1. Introduction
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of endogenous small noncoding RNAs (sncRNAs) that are found in most eukaryotes and have been linked to almost every aspect of physiological processes. Approximately 60% of human protein-coding genes are regulated by miRNAs [
1], and the dysregulation of miRNAs is a hallmark of various human diseases including cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, diabetes, and immune disorders [
2,
3]. MiRNAs bind to the 3’-untranslated regions (3'-UTR) of target mRNA molecules, which leads to the repression of gene transcription in most cases but can also lead to activation in some rare instances [
4]. As a result, miRNAs play a pivotal role in the regulation of cellular processes such as cell communication, proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis [
5]. Because a single miRNA molecule can regulate hundreds to thousands of genes, miRNAs are promising new biomarkers for disease diagnosis or prognosis and provide options for medical intervention against diverse pathogenic conditions [
6]. Since their discovery in 1993 [
7], 38,589 human miRNA entries have been recorded in miRbase (v22.1), including 1,881 pre-miRNAs and 2,588 mature miRNAs [
8].
MiRNAs exist in the genome in intergenic regions with their own promoters, as well as in introns or exons of host protein-coding genes. The expression of isomiRs is regulated dynamically and displays tissue-specific patterns [
9]. During miRNA maturation, various enzymes, including the ribonucleases Drosha and Dicer, can produce variations in the mature miRNA sequence, which are known as isomiRs. Initially considered as sequencing artifacts [
10], isomiRs are now known to be produced by shifts in the cleavage sites at the 3’- or 5’-terminus, nucleotide substitutions along the entire molecule, or nucleotide additions at either end that deviate from the reference sequence. In addition, isomiRs derived from the same precursor can possess different seed sequences (2 to 7 bases at the 5’-end), which enables them to target different mRNAs, and potentially interact with the canonical miRNA in a cooperative or competitive manner [
11,
12], thereby expanding their scope of post-transcriptional regulation.
Explanations for isomiR heterogeneity are based on the structure of miRNA precursors [
13], precursor processing [
14], and the AGO2 protein [
15]. In addition, studies on genetic variants, especially those in the promoter of precursor transcripts have identified miRNA expression quantitative trait loci (miR-QTLs) that regulate canonical miRNA expression [
16,
17,
18,
19]. However, the mechanism underlying the biogenesis of isomiRs is still largely unknown. In this study, we hypothesize that a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in the pre-miRNA sequence may affect the cleavage behaviors of enzymes such as Drosha and Dicer, leading to variations in the composition of isomiRs. By investigating the relationship between genetic variants and the prevalence of 5’-end isomiRs, we aim to explain the isomiR variation through genetic regulation and uncover the impacts of cis-acting genetic variants on 5’-end isomiR variation. These genetic associations may shed light on the mechanisms underlying isomiR biogenesis and provide new clues for developing targeted therapy by introducing genetic variants to modify in vivo isomiR composition.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets
The small RNA sequencing (sRNA-seq) data and metadata for 452 unrelated human lymphoblastoid cell lines were obtained from the Geuvadis project, and downloaded from ArrayExpress in fastq format (
https://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress/). The phase 3 genetic variants data (release 20130502, GRCh38) for 1000 Genomes samples were downloaded from the EBI FTP website (ftp://ftp.1000genomes.ebi.ac.uk/). The reference sequences for precursor and mature miRNAs were downloaded from miRBase (version 22, GRCh38) and filtered to include only human sequences. The mature miRNAs in miRBase ranged from 16 to 28 bases in length. The human whole genome reference sequence (GRCh38) was downloaded from the UCSC table browser (
https://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgTables). TCGA miRNA-seq and clinical data were obtained from the GDC Data Portal (
https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/, version 27.0).
