Submitted:
01 August 2023
Posted:
02 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
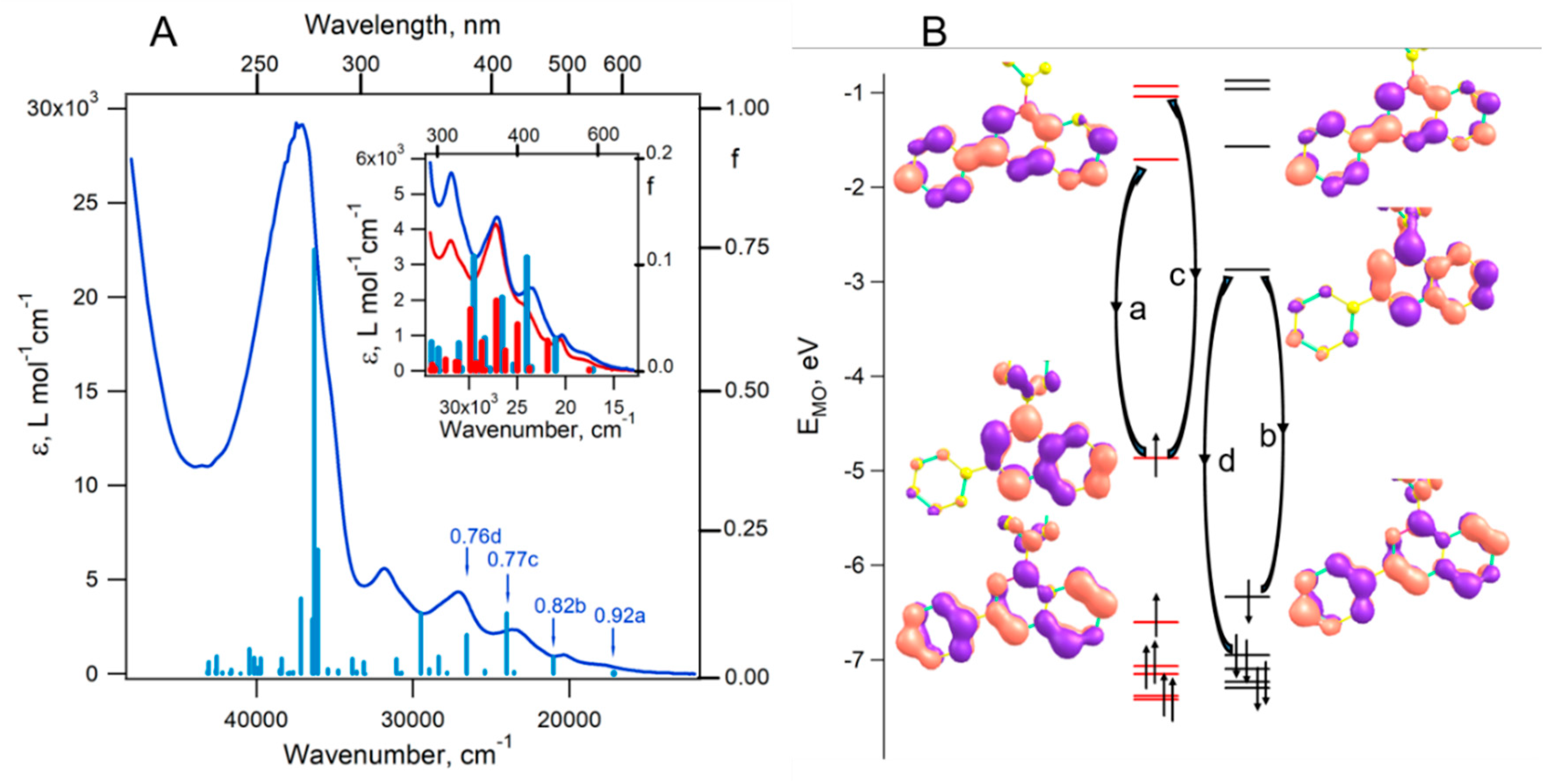
2. Results and Discussion
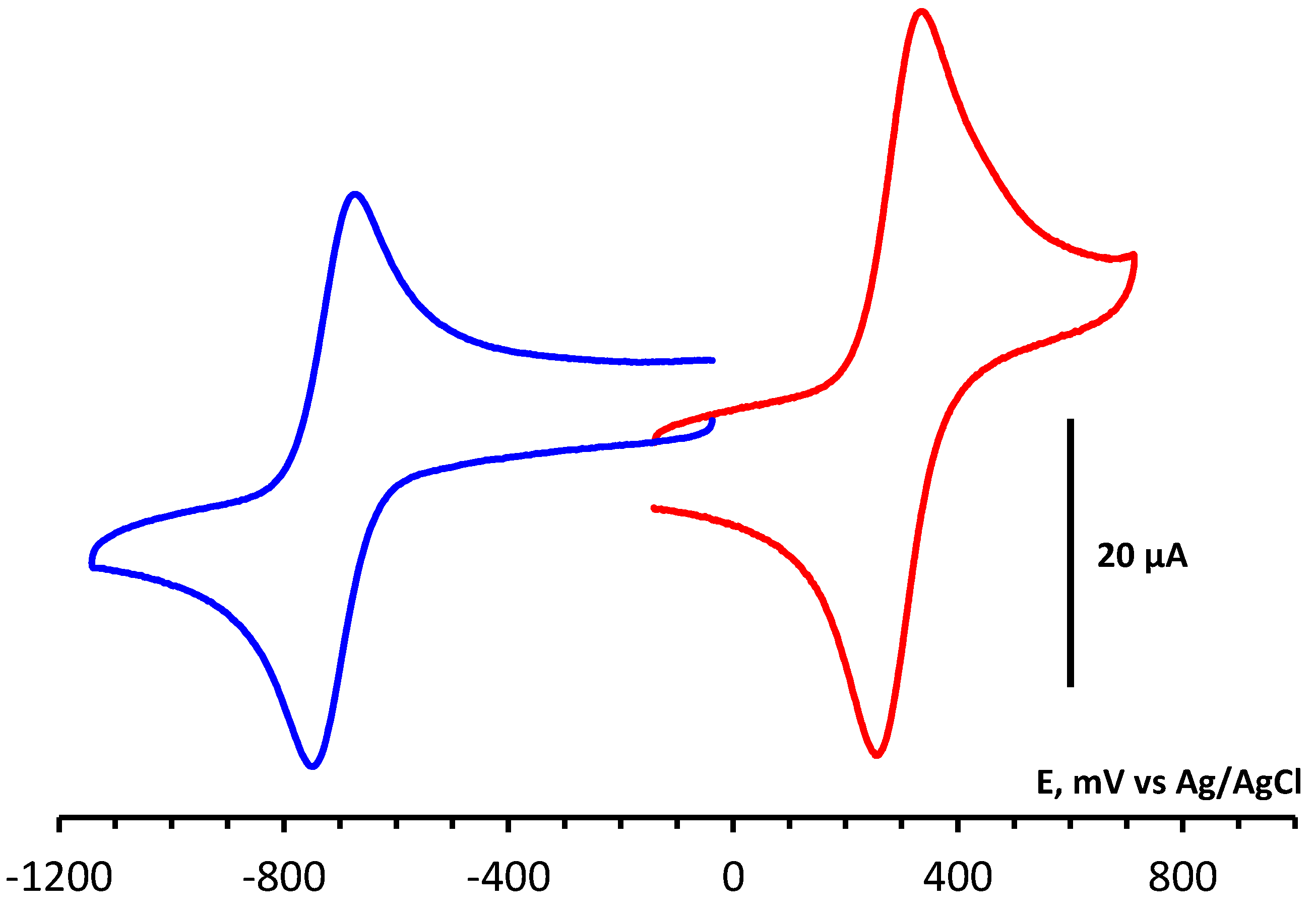
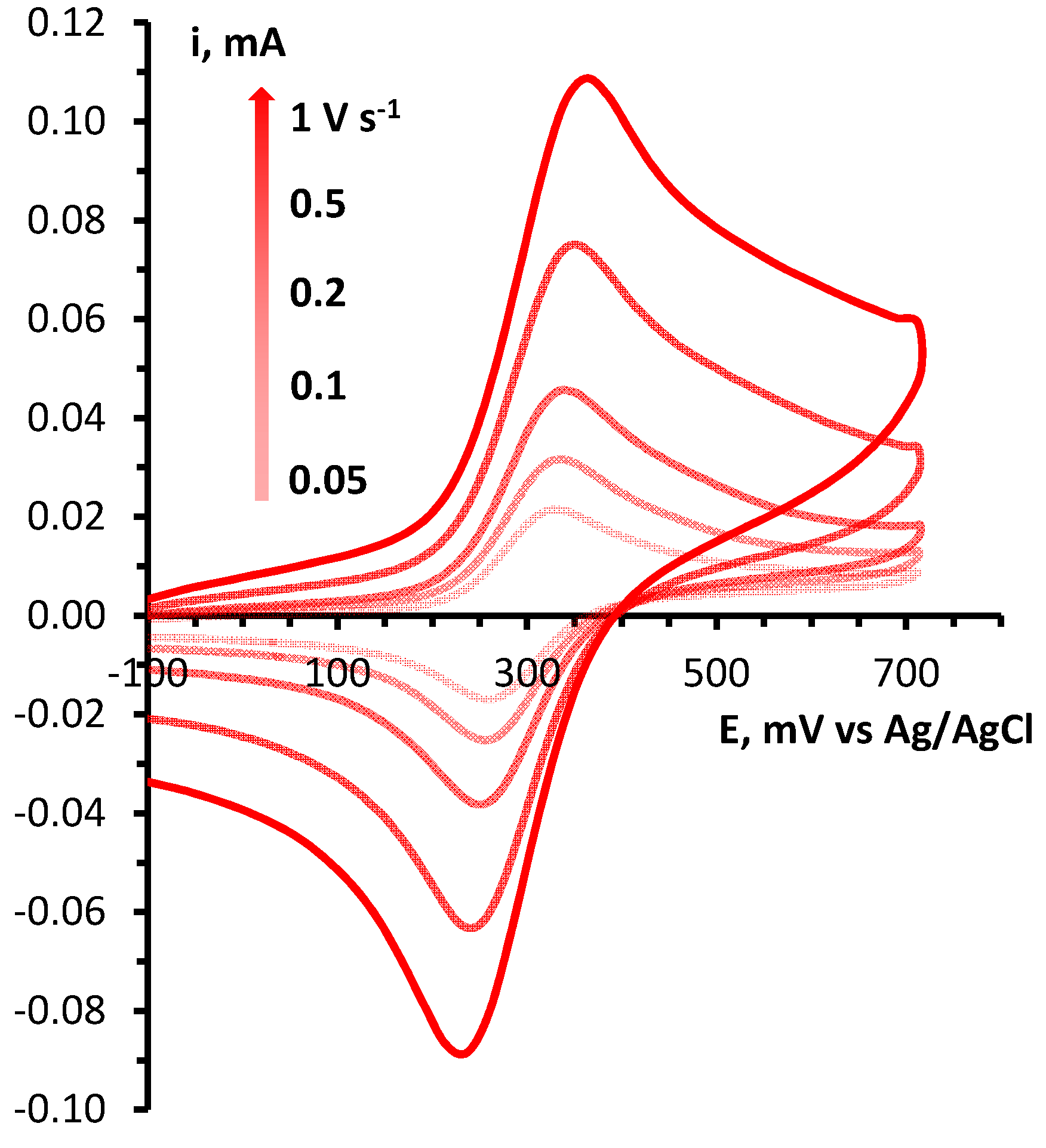
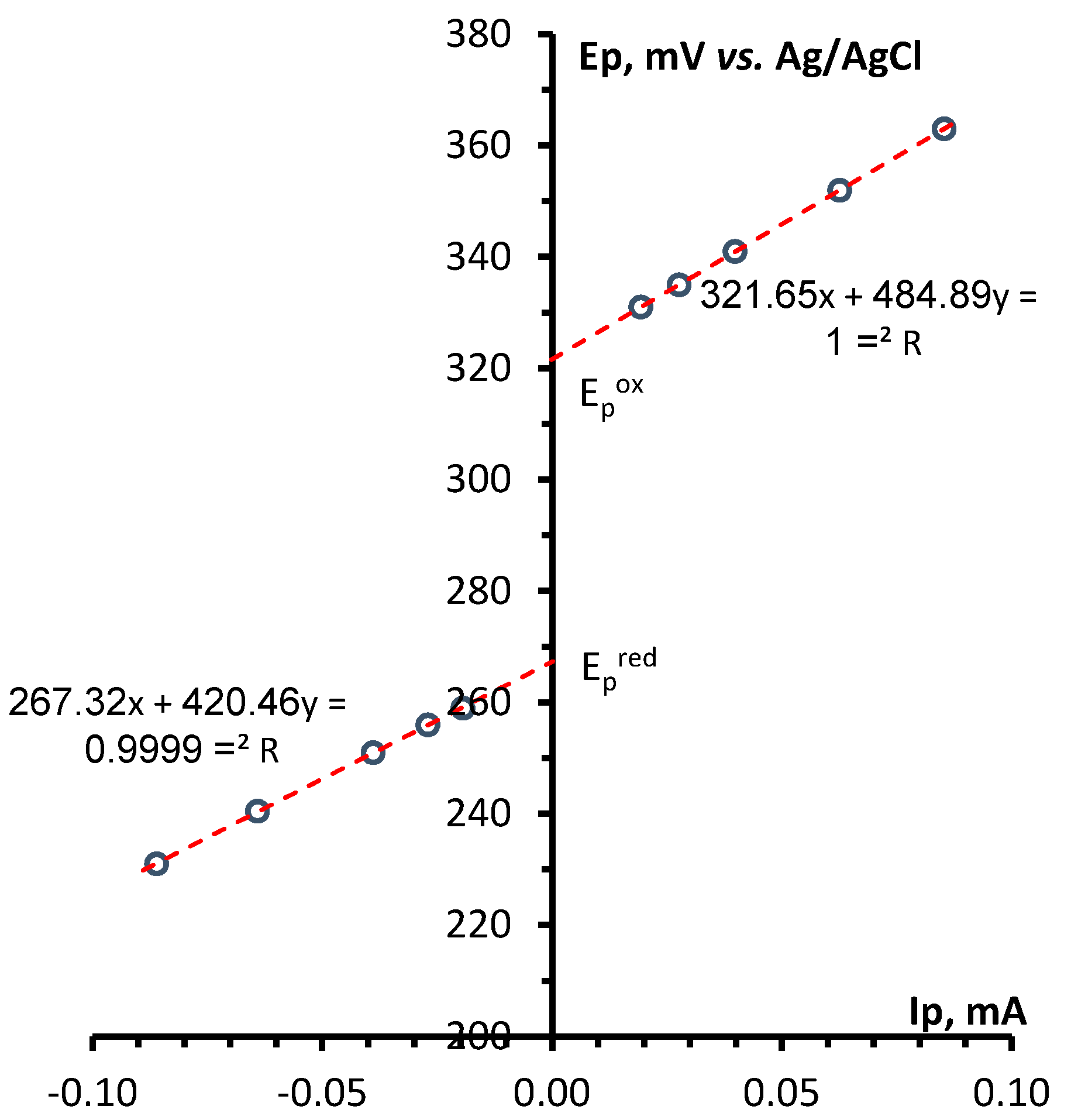
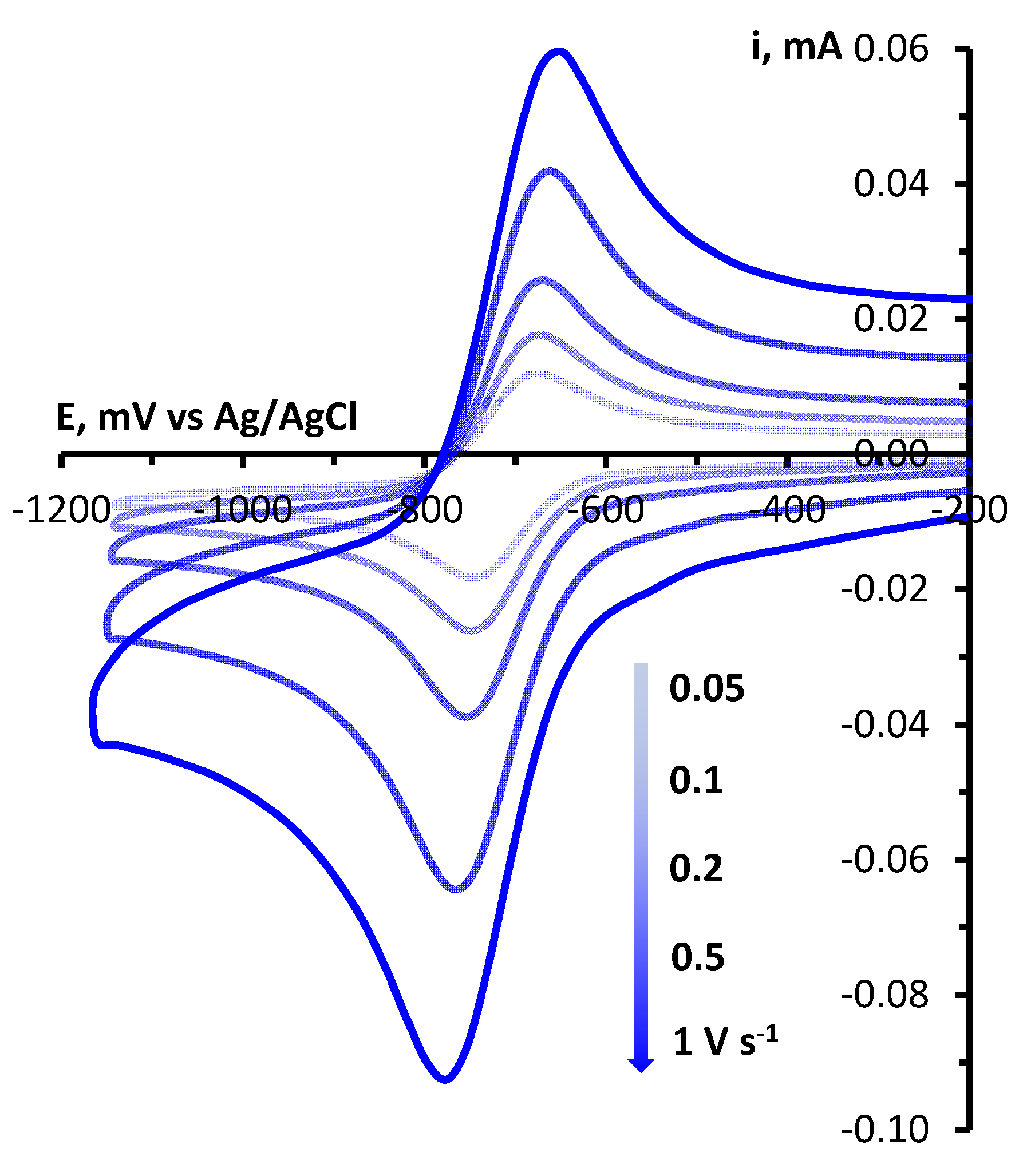
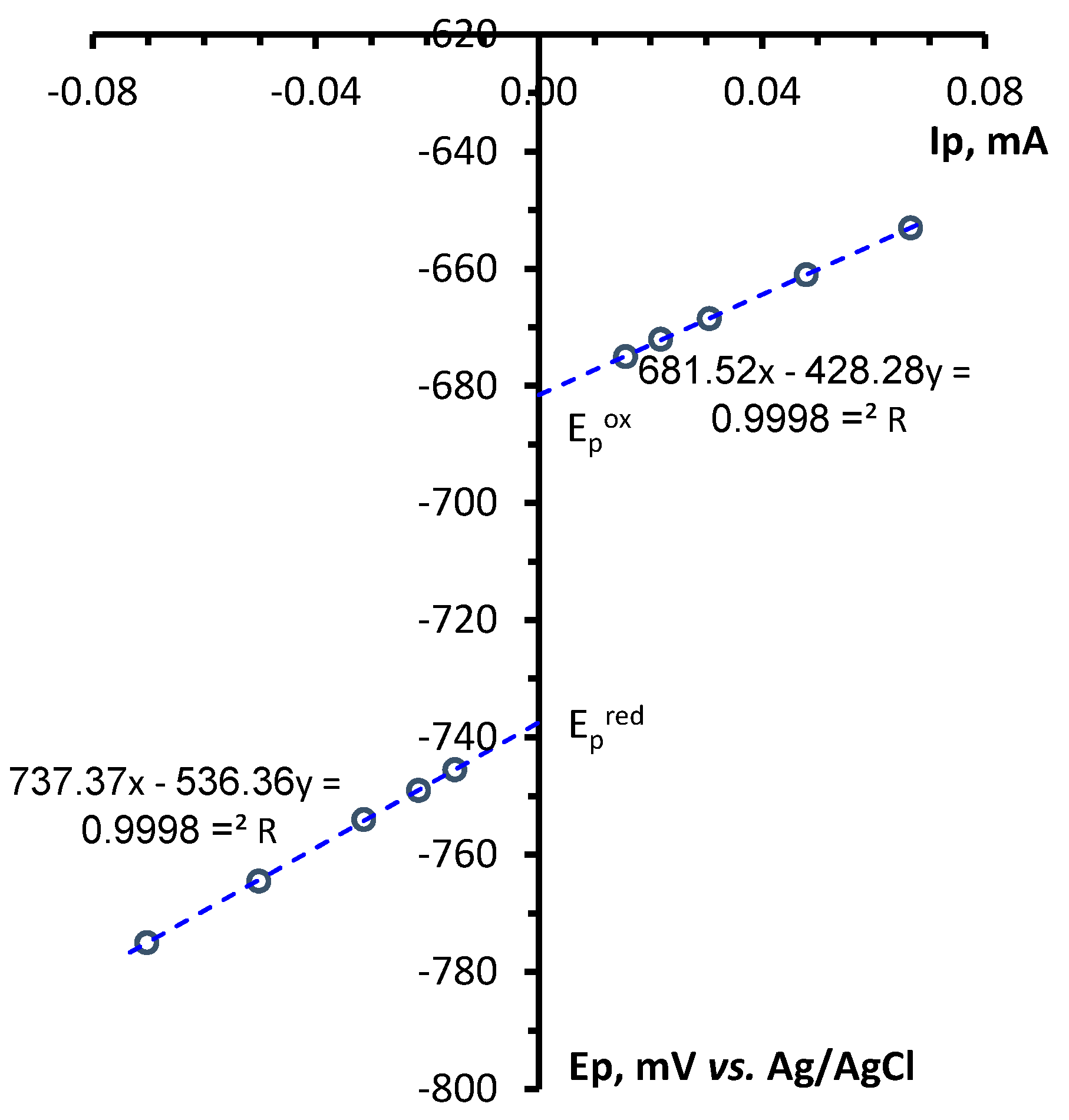
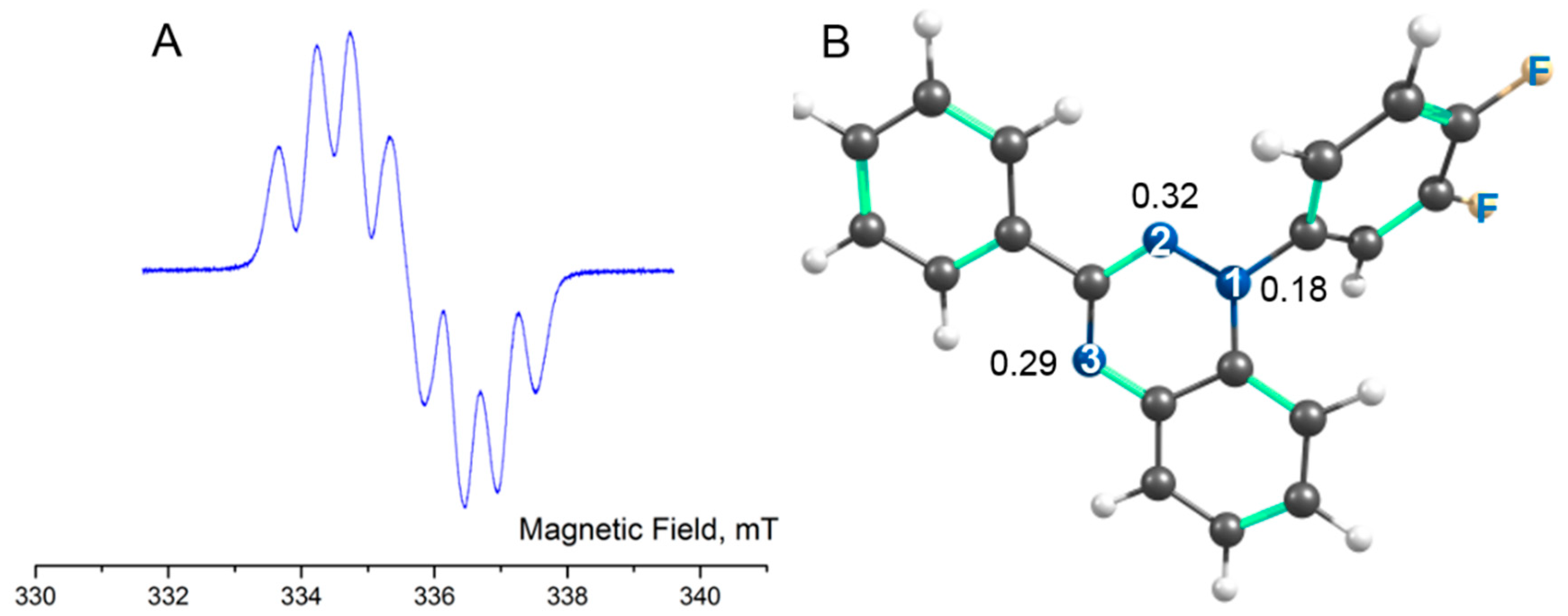
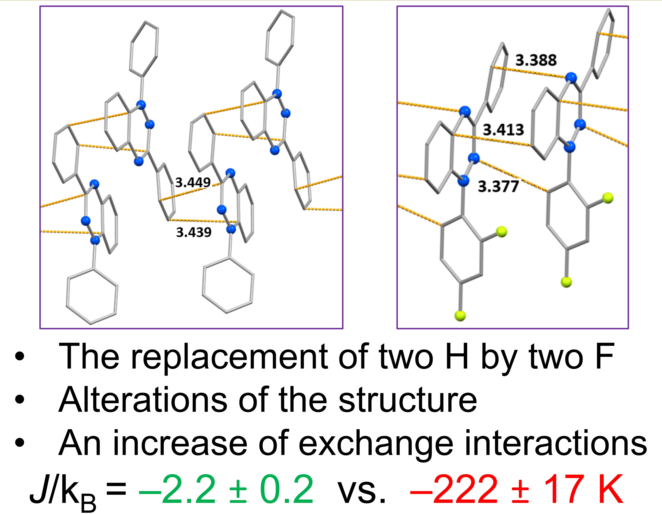
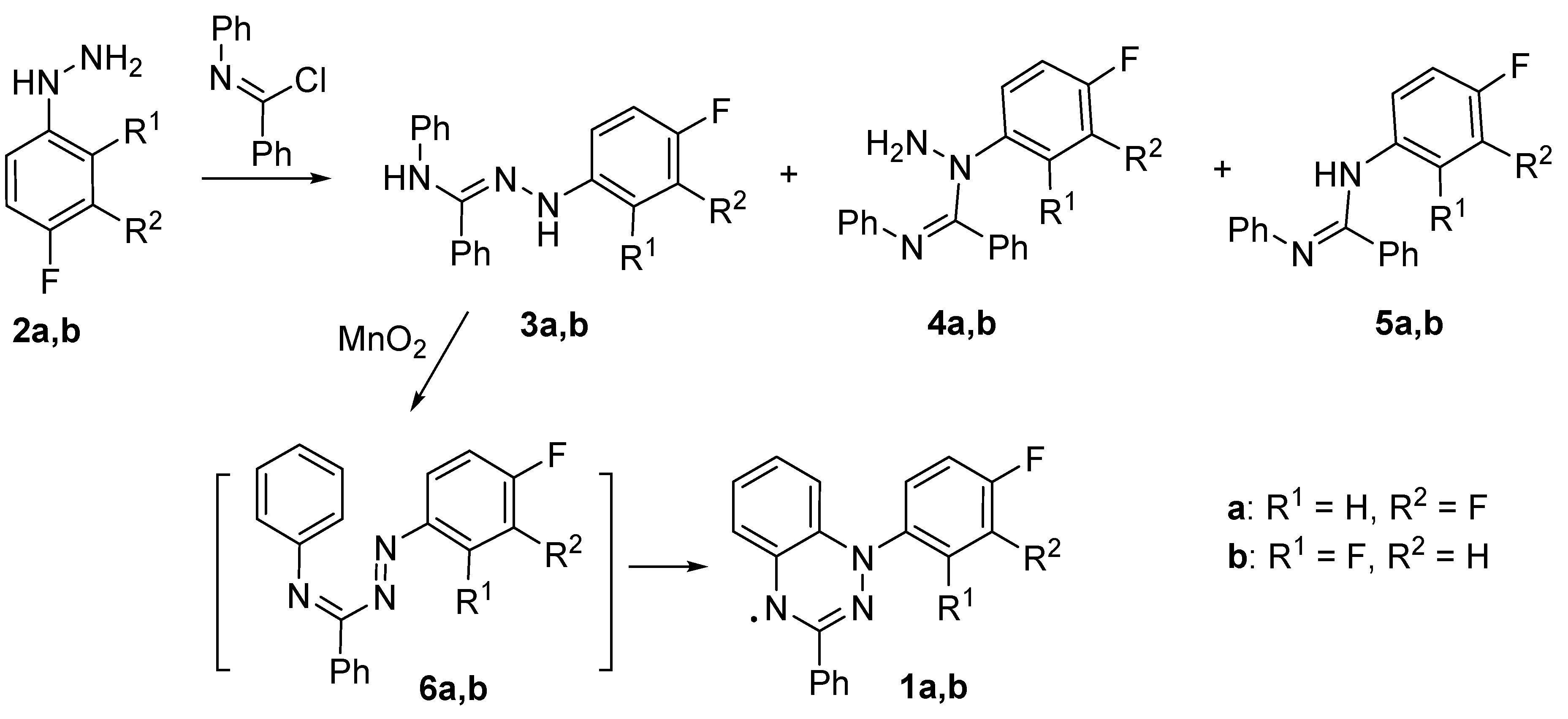
3. Conclusions
4. Experimental Part and Computational Details
4.1. Reagents and General Methods
4.2. Syntheses
4.3. EPR Spectroscopy
4.4. CV
4.5. Single-Crystal X-ray Diffractometry
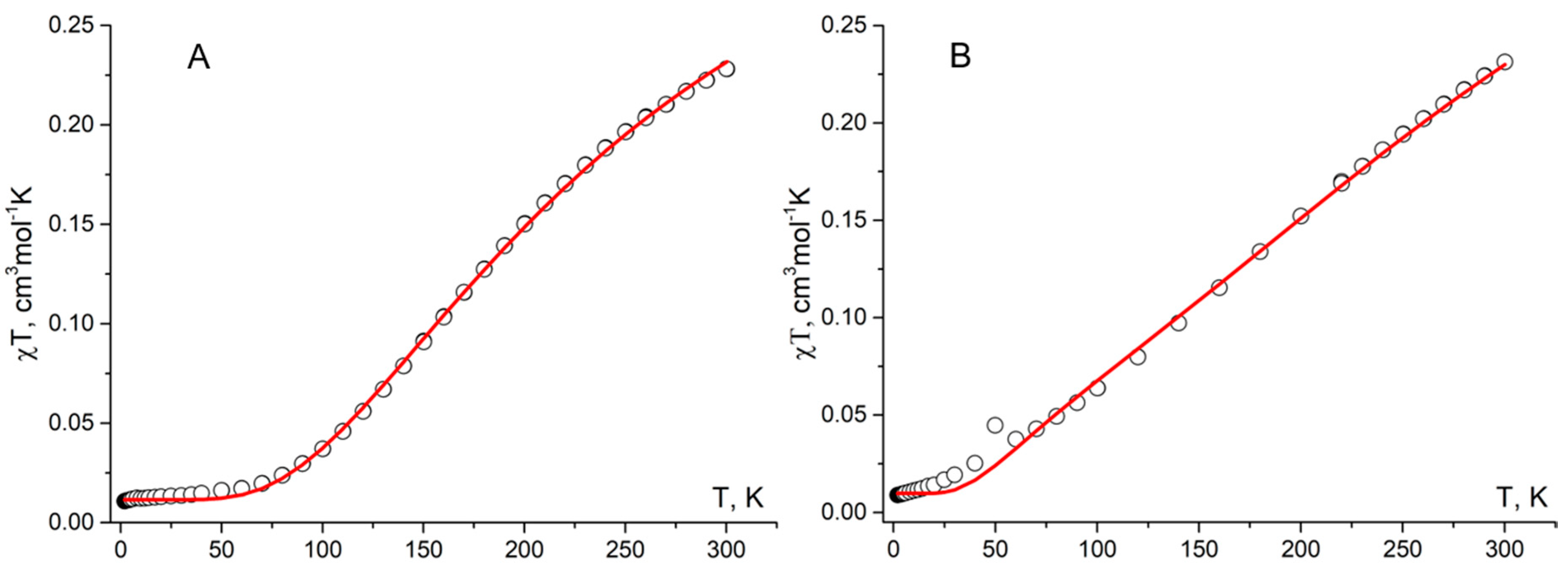
4.6. Magnetic Measurements
4.7. Computational Details
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Blatter, H.M.; Lukaszewski, H. A new stable free radical. Tetrahedron Lett. 1968, 9, 2701–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neugebauer, F.A.; Umminger, I. 1,4-Dihydro-1,2,4-benzotriazin-Radikalkationen. Chem. Ber. 1981, 114, 2423–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadirov, M.K.; Il'yasov, A.V.; Vafina, A.A.; Buzykin, B.I.; Gazetdinova, N.G.; Kitaev, Y.P. Double electron-nuclear resonance of free radical 1,3-diphenyl-1, 4-dihydro-1,2,4-benzotriazin-4-yl. Bull. Acad. Sci. USSR, Div. Chem. Sci. 1984, 33, 649–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, K.A.; Srdanov, G.; Menon, R.; Gabriel, J.-C.P.; Knight, B.; Wudl, F. A Pressure Sensitive Two-Dimensional Tetracyanoquinodimethane (TCNQ) Salt of a Stable Free Radical. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 13081–13082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, K.; Inoue, K.; Achiwa, N.; Jamali, J.B.; Krieger, C.; Neugebauer, F.A. Magnetic-properties of 1,4-dihydro-1,2,4-benzotriazin -4-yl radicals. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1994, 224, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, C.; Neugebauer, F.A. Columnar Stacking of 1,3-Diphenyl-1,2,4-benzotriazin-4(1H)-yl Radicals. Acta. Crystallogr. C 1996, 52, 3124–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Miao, M.S.; Dantelle, G.; Eisenmenger, N.D.; Wu, G.; Yavuz, I.; Chabinyc, M.L.; Houk, K.N.; Wudl, F. A solid-state effect responsible for an organic quintet state at room temperature and ambient pressure. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1718–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karecla, G.; Papagiorgis, P.; Panagi, N.; Zissimou, G.A.; Constantinides, C.P.; Koutentis, P.A.; Itskos, G.; Hayes, S.C. Emission from the stable Blatter radical. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 8604–8613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasinski, M.; Szczytko, J.; Pociecha, D.; Monobe, H.; Kaszyn´ski, P. Substituent-Dependent Magnetic Behavior of Discotic Benzo[e][1,2,4]triazinyls. