1. Introduction
Choosing a major in college is one of the important issues for twelfth-grade students. For some students, choosing a major and determining a career path is not an easy task, as evidenced by the number of students who feel confused when they want to choose a major in college. [
1].
Students who already know their interests will find it easier to choose their majors. Unlike students who do not have a clear idea about their future career, the decision to choose a college major tends to be influenced by their surrounding such as parents and peers, as well as their favorite majors. In addition, some students seek information first about the majors they will choose before making a decision.
Choosing the wrong major is understood in the context where a student chooses a major that is not based on their interests and continues their studies even though they feel unsuitable for it. Data shows that the number of such cases is quite high and can have a detrimental impact. Dariyo (2004) suggests that many parents force their personal preferences in choosing their child’s major, which may not necessarily match the child’s abilities, talents, and interests. As a result, many students fail to complete their studies and have to drop out or even switch majors because they feel unsuitable for their life choices.
Students who choose the wrong major experience psychological, academic, and relational conflicts. Psychological conflicts, such as feeling pressured, hopeless, depressed, uncomfortable, resentful, angry, tired, disappointed, and regretful. Social conflicts, such as negative labeling, being ignored by peers, not being close to classmates, feeling inferior, being underestimated, conflicts with professors, and conflicts with parents. Academic conflicts, such as low GPA, retaking courses, extending study time, skipping classes, lack of motivation, being lazy to study, difficulty understanding courses, and lack of development [
2].
Several factors are believed to play a role in students’ career decision-making. Intervention can be given to overcome students’ career indecisiveness by reducing their anxiety and fear in making career decisions and encouraging students to seek more information about the careers they want to pursue[
1].
As it is known, sometimes students choose a major or study program without careful consideration or just follow their friends, without looking at and considering their characteristics, talents, and abilities. However, choosing a major or study program that is suitable and in line with one’s talents, abilities, and personality is very important and will affect a student’s career development in the future. Therefore, there is a need for information services for teachers and students to help determine the majors or study programs that are suitable for them[
3].
With these considerations in mind, we proposed an information service which is a web application that gives introductory information for a major. With this information, we hope that it can help high school student choose their major.
2. Related Work
In[
4], the paper proposed that college student often change their major in their first year. To lessen the chances of changing majors in their first year, the author designs a system to check if a student is eligible to undergo a specific major. A student is eligible if they passed a certain amount score that the application set as the minimum. With this system, a student may fail in one major but succeed in another. However, that’s on the premise that they can take the test multiple times. There are limitations to this approach, which are the number of questions available and the repeatability of the test.
From [
5], an online advisor service has been built to help students choose their major. They use the past score to assess, which major will fit them. This method of assessment will leave an outlier, for example, students who recently focused on their studies and cross-interest from the course they selected in the past. As the assessment is based on past scores, it may impact the result.
In the journal [
6], the decision-making process of choosing a study program using the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) method was discussed. Although AHP is a popular method in decision-making, it also has some shortcomings when used to select a study program. These include subjectivity, where the assessment is often carried out by one person or a group, which can influence the final decision. In addition, inaccurate data may also be a concern as the AHP analysis heavily depends on relevant and accurate data. If the data used is inaccurate or incomplete, the final analysis result may be unreliable. Furthermore, the use of this method may result in a lack of flexibility.
In this research [
7], several machine learning models have been developed by the collaborative team members. However, the successful model developed has an accuracy level ranging from 13%-70%. The machine learning model to be used is a model with low accuracy, which uses deep learning with an accuracy range of 13%-14%. A model with a much better accuracy level cannot yet be used in the application because the collaborative team members encountered technical constraints that prevent the deployment of the model into the application.
In the journal [
8], there is a decision-making system using the forward chaining method. The result of the research is that students can determine their majors without having to meet with experts and are able to find out information about intelligence that matches students’ abilities. However, because this is an expert system, the research used is very dependent on data. When the data is not up to date, the results will be less accurate. So the data must always be updated.
3. Methodology
This research will involve five distinct steps to achieve its objectives. Each step will play a crucial role in the project’s success, and it will be executed in a sequential manner. By following this structured approach, the research team will ensure that every aspect of the project is thoroughly examined and evaluated.
3.1. Requirement Analysis
The first stage of this research is the requirement analysis. Requirement analysis typically involves identifying and defining the specific needs and objectives of the research project[
9]. With that said, it has become evident that there is a demand for information regarding university majors and their corresponding courses. To fulfill this requirement, an application is needed that can provide users with easy access to this information, thereby allowing them to make informed decisions about their academic pursuits.
3.2. Data Collection
The data collected consists of a comprehensive list of majors offered at universities along with the courses offered within each department. The information within the dataset encompasses the subjects covered as well as their associated career paths. This information will be utilized by the team in the development of their application.
3.3. Design
In this stage, the application design will be developed based on the requirements gathered in the previous step. Integrating these requirements into the application design will be a critical consideration, taking into account technical and user perspectives.
3.4. Testing
The application will undergo black box testing to evaluate its functionality. Black box testing is a technique that involves designing test cases based on specifications, with the aim of assessing the application’s behavior. In this approach, the application is treated like a "black box," with the tester having no visibility into its internal workings. [
10]
3.5. Implementation
The objective of this application is to aid prospective students in identifying majors that align with their interests, as opposed to following the choices of peers or being compelled to enroll in programs that don’t appeal to them. By doing so, the application seeks to reduce the discomfort experienced by students during their studies, which can often lead to poor academic performance.
4. Result and Discussion
4.1. Project Requirement
To initiate the project, we have established a set of requirements that will guide its development. These requirements include function, user, technical, and user permission specifications, which will serve as the foundation for the project’s creation. [
11]
- 1)
-
Function Requirement
This web application is built to help people find their interests or passion. To achieve it, the website needs to be able to display information regarding a college major and the purpose of our web. Information about the college major that’ll need to be displayed is the name of the college major, a general description and a short description of said major, related courses, related work, and which universities offer said major.
