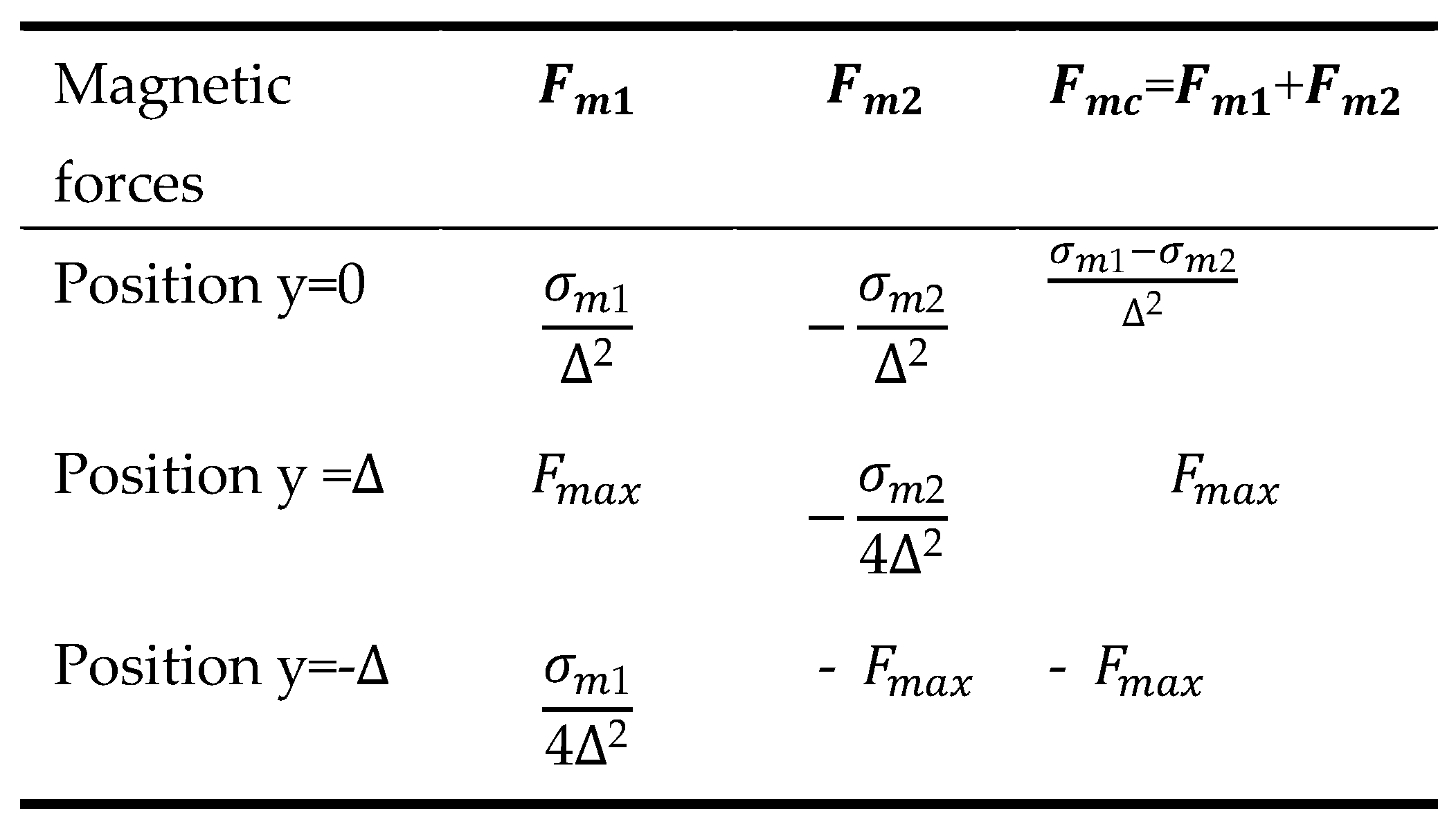1. Introduction
Nowadays in the context of
COVID-19, wearable IOT devices play a crucial rule in telemedicine since they can reduce risks of infections by remote assess of human vital signs. The current commercial model of wearable IOT devices are powered by battery technology and it has been recognized that there is undeniable need of energy requirement of ambulatory devices to be addressed [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6]. Furthermore, wearable devices are embedded systems having no access to charging source for their battery, which causes discontinuities to the monitoring process. In this regard, continuous monitoring of health data remains a considerable challenge for wearable IOT devices. This is despite the fact that battery technology has gone through considerable research and improvement [
7].The concern is to achieve both portability(smallest size) and operating time(back up time). Analog integrated circuits and low power microcontrollers (MCUs) are available for lowering the power required by wearable devices. But achieving low power demand by leveraging most of the latest design technologies and without enhancing power management wouldn’t be efficient. There have been undertakings to develop IoT devices with low power demand in an attempt to improve the monitoring time, such as ECG data compression methods developed in [
3,
4,
5], which uses Fourier and wavelet transforms for compressing ECG signal and reduce power required for transmission. Online dictionaries based approach presented in [
3] further extends the compression algorithms to other biosignals such as respiratory rates (RESP) and photo-plethysmographic(PPG) and quantitatively assesses the compression, reconstruction and energy consumption performance of different schemes. Even though signal compression approaches can considerably lower energy demand for transmission, bio-signal quality and precision after compression still remains an open question. However, harvesting devices generating electric energy from environment through direct energy conversion for biomedical devices has proven to be an effective alternative [
8,
9,
10], which do not alter health data. Intensive studies of power harvester using human body motion to power biomedical sensors nodes have been carried out by Paulo & Gaspar in 2010 [
11] and Jaeseok & all in 2011 [
12]. Many researches have focused on remote heart beat rate monitoring and some commercial devices powered by battery technology are available [
1] and [
20,
21,
22].
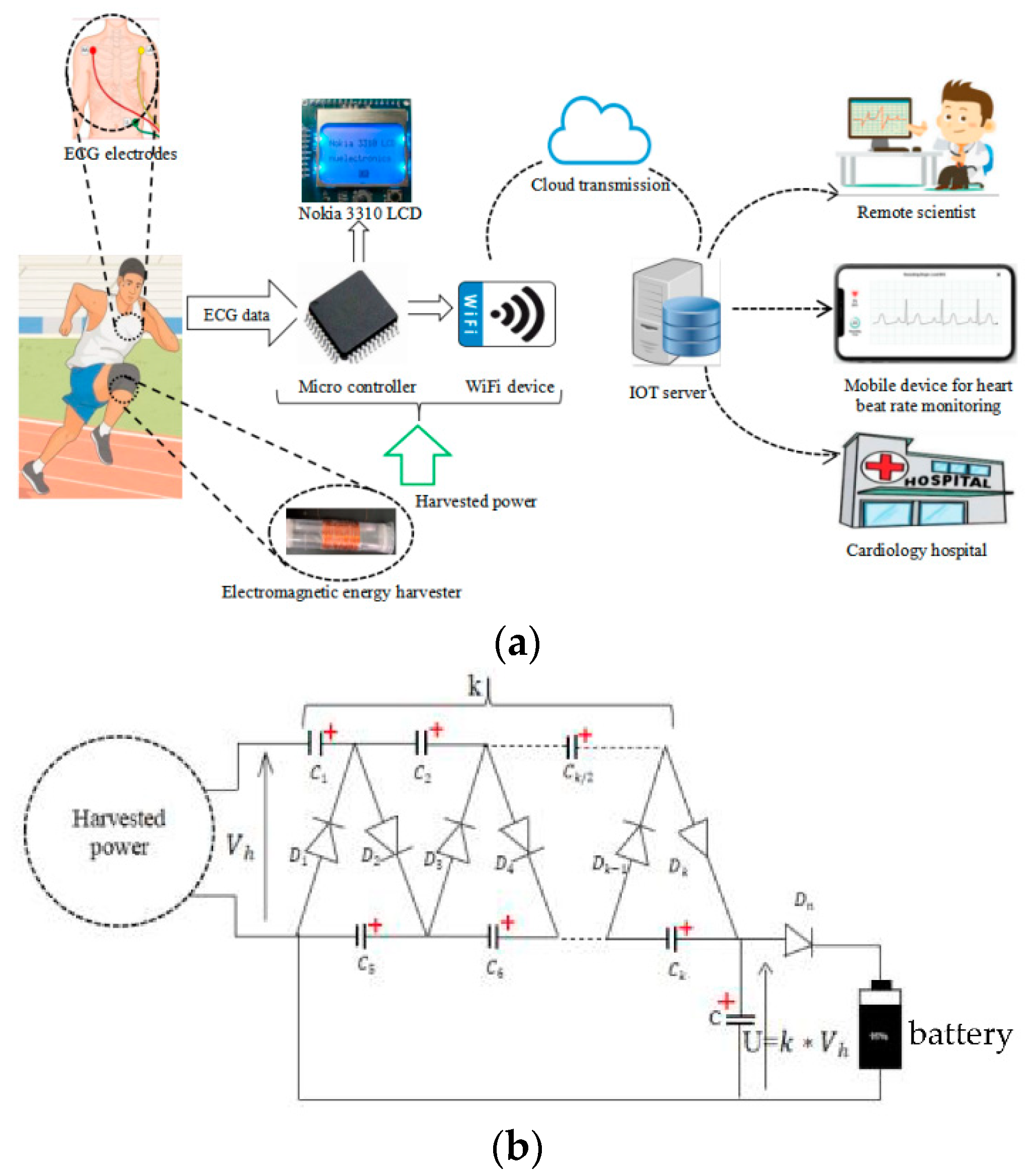
This article presents an IOT based heart beat rate monitoring device, which is powered by battery and sustained by human kinetic energy harvester for improving the monitoring time. The ECG device is a stress or exercise type, which can continuously monitor the heart beat rate of patients during normal daily activities such as walking, running and jumping. The experimental prototype in (
Figure 15a) monitors heart beat rate with electrocardiogram electrodes(AD8232) in (
Figure 3), the data are processed with micro-controller (
Figure 1) and sent to the IOT server through WIFI serial transceiver device (ESP8266) in (
Figure 2). This research makes use of Matlab server which is accessible by creating a personal space for storage on cloud. The heart beat rate can be accessed by any mobile device, cardiology hospital or any other off site scientist. Moreover, it is essential to improve the monitoring time of the device, enhance the device by harvester to supply perpetual energy. This function is assumed by electromagnetic energy harvester which collects vibration energy from human motion and transform into electricity. Due to nonlinear interaction force of the magnets, the dynamic equation illustrating the motion of electromagnetic harvester has inverse quadratic nonlinearity, which relates the magnetic force to the separation distance between the magnets. The same approach was described by other authors [
13,
14].