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 9421–9424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasinski, M.; Kapuscinski, S.; Kaszynski, P. Stability of a columnar liquid crystalline phase in isomeric derivatives of the 1,4-dihydrobenzo[e][1,2,4]triazin-4-yl: Conformational effects in the core. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 277, 1054–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areephong, J.; Mattson, K.M.; Treat, N.J.; Poelma, S.O.; Kramer, J.W.; Sprafke, H.A.; Latimer, A.A.; Read de Alaniz, J.; Hawker, C.J. Triazine-mediated controlled radical polymerization: new unimolecular initiators. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetriou, M.; Berezin, A.A.; Koutentis, P.A.; Krasia-Christoforou, T. Benzotriazinyl-mediated controlled radical polymerization of styrene. Polym. Int. 2014, 63, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, H.; Miao, M.S.; Wudl, F.; Nguyen, T.Q. Temperature Tunable Self-Doping in Stable Diradicaloid Thin-Film Devices. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 7412–7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Miao, M.; Kemei, M.C.; Seshadri, R.; Wudl, F. The Pyreno-Triazinyl Radical-Magnetic and Sensor Properties. Isr. J. Chem. 2014, 54, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, Y.; Yoshioka, N. p-Stacked structure of thiadiazolo-fused benzotriazinyl radical: Crystal structure and magnetic properties. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2015, 626, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Miao, M.; Kemei, M.C.; Seshadri, R.; Wudl, F. The Pyreno-Triazinyl Radical-Magnetic and Sensor Properties. Isr. J. Chem. 2014, 54, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinides, C.P.; Berezin, A.A.; Zissimou, G.A.; Manoli, M.; Leitus, G.M.; Bendikov, M.; Probert, M.R.; Rawson, J.M.; Koutentis, P.A. A magnetostructural investigation of an abrupt spin transition for 1-phenyl-3-trifluoromethyl-1,4-dihydrobenzo[e][1,2,4]triazin-4-yl. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 11906–11909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, B.; Cramen, J.; McDonald, R.; Frank, N.L. Ferromagnetic spin-delocalized electron donors for multifunctional materials: p-conjugated benzotriazinyl radicals. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 3201–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Miura, Y.; Yoshioka, N. Synthesis and properties of the 3-tert-butyl-7-trifluoromethyl-1,4-dihydro-1-phenyl-1,2,4-benzotriazin-4-yl radical. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 4783–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Tsuchiya, N.; Miura, Y.; Yoshioka, N. Magneto-structural correlation of cyano-substituted 3-tert-butyl-1-phenyl-1,2,4-benzotriazin-4-yl: spin transition behaviour observed in a 6-cyano derivative. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 9949–9955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhao, L.; Chen, H.; Ding, Y.; Zheng, Y.-Z.; Miao, M.-S.; Zheng, Y. Air stable high-spin blatter diradicals: non-Kekulé versus Kekulé structures. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 6559–6563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, N.M.; Bauer, J.J.; Pink, M.; Rajca, S.; Rajca, A. High-Spin Organic Diradical with Robust Stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 9377–9380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, N.; Zhang, H.; Junghoefer, T.; Giangrisostomi, E.; Ovsyannikov, R.; Pink, M.; Rajca, S.; Casu, M.B.; Rajca, A. Thermally and Magnetically Robust Triplet Ground State Diradical. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 4764–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, I.S.; Mansikkamäki, A.; Loizou, G.A.; Koutentis, P.A.; Rouzières, M.; Clérac, R.; Tuononen, H.M. Coordination Complexes of a Neutral 1,2,4-Benzotriazinyl Radical Ligand: Synthesis, Molecular and Electronic Structures, and Magnetic Properties. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 15843–15853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, I.S.; Mansikkamäki, A.; Rouzières, M.; Clérac, R.; Tuononen, H.M. Coexistence of long-range antiferromagnetic order and slow relaxation of the magnetization in the first lanthanide complex of a 1,2,4-benzotriazinyl radical. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 12790–12793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- F Ciccullo, F.; Gallagher, N.M.; Geladari, O.; Chassé, T.; Rajca, A.; Casu, M.B. A Derivative of the Blatter Radical as a Potential Metal-Free Magnet for Stable Thin Films and Interfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 1805–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casu, M.B. Nanoscale Studies of Organic Radicals: Surface, Interface, and Spinterface. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, J.Z.; Kladnik, G.; Patera, L.L.; Sokolov, S.; Lovat, G.; Kumarasamy, E.; Repp, J.; Campos, L.M.; Cvetko, D.; Morgante, A.; Venkataraman, L. The Environment-Dependent Behavior of the Blatter Radical at the Metal–Molecule Interface. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 2543–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patera, L.L.; Sokolov, S.; Low, J.Z.; Campos, L.M.; Venkataraman, L.; Repp, J. Resolving the Unpaired-Electron Orbital Distribution in a Stable Organic Radical by Kondo Resonance Mapping. