1. Introduction
Shape memory alloys (SMAs) are a unique class of functional materials that exhibit shape recovery upon heating, as well as superelasticity upon loading. Both properties result from a reversible solid state phase transformation, called thermoelastic martensite transformation. Many shape memory alloys [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5] have been used for specialized commercial applications and have shown great potential in emerging fields, such as elastocaloric solid-state refrigerators [
6,
7,
8] or flexible electronics [
9,
10]. Within the most important SMA systems, Cu-based shape-memory alloys are of particular interest because of their large range of transformation temperatures and high electrical conductivity [
11]. Single crystals of these Cu-based SMAs exhibit excellent shape-memory and superelastic effects [
12,
13]. However, due to the stress concentration or incompatibility at grain boundary and triple junction, the bulk polycrystals of Cu-based SMAs usually undergo brittle intergranular fracture during deformation [
14,
15], which severely prevents its widespread applications.
Two opposite strategies were applied to improve the mechanical property of Cu-based SMAs: increasing or refining the grain size. The first strategy aims to improve deformation compatibility by reducing the total grain boundary area and removal of triple junctions. The development of bamboo-like grained (BLG) Cu-based SMAs is a typical representative. Omori et al. [
16,
17] prepared BLG Cu-Al-Mn SMAs by cyclic heat treatment process. Schuh et al. [
18,
19,
20] produced BLG Cu-Al-Ni and Cu-Zn-Al SMAs microwires with superelasticity of over 7 %. Another strategy attempts to suppress intergranular fracture by refining the grain size. For example, Font et al. [
21] reported Cu-Al-Ni-based ribbon by a single roll melt-spinning technique. Ochin et al. [
22] reported the Cu-Al-Ni wire by an in-rotating-water spinning method. However, mechanical properties of such ribbon and wire were not improved greatly, because the grain size is still in the scale of tens of micrometer.
Amongst the Cu-based SMAs, the Cu-Sn system has been least investigated, possibly due to the poor shape-memory and superelastic effect of bulk polycrystals [
23,
24,
25,
26]. Li et al reported good shape memory effect of rapidly quenched ribbons of Cu-Sn polycrystalline alloys with a grain size of about 1.5 µm. However, the superelastic effect was not further investigated in these ribbons. In the present study, Cu-Sn microwires with a diameter of 10 ~ 200 µm were prepared by a glass-coated melt spinning method. Due to the rapid cooling rate, the grain size of the as-cast microwires was refined down to micrometer scale. Significant superelastic effect were found in these microwires, and effects of Sn content on the microstructure and superelastic behavior of Cu-Sn microwires were investigated systematically. Interestingly, by annealing at 750°C for 5 hours before quenching in water, a bamboo-like grain structure was obtained in the Cu-Sn microwire, which also shows excellent superelasticity. The results indicate that the two opposite strategies of refining the grain size to micrometer level or increasing the grain size to one dimensional size of specimen, e.g., the diameter of the wire, are both effective to improve superelasticity of Cu-Sn alloy.
2. Experimental
Cu-Sn ingots with variable Sn content were prepared by inductively melting the mixture of high pure Cu and Sn (>99.9%) in a quartz glass tube under argon atmosphere. They are named as A1~A6, and their atomic composition is given in
Table 1. Microwires with different composition were fabricated by rapid solidification using a glass-coated melt spinning method [
27,
28]. The schematic illustration of the glass-coated melt spinning is shown in
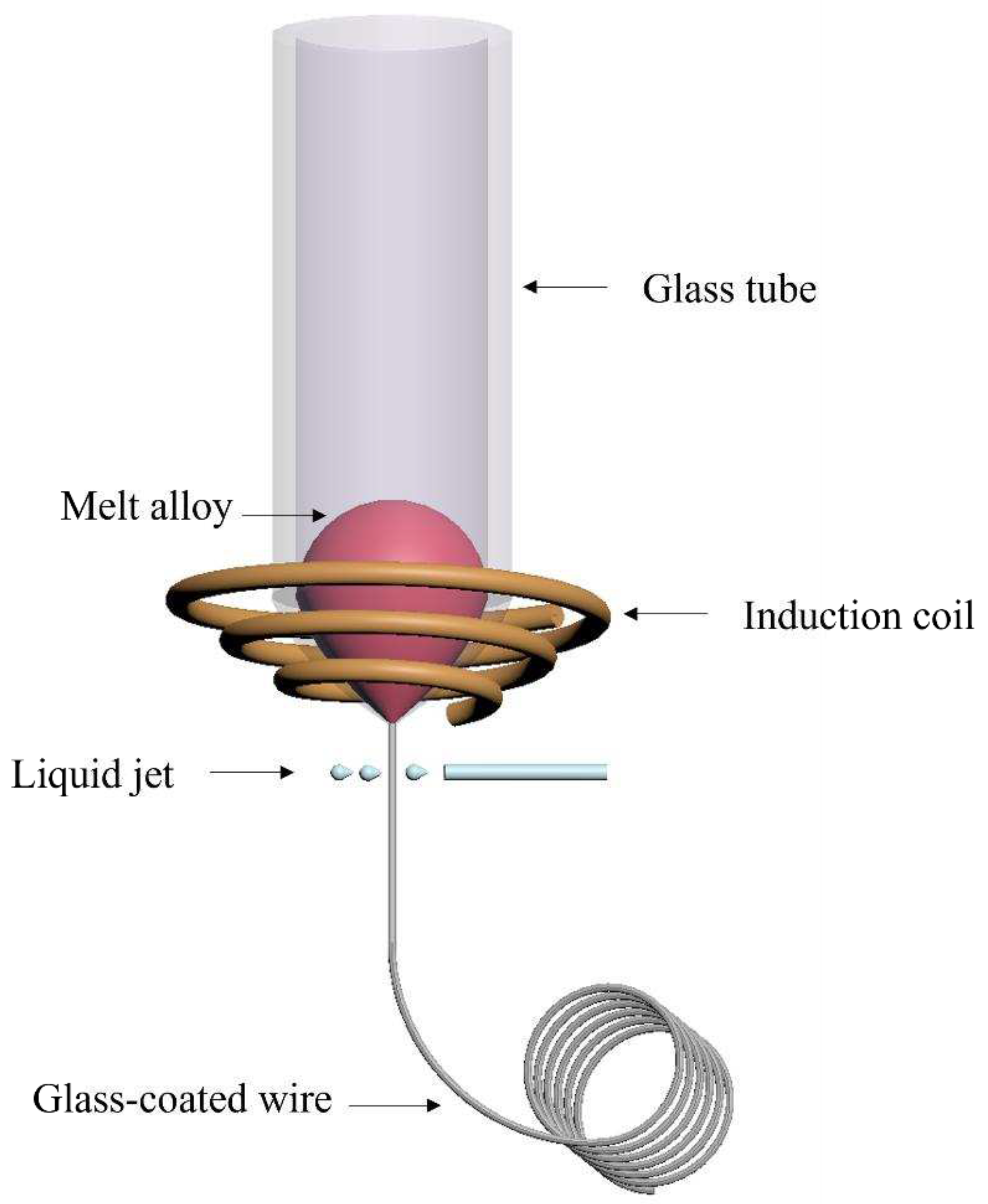
Figure 1. Firstly, the ingot was cut into small pieces of approximately 1-2 grams, which was placed into a Pyrex glass tube. Then we placed the bottom of the glass tube in a high-frequency induction heater and introduced argon gas from the top of the glass tube. Afterwards, the alloy was heated to the melting point through the inductor heater, forming a droplet. When the alloy melts, the bottom of the glass tube adjacent to the molten alloy softens and surrounds the droplet. When we used a glass rod with an ultra-fine tip to contact the bottom of the glass tube and pulled the glass bar, a glass capillary with the molten alloy as its core was drawn down. The molten alloy solidifified rapidly through water cooling. Therefore, a microwire is formed where the metal core is completely covered by a glass shell. The microwire is wound around the receiving coil, and the rotational speed determines the wire diameter and glass thickness.
In order to obtain Cu-Sn microwires with different diameter, we annealed the glass-coated microwires at 750˚C for 5 hours, and then quenched it in water. Finally, the glassy cover was carefully removed. The surface morphology was examined by the scanning electron microscopy (SEM). In order to observe the microstructure, the longitudinal section of wires was polished and then etched by solution of 5 g (FeCl3) + 15 ml (HCl) + 100 ml (C2H5OH). Pieces of wires were closely arrayed on a glass slide, and the structure was examined by X-ray diffraction (XRD) with Cu Kα radiation. Tensile test of microwires was performed using an Instron 5969 Micro-Tester, and the loading-unloading tensile test was done to study the superelastic effect. The wires were bonded to a specially designed paper frame with Aron-Alpha adhesive. All the tensile test was performed at room temperature.
