1. Introduction
Anesthetic management for pregnant patients suffering from airway pathology poses unique challenges. Pregnancy-induced reduction in functional residual capacity, in conjunction with increased oxygen consumption, lowers the oxygen reserve of the mother. Also, engorged vessels and edema of upper airway during pregnancy increase the risk of upper airway obstruction and trauma [
1,
2,
3]. Furthermore, deoxygenation in pregnant patients can have tragic consequences due to its impact on the fetus.
Vocal cord granulomas are benign lesions commonly found in the posterior glottis. They can result from various causes, such as gastroesophageal reflux, intubation trauma, and vocal abuse. Granulomas caused by intubation usually appear 2 to 10 weeks after the event. Although vocal cord granulomas can occur in individuals of any age or gender, they are predominantly found in women who have undergone intubation [
4,
5,
6]. Symptoms typically include hoarseness, sensation of lump or discomfort, dyspnea, cough, and hemoptysis [
7]. The primary treatment approach is conservative, but the course of treatment varies based on the underlying cause. Surgery is indicated in cases of airway obstruction and histopathologic diagnosis [
8,
9]. In this particular case, a pregnant patient had symptomatic bilateral vocal cord granuloma. Due to symptoms and limitations in medication options for the fetus, surgery under general anesthesia was chosen as the optimal option. However, the presence of giant bilateral vocal cord granuloma posed challenges during general anesthesia, as it could interfere with intubation and ventilation, increasing the risk of hypoxia, especially considering its potential impact on the fetus.
Preoxygenation is crucial prior to endotracheal intubation, as there is an unavoidable period of apnea during the insertion of the endotracheal tube. Adequate preoxygenation in patients without specific underlying conditions prevents desaturation for up to 9 minutes [
10]. To minimize apnea duration during intubation and enhance oxygen levels, the use of high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) during intubation may be considered [
11]. HFNC delivers heated and humidified oxygen at a maximum flow of 60 l/min without the need for invasive techniques. Additionally, HFNC generates positive airway pressure, effectively clearing the nasopharyngeal dead space [
12].
Pulse oximetry is a vital tool for straightforward monitoring of patient oxygenation. However, pulse oximetry cannot accurately measure oxygen content that is fully saturated above 97%. On the other hand, multiwavelength pulse co-oximetry, specifically oxygen reserve index (ORi) monitoring, allows measurement of PaO
2 within the range of 100 to 200mmHg [
13]. ORi monitoring is particularly useful during preoxygenation, extending the acceptable apnea time and identifying inadequate preoxygenation by detecting interruptions in oxygen delivery [
13].
This case report highlights the airway management of a patient with a giant vocal granuloma undergoing surgery, with a specific emphasis on the patient’s oxygen reserve. To ensure sufficient oxygen levels and enhance safety, the anesthesia plan involved the use of HFNC oxygenation combined with ORi monitoring, representing a novel approach for managing anesthesia in patients with potential difficult intubation.
2. Case Report
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for the publication of this case report.
We report a case of a 33-year-old pregnant woman (height, 153 cm; weight, 61 kg) at 13 weeks gestation. She had been experiencing hoarseness and bilateral granuloma, requiring surgical intervention.
Six month ago, she was admitted to Korea University Guro Hospital’s emergency room with unstable mental condition. She experienced severe vomiting and diarrhea prior to admission, and shortly after the urgent admission, she suffered a cardiac arrest with pulseless electrical activity. Cardiac compressions were initiated right away, and she was intubated with a 7.5 inner diameter tube. After three cycles of cardiopulmonary resuscitation, spontaneous circulation was restored. Computed tomography revealed the hemoperitonium that was caused by ovarian cyst rupture. Her vital sign and hypovolemic condition were managed in the emergency room. Her mental conditions improved with the recovery of vital signs. However, four hours after intubation, she accidently removed the intubated tube. Shortly after this incident, the patient was transferred to the operating room for emergency laparoscopic exploration. Intubation was reperformed before the surgery in operating room. The surgery lasted one hour. After the surgery,she was transferred to the intensive care unit and her endotracheal tube was maintained due to the possibility of unstable vital signs. Fifteen hours after the surgery, extubation was performed, and she was able to breathe spontaneously without discomfort. After spending two days in the ICU, she recovered well and resumed her daily life.
