Submitted:
21 July 2023
Posted:
24 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
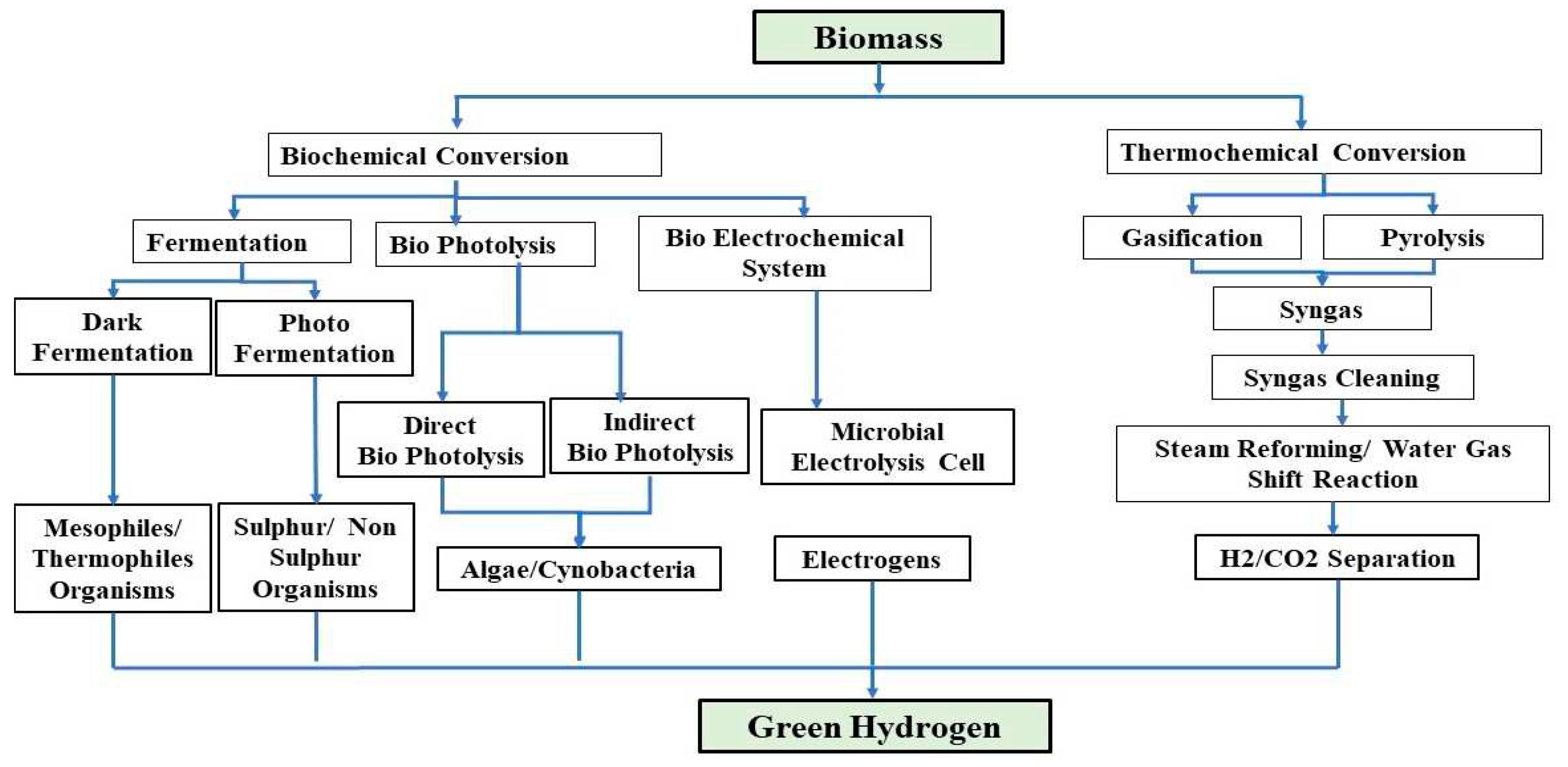
2. Bio hydrogen production technologies
2.1. Fermentation
2.1.1. Dark fermentation
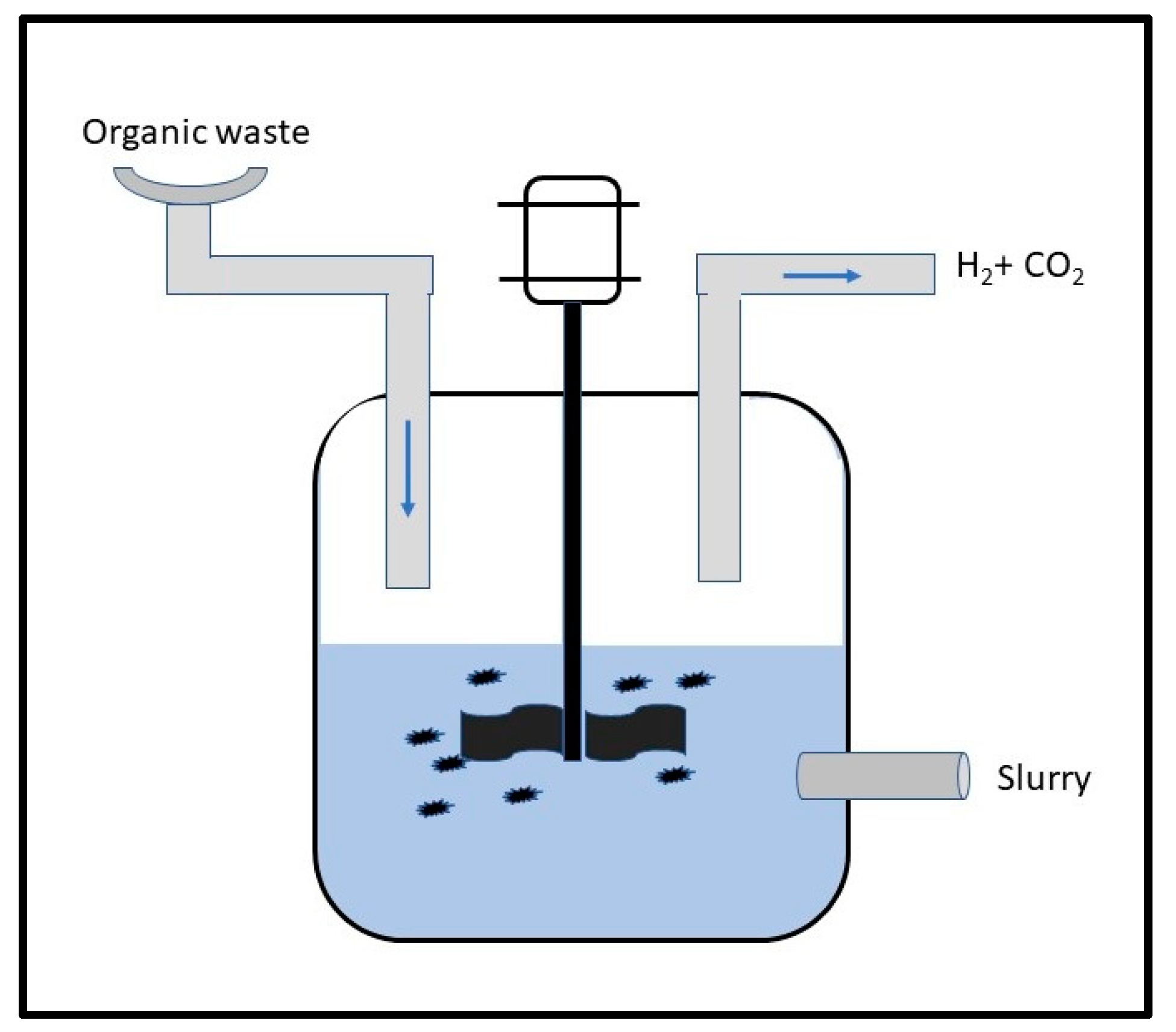
2.1.2. Photofermentation
2.2. Biophotolysis
2.2.1. Direct biophotolyisis
2.2.2. Indirect Biophotolysis
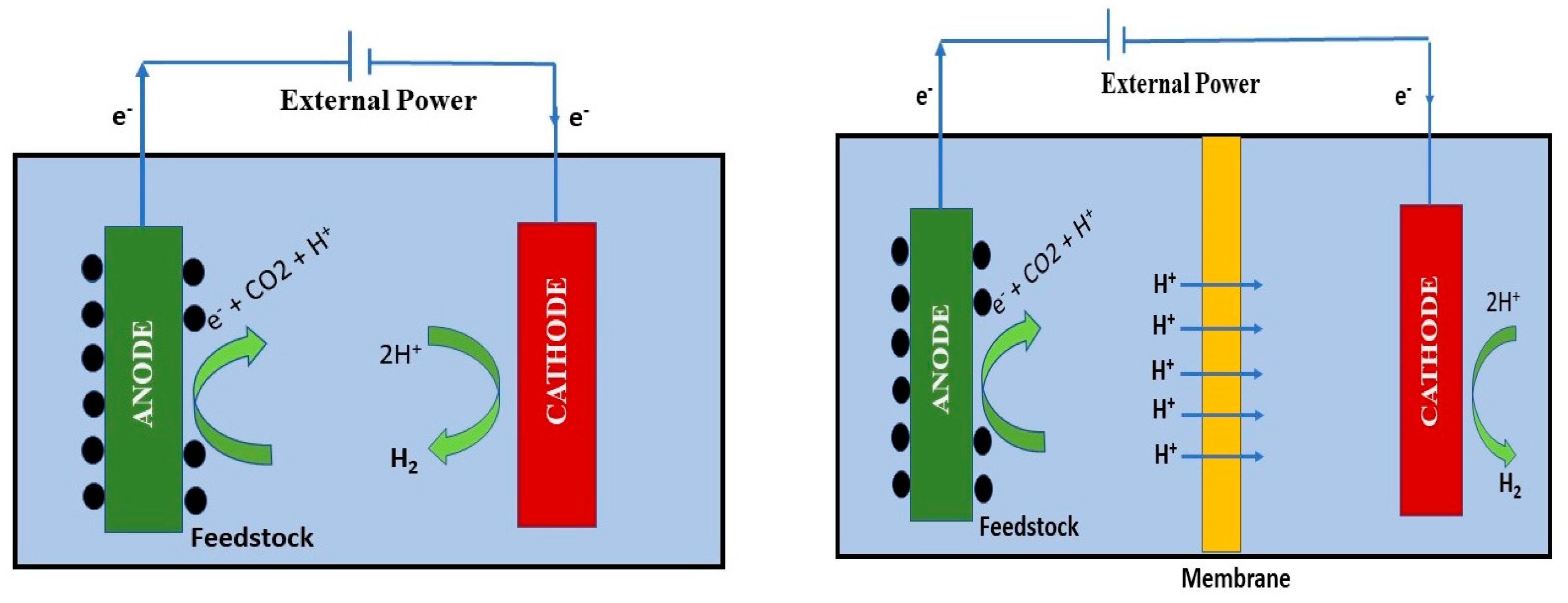
2.3. Bio hydrogen production using microbial electrolysis cells (MECs)
2.4. Thermochemical Conversion of Biomass
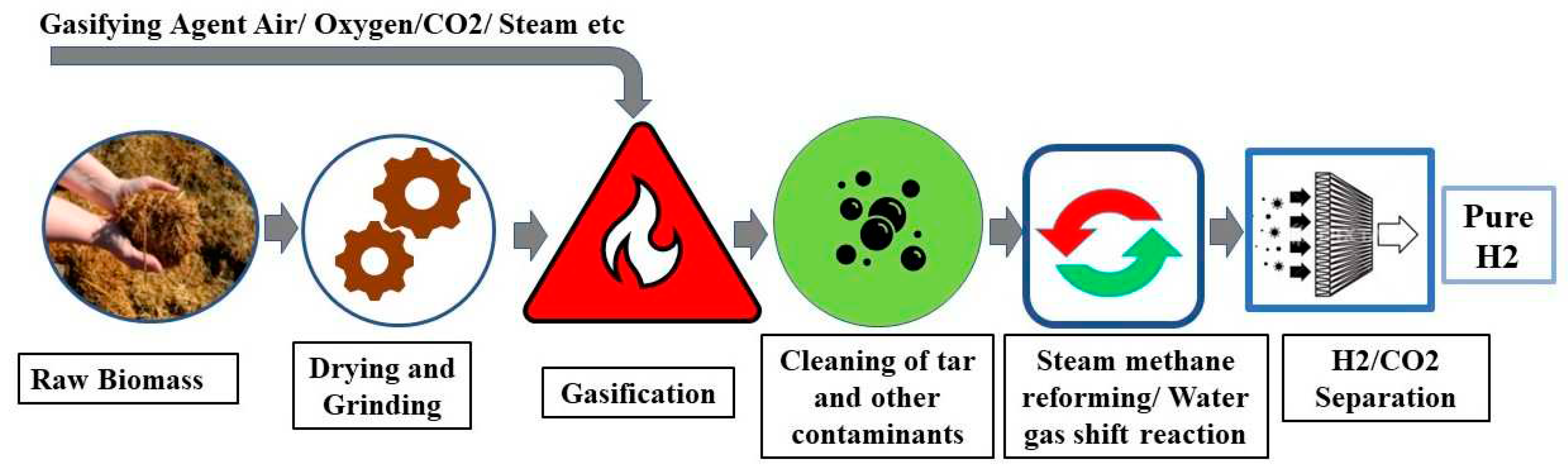
2.4.1. Gasification
2.4.1.1. Air Gasification
2.4.1.2. Oxy blown gasification
2.4.1.3. Steam blown gasification
2.4.1.4. Supercritical water gasification
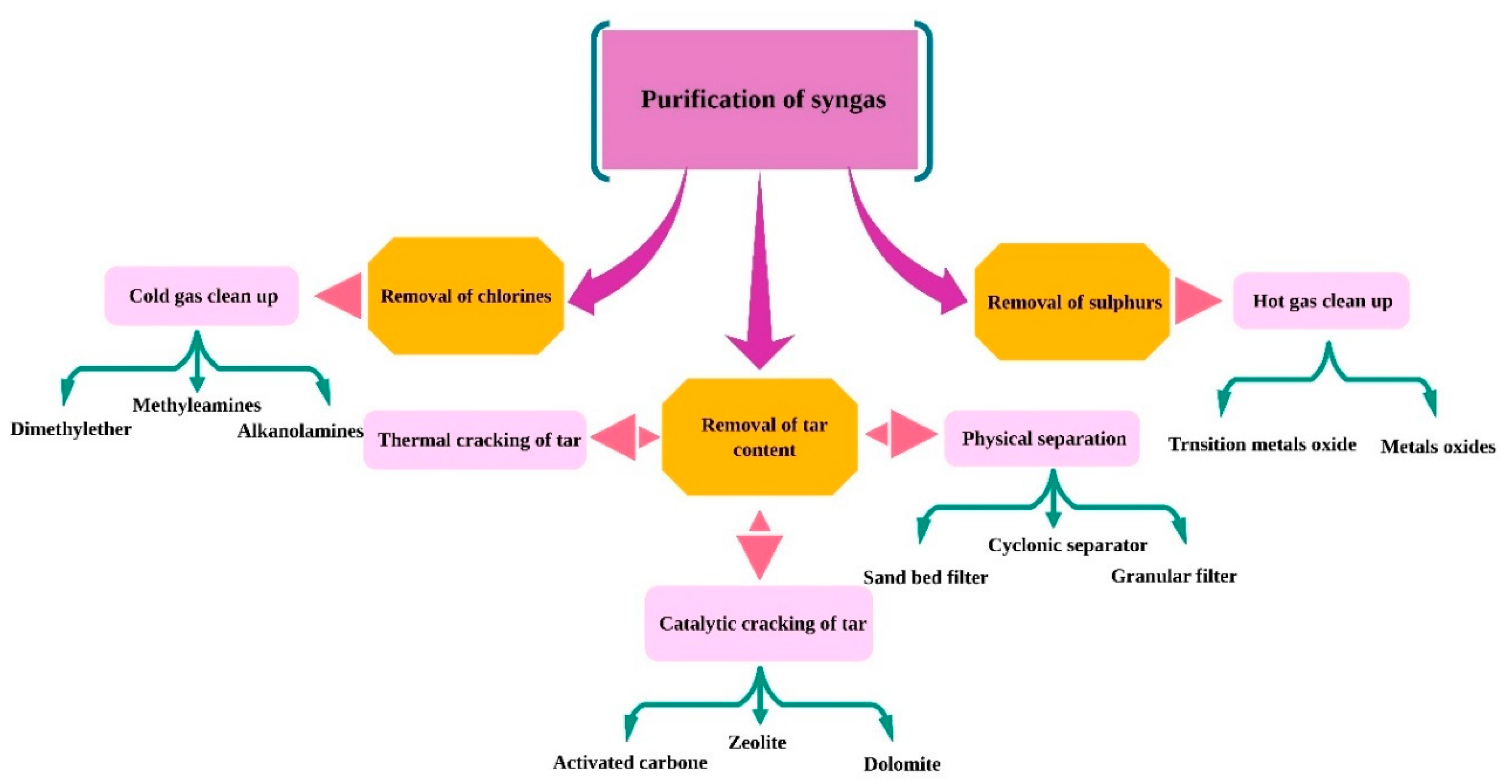
3. Cleaning and processing the gas
3.1. Producer gas reforming
3.1.1. Steam- Methane Reforming
3.1.2. Water-gas shift reaction
3.2. Separation and purification of Hydrogen
3.2.1. Removal of tars
3.2.1.1. Removal of tar using catalysts
3.2.1.2. Removal of tars by physical methods
3.2.2. Removal of Sulphur
3.2.3. Removal of Chlorine
4. Energy efficiency and green house gas emission footprints different hydrogen production routes
| Pathway | Conventional energy use (MJ) | Energy efficiency (%) | GHGs emission (kg CO2 eq) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermochemical Conversion | 256.8 | 43-70 | 2.14 | [154] |
| Dark Fermentation | 61.7 | 1-10 | -87 | [155] |
| Photo Fermentation | 40.1 | 1-25 | -21.9 | [155] |
| Dark+ Photofermentation | 39.3 | 27.2 | -19.5 | [156] |
| Microbial Electrolysis | 64.8 | 6-26 | -17.5 | [156] |
5. Comparison between different bio hydrogen production methods
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mandal, S.; Haydary, J.; Bhattacharya, T.K.; Tanna, H.R.; Husar, J.; Haz, A. Valorization of Pine Needles by Thermal Conversion to Solid, Liquid and Gaseous Fuels in a Screw Reactor. Waste Biomass Valorization 2019, 10, 3587–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Sharma, R.K.; Bhattacharya, T.K.; Tanna, H.; Haydary, J. Charring of Pine Needles Using a Portable Drum Reactor. Chemical Papers 2022, 76, 1239–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasik, P.; Horton, D. Enzymatic Conversions of Starch. In; 2012; pp. 59–436.
- Rizwan, M.; Shah, S.H.; Mujtaba, G.; Mahmood, Q.; Rashid, N.; Shah, F.A. Ecofuel Feedstocks and Their Prospect. In Advanced Biofuels; Elsevier, 2019; pp. 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Mona, S.; Kumar, S.S.; Kumar, V.; Parveen, K.; Saini, N.; Deepak, B.; Pugazhendhi, A. Green Technology for Sustainable Biohydrogen Production (Waste to Energy): A Review. Science of The Total Environment 2020, 728, 138481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghimire, A.; Frunzo, L.; Pirozzi, F.; Trably, E.; Escudie, R.; Lens, P.N.L.; Esposito, G. A Review on Dark Fermentative Biohydrogen Production from Organic Biomass: Process Parameters and Use of by-Products. Appl Energy 2015, 144, 73–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallenbeck, P.C. Fermentative Hydrogen Production: Principles, Progress, and Prognosis. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 7379–7389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarangi, P.K.; Nanda, S. Biohydrogen Production Through Dark Fermentation. Chem Eng Technol 2020, 43, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dincer, I.; Acar, C. Review and Evaluation of Hydrogen Production Methods for Better Sustainability. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 11094–11111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Li, J.; Yan, M.; Tong, Y.W.; Wang, C.-H.; Wang, X. Organic Waste to Biohydrogen: A Critical Review from Technological Development and Environmental Impact Analysis Perspective. Appl Energy 2019, 256, 113961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibardi, L.; Cossu, R. Effects of Carbohydrate, Protein and Lipid Content of Organic Waste on Hydrogen Production and Fermentation Products. Waste Management 2016, 47, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Li, Z.; Fan, Y.; Hou, H. Biohydrogen Production from Dairy Manures with Acidification Pretreatment by Anaerobic Fermentation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2010, 17, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafieenia, R.; Lavagnolo, M.C.; Pivato, A. Pre-Treatment Technologies for Dark Fermentative Hydrogen Production: Current Advances and Future Directions. Waste Management 2018, 71, 734–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamimin, C.; Singkhala, A.; Kongjan, P.; Suraraksa, B.; Prasertsan, P.; Imai, T.; O-Thong, S. Two-Stage Thermophilic Fermentation and Mesophilic Methanogen Process for Biohythane Production from Palm Oil Mill Effluent. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 6319–6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Zhen, G.; Sivagurunathan, P.; Bakonyi, P.; Nemestóthy, N.; Bélafi-Bakó, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Xu, K.-Q. Biogenic H2 Production from Mixed Microalgae Biomass: Impact of PH Control and Methanogenic Inhibitor (BESA) Addition. Biofuel Research Journal 2016, 3, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, K.; Lee, Y.-J.; Lee, D.-W. Biohydrogen Production: Strategies to Improve Process Efficiency through Microbial Routes. Int J Mol Sci 2015, 16, 8266–8293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, K.; Venkata Mohan, S. Bio-Electrohydrolysis as a Pretreatment Strategy to Catabolize Complex Food Waste in Closed Circuitry: Function of Electron Flux to Enhance Acidogenic Biohydrogen Production. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 11411–11422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Integration of Biological H2 Producing Processes. In State of the Art and Progress in Production of Biohydrogen; Azbar, N., Levin, D.B., Eds.; BENTHAM SCIENCE PUBLISHERS, 2012; pp. 78–93. [Google Scholar]