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Sn Content on the Microstructure of Cu-Sn Microwires
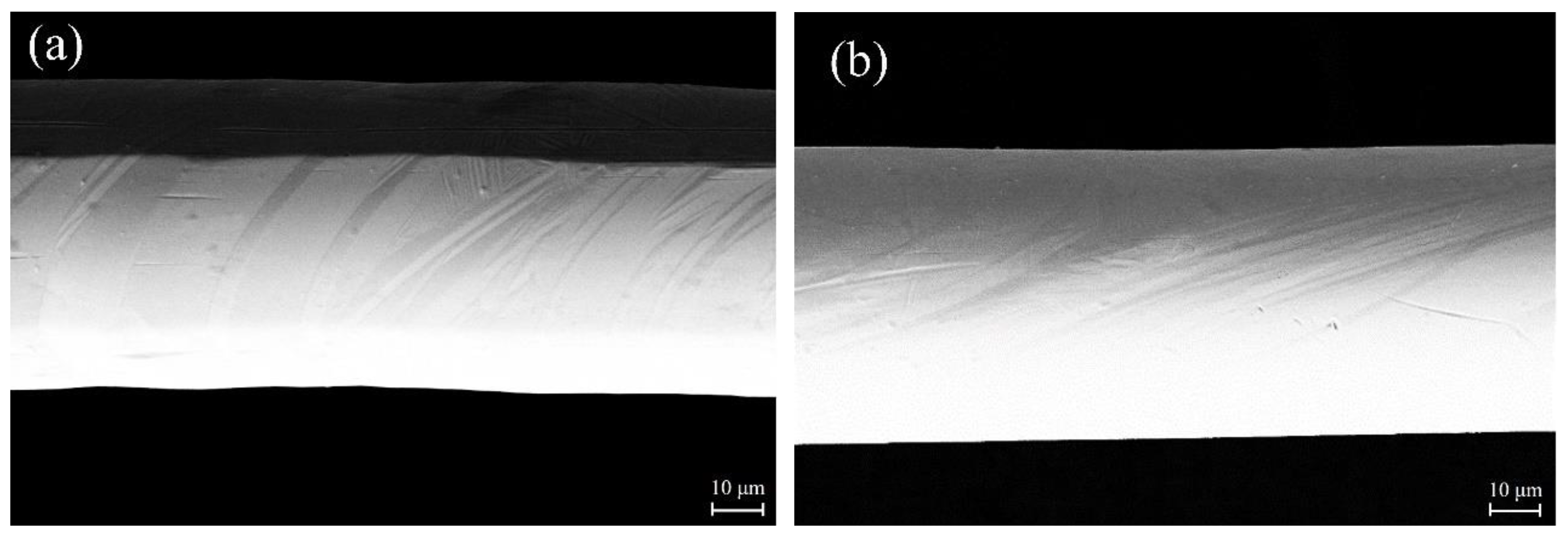
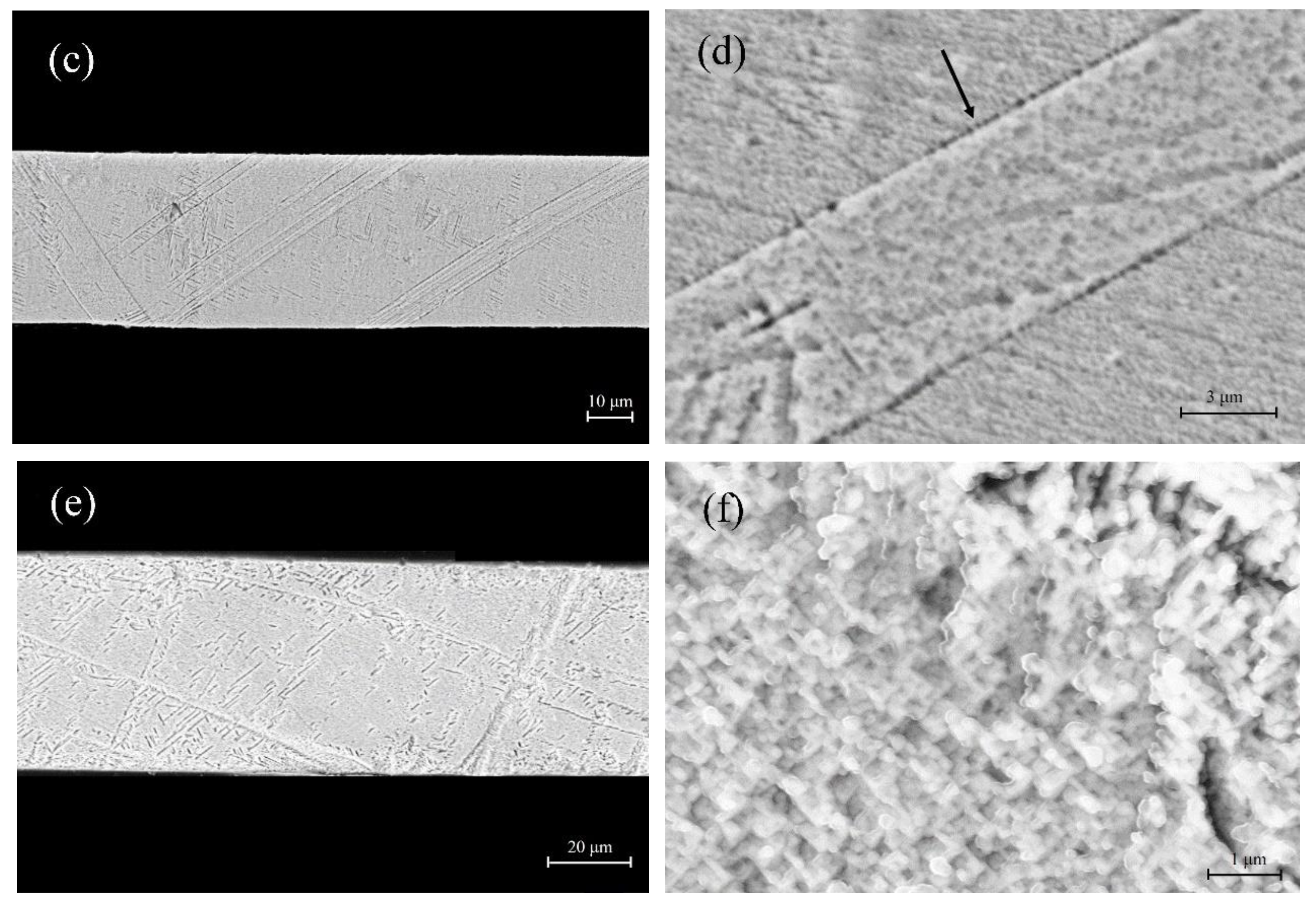
Figure 1 shows SEM images of the surface morphology of microwires with different composition. Martensites, which close to each other and go through the cross section, could be seen clearly on the surface of A1 as shown in
Figure 1(a).
Figure 1(b) shows that some banded martensites, which are not as dense as A1, go through cross section of A2.
Figure 1(c), (d), (e) and (f) correspond to A3, A4, A5 and A6, respectively. It is clear that the wires are almost flawless and precisely circular. The length of microwires could reach up to hundreds of meters, implying that the glass-coated melt spinning method is a very effective technique to produce high-quality Cu-Sn microwires.
Figure 1.
SEM images of the surface morphology of Cu-Sn microwires with different Sn content: (a) A1, (b) A2, (c) A3, (d) A4, (e) A5, (f) A6.
Figure 1.
SEM images of the surface morphology of Cu-Sn microwires with different Sn content: (a) A1, (b) A2, (c) A3, (d) A4, (e) A5, (f) A6.
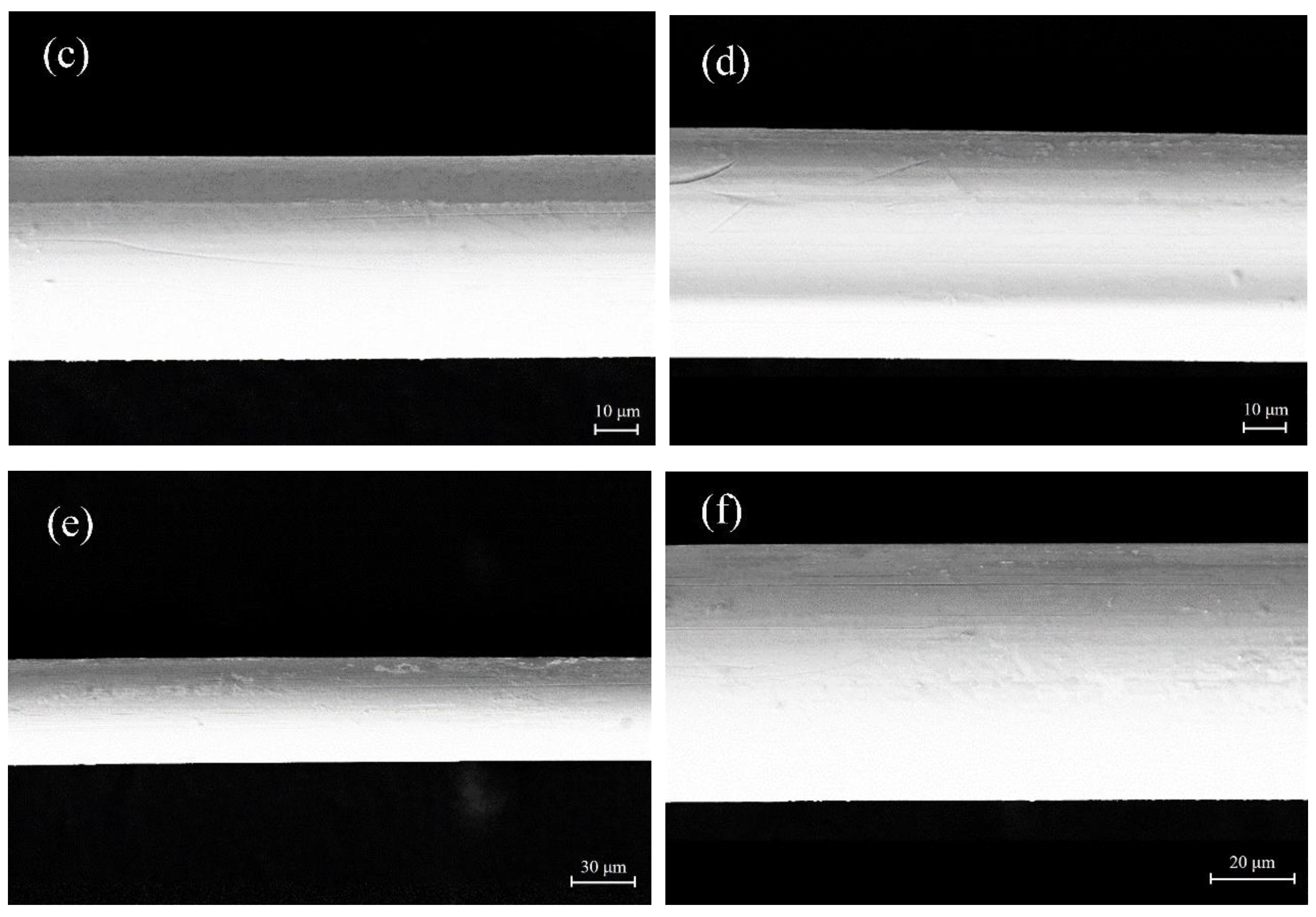
Microstructure of the longitudinal cross-section of A1 is shown in
Figure 2(a) and (b). A large number of wedge-shaped martensites with different width go through the cross-section of the microwire, and amount of lamellar martensites could also be observed. Sparse banded martensites, which have different micrograph compared with A1, could be seen in the longitudinal cross-section of A2 as shown in
Figure 2(c) and (d). In
Figure 2(d), a banded martensite was corroded severely, and the boundary between the martensite and the austenite is very clear, which is indicated by an arrow. The longitudinal cross-section of A3 is shown in
Figure 2(e) and (f). No martensite could be found, and amounts of grains with size of sub-micrometer scale could be seen in
Figure 2(f).