With the number of college majors in mind. We will be grouping several majors that are relevant to each other in a category and provide a search option to pinpoint a specific major.
For the sustainability of the application, we will need a way for a person to add and modify information about college majors. This however needs to be limited for a select view people, which means a login feature to limit access.
- 2)
-
User Requirement
There are two users for this application, which are admin and visitor. Here are the requirements for each user.
- 3)
User Permission
Table 1.
User Requirements.
Table 1.
User Requirements.
|
User |
Requirements |
|
Admin |
1. Add major information |
| |
2. Modify major information |
| |
3. View major information |
| Visitor |
1. View application purpose |
| |
2. View major information |
Table 2.
User Permission.
Table 2.
User Permission.
|
Menu |
Function |
Permission |
|
Login |
This menu offers users to input their account information which if it matches will grant access to the dashboard menu. |
Admin |
| Dashboard |
Users will be able to view, add, and modify information regarding majors in this menu. |
Admin |
| About |
The purpose of this application will be explained in this menu. |
Visitor |
| Major Selection |
This menu will display information for majors. In which users need to select what category of major they would like to see. Afterward, there will be a list of majors that users can choose to view their information further in the major information menu. |
Visitor |
| Major Information |
Major information will be displayed here. The information that will be displayed is the name of the college major, general description and short description of said major, related course, related work, and which universities offer said major. |
Visitor |
4.2. System Design
During this phase, we develop a process design that includes both Entity-Relationship Diagrams and Use Case Diagrams.
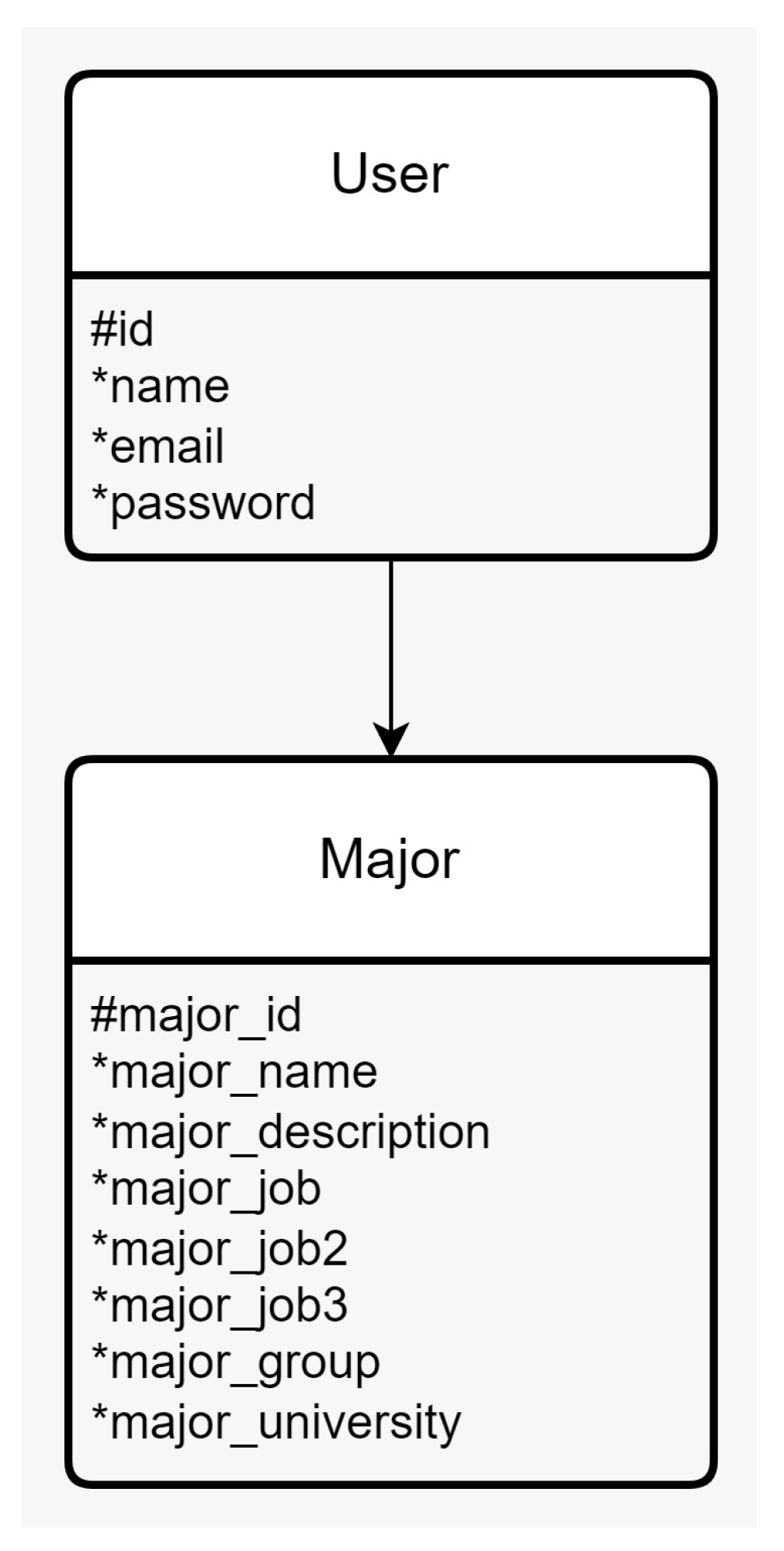
ERD (Entity-Relationship Diagram): is a method of data modeling that is utilized to depict the associations between entities in an information system. It serves to illustrate the data structure, entity relationships, and attributes for each entry. [
12]
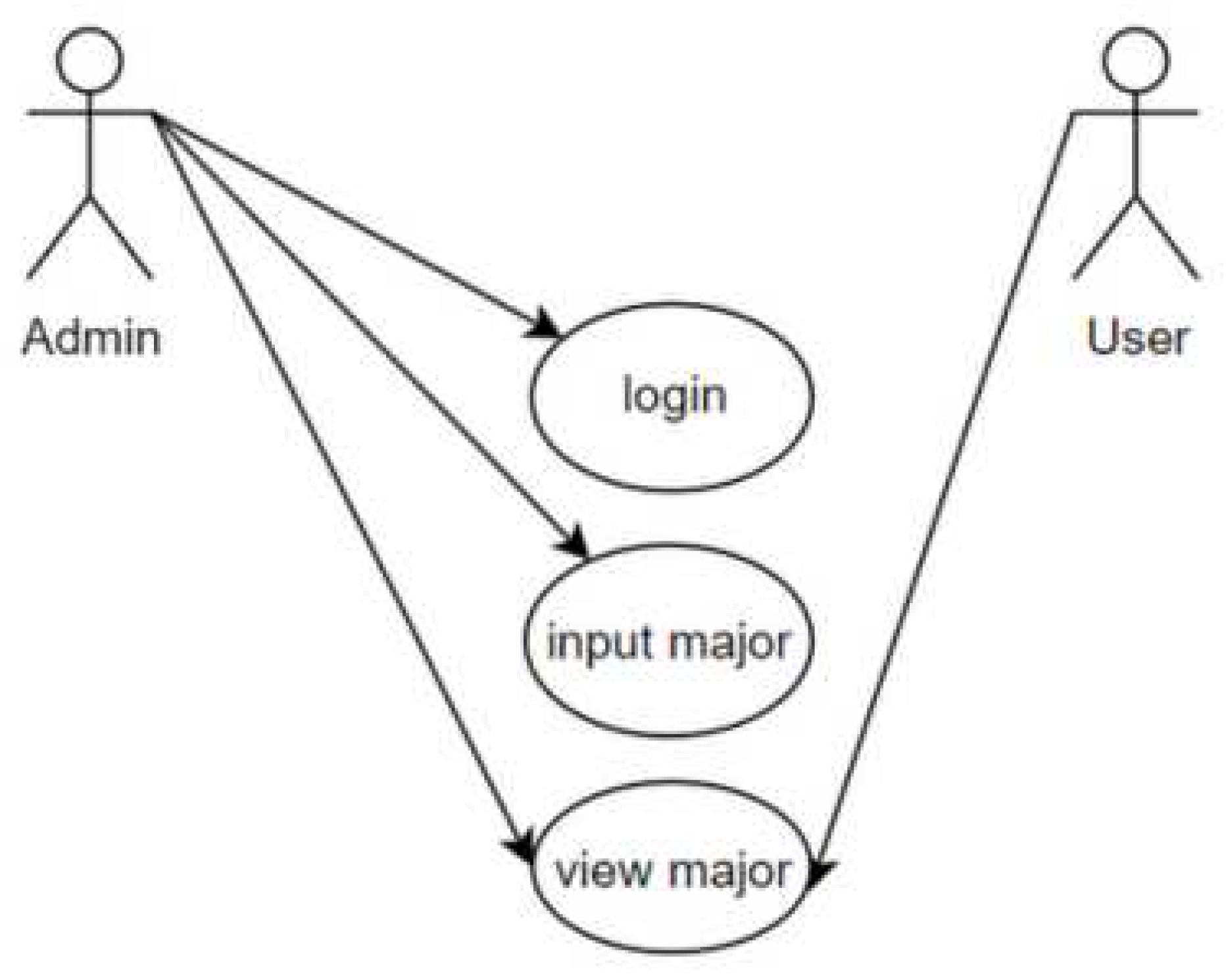
Use Case Diagram : A Use Case Diagram is a graphical representation that depicts the relationship between use cases and actors. Its purpose is to demonstrate the various actions that a user can perform within the system as a whole. [
13]
Figure 1.
Entity Relation Diagram.
Figure 1.
Entity Relation Diagram.
4.3. UI Design
User interface (UI) design is the process designers use to build interfaces in software or computerized devices, focusing on looks or style. Designers aim to create interfaces that users find easy to use and pleasurable. UI design refers to graphical user interfaces and other forms—e.g., voice-controlled interfaces.