2.2. sRNA-seq data preprocessing and isomiR identification
The small RNAseq reads were trimmed for 3’-adaptor sequences (TGGAATTCTCGGGTGCCAAGGAACTC) using cutadapt (version 1.9.1). Reads shorter than 16 nucleotides (the minimum length of mature miRNA) after trimming were excluded from further analysis. To identify isomiRs from the next-generation sequencing data, we employed the isomiRID software, which has demonstrated high sensitivity and specificity in a previous study [
39]. The isomiRID pipeline (version 0.53) [
40] follows a multi-step approach to identify isomiRs. In the first step (round 0), reads perfectly matched to the precursor sequences were mapped. Unmapped reads were then filtered using the whole genome reference to exclude reads from other genomic regions. In the second step (round 1), the remaining unmapped reads were then aligned to pre-miRNAs with one base mismatch to identify one-base substitution isomiRs. Reads with more than one-base substitution were not considered in our study. sRNA-seq reads not mapped were further subjected to up to 5 rounds of trimming where a single base on either the 5’ or 3’ end was removed at each round. The trimmed reads were mapped to the pre-miRNA reference to identify non-templated additions. Alignment was performed using Bowtie v1 with the parameters --norc -a -v [0|1] --best --strata. Only mapped reads of 16 to 28 nucleotides in length were retained for analysis. The output of isomiRID was a tab-delimited text file containing the small RNA-seq reads aligned with the reference pre-miRNA hairpin sequences [
40]. The isomiRs identified by isomiRID were further filtered to only keep sequence reads detected in at least 10 subjects.
2.3. IsomiR classification
IsomiR classification was conducted using our homemade Python program to compare the aligned sequences to mature miRNAs from miRbase, which were also aligned to their precursor. The classification was based on variations at the 5’- and 3’-ends, and assigned to categories such as canonical, substitution, trimming, templated extension, non-templated addition, or new isomiR categories. The canonical subtype had the same sequence as the mature miRNA. New isomiRs were defined as reads with less than 10 bases overlapping with canonical miRNAs. Trimming isomiRs had a shorter sequence, while extension isomiRs had longer sequences compared to canonical miRNAs. Both subtypes aligned perfectly with the reference pre-miRNA hairpin. In contrast, addition isomiRs differed from the reference precursor sequences at either or both termini.
In the case of nucleotide substitutions, the default mapping behavior of isomiRID was adopted and only one-base substitution in the sequence was considered. The substitutions at the seed regions (positions 2-7 of a miRNA [
41]) are crucial for mRNA target recognition and were classified as 5’-seed-substitution (5sSub isomiRs). Substitutions at the 5’ or 3’ termini were classified as single-base substitution (5Sub or 3Sub isomiRs) or multiple-base substitution (5mSub or 3mSub isomiRs). The frequency of isomiR subtypes identified for each pre-miRNA, and isomiR subtypes across all pre-miRNAs were assessed and illustrated.
2.4. Allele-specific alignment
The genomic coordinates for human miRNAs were obtained from miRBase (GRCh38). The genetic variants data from the 1000 Genomes project were filtered to retain variants mapping to the precursor miRNA using VCFtools (version 0.1.13). Quality control was performed to keep subjects having sRNA-seq data, and common variants with MAF greater than 1% among the study subjects.
By default, isomiRID uses the precursor sequences from miRBase as references and variations at the DNA level are not considered. This introduces biased alignments towards reference sequences and reads carrying alternative alleles were either mapped as single-base substitution or unmapped if they harbored more variants in the sequence. Possible solutions for the allele-specific alignment issues are, 1) allowing multiple mismatches in alignment; 2) masking the SNP positions with ambiguous letters; and 3) personalized references alignment. Incorporating multiple mismatches reduces the precision of the short reads mapping. SNP-masking in the reference sequence reduced the reference allele bias but created bias toward one of the aligned alleles [
42]. In our study, a personalized reference alignment method was used where sequences incorporating SNP alleles were generated as reference sequences. sRNA-seq reads were aligned to both miRBase precursor sequences and sequences with alternative alleles. Reads mapped to these customized references were merged to reads mapped to canonical references, in which reads mapped in an earlier round of isomiRID were kept. For example, if a canonical isomiR with an alternative allele aligned to the miRBase reference in round one as a 1-base mismatch, but it mapped to the customized reference as perfect match at round zero, then only the perfectly matched alignment from round 0 was kept. In this study, only SNPs used in genetic association studies were considered in the mapping.
