Submitted:
19 July 2023
Posted:
21 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Study design
Patient selection and sample size
Statistical analysis
Results
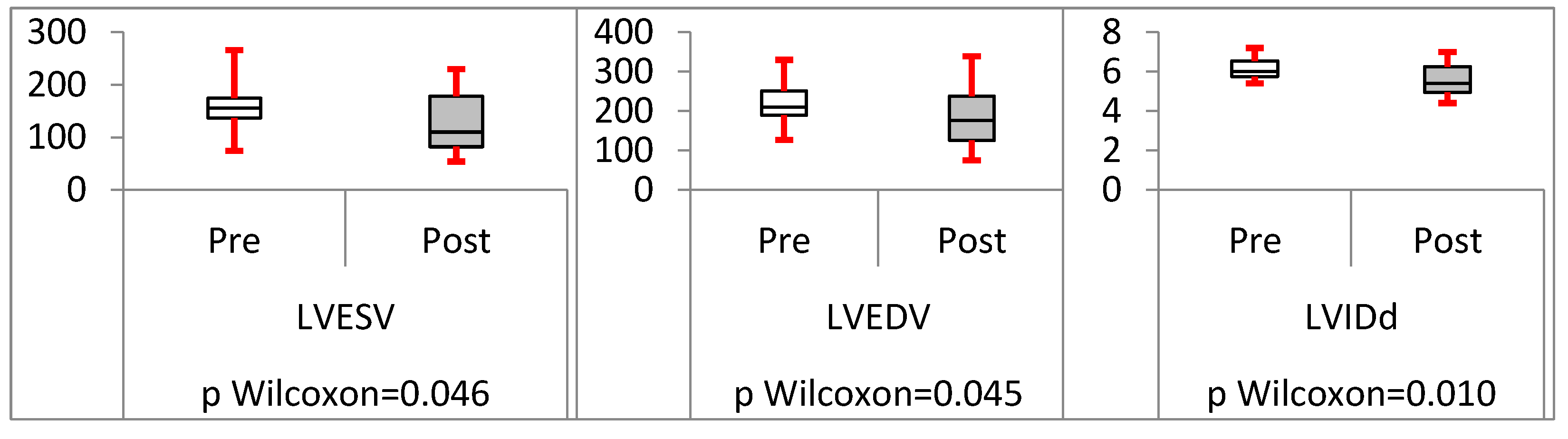
Analysis of trans-septal endocardial LV lead (TSLV)
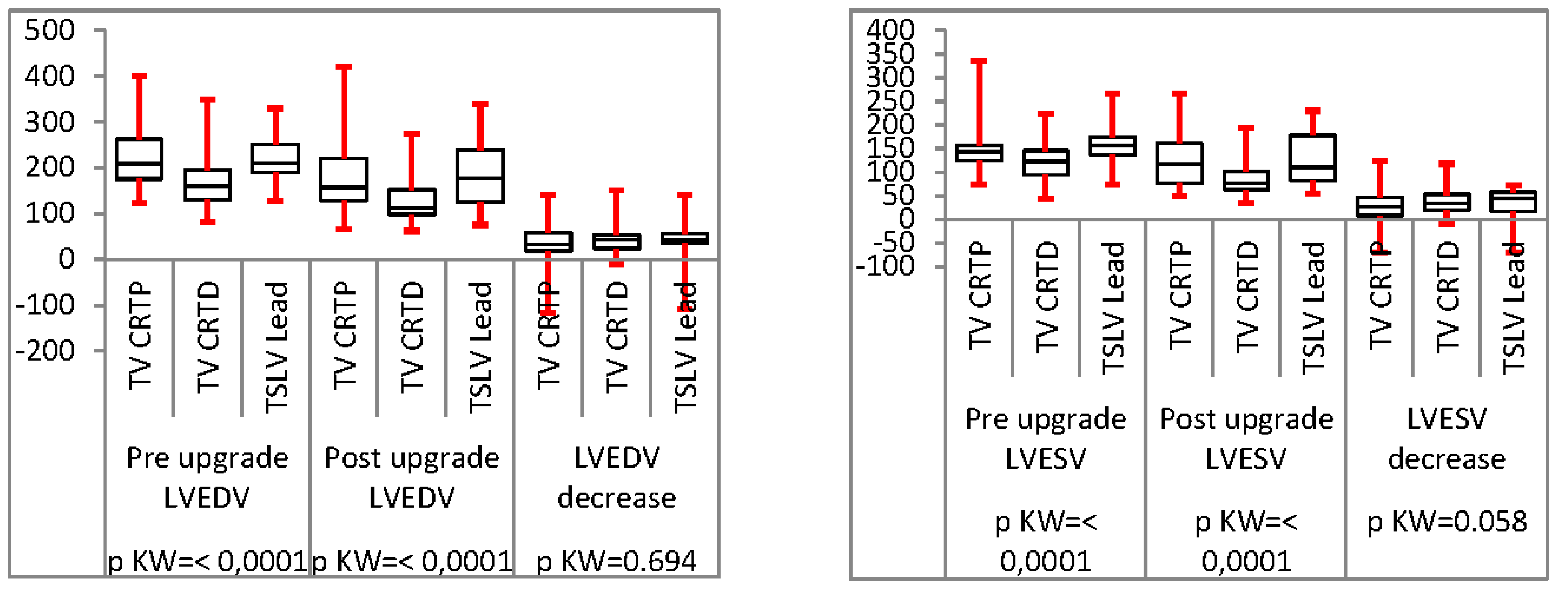
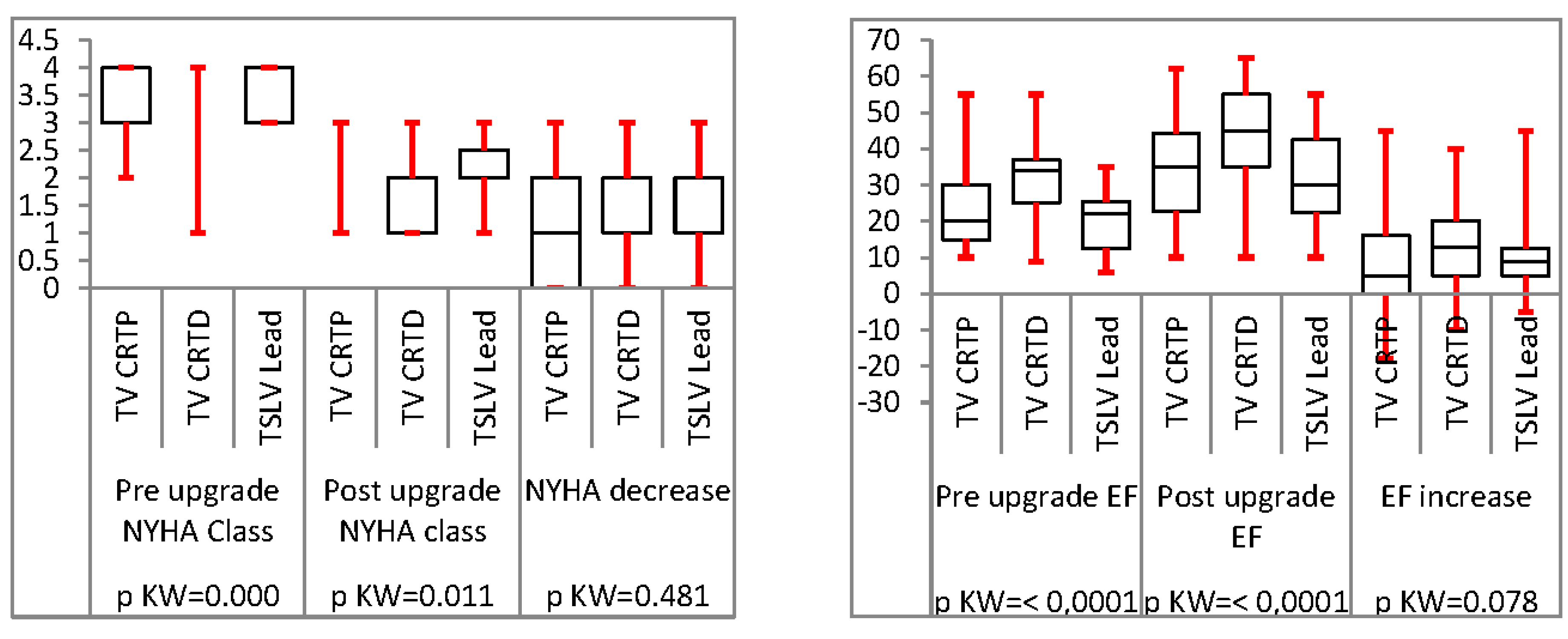
Analysis of TSLV compared to trans-venous CRT upgrade
Discussion
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TSLV | Trans septal left ventricle |
| TV | Trans-venous |
| CRT | Cardiac resynchronisation therapy |
| CRTD | Cardiac resynchronisation therapy Defibrillator |
| CRTP | Cardiac resynchronisation therapy Pacemaker |
| PPM | Permanent Pacemaker |
| ICD | implantable cardioverter defibrillator |
| LV | Left ventricle |
| LVSD | Left ventricle systolic dysfunction |
| LBBB | Left bundle branch block |
| HF | Heart Failure |
| CKD | Chronic Kidney disease |
| EF | Ejection fraction |
| LVEF | Left ventricle ejection fraction |
| LVIDd | Left ventricle internal diameter in diastole |
| LVEDV | Left ventricle end diastolic volume |
| LVESV | left ventricle end systolic volume |
| NYHA | New York heart association |
| ESC | European society of cardiology |
| AV | Atrioventricular |
| ARNi | angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor |
| MRA | Mineral receptor antagonists |
| SGLT-2 | Sodium-glucose transport protein 2 inhibitors |
References
- Moss, A.J.; Hall, W.J.; Cannom, D.S.; Klein, H.; Brown, M.W.; Daubert, J.P.; et al. Cardiac-resynchronization therapy for the prevention of heart-failure events. N Engl J Med 2009, 361, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, W.T.; Fisher, W.G.; Smith, A.L.; Delurgio, D.B.; Leon, A.R.; Loh, E.; et al. Multicenter InSync randomized clinical evaluation. Cardiac resynchronization in chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med 2002, 346, 1845–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, S.L.; Hummel, J.D.; Niazi, I.K.; Giudici, M.C.; Worley, S.J.; Saxon, L.A.; et al. Cardiac resynchronization therapy for the treatment of heart failure in patients with intraventricular