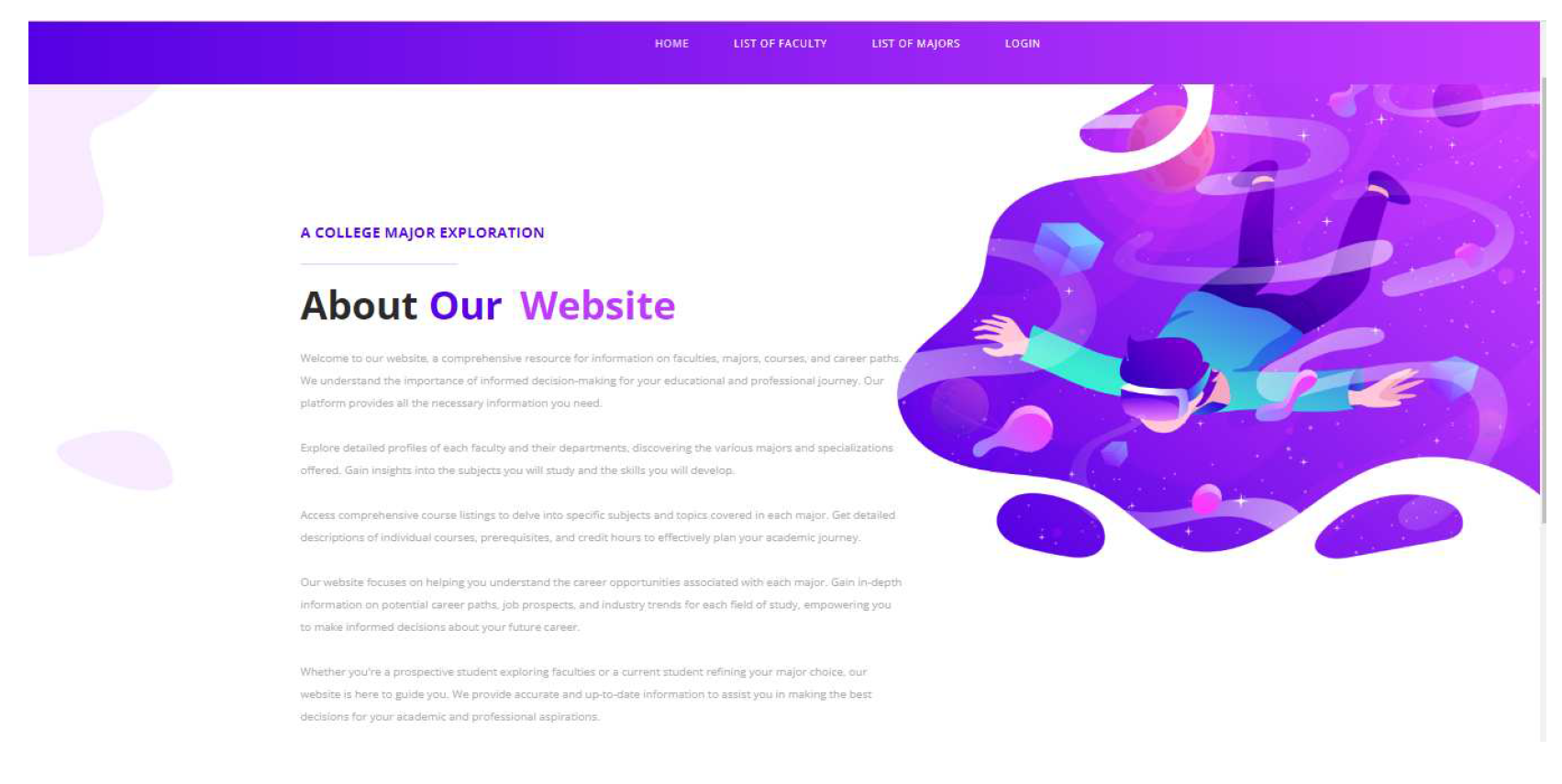
In
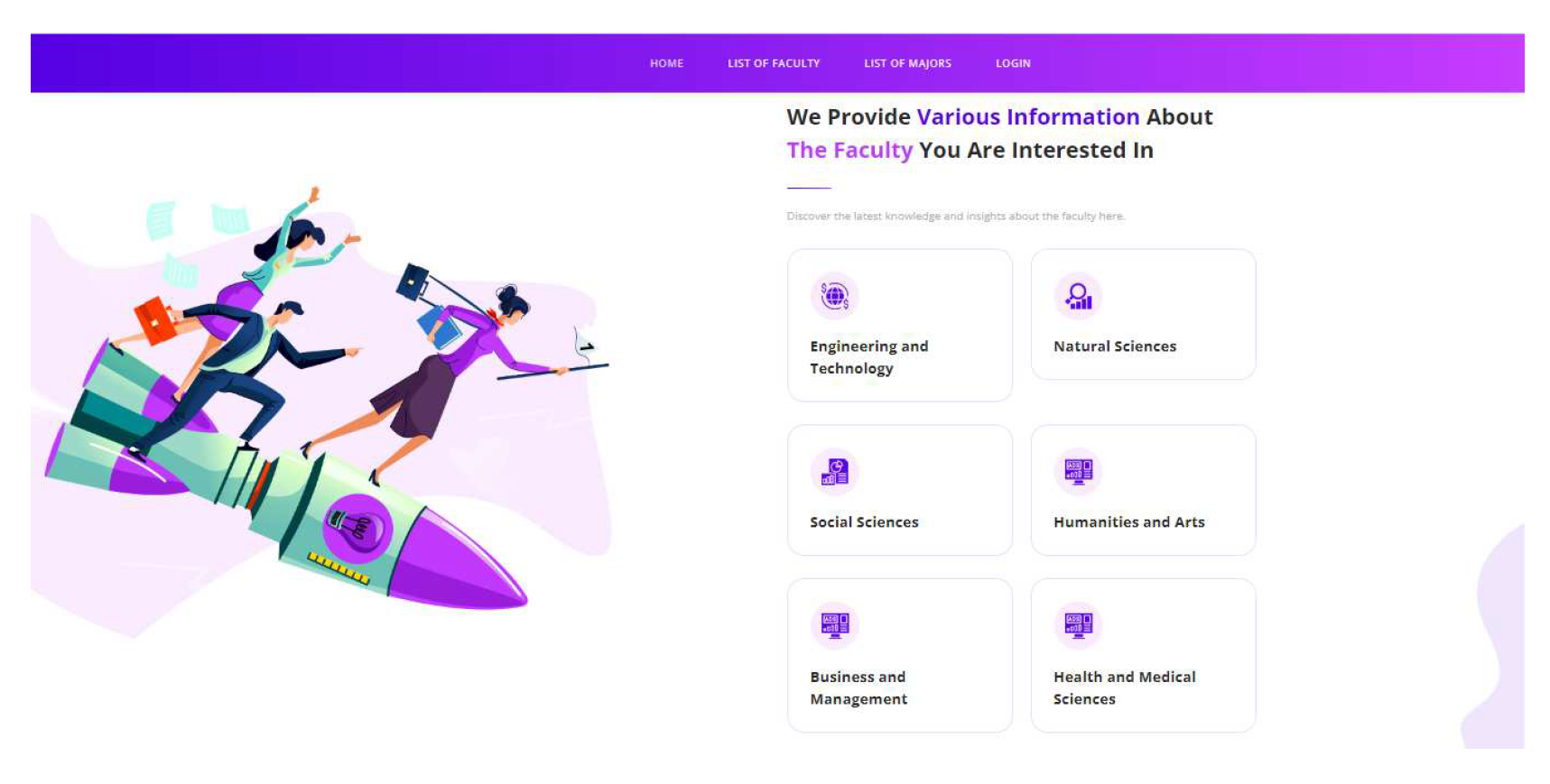
Figure 3 it shows the display of the landing page. Inside it, there are buttons for about, login, list of faculty, and list of majors.