2.5. Genetic association
Genetic associations were conducted between the cis-acting SNPs and the ratio of 5’-end isomiR variants (substitution, trimming, extension, and non-template adding) against all isomiRs identified for that specific mature miRNA. The analysis focused on isomiRs with a 5’-terminus within ± 8 bases relative to canonical miRNAs. Reads with the same length at the 5’-terminus as mature miRNA without substitution were considered as 5’-end canonical isomiRs. 5’-end substitution included reads with single or multi-base substitutions in the seed region. 5’-end trimming, extension, and addition were limited to modifications of a maximum 8 bases at the 5’-end and were further classified according to the number of base modifications. The observed counts were transformed by adding 0.5 to calculate the ratio. A non-parametric Kendal rank correlation [
43] was fitted using an additive genetic model where samples with none, one, or two rare alleles were coded as 0, 1, and 2. We conducted a principal component analysis (PCA) to detect and control for population stratification. The scatterplot of the first two principal components was used to illustrate the population stratification of the study subjects. The subjects included in the correlation analysis were from two populations, European Ancestry (CEU, FIN, GRB, TSI) and African Ancestry (YRI). To control for the population stratification, we conducted stratified Kendal rank correlation analyses with subjects from either the European or African population and required that the correlation be significant in overall correlation analysis and in correlation within either the European or African population. The Benjamini-Hochberg procedure [
44] was used to correct for multiple comparisons for 839 correlations across different subtypes of isomiRs, and the corrected p-value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
To study the association between isomiR expression and tumor susceptibility, differential analysis of isomiRs between TCGA tumor and normal samples was conducted with isomiR expression data from the GDC Data Portal. The normalized reads (reads per million miRNA mapped) for isomiRs with the same 5’-end variations were added together, and a Student's t-test was used to assess the differences between tumor and normal samples. The statistical analyses and data visualization were conducted in statistical environment R (v3.6.1). P value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
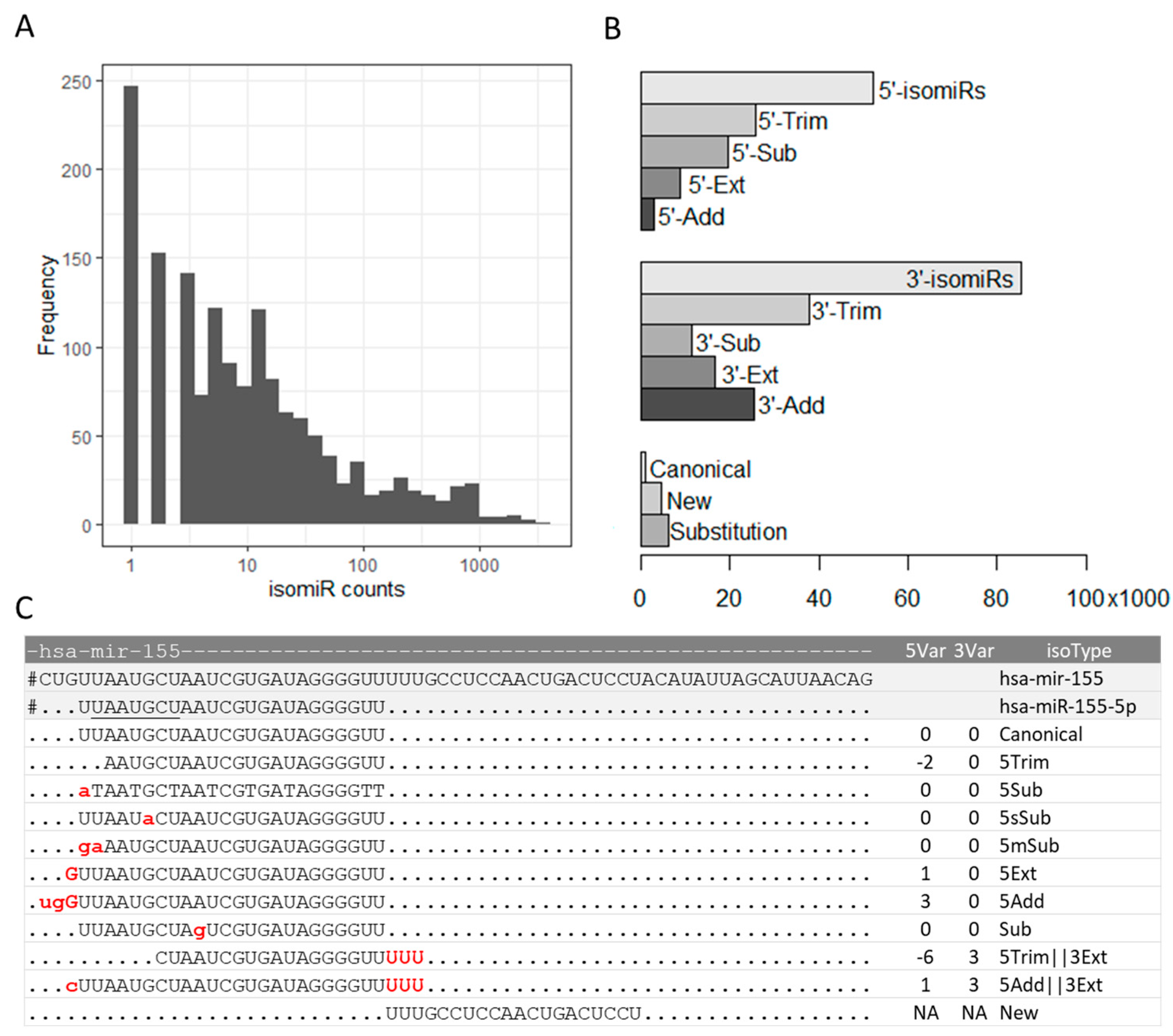
Our study aimed to investigate the genetic regulation of isomiRs, a type of variation in mature miRNA sequences, by characterizing their expression profiles in human lymphoblastoid cell lines. Published small RNA sequencing (sRNA-seq) data was gathered from 452 individuals and 652,778 isomiRs were mapped to 1,917 human precursor miRNA sequences. Quality filtering was applied to keep reads detected in at least 10 samples, resulting in 109,289 isomiRs mapping to 1,546 pre-mRNAs. The most abundant isomiR subtypes were found in hsa-mir-155 (3,501 isomiRs,