This study considers the case of electromechanical damping, the quadratic nonlinear force of the magnet is approximated in this research using MacLaurin expansion, which enables to provide an exact solution to the dynamic equation using classical methods for dynamic equations [
16], and find the suitable parameters for the harvester. A typical numerical application is done in Matlab and ODE 45 solver to verify the effectiveness of this method.(
Figure 4b) shows the bridge rectifier and voltage multiplier, which is made of low power switches(1N4001) and capacitors. The battery is used for backing up power with a total charge capacity of
. The whole scenario is illustrated in (
Figure 4a).
2. Architecture of IOT Based ECG Monitoring Device Powered by Energy Harvester
In this section, the architecture of IOT heart beat rate monitoring device with energy harvesting system is presented, which enable long-term monitoring of outpatients living with unstable health conditions and necessitating continuous monitoring. As illustrated in (
Figure 4a), the device consists of five typical parts:
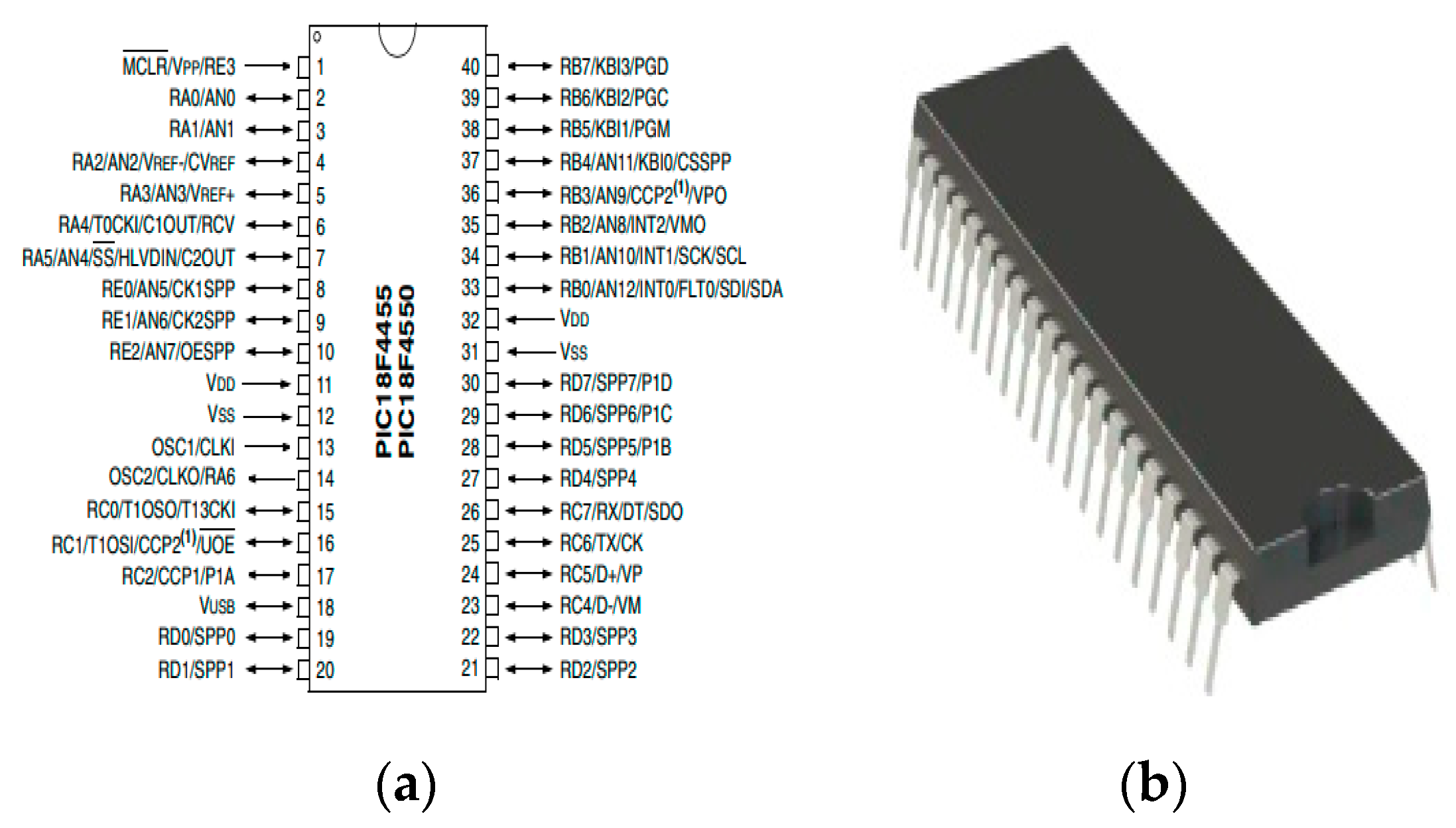
The microcontroller is used to connect and coordinate all components(Wi-Fi device, Display and ECG electrodes). ECG data and configuration data can be stored in the flash memory. Microcontroller is also used for transmitting AT commands to the Wi-Fi serial transceiver ESP8266. The microcontroller used is PIC18F4550, which is a High end 8bits microcontroller developed by Microchip Technology Inc, a publicly-listed American corporation. It is one of the most available and low cost micro-controller (nearly 2.21USD). Compared to other Mid-range microcontrollers, It has serial communication pins (PORT D), analog to digital conversion pins(PORT A), high computational performance, high endurance and enhanced flash program memory. PIC18F4550 has relatively low power consumption. In fact, when cocking the controller by timer or any internal oscillator, power consumption can be reduced for up to 90% during execution of code. Taking into account the power requirements for wearable devices, PIC18F4550 is one of the most reliable solution for achieving lowest power consumption. (
Figure 1) below shows pin out diagram (a) and physical model (b) of PIC18F4550.
- ■
IOT Server
IOT data server is a host computer, it’s a high reliable computer with non-programming data integration software. It’s used for health data collection, process, saving, notice and sharing with remote scientists. This experiment makes uses of an existing server, which is Matlab server available at “
https://thingspeak.com/” by creating a personal space for online data storage and retrieval.
Figure 1.
PIC18F4550, Pin out diagram (a) & physical model (b).
Figure 1.
PIC18F4550, Pin out diagram (a) & physical model (b).
- ■
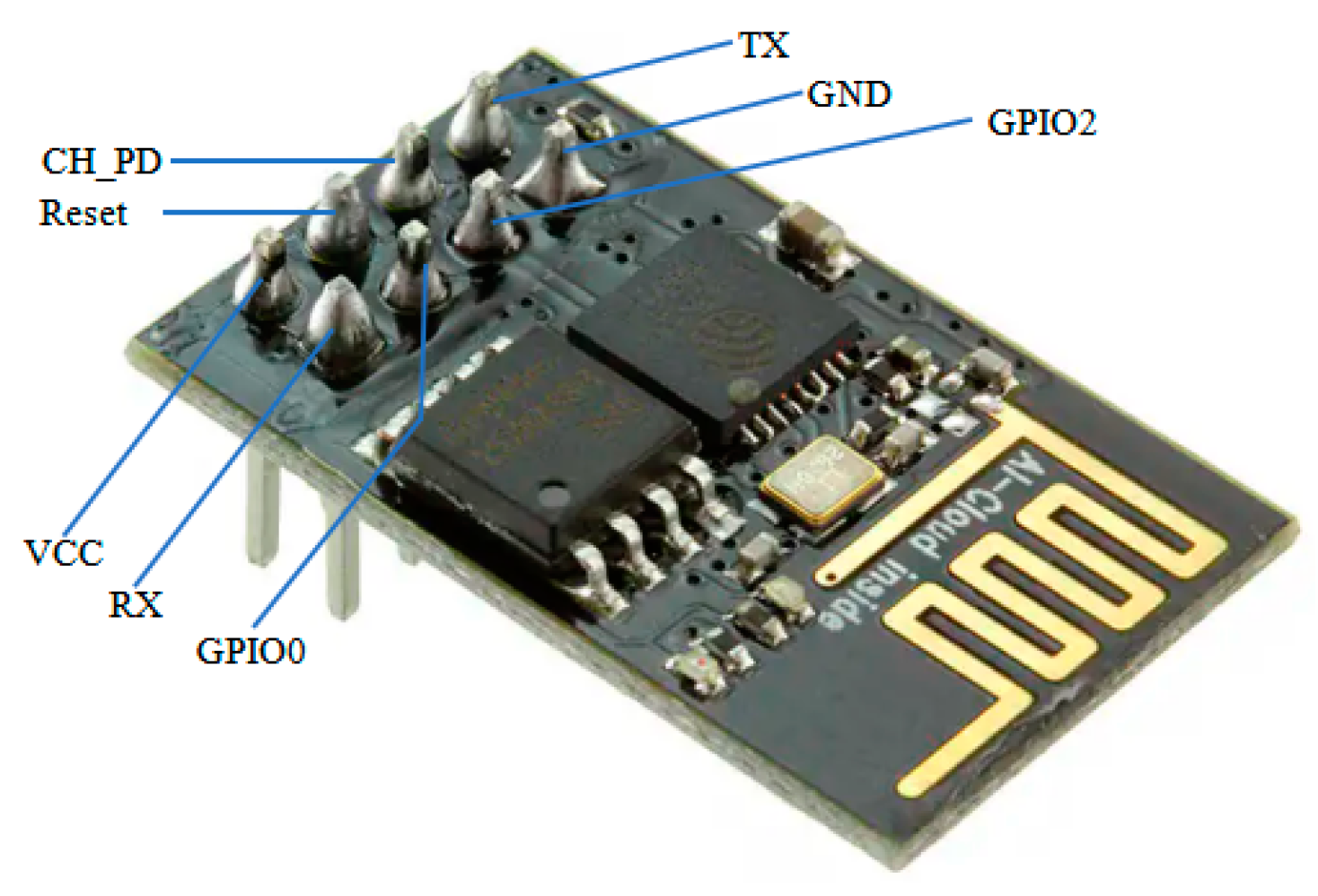
Wi-Fi serial transceiver module(ESP8266)
The chip was developed by Expressif Systems Shanghai Co Ltd, a public multinational, fabless semiconductor company with head office in Shanghai-China. It allows micro-controllers to connect to a Wi-Fi network and make simple TCP/IP connections using Hayes-style commands. In this study, It’s used for interfacing microcontroller and IOT server. In fact, Wi-Fi device receives health data from microcontroller in the form of digital signal and transmit it to the IOT server which reconstitute health data into analog signal. The main advantage of Wi-Fi serial transceiver ESP8266 over other existing wireless technology is its embedded wireless technology that is web friendly with no use of shield or any peripherals. It is relatively low cost (nearly 1USD) and low power consumption(, to ). Two pins TX and RX are used for interfacing with serial communication pins of PIC18F4550 microcontroller.
Figure 2.
Wi-Fi serial transceiver module.
Figure 2.
Wi-Fi serial transceiver module.