Figure 4 represents the design of the about page. Inside that page, there is an explanation about the website application itself, such as its purpose, etc.
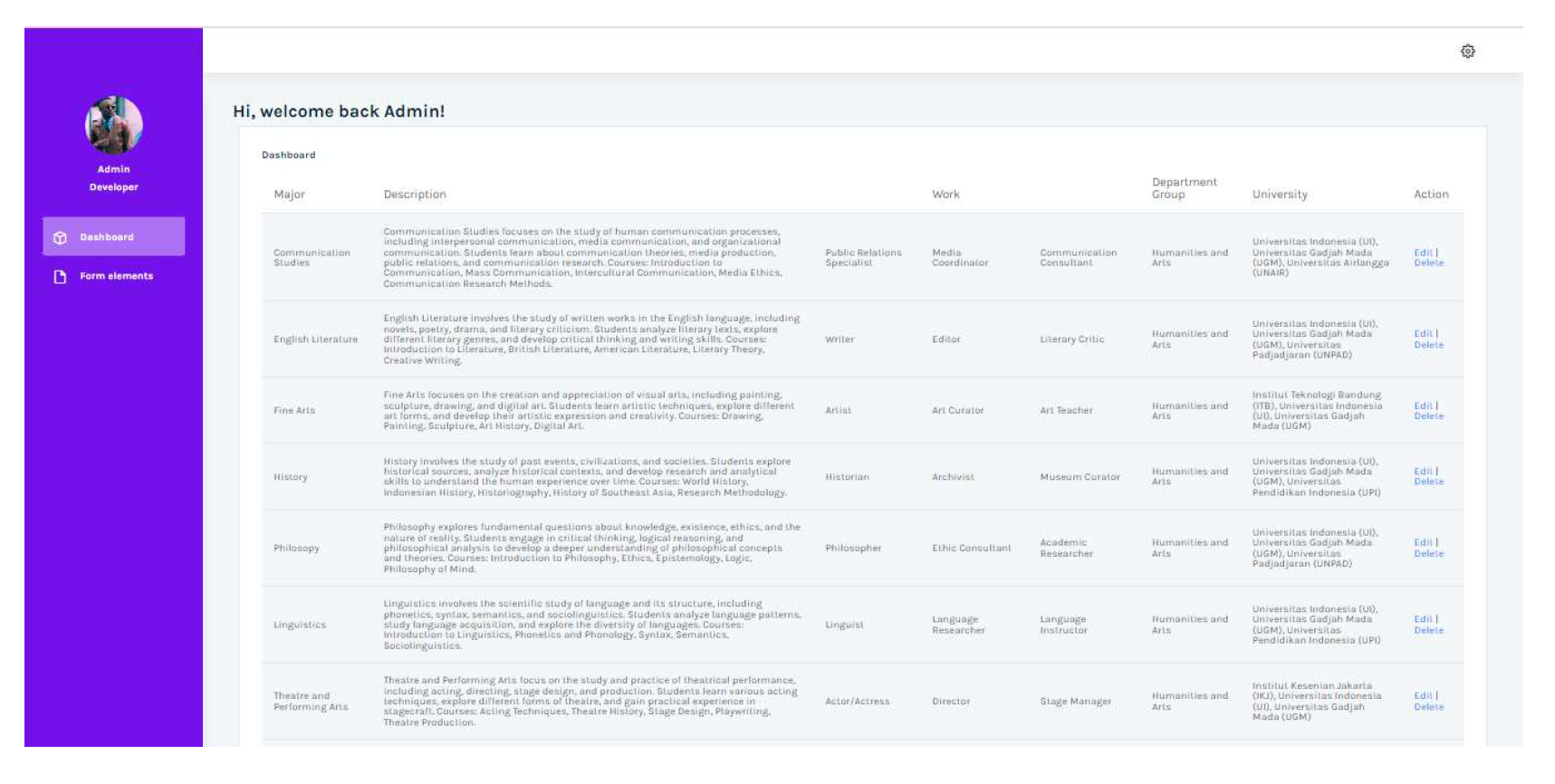
As we can see in
Figure 5, which displays the admin dashboard. Inside it, the admin adds, edits, or deletes the data that will be displayed on the website.