- Colombo, B.; Villegas Calvo, M.; Pepè Sciarria, T.; Scaglia, B.; Savio Kizito, S.; D’Imporzano, G.; Adani, F. Biohydrogen and Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) as Products of a Two-Steps Bioprocess from Deproteinized Dairy Wastes. Waste Management 2019, 95, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Ding, L.; Liu, M.; Cheng, J.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.-Y. Improving Biohydrogen Production through Dark Fermentation of Steam-Heated Acid Pretreated Alternanthera Philoxeroides by Mutant Enterobacter Aerogenes ZJU1. Science of The Total Environment 2020, 716, 134695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, W.; Wang, Q.; Rupani, P.F.; Krishnan, S.; Ahmad, F.; Rezania, S.; Rashid, M.A.; Sha, C.; Md Din, M.F. Biohydrogen Production via Thermophilic Fermentation: A Prospective Application of Thermotoga Species. Energy 2020, 197, 117199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Wang, J. Enhanced Hydrogen Production from Sewage Sludge by Co-Fermentation with Forestry Wastes. Energy & Fuels 2017, 31, 9633–9641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemahdi, N.; Che Man, H.; Abd Rahman, N.; Nasirian, N.; Yang, Y. Enhanced Mesophilic Bio-Hydrogen Production of Raw Rice Straw and Activated Sewage Sludge by Co-Digestion. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 16033–16044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Srivastava, M.; Kushwaha, D.; Gupta, V.K.; Manikanta, A.; Ramteke, P.W.; Mishra, P.K. Efficient Dark Fermentative Hydrogen Production from Enzyme Hydrolyzed Rice Straw by Clostridium Pasteurianum (MTCC116). Bioresour Technol 2017, 238, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroy, I.; Buitrón, G. Production of Polyhydroxybutyrate by Pure and Mixed Cultures of Purple Non-Sulfur Bacteria: A Review. J Biotechnol 2020, 317, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, D. Advances in Biohydrogen Production Processes: An Approach towards Commercialization. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 7349–7357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Krishnan, S.; Rana, S.; Singh, L.; Sakinah, M.; Ab Wahid, Z. Outlook of Fermentative Hydrogen Production Techniques: An Overview of Dark, Photo and Integrated Dark-Photo Fermentative Approach to Biomass. Energy Strategy Reviews 2019, 24, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, M.; Leung, D.Y.C.; Leung, M.K.H.; Sumathy, K. An Overview of Hydrogen Production from Biomass. Fuel Processing Technology 2006, 87, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, J.; Li, F.; Feng, C.; Guan, Y.; Wang, R.; Tang, N. Photosynthetic Bacteria Improved Hydrogen Yield of Combined Dark- and Photo-Fermentation. J Biotechnol 2019, 302, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azwar, M.Y.; Hussain, M.A.; Abdul-Wahab, A.K. Development of Biohydrogen Production by Photobiological, Fermentation and Electrochemical Processes: A Review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2014, 31, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, S.S.; Qazi, J.I.; Liang, Y.; Chen, S. Growth Characteristics and Photofermentative Biohydrogen Production Potential of Purple Non Sulfur Bacteria from Sugar Cane Bagasse. Fuel 2019, 255, 115805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Sánchez, R.; Ramos-Ibarra, R.; Guatemala-Morales, G.; Arriola-Guevara, E.; Toriz-González, G.; Corona-González, R.I. Photofermentation of Tequila Vinasses by Rhodopseudomonas Pseudopalustris to Produce Hydrogen. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 15857–15869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurinavichene, T.; Tekucheva, D.; Laurinavichius, K.; Tsygankov, A. Utilization of Distillery Wastewater for Hydrogen Production in One-Stage and Two-Stage Processes Involving Photofermentation. Enzyme Microb Technol 2018, 110, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, R.G.; Moreira, F.S.; Batista, F.R.X.; Ferreira, J.S.; Cardoso, V.L. Repeated Batch Cycles as an Alternative for Hydrogen Production by Co-Culture Photofermentation. Energy 2018, 153, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, T.; Hallenbeck, P.C. Hydrogen Production from Sugar Industry Wastes Using Single-Stage Photofermentation. Bioresour Technol 2012, 112, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Li, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, H.; Jing, Y.; Jiang, D.; He, C.; Zhang, Z. Evaluation of Biohydrogen Yield Potential and Electron Balance in the Photo-Fermentation Process with Different Initial PH from Starch Agricultural Leftover. Bioresour Technol 2020, 305, 122900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adessi, A.; Venturi, M.; Candeliere, F.; Galli, V.; Granchi, L.; De Philippis, R. Bread Wastes to Energy: Sequential Lactic and Photo-Fermentation for Hydrogen Production. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 9569–9576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Lu, C.; Wang, K.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Jing, Y.; Zhang, Q. Enhancement of PH Values Stability and Photo-Fermentation Biohydrogen Production by Phosphate Buffer. Bioengineered 2020, 11, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-S.; Kim, D.