- ■
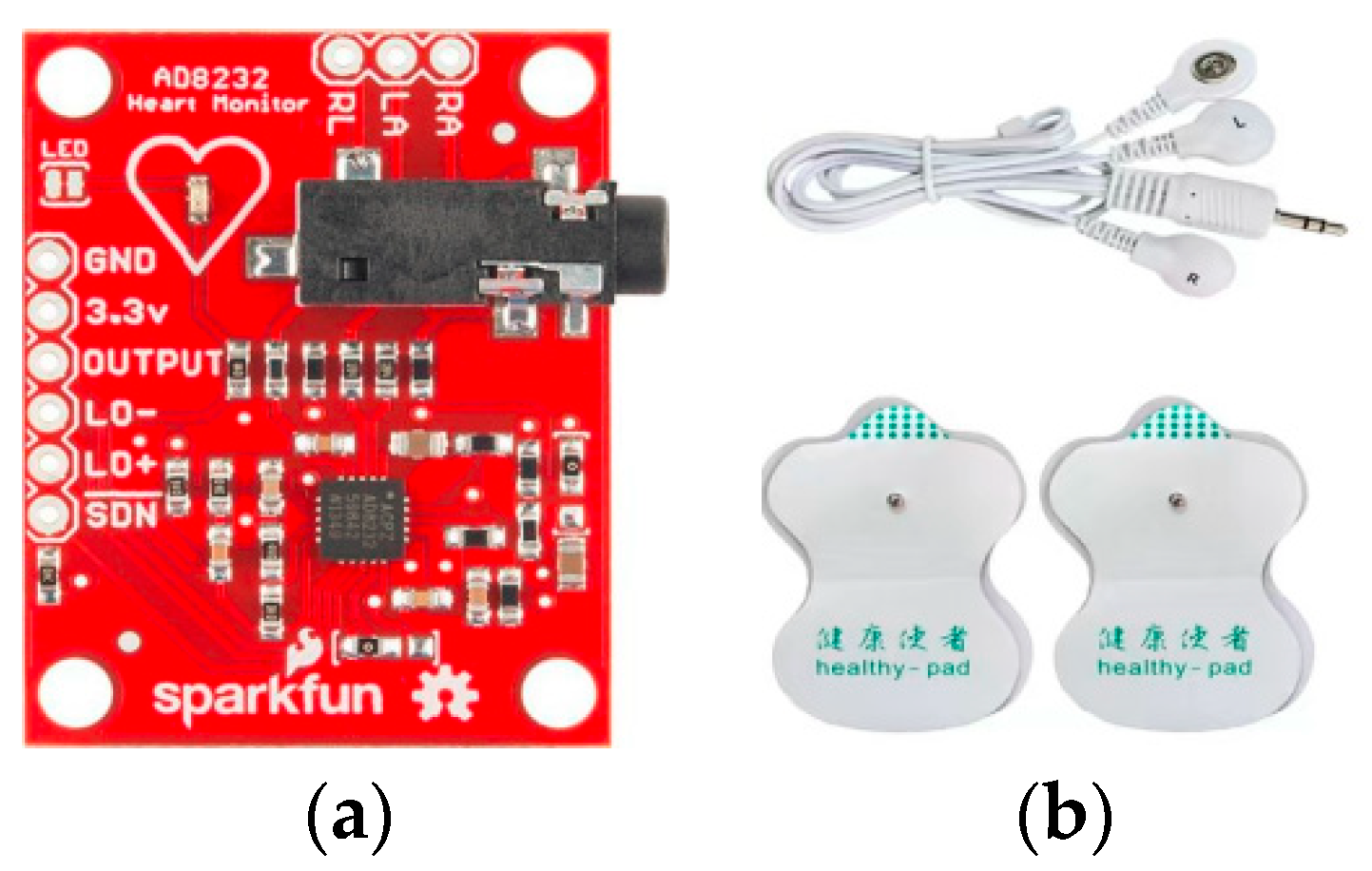
Heart beat rate sensor (AD8232)
AD8232 is a cost-effective ECG analog sensor(4.14USD). compared to other types of heart beat rate sensors technology, AD8232 has an integrated signal conditioning block made of high-pass filter for eliminating artifacts and electrodes half-cell potential. It requires ultra low power for operation(to and), it is a suitable solution for wearable Applications.
Figure 3.
Heart beat rate sensor (AD8232), Pins out (a) & electrodes (b).
Figure 3.
Heart beat rate sensor (AD8232), Pins out (a) & electrodes (b).
- ■
Electromagnetic energy harvester
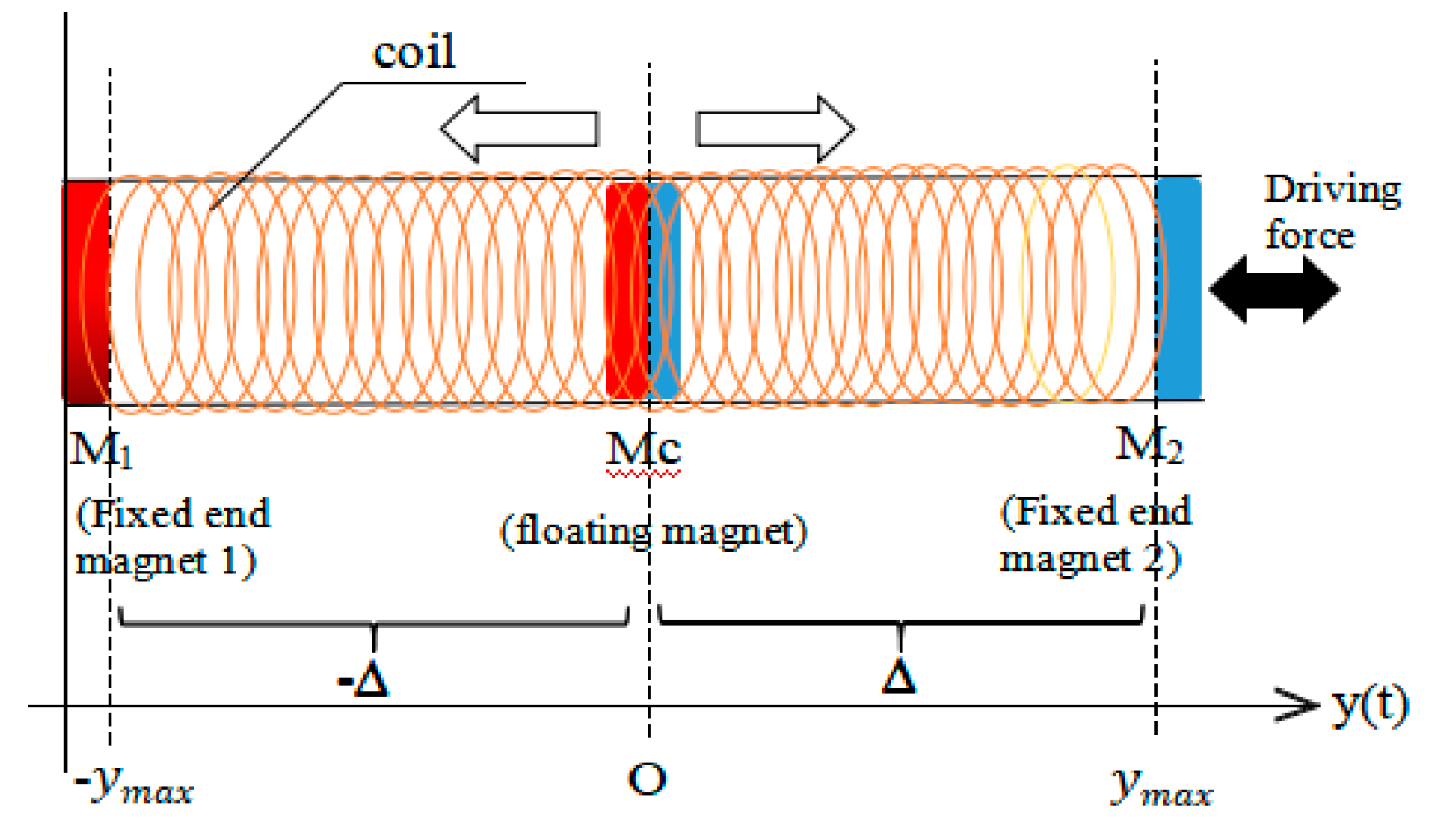
EMH is made of coil-magnet, it collects vibration energy from human daily activities such as walking, running and jumping to generate electricity. It consists of two end magnets and a middle magnet with each pole facing the opposite pole of each end magnet. The coil is wrapped around a cylindrical tube inside which the magnets are aligned. The harvester is attached to the lower extremity of the body as illustrated in (
Figure 4a). Human motion induces the displacement of the central magnet of the harvester, which causes changes on the magnetic flux around the coil and generates electricity based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. The physical model of harvester is presented in (
Figure 7). The voltage multiplier and rectifier in (
Figure 4b) is made of ultra-low power electronic switches and electrolytic capacitors. It’s designed to get a multiplier ratio k=16, It’s used for rectifying the power from harvester and adapt the harvested voltage to the battery voltage for charging. Both first switches
D1 and
D2 with capacitor
C1 form the first Schenkel Doubler [
19], which charge the capacitor
C5 at a maximum value 2*
Vhmax.
D3 and
D4 with capacitor
C2 form the second doubler, charging the capacitor
C6 at a maximum value 4*
Vhmax.
Dk−1 and
Dk with capacitor
Ck/2 form the last doubler, charging the capacitor
Ck at a maximum value k ∗
Vhmax. The capacitor
C is used for filtering the multiplied voltage and the voltage across the capacitor
U =
k ∗
Vh is used for charging the battery. The switch
Dn limits reverse current from battery. The harvested power is used for charging the battery of wearable device and improves the monitoring time.