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 11063–11067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccullo, F.; Calzolari, A.; Bader, K.; Neugebauer, P.; Gallagher, N.M.; Rajca, A.; van Slageren, J.; Casu, M.B. Interfacing a Potential Purely Organic Molecular Quantum Bit with a Real-Life Surface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 1571–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezin, A.A.; Zissimou, G.; Constantinides, C.P.; Beldjoudi, Y.; Rawson, J.M.; Koutentis, P.A. Route to Benzo- and Pyrido-Fused 1,2,4-Triazinyl Radicals via N′-(Het)aryl-N′-[2-nitro(het)aryl]hydrazides. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 314–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savva, A.C.; Mirallai, S.I.; Zissimou, G.A.; Berezin, A.A.; Demetriades, M.; Kourtellaris, A.; Constantinides, C.P.; Nicolaides, C.; Trypiniotis, T.; Koutentis, P.A. Preparation of Blatter Radicals via Aza-Wittig Chemistry: The Reaction of N-Aryliminophosphoranes with 1-(Het)aroyl-2-aryldiazenes. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 7564–7575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantinides, C.P.; Obijalska, E.; Kaszynski, P. Access to 1,4-Dihydrobenzo[e][1,2,4]triazin-4-yl Derivatives. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 916–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, J.A.; Lu, Z.; Tucker, D.E.; Hockin, B.M.; Yufit, D.S.; Fox, M.A.; Kataky, R.; Chechik, V.; O'Donoghue, A.M.C. New Blatter-type radicals from a bench-stable carbine. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tretyakov, E.; Fedyushin, P.; Bakuleva, N.; Korlyukov, A.; Dorovatovskii, P.; Gritsan, N.; Dmitriev, A.; Akyeva, A.; Syroeshkin, M.; Stass, D.; Zykin, M.; Efimov, N.; Luneau, D. Series of Fluorinated Benzimidazole-Substituted Nitronyl Nitroxides: Synthesis, Structure, Acidity, Redox Properties, and Magnetostructural Correlations. J. Org. Chem. 2022. ASAP. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedyushin, P. A.; Serykh, A. A.; Vinogradov, A. S.; Mezhenkova, T. V.; Platonov, V. E.; Nasyrova, D. I.; Samigullina, A. I.; Fedin, M. V.; Zayakin, I. A.; Tretyakov, E. V. Biradical with a polyfl uorinated terphenylene backbone. Russ. Chem. Bull., 2022, 71, 1670–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serykh, A.; Tretyakov, E.; Fedyushin, P.; Ugrak, B.; Dutova, T.; Lalov, A.; Korlyukov, A.; Akyeva, A.; Syroeshkin, M.; Bogomyakov, A.; Romanenko, G.; Artiukhova, N.; Egorov, M.; Ovcharenko, V. N-Fluoroalkylpyrazolyl-substituted Nitronyl Nitroxides. J. Mol. Struct., 2022, 1269, 133739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedyushin, P. A.; Akyeva, A. Ya.; Syroeshkin, M. A.; Rybalova, T. V.; Stass, D. V.; Korolev, V. A.; Tretyakov, E. V.; Egorov, M. P. Synthesis, structure, and properties of tert-butyl perfluorobiphenyl