conduction delay and malignant ventricular tachyarrhythmias. J Am Coll Cardiol 2003, 42, 1454–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, W.T.; Young, J.B.; León, A.R.; Adler, S.; Bank, A.J.; Hall, S.A.; et al. Effects of cardiac resynchronization on disease progression in patients with left ventricular systolic dysfunction, an indication for an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator, and mildly symptomatic chronic heart failure. Circulation 2004, 110, 2864–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewhurst, M.J.; Linker, N.J. Current evidence and recommendations for cardiac resynchronization therapy. Arrhythm Electrophysiol Rev 2014, 3, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosztin, A.; Vamos, M.; Aradi, D.; Schwertner, W.R.; Kovacs, A.; Nagy, K.V.; et al. De novo implantation vs. upgrade cardiac resynchronization therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart Fail Rev 2018, 23, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- León, A.R.; Abraham, W.T.; Curtis, A.B.; Daubert, J.P.; Fisher, W.G.; Gurley, J.; Hayes, D.L.; Lieberman, R.; Petersen-Stejskal, S.; Wheelan, K.; MIRACLE Study Program. Safety of transvenous cardiac resynchronization system implantation in patients with chronic heart failure: combined results of over 2, 000 patients from a multicenter study program. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005, 46, 2348–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamble, J.H.P.; Herring, N.; Ginks, M.; Rajappan, K.; Bashir, Y.; Betts, T.R. Procedural success of left ventricular lead placement for cardiac resynchronization therapy: A meta-analysis. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2016, 2, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ypenburg, C.; Schalij, M.J.; Bleeker, G.B.; Steendijk, P.; Boersma, E.; Dibbets-Schneider, P.; Stokkel, M.P.; van der Wall, E.E.; Bax, J.J. Impact of viability and scar tissue on response to cardiac resynchronization therapy in ischaemic heart failure patients. Eur Heart J. 2007, 28, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gellér, L.; Salló, Z.; Molnár, L.; Tahin, T.; Özcan, E.E.; Kutyifa, V.; Osztheimer, I.; Szilágyi, S.; Szegedi, N.; Ábrahám, P.; Apor, A.; Nagy, K.V.; Kosztin, A.; Becker, D.; Herczeg, S.; Zima, E.; Merkely, B. Long-term single-centre large volume experience with transseptal endocardial left ventricular lead implantation. Europace. 