Submitted:
31 July 2023
Posted:
01 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
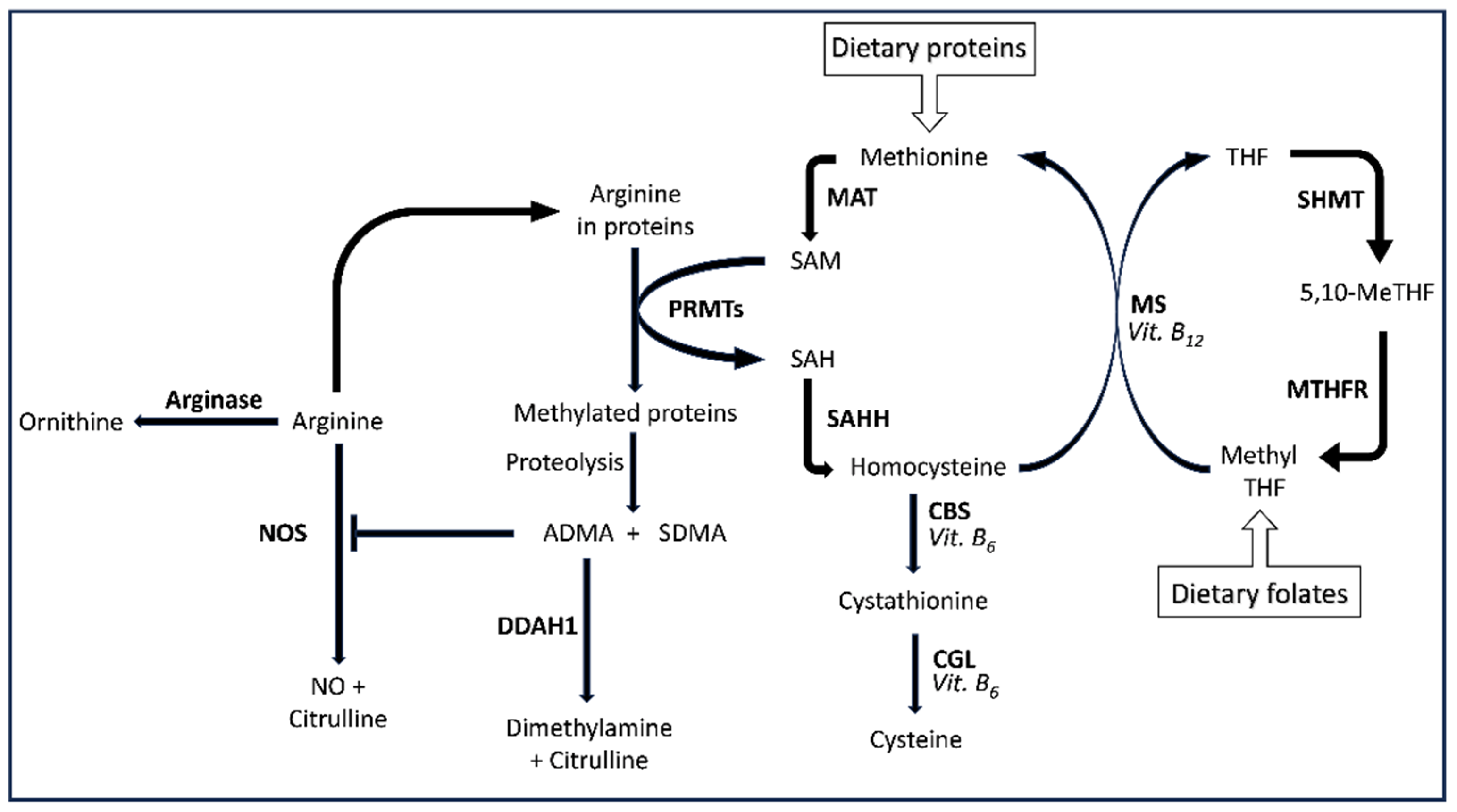
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study selection
2.2. Statistical analysis
3. Results
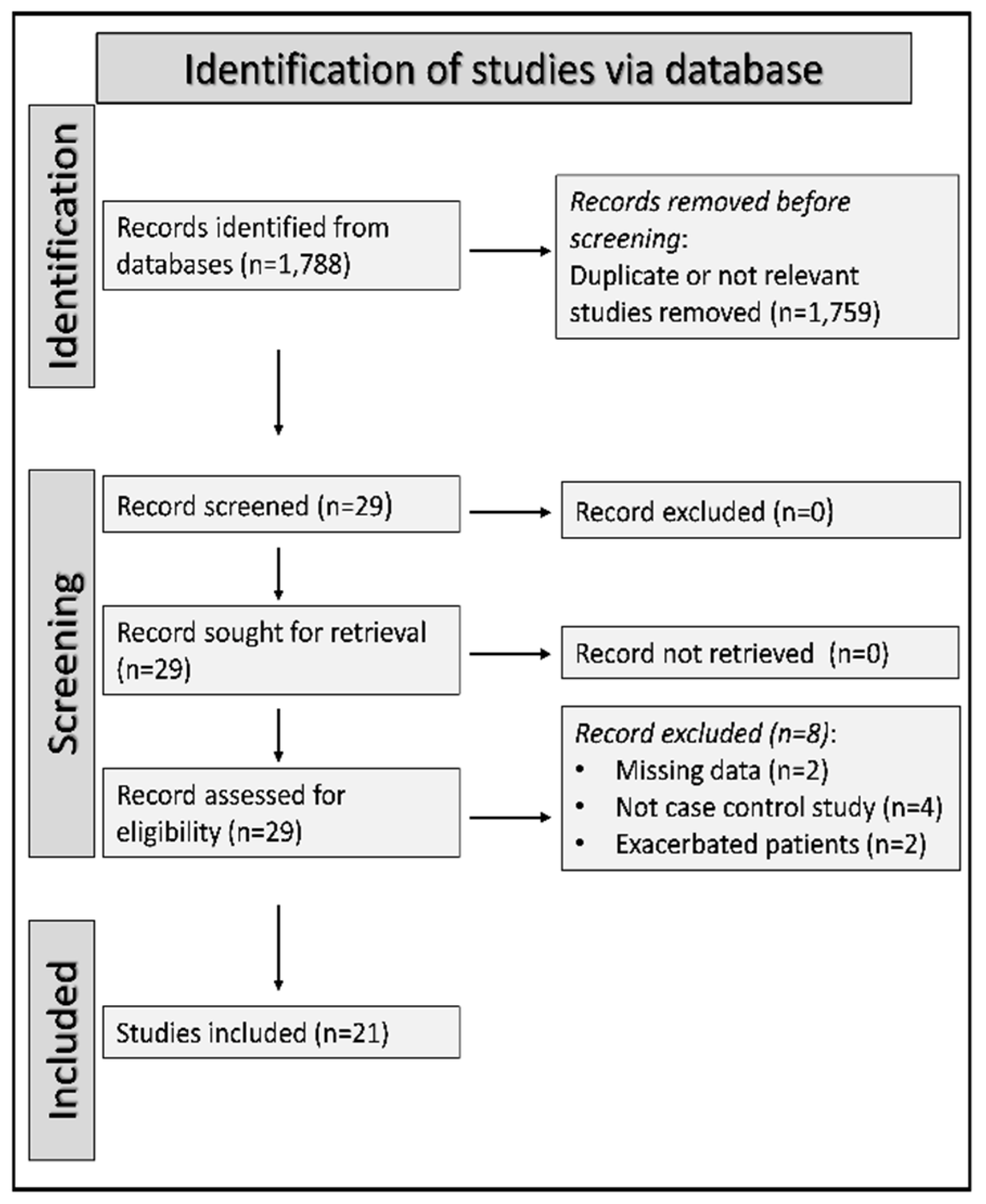
3.1. Literature search
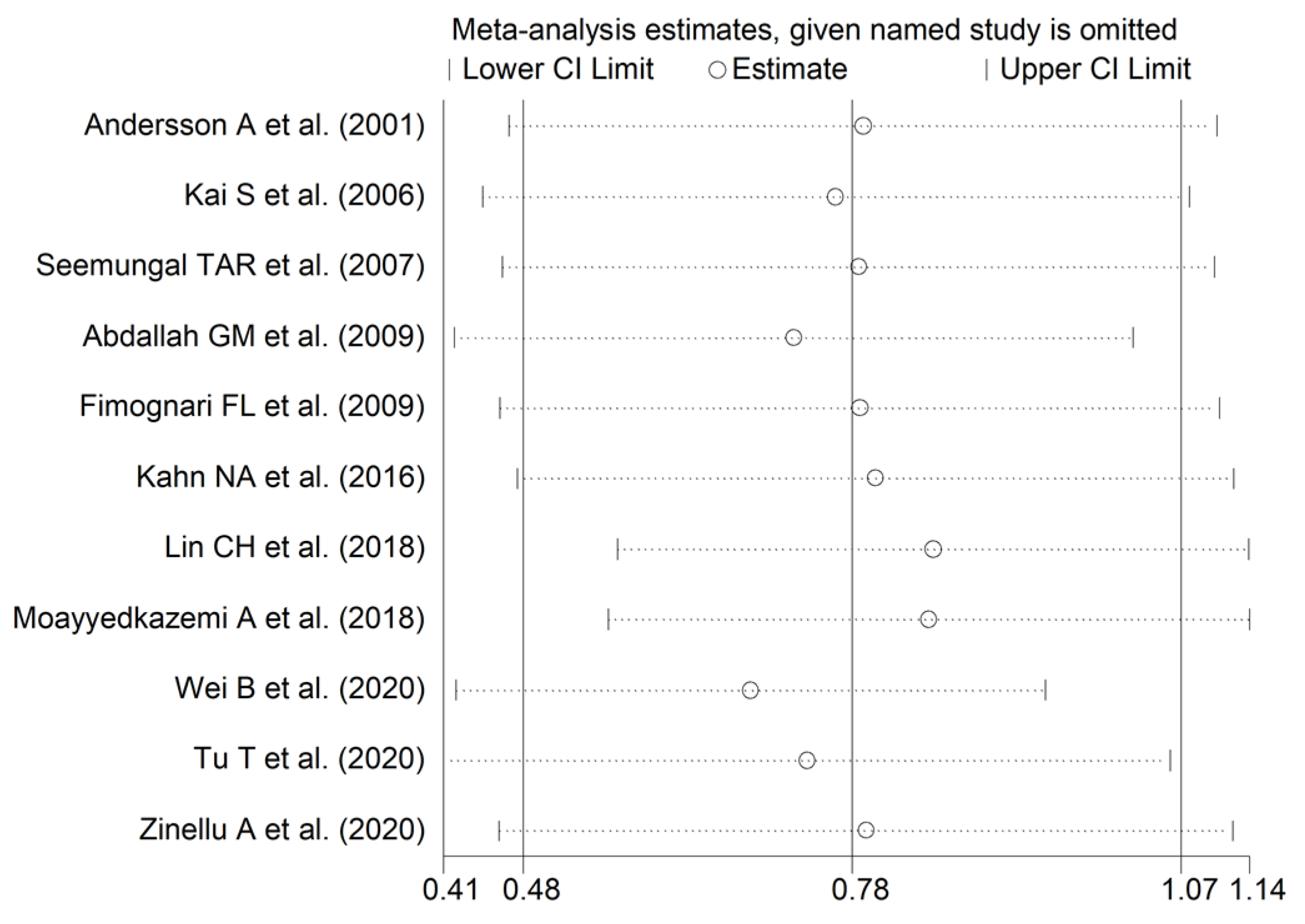
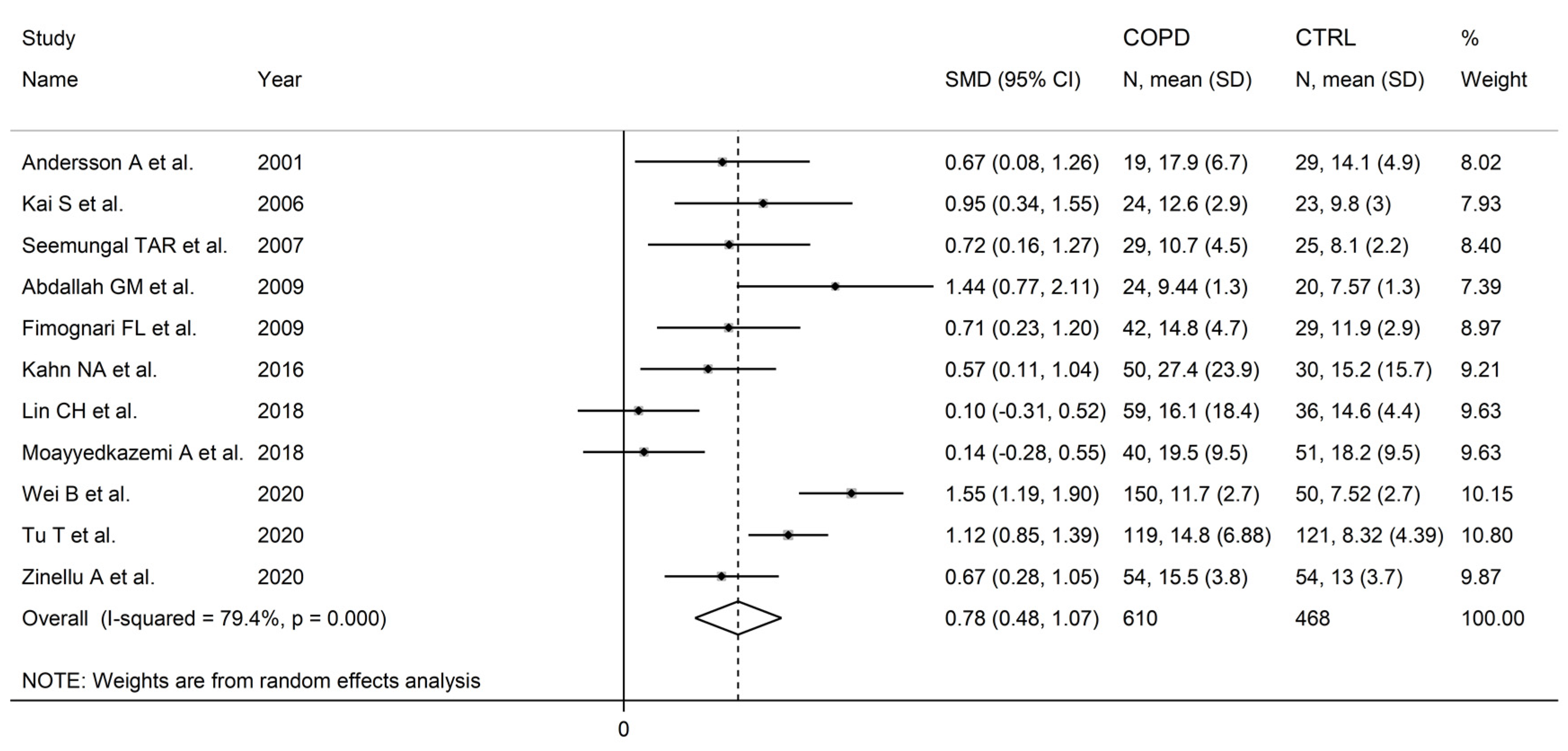
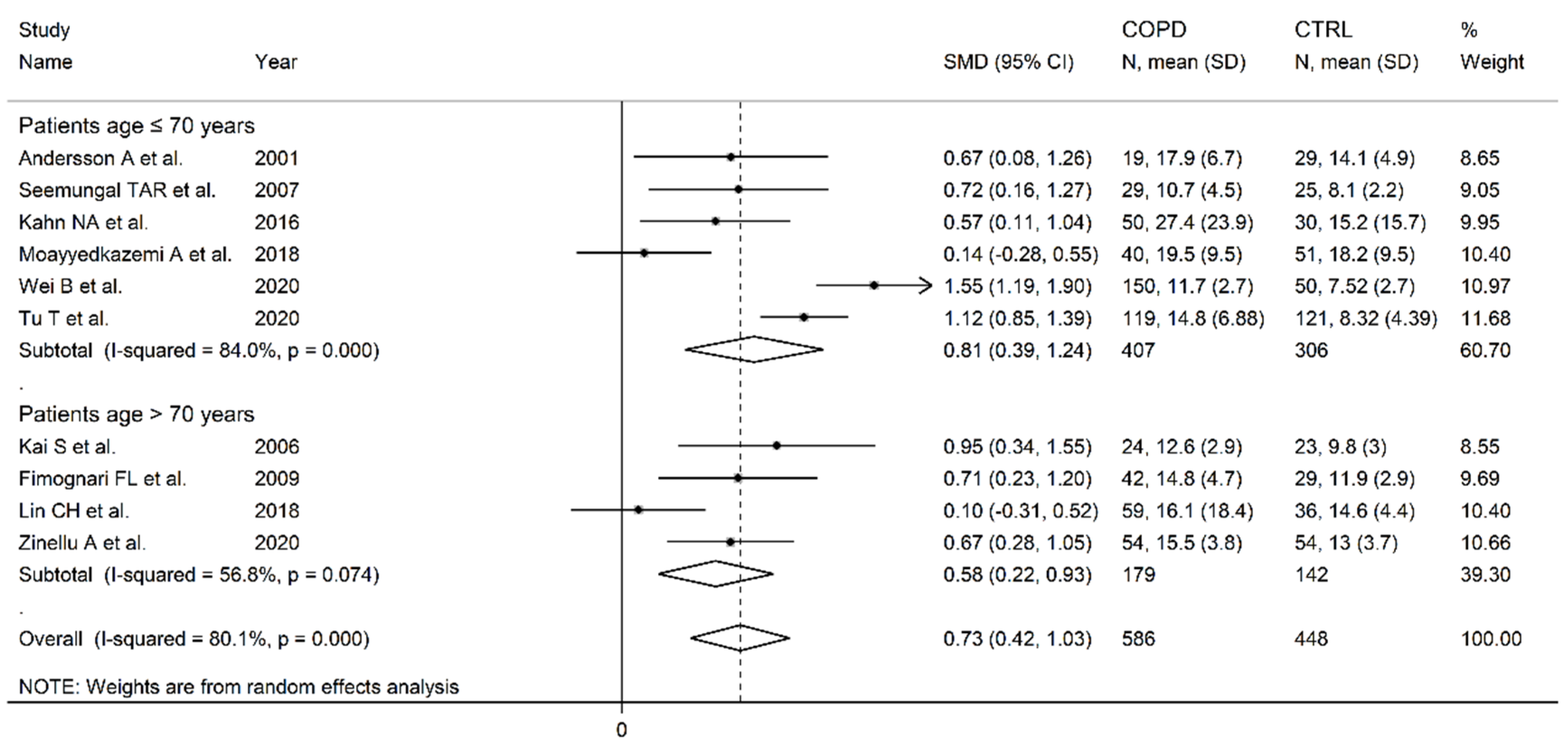
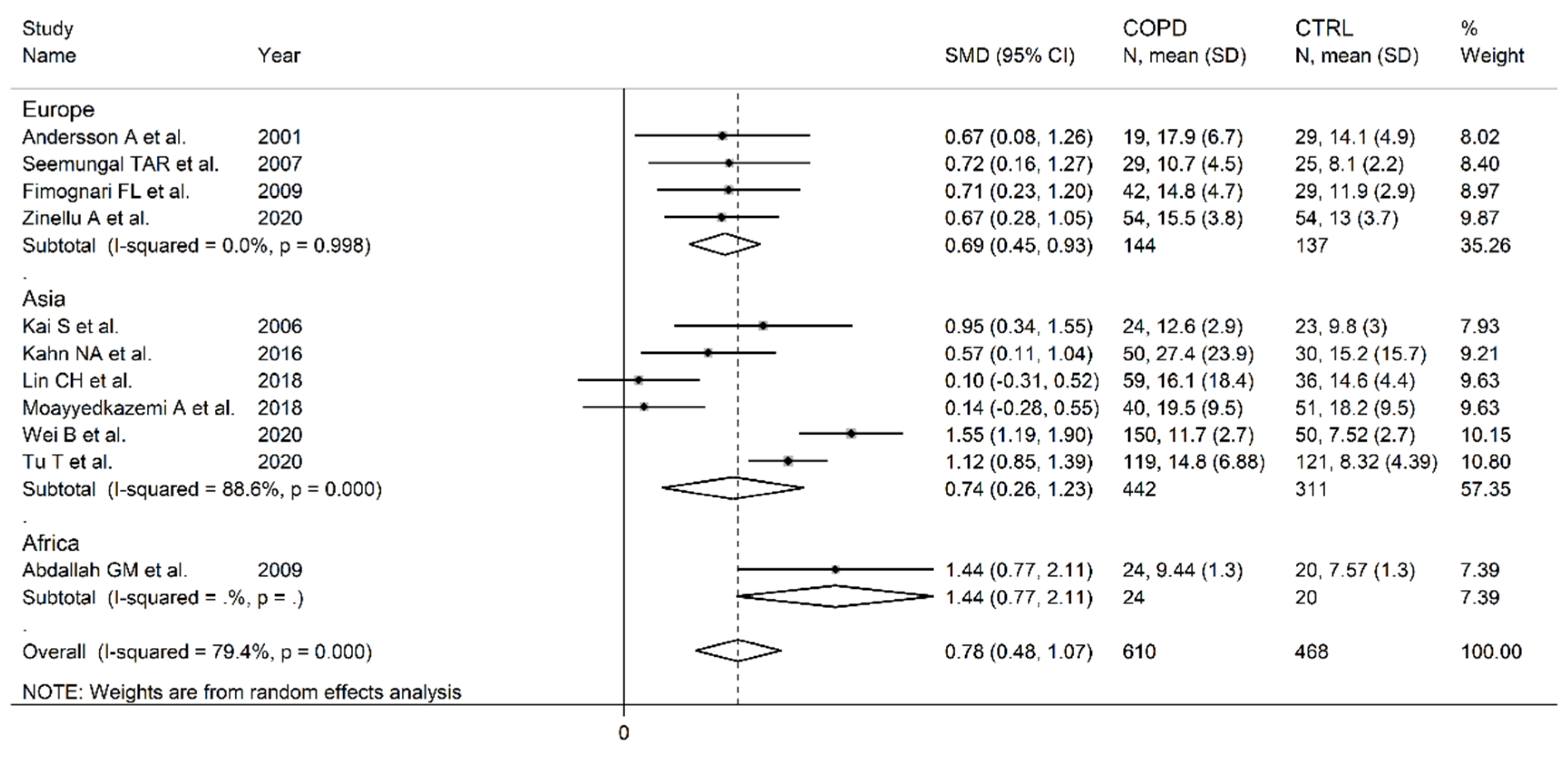
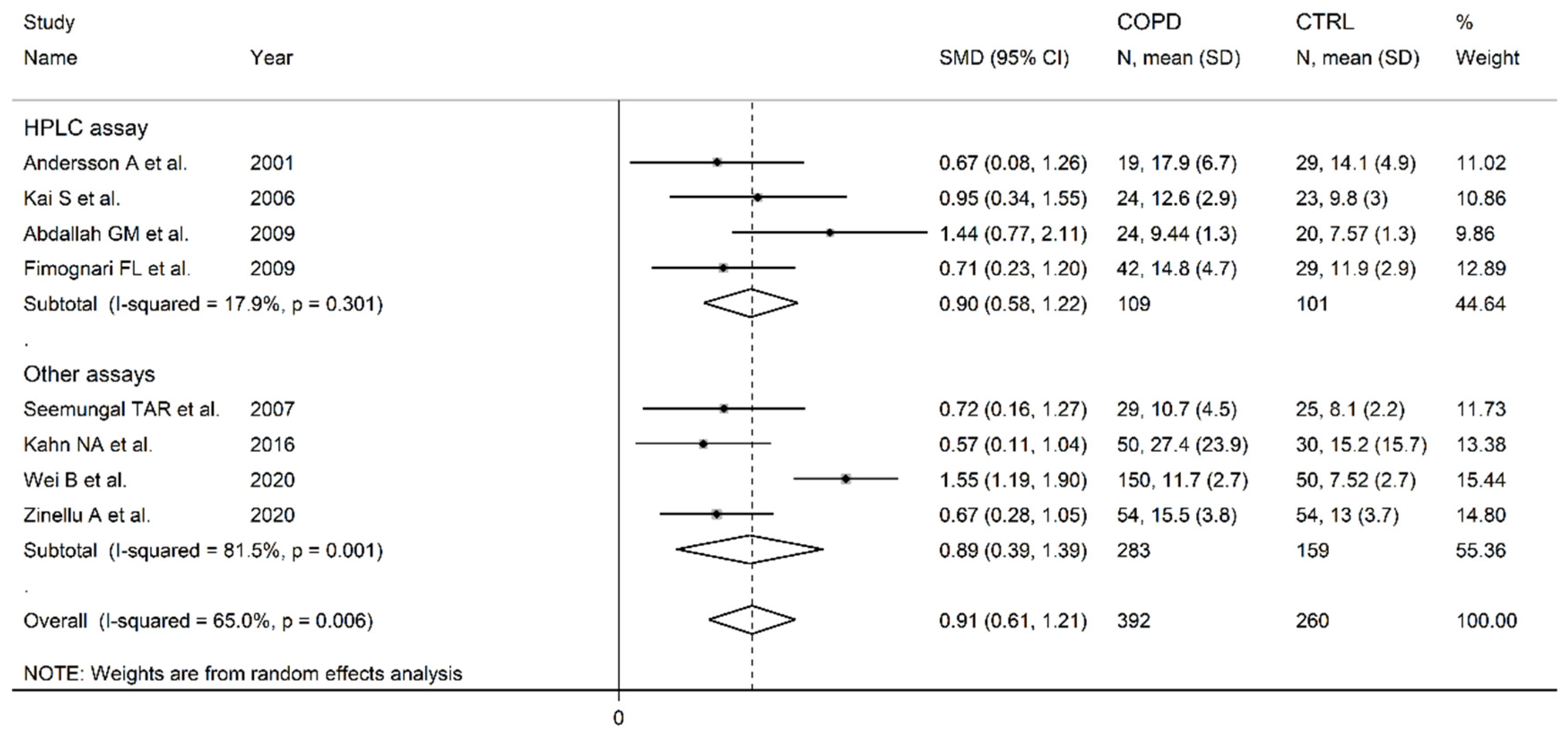
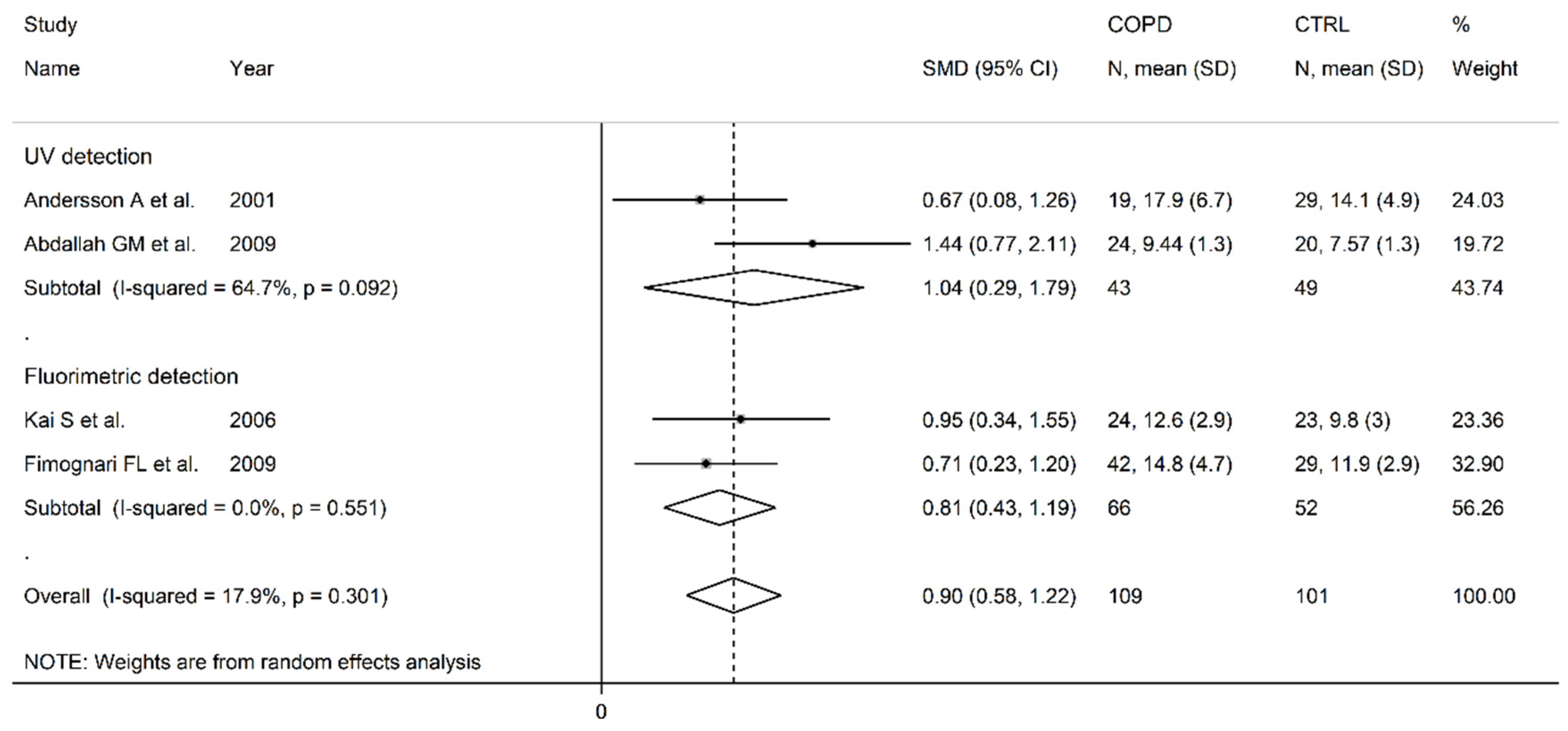
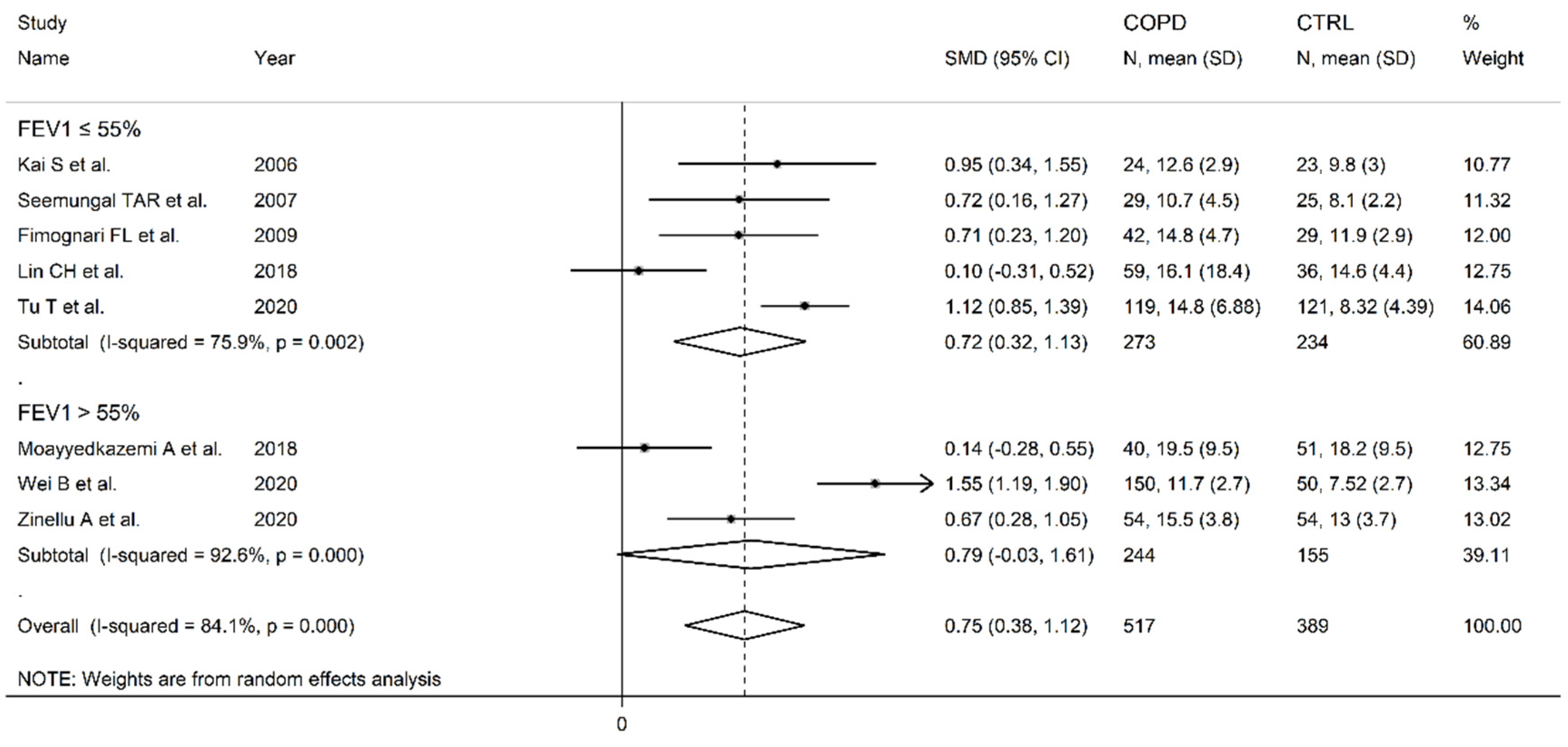
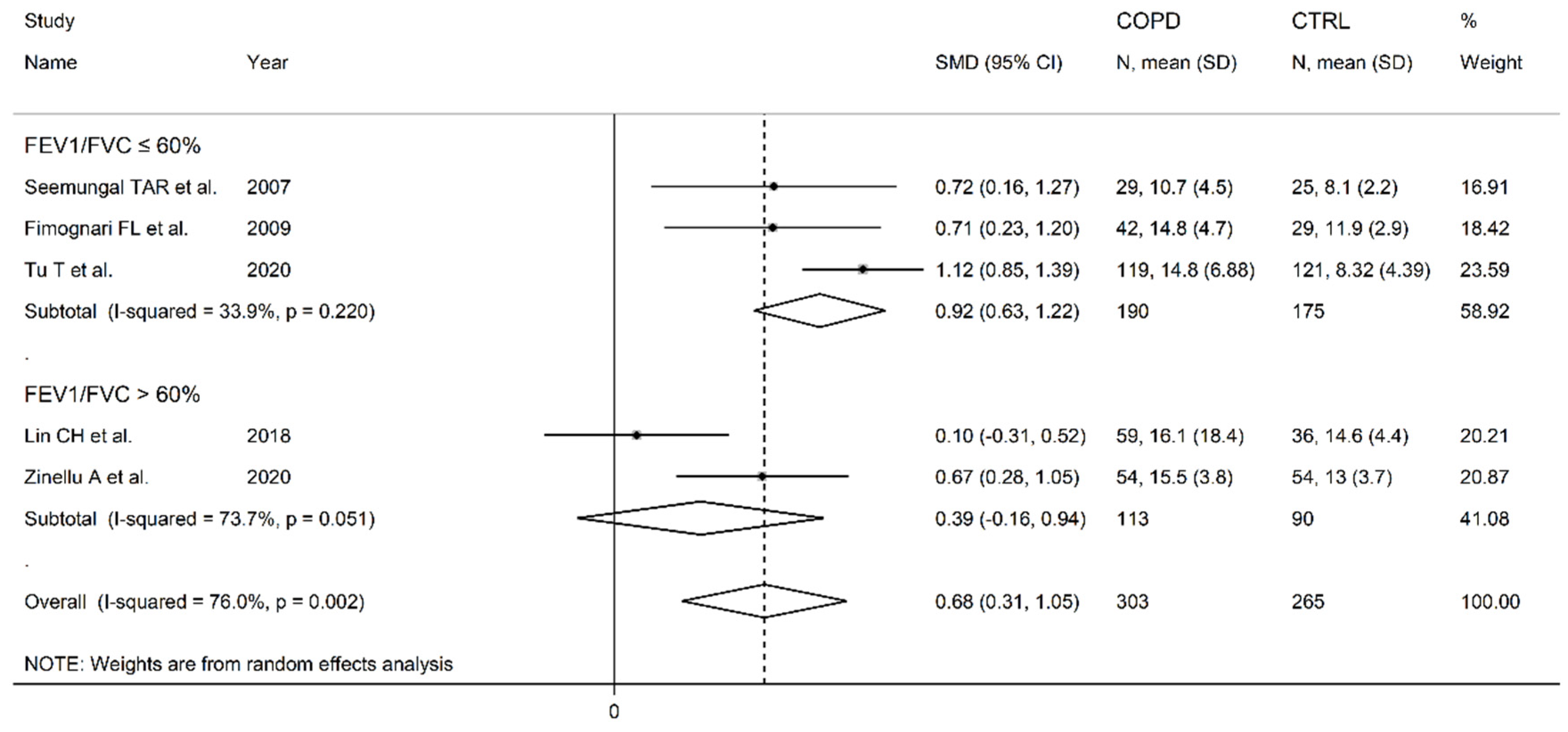
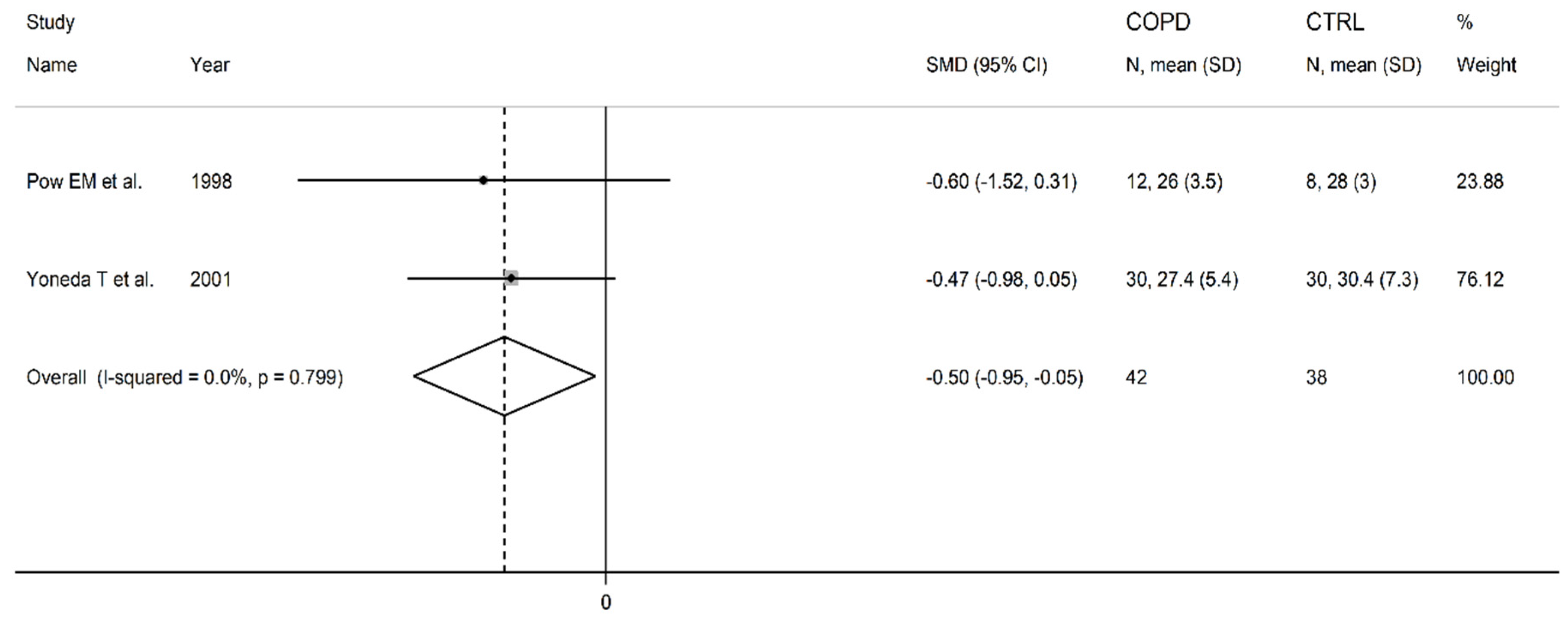
3.2. Homocysteine
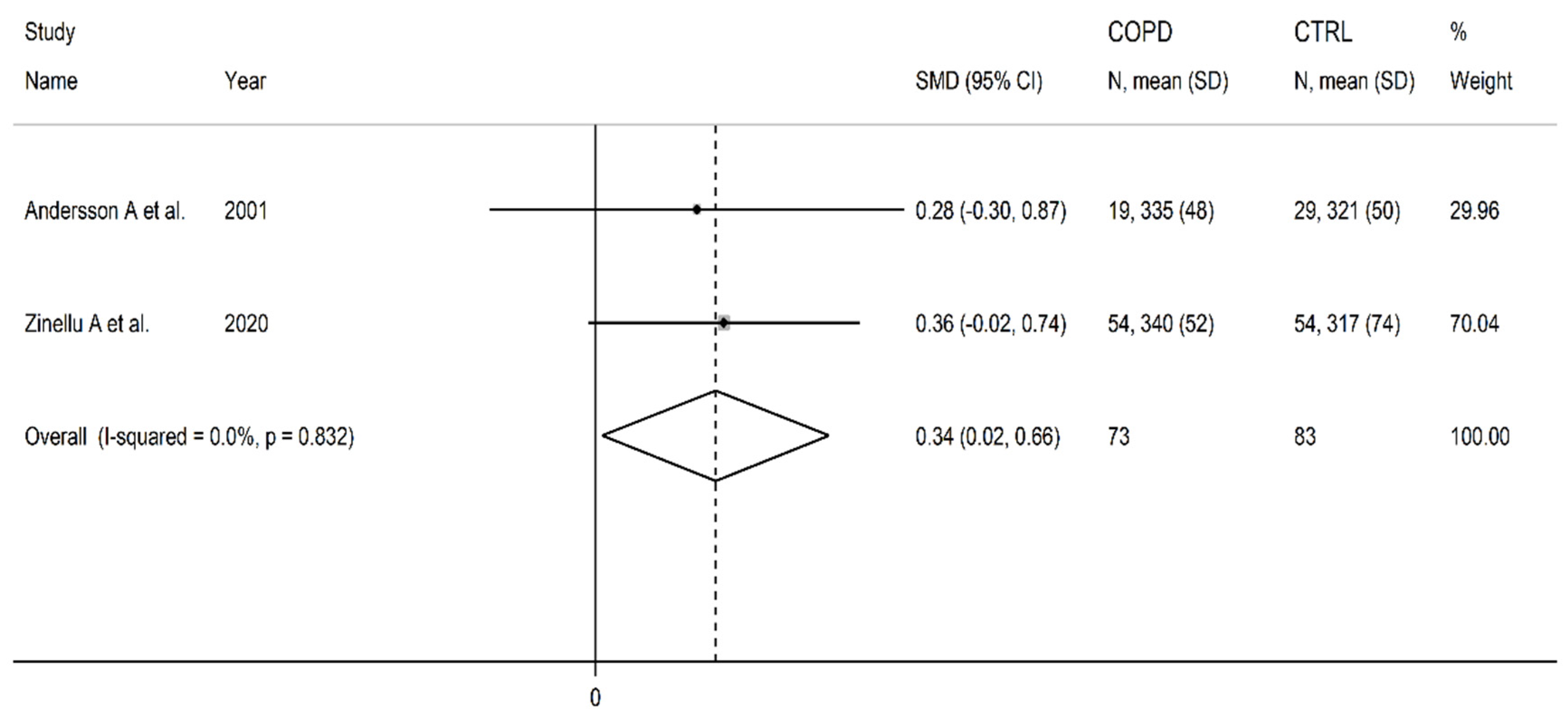
3.2. Cysteine
3.3. Methionine
3.4. Vitamin B12
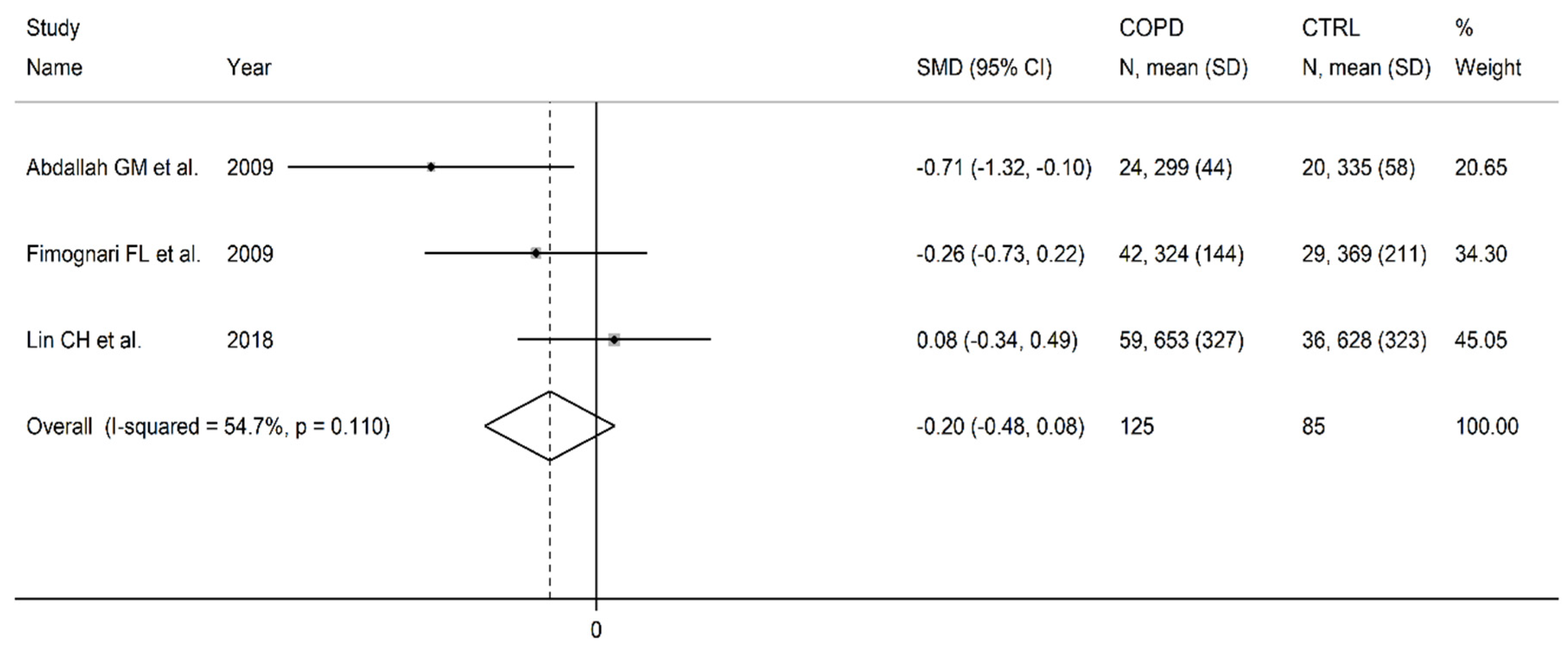
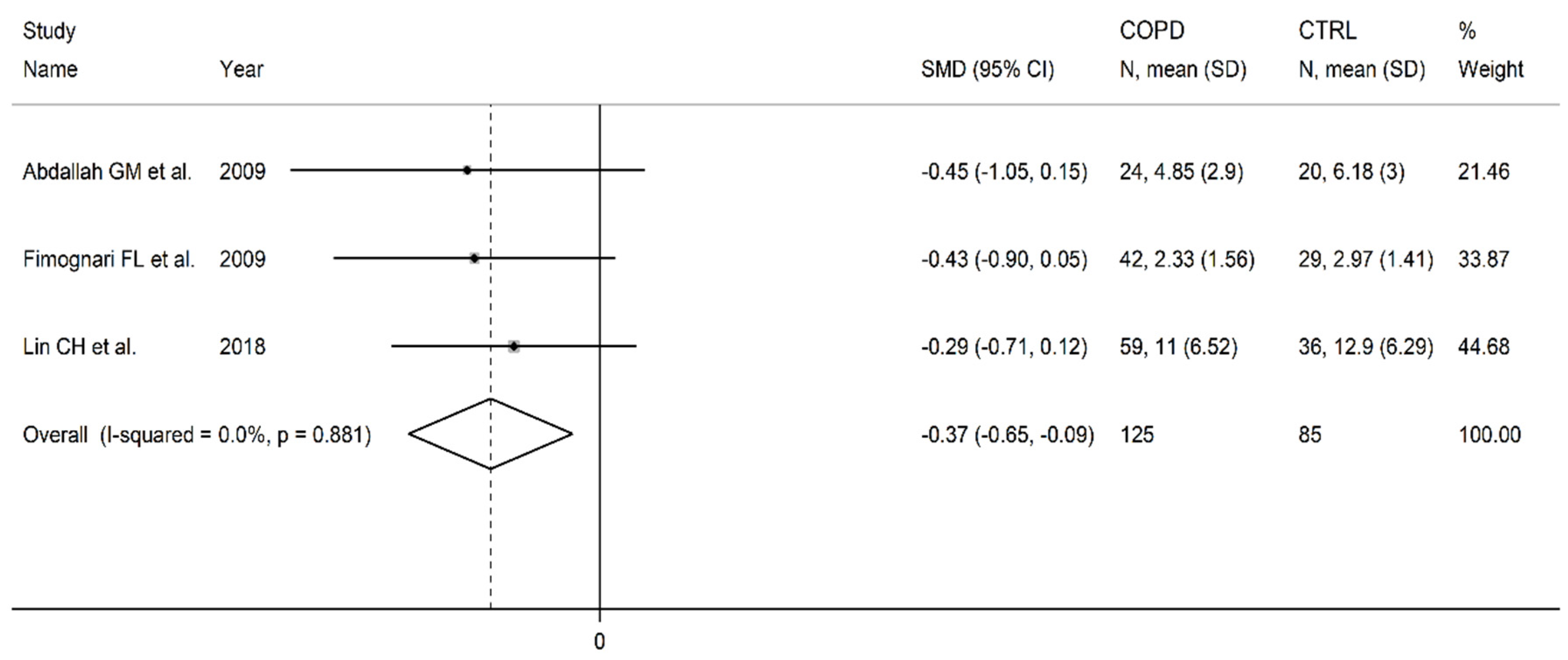
3.5. Folic acid
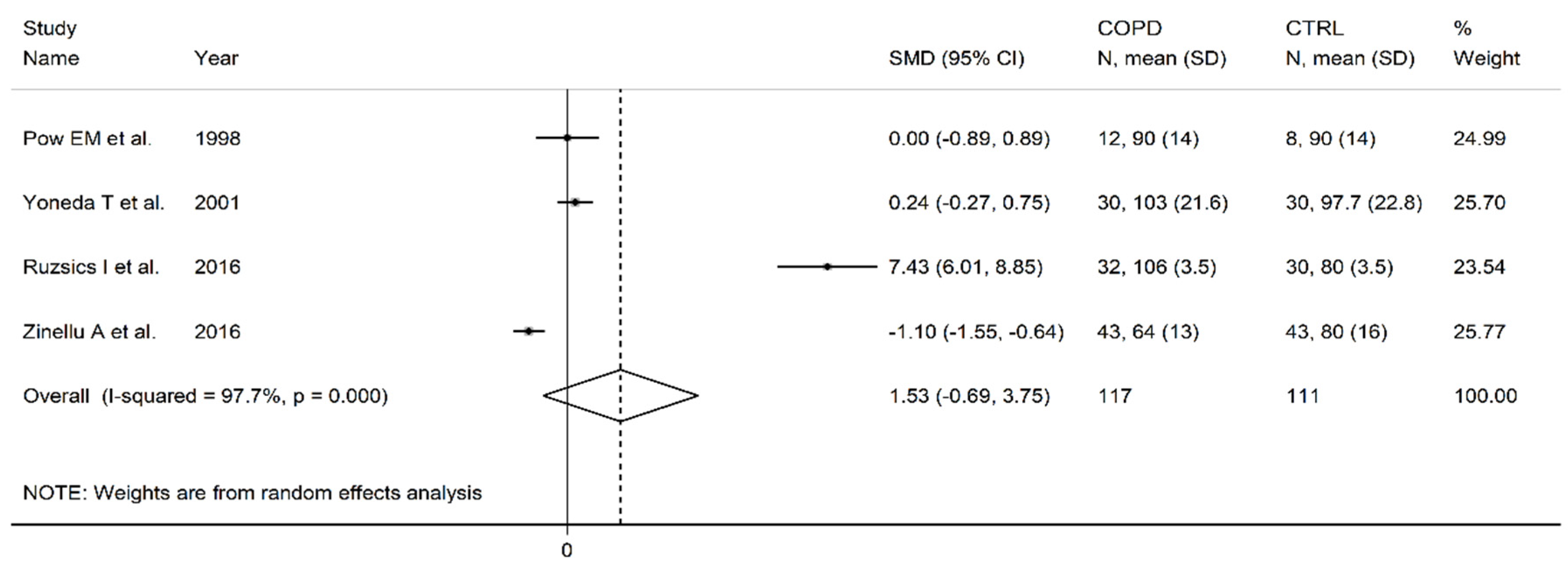
3.5. Arginine
3.6. Asymmetric dimethylarginine
3.7. Symmetric dimethylarginine
3.8. Ornithine
3.9. Vitamin B6 and citrulline
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H.; Ye, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ling, S. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease from 1990 to 2019. Front Physiol 2022, 13, 925132. [CrossRef]
- May, S.M.; Li, J.T. Burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Healthcare costs and beyond. Allergy Asthma Proc 2015, 36, 4-10. [CrossRef]
- Adeloye, D.; Song, P.; Zhu, Y.; Campbell, H.; Sheikh, A.; Rudan, I.; Unit, N.R.G.R.H. Global, regional, and national prevalence of, and risk factors for, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in 2019: A systematic review and modelling analysis. Lancet Respir Med 2022, 10, 447-458. [CrossRef]
- Safiri, S.; Carson-Chahhoud, K.; Noori, M.; Nejadghaderi, S.A.; Sullman, M.J.M.; Ahmadian Heris, J.; Ansarin, K.; Mansournia, M.A.; Collins, G.S.; Kolahi, A.A.; et al. Burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and its attributable risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. BMJ 2022, 378, e069679. [CrossRef]
- Matera, M.G.; Cazzola, M.; Page, C. Prospects for COPD treatment. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2021, 56, 74-84. [CrossRef]
- Riley, C.M.; Sciurba, F.C. Diagnosis and Outpatient Management of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Review. JAMA 2019, 321, 786-797. [CrossRef]
- Wouters, E.F.; Posthuma, R.; Koopman, M.; Liu, W.Y.; Sillen, M.J.; Hajian, B.; Sastry, M.; Spruit, M.A.; Franssen, F.M. An update on pulmonary rehabilitation techniques for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Expert Rev Respir Med 2020, 14, 149-161. [CrossRef]
- Christenson, S.A.; Smith, B.M.; Bafadhel, M.; Putcha, N. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet 2022, 399, 2227-2242. [CrossRef]
- Brandsma, C.A.; Van den Berge, M.; Hackett, T.L.; Brusselle, G.; Timens, W. Recent advances in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease pathogenesis: From disease mechanisms to precision medicine. J Pathol 2020, 250, 624-635. [CrossRef]
- Ferrera, M.C.; Labaki, W.W.; Han, M.K. Advances in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Annu Rev Med 2021, 72, 119-134. [CrossRef]
- Ko, F.W.S.; Sin, D.D. Twenty-five years of Respirology: Advances in COPD. Respirology 2020, 25, 17-19. [CrossRef]