nitroxide. Russ. Chem. Bull., 2022, 71, 1474–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tretyakov, E. V.; Fedyushin, P. A. Polyfluorinated organic paramagnets. Russ. Chem. Bull., 2021, 70, 2298–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L. V. Politanskaya, P. A. Fedyushin, T. V. Rybalova, A. S. Bogomyakov N. B. Asanbaeva, E. V. Tretyakov. Fluorinated Organic Paramagnetic Building Blocks for Cross-Coupling Reactions. Molecules, 2020, 25, 5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurskaya, L.; Rybalova, T.; Beregovaya, I.; Zaytseva, E.; Kazantsev, M.; Tretyakov, E. Aromatic nucleophilic substitution: A case study of the interaction of a lithiated nitronyl nitroxide with polyfluorinated quinoline-N-oxides. J. Fluor. Chem., 2020, 237, 109613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedyushin, P.; Rybalova, T.; Asanbaeva, N.; Bagryanskaya, E.; Dmitriev, A.; Gritsan, N.; Kazantsev, M.; Tretyakov, E. Synthesis of Nitroxide Diradical Using a New Approach. Molecules, 2020, 25, 2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tretyakov, E.; Fedyushin, P.; Panteleeva, E.; Gurskaya, L.; Rybalova, T.; Bogomyakov, A.; Zaytseva, E.; Kazantsev, M.; Shundrina, I.; Ovcharenko, V. Aromatic SNF-Approach to Fluorinated Phenyl tert-Butyl Nitroxides. Molecules, 2019, 24, 4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedyushin, P.; Gurskaya, L.; Panteleeva, E.; Koshcheev, B.; Maksimov, A.; Rybalova, T. V.; Zaytseva, E.; Tretyakov, E. Exploration of SNF-Approach toward Functionalized Nitronyl Nitroxides. Fluorine Notes, 2019, 123(2), 7–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhivetyeva, S. I.; Zayakin, I. A.; Bagryanskaya, I. Yu.; Zaytseva, E. V.; Bagryanskaya, E. G.; Tretyakov, E. V. Interaction of a lithiated nitronyl nitroxide with polyfluorinated 1,4-naphthoquinones. Tetrahedron, 2018, 74, 3924–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedyushin, P.; Panteleeva, E.; Bagryanskaya, I.; Maryunina, K.; Inoue, K.; Stass, D.; Tretyakov, E. An approach to fluorinated phthalonitriles containing a nitronyl nitroxide or iminonitroxide moiety. J. Fluor. Chem., 2019, 217, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tretyakov, E. V.; Fedyushin, P. A.; Panteleeva, E. V.; Stass, D. V.; Bagryanskaya, I. Yu.; Beregovaya, I. V.; Bogomyakov, A. S. Substitution of a Fluorine Atom in Perfluorobenzonitrile by a Lithiated Nitronyl Nitroxide. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 4179–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potts, K.T.; Roy, S.K.; Jones, D.P. 1,2,4-Triazoles. XVII. Meso-ionic compounds. 