Electronic design of the whole experimental setup including (Microcontroller, Heart beat rate sensor, Nokia LCD, Wi-Fi serial transceiver and power conditioning for harvested energy) is first made in ISIS professional software, “C” program is used for interfacing with ISIS professional software and perform virtual simulation before manufacturing. ARES software is used to design the printed circuit board (PCB). Pickit 3 device is used for transferring the program to the experimental prototype. (
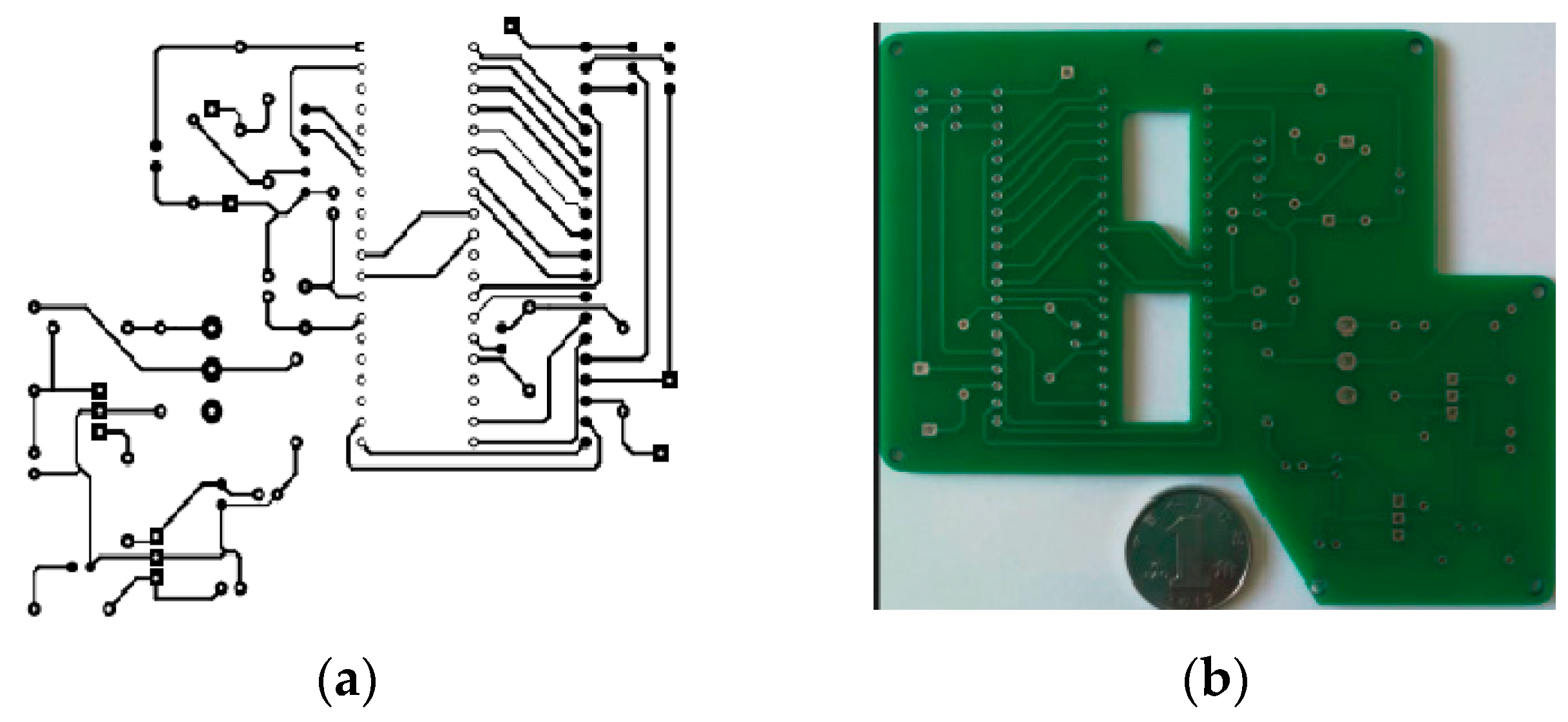
Figure 5) below shows the designed PCB board and the printed board.
Figure 4.
Architecture of IOT based ECG monitoring device powered by energy harvester (a), Voltage multiplier and rectifier (b).
Figure 4.
Architecture of IOT based ECG monitoring device powered by energy harvester (a), Voltage multiplier and rectifier (b).
Figure 5.
Printed circuit board for IOT based heart rate monitoring device: designed board (a), manufactured board (b).
Figure 5.
Printed circuit board for IOT based heart rate monitoring device: designed board (a), manufactured board (b).
3. Dynamic Analysis of electromagnetic energy harvester
In this section, a special oscillating system is studied, which consists of two fixed end magnets and a central floating magnet as illustrated in (
Figure 7), the central magnet is oriented for repulsion, provoking non linear magnetic field inside which appear different types of oscillations of the central magnet. The magnet body is subjected to the nonlinear magnetic field of the permanent magnets which has inverse quadratic dependence on distance.
The following assumptions hold with this study:
- -
The magnetic field produced by permanent magnets is non-conservative and there is loss of energy in the magnetic interaction due to electromechanical damping.
- -
The oscillations start by applying an initial force on the system.
Based on these assumptions, the law of motion for general case of study are found.
The ideal expression of magnetic force is considered in this study, the well known classical expression of magnetic force is [
17,
18]:
where, F
m is the magnetic force, σ
m is magnetic constant related to the strength of the magnet, y is the distance between magnets, Δ is the change of the distance between magnets.
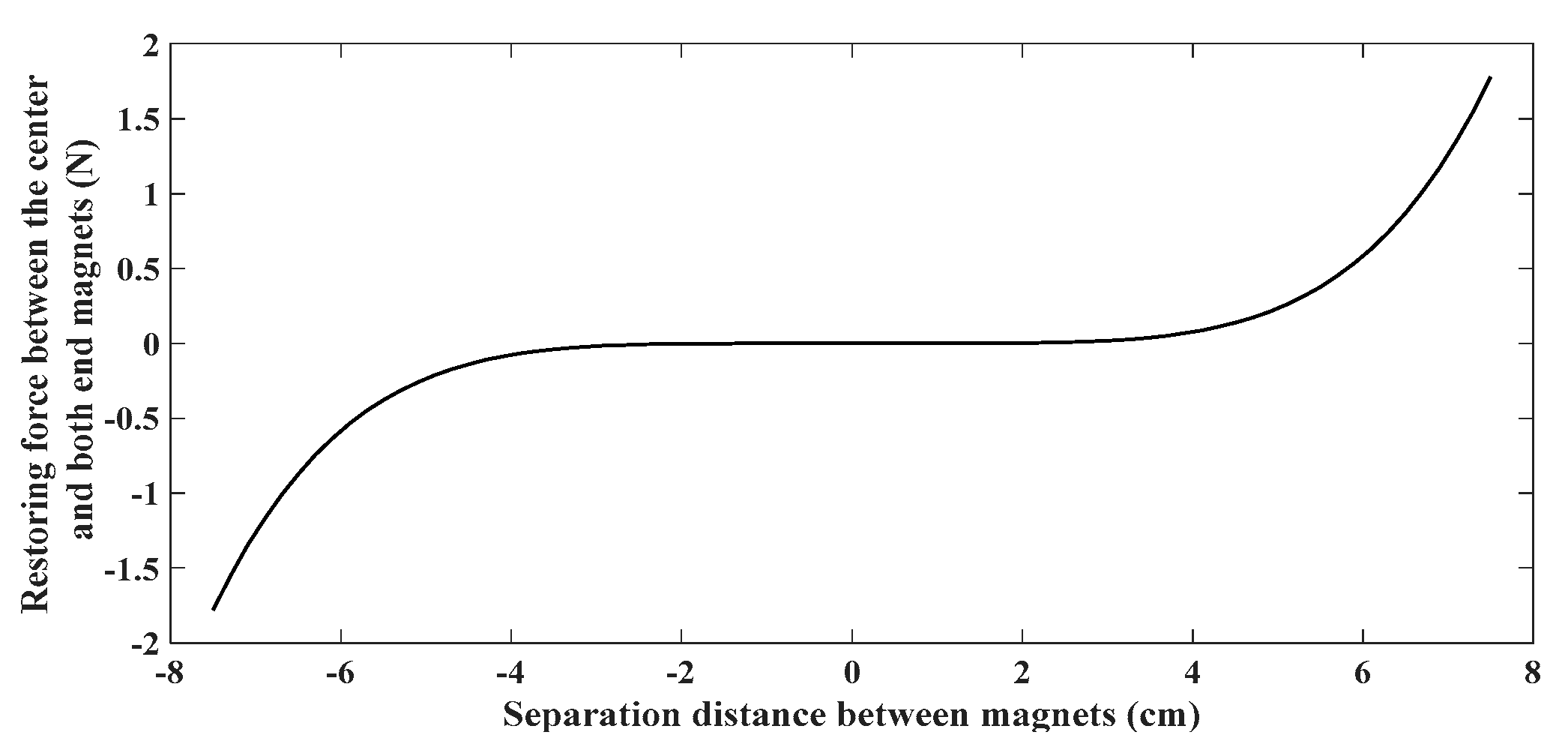
The maximum value of magnetic force occurs when the central magnet is near both end magnets. The relation between the force acting on the central magnet and the displacement is shown in the below Table I.
Figure 6 illustrates the influence of restoring force on the displacement of center magnet, the magnetic force is highest near both ends magnets.
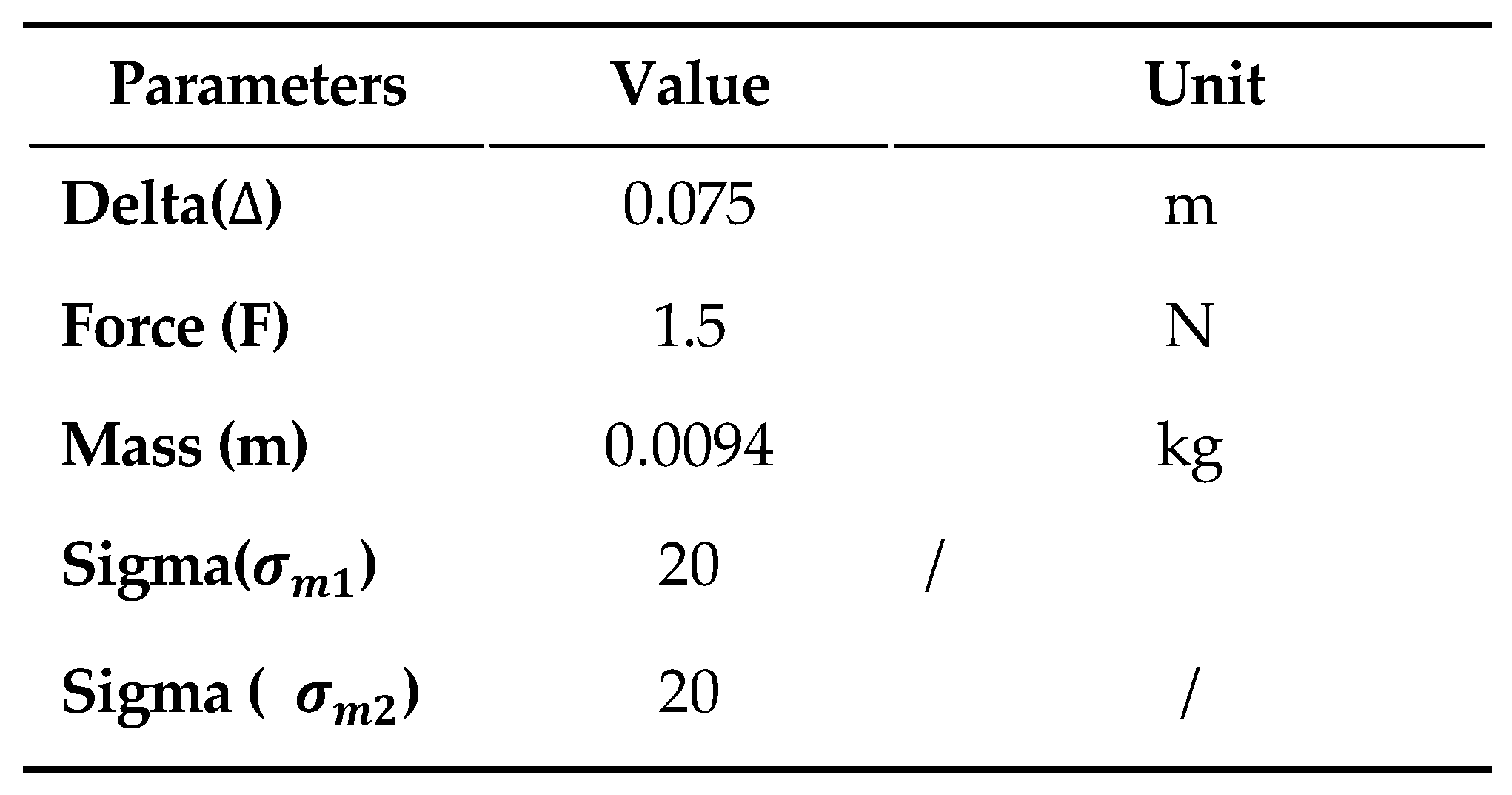
Table I. MAGNETIC FORCE VS MAGNET DISPLACEMENT.