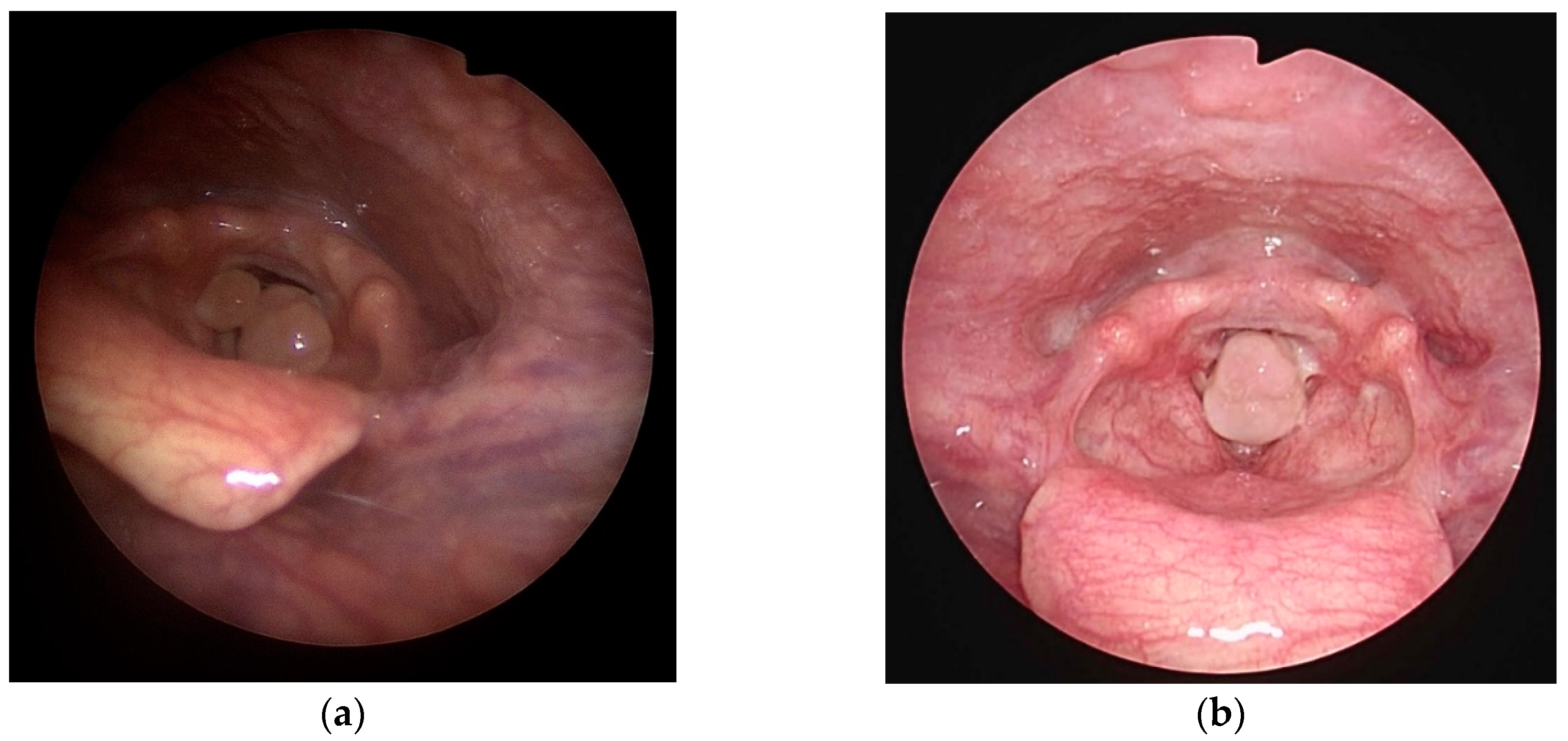
Approximately three months later, she became pregnant. At 11 weeks gestation, she returned to Korea University Guro Hospital’s emergency room with complaints of hoarseness and dyspnea. During medical examination, she mentioned that mild hoarseness had persisted since her last admission, but it worsened three days prior, accompanied by dyspnea and sore throat. She was referred to the otolaryngology department, where an examination of her glottis with indirect laryngoscopy revealed bilateral large vocal process granulomas that almost completely obstructed her glottis. (
Figure 1a) Initially, oral steroid and proton pump inhibitor were prescribed for treatment, despite the teratogenic risks. Her symptoms improved with oral medication. However, upon discontinuation of the medications after one week, her symptoms recurred. Due to the progression in size of granuloma and the burden of continuing steroid treatment, surgical intervention was deemed necessary. (
Figure 1b)
Due to the severe airway obstruction, intubation and ventilation were not deemed feasible. The medical team, including the anesthesiologist and otolaryngologist, discussed potential surgical options in advance. Tracheostomy was considered but deemed excessive for the patient's condition. Jet ventilation was considered as an option, but the healthcare providers in our center did not frequently practice it. Considering the anticipated short duration of the surgical procedure, the anesthetic plan focused on preoxygenation and maintaining adequate oxygen reserves to sustain any potential apneic period. HFNC oxygenation was chosen to ensure sufficient oxygen supply before anesthesia, and ORi monitoring was utilized as a tool to predict oxygen reserve and decreases of oxygen saturation during general anesthesia.
