1. Introduction
Water is one of the most essential natural resource to the existence of life. Sustainable development and management of water resources plays an important role in the socio-economic development of any society. Management of fresh water resources in a changing climate is one of the greatest challenges faced by global modern society following the changes in climate and rapid population growth. Addressing these issues requires knowledge of how water resources are affected by changes of various aspects of regional hydrological cycle [
1]. The sensitivity of regional hydrology to variable climate conditions makes climate-change projections essential for the assessment of future variations in the hydrologic cycle [
2].
Climate change will reduce water availability, irrigation potential, hydropower potential and changing seasonality of flows in many regions [
3]. Awash basin is more urbanized than the rest of Ethiopia, with approximately 25 per cent of its population living in cities compared to 19 percent across the rest of the country, and more industrialized [
4].
Arba river catchment is located in arid and semi-arid part of the middle Awash River basin. Climate in such areas could be sensitive to even insignificant changes in climatic characteristics. Therefore, quantitative estimates of hydrologic effects of climate change are essential for understanding and solving the potential water resource management problems associated with water supply for domestic and industrial water use, power generation, and agriculture as well as for future water resource planning, and protection of the natural environment and human lives from disasters like flood and drought. It is estimated that, by 2080s, the proportion of arid and semi-arid lands in Africa is likely to increase by 5-8% [
5].
Ethiopian population is experiencing climate change and its impacts on the environment and natural resources. Continued climate change is expected to bring greater variability and extreme weather events such as flood and droughts which will further drive degradation of the country’s ecosystems [
6].
With respect to available water resources, any climate change may affect the hydrological cycle and its water balance terms. For instance, changes in temperature and precipitation have direct impact on the processes of runoff production. Consequently, any change in the spatial and temporal availability of water resources affects agriculture, industry and urban development [
6,
7].
In West Africa and the horn, future climate assessment studies were carried out during the past years by using various GCMs and RCMs for trend assessment [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12], extremes analysis [
13,
14], and climate change impact studies [
15]. None of those studies explicitly exposed the selection process of the climate model used. Models were basically selected with reference to other studies where they were reported to be of good performance, or based on data processing constraints, and barely on the basis of a systematic selection. The performance of a model within a geographical region like West Africa could vary depending on the location under consideration[
16].
One of the important causes for vulnerability of Ethiopia to climate variability and change is very high dependence on rainfall patterns and rain fed farming for food production and uneven distribution of the rainfall, which can be linked to impacts of climate change. Between 80-90% of Ethiopia's water resources is found in the four river basins namely; Abay (Blue Nile), Tekeze, Baro Akobo, and Omo Gibe in the west and south-western part of Ethiopia where the population is no more than 30 to 40 percent. On the other hand, the water resources available in the east and central river basins are only 10 to 20 percent whereas the population in these basins is over 60 percent [
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23].
Existing power generation in Ethiopian is highly dominated by hydropower resources; this is the source of 95% of current total electricity. The consecutive impact of climate change may pose a serious potential threat on water resource availability in the watershed. However, recent climate change impact studies particularly in Arba river catchment and west Harerghe zone in general are limited. Hence, analyzing the impact of climate change at catchment level through bias correction of GCM or RCM simulations and knowing implication of climate change on the water resources is very important for accomplishing a comprehensive, probability-based estimation of climate changes impact assessments on stream flow [
24,
25,
26,
27]
The main objective of this study was to investigate the possible hydrological impact of climate change in stream flow of Arba River based on the downscaled precipitation and temperature data at West Harerghe Zone, Oromia regional state, Ethiopia. This is used as an input in planning approach and as decision support tool in planning, development and management; particularly in Arba river catchment and west Harerghe zone.
2. Methods
2.1. Materials
Awash River basin is located in central Ethiopia and it flows through 5 regional states (Oromia, Afar, Amhara, Somali, and SNNP) and 2 administrative councils (Dire Dawa and Addis Ababa). Its geographical location is from7o52’12’’-12o 08’ 24’’N and 37o 56’ 24”-43o 17’ 24” E. the study area is located in Oromia regional state, West Hararghe zone and covers gumbi bordode woreda and parts of Mieso woreda. Arba River is one of the tributaries of Awash River and the catchment of the river at bordode flow gauging station covers around 72 square kilometers. The altitude of the study area varies between 1194m to 2696m above mean sea level.
2.2. Data collection
2.2.1. Climate data
The rainfall and temperature data for the study area were collected from National Meteorological Agency of Ethiopia, from the below listed stations.
Table 2.1.
Description of selected meteorological stations.
Table 2.1.
Description of selected meteorological stations.
| No |
Name |
Latitude |
Longitude |
Elevation |
| 1 |
Bedesa |
8.917 |
40.767 |
1735.6 |
| 2 |
Asebot |
9.133 |
40.667 |
1450 |
| 3 |
Kora |
9.117 |
40.533 |
1530 |
| 4 |
Mieso |
9.233 |
40.75 |
1358.12 |
| 5 |
Awash |
8.983 |
40.15 |
978.242 |
2.2.2. Climate model data and scenario development
Dynamically downscaled Regional Climate Model (RCM) HIRHAM derived by ICHEC-EC-EARTH global climate model under two scenarios RCP 4.5 and 8.5 was used in this study. The climate model HIRHAM model was selected based on evaluation of climate model skill in simulating the historical rainfall and temperature in Arba catchment.