Table I. MAGNETIC FORCE VS MAGNET DISPLACEMENT.
The implied dynamic equation of the harvester is:
where, c is electromechanical damping constant, m is the mass of the floating magnet,
and
are constants related to the strength of magnet 1 and 2 respectively.
Figure 7.
Physical model of electromagnetic harvester.
Figure 7.
Physical model of electromagnetic harvester.
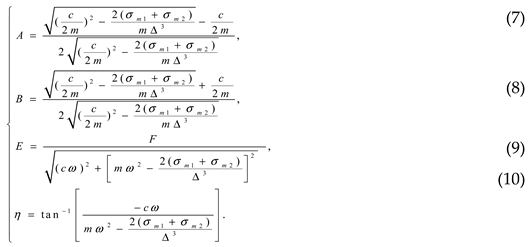
The magnetic force in (2)(2) is linearised by MacLaurin expansion to the first order and it is gotten:
Substituting (3) into (2)(2) , the corresponding dynamic equation for the harvester is gotten in (4),
The solution to the differential equation (4) is sufficiently investigated in Theory of Vibrations with Application book [
15] and could be expressed as:
where,
is homogeneous solution and
stands for particular solution.
After determining the particular solution for
y(0)=1 and
y’(0)=0, the final solution for (4). is given in (6).
where,
Equation (9) can be expressed in non dimensional form as:
where,
4. Dynamic Simulation of Electromagnetic Energy Harvester
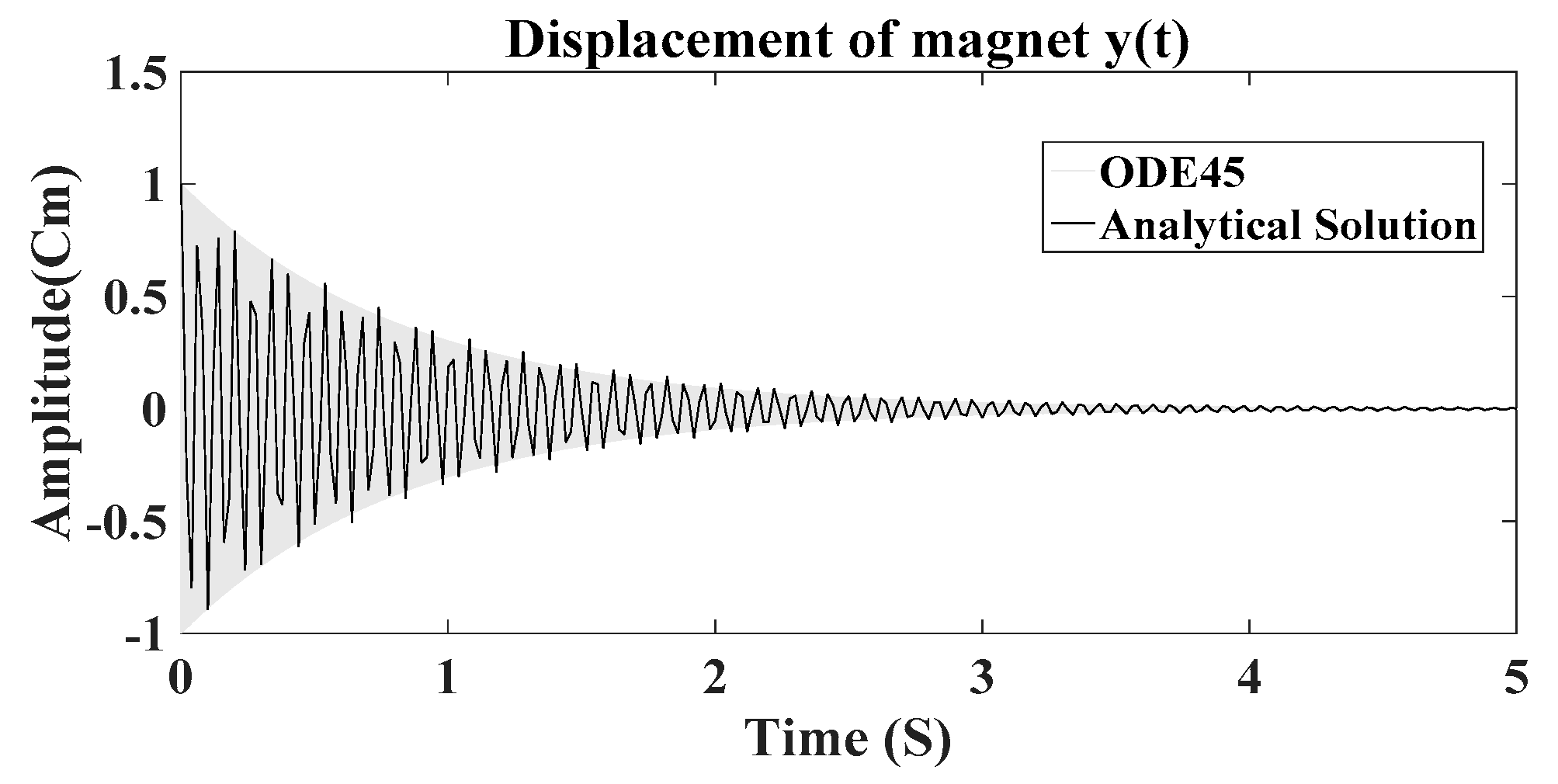
In this section, the dynamic system of the harvester is studied through numerical simulation with Matlab and ODE45 solver. Considering the construction parameters from Table II and some assumptions, the typical motion profile of the central magnet and the response frequency are given to illustrate the dynamic behavior of the harvester. (
Figure 8) shows the motion profile of the central magnet, which is enabled by initial excitation force
F and decays due to the influence of electromechanical damping. The magnitude increases and decreases during the decaying oscillation of central magnet.
Table II. EXPERIMENTAL PARAMETERS.
Table II. EXPERIMENTAL PARAMETERS.
For frequency ratio, the harvester is near it’s resonance frequency and the maximum power can be harvested. For greater than 0.06, the harvester exhibits anti-resonance behavior and the generated power is minimal.
5. Experimental Verifications
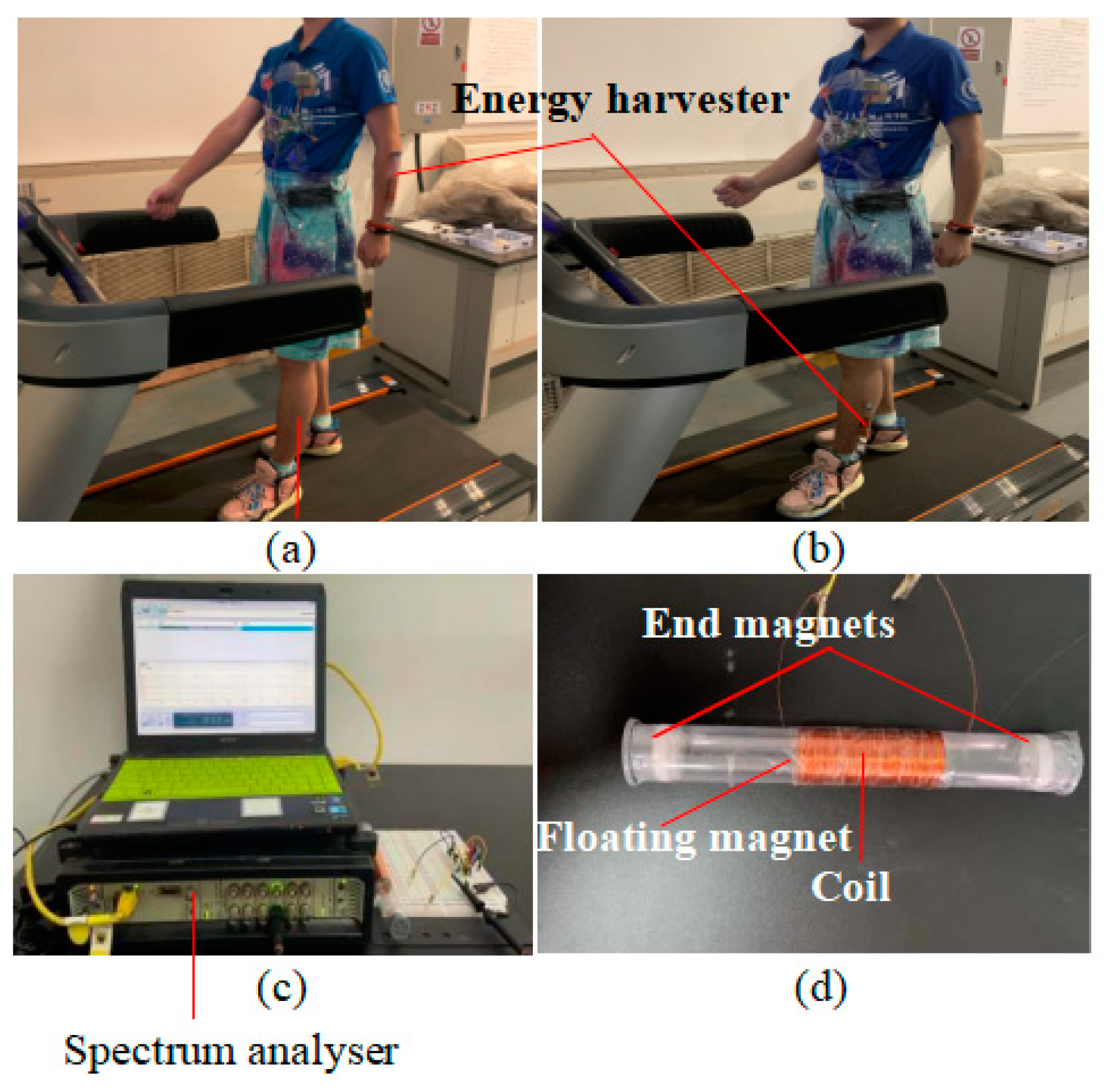
Experiments are conducted in two stages: In first step the capability of the harvester to sustain the power of experimental prototype (
Figure 10). And in second step, the effectiveness of the self-built experimental IOT heart beat rate monitoring device is evaluated. The harvester is attached to the arm or lower extremity as illustrated in (
Figure 10a) and (
Figure 10b). The treadmill speed is set to 3 mph (miles per hour), which corresponds to average walking speed of human being. Spectrum analyzer in (
Figure 10c) is used for measuring the experimental voltage while walking on the treadmill.