The essential laboratory data, including CBC, electrolytes, and blood coagulation, were within normal range. Due to dyspnea, the patient underwent chest x-ray and pulmonary function test. The chest x-ray showed no abnormalities, but the pulmonary function test revealed an extra-thoracic obstruction pattern, causing difficulty with inhalation. Due to her history of cardiac arrest, she underwent echocardiography. The echocardiography revealed grade 1 impairment of left ventricle diastolic function and normal left ventricle systolic function with an ejection fraction of 60-65%. A pre-anesthetic physical examination was conducted. Her Mallampati grade was 2, and she had unrestricted neck extension with full range of motion. Although she experienced hoarseness and dyspnea, there were no apparent neck or mandible swelling issues that could hinder mask bagging.
In the operating room, standard monitoring was implemented, including pulse oximetry, non-invasive blood pressure, and electrocardiography. Bispectorial index (BISTM, Medtronic, Minneapolis, USA) was used to estimate anesthetic depth, and electromyography (EMG, TwitchView®, Blink, Seattle, USA) was used for evaluate the degree of muscle relaxation. In addition, ORi was continuously monitored using a sensor attached to the patient’s finger through pulse oximetry (Radical-7™, Masimo Corp., Irvine, CA, USA), allowing for ongoing assessment of oxygen reserve. Following the placement of monitoring, pulse oximetry displayed a stable SpO2 of 100% along with consistent vital signs.
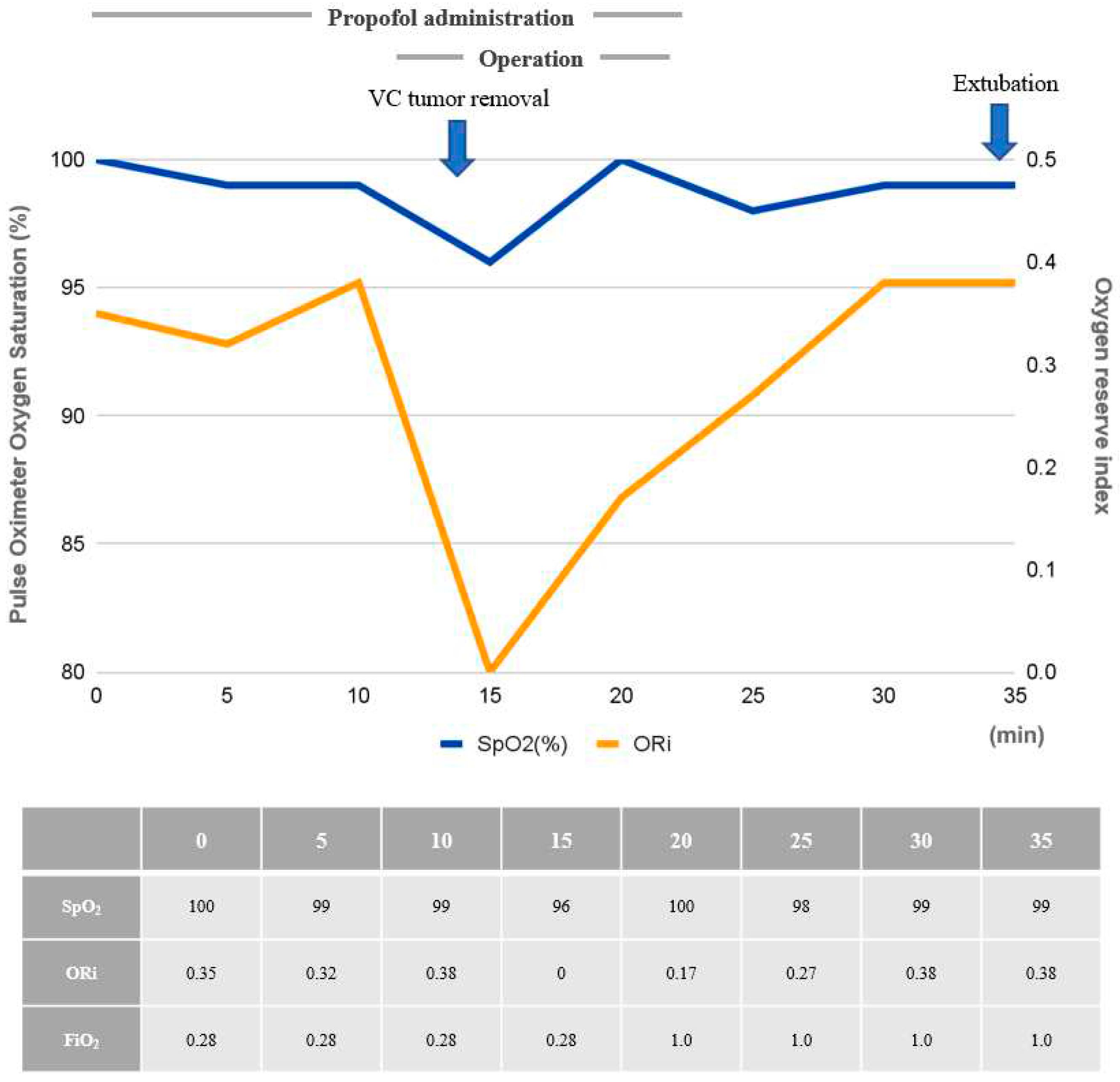