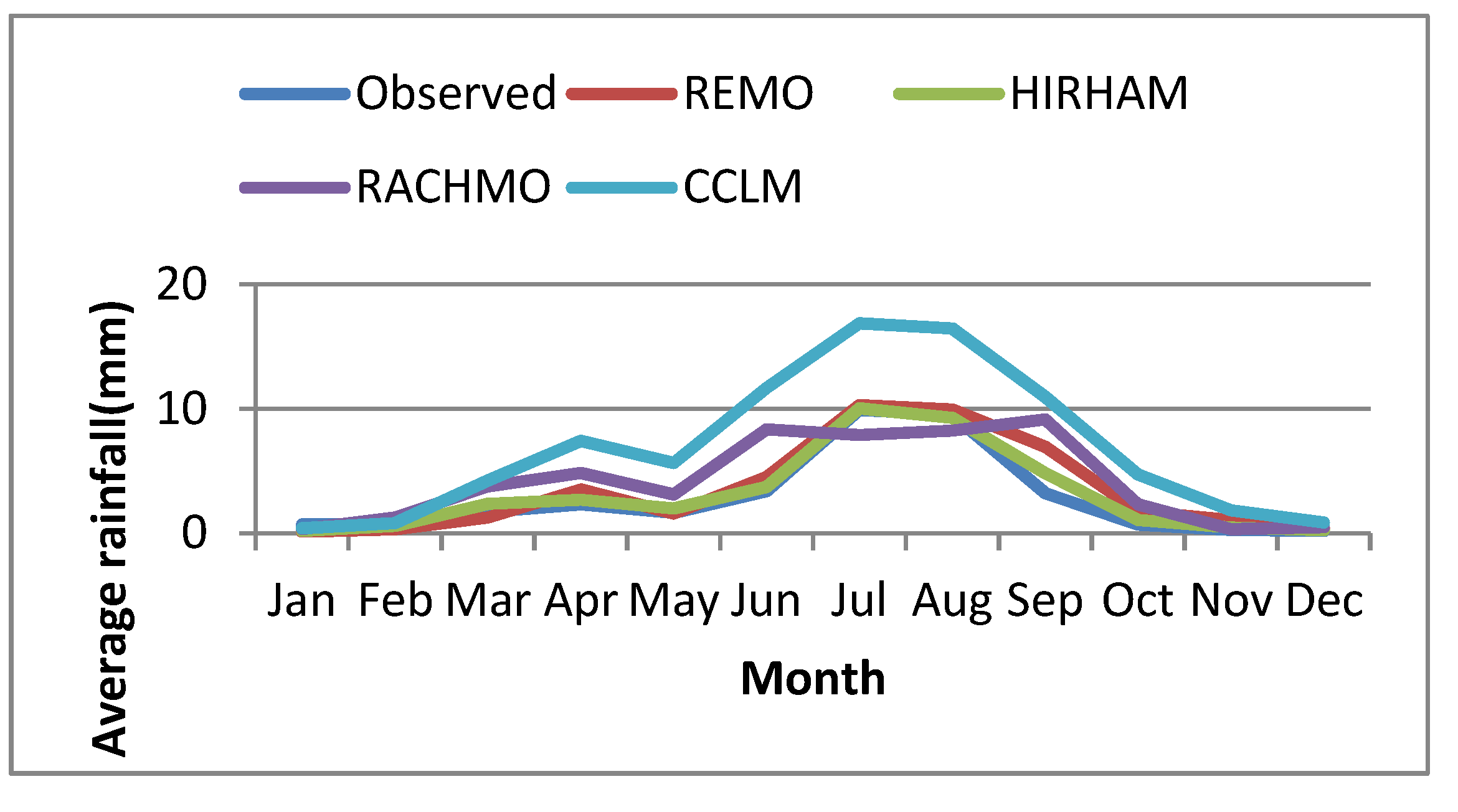
Four regional climate models (CCLM, REMO2009, RACMO22T and HIRHAM) were evaluated in simulating the historical observed rainfall of stations in Arba catchment. On Figure 3.2, HIRHAM showed better performance in capturing observed rainfall and selected for this study. This model also considered to represent the latest accomplishments in climate modeling science and technology, and is the most regionally accepted model [
28,
29,
30,
31].
Figure 2.1.
Comparison of different models in simulating observed rainfall during historical period for the selected stations.
Figure 2.1.
Comparison of different models in simulating observed rainfall during historical period for the selected stations.
2.3. Climate Change impact Analysis
To evaluate the future change in rainfall, temperature and stream flow, the future time periods were divided into two time horizons with equal length of time as the base line period. These time periods are 2021–2050 and 2051–2080, according to RCPs 4.5 and 8.5 and compared with the baseline years. The climate change periods were chosen so that all years in the 21st century are analyzed and easily comparable. Thus, the variations of mean precipitation, temperature, or discharge at different time periods were evaluated in relation to the baseline period. The variations are expressed as a percentage and are calculated according to the following formula:
Where X
horizon is the mean annual, seasonal and monthly value calculated over the specified future time period, Xbaseline is the mean annual, seasonal and monthly value calculated over the base line period (1976-2005). This rate of change represents the relative increase or decrease in precipitation, temperature, or discharge for the future period [
