Submitted:
26 July 2023
Posted:
28 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
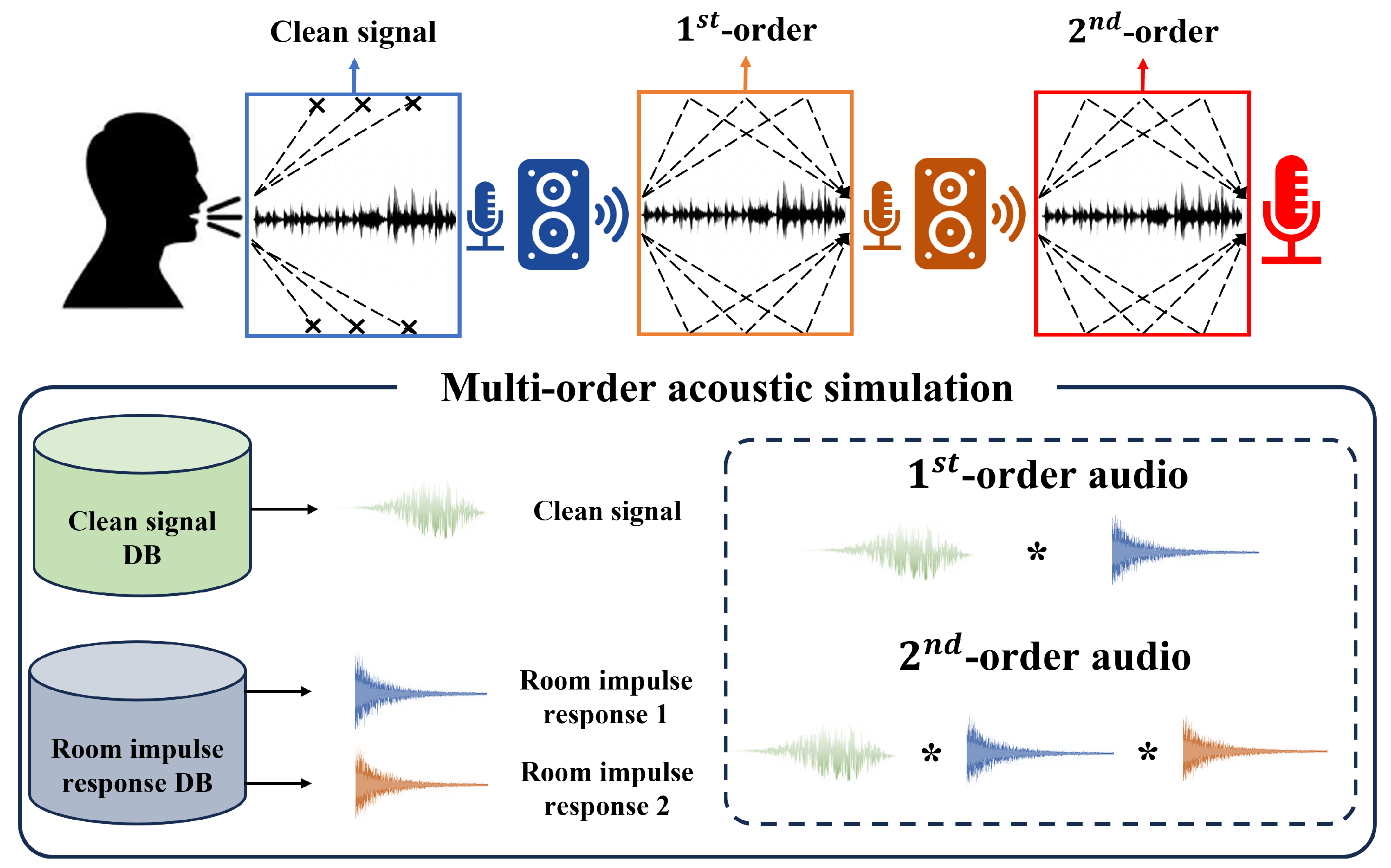
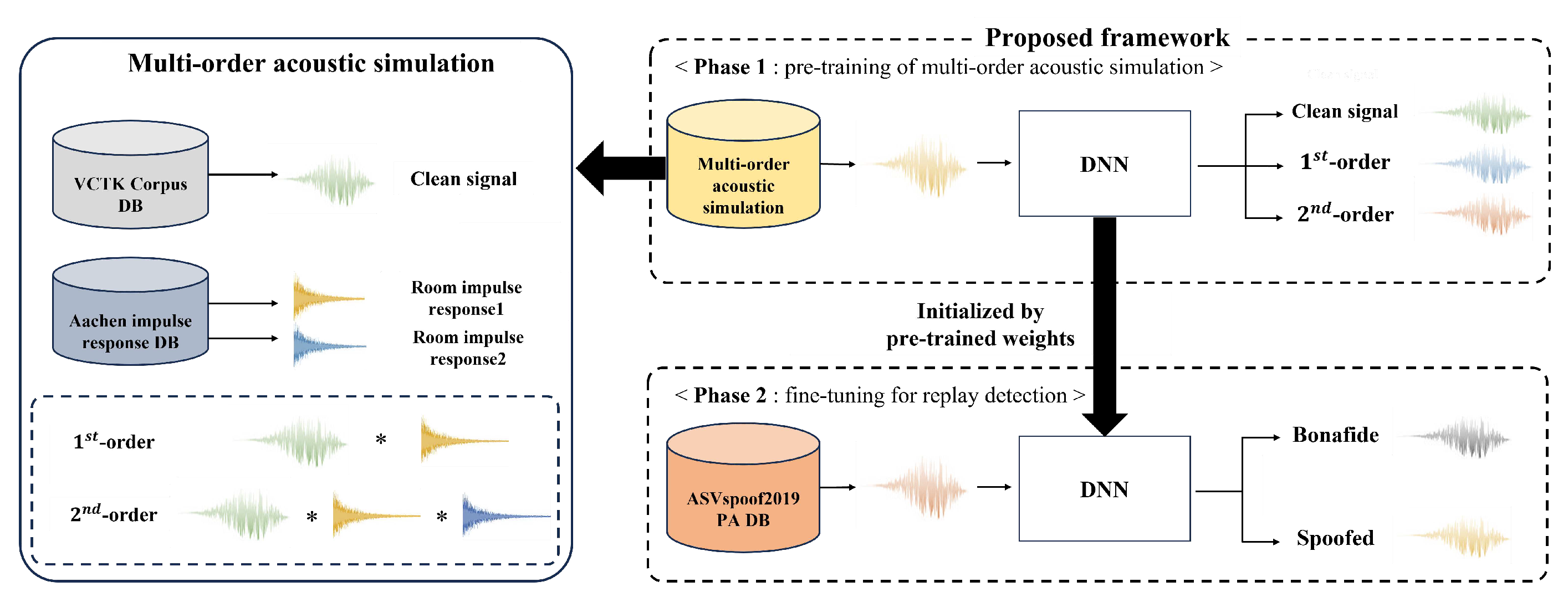
2. Multi-Order Acoustic Simulation
3. Replay Voice Spoofing Detection Framework
4. Experimental Setup
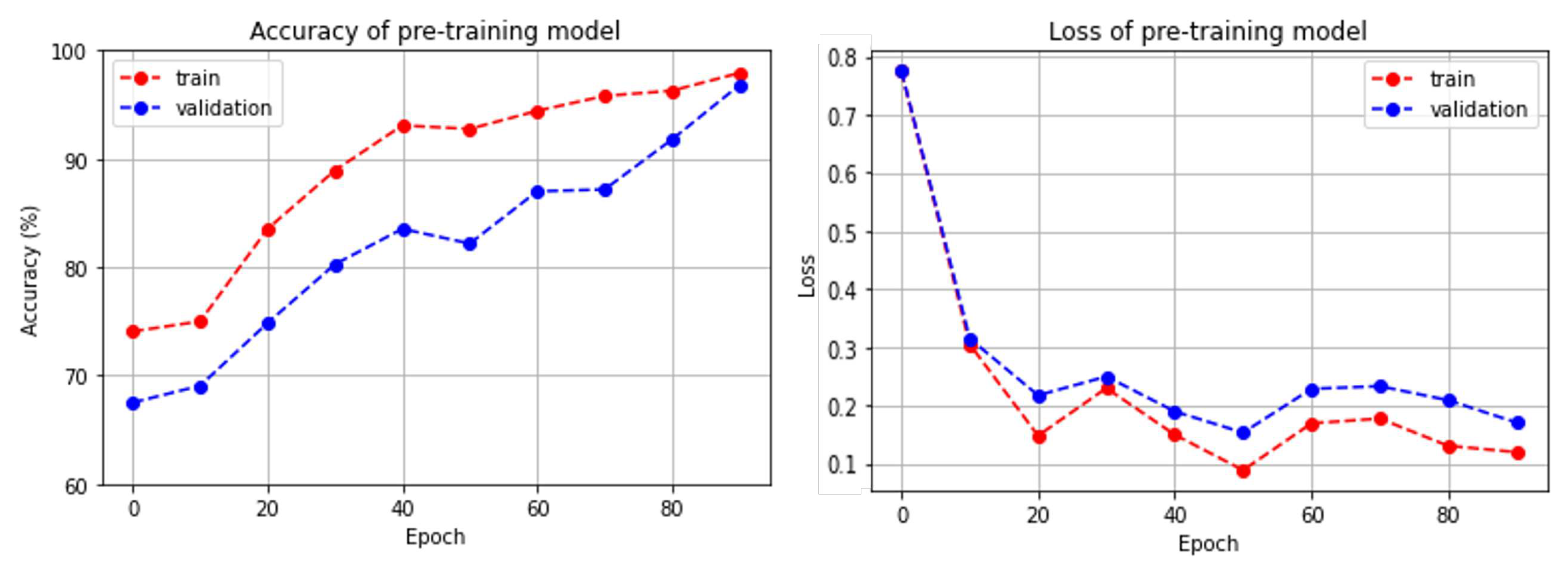
5. Result
6. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- T. Kinnunen, M. Sahidullah, H. Delgado, M. Todisco N. Evans, J. Yamagishi, and K. A. Lee, “The ASVspoof 2017 challenge: Assessing the limits of replay spoofing attack detection,” in Proc. Interspeech, pp. 2–6, Aug. 2017.
- M. Wester, Z. Wu, and J. Yamagishi, “Human vs machine spoofing detection on wideband and narrowband data,” in Proc. Interspeech, pp. 2047-2051, Sep. 2015. [CrossRef]
- R. Rahmeni, A. B. Aicha, and Y. B. Ayed, “Voice spoofing detection based on acoustic and glottal flow features using conventional machine learning techniques,” Multimedia Tools and Applications, vol. 81, pp. 1–25, Sep. 2022.