Prior to surgical mass removal, the patient received sufficient oxygen through HFNC oxygenation for five minutesHFNC was then used continuously untilbilateral granuloma excision, at which pointmask bagging became possible. After confirming the patient’s oxygen status through ORi monitoring of 0.35, total intravenous anesthesia with 2% propofol and remifentanil was initiated with the target-controlled infusion of propofol (Ce, 3-4 ng/ml) and remifentanil (Ce, 3-4 ng/kg), targeting the BIS under 60. Loss of consciousness was induced, but mask bagging was impeded by the mass. Twenty mg of rocuronium was immediately administered to facilitate laryngo-microscopic surgery and prevent movement, at which point the ORi was 0.32. After confirming muscle relaxation using train of four count (TOF) monitoring with the count of 0, the operation commenced. During surgery, anesthesia was maintained with a combination of propofol and remifentanil, targeting a BIS value under 60. Larynx was exposed with suspension laryngoscope after the patient lied in Boyce position. The bilateral granuloma was successfully removed with cup-head forcep and scissors. At that moment the ORi decreased to 0, and SpO2 was 96% and the surgical procedure was on hold for a minute. Mask ventilation was performed without difficulty and adequate mask bagging followed by HFNC oxygenation restored an ORi of 0.38 and SpO2 of 99% before completing the surgery. (
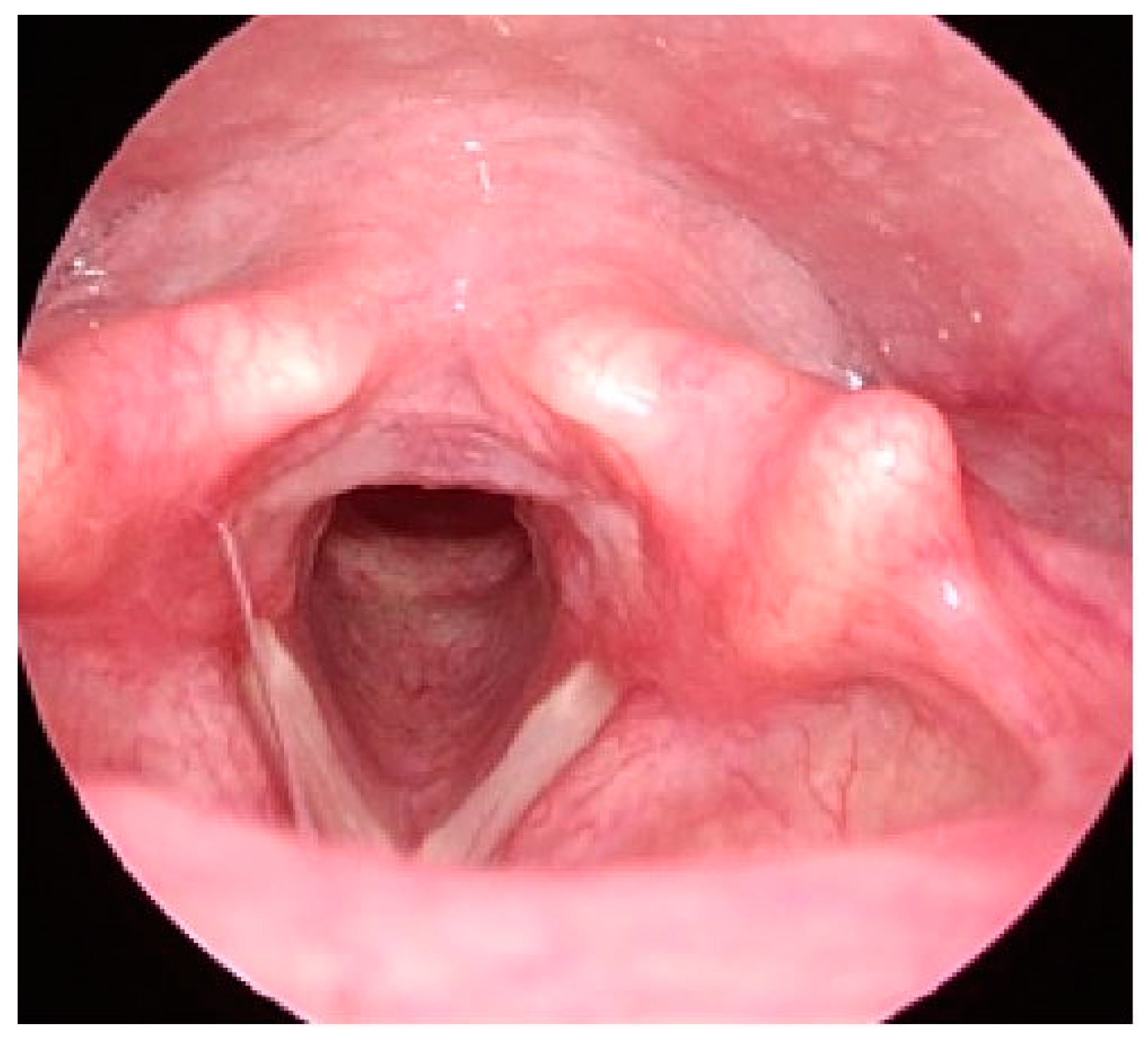
Figure 2) At the end of the procedure, anesthetic agents were discontinued, and the patient regained self-respiration after receiving sugammadex 120 mg. After confirming stable vital signs and spontaneous respiration, she was transferred to the post-anesthetic care unit (PACU). She experienced no complications in the PACU. On post-operative day (POD) 1, her follow-upindirect laryngoscope showed absence of granuloma on the vocal cords. (