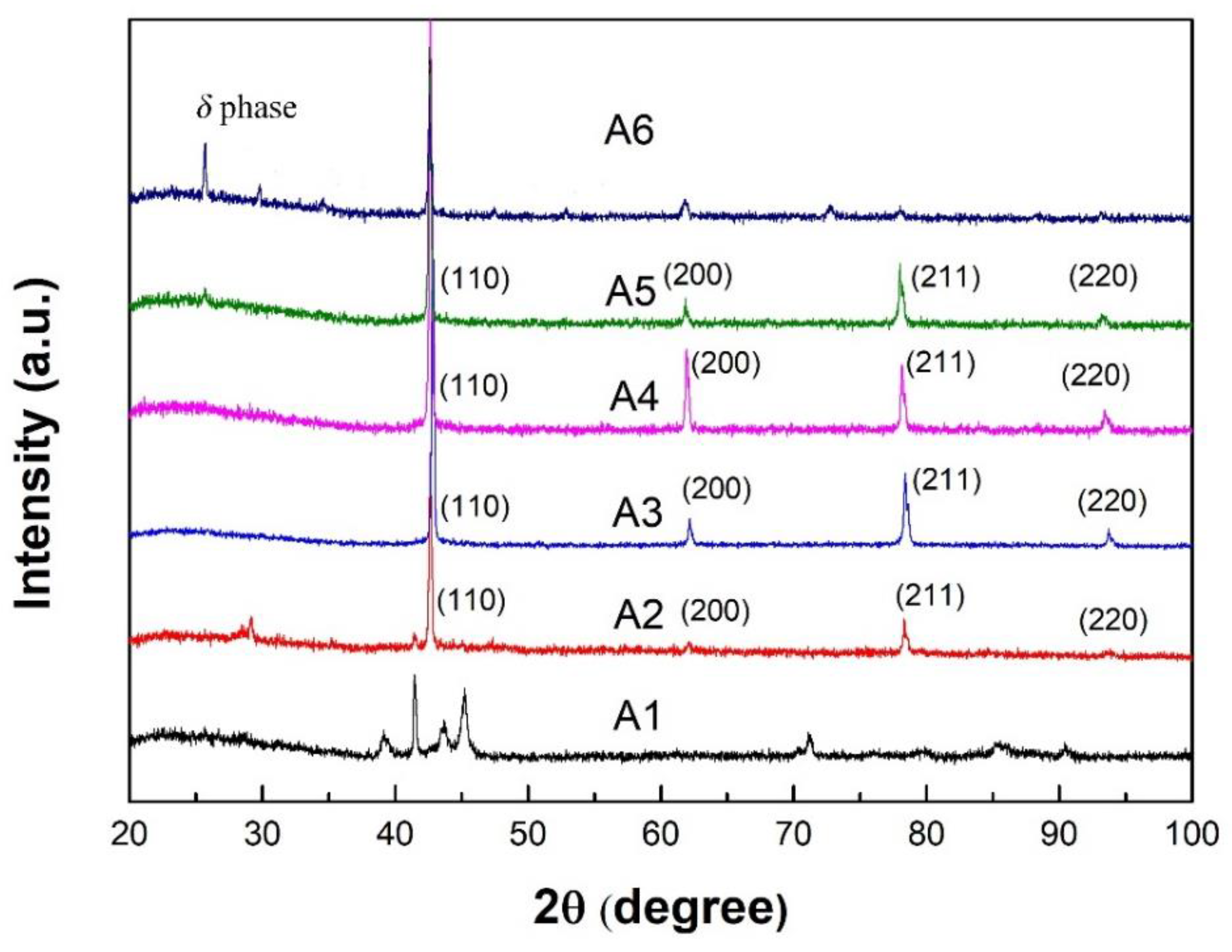
Figure 3 shows X-ray diffraction patterns of microwires with different composition. All identified peaks of A3 and A4 are indexed with a BCC cubic structure of the austenite phase. While all peaks of A1 are indexed with martensite. For A2 microwire, the phase is mainly austenite, with partial martensite as indicated by diffraction peaks from 29̊ to 42̊. The XRD pattern of A6 present complex structure of highly ordered intermetallic
δ phase. The results manifest that with the increase of Sn content, the phase transforms from martensite to austenite, and highly ordered intermetallic phase,
δ, formed in microwires with higher Sn content. The results are consistent with morphology and microstructure observation by SEM.
Saunders et al. [
29] summarized martensite structures formed on quenching from high-temperature
β or
γ solid phases in the Cu-Sn alloy system. With Sn content increasing, three types of martensite structure are usually observed:
β1ʹ,
β1ʹʹ, and
γ1ʹ. The
β1ʹ (18
R) martensite has an ordered orthorhombic structure and is found between 13 and 13.8 at.%Sn.
β1ʹʹ (18
R/2
H) martensite, found between 13.8 and 15 at.%Sn, is a lamellar composites of orthorhombic
β1ʹ and hexagonal
γ1ʹ martensites. The
γ1ʹ martensite, formed between 15 and 15.8 at.%Sn, is a twinned cph structure. The
β1ʹ and
β1ʹʹ martensites formed by water quenching from the high-temperature
β phase to room temperature. The
γ1ʹ martensite formed by two steps [
30]: specimens with composition between 15 and 15.8 at.%Sn transformed to
β1 phase with an ordered D0
3 structure by water quenching from the high-temperature
β phase, and then this ordered
β1 phase transformed to
γ1ʹ martensite by the following cooling to - 196 °C in liquid nitrogen.
For the as-cast A1 and A2 microwires with Sn content between 13.8 and 15.0 at.%, the martensite structure manifests the martensitic transformation temperature is above room temperature, and the phase may be
β1ʹʹ martensite in A1 and A2. With Sn content higher than 15 at.%, the martensitic transformation temperature is lower than room temperature, so the phase of the as-cast A3 and A4 is austenite. When the Sn content reaches up to 17.5 at.%, some highly ordered intermetallic phase
δ formed in A5. For A6, the
δ phase becomes the main phase. It means the eutectic transformation was not suppressed even by rapid cooling from melt when Sn content reaches up to above 17.5 at.%. The
δ phase was also reported to form by quenching Cu-18.5 at.%Sn alloy into water after annealing at 700 °C [
31].
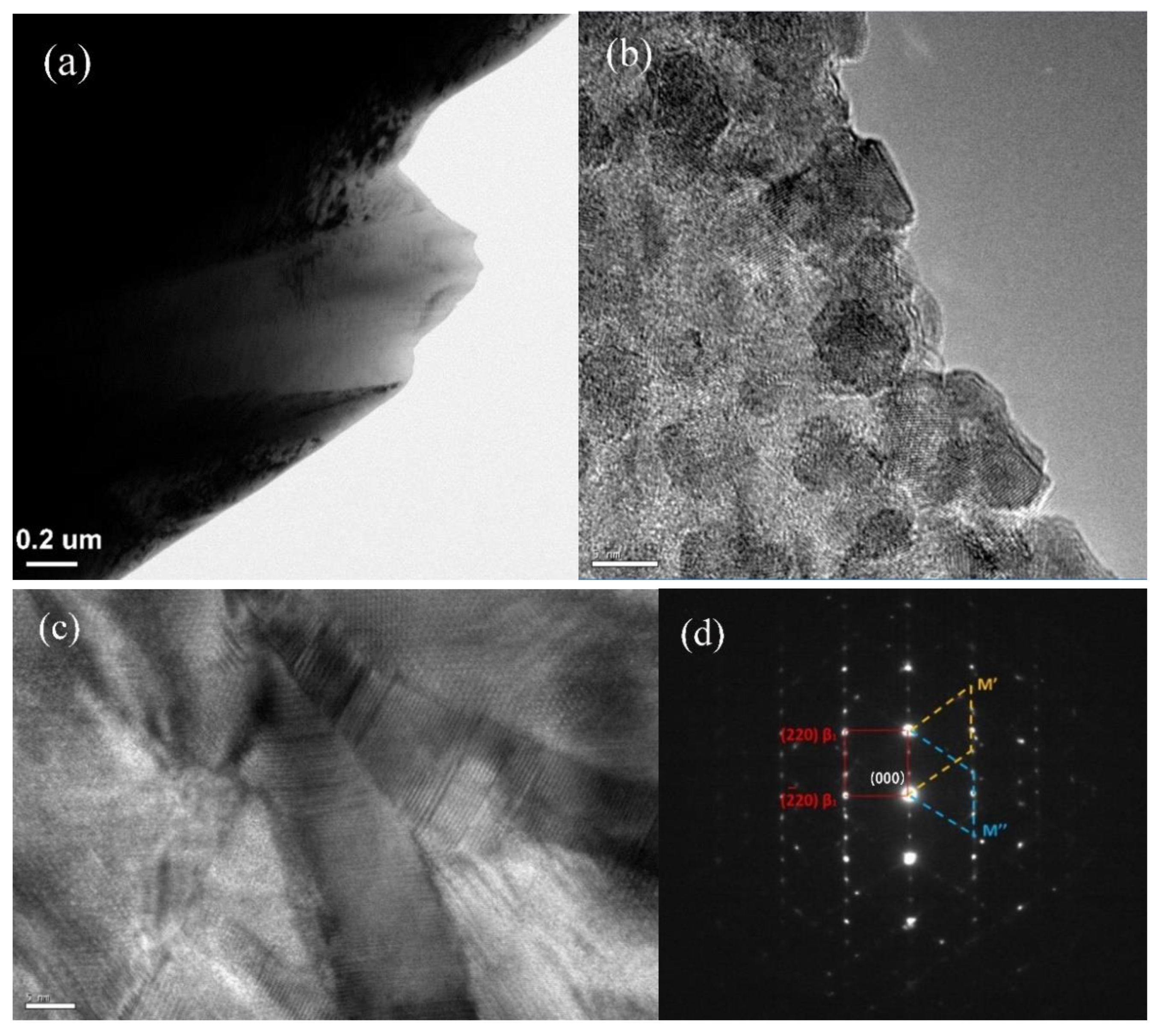
Figure 4(a) and (b) show TEM micrographs of the as-cast A1 microwire. Complicated microstructure, containing wedge-shaped martensite as shown in
Figure 4(a), and many nanocrystalline with size of about 5 nm in HRTEM image as shown in
Figure 4(b), could be observed. Morphology of the martensite in the as-cast A2 microwire is shown in
Figure 4(c). It is similar to the banded
β1ʹ martensite reported by literature [
32,
33]. Moreover, micro-twin structure of martensites could be observed. The corresponding selected-area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern is shown in
Figure 4(d), it presents three sets of diffraction spots, namely
β1 with D0
3 structure and mutual twins of martensitic variants.