- Leuzzi, G.; Galeone, C.; Taverna, F.; Suatoni, P.; Morelli, D.; Pastorino, U. C-reactive protein level predicts mortality in COPD: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Respir Rev 2017, 26. [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J. Inflammatory endotypes in COPD. Allergy 2019, 74, 1249-1256. [CrossRef]
- Brightling, C.; Greening, N. Airway inflammation in COPD: Progress to precision medicine. Eur Respir J 2019, 54. [CrossRef]
- David, B.; Bafadhel, M.; Koenderman, L.; De Soyza, A. Eosinophilic inflammation in COPD: From an inflammatory marker to a treatable trait. Thorax 2021, 76, 188-195. [CrossRef]
- Duca, L.; Ottolenghi, S.; Coppola, S.; Rinaldo, R.; Dei Cas, M.; Rubino, F.M.; Paroni, R.; Samaja, M.; Chiumello, D.A.; Motta, I. Differential Redox State and Iron Regulation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Coronavirus Disease 2019. Antioxidants (Basel) 2021, 10. [CrossRef]
- Kiyokawa, H.; Hoshino, Y.; Sakaguchi, K.; Muro, S.; Yodoi, J. Redox Regulation in Aging Lungs and Therapeutic Implications of Antioxidants in COPD. Antioxidants (Basel) 2021, 10. [CrossRef]
- Mumby, S.; Adcock, I.M. Recent evidence from omic analysis for redox signalling and mitochondrial oxidative stress in COPD. J Inflamm (Lond) 2022, 19, 10. [CrossRef]
- Sotgia, S.; Paliogiannis, P.; Sotgiu, E.; Mellino, S.; Zinellu, E.; Fois, A.G.; Pirina, P.; Carru, C.; Mangoni, A.A.; Zinellu, A. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Blood Glutathione Redox State in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Antioxidants (Basel) 2020, 9. [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Verma, S.K.; Kumar, S.; Ahmad, M.K.; Nischal, A.; Singh, S.K.; Dixit, R.K. Evaluation of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Status in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Scand J Immunol 2017, 85, 130-137. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, C.; Yin, D.; Wang, S.; Huang, K. Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide is Associated with the Severity of Stable COPD. COPD 2020, 17, 121-127. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Su, X.; Lei, T.; Yu, H.; Liu, J. Diagnostic value of fractional exhaled nitric oxide in differentiating the asthma-COPD overlap from COPD: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Rev Respir Med 2022, 16, 679-687. [CrossRef]
- Bayarri, M.A.; Milara, J.; Estornut, C.; Cortijo, J. Nitric Oxide System and Bronchial Epithelium: More Than a Barrier. Front Physiol 2021, 12, 687381. [CrossRef]
- Antus, B.; Barta, I. Blood Eosinophils and Exhaled Nitric Oxide: Surrogate Biomarkers of Airway Eosinophilia in Stable COPD and Exacerbation. Biomedicines 2022, 10. [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E. Nitric oxide signaling in health and disease. Cell 2022, 185, 2853-2878. [CrossRef]
- Gantner, B.N.; LaFond, K.M.; Bonini, M.G. Nitric oxide in cellular adaptation and disease. Redox Biol 2020, 34, 101550. [CrossRef]
- Gliozzi, M.; Scicchitano, M.; Bosco, F.; Musolino, V.; Carresi, C.; Scarano, F.; Maiuolo, J.; Nucera, S.; Maretta, A.; Paone, S.; et al. Modulation of Nitric Oxide Synthases by Oxidized LDLs: Role in Vascular Inflammation and Atherosclerosis Development. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cheng, C.K.; Yi, M.; Lui, K.O.; Huang, Y. Targeting endothelial dysfunction and inflammation. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2022, 168, 58-67. [CrossRef]
