction to full silicone, hydrogen-coated and siliconised latex catheters. Br. J. Urol. 1990, 66, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerkez, I.; Tulkens, P.M.; Tenson, T.; Van Bambeke, F.; Putrinš, M. Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Shows Antibiotic Tolerance and Growth Heterogeneity in an In Vitro Model of Intracellular Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e0146821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoharan, A.; Ognenovska, S.; Paino, D.; Whiteley, G.; Glasbey, T.; Kriel, F.H.; Farrell, J.; Moore, K.H.; Manos, J.; Das, T. N-Acetylcysteine Protects Bladder Epithelial Cells from Bacterial Invasion and Displays Antibiofilm Activity against Urinary Tract Bacterial Pathogens. Antibiotics (Basel) 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Mo, W.J.; Sebbel, P.; Min, G.; Neubert, T.A.; Glockshuber, R.; Wu, X.R.; Sun, T.T.; Kong, X.P. Uroplakin Ia is the urothelial receptor for uropathogenic Escherichia coli: evidence from in vitro FimH binding. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 4095–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, S.N.; Miao, Y. The nature of immune responses to urinary tract infections. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ligon, M.M.; Mysorekar, I.U. Trans-mission control in the urinary tract: Local cytokine regulation of monocyte proliferation to combat infection. J Leukoc Biol 2018, 103, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billips, B.K.; Forrestal, S.G.; Rycyk, M.T.; Johnson, J.R.; Klumpp, D.J.; Schaeffer, A.J. Modulation of host innate immune response in the bladder by uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 5353–5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, J.D.; Mulvey, M.A.; Vincent, C.D.; Lorenz, R.G.; Hultgren, S.J. Bacterial invasion augments epithelial cytokine responses to Escherichia coli through a lipopolysaccharide-dependent mechanism. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.G.; Palermo, J.J.; Schilling, J.D.; Roth, R.; Heuser, J.; Hultgren, S.J. Intracellular bacterial biofilm-like pods in urinary tract infections. Science 2003, 301, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, D.A.; Hooton, T.M.; Stamm, W.E.; Humphrey, P.A.; Hultgren, S.J. Detection of intracellular bacterial communities in human urinary tract infection. PLoS Med 2007, 4, e329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K.; Dhar, N.; Thacker, V.V.; Simonet, T.M.; Signorino-Gelo, F.; Knott, G.W.; McKinney, J.D. Dynamic persistence of UPEC intracellular bacterial communities in a human bladder-chip model of urinary tract infection. Elife 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghighitalab, A.; Matin, M.M.; Bahrami, A.R.; Iranshahi, M.; Saeinasab, M.; Haghighi, F. In vitro investigation of anticancer, cell-cycle-inhibitory, and apoptosis-inducing effects of diversin, a natural prenylated coumarin, on bladder carcinoma cells. Z Naturforsch C J Biosci 2014, 69, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Park, J.B. Evaluation of the effects of dimethylsulphoxide on morphology, cellular viability, mRNA, and protein expression of stem cells culture in growth media. Biomed Rep 2017, 7, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Miao, Y.; Abraham, S.N. The multiple antibacterial activities of the bladder epithelium. Ann Transl Med 2017, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowyer, G.S.; Loudon, K.W.; Suchanek, O.; Clatworthy, M.R. Tissue Immunity in the Bladder. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 40, 499–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karachalios, G.N.; Georgiopoulos, A.N.; Nasopoulou-Papadimitriou, D.D.; Adracta, D.J. Value of single-dose ciprofloxacin in the treatment of acute uncomplicated urinary tract infection in women. Drugs Exp. Clin. Res. 1991, 17, 521–524. [Google Scholar]
- Jakobsen, L.; Lundberg, C.V.; Frimodt-Møller, N. Ciprofloxacin Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics against Susceptible and Low-Level Resistant Escherichia coli Isolates in an Experimental Ascending Urinary Tract Infection Model in Mice. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justice, S.S.; Hunstad, D.A.; Seed, P.C.; Hultgren, S.J. Filamentation by Escherichia coli subverts innate defenses during urinary tract infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006, 103, 19884–19889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, D.; Dobrindt, U.; Tittel, A.; Peters, P.; Maurer, J.; Gutgemann, I.; Kaissling, B.; Kuziel, W.; Jung, S.; Kurts, C. Tumor necrosis factor alpha- and inducible nitric oxide synthase-producing dendritic cells are rapidly recruited to the bladder in urinary tract infection but are dispensable for bacterial clearance. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 6100–6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.G.; Benton, B.M.; Chin, D.; De Pascale, G.; Fuller, J.; Leeds, J.A.; Reck, F.; Richie, D.L.; Vo, J.; LaMarche, M.J. Synthesis of ciprofloxacin dimers for evaluation of bacterial permeability in atypical chemical space. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 2015, 25, 3468–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Pan, B.; Liu, M.L. Ciprofloxacin derivatives and their antibacterial activities. Eur J Med Chem 2018, 146, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.T. The mode of action of 4-quinolones and possible mechanisms of resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1986, 18 Suppl D, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verderosa, A.D.; Hawas, S.; Harris, J.; Totsika, M.; Fairfull-Smith, K.E. Isothiazolone-Nitroxide Hybrids with Activity against Antibiotic-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 5300–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndukwe, A.R.N.; Hawas, S.; Qin, J.; Wiedbrauk, S.; Totsika, M.; Boase, N.R.B.; Fairfull-Smith, K.E. Simple and Efficient Synthesis of 3-Aryl-2-oxazolidinone Scaffolds Enabling Increased Potency toward Biofilms. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 3484–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchings, M.I.; Truman, A.W.; Wilkinson, B. Antibiotics: past, present and future. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2019, 51, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