32,
33,
34].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation of downscaling methods
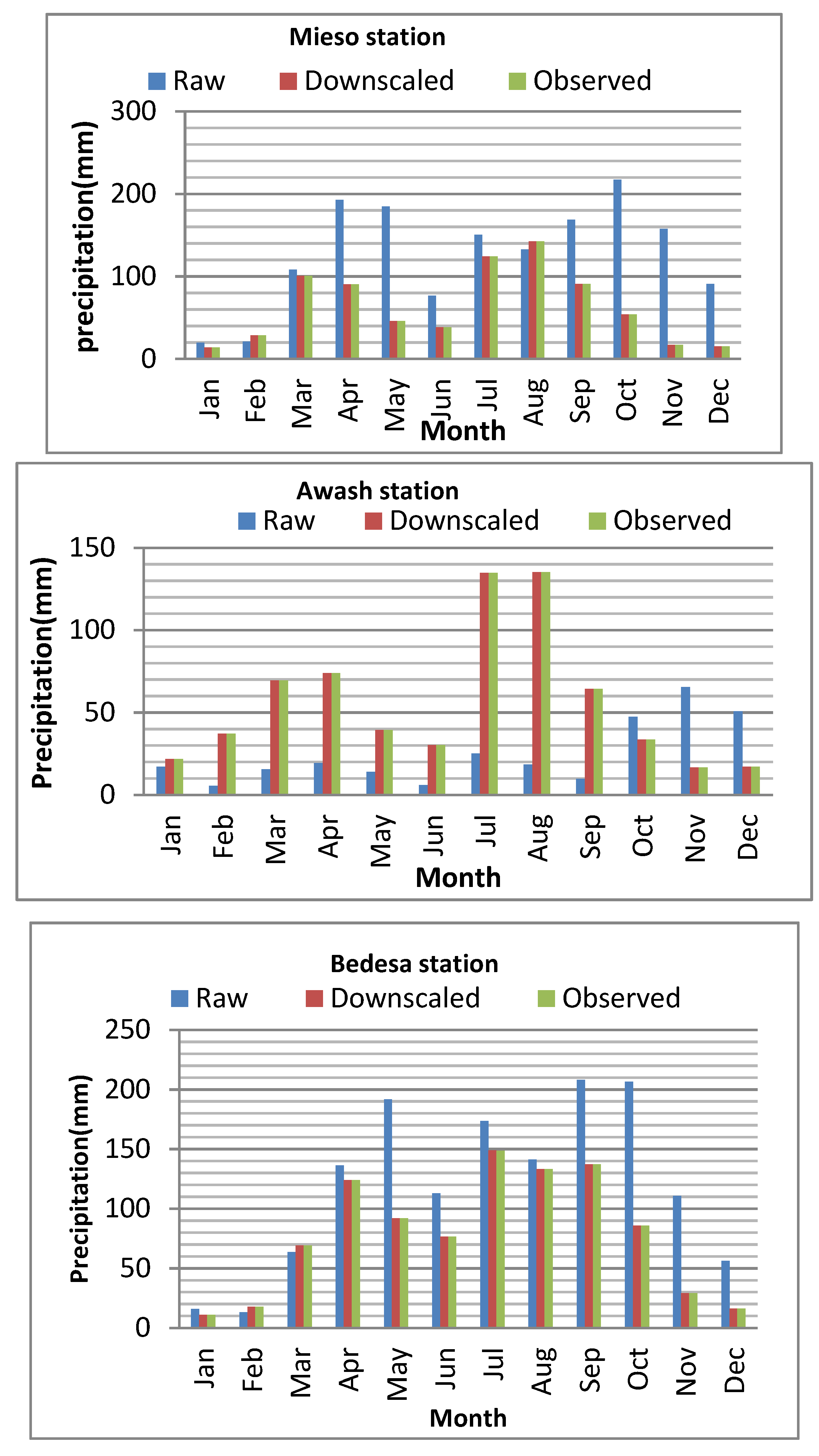
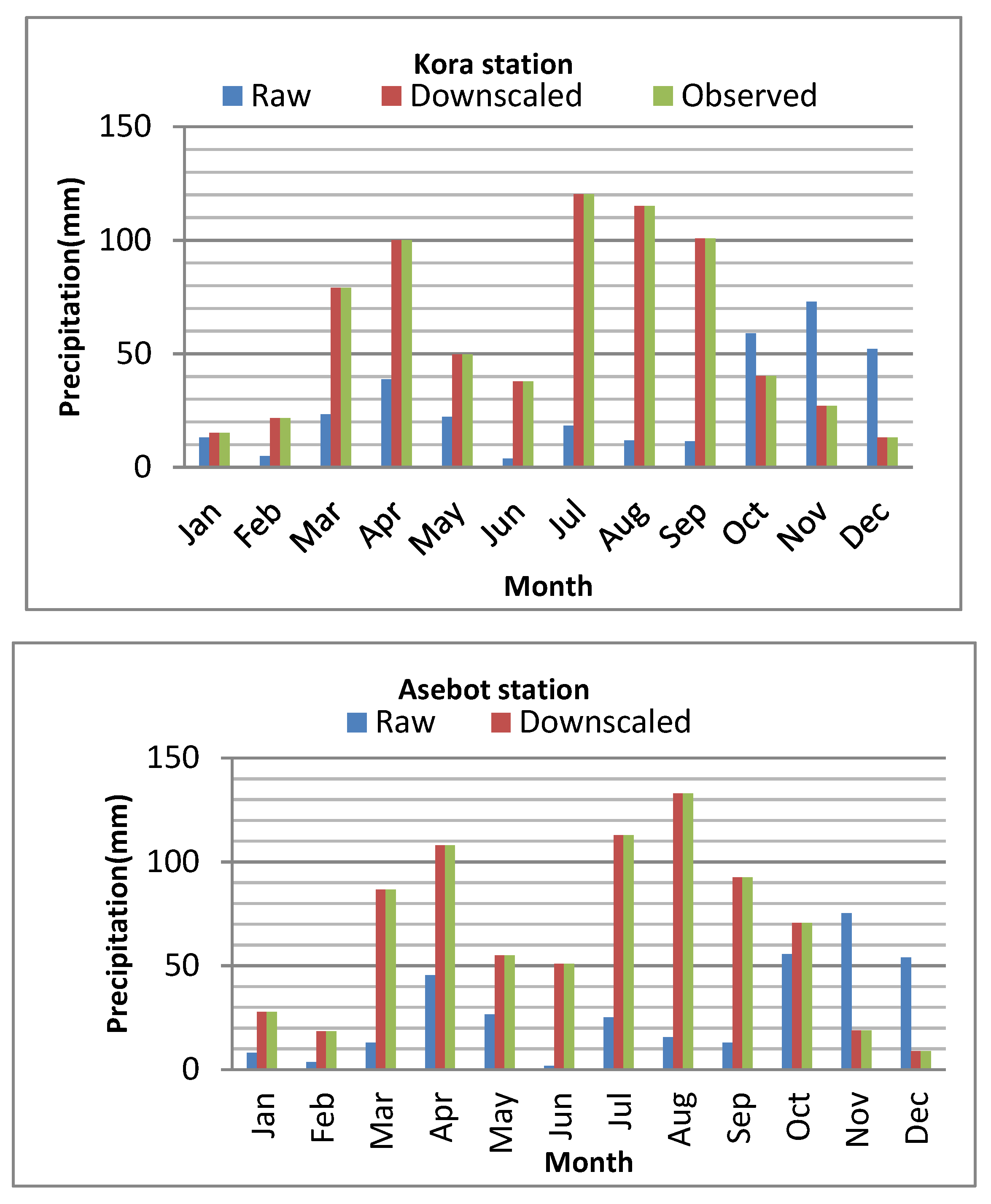
The average monthly rainfall of observed data, raw data (GCM data before bias correction), and downscaled GCM data of each station used for climate change impact assessment of Arba river for the historical period was indicated under Figure 3.1. As the result the climate model has overestimated the average monthly rainfall of Mieso and Bedesa stations and underestimated Awash, Kora and Asebot stations. However after downscaling method is applied the average monthly rainfall of all stations are close to the observed values.
Figure 3.1.
comparison of raw, downscaled and observed rainfall of each stations.
Figure 3.1.
comparison of raw, downscaled and observed rainfall of each stations.
The statistical parameters such as standard deviation (SD), percent of bias (Pbias) and root mean square error (RMSE) of the observed and downscaled data for the historical period at each of the selected stations are computed and compared. The statistical evaluation parameters of the observed and downscaled model data have a good relationship as per it listed down in Table 3.1.
Table 3.1.
Statistical parameters of the observed, raw RCM and downscaled rainfall data for base line period.
Table 3.1.
Statistical parameters of the observed, raw RCM and downscaled rainfall data for base line period.