- Batty, M.; Bennett, M.R.; Yu, E. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Atherosclerosis. Cells 2022, 11. [CrossRef]
- Forman, H.J.; Zhang, H. Targeting oxidative stress in disease: Promise and limitations of antioxidant therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2021, 20, 689-709. [CrossRef]
- Steven, S.; Frenis, K.; Oelze, M.; Kalinovic, S.; Kuntic, M.; Bayo Jimenez, M.T.; Vujacic-Mirski, K.; Helmstadter, J.; Kroller-Schon, S.; Munzel, T.; et al. Vascular Inflammation and Oxidative Stress: Major Triggers for Cardiovascular Disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019, 2019, 7092151. [CrossRef]
- Roversi, S.; Fabbri, L.M.; Sin, D.D.; Hawkins, N.M.; Agusti, A. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Cardiac Diseases. An Urgent Need for Integrated Care. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2016, 194, 1319-1336. [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Thomas, J.; Sadatsafavi, M.; FitzGerald, J.M. Risk of cardiovascular comorbidity in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Respir Med 2015, 3, 631-639. [CrossRef]
- Mullerova, H.; Agusti, A.; Erqou, S.; Mapel, D.W. Cardiovascular comorbidity in COPD: Systematic literature review. Chest 2013, 144, 1163-1178. [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.; Edwards, L.D.; Agusti, A.; Bakke, P.; Calverley, P.M.; Celli, B.; Coxson, H.O.; Crim, C.; Lomas, D.A.; Miller, B.E.; et al. Comorbidity, systemic inflammation and outcomes in the ECLIPSE cohort. Respir Med 2013, 107, 1376-1384. [CrossRef]
- Westerik, J.A.; Metting, E.I.; van Boven, J.F.; Tiersma, W.; Kocks, J.W.; Schermer, T.R. Associations between chronic comorbidity and exacerbation risk in primary care patients with COPD. Respir Res 2017, 18, 31. [CrossRef]
- Mannino, D.M.; Thorn, D.; Swensen, A.; Holguin, F. Prevalence and outcomes of diabetes, hypertension and cardiovascular disease in COPD. Eur Respir J 2008, 32, 962-969. [CrossRef]
- Divo, M.; Cote, C.; de Torres, J.P.; Casanova, C.; Marin, J.M.; Pinto-Plata, V.; Zulueta, J.; Cabrera, C.; Zagaceta, J.; Hunninghake, G.; et al. Comorbidities and risk of mortality in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2012, 186, 155-161. [CrossRef]
- Marrocco, I.; Altieri, F.; Peluso, I. Measurement and Clinical Significance of Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress in Humans. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017, 2017, 6501046. [CrossRef]
- Frijhoff, J.; Winyard, P.G.; Zarkovic, N.; Davies, S.S.; Stocker, R.; Cheng, D.; Knight, A.R.; Taylor, E.L.; Oettrich, J.; Ruskovska, T.; et al. Clinical Relevance of Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress. Antioxid Redox Signal 2015, 23, 1144-1170. [CrossRef]
- Dalle-Donne, I.; Rossi, R.; Colombo, R.; Giustarini, D.; Milzani, A. Biomarkers of oxidative damage in human disease. Clin Chem 2006, 52, 601-623. [CrossRef]
- Tsikas, D. Methods of quantitative analysis of the nitric oxide metabolites nitrite and nitrate in human biological fluids. Free Radic Res 2005, 39, 797-815. [CrossRef]
- Goshi, E.; Zhou, G.; He, Q. Nitric oxide detection methods in vitro and in vivo. Med Gas Res 2019, 9, 192-207. [CrossRef]
- Moller, M.N.; Rios, N.; Trujillo, M.; Radi, R.; Denicola, A.; Alvarez, B. Detection and quantification of nitric oxide-derived oxidants in biological systems. J Biol Chem 2019, 294, 14776-14802. [CrossRef]