2019; 21, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rademakers, L.M.; Van Gelder, B.M.; Scheffer, M.G.; Bracke, F.A. Mid-term follow up of thromboembolic complications in left ventricular endocardial cardiac resynchronization therapy. Hear Rhythm. 2014, 11, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Gelder, B.M.; Scheffer, M.G.; Meijer, A.; Bracke, F.A. Transseptal endocardial left ventricular pacing: an alternative technique for coronary sinus lead placement in cardiac resynchronization therapy. Heart Rhythm. 2007, 4, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, J.M.; Biffi, M.; Gellér, L.; Leclercq, C.; Ruffa, F.; Tung, S.; et al. ALternate Site Cardiac ResYNChronization (ALSYNC): a prospective and 355 multicentre study of left ventricular endocardial pacing for cardiac resynchronization therapy. Eur Heart J 2016, ehv723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriña-Vázquez, P.; Roa-Garrido, J.; Fernández-Gómez, J.M.; Venegas-Gamero, J.; Pichardo, R.B.; Carranza, M.H. Direct left ventricular endocardial pacing: An alternative when traditional resynchronization via coronary sinus is not feasible or effective. PACE - Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2013, 36, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.B.; Worley, S.J. Snare coupling of the pre-pectoral pacing lead delivery catheter to the femoral transseptal apparatus for endocardial cardiac resynchronization therapy: Mid-term results. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2013, 36, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geller L, Molnar L, Szilagyi S., Zima E, Szeplaki G, Osztheimer I, et al. Long term efficacy and safety of transseptal endocardial left ventricular lead implantation after left ventricular lead implantations. Eur Heart J. 2014, 35, P525.