-H.; Cha, J.; Lee, J.K. Effect of Carbon and Nitrogen Sources on Photo-Fermentative H2 Production Associated with Nitrogenase, Uptake Hydrogenase Activity, and PHB Accumulation in Rhodobacter Sphaeroides KD131. Bioresour Technol 2012, 116, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Lu, C.; Zhu, S.; He, C.; Ai, F.; Zhang, Q. Investigation of the Interaction between Lighting and Mixing Applied during the Photo-Fermentation Biohydrogen Production Process from Agricultural Waste. Bioresour Technol 2020, 312, 123570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Jing, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q. Rheological Properties of Corn Stover Hydrolysate and Photo-Fermentation Bio-Hydrogen Producing Capacity under Intermittent Stirring. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 3721–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, H.; Lee, D.J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Jing, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, C. Effects of Different Pretreatment Methods on the Structural Characteristics, Enzymatic Saccharification and Photo-Fermentative Bio-Hydrogen Production Performance of Corn Straw. Bioresour Technol 2020, 304, 122999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lee, D.J.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q. Effect of Enzymolysis Time on Biohydrogen Production from Photo-Fermentation by Using Various Energy Grasses as Substrates. Bioresour Technol 2020, 305, 123062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagakawa, H.; Takeuchi, A.; Takekuma, Y.; Noji, T.; Kawakami, K.; Kamiya, N.; Nango, M.; Furukawa, R.; Nagata, M. Efficient Hydrogen Production Using Photosystem I Enhanced by Artificial Light Harvesting Dye. Photochemical & Photobiological Sciences 2019, 18, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhimi, N.; Tavakoli, O. Improving Hydrogen Production Using Co-Cultivation of Bacteria with Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii Microalga. Mater Sci Energy Technol 2019, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kossalbayev, B.D.; Tomo, T.; Zayadan, B.K.; Sadvakasova, A.K.; Bolatkhan, K.; Alwasel, S.; Allakhverdiev, S.I. Determination of the Potential of Cyanobacterial Strains for Hydrogen Production. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 2627–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, T.; Johnson, D.J.; Scholz, M.; Cuello, J.L. Effects of Implementing PSI-Light on Hydrogen Production via Biophotolysis in Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii Mutant Strains. Biomass Bioenergy 2013, 59, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyberg, M.; Heidorn, T.; Lindblad, P. Hydrogen Production by the Engineered Cyanobacterial Strain Nostoc PCC 7120 ΔhupW Examined in a Flat Panel Photobioreactor System. J Biotechnol 2015, 215, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volgusheva, A.; Kukarskikh, G.; Krendeleva, T.; Rubin, A.; Mamedov, F. Hydrogen Photoproduction in Green Algae Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii under Magnesium Deprivation. RSC Adv 2015, 5, 5633–5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batyrova, K.; Gavrisheva, A.; Ivanova, E.; Liu, J.; Tsygankov, A. Sustainable Hydrogen Photoproduction by Phosphorus-Deprived Marine Green Microalgae Chlorella Sp. Int J Mol Sci 2015, 16, 2705–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.-Y.; Yu, H.-Q. Simultaneous Metabolism of Benzoate and Photobiological Hydrogen Production by Lyngbya Sp. Renew Energy 2016, 95, 474–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oncel, S.; Kose, A. Comparison of Tubular and Panel Type Photobioreactors for Biohydrogen Production Utilizing Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii Considering Mixing Time and Light Intensity. Bioresour Technol 2014, 151, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosourov, S.; Seibert, M.; Ghirardi, M.L. Effects of Extracellular PH on the Metabolic Pathways in Sulfur-Deprived, H2-Producing Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii Cultures. Plant Cell Physiol 2003, 44, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadier, A.; Simayi, Y.; Abdeshahian, P.; Azman, N.F.; Chandrasekhar, K.; Kalil, M.S. A Comprehensive Review of Microbial Electrolysis Cells (MEC) Reactor Designs and Configurations for Sustainable Hydrogen Gas Production. Alexandria Engineering Journal 2016, 55, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yossan, S.; Xiao, L.; Prasertsan, P.; He, Z. Hydrogen Production in Microbial Electrolysis Cells: Choice of Catholyte. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 9619–9624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Jain, A.; Aguilera, A.; He, Z. Effective Control of Biohythane Composition through Operational Strategies in an Innovative Microbial Electrolysis Cell. Appl Energy 2017, 206, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidrich, E.S.; Edwards, S.R.; Dolfing, J.; Cotterill, S.E.; Curtis, T.P. Performance of a Pilot Scale Microbial Electrolysis Cell Fed on Domestic Wastewater at Ambient Temperatures for a 12 Month Period. Bioresour Technol 2014, 173, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.; Jiang, Y.; Ge, Z.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ren, Z.J. Microbial Electrolysis Treatment of Post-Hydrothermal Liquefaction Wastewater with Hydrogen Generation. Appl Energy 2018, 212, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, R.C.; Regan, J.M.; Oh, S.-E.; Zuo, Y.; Logan, B.E. Hydrogen and Methane Production from Swine Wastewater Using Microbial Electrolysis Cells. Water Res 2009, 43, 1480–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escapa, A.; Gil-Carrera, L.; García, V.; Morán, A. Performance of a Continuous Flow Microbial Electrolysis Cell (MEC) Fed with Domestic Wastewater. Bioresour Technol 2012, 117, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusick, R.D.; Kiely, P.D.; Logan, B.E. A Monetary Comparison of Energy Recovered from Microbial Fuel Cells and Microbial Electrolysis Cells Fed Winery or Domestic Wastewaters. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 8855–8861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Xing, D.; Liu, B.; Ren, N. Enhanced Hydrogen Production from Waste Activated Sludge by Cascade Utilization of Organic Matter in Microbial Electrolysis Cells. Water Res 2012, 46, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, B.R.; Elbeshbishy, E.; Hafez, H.; Lee, H.-S. Hydrogen Production from Sugar Beet Juice Using an Integrated Biohydrogen Process of Dark Fermentation and Microbial Electrolysis Cell. Bioresour Technol 2015, 198, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Feng, H.; Huang, L.; Ying, X.; Shen, D.; Chen, T.; Shen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, Y. Continuous Hydrogen Production from Food Waste by Anaerobic Digestion (AD) Coupled Single-Chamber Microbial Electrolysis Cell (MEC) under Negative Pressure. Waste Management 2020, 103, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-H.; Liang, D.-W.; Bai, Y.-X.; Fan, Y.-T.; Hou, H.-W. Enhanced H2 Production from Corn Stalk by Integrating Dark Fermentation and Single Chamber Microbial Electrolysis Cells with Double Anode Arrangement. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 8977–8982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Enhancement of Sludge Decomposition and Hydrogen Production from Waste Activated Sludge in a Microbial Electrolysis Cell with Cheap Electrodes. Environ Sci (Camb) 2015, 1, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Singh, L.; Zularisam, A.W. Exoelectrogens: Recent Advances in Molecular Drivers Involved in Extracellular Electron Transfer and Strategies Used to Improve It for Microbial Fuel Cell Applications. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2016, 56, 1322–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, R.; Cheng, K.Y.; Selvam, A.; Bose, A.; Wong, J.W.C. Bioelectrohydrogenesis and Inhibition of Methanogenic Activity in Microbial Electrolysis Cells - A Review. Biotechnol Adv 2017, 35, 758–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.; Liu, Z.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Si, B.; Zhang, C.; Xing, X.-H. Microbial Electrolysis Cell to Treat Hydrothermal Liquefied Wastewater from Cornstalk and Recover Hydrogen: Degradation of Organic Compounds and Characterization of Microbial Community. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 4132–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Prasanna Kumar, G. V.; Bhattacharya, T.K.; Tanna, H.R.; Jena, P.C. Briquetting of Pine Needles (Pinus Roxburgii) and Their Physical, Handling and Combustion Properties. Waste Biomass Valorization 2019, 10, 2415–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdoulmoumine, N.; Adhikari, S.; Kulkarni, A.; Chattanathan, S. A Review on Biomass Gasification Syngas Cleanup. Appl Energy 2015, 155, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Wu, C.; Yan, Y. The Characteristics of Inorganic Elements in Ashes from a 1 MW CFB Biomass Gasification Power Generation Plant. Fuel Processing Technology 2007, 88, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikarwar, V.S.; Zhao, M.; Clough, P.; Yao, J.; Zhong, X.; Memon, M.Z.; Shah, N.; Anthony, E.J.; Fennell, P.S. An Overview of Advances in Biomass Gasification. Energy Environ Sci 2016, 9, 2939–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansaniwal, S.K.; Rosen, M.A.; Tyagi, S.K. Global Challenges in the Sustainable Development of Biomass Gasification: An Overview. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2017, 80, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trippe, F.; Fröhling, M.; Schultmann, F.; Stahl, R.; Henrich, E. Techno-Economic Assessment of Gasification as a Process Step within Biomass-to-Liquid (BtL) Fuel and Chemicals Production. Fuel Processing Technology 2011, 92, 2169–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pio, D.T.; Tarelho, L.A.C.; Nunes, T.F.V.; Baptista, M.F.; Matos, M.A.A. Co-Combustion of Residual Forest Biomass and Sludge in a Pilot-Scale Bubbling Fluidized Bed. J Clean Prod 2020, 249, 119309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inayat, M.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Bhayo, B.A.; Shahbaz, M. Application of Response Surface Methodology in Catalytic Co-Gasification of Palm Wastes for Bioenergy Conversion Using Mineral Catalysts. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 132, 105418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Huang, Y.; Jin, B.; Wang, X. Oxygen Gasification of Municipal Solid Waste in a Fixed-Bed Gasifier. Chin J Chem Eng 2014, 22, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Bhattacharya, A.; Datta, A. Modeling of Hydrogen Production Process from Biomass Using Oxygen Blown Gasification. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 18782–18790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiland, F.; Hedman, H.; Marklund, M.; Wiinikka, H.; Öhrman, O.; Gebart, R. Pressurized Oxygen Blown Entrained-Flow Gasification of Wood Powder. Energy & Fuels 2013, 27, 932–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, W.; Blasiak, W. Energy and Exergy Analysis of High Temperature Agent Gasification of Biomass. Energies (Basel) 2014, 7, 2107–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siedlecki, M.; de Jong, W. Biomass Gasification as the First Hot Step in Clean Syngas Production Process – Gas Quality Optimization and Primary Tar Reduction Measures in a 100 KW Thermal Input Steam–Oxygen Blown CFB Gasifier. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, S40–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, G.; Cortazar, M.; Alvarez, J.; Amutio, M.; Bilbao, J.; Olazar, M. Assessment of a Conical Spouted with an Enhanced Fountain Bed for Biomass Gasification. Fuel 2017, 203, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.-X.; Yang, G.-H.; Ding, G.-Z.; Li, Z.; Du, K.-S.; Hu, Z.-F.; Tian, S.-R. Experimental Study on Catalytic Cracking of Model Tar Compounds in a Dual Layer Granular Bed Filter. Appl Energy 2016, 170, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anis, S.; Zainal, Z.A. Tar Reduction in Biomass Producer Gas via Mechanical, Catalytic and Thermal Methods: A Review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2011, 15, 2355–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Xiao, B.; Hu, Z.; Liu, S.; Guo, X.; He, M. Hydrogen-Rich Gas from Catalytic Steam Gasification of Biomass in a Fixed Bed Reactor: Influence of Temperature and Steam on Gasification Performance. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, S.Z.; Xu, D.H.; Gong, Y.M.; Ma, H.H.; Tang, X.Y. Review of Catalytic Supercritical Water Gasification for Hydrogen Production from Biomass. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2010, 14, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzavara, Y.; Joussot-Dubien, C.; Boissonnet, G.; Sarrade, S. Evaluation of Biomass Gasification in Supercritical Water Process for Hydrogen Production. Energy Convers Manag 2005, 46, 615–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, F.; Javani, N.; Yumurtaci, Z. Hydrogen Production via Supercritical Water Gasification of Almond Shell over Algal and Agricultural Hydrochars as Catalysts. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GAO, N.; LI, A.; QUAN, C.; GAO, F. Hydrogen-Rich Gas Production from Biomass Steam Gasification in an Updraft Fixed-Bed Gasifier Combined with a Porous Ceramic Reformer. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 5430–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, M.; Li, G.; Guan, Y.; Li, C.; Zhou, R.; Zarnegar, A.-M. Hydrogen and Syngas Production from Steam Gasification of Biomass Using Cement as Catalyst. Biomass Convers Biorefin 2020, 10, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TURN, S. An Experimental Investigation of Hydrogen Production from Biomass Gasification. Int J Hydrogen Energy 1998, 23, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.C.C.; Chang, H.-F.; Lin, F.-J.; Lin, K.-H.; Chen, C.-H. Biomass Gasification for Hydrogen Production. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 14252–14260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onwudili, J.A.; Williams, P.T. Hydrogen and Methane Selectivity during Alkaline Supercritical Water Gasification of Biomass with Ruthenium-Alumina Catalyst. Appl Catal B 2013, 132–133, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antal, M.J.; Allen, S.G.; Schulman, D.; Xu, X.; Divilio, R.J. Biomass Gasification in Supercritical Water. Ind Eng Chem Res 2000, 39, 4040–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacquart, T.; Moore, N.; Storms, W.; Chramosta, N.; Morris, A.; Murugan, A.; Gozlan, B.; Lescornez, Y.; Férat, S.; Pinte, G.; et al. Hydrogen Fuel Quality for Transport – First Sampling and Analysis Comparison in Europe on Hydrogen Refuelling Station (70 MPa) According to ISO 14687 and EN 17124. Fuel Communications 2021, 6, 100008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Zhao, C.; Wu, X.; Liang, C.; Chen, X.; Shen, J.; Wang, Z. Formation of NOx Precursors during Wheat Straw Pyrolysis and Gasification with O2 and CO2. Fuel 2010, 89, 1064–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Donald, J.; Byambajav, E.; Ohtsuka, Y. Recent Advances in Catalysts for Hot-Gas Removal of Tar and NH3 from Biomass Gasification. Fuel 2010, 89, 1784–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, K.Y.; Lu, C.H.; Lin, M.H.; Chien, K.L. Reducing Tar Yield in Gasification of Paper-Reject Sludge by Using a Hot-Gas Cleaning System. Energy 2013, 50, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halabi, M.H.; De Croon, M.H.J.M.; Van Der Schaaf, J.; Cobden, P.D.; Schouten, J.C. Low Temperature Catalytic Methane Steam Reforming over Ceria–Zirconia Supported Rhodium. Appl Catal A Gen 2010, 389, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T.N.L.T.; Chiang, K.Y.; Liu, C.F.; Chang, Y.H.; Wan, H.P. Hydrogen Production Enhancement Using Hot Gas Cleaning System Combined with Prepared Ni-Based Catalyst in Biomass Gasification. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 11269–11283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarlan, A.; Maffei, N. Assessing a Commercial Steam Methane Reforming Catalyst for Tar Removal in Biomass Gasification. Bioresour Technol Rep 2022, 17, 100968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swierczynski, D.; Courson, C.; Kiennemann, A. Study of Steam Reforming of Toluene Used as Model Compound of Tar Produced by Biomass Gasification. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification 2008, 47, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammal, S.C.; Heyden, A. Origin of the Unique Activity of Pt/TiO2 Catalysts for the Water–Gas Shift Reaction. J Catal 2013, 306, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S. Recent Advances in Thermochemical Conversion of Woody Biomass for Production of Green Hydrogen and CO2 Capture: A Review. Journal of Bioresources and Bioproducts 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, J.S.; Teoh, Y.H.; How, H.G.; Le, T.D.; Jason, Y.J.J.; Nguyen, H.T.; Loo, D.L. The Potential of Sustainable Biomass Producer Gas as a Waste-to-Energy Alternative in Malaysia. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraj, E.; Ciahotný, K.; Hlinčík, T. The Water Gas Shift Reaction: Catalysts and Reaction Mechanism. Fuel 2021, 288, 119817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Chen, C.Y. Water Gas Shift Reaction for Hydrogen Production and Carbon Dioxide Capture: A Review. Appl Energy 2020, 258, 114078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.W.; Lee, M.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, S.; Eom, H.J.; Moon, D.J.; Lee, K.Y. The Review of Cr-Free Fe-Based Catalysts for High-Temperature Water-Gas Shift Reactions. Catal Today 2013, 210, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, T.K.; Sheth, P.N. Biomass Gasification Coupled with Producer Gas Cleaning, Bottling and HTS Catalyst Treatment for H2-Rich Gas Production. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 11602–11616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noichi, H.; Uddin, A.; Sasaoka, E. Steam Reforming of Naphthalene as Model Biomass Tar over Iron–Aluminum and Iron–Zirconium Oxide Catalyst Catalysts. Fuel Processing Technology 2010, 91, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, D.; Kelleher, B.; Ross, J.R.H. Review of Literature on Catalysts for Biomass Gasification. Fuel Processing Technology 2001, 73, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anis, S.; Zainal, Z.A. Tar Reduction in Biomass Producer Gas via Mechanical, Catalytic and Thermal Methods: A Review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2011, 15, 2355–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, J.; Aznar, M.P.; Corella, J. Biomass Gasification with Steam in Fluidized Bed: Effectiveness of CaO, MgO, and CaO−MgO for Hot Raw Gas Cleaning. Ind Eng Chem Res 1997, 36, 1535–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallozzi, V.; Di Carlo, A.; Bocci, E.; Carlini, M. Combined Gas Conditioning and Cleaning for Reduction of Tars in Biomass Gasification. Biomass Bioenergy 2018, 109, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orío, A.; Corella, J.; Narváez, I. Performance of Different Dolomites on Hot Raw Gas Cleaning from Biomass Gasification with Air. Ind Eng Chem Res 1997, 36, 3800–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, F.; André, R.N.; Carolino, C.; Miranda, M.; Abelha, P.; Direito, D.; Dohrup, J.; Sørensen, H.R.; Girio, F. Effects of Experimental Conditions and of Addition of Natural Minerals on Syngas Production from Lignin by Oxy-Gasification: Comparison of Bench- and Pilot Scale Gasification. Fuel 2015, 140, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, E.; De Andrés, J.M.; Narros, A.; Rodríguez, M.E. Air and Air-Steam Gasification of Sewage Sludge. The Influence of Dolomite and Throughput in Tar Production and Composition. Fuel 2014, 115, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, Y.; Blin, J.; Julbe, A. A Short Overview on Purification and Conditioning of Syngas Produced by Biomass Gasification: Catalytic Strategies, Process Intensification and New Concepts. Prog Energy Combust Sci 2012, 38, 765–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simell, P.A.; Leppälahti, J.K.; Bredenberg, J.B. son Catalytic Purification of Tarry Fuel Gas with Carbonate Rocks and Ferrous Materials. Fuel 1992, 71, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taralas, G.; Vassilatos, V.; Sjöström, K.; Delgado, J. Thermal and Catalytic Cracking of n -Heptane in Presence of CaO, MgO and Calcined Dolomites. Can J Chem Eng 1991, 69, 1413–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taralas, G. Catalytic Steam Cracking of n -Heptane with Special Reference to the Effect of Calcined Dolomite. Ind Eng Chem Res 1996, 35, 2121–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomi, S.; Kurkela, E.; Simell, P.; Reinikainen, M. Behaviour of Tars on the Filter in High Temperature Filtration of Biomass-Based Gasification Gas. Fuel 2015, 139, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeone, E.; Siedlecki, M.; Nacken, M.; Heidenreich, S.; De Jong, W. High Temperature Gas Filtration with Ceramic Candles and Ashes Characterisation during Steam–Oxygen Blown Gasification of Biomass. Fuel 2013, 108, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anis, S.; Zainal, Z.A. Tar Reduction in Biomass Producer Gas via Mechanical, Catalytic and Thermal Methods: A Review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2011, 15, 2355–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapagnà, S.; Gallucci, K.; Foscolo, P.U. Olivine, Dolomite and Ceramic Filters in One Vessel to Produce Clean Gas from Biomass. Waste Management 2018, 71, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savuto, E.; Di Carlo, A.; Steele, A.; Heidenreich, S.; Gallucci, K.; Rapagnà, S. Syngas Conditioning by Ceramic Filter Candles Filled with Catalyst Pellets and Placed inside the Freeboard of a Fluidized Bed Steam Gasifier. Fuel Processing Technology 2019, 191, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasler, P.; Nussbaumer, Th. Gas Cleaning for IC Engine Applications from Fixed Bed Biomass Gasification. Biomass Bioenergy 1999, 16, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Kitano, S.; Yoshikawa, K. Biomass Gasification Process with the Tar Removal Technologies Utilizing Bio-Oil Scrubber and Char Bed. Appl Energy 2016, 170, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, W.; Ünal, Ö.; Andries, J.; Hein, K.R.G.; Spliethoff, H. Biomass and Fossil Fuel Conversion by Pressurised Fluidised Bed Gasification Using Hot Gas Ceramic Filters as Gas Cleaning. Biomass Bioenergy 2003, 25, 59–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, P.C.A., B.H.B.H.. et al TAR Removal with A Wet Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP); A Parametric Study,” Exhibition, Presented at “the 2nd World Conference and Technology on Biomass for Energy, Industry and Climate Protection” in Rome. 2004.