Figure 3) Also, she had no symptom of dyspnea. She was discharged on POD 1 since she had no complications after the surgery.
Due to the patient’s increased risk of bleeding resulting from partial placental previa, a condition in which the placenta partially covers the cervix, a decision was made to schedule a cesarean section. This surgical procedure, aimed at ensuring the safety of both the mother and the baby, was scheduled to take place 5 months after the vocal surgery. She underwent an indirect laryngoscope prior to the surgery, revealing clear vocal cords without any granuloma. In addition to the clear findings on the indirect laryngoscope, the patient provided reassurance by reporting the absence of any recurring symptoms that were experienced prior to the development of bilateral granuloma. Specifically, she did not complain of dyspnea, hoarseness, or any discomfort in her throat. These reassuring reports further indicated the positive outcome of the procedure and her overall improved vocal health. To ensure a comprehensive evaluation, an otolaryngologic consultation was conducted to assess the condition of her vocal cords. During the consultation, the clinician carefully examined the patient’s vocal cord movement and observed no abnormal or irregular patterns. This further confirmed the successful outcome of the surgery and provided additional reassurance regarding the patient’s vocal cord health. As a result, it was deemed feasible for her to undergo general anesthesia with endotracheal intubation. Despite undergoing surgery under spinal anesthesia, she experienced no complications, and the neonate showed no signs ofdistress perioperatively.