| Station |
|
Parameters |
| SD |
Pbias (%) |
RMSE |
| Bedesa |
Observed |
6.83 |
- |
- |
| Raw |
4.83 |
-0.49 |
8.14 |
| downscaled |
6.84 |
0 |
7 |
| Mieso |
observed |
4.84 |
- |
- |
| Raw |
2.53 |
0.47 |
5.4 |
| downscaled |
5 |
0 |
6.79 |
| Kora |
observed |
6.06 |
- |
- |
| Raw |
4.4 |
-0.44 |
7.3 |
| downscaled |
6.07 |
0 |
6.6 |
| Asebot |
observed |
6.18 |
- |
- |
| Raw |
4.4 |
-0.46 |
7.4 |
| downscaled |
6.14 |
0 |
6.1 |
| Metehara |
observed |
4.8 |
- |
- |
| Raw |
2.3 |
0.43 |
6.1 |
| downscaled |
4 |
0 |
5.2 |
3.4. Climatic trends of the historical data in the Arba catchment
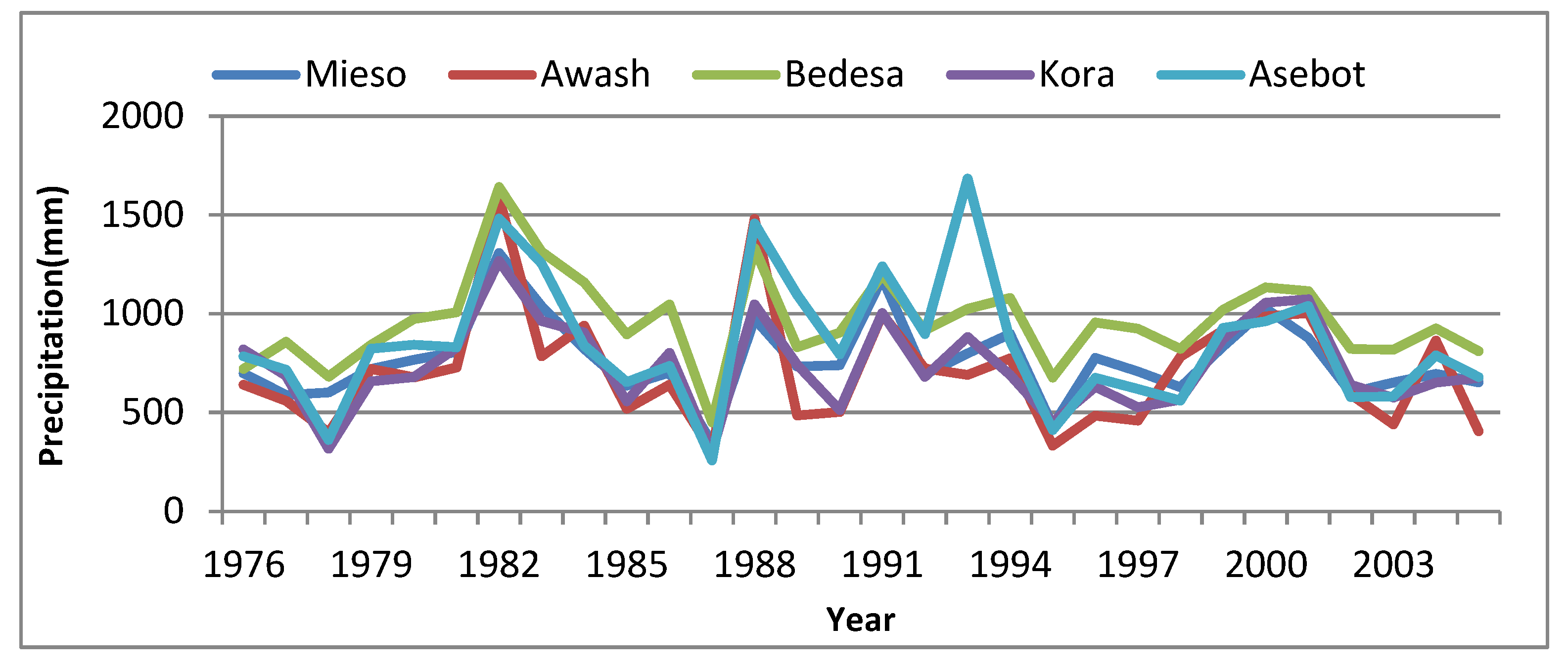
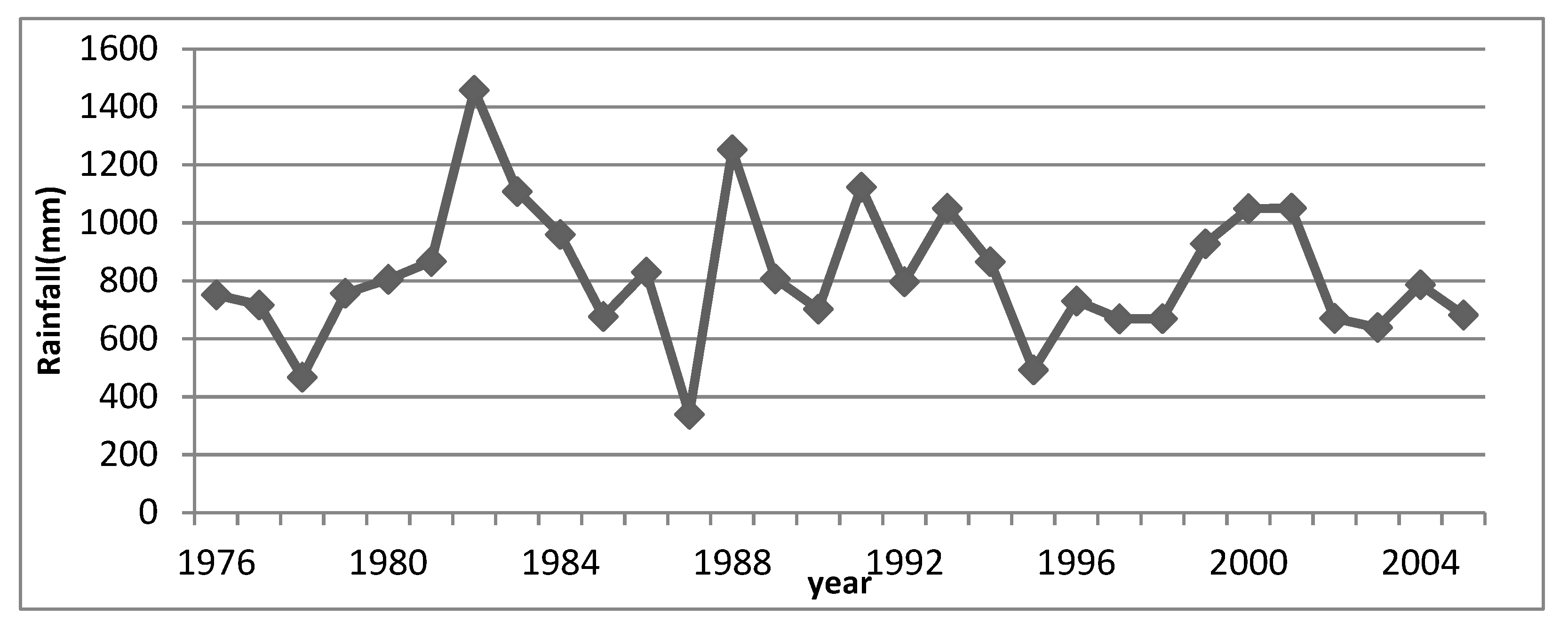
Figure below shows the annual historical precipitation trends of Arba catchment for the period from 1976-2005. As indicated in the Figure 3.2 the study area receives maximum precipitation from Bedesa and Asebot stations relative to Mieso, Kora and Awash stations. For all stations the annual rainfall showed a significant increment from 1978-1982, 1987-1988, and 1990-1991 whereas the year between 1983 and 1986 have showed a significant reduction in annual rainfall.
Figure 3.2.
Annual rainfall trends of stations in Arba catchments.
Figure 3.2.
Annual rainfall trends of stations in Arba catchments.