- ■
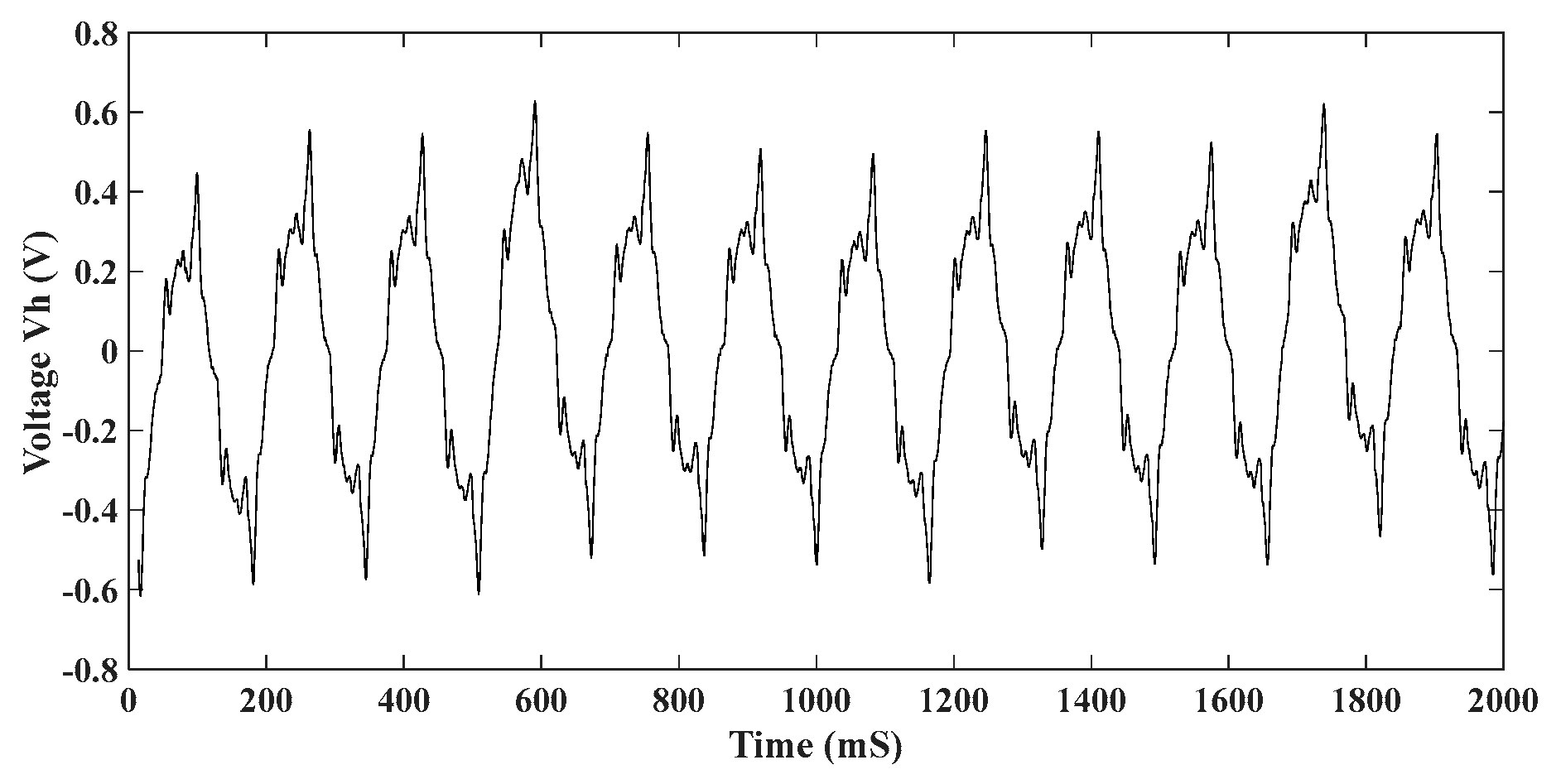
Voltage produced by the harvester
The harvester is disconnected from the load and from voltage multiplier. Both ends of the coils are directly connected to the spectrum analyzer. The voltage generated by the harvester during normal walking is shown in (
Figure 11).
- ■
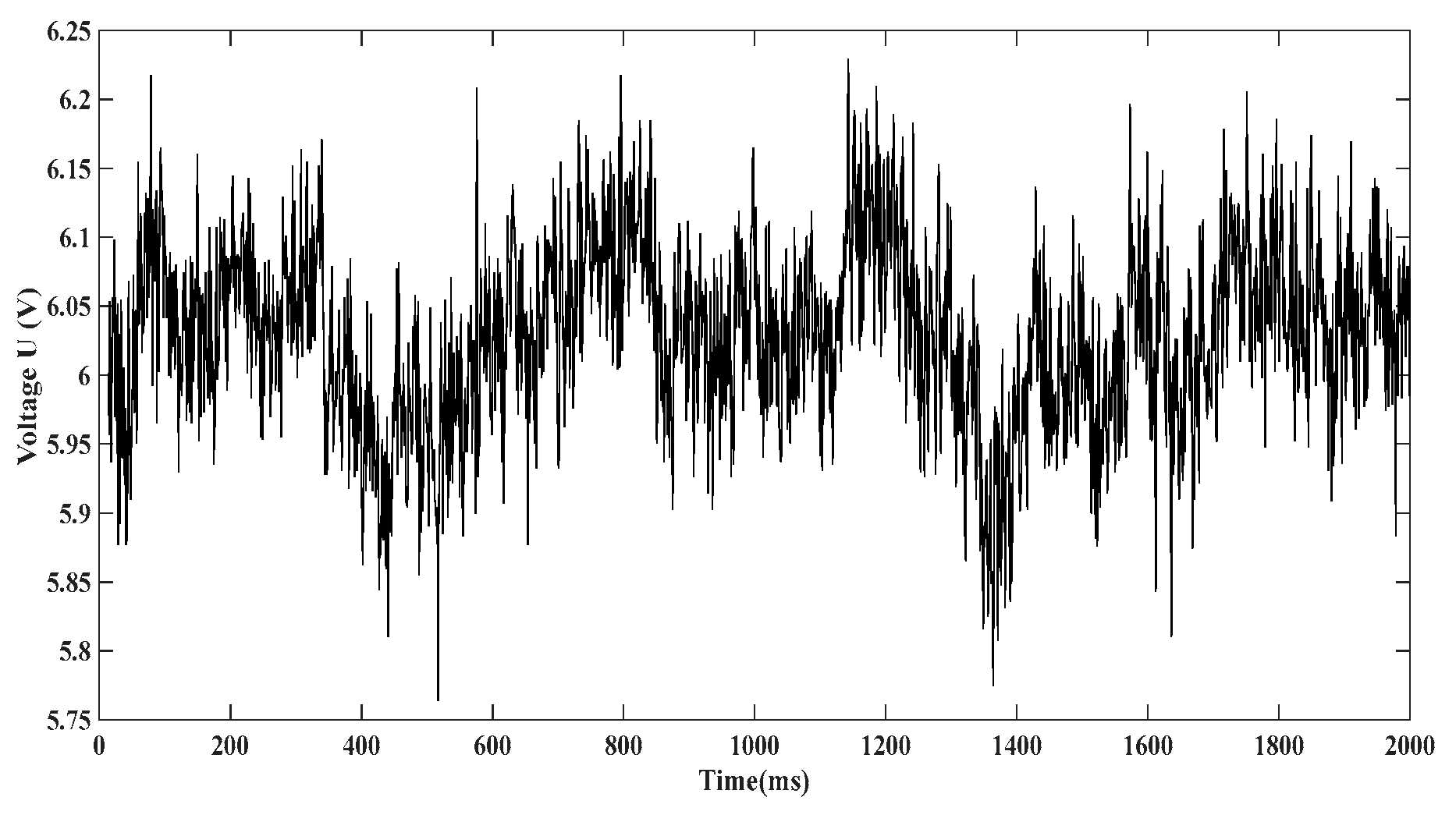
.Voltage U across the capacitor
The harvester is connected at to the rectifier bridge, which multiplies the harvested voltage with a coefficient k=16 as illustrated in (
Figure 4b). The voltage U in (
Figure 12). is measured directly across the capacitor
C.
- ■
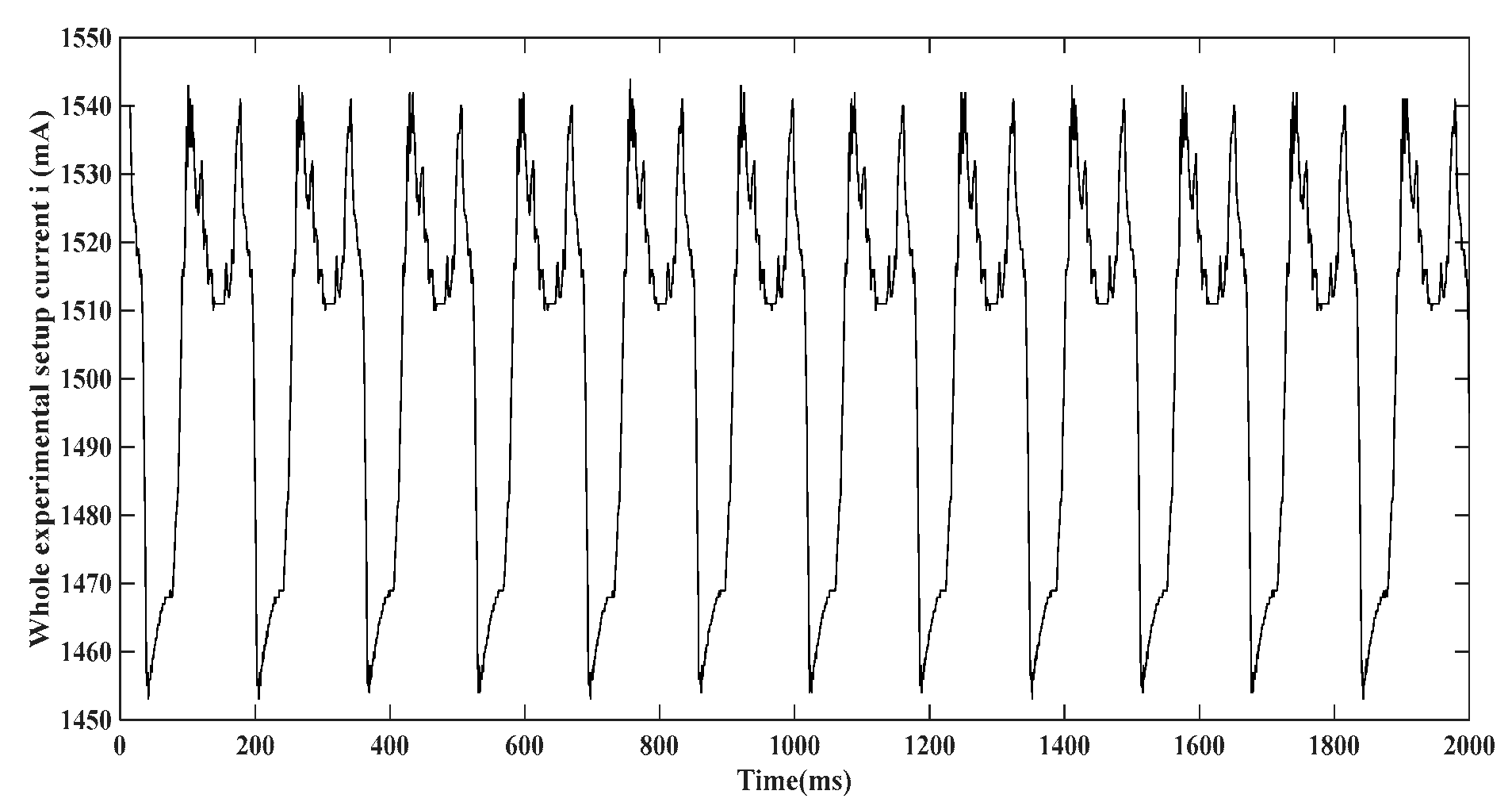
Current consumed by the experimental prototype of IOT based heart rate monitoring device.