3.2. Effect of Sn Content on the Superelasticity of Cu-Sn Microwires
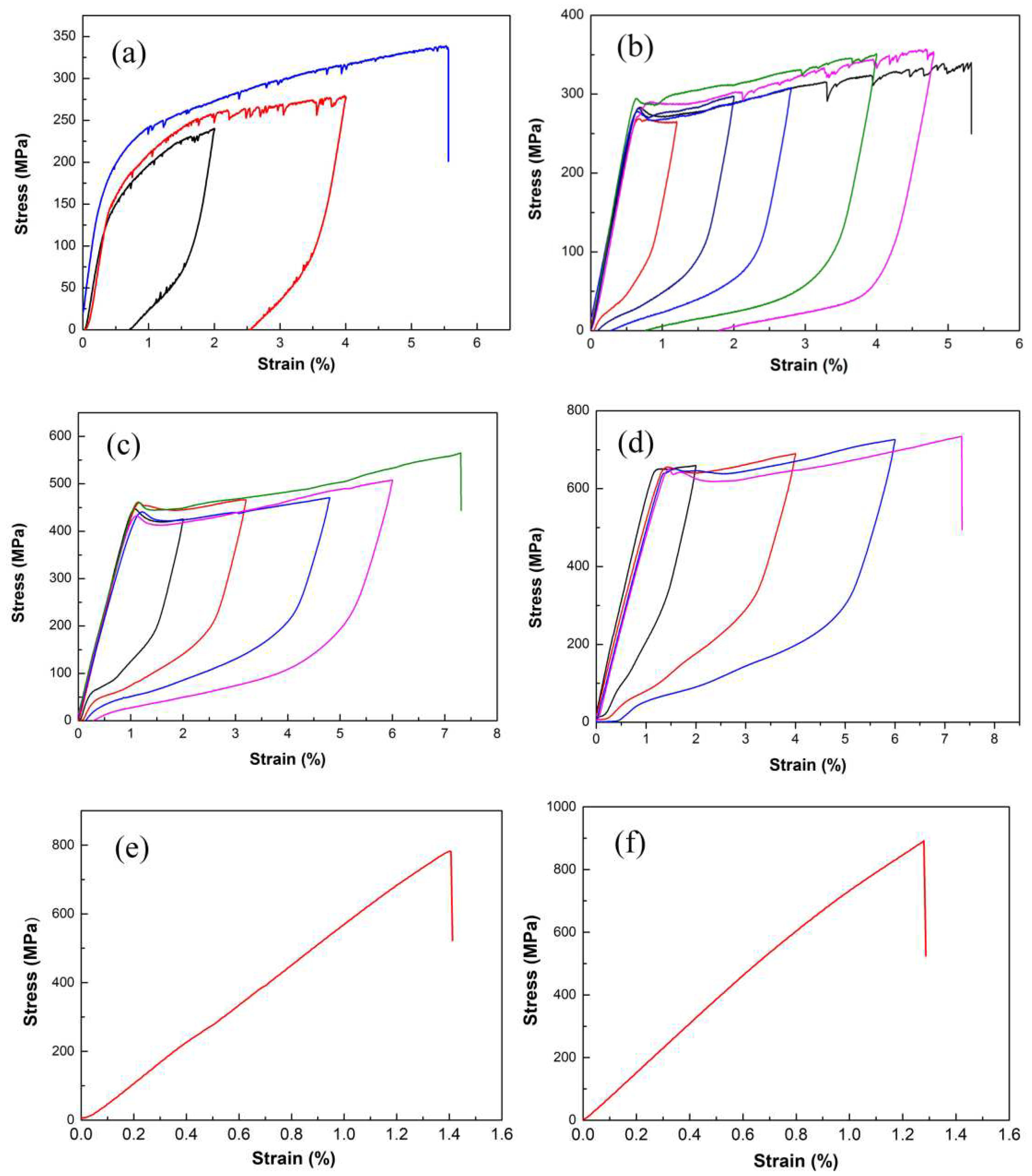
Figure 5 shows stress-strain curves of microwires with diameter of 40 ~ 60 µm. The gauge length is fixed at 25 mm, and the strain rate is 1.33 × 10
-3s
-1. It shows that partial strain recovered after unloading for A1 and A2, while nearly total strain recovered for A3 and A4. The stress-strain curves of A3 and A4 show typical superelastic effect, exhibiting a reversible strain of several percent. This strain relies on the occurrence of a thermoelastic martensitic transformation and arises from a combination of transformation of stress-induced martensitic transformation upon loading and its reverse transformation upon unloading [
34,
35,
36]. Different from the stress-strain curve with two plateaus in Cu-Sn bulk single crystals [
37], which are associated with the successive martensitic transformation, there is only one plateau on stress-strain curve for all superelastic microwire. The microwires fractured only after elastic deformation for A5 and A6, because of highly ordered brittle δ phase.
It’s interesting that serration behavior appeared immediately after yield on the stress-strain curve of A1 microwire, and it also appeared during unloading. While for A2 microwire, serration behavior happened after yield with more than 2 % strain upon loading, and it did not appear during unloading. No serration flow appeared for A3 and A4. Serration phenomenon was also reported in other materials [
38,
39,
40]. This serration behavior may be related with the accumulated formation of micro-twins of martensite during loading, which was also observed in stress-strain curves of Cu-Al wires produced by a horizontal in-rotating-liquid-spinning method [
41].
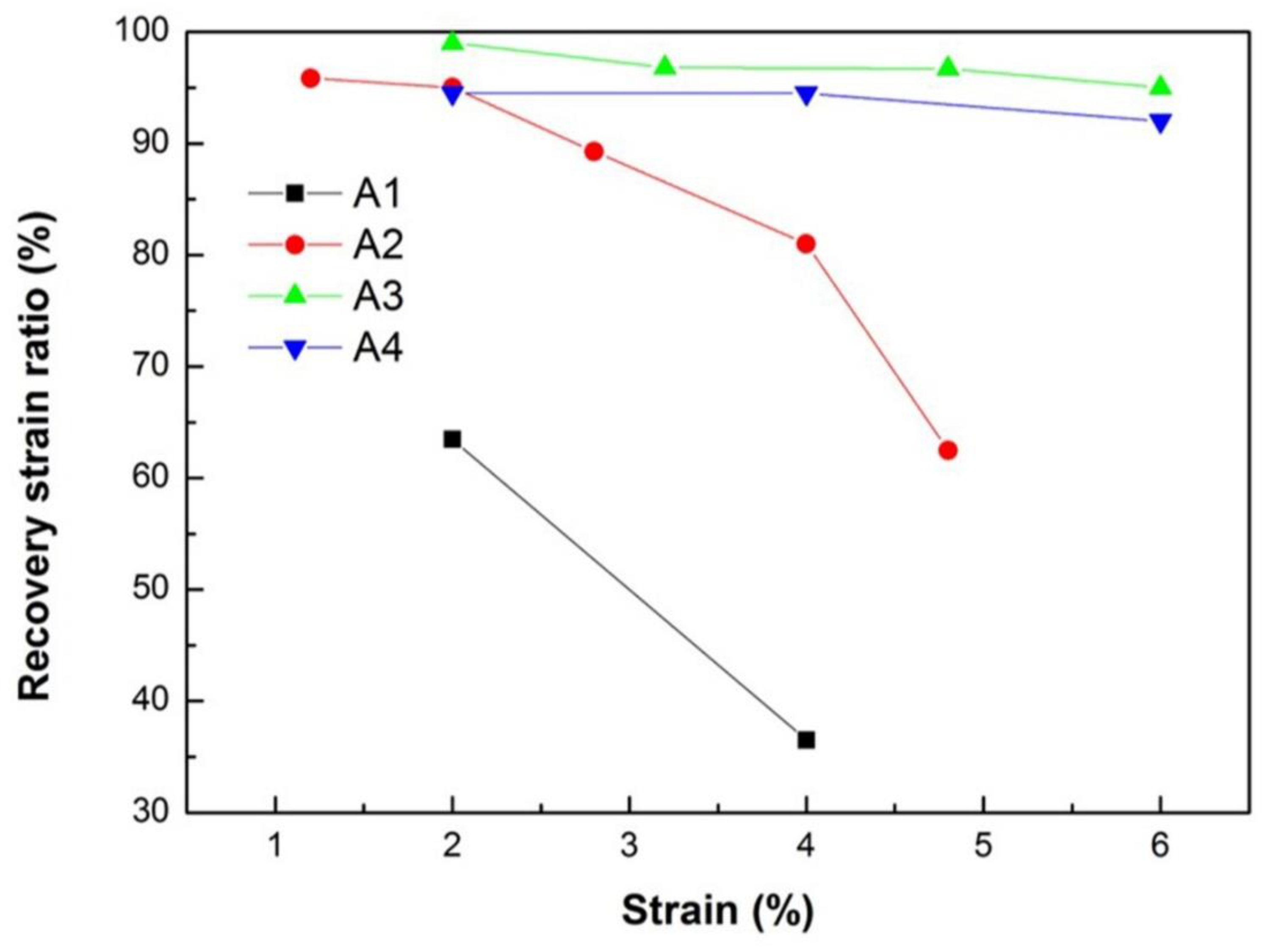
Figure 6 shows the relationship between the recovery ratio and the total strain. The recovery ratio of A1 is minimal. It decreases rapidly with total strain increasing for A2, while it does not change remarkably for A3 and A4. When the total strain is 6 %, the recovery ratios for A3 and A4 reach up to 95 % and 92 %, respectively. These results are in accordance with microstructure, as only austenite phase exhibits superelastic effect. A1 mainly contains martensite, so little superelastic effect was observed. A2 shows partial superelastic recovery as it is a mixture of austenite and martensite. A3 and A4 mainly contains austenite, which results in significant superelastic effect.