2. Derivatives of the s-triazole series. J. Org. Chem. 1967, 32, 2245–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinides, C.P.; Koutentis, P.A.; Krassos, H.; Rawson, J.M.; Tasiopoulos, A.J. Characterization and Magnetic Properties of a “Super Stable” Radical 1,3-Diphenyl-7-trifluoromethyl-1,4-dihydro-1,2,4-benzotriazin-4-yl. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 2798–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantinides, C.P.; Berezin, A.A.; Manoli, M.; Leitus, G.M.; Bendikov, M.; Rawson, J.M.; Koutentis, P.A. Effective exchange coupling in alternating-chains of a π-extended 1,2,4-benzotriazin-4-yl. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinides, C.P.; Berezin, A.A.; Manoli, M.; Leitus, G.M.; Zissimou, G.Z.; Bendikov, M.; Rawson, J.M.; Koutentis, P.A. Structural, Magnetic, and Computational Correlations of Some Imidazolo-Fused 1,2,4-Benzotriazinyl Radicals. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 5388–5396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Miura, Y.; Yoshioka, N. Synthesis and properties of the 3-tert-butyl-7-trifluoromethyl-1,4-dihydro-1-phenyl-1,2,4-benzotriazin-4-yl radical. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 4783–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications. New York: Wiley, 2001, 2nd ed. Russ. J. Electrochem. 2002, 38, 1364–1365. [Google Scholar]
- Karecla, G.; Papagiorgis, P.; Panagi, N.; Zissimou, G.A.; Constantinides, C.P.; Koutentis, P.A.; Itskos, G.; Hayes, S.C. Emission from the stable Blatter radical. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 8604–8613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tretyakov, E.V.; Ovcharenko, V.I.; Terent'ev, A.O.; Krylov, I.B.; Magdesieva, T.V.; Mazhukin, D.G.; Gritsan, N.P. Conjugated nitroxides. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2022, 91, RCR5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tretyakov, E.V.; Petunin, P.V.; Zhivetyeva, S.I.; Gorbunov, D.E.; Gritsan, N.P.; Fedin, M.V.; Stass, D.V.; Samoilova, R.I.; Bagryanskaya, I.Yu.; Shundrina, I.K.; Bogomyakov, A.S.; Kazantsev, M.S.; Postnikov, P.S.; Trusova, M.E.; Ovcharenko, V.I. Platform for High-Spin Molecules: A Verdazyl-Nitronyl Nitroxide Triradical with Quartet Ground State. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 8164–8176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieger, C.; Neugebauer, F.A. Columnar Stacking of 1,3-Diphenyl-1,2,4-benzotriazin-4(1H)-yl Radicals. Acta Crystallogr. C 1996, 52, 3124–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubaidullin, A.T.; Buzykin, B.I.; Litvinov, I.A.; Gazetdinova, N.G. Molecular and Crystal Structure of a Superstable Free Radical, 1,3-Diphenyl-1,4-dihydro-1,2,4-benzotriazin-4-yl. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2004, 74, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, K.; Inoue, K.; Achiwa, N.; Jamali, J.B.; Krieger, C.; Neugebauer, F.A. Magnetic-properties of 1,4-dihydro-1,2,4-benzotriazin -4-yl radicals. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1994, 224, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Xie, X.; Sun, R.; Chen, H.; Li, S.; Liu, Y. Titanium-mediated cross-coupling reactions of 1,3-butadiynes with α-iminonitriles to 3-aminopyrroles: observation of an imino aza-Nazarov cyclization. Org. Chem. Front. 2014, 1, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Gao, L.; Li, H.; Sun, P.; Meng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Sun, B.; Zhou, S.; Ma, Y.; Xiong, L.; Yang, N.; Li, Y.; Li, Z. Synthesis, Insecticidal Activities, and Structure–Activity Relationship of Phenylpyrazole Derivatives Containing a Fluoro-Substituted Benzene Moiety. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 11282–11289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duling, D.R. Simulation of multiple isotropic spin trap EPR spectra. J. Magn. Reson. B 1994, 104, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, L.; Herbst-Irmer, R.; Sheldrick, G.M.; Stalke, D. Comparison of silver and molybdenum microfocus X-ray sources for single-crystal structure determination. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2015, 48, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT - Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Cryst. A 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Cryst. C 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, H.; Nishino, M.; Shigeta, Y.; Soda, T.; Kitagawa, Y.; Onishi, T.; Yoshika, Y.; Yamaguchi, K. Theoretical studies on effective spin interactions, spin alignments and macroscopic spin tunneling in polynuclear manganese and related complexes and their mesoscopic clusters. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2000, 198, 265–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soda, T.; Kitagawa, Y.; Onishi, T.; Nagao, H.; Yoshioka, Y.; Yamaguchi, K. Ab initio computations of effective exchange integrals for H–H, H–He–H and Mn2O2 complex: comparison of broken-symmetry approaches. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2000, 319, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- a) Lee, C.; Yang, W.; Parr, R.G. Development of the Colle-Salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 785–789. b) Becke, A.D. Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [CrossRef]