3. Discussion
Intubation-related trauma can cause vocal process granuloma [
14]. The occurrence rate of intubated granulomas after endotracheal intubation is around 0.1~3.3% [
15]. While most cases resolve spontaneously, some cases require surgical intervention [
16]. In this case, the patient underwent repeated intubations of prolonged duration, potentially leading to vocal process abrasion and granuloma formation. Females have a higher frequency of reported cases due to the relatively larger size of the tube used in comparison to the larynx, and the thinner mucosal layer of the arytenoid vocal cord (59 μm in females compared to 97 μm in males) [
17]. Moreover, physiological changes during pregnancy could affect gastroesophageal reflux due to increased abdominal pressure and congestion of capillaries, and contribute to edema in the respiratory mucosa of various structures, including the nasopharynx, pharynx, larynx, arytenoid, and posterior cricoid cartilage, trachea, etc. In this case, the patient presented with bilateral granuloma occupying a significant portion of the vocal cord, highlighting the invasive nature of endotracheal intubation and the importance of careful attention. Furthermore, to minimize complications associated with endotracheal intubation, it is crucial to select an appropriate tube size to prevent abrasion of the vocal process. Excessive manipulation of the intubated tube can also lead to vocal cord injury, necessitating proper fixation and reduced movement of the tube.
Treatment options for vocal process granulomas include voice therapy, managing gastroesophageal reflux, and various medical interventions, such as surgery, antibiotics, steroids, observation, irradiation, botulinum neurotoxin injection, and membranous vocal fold augmentation [
5]. Surgery is typically reserved for cases involving airway obstruction or suspicion of carcinoma due to the high recurrence rates associated with granulomas. In this case, the patient’s giant granuloma and persistent dyspnea necessitated surgical management, considering the risks to fetal well-being. The case report highlights the successful airway management of the patient despite the challenges posed by the narrowed glottis opening, demonstrating the effective use of appropriate anesthesia techniques to ensure a safe surgical procedure.
In difficult airway cases like this, management options include tracheostomy or jet ventilation, with the choice depending on factors such as anesthesiologist experience, available equipment, urgency, patient co-morbidities, and site of airway obstruction. Tracheostomy is invasive, and jet ventilation has been associated with severe complications in laryngeal microsurgery [
18]. In this case, sufficient preoxygenation with HFNC provided effective oxygenation and reduced the risk of desaturation during airway manipulation. In addition, retaining oxygen reserve with HFNC does not require complex skills from practitioners. Moreover, the use of ORi monitoring facilitated early detection of hypoxemia, enabling prompt intervention to prevent respiratory complications. To our knowledge, there have not been a clinical report of ORi-monitored non-intubated general anesthesia in pregnant patients with airway difficulty.
HFNC is increasingly utilized for patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure, and its applications are expanding to ensure adequate oxygenation. HFNC has been shown to improve safety in procedures involving a risk of apnea, such as intubation or bronchoscopy [
11]. In this particular case, HFNC demonstrated its potential as a more convenient option for managing difficult intubation, as evidenced by ORi monitoring. In other word, ORi monitoring can guide the appropriate approach to difficult intubation. If the ORi decreased rapidly before surgery, we could have concluded that HFNC was not suitable for the patient, and alternative methods to secure the airway would have been considered. However, in this case, the ORi provided sufficient time to safely remove the vocal mass, confirming the appropriateness of using HFNC. Ultimately, the combination of HFNC and ORi monitoring appeared to have a synergistic effect, enhancing their individual benefits. Additionally, ORi demonstrated a strong correlation with the decline in pulse oximeter oxygen saturation (SpO
2). In our case, ORi exhibited a more rapid decrease compared to SpO
2. This indicates that ORi can serve as a useful guide for tracking SpO2 decline, allowing for efficient determination of the need for additional oxygenation.
However, ORi, which measures oxygen levels based on finger wavelength, can be influenced by finger blood flow, temperature, and carbon dioxide content, impacting the interpretation of ORi monitoring [
13]. In situations involving high-dose vasopressors or shock, the accuracy of ORi monitoring decreases. Additionally, it’s important to note that ORi is not equivalent to arterial oxygen content and cannot replace blood gas tests. HFNC also has certain limitations. It cannot be used in patients with facial trauma, and caution should be excercised in cases with a higher risk of aspiration.