Different from the reported experiments related to the martensitic transformation in Cu-Sn system [
30,
42], where bulk specimens are always quenched from a high-temperature
β or
γ solid phase, Cu-Sn microwires were directly prepared from the melt by rapid solidification using the method of glass-coated melt spinning in this work. The mechanical and superelastic effect for A3 and A4 was improved greatly, due to the high cooling rate, which suppressed precipitation of unwanted equilibrium phases and refined grains to the scale of micrometer or sub-micrometer.
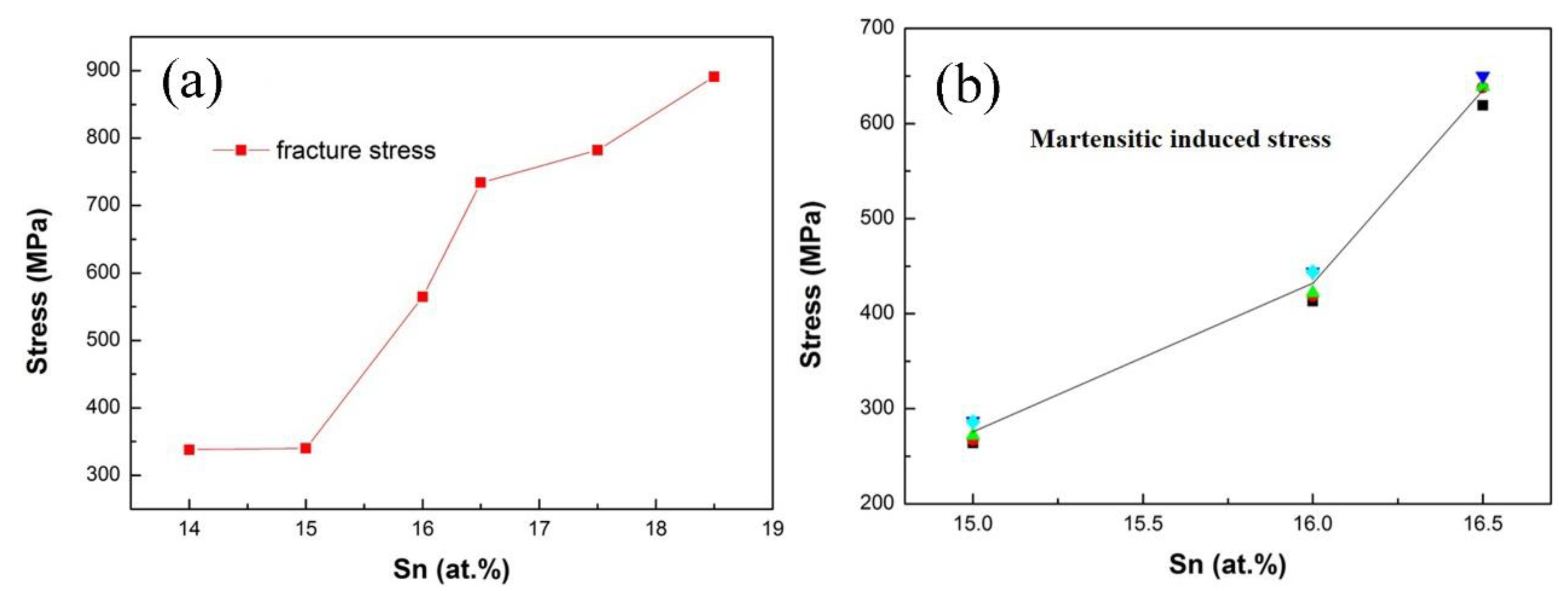
The Sn content dependence of the fracture stress is shown in
Figure 7(a). It is clear that the fracture stress,
σf, increases with Sn content increasing.
Figure 7(b) shows the critical stress for martensitic transformation,
σMs, which corresponds to an effective yield stress in superelastic behavior, increases with Sn content increasing. Since the martensitic transformation temperature decreases with Sn content increasing in Cu-Sn alloy [
30], and it is lower than room temperature with Sn content higher than 15 at.%, the austenite phase becomes more stable at room temperature with Sn content increasing from 15 at.% to 16.5 at.%, so it leads to higher critical stress to induce the martensitic transformation. The relationship between the critical stress for stress-induced martensitic transformation,
σMs, and the temperature,
T, is usually in agreement with the Clausius-Clapeyron relation [
36] for a certain component of shape memory alloy:
where
∆S is the molar entropy difference between the parent and martensite phases,
ε is the strain caused by the phase transformation, and
Vm is the molar volume. Since
σMs equals to zero at martensitic transformation start temperature, the relationship could be described as
σMs =
, where
is the temperature difference between test temperature and
Ms. In this study, the test temperature is room temperature. As
Ms decreases with Sn content increasing,
will increase, and it leads to higher critical stress for stress-induced martensitic transformation.
3.3. Effect of Strain Rate on the Superelasticity of Cu-Sn Microwires
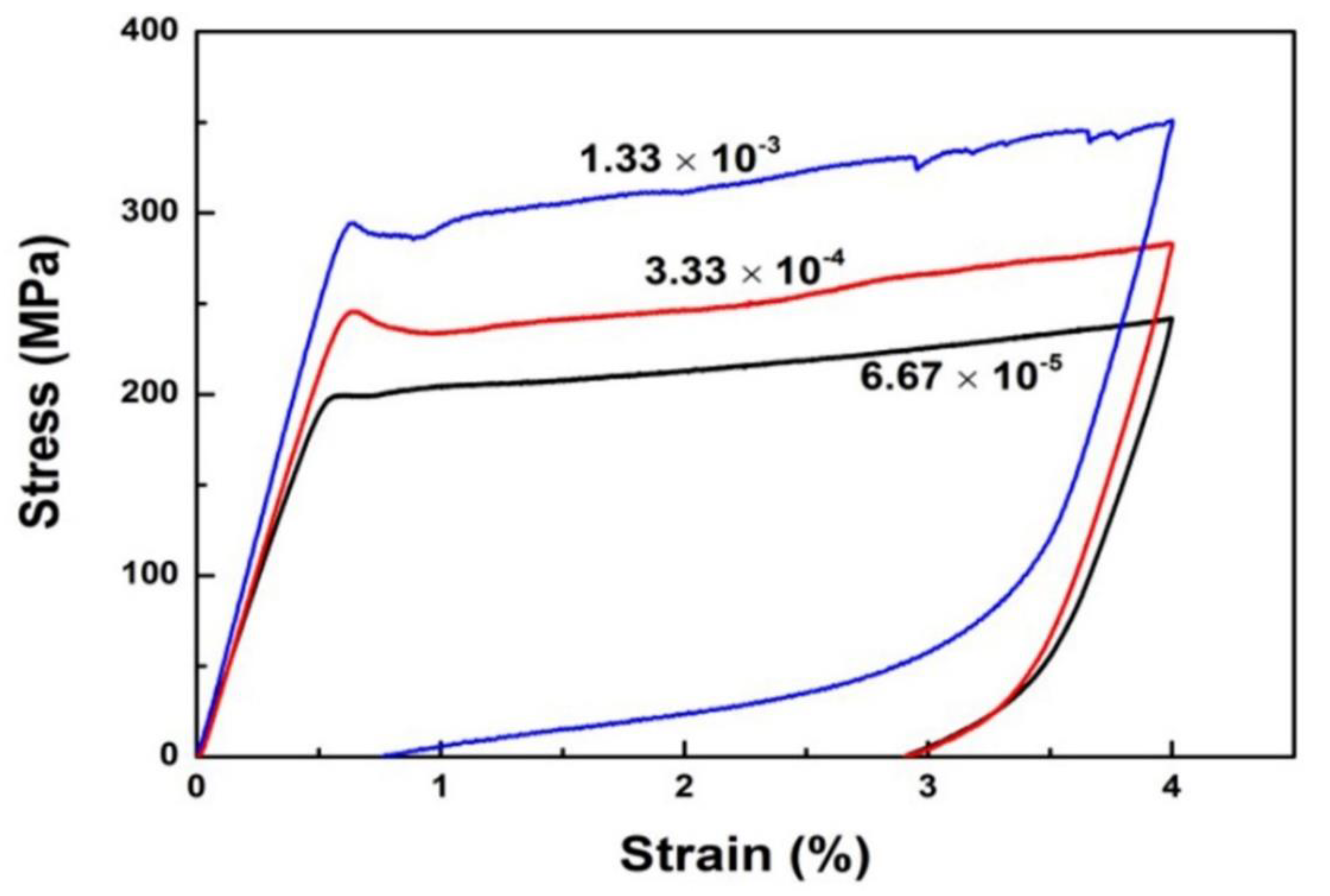
The tensile stress-strain curves at various strain rate for A2 microwire are shown in
Figure 8. The residual strains at strain rate of 6.67 × 10
-5, 3.33 × 10
-4 and 1.33 × 10
-3 are 2.91 %, 2.91 % and 0.75 %, respectively. It manifests that the strain rate becomes larger, the superelastic effect becomes dominant. The critical stress for martensitic transformations,
σMs, increases with strain rate increasing. This phenomenon was also reported in Cu-15.0 at.%Sn single crystal [
43].