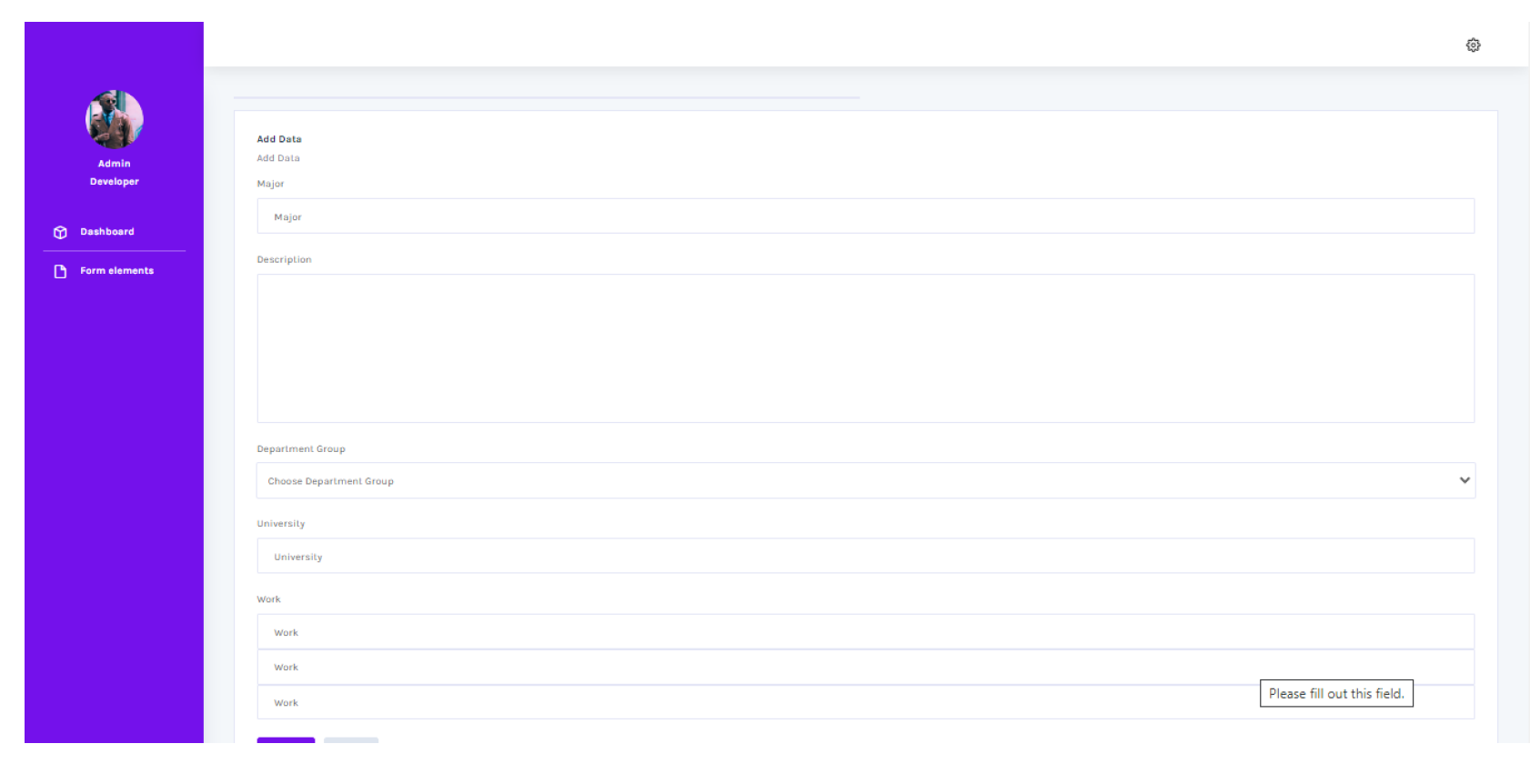
Figure 6 represents the display of the admin form page for adding data that will be displayed on the main page.
In
Figure 7, it shows the display of the list of faculty, where there are several faculties inside it, and later there will be several majors within them.
Inside
Figure 8 is the display list of majors, where inside it contains the majors that exist within a specific faculty. The list of majors that are being presented correlates with what faculty is chosen.