- H. Liang, X. Lin, Q. Zhang, and X. Kang, “Recognition of spoofed voice using convolutional neural networks,” in Proc. IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP), pp. 293–297, Nov. 2017. [CrossRef]
- A. Gomez-Alanis, A. M. Peinado, J. A. Gonzalez, and A. M. Gomez, "A Gated recurrent convolutional neural network for robust spoofing detection," IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, vol. 27, no. 12, pp. 1985-1999, Dec. 2019.
- Z. Wu, R. K. Das, J. Yang, and H. Li, “Light convolutional neural network with feature genuinization for detection of synthetic speech attacks,” in Proc. Interspeech, pp. 1101–1105, Oct. 2021.
- X. Cheng, M. Xu, and T. F. Zheng, “Replay detection using CQT based modified group delay feature and ResNeWt network in ASVspoof 2019,” in Proc. Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC), pp. 540–545, Nov. 2019.
- W. Cai, H. Wu, D. Cai, and M. Li, “The DKU replay detection system for the ASVspoof 2019 challenge: On data augmentation, feature representation, classification, and fusion,” in Proc. Interspeech, pp. 1023–1027, Sep. 2019.
- G. Lavrentyeva, S. Novoselov, A. Tseren, M. Volkova, A. Gorlanov, and A. Kozlov, “STC antispoofing systems for the ASVspoof2019 challenge,” in Proc. Interspeech, pp. 1033–1037, Sep. 2019.
- C. I. Lai, N. Chen, J. Villalba, and N. Dehak, “ASSERT: Anti-spoofing with squeeze-excitation and residual networks,” in Proc. Interspeech, pp. 1013–1017, Sep. 2019. [CrossRef]
- [11] A. Nautsch, X.Wang, N. Evans, T. H. Kinnunen, V. Vestman, M. Todisco, H. Delgado, M. Sahidullah, J. Yanmagishi, and K. A. Lee,, “ASVspoof 2019: Future horizons in spoofed and fake audio detection,” in Proc. Interspeech, pp. 1008–1012, Sep. 2019.