The shape memory effect and superelasticity are characterized by the reversible motion of an interface between the autensite and martensite. The origin of the strain rate dependence could be attributed to the thermally activated motion of the interface. Kato [
43] thought that when the velocity of an interface is slow, Sn atoms would be trapped at the interface through the interaction between them, and the mobility of an interface will decrease. It implies that for higher strain rates, the interface moves easier, and the stress-strain behavior becomes superelastic.
3.4. Superelastic Effect of Bamboo-like Grain Structured Cu-Sn Microwires
In Cu-based SMAs, the grain size has great influence on the superelastic properties. Sutou [
44,
45] found that with the increase of grain size, the recoverable strain gradually increased in Cu-Al-Mn shape memory alloy wires and sheets. Ueland [
18,
19] obtained bamboo-like grained Cu-Al-Ni and Cu-Zn-Al microfibers with great superelastic and two-way shape memory effect. Schuh [
19] referred to this type of microfiber with a bamboo-like structure as an oligocrystalline shape memory alloy. Here, a bamboo-like grain structure was obtained in microwires with Sn content of 16 at.% (A3) via heat treatment by annealing at 750˚C for 5 hours before quenching in water.
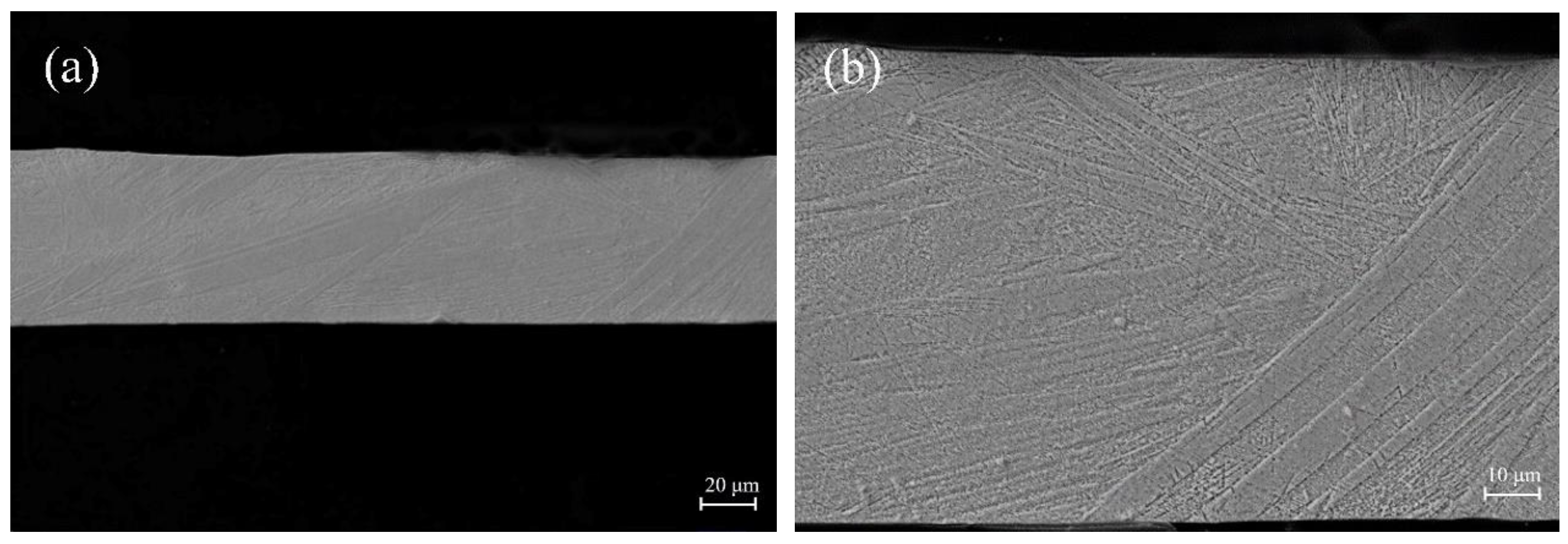
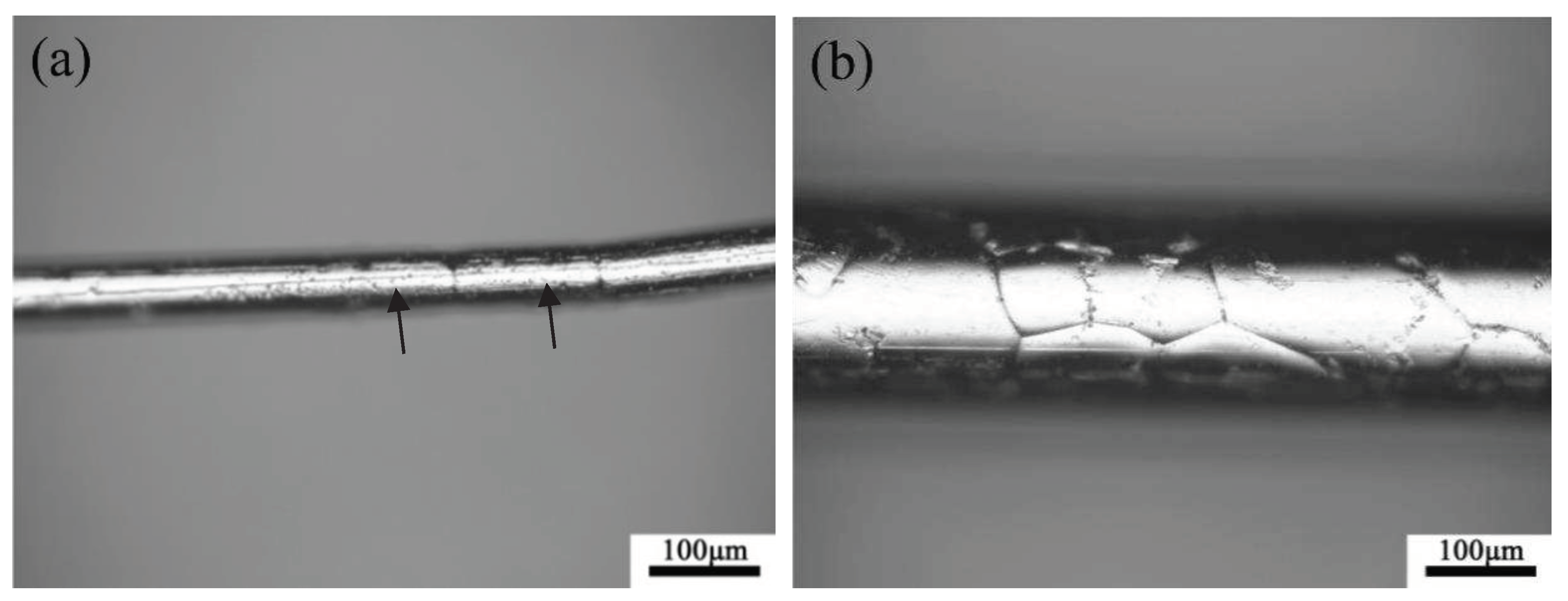
Figure 9 shows the metallograph photos of the surface morphology of microwires with different diameters. It could be seen that the grains of microwire with a diameter of 56 µm span the entire cross-section of the wire, presenting a typical bamboo-like structure. While on the surface of the microwire with a diameter of 179 µm, several triple junctions could be observed, with grain size smaller than the diameter of the microwire.