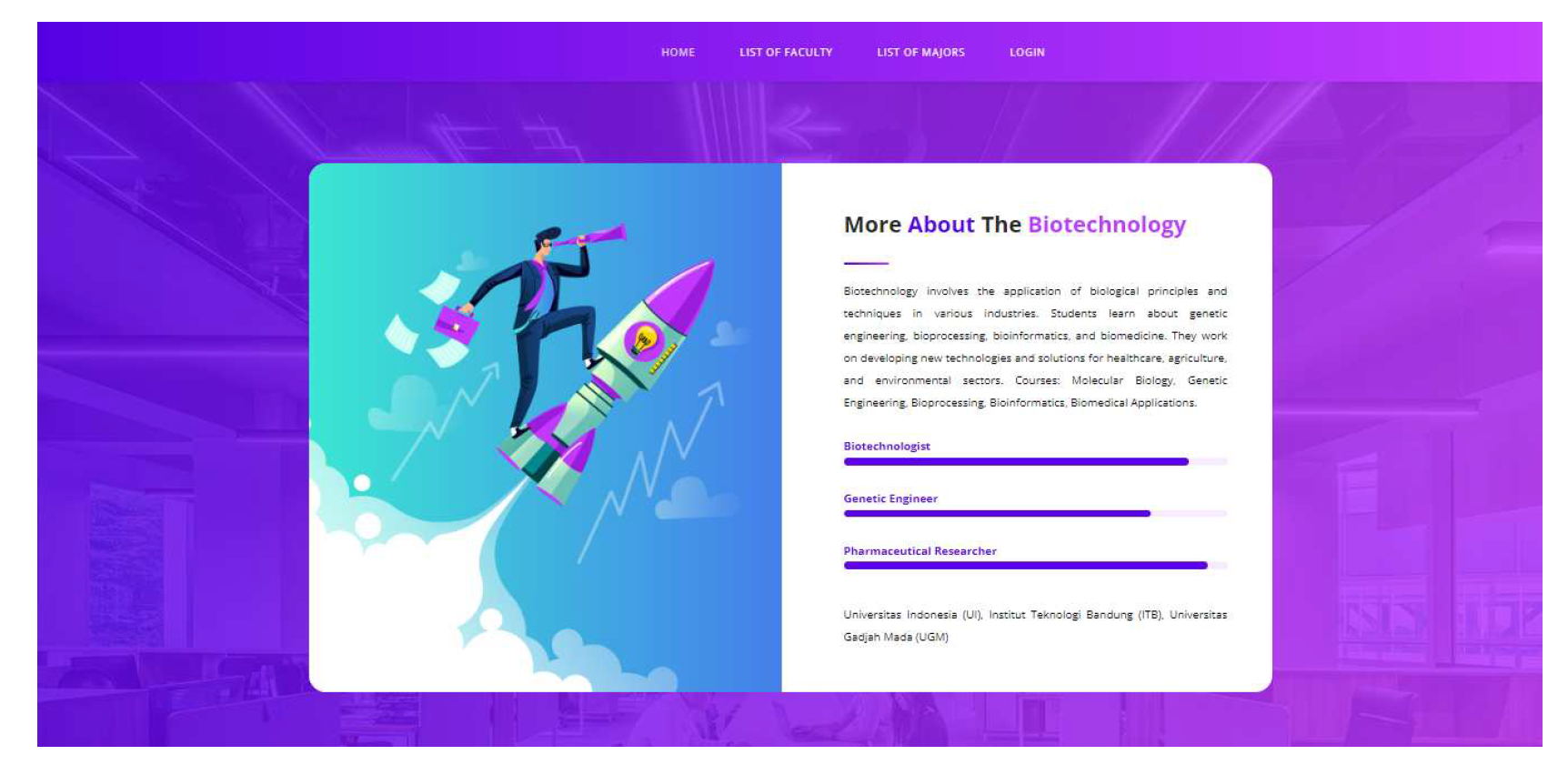
Figure 9 represents the display of the detail for each major, where inside it, there is information about the specific details of the major such as courses, related careers, and also recommended universities for that major.
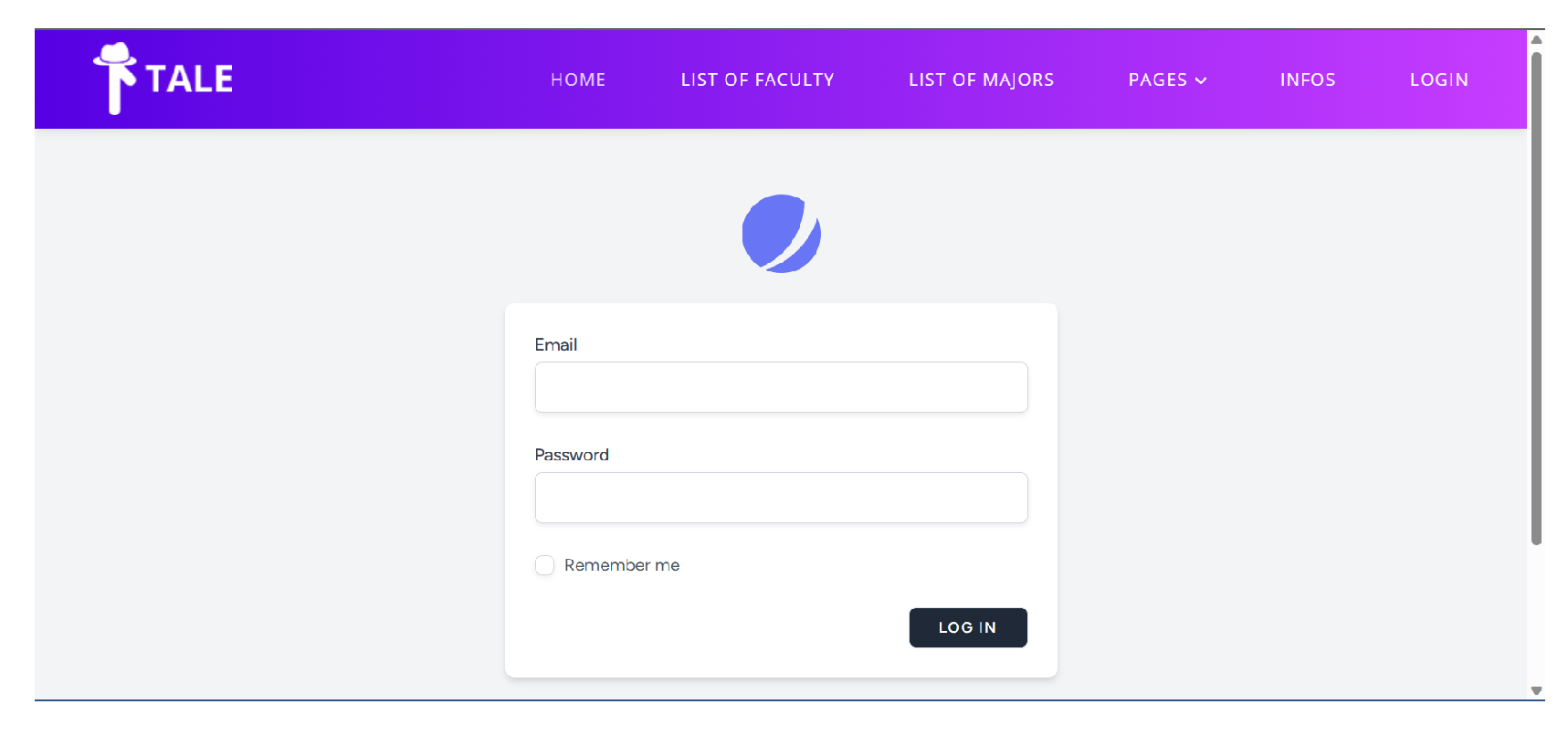
Figure 10 displays the login page design. Which admin can use by providing their credentials to access the dashboard page.