- Garrigue, S.; Jaïs, P.; Espil, G.; Labeque, J.N.; Hocini, M.; Shah, D.C.; et al. Comparison of chronic biventricular pacing between epicardial and 395 endocardial left ventricular stimulation using Doppler tissue imaging in patients with heart failure. Am J Cardiol. 2001, 88, 858–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, P.A.; Yue, A.M.; Watts, E.; Zeb, M.; Roberts, P.R.; Morgan, J.M. Transseptal left ventricular endocardial pacing reduces dispersion of ventricular repolarization. PACE - Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2011, 34, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugo, J.; Gamble, P.; Herring, N.; Ginks, M.; Rajappan, K.; Bashir, Y.; et al. Endocardial left ventricular pacing for cardiac resynchronization: systematic review and meta-analysis. Europace [Internet]. 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.R.; Lim, K.; Park, S.J.; Park, J.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Chung, S.; Jung, D.S.; Park, K.M.; On, Y.K.; Kim, J.S. Thoracoscopic Implantation of Epicardial Left Ventricular Lead for Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2022, 9, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navia, J.L.; Atik, F.A.; Grimm, R.A.; Garcia, M.; Vega, P.R.; Myhre, U.; Starling, R.C.; Wilkoff, B.L.; Martin, D.; Houghtaling, P.L.; Blackstone, E.H.; Cosgrove, D.M. Minimally invasive left ventricular epicardial lead placement: surgical techniques for heart failure resynchronization therapy. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005, 79, 1536–1544; discussion 1536-44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, K.E.; Bates, M.G.; Turley, A.J.; Linker, N.J.; Owens, W.A. Video-assisted thoracoscopic left ventricular pacing in patients with and without previous sternotomy. Ann Thorac Surg. 2013, 95, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.L.; Kramer, D.B.; Lewis, E.F.; Koplan, B.; Epstein, L.M.; Tedrow, U. Event-free survival following CRT with surgically implanted LV leads versus standard transvenous approach. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2011, 34, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba-Pichardo, R.; Manovel Sanchez, A.; Fernandez-Gomez, J.M.; et al. Ventricular resynchronization therapy by direct His-bundle pacing using an internal cardioverter defibrillator. Europace. 2013, 15, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustgarten, D.L.; Crespo, E.M.; Arkhipova-Jenkins, I.; Lobel, R.; Winget, J.; Koehler, J.; Liberman, E.; Sheldon, T. His-bundle pacing versus biventricular pacing in cardiac resynchronization therapy patients: A crossover design comparison. Heart Rhythm. 2015, 12, 1548–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Su, L.; Wu, S.; et al. Long-term outcomes of His bundle pacing in patients with heart failure with left bundle branch block. Heart. 2019, 105, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraman, P.; Subzposh, F.A.; Naperkowski, A.; et al. Prospective evaluation of feasibility, electrophysiologic and echocardiographic characteristics of left bundle branch area pacing. Heart Rhythm. 2019, 16, 1774–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Su, L.; Vijayaraman, P.; et al. Left bundle branch pacing for cardiac resynchronization therapy: nonrandomized on-treatment comparison with His bundle pacing and biventricular pacing. Can J Cardiol. 