According to the Cu-Sn phase diagram [
29,
31], the equilibrium phase of the Cu-Sn alloy with Sn content of 16 at.% is disordered
β phase at 750°C, which would transform to
β1 phase with an ordered D0
3 structure by the following water quenching. At room temperature, stress-induced martensitic transformation would happen in ordered
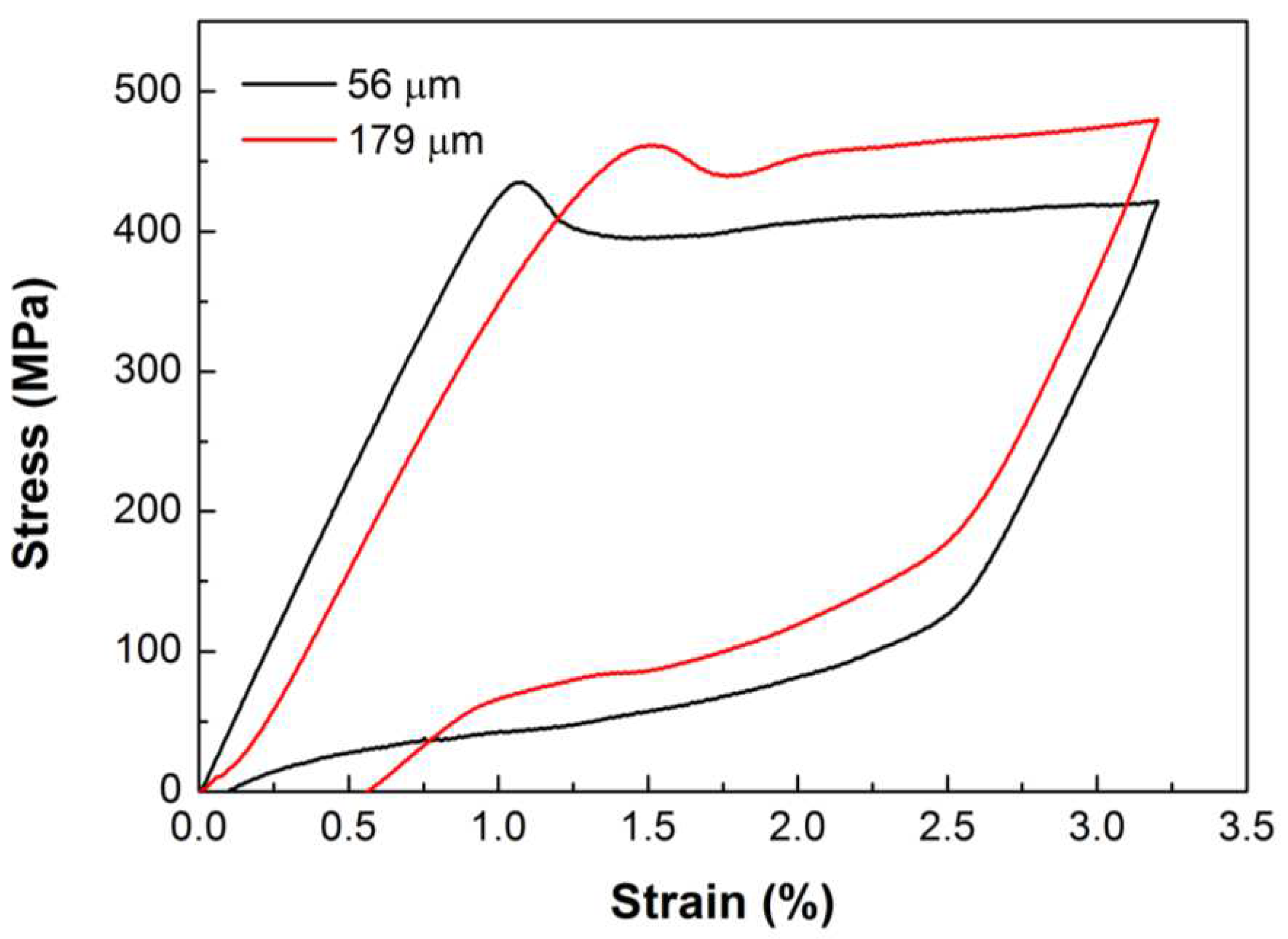
β1 phase. The loading-unloading stress–strain curves of the microwires with diameter of 56 μm and 179 μm are shown in
Figure 10. It shows that after unloading from 3.2% strain, the residual strain of 56 μm diameter microwire is 0.11%, while that of 179 μm diameter microwire is 0.57%. The results indicate the 56 μm diameter microwire with bamboo-like structure have better superelastic properties than the 179 μm diameter microwire with triple junctions. This is consistent with the results observed in other Cu-based shape memory alloy wires and sheets [
18,
19,
44,
45].
4. Discussion
The above experimental results indicate that the superelastic effect of Cu-Sn microwires does not change monotonically with the grain size. When the grain size of the glass-coated microwires prepared by water cooling is refined to micrometer level, the alloy has good mechanical and superelastic properties. When the grain of the microwire grows to be equivalent to the one-dimensional size of the specimen after annealing, the mechanical property could also be improved. However, when the grain size is between the two rules, the superelastic properties decay. Notably, although Schuh et al. [
18,
19] have concluded that bamboo-like structures have better mechanical and superelastic properties than coarse-grained polycrystals in Cu-Zn-Al microfibers, they have not reported microfibers with ultrafine grains. This is because they used the most traditional Taylor method to make microfibers, without the use of water-cooling device to rapidly cool the microfiber, so it is difficult to obtain ultrafine crystal structures.
In this work, the Cu-Sn microwires are in austenitic state at room temperature, and there are two competing deformation mechanisms under applied stress, namely, irreversible dislocation slip and reversible stress-induced martensitic phase transition. The grain size of Cu-Sn microwires prepared by the glass coating method has been refined to the micrometer level, thereby improving their grain boundary strength. During the transformation into martensite under applied stress, the strain is dispersed by amounts of small grains, so the stress concentration at the grain boundary is negligible, and the strain can be coordinated among grains. Therefore, the fracture strength of Cu-Sn microwires prepared by water cooling is improved, and the microwires show excellent superelastic properties.
With the grain size increasing, the coarse grains form triple junctions with each other. Under the applied external force, martensite variants formed with the same orientation in coarse grains with different crystal orientations. Due to the limitation of grain boundaries, it is difficult to coordinate the strains of adjacent grains, so it results in great stress concentration at the triple junctions and seriously deteriorate superelasticity. When the grain size increases to match the one-dimensional size of the specimen, bamboo-grained microwires formed where triple junctions are eliminated and grain boundaries are sparse. In these microwires, the surface area is larger than the total grain boundary area, meaning that grains are coordinated mostly by unconfifined free surfaces rather than rigid boundaries. Due to the reduction of grain boundary restriction in space, the free surface can effectively relieve the transformation stresses and reduce the transformation incompatibilities. As a result, each individual grain can undergo transformation like a single crystal and shows excellent superelasticity.
In the present study, by controlling the process conditions, we obtained Cu-Sn microwires with different grain sizes from ultrafine grains to bamboo-like grains. The relationship between superelasticity and grain size was studied, which indicates that two opposite strategies of refining the grain size to micrometer level or increasing the grain size to one dimensional size of specimen, e.g., the diameter of the wire, are both effective to improve superelasticity of Cu-Sn alloy.
5. Conclusions
To summarize, Cu-Sn shape-memory microwires were fabricated by a glass-coated melt spinning method. Effects of Sn content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Cu-Sn microwires were investigated, and the relationship between superelasticity and grain size was studied. The main findings can be summarized as follows:
(1) Cu-Sn microwires with diameter of 10 ~ 200 µm were fabricated successfully by glass-coated melt spinning method. For the high cooling rate, the grain size of as-cast Cu-Sn microwires could be refined to the scale of micrometer. The phase in the as-cast microwires transforms from martensite to austenite with Sn content increasing from 14.0 at.% to 16.5 at.%. When the Sn content is more than 16.5 at.%, highly ordered intermetallic phase, δ, formed.
(2) Microwires with Sn content of 16 at.% (A3) and 16.5 at.% (A4) show excellent superelasticity. The fracture stress, σf, and the critical stress for stress-induced martensitic transformation, σMs, increases with Sn content increasing. Strain rate has a significant influence on the superelasticity of microwires that at high strain rate, the microwire shows excellent superelastic, while at low strain rate, the superelasticity deteriorate.
(3) A bamboo-grained structure was formed in the Cu-Sn microwire with Sn content of 16 at.% (A3) by annealing at 750°C for 5 hours before quenching in water. Due to the unconfifined free surfaces and absence of triple junctions, the bamboo-grained microwires also show excellent superelasticity. The results manifest that those two opposite strategies of refining the grain size to micrometer level or increasing the grain size to one dimensional size of specimen are both effective to improve superelasticity of Cu-Sn alloy.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the funding support from the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20200259), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52273280), the Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation (20224ACB212001), and the Youth Promotion Association of Chinese Academy of Sciences (2020320).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
- Ölander A. An electrochemical inverstigation of solid cadmium-gold alloys. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1932, 56, 3819-3833.
- Otsuka K.; Ren X. Physical metallurgy of Ti-Ni-based shape memory alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2005, 50, 511-678.
- Chluba, C.; Ge, W.W.; Miranda, R.L.; Strobel, J.; Kienle, L.; Quandt, E.; Wuttig, M. Ultralow-fatigue shape memory alloy films. Science 2015, 348, 1004-1107. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1261164.
- Kainuma, R.; Imana, Y.; Ito, W.; Sutou, Y.; Morito, H.; Okamoto, S.; Kitakami, O.; Oikawa, K.; Fujita, A.; Kanomata T.; Ishida K. Magnetic-field-induced shape recovery by reverse phase transformation. Nature 2006, 439, 957-960. [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, Y.; Ando, D.; Sutou Y.; Koike J. A lightweight shape-memory magnesium alloy. Science 2016, 353, 368-370. [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Simsek, E.; Ma T.; et al. Fatigue-resistant high-performance elastocaloric materials made by additive manufacturing. Science 2019, 366, 1116-1121. [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Catalini, D.; Muehlbauer J.; et al. High-performance multimode elastocaloric cooling system. Science 2023, 380, 722-727. [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Fang, S.; Xiao Y.; et al. Torsional refrigeration by twisted, coiled, and supercoiled fibers. Science 2019, 366, 216-221.
- Zhao, Y.; Zhou, W.; Shi Y.; Yang X.; Bai Y.; Li L.; Wang S.; Li T.; Feng S.; Zhang T. Superelastic alloy based electrical interconnects for highly stretchable electronics. Npj Flex. Electron. 2022, 6, 8.
- Curtis, S.M.; Gugat, J.L.; Bumke L.; Duygu D.; Seigner L.; Schmadel D.; Lazarus N.S.; Quandt E. Thin-film superelastic alloys for stretchable electronics. Shape Mem. Superelast. 2023, 9, 35-49. [CrossRef]
- Lovey, F.C.; Torra, V. Shape memory in Cu-based alloys: phenomenological behavior at the mesoscale level and interaction of martensitic transformation with structural defects in Cu-Zn-Al. Prog. Mater. Sci. 1999, 44, 189-289. [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Otsuka, K.; Wayman, C.M.; Nakai, K.; Sakamoto, H. Superelasticity effects and stress-induced martensitic transformation in Cu-Al-Ni alloys, Acta Metall. 1976, 24(3), 207-226. [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Rimoli, J.J.; Chen, Y.; Schuh, C.A.; Radovitzky, R.; Nonlocal superelastic model of size-dependent hardening and dissipation in single crystal Cu-Al-Ni shape memory alloys. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 085504. [CrossRef]
- Horikawa, H.; Ichinose, S.; Morii, K.; Miyazaki, S.; Otsuka, K. Orientation dependence of β1→β1ʹ stress-induced martensitic transformation in a Cu-Al-Ni alloy. Metall. Trans. A 1988, 19A, 915-923.