- Ma, L.; Verelst, H.; Baron, G. V. Integrated High Temperature Gas Cleaning: Tar Removal in Biomass Gasification with a Catalytic Filter. Catal Today 2005, 105, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelen, K.; Zhang, Y.; Draelants, D.J.; Baron, G. V. A Novel Catalytic Filter for Tar Removal from Biomass Gasification Gas: Improvement of the Catalytic Activity in Presence of H2S. Chem Eng Sci 2003, 58, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khummongkol, D.; Tangsathitkulchai, C. A Model for Tar-Removal Efficiency from Biomass-Produced Gas Impinging on a Water Surface. Energy 1989, 14, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhansu; Karmakar, M. K.; Chandra, P.; Chatterjee, P.K. A Review on the Fuel Gas Cleaning Technologies in Gasification Process. J Environ Chem Eng 2015, 3, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhave, A.G.; Vyas, D.K.; Patel, J.B. A Wet Packed Bed Scrubber-Based Producer Gas Cooling–Cleaning System. Renew Energy 2008, 33, 1716–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, S.; Carpenter, D.L.; Magrini-Bair, K.A. Review of Mid- to High-Temperature Sulfur Sorbents for Desulfurization of Biomass- and Coal-Derived Syngas. Energy & Fuels 2009, 23, 5291–5307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husmann, M.; Zuber, C.; Maitz, V.; Kienberger, T.; Hochenauer, C. Comparison of Dolomite and Lime as Sorbents for In-Situ H2S Removal with Respect to Gasification Parameters in Biomass Gasification. Fuel 2016, 181, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.P.; O’Brien, W.S. Desulfurization of Hot Syngas Containing Hydrogen Chloride Vapors Using Zinc Titanate Sorbents. Ind Eng Chem Res 2000, 39, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.A.; Maiti, A. Adsorption and Decomposition of H 2 S on MgO(100), NiMgO(100), and ZnO(0001) Surfaces: A First-Principles Density Functional Study. J Phys Chem B 2000, 104, 3630–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimane, R.B.; Abbasian, J. Copper-Based Sorbents for Coal Gas Desulfurization at Moderate Temperatures. Ind Eng Chem Res 2000, 39, 1338–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Kaytakoglu, S.; Harrison, D.P. Reduced Cerium Oxide as an Efficient and Durable High Temperature Desulfurization Sorbent. Chem Eng Sci 2000, 55, 4893–4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; de Jong, W.; Pal, R.; Verkooijen, A.H.M. In Bed and Downstream Hot Gas Desulphurization during Solid Fuel Gasification: A Review. Fuel Processing Technology 2010, 91, 964–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, S.; Sarofim, A.F.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Sulfidation of Zinc Titanate and Zinc Oxide Solids. Ind Eng Chem Res 1992, 31, 1890–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAN, H.-L.; LI, C.-H.; LI, C.-H. Testing of Iron Oxide Sorbent for High-Temperature Coal Gas Desulfurization. Energy Sources 2005, 27, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yrjas, K.P.; Zevenhoven, C.A.P.; Hupa, M.M. Hydrogen Sulfide Capture by Limestone and Dolomite at Elevated Pressure. 1. Sorbent Performance. Ind Eng Chem Res 1996, 35, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ephraim, A.; Ngo, L.; Pham Minh, D.; Lebonnois, D.; Peregrina, C.; Sharrock, P.; Nzihou, A. Valorization of Waste-Derived Inorganic Sorbents for the Removal of HCl in Syngas. Waste Biomass Valorization 2019, 10, 3435–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdone, N.; De Filippis, P. Reaction Kinetics of Hydrogen Chloride with Sodium Carbonate. Chem Eng Sci 2006, 61, 7487–7496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsuka, Y.; Tsubouchi, N.; Kikuchi, T.; Hashimoto, H. Recent Progress in Japan on Hot Gas Cleanup of Hydrogen Chloride, Hydrogen Sulfide and Ammonia in Coal-Derived Fuel Gas. Powder Technol 2009, 190, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, G.; Gupta, R. DEVELOPMENT OF DISPOSABLE SORBENTS FOR CHLORIDE REMOVAL FROM HIGH TEMPERATURE COAL-DERIVED GASES; Pittsburgh, PA, and Morgantown, WV (United States), 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, B.; Wang, C.; Chen, H.; Song, Y.; Xie, B.; Xu, Y.; Tan, C. Research Progress of Hot Gas Filtration, Desulphurization and HCl Removal in Coal-Derived Fuel Gas: A Review. Chemical Engineering Research and Design 2012, 90, 1901–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Rokni, E.; Liu, Y.; Levendis, Y.A. Reduction of HCl Emissions from Combustion of Biomass by Alkali Carbonate Sorbents or by Thermal Pretreatment. Journal of Energy Engineering 2018, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.-I.; Eom, T.H.; Lee, J.B.; Jegarl, S.; Ryu, C.K.; Park, Y.C.; Jo, S.-H. Cleaning of Gaseous Hydrogen Chloride in a Syngas by Spray-Dried Potassium-Based Solid Sorbents. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering 2015, 32, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fremaux, S.; Beheshti, S.M.; Ghassemi, H.; Shahsavan-Markadeh, R. An Experimental Study on Hydrogen-Rich Gas Production via Steam Gasification of Biomass in a Research-Scale Fluidized Bed. Energy Convers Manag 2015, 91, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaidis, P.; Poullikkas, A. A Comparative Overview of Hydrogen Production Processes. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2017, 67, 597–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manish, S.; Banerjee, R. Comparison of Biohydrogen Production Processes. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Feedstock | Preparation of Feedstock | Microorganism | pH | Temperature (°C) | H2 yield (mL/g VS) | [Ref.] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dairy manure | Treatment with hydrochloric acid (0.2% concentration), boiling, and exposure to infrared radiation. | Mixed culture | 5.0 | 36.0 ± 1 | 31.5 | [12] |
| Poplar residue with sewage sludge | - | - | - | - | 20.8 | [22] |