The average annual rainfall of the study area as indicated in Figure 3.3 Shows that maximum annual rainfall is recorded in 1982 where as the worst one is recorded in 1987. The study results of annual rainfall are consistent to some extent with other annual analysis of rainfall conducted in some other parts of the Ethiopia. [
35], found decreasing trends in annual rainfall series in some stations of their respective study area.
As noted by [
35] annual rainfall decreased during the 1980s in many parts of Ethiopia, recovered during the 1990s and 2000s, except 2002–2003 being the worst drought year in the country. The average annual rainfall of the study area shows higher variations from 1976-1988 and this variation is relatively stable from 1999-2005.
Figure 3.3.
Average annual rainfall of the study area.
Figure 3.3.
Average annual rainfall of the study area.
3.2. Change in stream Flow due to climate change Compared to Baseline Period
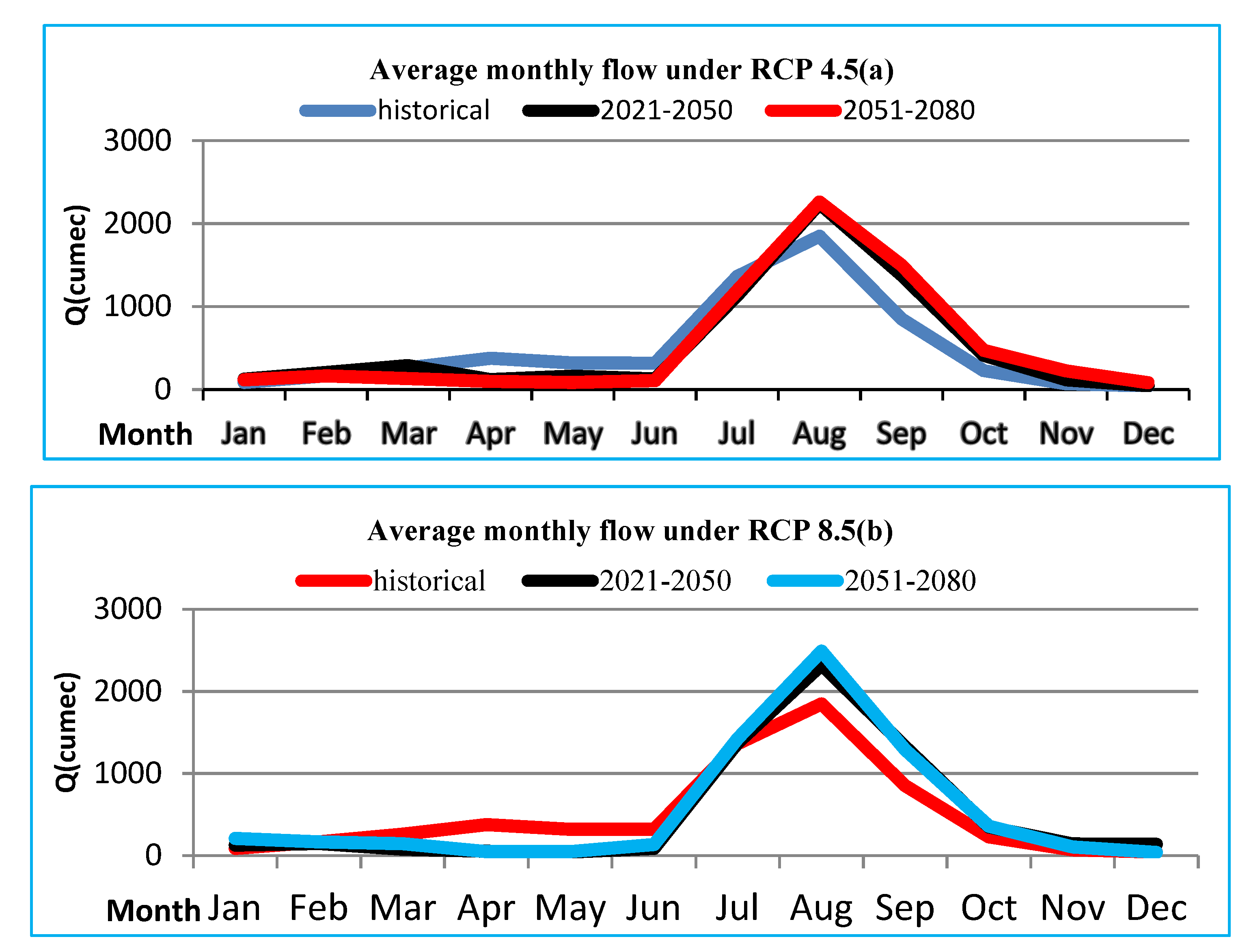
After successful calibration and validation of HEC-HMS hydrological model, bias corrected data was used to simulate flow for future periods of (2021-2050) and (2051-2080) at the outlet of Arba river and the simulated flow was compared to baseline period (1976-2005) to evaluate the change in stream flow due to climate changes. The simulated monthly average flow for both future period under both scenarios are shown in Figure 3.11a and b.
As shown in Figure 3.11a, under RCP 4.5 from mid of February to July, for future periods the average monthly simulated flow is less compared to baseline period. Nevertheless, from end of July to December the simulated flow is expected to increase and the graph of the simulated flow lies above the baseline graph. The expected flow will be higher in the months of August and September relative to other months.
In Figure 3.12b, the pattern of the graph of simulated for both period under RCP8.5 similar to baseline period with overestimation and underestimation. August month is the highest projected flow over the base period. Relatively November, December, January and February expected flow is almost similar with reference period.
Figure 3.4.
Flow patterns of simulated (2021-2050 and 2051-2080) and historical (1976-2005) under (a) RCP4.5 and (b) RCP8.5.
Figure 3.4.
Flow patterns of simulated (2021-2050 and 2051-2080) and historical (1976-2005) under (a) RCP4.5 and (b) RCP8.5.