- Miyazaki, S.; Kawai, T.; Otsuka, K. On the origin of intergranular fracture in β phase shape memory alloys. Scr. Metall. 1982, 16(4), 431-436. [CrossRef]
- Omori, T.; Kusama, T.; Kawata, S.; Ohnuma, I.; Sutou, Y.; Araki, Y.; Ishida, K.; Kainuma, R. Abnormal grain growth induced by cyclic heat treatment. Science 2013, 341, 1500-1502. [CrossRef]
- Kusama, T.; Omori, T.; Saito, T.; Kise, S.; Tanaka, T.; Araki, Y.; Kainuma, R. Ultra-large single crystals by abnormal grain growth. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8(354), 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Ueland, S.M.; Schuh, C.A. Superelasticity and fatigue in oligocrystalline shape memory alloy microwires. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 282-292. [CrossRef]
- Ueland, S.M.; Chen, Y.; Schuh, C.A. Oligocrystalline Shape memory alloys. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2094-2099. [CrossRef]
- Tuncer, N.; Schuh, C.A. Melt-cast microfibers of Cu-based shape memory alloy adopt a favorable texture for superelasticity. Scr. Mater. 2016, 117, 46-50. [CrossRef]
- Font, J.; Cesari, E.; Muntasell, J.; Pons, J. Thermomechanical cycling in Cu-Al-Ni-based melt-spun shape-memory ribbons. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 354, 207-211.
- Ochin, P.; Dezellus, A.; Plaindoux, Ph.; Pons, J.; Vermaut, Ph.; Portier, R.; Cesari, E. Shape memory thin round wires produced by the in rotating water melt-spinning technique. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 1877-1885. [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, M.; Zengin, R. Shape memory properties and oxidation behaviour of a rapidly liquid quenched Cu–Sn alloy. J. Mater. Process Tech. 2000, 97, 148-152. [CrossRef]
- Kamal, M. Mechanical properties of rapidly solidified of Cu-Sn shape memory alloys. Radiat. Eff. Defect S. 2006, 161, 189-191. [CrossRef]
- Li, D.S.; Rong, Q.G.; Zhu, Y. The shape memory effect (SME) of liquid rapidly quenched (LRQ) Cu-Sn alloys. Rapidly Quenched Metals, Elsevier Science Publishers B.V 1985, 1425-1428.
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.S.; Zhang, Y.; Liaw, P.K. Shape memory and superelasticity in amorphous/nanocrystalline Cu-15.0 atomic percent (at.%) Sn wires. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2014, 16(1), 40-44. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Li, H.; Hao, H.Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liaw, P.K. Microwires fabricated by glass-coated melt spinning. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2013, 84, 075102. [CrossRef]
- Larin, V.S.; Torcunov, A.V.; Zhukov, A.; González, J.; Vazquez M.; Panina. L. Preparation and properties of glass-coated microwires. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2002, 249, 39-45. [CrossRef]
- Saunders, N.; Miodownlk. A.P. The Cu-Sn (Copper-Tin) System. Bulletin of Alloy Phase Diagrams 1990, 11, 279-285.
- Kennon, N.F.; Miller, T.M. Martensitic transformations in β1 Cu-Sn alloy. Trans. JIM 1972, 13, 322-326.
- Fürtauer, S.; Li, D.; Cupid, D.; Flandorfer, H. The Cu-Sn phase diagram, Part I: new experimental results. Intermetallics 2013, 34, 142-147. [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.I.; Sakamoto, H.; Otsuka, K. On the crystal structure of the banded martensite in Cu-24.5 wt% Sn alloy. Trans. JIM 1975, 16(9), 581-590. [CrossRef]
- Kuwano, N.; Wayman, C.M. Precipitation Processes in a β-Phase Cu-15 at.% Sn Shape Memory Alloy. Trans. JIM 1983, 24, 499-503.
- Jani, J.M.; Leary, M. A. Subic and M.A. Gibson. A review of shape memory alloy research, applications and opportunities. Mater. Design 2014, 56, 1078-1113. [CrossRef]
- Juan, J.M.S.; Nό, M.L.; Schuh, C.A. Superelasticity and shape memory in micro- and nanometer-scale pillars. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 272-278. [CrossRef]
- Omori, T.; Ando, K.; Okano, M.; Xu, X.; Tanaka, Y.; Ohnuma, I.; Kainuma, R.;Ishida, K. Superelastic effect in polycrystalline ferrous alloys. Science 2011, 333, 68-71. [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Miura, S. Thermodynamical analysis of the stress-induced martensitic transformation in Cu15.0 at.% Sn alloy single crystals. Acta Metall. Mater. 1995, 43, 351-360.
- Li, R.; Hao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Weibull Statistical Reliability Analysis of Mechanical and Magnetic Properties of FeCuNbxSiB Amorphous Fibers. Metals 2017, vol. 7, 76. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.P.; Chen, S.Y.; Xie, X.; Liaw, P.K.; Dahmen, K.A.; Qiao, J.W.; Wang, Y.L. Serration and noise behaviors in materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2017, 90, 358-460. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.D.; Lin, J.P.; Dahmen, K.A.; Wang, Z.L.; Liaw, P.K. Superelasticity and Serration Behavior in Small-Sized NiMnGa Alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2014, 16, 955-959. [CrossRef]
- Zeller, S.; Gnauk, J. Shape memory behavior of Cu-Al wires produced by horizontal in-rotating-liquid-spinning. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 481-482, 562-566.
- Miura, S.; Morita, Y.; Nakanishi, N. Superplasticity and Shape Memory Effect in Cu-Sn Alloys. In Shape Memory Effect in Alloys; J. Perkins, Ed., Plenum Press, New York, NY, USA, 1976, 389-405.
- Kato, H.; Hirata, N.; Miura, S. Effects of aging on pseudoelastic behaviour in Cu-15.0 at.%Sn alloy single crystals. Acta Metall. 1995, 43(1), 361-369. [CrossRef]
- Sutou, Y.; Omori, T.; Yamauchi, K; et al. Effect of grain size and texture on pseudoelasticity in Cu-Al-Mn-based shape memory wire. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 4121-4133. [CrossRef]
- Sutou, Y.; Omori, T.; Kainuma, R.; Ishida K. Grain size dependence of pseudoelasticity in polycrystalline Cu-Al-Mn-based shape memory sheets. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 3842-3850. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the glass-coated melt spinning process. The alloy is under argon protection during preparation.
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the glass-coated melt spinning process. The alloy is under argon protection during preparation.
Figure 2.
SEM images of longitudinal cross-sections of Cu-Sn microwires with different Sn content: (a)(b): A1, (c)(d): A2, (e)(f): A3.
Figure 2.
SEM images of longitudinal cross-sections of Cu-Sn microwires with different Sn content: (a)(b): A1, (c)(d): A2, (e)(f): A3.
Figure 3.
X-ray diffraction patterns of Cu-Sn microwires with different Sn content.
Figure 3.
X-ray diffraction patterns of Cu-Sn microwires with different Sn content.
Figure 4.
Bright-field image (a) and HRTEM image (b) for A1 microwire; HRTEM image (c) and corresponding selected-area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern (d) for A2 microwire.
Figure 4.
Bright-field image (a) and HRTEM image (b) for A1 microwire; HRTEM image (c) and corresponding selected-area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern (d) for A2 microwire.
Figure 5.
Loading-unloading tensile stress-strain curves of Cu-Sn microwires with different Sn content at different unloading strains : (a) A1, (b) A2, (c) A3, (d) A4, (e) A5, (f) A6.
Figure 5.
Loading-unloading tensile stress-strain curves of Cu-Sn microwires with different Sn content at different unloading strains : (a) A1, (b) A2, (c) A3, (d) A4, (e) A5, (f) A6.
Figure 6.
The relationship between the recovery strain ratio and the total strain for A1, A2, A3 and A4 microwires.
Figure 6.
The relationship between the recovery strain ratio and the total strain for A1, A2, A3 and A4 microwires.
Figure 7.
The fracture stress, σf, (a), and the critical stress for martensitic transformation, σMs (b), versus Sn content.
Figure 7.
The fracture stress, σf, (a), and the critical stress for martensitic transformation, σMs (b), versus Sn content.
Figure 8.
Loading-unloading tensile stress-strain curves at various strain rate for A2 microwire.
Figure 8.
Loading-unloading tensile stress-strain curves at various strain rate for A2 microwire.
Figure 9.
Metallograph photos of the surface morphology of microwires with different diameters: (a) 56 µm, (b) 179 µm.
Figure 9.
Metallograph photos of the surface morphology of microwires with different diameters: (a) 56 µm, (b) 179 µm.
Figure 10.
Loading-unloading stress-strain curves of annealed microwires.
Figure 10.
Loading-unloading stress-strain curves of annealed microwires.
Table 1.
Nominal composition of Cu-Sn microwires, which are named as A1~A6.
Table 1.
Nominal composition of Cu-Sn microwires, which are named as A1~A6.
| Composition |
A1 |
A2 |
A3 |
A4 |
A5 |
A6 |
| Cu (at.%) |
86 |
85 |
84 |
83.5 |
82.5 |
81.5 |
| Sn (at.%) |
14 |
14.5 |
16 |
16.5 |
17.5 |
18.5 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).