- X. Wang, M. Todisco, V. Vestman, M. Sahidullah, H. Delgado,A. Nautsch, J. Yamagishi, N. Evans, T. Kinnunen, and K. A. Lee, “ASVspoof 2019: A large-scale public database of synthetic, converted and replayed speech,” Computer Speech & Language (CSL), vol. 64, pp. 101-114, Nov. 2020.
- A. Javed, K. M. Malik, H. Malik, and A. Irtaza, “Voice spoofing detector: A unified anti-spoofing framework,” Computer Speech & Language (CSL), vol. 198, July 2022. [CrossRef]
- R. Baumann, K. M. Malik, A. Javed, A. Ball, B. Kujawa, and H. Malik, “Voice spoofing detection corpus for single and multi-order audio replays,” Computer Speech & Language (CSL). vol. 65, Jan. 2021.
- H. Salman, A. Ilyas, L. Engstrom, A. Kapoor, and A. Madry, "Do adversarially robust ImageNet models transfer better?," in Proc. The 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing System (NeurIps), pp. 3533-3545, Dec. 2020.
- B. Recht, R. Roelofs, L. Schmidt, and V. Shankar, “Do ImageNet classifiers generalize to ImageNet?,” in Proc. 36th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), pp. 5389–5400, Feb. 2019.
- J. S. Chung, A. Nagrani, and A. Zisserman, “Voxceleb2: Deep speaker recognition,” in Proc. Interspeech, pp. 1086–1090, Sep. 2018. [CrossRef]
- H. Shim, H. Heo, J. Jung, and H. Yu, “Self-supervised pre-training with acoustic configurations for replay spoofing detection,” in Proc. Interspeech, pp. 1091-1095, Oct. 2019.
- C. Veaux, J. Yamagishi, and K. MacDonald, “CSTR VCTK: English multi-speaker corpus for CSTR voice cloning toolkit,” University of Edinburgh. The Centre for Speech Technology Research (CSTR), Nov. 2019.
- M. Jeub, M. Schafer, and P. Vary, "A binaural room impulse response database for the evaluation of dereverberation algorithms," in Proc. 16th International Conference on Digital Signal Processing (ICDSP), pp. 1-5, July 2009.
- K. Kinoshita, M. Delcroix, T. Yoshioka, T. Nakatani, A. Sehr, W. Kellermann, and R. Maas, “The reverb challenge: A common evaluation framework for dereverberation and recognition of reverberant speech,” in Proc. IEEE Workshop on Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics (WASPAA), pp. 1–4, Oct. 2013.
- J. B. Allen and D. A. Berkley, “Image method for efficiently simulating small-room acoustics,” The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, vol. 65, no. 4, pp. 943–950, Apr. 1979. [CrossRef]
- A. Ratnarajah, S. X. Zhang, M. Yu, Z. Tang, D. Manocha, and D. Yu, “FAST-RIR: Fast neural diffuse room impulse response generator,” in Proc. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 571–575, May 2022.
- E. Habets, “Room impulse response generator,” Technical Report, Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, Sep. 2010.
- K. He, X. Zhang, S. Ren, and J. Sun, “Deep residual learning for image recognition,” in Proc. IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference (CVPR), pp. 770-778, June 2016. [CrossRef]
- D. P. Kingma and J. Ba, “Adam: A method for stochastic optimization,” in Proc. International Conference for Learning Representations (ICLR), vol. 8, pp. 1-15, July 2015.
- J. W. Cooley, P. A. W. Lewis, and P. D. Welch, "The fast Fourier transform and its applications," IEEE Transactions on Education, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 27-34, Mar. 1969. [CrossRef]

| Dataset | Type | Dataset for pre-training model validation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clean Signal | 1st-order | 2nd-order | ||
| VCTK Aachen | Validation | 29,365 | 29,339 | 29,554 |
| Type | Model | Accuracy(%) |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-training | Resnet34 | 98.76% |
| Dataset | System | With Pre-training | Fine-tuning layer | Accuracy(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASVspoof2019 PA |
Conventional | - | All layers | 92.94 |
| Proposed | √ | FC | 88.6 | |
| √ | Block 4 + FC | 93.7 | ||
| √ | Block 3, 4 + FC | 96.2 | ||
| √ | Block 2, 3, 4 + FC | 97.08 | ||
| √ | Block 1, 2, 3, 4 + FC | 98.16 | ||
| √ | All layers | 98.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