- Viinikka, L. Nitric oxide as a challenge for the clinical chemistry laboratory. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 1996, 56, 577-581. [CrossRef]
- Morris, S.M., Jr. Arginine Metabolism Revisited. J Nutr 2016, 146, 2579S-2586S. [CrossRef]
- Stanhewicz, A.E.; Kenney, W.L. Role of folic acid in nitric oxide bioavailability and vascular endothelial function. Nutr Rev 2017, 75, 61-70. [CrossRef]
- Sbodio, J.I.; Snyder, S.H.; Paul, B.D. Regulators of the transsulfuration pathway. Br J Pharmacol 2019, 176, 583-593. [CrossRef]
- van Dyk, M.; Mangoni, A.A.; McEvoy, M.; Attia, J.R.; Sorich, M.J.; Rowland, A. Targeted arginine metabolomics: A rapid, simple UPLC-QToF-MS(E) based approach for assessing the involvement of arginine metabolism in human disease. Clin Chim Acta 2015, 447, 59-65. [CrossRef]
- Sotgia, S.; Zinellu, A.; Paliogiannis, P.; Pinna, G.A.; Mangoni, A.A.; Milanesi, L.; Carru, C. A diethylpyrocarbonate-based derivatization method for the LC-MS/MS measurement of plasma arginine and its chemically related metabolites and analogs. Clin Chim Acta 2019, 492, 29-36. [CrossRef]
- Zinellu, A.; Sotgia, S.; Scanu, B.; Pisanu, E.; Sanna, M.; Sati, S.; Deiana, L.; Sengupta, S.; Carru, C. Determination of homocysteine thiolactone, reduced homocysteine, homocystine, homocysteine-cysteine mixed disulfide, cysteine and cystine in a reaction mixture by overimposed pressure/voltage capillary electrophoresis. Talanta 2010, 82, 1281-1285. [CrossRef]
- Zinellu, A.; Pinna, A.; Zinellu, E.; Sotgia, S.; Deiana, L.; Carru, C. High-throughput capillary electrophoresis method for plasma cysteinylglycine measurement: Evidences for a clinical application. Amino Acids 2008, 34, 69-74. [CrossRef]
- Mangoni, A.A.; Rodionov, R.N.; McEvoy, M.; Zinellu, A.; Carru, C.; Sotgia, S. New horizons in arginine metabolism, ageing and chronic disease states. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 776-782. [CrossRef]
- Jarzebska, N.; Mangoni, A.A.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Bode-Boger, S.M.; Rodionov, R.N. The Second Life of Methylarginines as Cardiovascular Targets. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20. [CrossRef]
- Wadham, C.; Mangoni, A.A. Dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase regulation: A novel therapeutic target in cardiovascular disease. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 2009, 5, 303-319. [CrossRef]
- Mangoni, A.A. The emerging role of symmetric dimethylarginine in vascular disease. Adv Clin Chem 2009, 48, 73-94. [CrossRef]
- Ragavan, V.N.; Nair, P.C.; Jarzebska, N.; Angom, R.S.; Ruta, L.; Bianconi, E.; Grottelli, S.; Tararova, N.D.; Ryazanskiy, D.; Lentz, S.R.; et al. A multicentric consortium study demonstrates that dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 2 is not a dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 3392. [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, R.W.; Rodriguez, P.C.; Toque, H.A.; Narayanan, S.P.; Caldwell, R.B. Arginase: A Multifaceted Enzyme Important in Health and Disease. Physiol Rev 2018, 98, 641-665. [CrossRef]
- Brosnan, J.T.; Brosnan, M.E. The sulfur-containing amino acids: An overview. J Nutr 2006, 136, 1636S-1640S. [CrossRef]