For this measurement, the experimental prototype in (
Figure 15a) is set on normal working conditions. A
resistor is connected in series on the power wire of the experimental prototype. The drop voltage
is measured across the resistor
and the current
in (
Figure 13) is calculated based on the formula
.
- ■
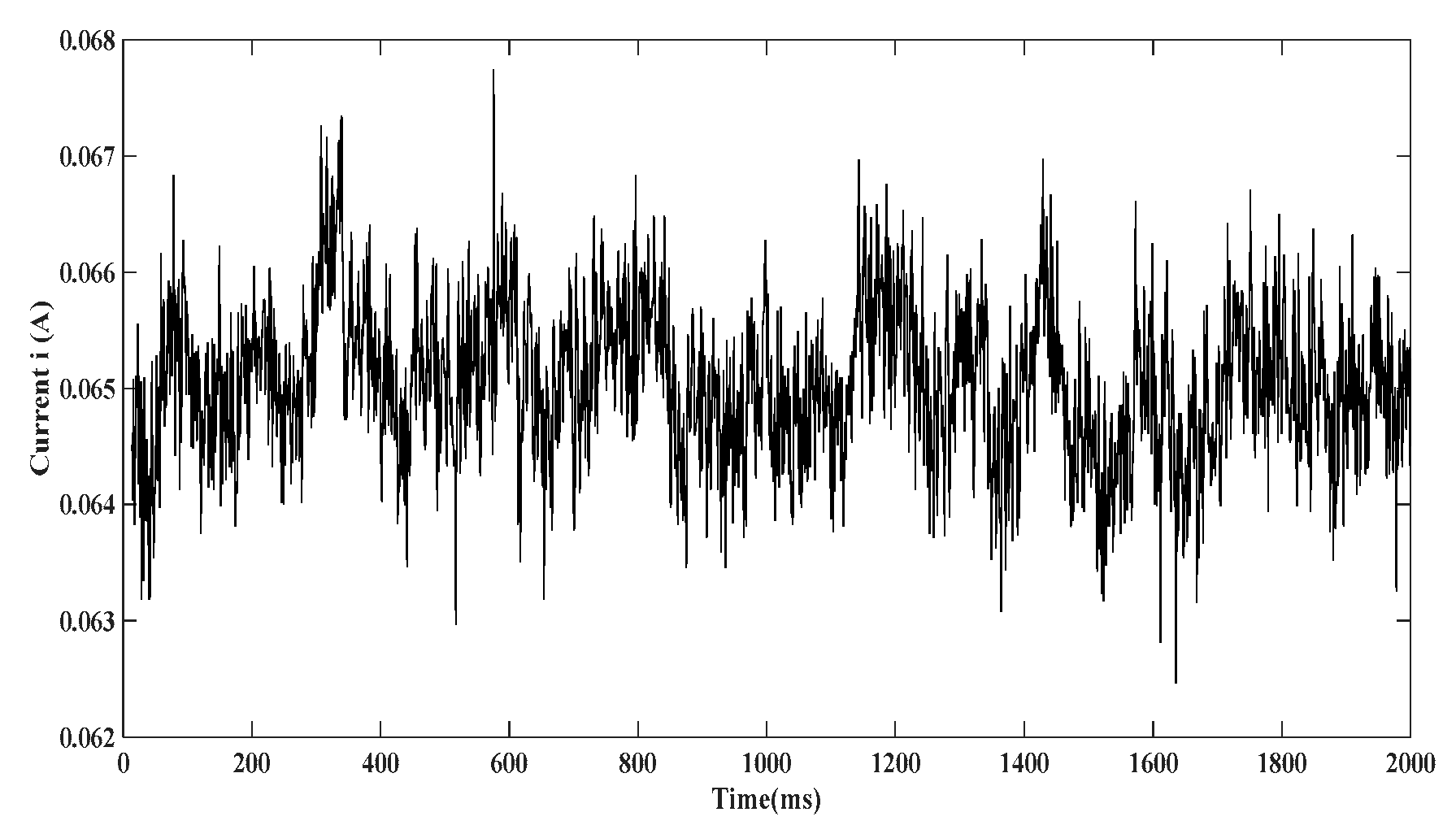
Current generated by the harvester for charging the battery
First the battery of
is fully discharged and connected to the power rectifier as illustrated in (
Figure 4b). A
resistor is placed in series with electronic switch
and the drop voltage
is measured directly across the resistor. The charging current of the battery is then calculated based on the formula
The current generated by the harvester for charging the battery under normal walking conditions (
Figure 14) is relatively low, (approximately 4.33%) of the total current consumed by the experimental prototype (
Figure 13). under running conditions, higher amplitude vibration energy can be harvested, which can better improve this result.
Furthermore, for a state of art manufacturing of such system, deep investigations have to be conducted on the harvester to match the power harvested to the power required for operating the wearable device. Leveraging electronic design by using microelectronics devices can considerably lower the total current necessary for IOT device.
- ■
Experimental setup for IOT based heart rate monitoring device.
A personal space is created on Matlab server “
https://thingspeak.com/” for storing the heart beat rate. The IP address of the server and channel ID are used in the code to access to the host computer. Pickit 3 device is used for transferring the code to microcontroller. A personal mobile phone is used as Wi-Fi hotspot for connecting the experimental prototype to Wi-Fi.
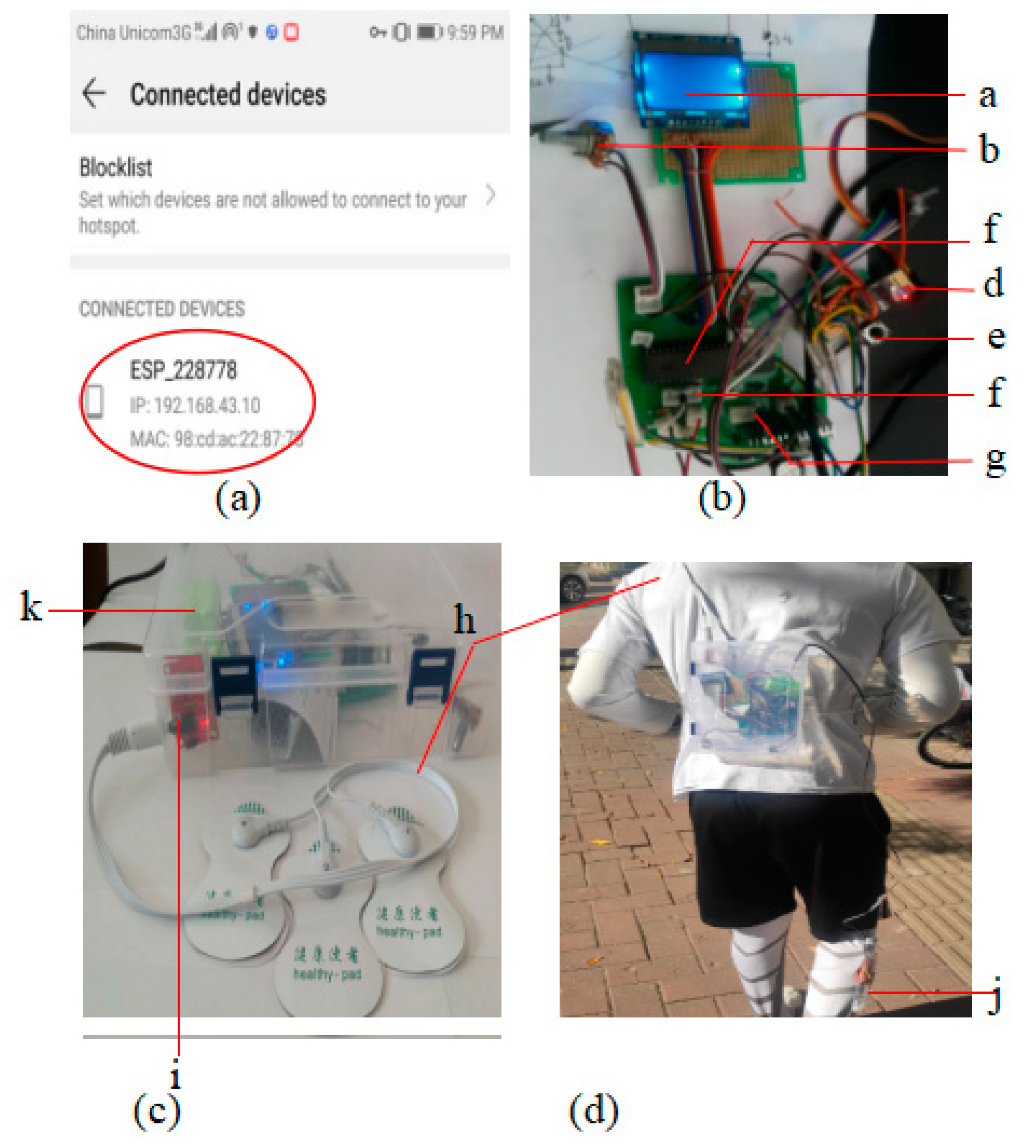
Figure 15a shows the experimental prototype connected to Wi-Fi and ready to share the health data. Different parts of the experimental setup are shown in (
Figure 15b) and (
Figure 15d) shows the overall setup with energy harvester and ECG electrodes.
a: Screen;
b: adjust contrast for screen;
c: Microcontroller
d: Wi-Fi serial transceiver;
e: Reset switch;
f: Pins for ECG sensor;
g: Power pins for harvester;
h: connection wires for ECG electrodes(connected on the chest)
i: ECG sensor;
j: Harvester
k: Battery
Figure 15.