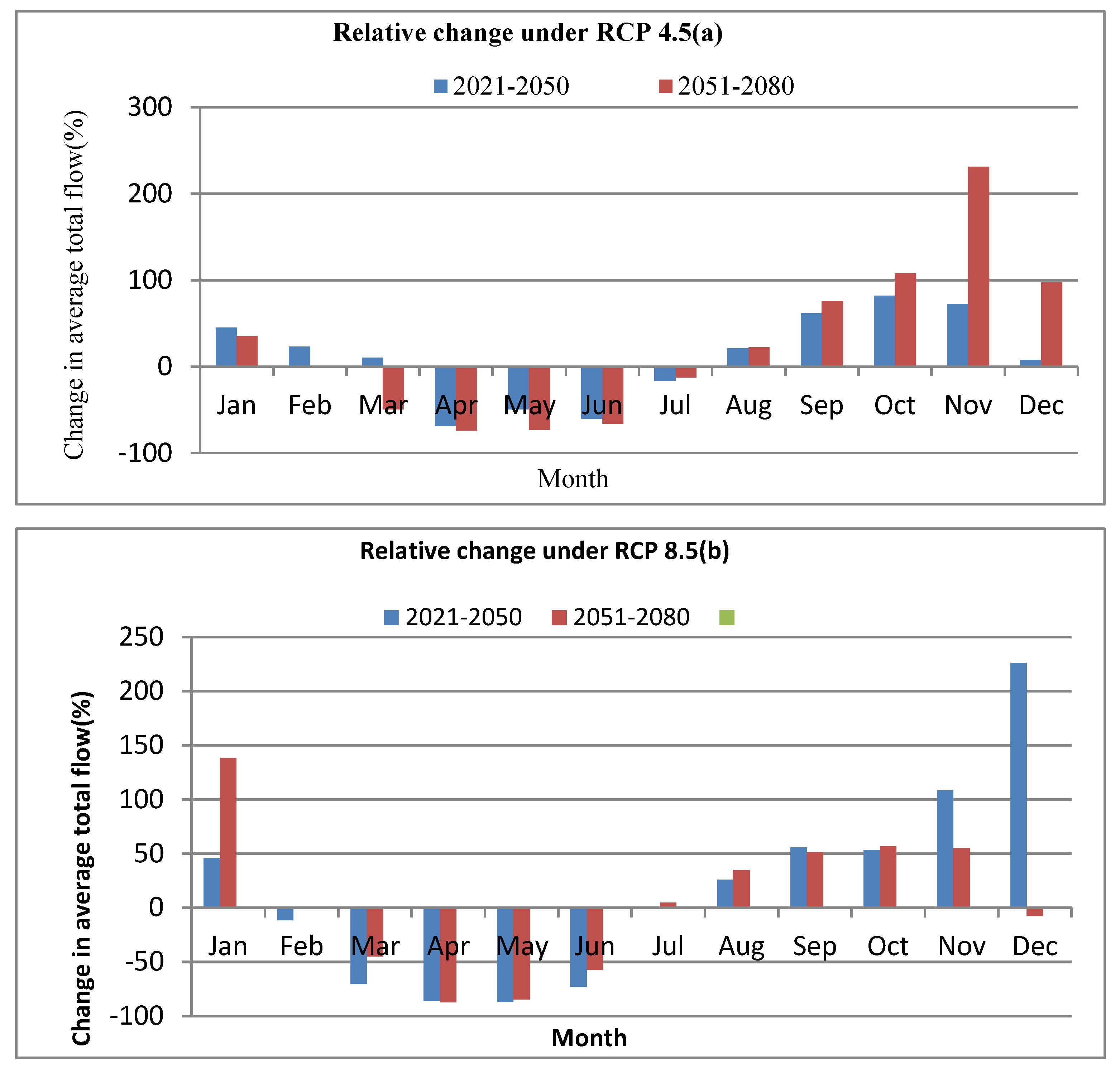
On average, annual flow expected to be increase by more than 17% and 9% over the study area under RCP4.5 and RCP8.5 scenarios respectively. However, there is a significant variation in monthly flow than yearly. The average monthly percentage change of simulated flow for both time horizons are summarized in Figure 3.12 (a and b). The average monthly percentage change (increment) may vary from (7.6 to 81.8) for 2021-2050 and (22.3 to 107.8) for 2051-2080 under RCP4.5. The maximum percentage increment will be expected in the month of October for both time periods. The values are, 81.8% and 107.8% for 2021-2050 and 2051-2080 respectively. There is also reduction in percentage of flow for certain months. The maximum reduction in percent will be expected in April for both time period (Figure 3.12a).
Under RCP8.5 scenario, from July to January except the December for 2021-2050, simulated flow is expected to increase while from February to June decreases for both time horizons. January is the highest increment of flow for 2051-2080 and December for 2021-2050. Figure 3.12b Generally, the flow change will have less variation than the precipitation change.
Figure 3.5.
Projected change in percent of average monthly flow (A) RCP4.5 and (B) RCP8.5 in 2021-2050 and 2051-2080 compared to baseline period 1976-2005).
Figure 3.5.
Projected change in percent of average monthly flow (A) RCP4.5 and (B) RCP8.5 in 2021-2050 and 2051-2080 compared to baseline period 1976-2005).
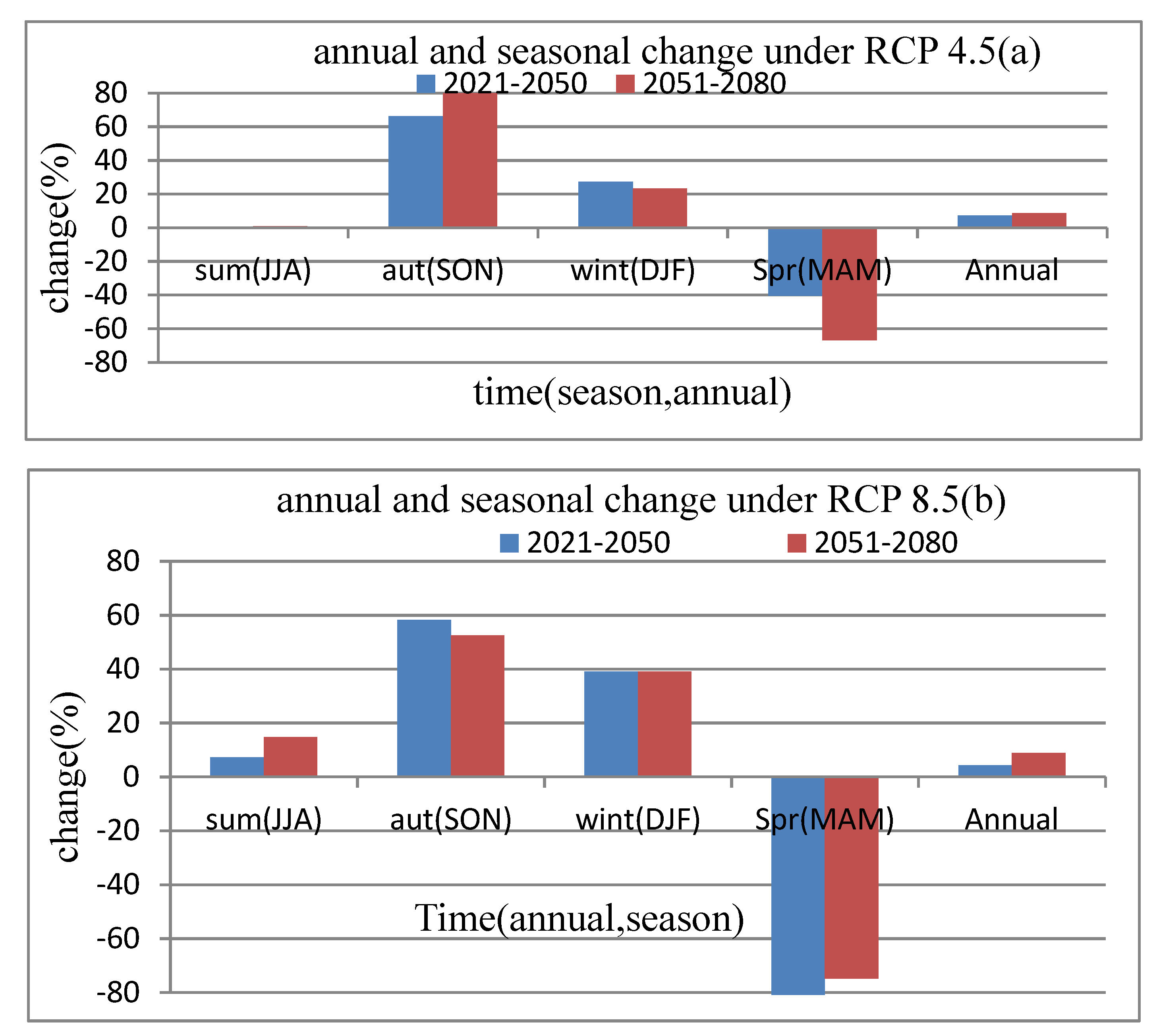
As presented in Figure 3.13a, the seasonal variation will be vary from (-81.8% to +58.3%). During spring (MAM) the flow expected to decreases while increases in summer (JJA), autumn (SON) and winter (DJF) in both time period of 2021-2050 and 2051-2080 under scenario of RCP8.5. The average annual change in flow over study area under RCP8.5 is 4.3% and 8.8% in 2021-2050 and 2051-2080 respectively. The increase will be high in 2051-2080 compared to 2021-2050 Figure 3.13b
For scenario RCP4.5 the flow relatively will increases winter (DJF), autumn (SON) except in summer (JJA) in the period of 2021-2050 which is expected to show a slight decreases. However, in spring (MAM) seasons, the flow may decreases in future compared to base period (1976-2005). Figure 3.13a
Generally the flow in future for this particular study area under selected climate scenario and climate model, is expected to increase and the increment is higher in near time period (2021-2050) than far period (2051-2080).
Figure 3.6.
Average seasonal and annual percentage change in flow under (a) RCP4.5 and (b) RCP 8.5 compared to base period (1976-2005).
Figure 3.6.
Average seasonal and annual percentage change in flow under (a) RCP4.5 and (b) RCP 8.5 compared to base period (1976-2005).
4. Conclusion
This result show that the linear scaling method has improved the quality of model simulated rainfall data and this model could be reliably used for climate change study in Arba River catchment for future time period. The seasonal flow variation of the study area vary from (-81.8% to +58.3%). During spring (MAM) the flow expected to decreases while increases in summer (JJA), autumn (SON) and winter (DJF) in both time period of 2021-2050 and 2051-2080 under scenario of RCP8.5. The average annual change in flow over study area under RCP8.5 is 4.3% and 8.8% in 2021-2050 and 2051-2080 respectively.