- Bailey, L.B.; Gregory, J.F., 3rd. Folate metabolism and requirements. J Nutr 1999, 129, 779-782. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Cantley, L.C. Toward a better understanding of folate metabolism in health and disease. J Exp Med 2019, 216, 253-266. [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.J.; Tommasi, S.; Faull, R.; Gleadle, J.M.; Mangoni, A.A.; Selvanayagam, J.B. Arginine Metabolites as Biomarkers of Myocardial Ischaemia, Assessed with Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Chronic Kidney Disease. Biomolecules 2021, 11. [CrossRef]
- Mangoni, A.A.; Tommasi, S.; Sotgia, S.; Zinellu, A.; Paliogiannis, P.; Piga, M.; Cauli, A.; Pintus, G.; Carru, C.; Erre, G.L. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine: A Key Player in the Pathophysiology of Endothelial Dysfunction, Vascular Inflammation and Atherosclerosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis? Curr Pharm Des 2021, 27, 2131-2140. [CrossRef]
- Mangoni, A.A.; Zinellu, A.; Carru, C.; Attia, J.R.; McEvoy, M. Transsulfuration pathway thiols and methylated arginines: The Hunter Community Study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54870. [CrossRef]
- Mangoni, A.A.; Zinellu, A.; Carru, C.; Attia, J.R.; McEvoy, M. Serum thiols and cardiovascular risk scores: A combined assessment of transsulfuration pathway components and substrate/product ratios. J Transl Med 2013, 11, 99. [CrossRef]
- Mangoni, A.A.; Jackson, S.H. Homocysteine and cardiovascular disease: Current evidence and future prospects. Am J Med 2002, 112, 556-565. [CrossRef]
- Mangoni, A.A.; Sherwood, R.A.; Asonganyi, B.; Swift, C.G.; Thomas, S.; Jackson, S.H. Short-term oral folic acid supplementation enhances endothelial function in patients with type 2 diabetes. Am J Hypertens 2005, 18, 220-226. [CrossRef]
- Mangoni, A.A.; Arya, R.; Ford, E.; Asonganyi, B.; Sherwood, R.A.; Ouldred, E.; Swift, C.G.; Jackson, S.H. Effects of folic acid supplementation on inflammatory and thrombogenic markers in chronic smokers. A randomised controlled trial. Thromb Res 2003, 110, 13-17. [CrossRef]
- Mangoni, A.A.; Sherwood, R.A.; Swift, C.G.; Jackson, S.H. Folic acid enhances endothelial function and reduces blood pressure in smokers: A randomized controlled trial. J Intern Med 2002, 252, 497-503. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Geng, T.; Wan, Z.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, Z.; Li, L.; Zhu, K.; Liu, L.; Pan, A.; et al. Associations of Serum Folate and Vitamin B12 Levels With Cardiovascular Disease Mortality Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. JAMA Netw Open 2022, 5, e2146124. [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Li, J.; Qin, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; Gottesman, R.F.; Tang, G.; Wang, B.; Chen, D.; He, M.; et al. Efficacy of folic acid therapy in primary prevention of stroke among adults with hypertension in China: The CSPPT randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2015, 313, 1325-1335. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, T.; Zheng, Y.; Muka, T.; Troup, J.; Hu, F.B. Folic Acid Supplementation and the Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J Am Heart Assoc 2016, 5. [CrossRef]
- Moola, S.; Munn, Z.; Tufanaru, C.; Aromataris, E.; Sears, K.; Sfetcu, R.; Currie, M.; Qureshi, R.; Mattis, P.; Lisy, K.; et al. Systematic reviews of etiology and risk. In Joanna Briggs Institute Reviewer’s Manual, Aromataris, E., Munn, Z., Eds.; Johanna Briggs Institute: Adelaide, Australia, 2017.