Experimental setup: using the mobile phone as Wi-Fi hotspot for connecting the experimental setup(a); experimental setup connected to Wi-Fi (b).
Figure 15.
Experimental setup: using the mobile phone as Wi-Fi hotspot for connecting the experimental setup(a); experimental setup connected to Wi-Fi (b).
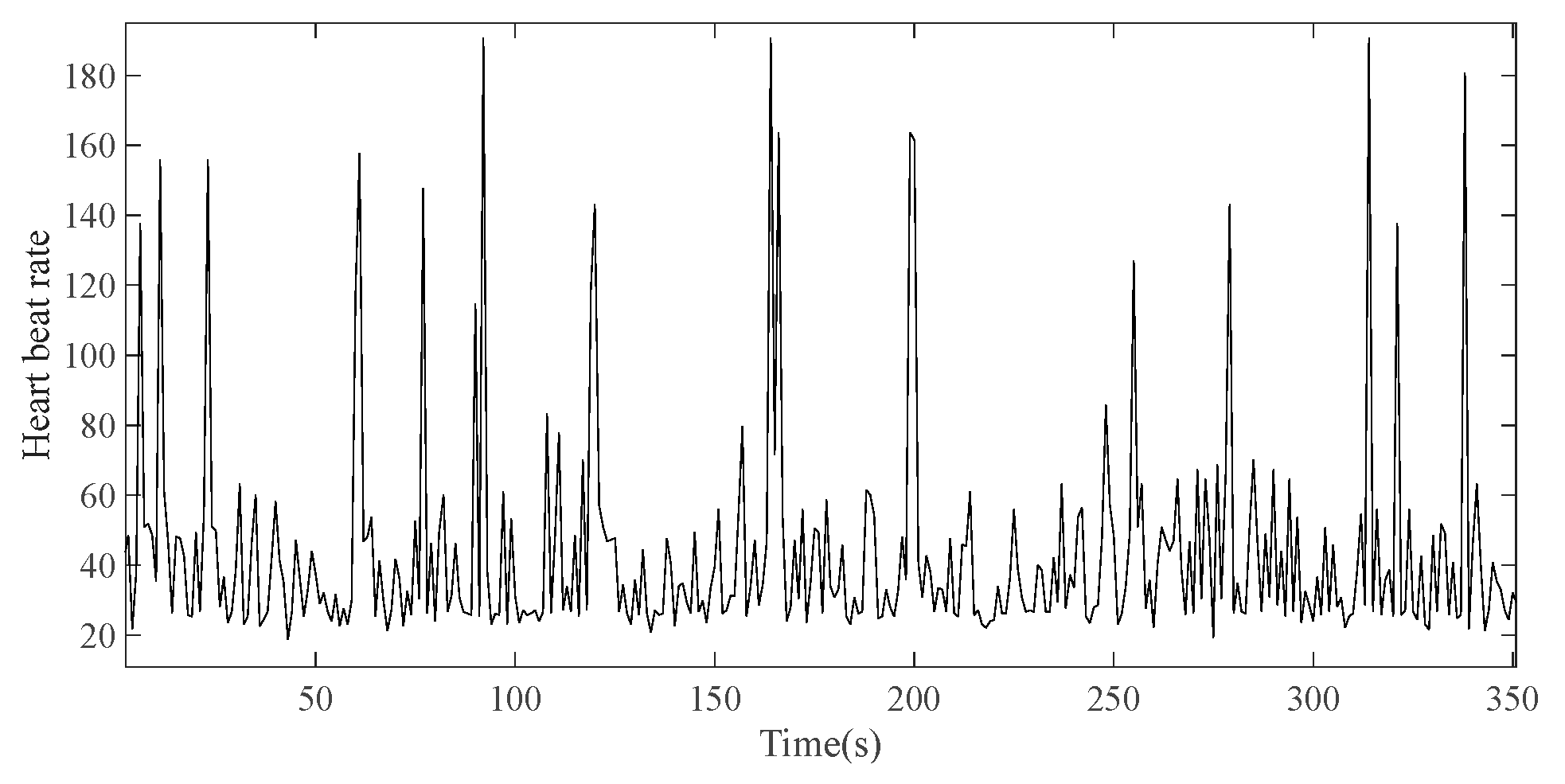
Figure 16.
Experimental ECG wave form.
Figure 16.
Experimental ECG wave form.
Conclusion
In this work, the feasibility of using harvested human kinetic energy for sustaining the power of biomedical devices is studied. The experimental prototype in (
Figure 15) is based on a self built IOT based heart beat rate monitoring device for remote monitoring of patients living with unstable health conditions. A non linear electromagnetic harvester is implemented, and the nonlinear restoring force of the magnet has inverse quadratic dependence on the separation distance between the magnets. The same approach was used in [
15].This research considers the case of electromechanical damping and apply MacLaurin expansion to transform the inverse quadratic nonlinearity of magnetic force into polynomial form. Which enables to provide the law of motion for general cases. A typical numerical application is computed using Matlab software and ODE45 based on the construction parameters of the harvester and some reasonable assumptions. Experiments are conducted on energy harvester and experimental prototype of IOT based heart rate monitoring device to evaluate the capability of the harvester for sustaining the power of wearable device. It came out that under human normal walking conditions of 1.4 meters per second, the harvester can sustain approximately 4.33% of the total current required by the wearable device, Which is relatively low. This result can be better improved under running conditions since the amplitude of excitation force generated is higher. Further more, for a state of art manufacturing of such system, deep investigations have to be conducted on harvester structure to match the power produced by the harvester to power required by wearable device. Improving the electronic design by using microelectronics devices can considerably reduce the power required by the wearable device.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, DJAKOU NEKUI Olivier and Wei Wang; methodology, DJAKOU NEKUI Olivier ; software, DJAKOU NEKUI Olivier; validation,Cheng Liu and Bei Ding ; data curation, Zhixia wang; writing—original draft preparation, DJAKOU NEKUI Olivier; writing—review and editing, Wei Wang; visualization, DJAKOU NEKUI Olivier ; supervision, Wei Wang.; project administration, Wei Wang ; funding acquisition, DJAKOU NEKUI Olivier. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Please add: This research was funded by CHINA SCHOLARSHIP COUNCIL (CSC), grant number : 2019GXZ012914.
Acknowledgments
DJAKOU NEKUI Olivier would like to express his deepest gratitude to his mother KAKONG Marie Eleanor and brother TAFFO NEKUI Raphael for their good understanding and support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results”.
References
- Gloria, G.& all, “Wireless ECG and cardiac monitoring systems: State of the art, available commercial devices and useful electronic components,”. Measurement 2021, 177, 109243.
- Nizar AI Bassam & all, “IoT based wearable device to monitor the signs of quarantined remote patient of COVID-19,”. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked 2021, 24, 100588.
- Mohsen Hooshmad & all,”Boosting the Battery Life of Wearables for health monitoring through the compression of Biosignals,”. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2017, 4, 1647–1662.
- R. Shankara and I.S.N. Murthy, “ECG Data compression Using Fourier Descriptors,”. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 1996, 33, 428–434.
- H.Lee and K.M. Buckley,”ECG Data Compression Using Cut and Align Beats Approch and 2-D Transforms,”. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 1999, 46, 556–564. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcoran P, Coughlin T. “Safe Advanced Mobile Power Workshop,”. IEEE Consumer Electronics Magazine 2015, 4, 10–20. [CrossRef]
- Bouchet, R. Batteries: A stable lithium metal interface. Nature nanotechnology 2014, 9, 572–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- P.D Mitcheson, E.M. yeatman, G.K. Rao, A.S. Holmes, T.C. Green ”Energy Harvesting from Human and Machine Motion for Wireless Electronics Devices,”. Proceeding of the IEEE 2008, 96, 1457–1486. [CrossRef]
- K A Cook-chennault, N Thambi and A M Sastry,” Powering MEMS portable devices - A review of non-regenerative and regenerative power supply systems with special emphasis on piezoelectric energy harvesting systems,”. Smart Materials and Structures 2008, 17, 043001. [CrossRef]
- Khaligh A, Peng z,Cong z,”Kinetic energy harvesting using piezoelectric and electromagnetic Technologies,”. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 2010, 57, 850–860. [CrossRef]
- Paulo J, Gaspar PD,”Review and Future Trend of Energy Harvesting Methods for Portable Medical Devices,” In proceeding of the World Congress on Engineering(WCE). lONDON, U.K 2010 1-6. 2010.
- Jaeseok Y, Shwetak N, Patel M, Reynolds S, Gregory AD,” Design and Performance of an Optimal Inertial Power Harvester for Human-powered Devices,”. IEEE Trans Mobile Comput 2011, 10, 669–683. [CrossRef]
- Todor Todorov, Rumen Nikolov. “Dynamical modeling of mechanical oscillations in magnetic field,”. Recent Journal. 2008, 9, 1.
- Guoce Zhang and Bo Zhang.”Secondary Resonance Energy Harvesting with Quadratic Nonlinearity,”. Journal of Materials 2020, 13, 3389. [CrossRef]
- Nicusor Nistor, Constantin Gheorghies and Nelu Cazacu,” The Motion Equation of a Spring-Magnet-Mass System Placed in Nonlinear Magnetic Field. An Analytical Solution of Elliptic Sine form Functions”. British Journal of Mathematics & Computer Science 2016, 12, 1–15.
- William T. Thomson, Marie Dillon Dahleh, V.” the Theory of Vibration with Applications”,fifth edition, p. 16-88 (in english).
- Greg Poole,” Theory of Electromagnetism and Gravity- Modeling Earth as a Rotating Solenoid Coil”. Journal of High Energy Physics, Gravitation and Cosmology” 2017, 3, 663–692. [CrossRef]
- Resnick and Halliday,”Fundamental Relationships,”Physics, Part I, Wiley, (1968).
- Alex Mouapi,”Piezoelectric micro generator design and characterization for self-supplying industrial wireless node”. Memories-Materials,Devices,Circuits and Systems 2022, 1, 100002. [CrossRef]
- Nordic Semiconductor Company, Norway”Wearable ECG Monitoring Enables Remote Care of Cardiac Patients”. Available online: https://www.nordicsemi.com/News/2020/11/Wearable-ECG-monitor-enables-remote-care-of-cardiac-patients.
- Philips Healthcare store, USA. Available online: https://www.patientcare.shop.philips.com/Philips-Global-Category/diagnostic-ecg.
- Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research (MFMER),Florida,USA,”Holter Monitor”. Available online: https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/holter-monitor/about/pac-20385039.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).