The increase will be high in 2051-2080 compared to 2021-2050. For scenario RCP4.5 the flow relatively will increases winter (DJF), autumn (SON) except in summer (JJA) in the period of 2021-2050 which is expected to show a slight decreases. However, in spring (MAM) seasons, the flow may decreases in future compared to base period (1976-2005). Generally the flow in future for this particular study area under selected climate scenario and climate model, is expected to increase and the increment is higher in near time period (2021-2050) than far period (2051-2080).
As per this finding the below listed recommendation were featured.
❖ Environmental protection is the primary measurement to control the climate change and reduction of rainfall on the study area.
❖ The catchment water management system should be in accordance with the future trends of rainfall peaks as the temporal shift in peak rainfall showed a direct impact on the flow of Arba river catchment.
❖ Water harvesting during rainy season and use during the dry period will be improve the problem of water scarcity at period of flow reduction in the river.
❖ The feature proposed projects and any activity on the river should be water balanced targeted, this means supply and demand should be balanced.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology: A.G and H.M.; formal analysis: A.G.; resources: H.M. and W.D.; writing – original draft preparation: A.G. and H.M.; writing – review and editing: H.M., A.G., W.D.
Funding
No source of fund.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to Research and Community Engagement vice President office, Oda Bultum University for sponsoring this research. Thanks for West Harerghe water and energy office for their kind assistance provided during the experimental works.
Conflicts of Interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Guo, H., Qi, H. and Jiang, T: Annual and seasonal stream flow responses to climate and land-cover changes in the Poyang Lake basin, Journal of Hydrology. 2008. 355, Pp106–122. [CrossRef]
- Claudia et al. Bias correction of regional climate model simulations for hydrological climate-change impact studies: Review and evaluation of different methods. Journal of Hydrology. 2012. 456–457 Pp12–29. [CrossRef]
- Houghton, J.T.,Y. Ding, D.J. Griggs, M. Noguer, P.J. van der Linden, X. Dai, K. Maskell, and C.A. Johnson (eds.) IPCC, Climate Change (2001): The scientific basis. Contribution of working group I to the third assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, 2010. 881 p. DOI: 10.1002/joc.763. [CrossRef]
- Growth, G. Water resources and extreme events in the awash basin: economic effects and policy implications. , Report prepared for the Global Green Growth Institute, April.2016.
- M.L. Parry, O.F. Canziani, J.P. Palutikof, P.J. van der Linden and C.E. Hanson, Eds., IPCC: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 2007. Pp 976. DOI: 10.1016/B978-008044910-4.00250-9. [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A. K.; Markus, D. rer. nat. R. J. The Effect of Climate Change on Water Resources Potential of Omo Gibe Basin, Ethiopia. A Dissertation of Doctoral Degree, Engineering Capacity Building Program (ECBP), Universität Der Bundeswehr München, German, 2013, 203 p. https://d-nb.info/1047194740/34.