- Balshem, H.; Helfand, M.; Schunemann, H.J.; Oxman, A.D.; Kunz, R.; Brozek, J.; Vist, G.E.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Meerpohl, J.; Norris, S.; et al. GRADE guidelines: 3. Rating the quality of evidence. J Clin Epidemiol 2011, 64, 401-406. [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Tong, T. Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range. BMC Med Res Methodol 2014, 14, 135. [CrossRef]
- Hozo, S.P.; Djulbegovic, B.; Hozo, I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol 2005, 5, 13. [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 2002, 21, 1539-1558. [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557-560. [CrossRef]
- Tobias, A. Assessing the influence of a single study in the meta-analysis estimate. Stata Technical Bulletin 1999, 47, 15-17.
- Begg, C.B.; Mazumdar, M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 1994, 50, 1088-1101. [CrossRef]
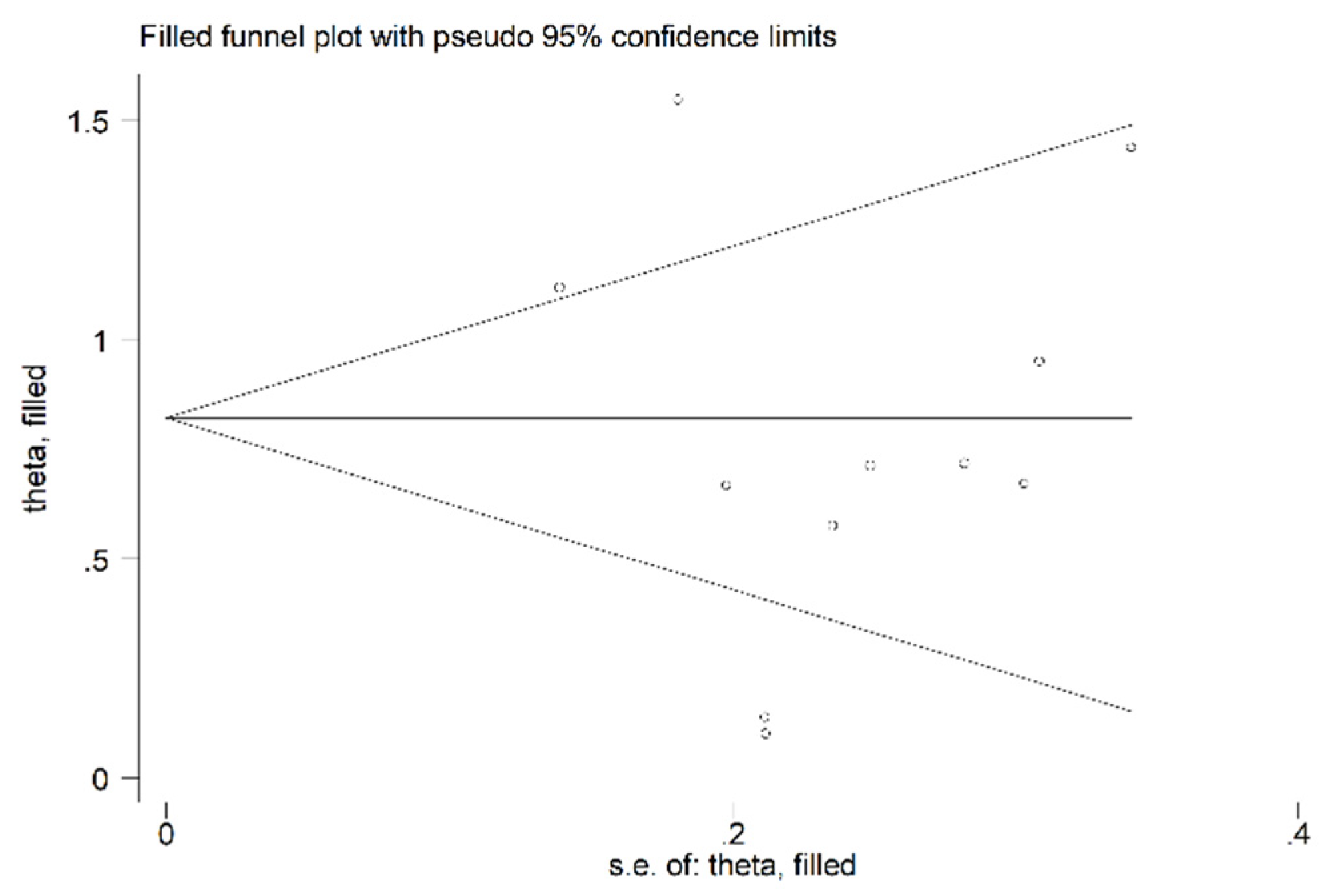
- Sterne, J.A.; Egger, M. Funnel plots for detecting bias in meta-analysis: Guidelines on choice of axis. J Clin Epidemiol 2001, 54, 1046-1055. [CrossRef]
- Duval, S.; Tweedie, R. Trim and fill: A simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics 2000, 56, 455-463. [CrossRef]
- Pouw, E.M.; Schols, A.M.; Deutz, N.E.; Wouters, E.F. Plasma and muscle amino acid levels in relation to resting energy expenditure and inflammation in stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998, 158, 797-801. [CrossRef]
- Andersson, A.; Ankerst, J.; Lindgren, A.; Larsson, K.; Hultberg, B. Hyperhomocysteinemia and changed plasma thiol redox status in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Clin Chem Lab Med 2001, 39, 229-233. [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, T.; Yoshikawa, M.; Fu, A.; Tsukaguchi, K.; Okamoto, Y.; Takenaka, H. Plasma levels of amino acids and hypermetabolism in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nutrition 2001, 17, 95-99. [CrossRef]
- Kai, S.; Nomura, A.; Morishima, Y.; Ishii, Y.; Sakamoto, T.; Hegab, A.E.; Sekizawa, K. The effect of smoking-related hyperhomocysteinemia on spirometric declines in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in elderly Japanese. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 2006, 42, 117-124. [CrossRef]
- Seemungal, T.A.; Lun, J.C.; Davis, G.; Neblett, C.; Chinyepi, N.; Dookhan, C.; Drakes, S.; Mandeville, E.; Nana, F.; Setlhake, S.; et al. Plasma homocysteine is elevated in COPD patients and is related to COPD severity. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis 2007, 2, 313-321. [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, G.M.; Abdullah, A.; Omran, G.A.; Mariee, A.D. Serum Homocystein Level In COPD Patients: Possible Beneficial Effect Of Antioxidants. Res J Med Med Sci 2009, 4, 306-310.
- Fimognari, F.L.; Loffredo, L.; Di Simone, S.; Sampietro, F.; Pastorelli, R.; Monaldo, M.; Violi, F.; D’Angelo, A. Hyperhomocysteinaemia and poor vitamin B status in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2009, 19, 654-659. [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A.; Saini, H.; Mawari, G.; Kumar, S.; Hira, H.S.; Daga, M.K. The Effect of Folic Acid Supplementation on Hyperhomocysteinemia and Pulmonary Function Parameters in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Pilot Study. J Clin Diagn Res 2016, 10, OC17-OC21. [CrossRef]
- Ruzsics, I.; Nagy, L.; Keki, S.; Sarosi, V.; Illes, B.; Illes, Z.; Horvath, I.; Bogar, L.; Molnar, T. L-Arginine Pathway in COPD Patients with Acute Exacerbation: A New Potential Biomarker. COPD 2016, 13, 139-145. [CrossRef]
- Zinellu, A.; Fois, A.G.; Sotgia, S.; Sotgiu, E.; Zinellu, E.; Bifulco, F.; Mangoni, A.A.; Pirina, P.; Carru, C. Arginines Plasma Concentration and Oxidative Stress in Mild to Moderate COPD. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160237. [CrossRef]
- Aydin, M.; Altintas, N.; Cem Mutlu, L.; Bilir, B.; Oran, M.; Tulubas, F.; Topcu, B.; Tayfur, I.; Kucukyalcin, V.; Kaplan, G.; et al. Asymmetric dimethylarginine contributes to airway nitric oxide deficiency in patients with COPD. Clin Respir J 2017, 11, 318-327. [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, L.; Pedone, C.; Battistoni, F.; Chiurco, D.; Santangelo, S.; Antonelli-Incalzi, R. Relationship between FEV(1) and arterial stiffness in elderly people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Aging Clin Exp Res 2017, 29, 157-164. [CrossRef]
- Urban, M.H.; Eickhoff, P.; Funk, G.C.; Burghuber, O.C.; Wolzt, M.; Valipour, A. Increased brachial intima-media thickness is associated with circulating levels of asymmetric dimethylarginine in patients with COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis 2017, 12, 169-176. [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Chen, K.H.; Chen, C.M.; Chang, C.H.; Huang, T.J.; Lin, C.H. Risk factors for osteoporosis in male patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Taiwan. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4232. [CrossRef]
- Moayyedkazemi, A.; Rahimirad, M. Evaluating the Serum Homocysteine Level in the Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and its Correlation with Severity of the Disease. J Res Med Dent Sci 2018, 6.
- Telo, S.; Kirkil, G.; Kuluozturk, M.; Balin, M.; Deveci, F. Can ADMA play a role in determining pulmonary hypertension related to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease? Clin Respir J 2018, 12, 1433-1438. [CrossRef]
- Csoma, B.; Bikov, A.; Nagy, L.; Toth, B.; Tabi, T.; Szucs, G.; Komlosi, Z.I.; Muller, V.; Losonczy, G.; Lazar, Z. Dysregulation of the endothelial nitric oxide pathway is associated with airway inflammation in COPD. Respir Res 2019, 20, 156. [CrossRef]
- Kuo, W.K.; Liu, Y.C.; Chu, C.M.; Hua, C.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Liu, M.H.; Wang, C.H. Amino Acid-Based Metabolic Indexes Identify Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease And Further Discriminates Patients In Advanced BODE Stages. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis 2019, 14, 2257-2266. [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Tian, T.; Liu, Y.; Li, C. The diagnostic value of homocysteine for the occurrence and acute progression of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. BMC Pulm Med 2020, 20, 237. [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Niu, W.; Niu, H.; Duan, R.; Dong, F.; Yang, T. Chitinase 3-like 1 polymorphisms and risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma in a Chinese population. J Gene Med 2020, 22, e3208. [CrossRef]
- Zinellu, A.; Zinellu, E.; Sotgiu, E.; Fois, A.G.; Paliogiannis, P.; Scano, V.; Piras, B.; Sotgia, S.; Mangoni, A.A.; Carru, C.; et al. Systemic transsulfuration pathway thiol concentrations in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients. Eur J Clin Invest 2020, e13267. [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.K.; Kan, M.Y. Homocysteine-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction. Ann Nutr Metab 2015, 67, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.Q.; Chen, T.N.; Zhang, J.L.; Yang, Q.; He, G.W. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase enhancer AVE3085 reverses endothelial dysfunction induced by homocysteine in human internal mammary arteries. Nitric Oxide 2018, 81, 21-27. [CrossRef]
- Stuhlinger, M.C.; Tsao, P.S.; Her, J.H.; Kimoto, M.; Balint, R.F.; Cooke, J.P. Homocysteine impairs the nitric oxide synthase pathway: Role of asymmetric dimethylarginine. Circulation 2001, 104, 2569-2575. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Jin, H.; Ebin, Z.; Brodsky, S.; Goligorsky, M.S. Effects of homocysteine on endothelial nitric oxide production. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2000, 279, F671-678. [CrossRef]
- McCully, K.S. Chemical pathology of homocysteine. IV. Excitotoxicity, oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction, and inflammation. Ann Clin Lab Sci 2009, 39, 219-232.