4.4. Testing
The application will undergo black box testing to evaluate its functionality. Black box testing is a technique that involves designing test cases based on specifications, with the aim of assessing the application’s behavior. In this approach, the application is treated like a "black box," with the tester having no visibility into its internal workings.
Table 3.
Testing
|
Testing Activity |
Expected Realization |
Test Result |
Conclusion |
|
Access home page |
Home page loads successfully without any errors |
Display the expected features |
Accepted |
| Click on the “About” |
Display information about the web application |
The button functions as expected |
Accepted |
| Click on the “List of Faculty |
Display options for selecting faculty |
The button functions as expected |
Accepted |
| Click on one of the faculty |
Display the list of majors belonging to the selected group |
The button functions as expected and can filter the available majors |
Accepted |
| Click on one of the majors |
Display information about the selected major, such as courses, career opportunities, and recommended campuses |
The button functions as expected and desired outcome |
Accepted |
| Click on “Login” |
User can enter a valid email and password, click login, and be redirected to the dashboard page |
Login feature with entering the correct email and password functions properly |
Accepted |
| Invalid email or password |
User enters an invalid email or password, clicks login, and an error message appears indicating an invalid email or password |
Unable to access the dashboard |
Accepted |
| Click the “Form” on the dashboard page |
Display a form to add data |
The button functions as expected and desired outcome |
Accepted |
| Click on “Add” on the form page |
The entered data is stored in the database and appears on the home page |
The data is successfully saved |
Accepted |
| Click on “Edit” on the dashboard page |
Display the selected data form and allow editing of the data |
The edit function works properly |
Accepted |
| Click the “Delete” on the dashboard page |
The data will be deleted from the database and removed from the display |
The delete function works properly |
Accepted |
5. Conclusions
The conclusion of the article is the importance of choosing a college major that aligns with students’ interests. Many students feel confused and influenced by their surroundings when making this decision. It can have negative consequences if the chosen major does not match their interests and abilities. In this study, a solution has been proposed in the form of developing a web application that provides introductory information for each major. The design approach was utilized in the development of this application, with the goal of assisting prospective students in identifying majors that align with their interests. One of the main objectives of this application is to reduce students’ discomfort during their studies, which often leads to academic performance decline.
By using this web application, students can avoid choosing majors solely based on peer pressure or parental pressure. They can obtain comprehensive information about each major and identify their own interests and abilities to make better career decisions. This application is expected to assist students in making more informed choices and provide them with support in achieving academic and professional success in the future.
Acknowledgments
The author’s wishes to acknowledge the Informatics Department UIN Sunan Gunung Djati Bandung, which partially supports this research work.
References
- Akmal, S.Z. Faktor-faktor yang menentukan kebimbangan karier pada siswa sma kelas xii. Jurnal Psikologi 2019, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurdin, A.A. Psychological well-being ditinjau dari coping strategy mahasiswa salah jurusan. Ph.D. Dissertation, Universitas Negeri Makassar, Makassar, Indonesia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Prayoga, M.F.E.P.; Martunis, M.; A’yuna, Q. Studi layanan informasi terhadap perubahan sikap siswa dalam pemilihan jurusan perguruan tinggi. JIMBK: Jurnal Ilmiah Mahasiswa Bimbingan & Konseling 2018, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Jurnal, R.T. Perancangan pemodelan sistem penentuan keputusan untuk pemilihan jurusan menggunakan metode perbandingan eksponensial (mpe) perguruan tinggi di jawa barat. Petir 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, X.; Zhao, S. A first-order logic framework of major choosing decision making with an uncertain reasoning function. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems 2018, 48, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syafar, A.M. Sistem pengambilan keputusan memilih program studi di uin alauddin berbasis web dengan metode analytic hierarcy process (ahp). Jurnal INSTEK (Informatika Sains dan Teknologi) 2018, 3, 309–318. [Google Scholar]
- Pratama, A.T.M.; Pratama, A.R. Rancang bangun aplikasi android “kuliah apa?” berbasis flutter dan tensorflow lite. Automata 2021, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Mulyani, E.D.S.; Hidayat, C.R.; Ulfa, T.C. Sistem pakar untuk menentukan jurusan kuliah berdasarkan minat dan bakat siswa sma dengan menggunakan metode forward chaining. CSRID (Computer Science Research and Its Development Journal) 2021, 10, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budiyono, N.R.; Aji, A.S. Aplikasi konsultasikarir untuk memilih jurusan dan strategi perencanaan karir. Jurnal Penelitian Bimbingan dan Konseling 2021, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Cholifah, W.N.; Yulianingsih, Y.; Sagita, S.M. Pengujian black box testing pada aplikasi action & strategy berbasis android dengan teknologi phonegap. STRING (Satuan Tulisan Riset dan Inovasi Teknologi) 2018, 3, 206–210. [Google Scholar]
- Haleem, M.; Farooqui, M.F.; Faisal, M. Tackling requirements uncertainty in software projects: a cognitive approach. International Journal of Cognitive Computing in Engineering 2021, 2, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latukolan, M.L.A.; Arwan, A.; Ananta, M.T. Pengembangan sistem pemetaan otomatis entity relationship diagram ke dalam database. Jurnal Pengembangan Teknologi Informasi dan Ilmu Komputer 2019, 3, 4058–4065. [Google Scholar]
- Fauzan, R.; Siahaan, D.; Rochimah, S.; Triandini, E. Use case diagram similarity measurement: A new approach. In Proceedings of the 2019 12th International Conference on Information & Communication Technology and System (ICTS), Surabaya, Indonesia, 18 July 2019; pp. 3–7. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).