- Weigend, F.; Ahlrichs, R. Balanced basis sets of split valence, triple zeta valence and quadruple zeta valence quality for H to Rn: Design and assessment of accuracy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2005, 7, 3297–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimme, S.; Antony, J.; Ehrlich, S.; Krieg, H. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 154104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S. Semiempirical GGA-type density functional constructed with a long-range dispersion correction. J. Comput. Chem. 2006, 27, 1787–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigend, F. Accurate Coulomb-fitting basis sets for H to Rn. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, V.; Cossi, M. Quantum Calculation of Molecular Energies and Energy Gradients in Solution by a Conductor Solvent Model. J. Phys. Chem. A 1998, 102, 1995–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, C.; Barone, V. Toward Reliable Density Functional Methods without Adjustable Parameters: The PBE0 Model. J Chem Phys 1999, 110, 6158–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreuw, A.; Head-Gordon, M. Single-Reference ab Initio Methods for the Calculation of Excited States of Large Molecules. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 4009–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neese, F. Software update: The ORCA program system, version 4.0. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2018, 8, e1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadilenko, E.M.; Gritsan, N.P.; Tretyakov, E.V.; Fokin, S.V.; Romanenko, G.V.; Bogomyakov, A.S.; Gorbunov, D.E.; Schollmeyer, D.; Baumgarten, M.; Ovcharenko, V.I. A black-box approach to the construction of metal-radical multispin systems and analysis of their magnetic properties. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 16916–16927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
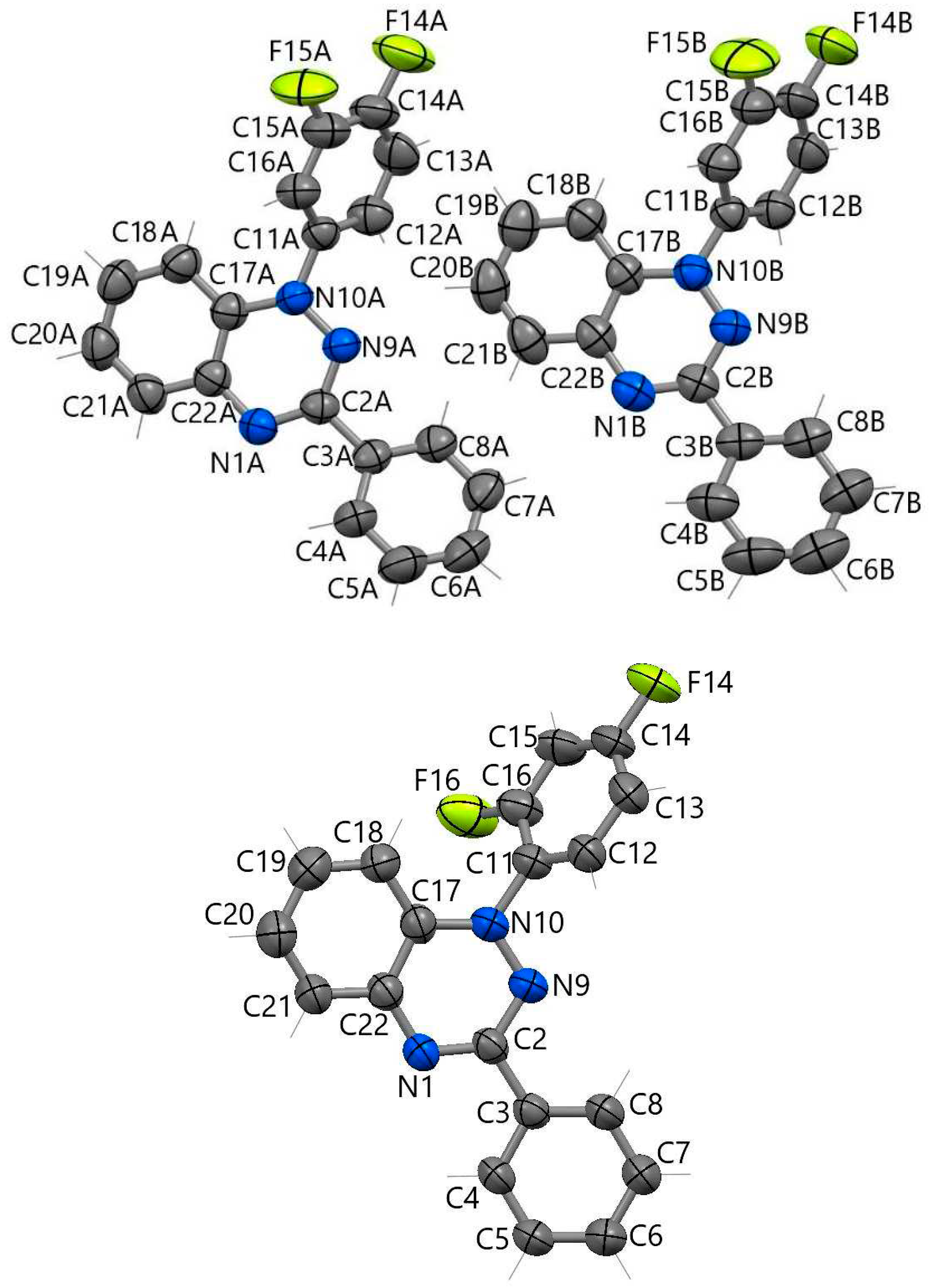
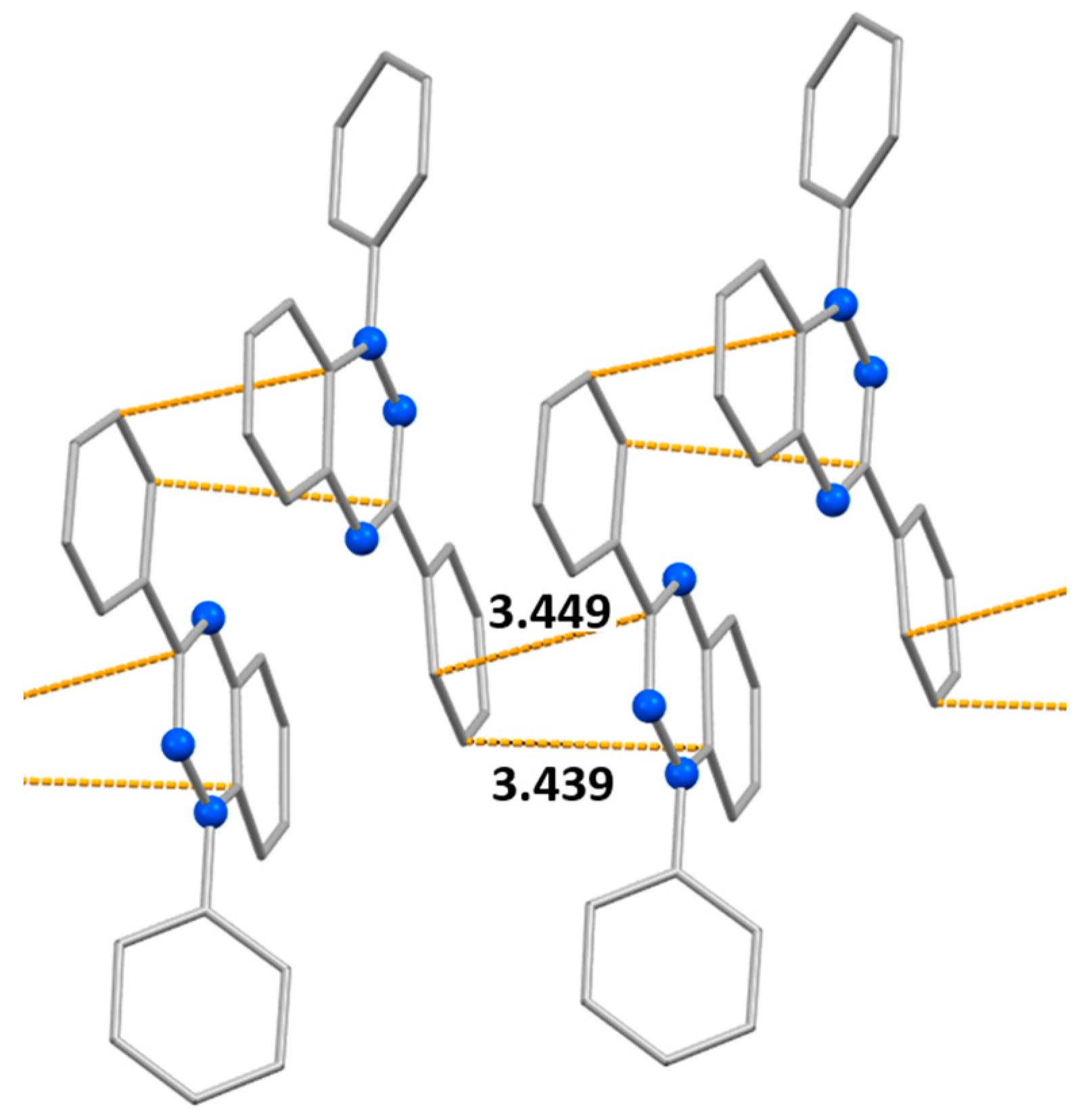
| Bond | d | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1aA | 1aB | 1b | |
| N(1A)-C(2A) | 1.330(2) | 1.332(2) | 1.333(2) |
| N(1A)-C(22A) | 1.373(2) | 1.366(2) | 1.369(2) |
| C(2A)-N(9A) | 1.332(2) | 1.333(2) | 1.337(2) |
| N(9A)-N(10A) | 1.364(2) | 1.358(2) | 1.371(2) |
| N(10A)-C(17A) | 1.386(2) | 1.389(2) | 1.385(2) |
| C(17A)-C(22A) | 1.407(2) | 1.412(2) | 1.412(2) |
| Torsion angle | ω | ||
| N(9)C(2)C(3)C(8) | -22.8(3) | 5.0(3) | 10.5(3) |
| N(9)N(10)C(11)C(12) | 51.2(2) | 52.4(2) | –58.3(2) |
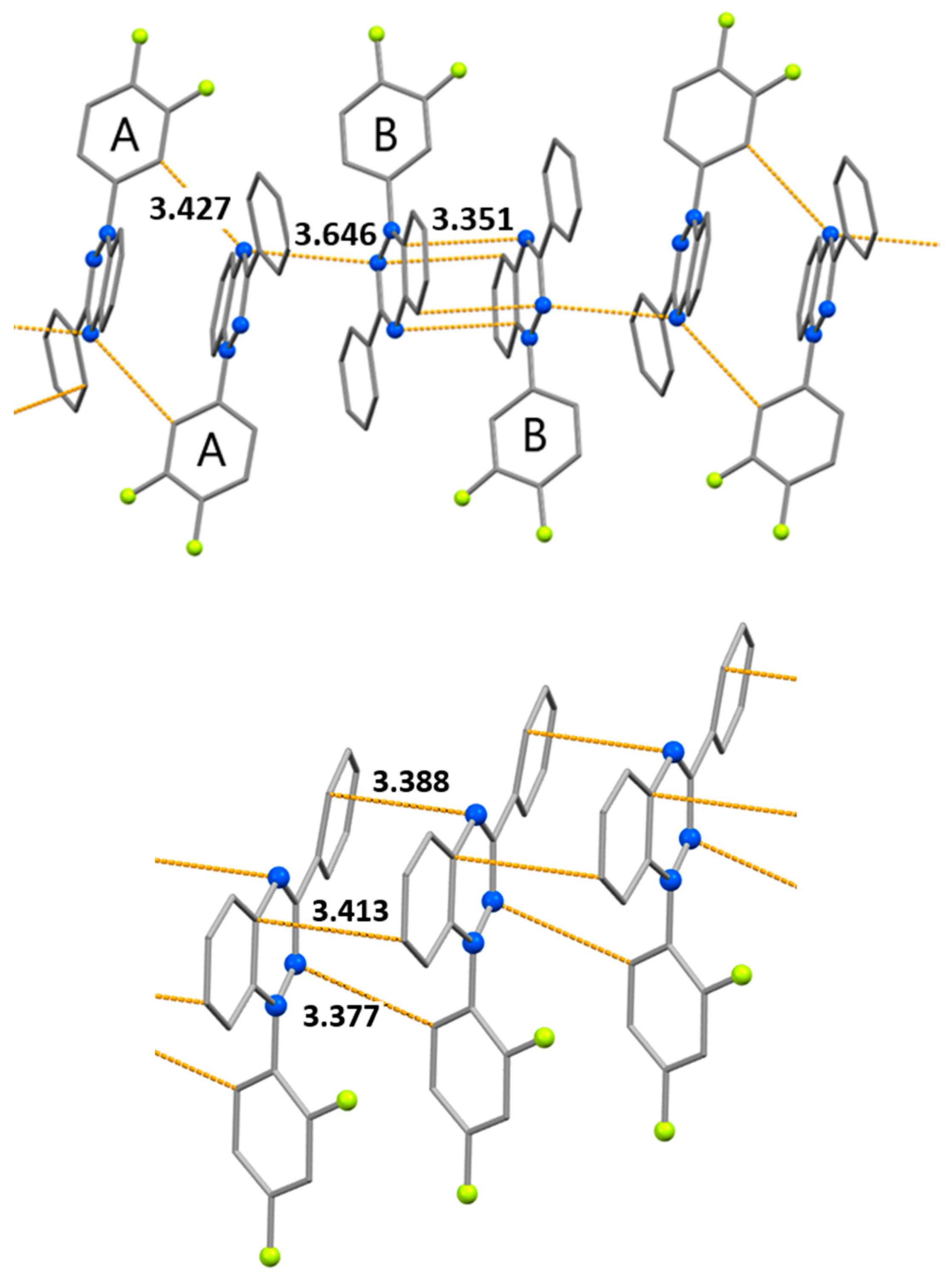
| Contact | d | ||
| N1B…C17B | 3.351(3) | ||
| N9B…C21B | 3.444(3) | ||
| N1A…C16A (N…H-C) | 3.427(3) | ||
| C4A…C12B' | 3.449(3) | ||
| N1A…N9B' | 3.646(2) | ||
| C12'…N9 (N…H-C) | 3.377(3) | ||
| N1…C4 ' | 3.388(2) | ||
| C19…C22' | 3.413(3) | ||
| N(9)…N(10') | 3.784(2) | ||
| Radical | 1a | 1b | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | J1aA…1aA | J1aA…1aB | J1aB…1aB | J1b…1b |
| Jcalc, cm-1 | −116.6 | −14.3 | −70.5 | −86.0 |
| Jcalc/kB, K | −167.8 | −20.6 | −101.4 | −123.7 |
| Jexp/kB, K | –292 ± 10 | − | − | –222 ± 17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