- McCully, K.S. Homocysteine and the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol 2015, 8, 211-219. [CrossRef]
- Weiss, N.; Heydrick, S.J.; Postea, O.; Keller, C.; Keaney, J.F., Jr.; Loscalzo, J. Influence of hyperhomocysteinemia on the cellular redox state--impact on homocysteine-induced endothelial dysfunction. Clin Chem Lab Med 2003, 41, 1455-1461. [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, L.; Miao, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.C.; Feng, J.; Wang, L. Homocysteine causes vascular endothelial dysfunction by disrupting endoplasmic reticulum redox homeostasis. Redox Biol 2019, 20, 46-59. [CrossRef]
- Bourgonje, A.R.; Abdulle, A.E.; Al-Rawas, A.M.; Al-Maqbali, M.; Al-Saleh, M.; Enriquez, M.B.; Al-Siyabi, S.; Al-Hashmi, K.; Al-Lawati, I.; Bulthuis, M.L.C.; et al. Systemic Oxidative Stress Is Increased in Postmenopausal Women and Independently Associates with Homocysteine Levels. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [CrossRef]
- Veeranna, V.; Zalawadiya, S.K.; Niraj, A.; Pradhan, J.; Ference, B.; Burack, R.C.; Jacob, S.; Afonso, L. Homocysteine and reclassification of cardiovascular disease risk. J Am Coll Cardiol 2011, 58, 1025-1033. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Mason, A.M.; Carter, P.; Burgess, S.; Larsson, S.C. Homocysteine, B vitamins, and cardiovascular disease: A Mendelian randomization study. BMC Med 2021, 19, 97. [CrossRef]
- McEvoy, M.A.; Schofield, P.W.; Smith, W.T.; Agho, K.; Mangoni, A.A.; Soiza, R.L.; Peel, R.; Hancock, S.J.; Carru, C.; Zinellu, A.; et al. Serum methylarginines and spirometry-measured lung function in older adults. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58390. [CrossRef]
- Nunomiya, K.; Shibata, Y.; Abe, S.; Inoue, S.; Igarashi, A.; Yamauchi, K.; Aida, Y.; Kishi, H.; Sato, M.; Watanabe, T.; et al. Hyperhomocysteinaemia predicts the decline in pulmonary function in healthy male smokers. Eur Respir J 2013, 42, 18-27. [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, F.; Lee, A.H.; Terasawa, K.; Kagawa, Y. Folate intake associated with lung function, breathlessness and the prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2010, 19, 103-109.
- Kim, T.; Oak, C.H.; Jung, M.H.; Jang, T.W.; Kim, J. High Serum Folate Concentration Is Associated with Better Lung Function in Male Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patients Who Are Current Smokers: Analysis of Nationwide Population-Based Survey. Nutrients 2020, 12. [CrossRef]
- Koyama, K.; Ito, A.; Yamamoto, J.; Nishio, T.; Kajikuri, J.; Dohi, Y.; Ohte, N.; Sano, A.; Nakamura, H.; Kumagai, H.; et al. Randomized controlled trial of the effect of short-term coadministration of methylcobalamin and folate on serum ADMA concentration in patients receiving long-term hemodialysis. Am J Kidney Dis 2010, 55, 1069-1078. [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.S.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.Z.; Ma, J.P.; Wu, C.J. Supplementation of folic acid and vitamin B(1)(2) reduces plasma levels of asymmetric dimethylarginine in patients with acute ischemic stroke. J Clin Neurosci 2014, 21, 1586-1590. [CrossRef]
- Paul, B.; Whiting, M.J.; De Pasquale, C.G.; Mangoni, A.A. Acute effects of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate on endothelial function and asymmetric dimethylarginine in patients with chronic heart failure. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2010, 20, 341-349. [CrossRef]
- Vukotic, R.; Di Donato, R.; Roncarati, G.; Simoni, P.; Renzulli, M.; Gitto, S.; Schepis, F.; Villa, E.; Berzigotti, A.; Bosch, J.; et al. 5-MTHF enhances the portal pressure reduction achieved with propranolol in patients with cirrhosis: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. J Hepatol 2023. [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.J.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Wang, C.X.; Ma, J.P.; Xia, X.S. [Impact of adding folic acid, vitamin B(12) and probucol to standard antihypertensive medication on plasma homocysteine and asymmetric dimethylarginine levels of essential hypertension patients]. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi 2012, 40, 1003-1008.
- Ghosh, S.K.; Paik, W.K.; Kim, S. Purification and molecular identification of two protein methylases I from calf brain. Myelin basic protein- and histone-specific enzyme. J Biol Chem 1988, 263, 19024-19033.
- Rawal, N.; Rajpurohit, R.; Paik, W.K.; Kim, S. Purification and characterization of S-adenosylmethionine-protein-arginine N-methyltransferase from rat liver. Biochem J 1994, 300 ( Pt 2), 483-489. [CrossRef]
- Closs, E.I.; Basha, F.Z.; Habermeier, A.; Forstermann, U. Interference of L-arginine analogues with L-arginine transport mediated by the y+ carrier hCAT-2B. Nitric Oxide 1997, 1, 65-73. [CrossRef]
- Feliers, D.; Lee, D.Y.; Gorin, Y.; Kasinath, B.S. Symmetric dimethylarginine alters endothelial nitric oxide activity in glomerular endothelial cells. Cell Signal 2015, 27, 1-5. [CrossRef]
- Strobel, J.; Muller, F.; Zolk, O.; Endress, B.; Konig, J.; Fromm, M.F.; Maas, R. Transport of asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) by cationic amino acid transporter 2 (CAT2), organic cation transporter 2 (OCT2) and multidrug and toxin extrusion protein 1 (MATE1). Amino Acids 2013, 45, 989-1002. [CrossRef]
- Gaddam, S.; Gunukula, S.K.; Lohr, J.W.; Arora, P. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pulm Med 2016, 16, 158. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Liao, K.M. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease is associated with risk of Chronic Kidney Disease: A Nationwide Case-Cohort Study. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 25855. [CrossRef]
- Corsonello, A.; Aucella, F.; Pedone, C.; Antonelli-Incalzi, R. Chronic kidney disease: A likely underestimated component of multimorbidity in older patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Geriatr Gerontol Int 2017, 17, 1770-1788. [CrossRef]
- Zakrzewicz, D.; Zakrzewicz, A.; Preissner, K.T.; Markart, P.; Wygrecka, M. Protein Arginine Methyltransferases (PRMTs): Promising targets for the treatment of pulmonary disorders. Int J Mol Sci 2012, 13, 12383-12400. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Cook, J.R.; Yang, Z.H.; Mirochnitchenko, O.; Gunderson, S.I.; Felix, A.M.; Herth, N.; Hoffmann, R.; Pestka, S. PRMT7, a new protein arginine methyltransferase that synthesizes symmetric dimethylarginine. J Biol Chem 2005, 280, 3656-3664. [CrossRef]
- Jain, K.; Clarke, S.G. PRMT7 as a unique member of the protein arginine methyltransferase family: A review. Arch Biochem Biophys 2019, 665, 36-45. [CrossRef]