2021, 37, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayaraman, P.; Ponnusamy, S.S.; Cano, O.; et al. Left bundle branch pacing for cardiac resynchronization therapy: results from International LBBP Collaborative Study Group. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2021, 7, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraman, P.; Herweg, B.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; et al. His-optimized cardiac resynchronization therapy to maximize electrical resynchronization. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2019, 12, e006934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Demographics | |
| 1.Male | 9 (81%) |
| 2.Female | 2 (18%) |
| Underlying Rhythm | |
| 1.Sinus | 8(72.7 %) |
| 2.Atrial arrhythmia | 3 (27.3 %) |
| Age | 76 ± 9 years old |
| Aetiology | |
| 1.Ischaemic cardiomyopathy | 8(72.7 %) |
| 2.Non-ischaemic cardiomyopathy | 3 (27.3 %) |
| 3.Inherited Cardiac Conditions | 1 (9%) |
| 4.Valvular heart disease | 2 (18%) |
| Medication History | |
| 1.Beta-Blockers | 11 (100%) |
| 2.Mineral receptor antagonists (MRA) | 10 (90.9%) |
| 3.Angiotensin receptor-neprilysin Inhibitors ( ARNi) | 7 (63.4%) |
| 4.Sodium-glucose transport protein 2 inhibitors ( SGLT-2) | 7 (63.4%) |
| Comorbidities | |
| 1.Diabetes | 5 (45.4%) |
| 2.CKD stage | |
| 2.1: CKD Stage II | 2(27.7%) |
| 2.2: CKD stage IIIa | 4 (36.36%) |
| 2.3: CKD stage IIIb | 2(18.18%) |
| 2.4 CKD stage IV | 2 (18.18%) |
| 2.5 CKD Stage V | - |
| 3.Hypertension | 11 (100%) |
| Dermographics | |
| 3.Male | 64 (69%) |
| 4.Female | 29 (31%) |
| Underlying Ryhthm | |
| 3.Sinus | 62 (66%) |
| 4.Atrial arryhthmia | 31 (34%) |
| Age | 82±10 years old |
| Aetiology | |
| 5.Ischaemic cardiomyopathy | 35 (37%) |
| 6.Non-ischaemic cardiomyopathy | 56 (60%) |
| 7.Inherited Cardiac Conditions | 5 (5.38%) |
| 8.Valvular heart disease | 14 (15%) |
| Medication History | |
| 5.Beta-Blockers | 93 (100%) |
| 6.Mineral receptor antagonists (MRA) | 79 (85%) |
| 7.Angiotensin receptor-neprilysin Inhibitors ( ARNi) | 46 (49.4%) |
| 8.Sodium-glucose transport protein 2 inhibitors ( SGLT-2) | 43 (46%) |
| Comorbidities | |
| 4.Diabetes | 33 (35.4%) |
| 5. CKD stage | |
| 2.1: CKD Stage II | 42 (45.16%) |
| 2.2: CKD stage IIIa | 34 (36.5%) |
| 2.3: CKD stage IIIb | 4 (4.3%) |
| 2.4 CKD stage IV | 6 (6.45%) |
| 2.5 CKD Stage V | - |
| 6.Hypertension | 83 (89.5%) |
| Dermographics | |
| 5.Male | 42 (73%) |
| 6.Female | 16 (27%) |
| Underlying Ryhthm | |
| 5.Sinus | 42 (73%) |
| 6.Atrial arryhthmia | 16 (33%) |
| Age | 76±10 years old |
| Aetiology | |
| 9.Ischaemic cardiomyopathy | 42 (72.4%) |
| 10.Non-ischaemic cardiomyopathy | 11 (18.9%) |
| 11.Inherited Cardiac Conditions | 9 (15.5%) |
| 12.Valvular heart disease | 3 (5.17%) |
| Medication History | |
| 9.Beta-Blockers | 58 (100%) |
| 10.Mineral receptor antagonists (MRA) | 44 (75.8%) |
| 11.Angiotensin receptor-neprilysin Inhibitors ( ARNi) | 36 (62%) |
| 12.Sodium-glucose transport protein 2 inhibitors ( SGLT-2) | 33 (57%) |
| Comorbidities | |
| 7.Diabetes | 29 (50%) |
| 8.CKD stage | |
| 2.1: CKD Stage II | 23 (39.6%) |
| 2.2: CKD stage IIIa | 19 (32.7%) |
| 2.3: CKD stage IIIb | 8 (13.8%) |
| 2.4 CKD stage IV | 6 (10.34%) |
| 2.5 CKD Stage V | - |
| 9.Hypertension | 49 (84.5%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