| Rice straw | Drying at 80-100 C | Activated sewage sludge | 4.0-5.5 | 35.0 | 14.5 + 0.3 | [23] |
| Rice straw | Size reduction less than 2 mm, 1.0% alkali pre-treatment, cellulose hydrolysis | Clostridium pasteurianum | 7.5 | 37.0 ± 2 | 2.6(47.6 mL/g released sugar) | [24] |
| Sugarcane bagasse | Pre-treated with H2SO4 | Enterobacter aerogenes | 6.8 | 30.0 | 1000.0 | |
| Wheat straw | Acetic acid pre-treatment followed by steam exposure at 190 °C for 10 minutes and enzymatic hydrolysis lasting 72 hours | Caldicellulosiruptor saccharolyticus | 6.5±0.1 | 70.0 | 134.0 |
| Feedstock | Microorganisms | Enzyme | H2 yield | [Ref.] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Potato residue | Rhodospirillum rubrum, Rhodobacter capsulatus and Rhodopseudomonas palustris | Alpha-amylase | 642 mL /(L h) | [36] |
| Bread Waste | R. palustris | - | 3.1 mol H2/mol | [37] |
| Corn stalk | Rhodospirillum rubrum, R. capsulata, R. pulastris, Rhodobacter sphaeroides, Rhodobacter capsulatus | Cellulose | 23.96 mL/h H2 | [38] |
| Fermented Waste Food | Rhodobacter sphaeoides KD131 | - | 24 % Substrate conversion efficiency (%) | [39] |
| Corncob | Rhodospirillum rubrum, Rhodobacter capsulatus, Rhodopseudomonas palustri | Cellulase | 84.7 mL H2/g TS | [40] |
| Corn stover | HAU-M1 | Cellulase | 57.63 mL/g VS | [41] |
| Corn straw | Rhodospirillum rubrum, Rhodopseudomonas capsulate, Rhodopseudomonas palustris, Rhodobacter sphaeroides and Rhodobacter capsulatus | Cellulase | 137.76 mL H2/g TS | [42] |
| Energy grass | Rhodospirillum rubrum, R. capsulata, R. pulastris, Rhodobacter sphaeroides, Rhodoba | Cellulase | 5.53 mL H2/(h g TS) | [43] |
| Microalgae/cyanobacteria | Process condition | Light Intensity(W/m2 ) | H2 production | [Ref.] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nostoc PCC 7120 | BG110 medium, supplied with a mixture of red and white light, altering 100% Ar and Ar/N2 (20/80) | 18.8 | 6.2 ml/L/h | [48] |
| C. reinhardtii cbn 1–48 | Tris-acetate-phosphate medium, 5% CO2, dark anaerobic adaptation | 426.6 | 40.2 mL/kg | [47] |
| C. reinhardtii Dang 137+ | TAP (Tris-acetate-phosphate) medium | 34.1 | 6.0 mmol/L | [49] |
| Chlorella sp. IOAC707S | TAP-seawater medium | 10.7 | 38.0 mL/L | [50] |
| yngby asp. (benzoate as a carbon source) | Basal medium, 600 mg/l benzoate at late exponential phase | 31.6 | 17.1 μmol H2/g Chl a/h | [51] |
| C. reinhardtii (CC124) | Sulphur-free TAP medium | 64.0 | 1.3 ± 0.1 mL/L/h | [52] |
| C. reinhardtii CC-425 strain | TAP medium, TAP-sulphur | 121.6 | 0.8 μmol/mg Chl /h | [53] |
| Type of waste | Type of MEC reactor | Temperature (°C) | pH | External voltage (V) | H2 yield (L/L/d) | [Ref.] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Swine manure + waste water | Two-chamber | 25.0 ± 2 | 7.0 | 1.2 | 5.1 | [58] |
| Waste activated sludge | Single-chamber | 20.0 | 7.0 ± 0.2 | 0.6 | 90.6 | [66] |
| Waste of sugar beet juice | Two-chamber | 25.0 | 7.2 | 0.4 | 306.0 | [63] |
| Cornstalk wastewater | Two-chamber | 25.0 ± 2 | 7.0 | 1.0 | 3.9 | [69] |
| Type of Biomass | Type of gasification | Operating Conditions | H2 Yield | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pine Sawdust | Steam Blown | S/B=1.05-3.47 Temperature 800-950 °C |
55.87 % Volume | [90] |
| Wood Chips | Steam Blown | S/B= 0.18-1.32 Temperature: 800-950 °C |
50.3 % Volume | [91] |
| Sawdust | Steam and Oxy Blown | S/B= 1.1-4.7 ER= 0-0.37 Temperature: 750-950 °C |
57.4 % Volume | [92] |
| Lignocellulosic Biomass | Air | ER=0.20-0.34 Temperature: 600-1000 °C |
29.54 % Volume | [93] |
| Sawdust | Supercritical water | Temperature: 550 °C Pressure: 36-40 MPa |
10.40 mol/kg | [94] |
| Corn Starch | Supercritical water | Temperature: 745 °C Pressure: 280 bar |
55 % volume | [95] |
| Standard | ISO 14687-2019 SAE J2719-202003 |
|---|---|
| Purity of Hydrogen | 99.97% |
| Total non hydrogen gases | 300 ppm |
| H2O | 5 ppm |
| hydrocarbons without CH4 | 2 ppm |
| CH4 | 100 ppm |
| O2 | 5 ppm |
| He | 300 ppm |
| N2 | 300 ppm |
| Ar | 300 ppm |
| CO2 | 2 ppm |
| CO | 0.2 ppm |
| S.No | Technology | Type of Cleaning Methods | Tar removal efficiency (%) | Operational temperature ( oC) | Rank | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cyclonic separator | Dry | 30-70 | 100-900 | 10 | [128] |
| 2. | Fabric filter | Dry | 0-50 | Up to 600 | 12 | [128] |
| 3. | Sand bed filter | Dry | 50-90 | 20 | 6 | [128] |
| 4. | Bio-Oil scrubber | Wet | 60 | 50 | 11 | [129] |
| 5. | Quartz filter | Dry | 75-95 | 650-770 | 5 | [130] |
| 6. | Activated carbon as adsorbent | Dry | 80 | 20 | 4 | [129] |
| 7. | Electrostatic precipitator | Wet | 40-70 | 20-30 | 9 | [131] |
| 8. | Permeable catalytic filter disk [Aluminum Oxide (2.5%wt) ; Nickle (1.0% wt); Magnesium (0.5%wt)] | Dry | 77-99 | 800900 | 3 | [132] |
| 9. | Permeable catalytic filter disk [Nickle (1%wt)/ Calcium Oxide (0.5%wt)] | Dry | 96-98 | 900 | 1 | [133] |
| 10. | Impinger | Wet | 70 | 50 | 8 | [134] |
| 11. | Three impingers in series | Wet | >95 | 50 | 2 | [134] |
| 12. | Washing tower | Wet | 10-25 | 50-60 | 14 | [128] |
| 13. | Venturi scrubber | Wet | 50-90 | 20-100 | 6 | [135] |
| 14. | Packed bed scrubber | Wet | 75 | 300 | 7 | [136] |
| 15. | Water scrubber | Wet | 22 | 20-100 | 13 | [135] |
| Sorbent | Ideal sorption capacity (g S/g sorbent) | Operating Temperature (OC) | Rank | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cerium oxide | 0.093 | 500-700 | 7 | [143] |
| Copper oxide | 0.224 | 540-700 | 6 | [143] |
| Zinc Copper Ferrite | 0.398 | 540-680 | 3 | [143] |
| Zinc oxide | 0.395 | 450-650 | 4 | [144] |
| Manganese oxide | 0.400 | 400-900 | 2 | [143] |
| Iron oxide | 0.245 | 450-700 | 5 | [145] |
| Lime Powder | 0.571 | 815-980 | 1 | [146] |
| H2 production processes | Advantages | Constraint |
|---|---|---|
| Dark fermentation |
|
|
| Photo fermentation |
|
|
| Bio photolysis |
|
|
| MEC |
|
|
| Gasification |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