Anesthetic management for pregnant patients with bilateral vocal cord granuloma necessitates a customized approach to optimize oxygenation and minimize the potential for airway compromise. The innovative approach in a pregnant patient with bilateral vocal cord granuloma offers valuable insights for patient safety and surgical success. The case report emphasizes the challenges encountered, the selected anesthetic management strategy, and the benefits of using HFNC oxygenation with ORi monitoring in this unique scenario. The combination of high-flow nasal cannula oxygenation and ORi monitoring effectively ensured sufficient oxygenation and enabled early detection of hypoxemia in this case. Further research and more extensive studies are necessary to validate the benefits of this approach in similar cases.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, SKO; methodology, JEL, JC, and SKO; writing—original draft preparation, HSK, SKO; writing—review and editing, HSK, HAL, and SKO; visualization, JEL; supervision, SKO. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was provided by the patient, including the use of photographic images.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Heidemann, B.H. and J.H. McClure, Changes in maternal physiology during pregnancy. BJA CEPD Reviews, 2003. 3(3): p. 65-68. [CrossRef]
- 2. M.Harmer, Diffucult and failed intubation in obstetrics. International Journal of Obstetric Anesthesia, 1997. 6: p. 25-31. [CrossRef]
- LoMauro, A. and A. Aliverti, Respiratory physiology of pregnancy: Physiology masterclass. Breathe (Sheff), 2015. 11(4): p. 297-301. [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.M., A. Afrassiabi, and E.A. Weymuller, Jr., Risk factors associated with prolonged intubation and laryngeal injury. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 1994. 111(4): p. 453-9. [CrossRef]
- de Lima Pontes, P.A., N.G. De Biase, and E.C. Gadelha, Clinical evolution of laryngeal granulomas: treatment and prognosis. Laryngoscope, 1999. 109(2 Pt 1): p. 289-94. [CrossRef]
- Devaney, K.O., A. Rinaldo, and A. Ferlito, Vocal process granuloma of the larynx-recognition, differential diagnosis and treatment. Oral Oncol, 2005. 41(7): p. 666-9. [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.J., et al., Vocal cord granuloma after transoral thyroidectomy using oral endotracheal intubation: two case reports. BMC Anesthesiol, 2021. 21(1): p. 170. [CrossRef]
- Karkos, P.D., et al., Vocal process granulomas: a systematic review of treatment. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 2014. 123(5): p. 314-20. [CrossRef]
- Boran, Ö.F., et al., Anesthetİc Management of a Patİent Wİth Gİant Vocal Process Granuloma. Kahramanmaraş Sütçü İmam Üniversitesi Tıp Fakültesi Dergisi, 2020. 15(3): p. 105-108.
- Benumof, J.L., preoxygenation : best method for both efficacy and efficiency? Anesthesiology, 1999. 91: p. 603-5. [CrossRef]
- Miguel-Montanes, R., et al., Use of high-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy to prevent desaturation during tracheal intubation of intensive care patients with mild-to-moderate hypoxemia. Crit Care Med, 2015. 43(3): p. 574-83. [CrossRef]
- Sztrymf, B., et al., Beneficial effects of humidified high flow nasal oxygen in critical care patients: a prospective pilot study. Intensive Care Med, 2011. 37(11): p. 1780-6. [CrossRef]
- Scheeren, T.W.L., F.J. Belda, and A. Perel, The oxygen reserve index (ORI): a new tool to monitor oxygen therapy. J Clin Monit Comput, 2018. 32(3): p. 379-389. [CrossRef]
- Sadoughi, B., S.M. Rickert, and L. Sulica, Granulomas of the membranous vocal fold after intubation and other airway instrumentation. Laryngoscope, 2019. 129(2): p. 441-447. [CrossRef]
- Balestrieri F, W.C., Intubation granuloma. Otolaryngol Clin Nort Am., 1982. 15: p. 567-79. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R., et al., [Clinical analysis of 46 cases of female laryngeal contact granuloma]. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi, 2020. 34(4): p. 360-363. [CrossRef]
- An KH, K.S., Kim JH, CHU KC, A clinical analysis of intubation granuloma. Korean J Otolaryngol, 1988. 29: p. 213-217.
- Leemann, B., et al., A severe complication after laser-induced damage to a transtracheal catheter during endoscopic laryngeal microsurgery. Anesth Analg, 2004. 98(6): p. 1807-1808. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).