- Mosharov, E.; Cranford, M.R.; Banerjee, R. The quantitatively important relationship between homocysteine metabolism and glutathione synthesis by the transsulfuration pathway and its regulation by redox changes. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 13005-13011. [CrossRef]
- Stipanuk, M.H.; Ueki, I. Dealing with methionine/homocysteine sulfur: Cysteine metabolism to taurine and inorganic sulfur. J Inherit Metab Dis 2011, 34, 17-32. [CrossRef]
- Vitvitsky, V.; Garg, S.K.; Banerjee, R. Taurine biosynthesis by neurons and astrocytes. J Biol Chem 2011, 286, 32002-32010. [CrossRef]
- Gebel, S.; Gerstmayer, B.; Kuhl, P.; Borlak, J.; Meurrens, K.; Muller, T. The kinetics of transcriptomic changes induced by cigarette smoke in rat lungs reveals a specific program of defense, inflammation, and circadian clock gene expression. Toxicol Sci 2006, 93, 422-431. [CrossRef]
- Imamura, M.; Waseda, Y.; Marinova, G.V.; Ishibashi, T.; Obayashi, S.; Sasaki, A.; Nagai, A.; Azuma, H. Alterations of NOS, arginase, and DDAH protein expression in rabbit cavernous tissue after administration of cigarette smoke extract. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2007, 293, R2081-2089. [CrossRef]
- Tadie, J.M.; Henno, P.; Leroy, I.; Danel, C.; Naline, E.; Faisy, C.; Riquet, M.; Levy, M.; Israel-Biet, D.; Delclaux, C. Role of nitric oxide synthase/arginase balance in bronchial reactivity in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2008, 294, L489-497. [CrossRef]
- Guzman-Grenfell, A.; Nieto-Velazquez, N.; Torres-Ramos, Y.; Montoya-Estrada, A.; Ramirez-Venegas, A.; Ochoa-Cautino, L.; Flores-Trujillo, F.; Hicks, J.J. Increased platelet and erythrocyte arginase activity in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease associated with tobacco or wood smoke exposure. J Investig Med 2011, 59, 587-592. [CrossRef]
- Petta, I.; Peene, I.; Elewaut, D.; Vereecke, L.; De Bosscher, K. Risks and benefits of corticosteroids in arthritic diseases in the clinic. Biochem Pharmacol 2019, 165, 112-125. [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, M.P.; Meurs, H.; Gosens, R. Targeting arginase and nitric oxide metabolism in chronic airway diseases and their co-morbidities. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2018, 40, 126-133. [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.A.; Maarsingh, H.; Holguin, F.; Grasemann, H. Arginine Therapy for Lung Diseases. Front Pharmacol 2021, 12, 627503. [CrossRef]
- Doman, A.J.; Tommasi, S.; Perkins, M.V.; McKinnon, R.A.; Mangoni, A.A.; Nair, P.C. Chemical similarities and differences among inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase, arginase and dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase-1: Implications for the design of novel enzyme inhibitors modulating the nitric oxide pathway. Bioorg Med Chem 2022, 72, 116970. [CrossRef]

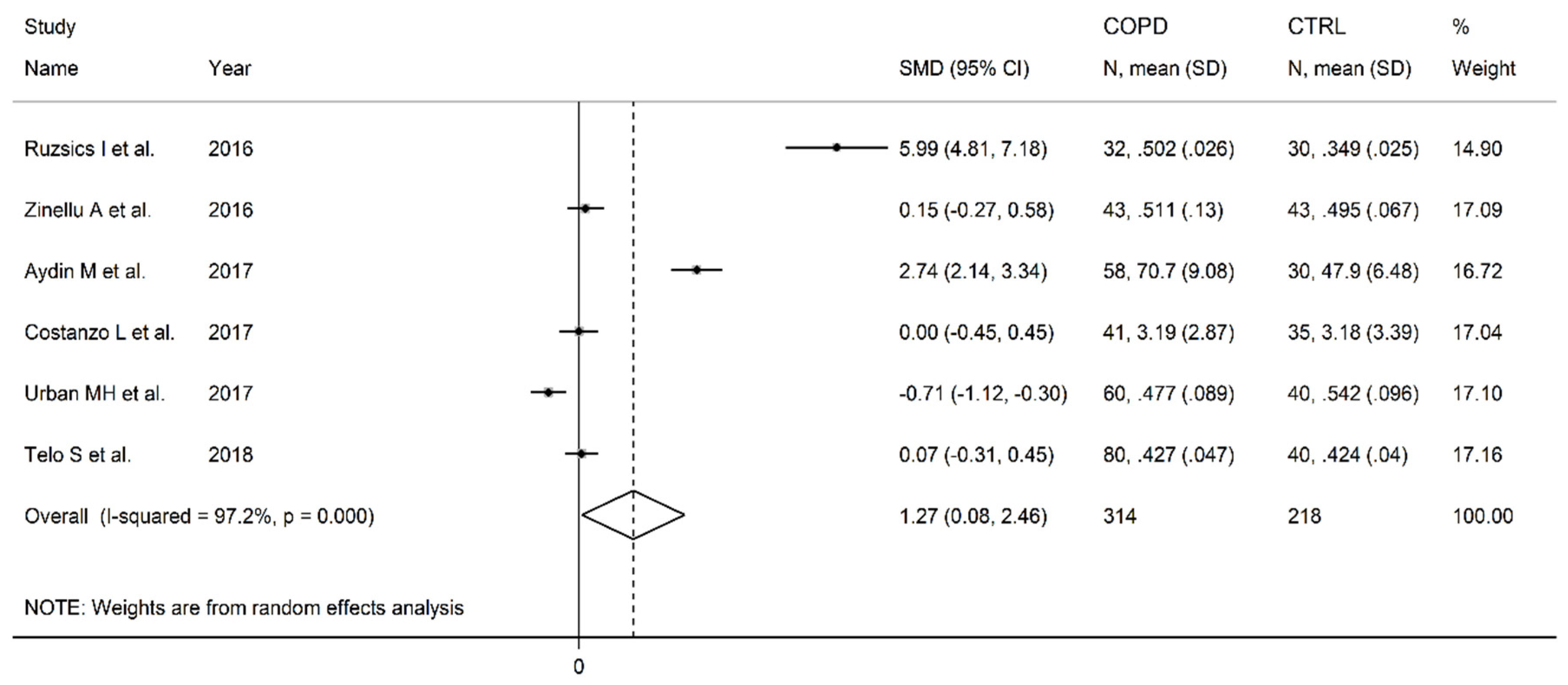
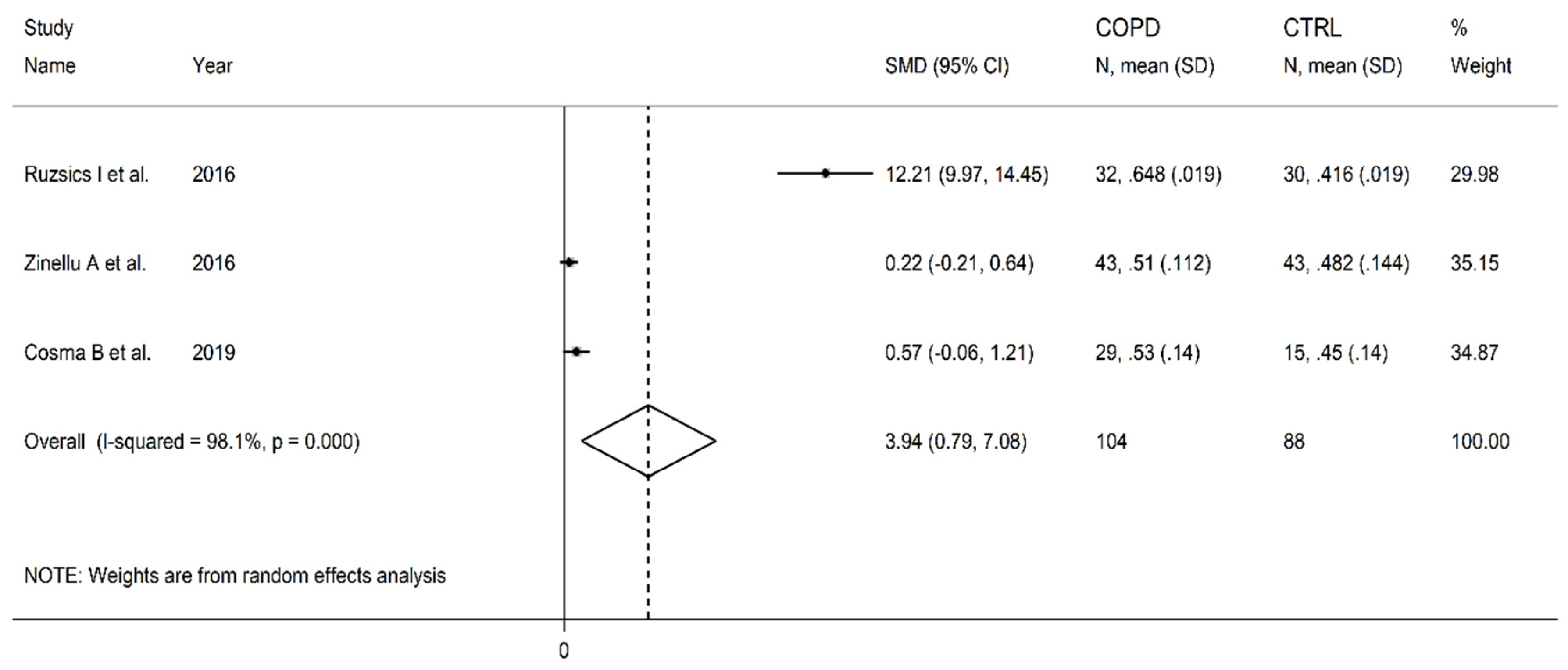
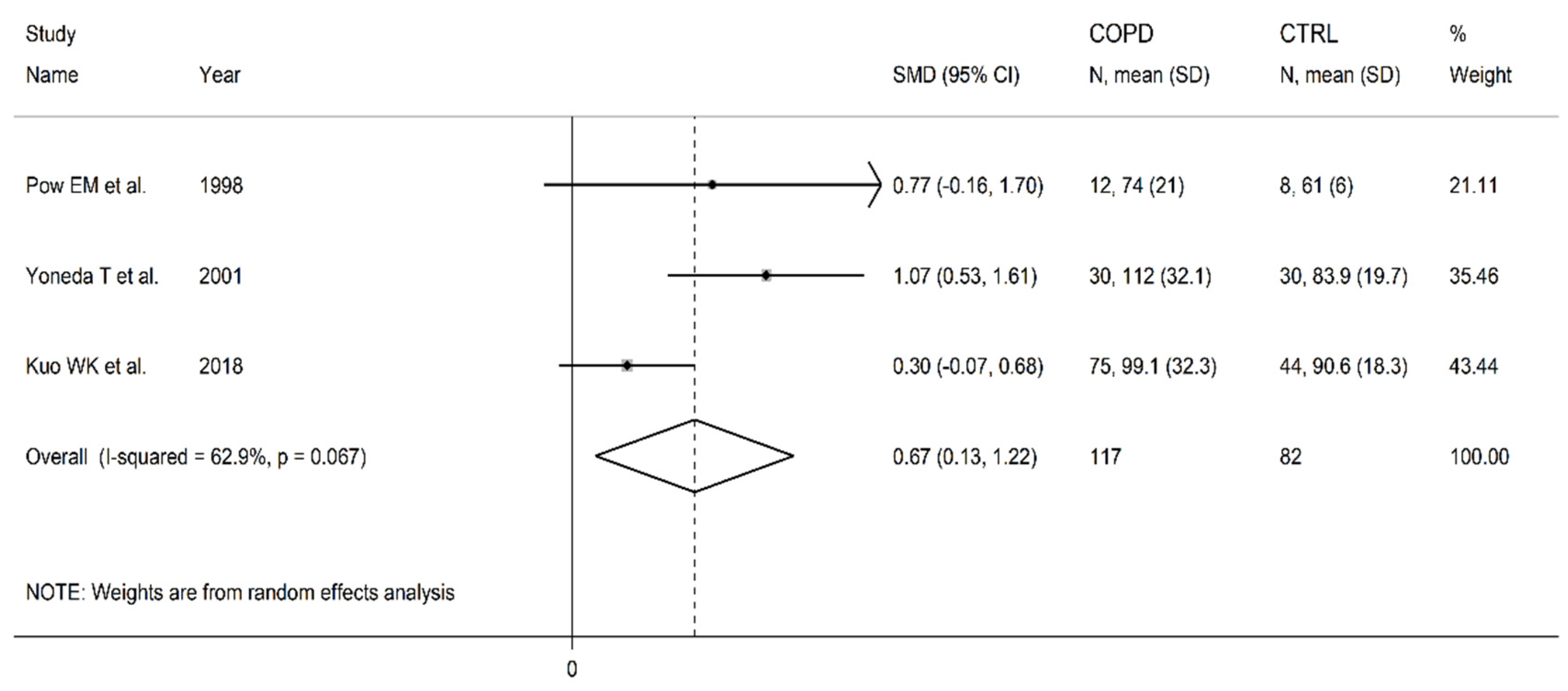
| Healthy controls | Patients with COPD | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study |
n |
Age (Years) |
M/F | Homocysteine Cysteine Methionine Vitamin B6 Vitamin B12 Folic acid (Mean±SD) |
Arginine ADMA SDMA Ornithine Citrulline (Mean±SD) |
n | Age (Years) |
M/F | Homocysteine Cysteine Methionine Vitamin B6 Vitamin B12 Folic acid (Mean±SD) |
Arginine ADMA SDMA Ornithine Citrulline (Mean±SD) |
| Pow EM et al. 1998, The Netherlands [84] | 8 | 64 | NR | NR NR 28±3 NR NR NR |
90±14 NR NR 61±6 54±7 |
12 | 66 | NR | NR NR 26±3.5 NR NR NR |
90±14 NR NR 74±21 48±6 |
| Andersson A et al. 2001, Sweden [85] | 29 | 64 | 14/15 | 14.1±4.9 321±50 NR NR NR NR |
NR NR NR NR NR |
19 | 68 | 8/11 | 17.9±6.7 340±52 NR NR NR NR |
NR NR NR NR NR |
| Yoneda T et al. 2001, Japan [86] | 30 | NR | NR | NR NR 30.4±7.3 NR NR |
97.7±22.8 NR NR 83.9±19.7 NR |
30 | 64 | NR | NR NR 27.4±5.4 NR NR |
103±21.6 NR NR 112.4±32.1 NR |
| Kai S et al. 2006, Japan [87] |
23 | 63 | 23/0 | 9.8±3.0 NR NR NR NR NR |
NR NR NR NR NR |
24 | 71 | 24/0 | 12.6±2.9 NR NR NR NR NR |
NR NR NR NR NR |
| Seemungal TAR et al. 2007, England [88] | 25 | 65 | 16/9 | 8.1±2.2 NR NR NR NR NR |
NR NR NR NR NR |
29 | 69 | 23/6 | 10.7±4.5 NR NR NR NR NR |
NR NR NR NR NR |
| Abdallah GM et al. 2009, Egypt [89] | 20 | NR | 12/8 | 7.6±1.3 NR NR NR 335±58 6.2±3.0 |
NR NR NR NR NR |
24 | NR | 18/6 | 9.4±1.3 NR NR NR 299±44 4.8±2.9 |
NR NR NR NR NR |
| Fimognari FL et al. 2009, Italy [90] | 29 | 71 | 21/8 | 11.9±2.9 NR NR 9.1±6.4 369±211 3.0±1.4 |
NR NR NR NR NR |
42 | 71 | 36/6 | 14.8±4.7 NR NR 5.6±5.1 324±144 2.3±1.6 |
NR NR NR NR NR |
| Kahn NA et al. 2016, India [91] | 30 | 52 | 13/17 | 15.2±15.7 NR NR NR NR NR |
NR NR NR NR NR |
50 | 58 | 43/7 | 27.4±27.9 NR NR NR NR NR |
NR NR NR NR NR |
| Ruzsics I et al. 2016, Hungary [92] | 30 | 51 | 15/15 | NR NR NR NR NR NR |
80±3.5 0.35±0.02 0.42±0.02 NR NR |
32 | 59 | 14/18 | NR NR NR NR NR NR |
106±3.5 0.50±0.03 0.65±0.02 NR NR |
| Zinellu A et al. 2016, Italy [93] | 43 | 73 | 34/9 | NR NR NR NR NR NR |
80±16 0.50±0.07 0.48±0.18 NR NR |
43 | 75 | 34/9 | NR NR NR NR NR NR |
64±13 0.51±0.13 0.51±0.11 NR NR |
| Aydin M et al. 2017, Turkey [94] | 30 | 64 | 21/9 | NR NR NR NR NR NR |
NR 47.9±6.5 NR NR NR |
58 | 62 | 48/10 | NR NR NR NR NR NR |
NR 70.7±9.1 NR NR NR |
| Costanzo L et al. 2017, Italy [95] | 35 | 74 | 16/9 | NR NR NR NR NR NR |
NR 3.18±3.39 NR NR NR |
41 | 74 | 23/18 | NR NR NR NR NR NR |
NR 3.19±2.87 NR NR NR |
| Urban MH et al. 2017, Austria [96] | 40 | 62 | 14/26 | NR NR NR NR NR NR |
NR 0.54±0.10 NR NR NR |
60 | 64 | 32/28 | NR NR NR NR NR NR |
NR 0.48±0.09 NR NR NR |
| Lin CH et al. 2018, Taiwan [97] | 36 | 71 | 36/0 | 14.6±4.4 NR NR NR 628±323 12.9±6.3 |
NR NR NR NR NR |
59 | 71 | 59/0 | 16.1±18.4 NR NR NR 653±327 11.0±6.5 |
NR NR NR NR NR |
| Moayyedkazemi A et al. 2018, Iran [98] | 51 | 66 | 29/22 | 18.2±9.5 NR NR NR NR NR |
NR NR NR NR NR |
40 | 67 | 22/18 | 19.5±9.5 NR NR NR NR NR |
NR NR NR NR NR |
| Telo S et al. 2018, Turkey [99] | 40 | 69 | 31/9 | NR NR NR NR NR NR |
NR 0.42±0.04 NR NR NR |
80 | 69 | 65/15 | NR NR NR NR NR NR |
NR 0.43±0.05 NR NR NR |
| Csoma B et al. 2019, Hungary [100] | 15 | 51 | 6/9 | NR NR NR NR NR NR |
NR NR 0.45±0.14 NR NR |
29 | 63 | 13/16 | NR NR NR NR NR NR |
NR NR 0.53±0.14 NR NR |
| Kuo WK et al. 2018, Taiwan [101] | 44 | 53 | 36/8 | NR NR NR NR NR NR |
NR NR NR 90.6±18.3 NR |
75 | 72 | 67/8 | NR NR NR NR NR NR |
NR NR NR 99.1±32.3 NR |
| Wei B et al. 2020, China [102] | 50 | 58 | 28/22 | 7.5±2.7 NR NR NR NR NR |
NR NR NR NR NR |
150 | 62 | 90/60 | 11.7±2.7 NR NR NR NR NR |
NR NR NR NR NR |
| Yu T et al. 2020, China [103] | 121 | 59 | 77/44 | 8.3±4.4 NR NR NR NR NR |
NR NR NR NR NR |
119 | 59 | 86/33 | 14.8±6.9 NR NR NR NR NR |
NR NR NR NR NR |
| Zinellu A et al. 2020, Italy [104] | 54 | 73 | 40/14 | 13.0±3.7 317±74 NR NR NR NR |
NR NR NR NR NR |
54 | 73 | 40/14 | 15.5±3.8 340±52 NR NR NR NR |
NR NR NR NR NR |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