- Abeyou Wale Worqlul. Impact of Climate Change on Stream flow Hydrology in Headwater Catchments of the Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia, Blackland Research Center, Texas A&M Agri Life Research, Temple, TX 76502, USA. 2018, 10(2), 120 p. [CrossRef]
- Batablinle, L.; Lawin, E.; Agnide, S.; Celestin, M. Africa-Cordex simulations projection of future temperature, precipitation, frequency and intensity indices over Mono Basin in West Africa. Journal of Earth Science and climate Change, 09(09). 2018, Pp 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Djan’na Koubodana, H.; Adounkpe, J.; Tall, M.; Amoussou, E.; Atchonouglo, K.; Mumtaz, M. Trend Analysis of Hydro-climatic Historical Data and Future Scenarios of Climate Extreme Indices over Mono River Basin in West Africa. American Journal of Rural Development. 2020; 8(1):Pp37-52. [CrossRef]
- Lamboni, B.; Emmanuel, L.A.; Manirakiza, C.; Djibib, Z.M. Variability of Future Rainfall over the Mono River Basin of West-Africa. Am. J. Clim. Chang. 2019, 8, Pp137–155. [CrossRef]
- Lawin, A.E.; Hounguè, N.R.; Biaou, C.A.; Badou, D.F. Statistical analysis of recent and future rainfall and temperature variability in the Mono River watershed (Benin, Togo). Climate 2019, 7(1), 8 p. [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, S. M., Wahed, O., El-Nashar, W. Y., El-Marsafawy, S. M., Zelenáková, M., & Abd-Elhamid, H. F. Erratum to: Potential climate change impacts on water resources in Egypt (Water 2021, 13, 1715). Water (Switzerland), 2021, 13(14). [CrossRef]
- Amoussou, E.; Awoye, H.; Vodounon, H.S.T.; Obahoundje, S.; Camberlin, P.; Diedhiou, A.; Kouadio, K.; Mahé, G.; Houndénou, C.; Boko, M. Climate and extreme rainfall events in the mono river basin (West Africa): Investigating future changes with regional climate models. Water (Switzerland), 2020, 12(3), Pp833. [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, L.A.; Batablinlè, L.; Célestin, M.; Hodabalo, K. Future Extremes Temperature: Trends and Changes Assessment over the Mono River Basin, Togo (West Africa). Journal of Water Resource and protection. 2019, 11, Pp82–98. [CrossRef]
- Lawin, A. E., Hounguè, R., M’Po, Y. N. T., Hounguè, N. R., Attogouinon, A., & Afouda, A. A. Mid-century climate change impacts on Ouémé River discharge at Bonou Outlet (Benin). Hydrology, 2019, 6(3). [CrossRef]
- Akinsanola, A.A.; Ogunjobi, K.O. Evaluation of present-day rainfall simulations over West Africa in CORDEX regional climate models. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 366 p. [CrossRef]
- Abreha Adugna Ashenafi, Modeling Hydrological Responses to Changes in Land Cover and Climate in Geba River Basin, Northern Ethiopia. A Dissertation of Doctoral Degree Department of Earth Sciences, Institute of Geographic Sciences Physical Geography, Freien Universität Berlin. 2014.
- Bodian, A., Dezetter, A., Diop, L., Deme, A., Djaman, K., & Diop, A. Future climate change impacts on stream flows of Two Main West Africa River Basins: Senegal and Gambia. Laboratoire Leïdi “Dynamique des Territoires et développement”, Université Gaston Berger (UGB), BP 234-Saint-Louis, Senegal, .Hydrology, 5(1), 2018. [CrossRef]
- Roth, V., Lemann, T., Zeleke, G., & Teklay, A. Effects of climate change on water resources in the upper Blue Nile Basin of Ethiopia. Heliyon, November 2017. [CrossRef]
- Heyi, E. A., Dinka, M. O., and Mamo, G. Assessing the impact of climate change on water resources of upper Awash River sub-basin, Ethiopia. Journal of Water and Land Development, 2022, 52, Pp232–244. [CrossRef]
- Ayalew, D. W., Asefa, T., Moges, M. A., & Leyew, S. M. Evaluating the potential impact of climate change on the hydrology of Ribb catchment, Lake Tana Basin, Ethiopia. Journal of Water and Climate Change, (2022) 13(1), Pp 190–205. [CrossRef]
- Tibebe, D., Teferi, E., Bewket, W., & Zeleke, G. Climate induced water security risks on agriculture in the Abbay river basin: A review. Frontiers in Water, 2022, 4 p. [CrossRef]
- WaleWorqlul, A., Taddele, Y. D., Ayana, E. K., Jeong, J., Adem, A. A., & Gerik, T. Impact of climate change on streamflow hydrology in headwater catchments of the upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Water (Switzerland), 2018, 10(2). [CrossRef]
- Tadese, M., Kumar, L., & Koech, R. Long-term variability in potential evapotranspiration, water availability and drought under climate change scenarios in the Awash River Basin, Ethiopia. Atmosphere, 2020, 11(9). [CrossRef]
- Emiru, N. C., Recha, J. W., Thompson, J. R., Belay, A., Aynekulu, E., Manyevere, A., Demissie, T. D., Osano, P. M., Hussein, J., Molla, M. B., Mengistu, G. M., & Solomon, D.. Impact of Climate Change on the Hydrology of the Upper Awash River Basin, Ethiopia. Hydrology, 2022, 9(1). [CrossRef]
- Abebaw, W. A. Climate Change and Water Resource Management in Ethiopia. Journal of Geology & Geophysics, 11, 1043, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Kahsay, K. D., Pingale, S. M., and Hatiye, S. D. Impact of climate change on groundwater recharge and base flow in the sub-catchment of Tekeze basin, Ethiopia. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 2018. 6 p, 121–133. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y, Bi P, Hiller J, Sun Y, Ryan P. Climate variations and bacillary dysentery in northern and southern cities of China. Journal of Infection. 2007; 55:194–200. [CrossRef]
- Hounguè, N. R., Almoradie, A. D. S., & Evers, M. A Multi Criteria Decision Analysis Approach for Regional Climate Model Selection and Future Climate Assessment in the Mono River Basin, Benin and Togo. Atmosphere, 2022, 13(9). [CrossRef]
- Republic, S. A., Balzannikov, M. I., State, S., Re-, S., Centre, E., Borovkov, A. I., Borodinecs, A., Tech-, R., Veljkovic, M., Garg, R. D., Garifullin, M., Copernicus, I., Gries, T., Petersburg, S., Engineer-, C., Sergeev, V. V, Elistratov, V. V, Univer-, L., Kozinetc, G. L., Heck, D. (n.d.). A Multi Criteria Decision Analysis Approach for Regional Climate Model Selection and Future Climate Assessment in the Mono River Basin, Benin and Togo. Magazine of Civil Engineering. 2022. 113 (5), Magazine of Civil Engineering.
- Urama, K. C., & Ozor, N. Impacts of climate change on water resources in Africa : the Role of Adaptation. Network, December, 2010. 1–29. [CrossRef]
- Zabel, F. Impact of climate change on water availability. Regional Assessment of Global Change Impacts: The Project GLOWA-Danube, 2016. 2000(1), Pp463–469. [CrossRef]
- Bewket W, Radeny M, and Mungai C. Agricultural Adaptation and Institutional Responses to Climate Change Vulnerability in Ethiopia. CCAFS Working Paper no. 106. CGIAR Research Program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS). Copenhagen, Denmark 2015. [CrossRef]
- Waseem, M., Mani, N., Andiego, G., & Usman, M. A Review of Criteria of Fit for Hydrological Models. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology, 2008. 9001, Pp1765. www.irjet.net.
- Taye, M. T., Dyer, E., Hirpa, F. A., and Charles, K. Climate change impact on water resources in the awash basin, Ethiopia. Water (Switzerland), 2018. 10(11), Pp1–16. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).