Figure 1A), which is consistent with the high levels of miR-155 expression in various human tissues and cell types and its multifunctional physiological roles [
20]. IsomiRs were classified according to variations at the 3-’ or 5’-ends compared to a nearby mature miRNA (e.g., 5p or 3p miRNA). Consistent with previous reports [
21,
22], we found that the variability in isomiR sequences occurred more frequently at the 3’-end, with 78% of isomiRs carrying variations at the 3’-end, 48% at the 5’-end, and more than one-third of isomiRs had variations at both ends (
Figure 1B). Because sequencing library adaptor trimming during data preprocessing may affect variant calling at the 3’-end, we focused our study on 5’-end alterations, with base trimming being the most prevalent isomiR subtype (
Figure 1B). Examples of 5’-end isomiR subtypes for hsa-miR-155 are shown in
Figure 1C.
3.1. 5’-end base nucleotide substitution and stability
MiRNAs possess distinct half-lives in human cells, and miRNA stability is important for the dynamic regulation of cellular miRNA activity. Some of the factors that influence miRNA homeostasis include sequence modification, AGO protein complex formation, and mRNA target interaction [
23,
24]. Furthermore, the nucleotide at the 5’-end was reported to influence mature miRNA stability, whereby miRNAs with a uracil (U) at the 5’-end, compared to guanine (G) or adenine (A), generally had significantly longer half-lives [
25]. Therefore, we compared the frequency of the 5’-end bases between canonical and 5’-substitution isomiRs. Among 1,150 canonical miRNAs used for isomiR classifications, 42% contained a U at the 5’-end. In contrast, only 12.45% of substitution isomiRs had a U on the 5’-end. The most common end base in 5’-substitution isomiRs was G (39.21%), followed by A (24.90%) and cytosine (C) (23.44%). These results suggest that, in comparison to canonical miRNAs, 5’-end base substitution isomiRs are predicted to have shorter half-lives.
3.2. Canonical subtypes may not be the most abundant isomiRs
A previous study reported that a one-base shift isomiR of miR-140-3p (i.e., 1-base 5’-trim plus a 3’-extension) was expressed at higher levels compared to its canonical counterpart in breast cancer progression [
26]. We asked whether the human lymphoblastoid cell lines used in this study exhibited the same characteristic. To address this question, we compared read counts of the shifted isomiRs to the standard miR-140-3p miRNA, and discovered that the shifted isomiRs were more prevalent in 99% of the cells (448 out of 452). In addition, it is worth noting that canonical miRNAs annotated by miRBase were also not the predominant isomiRs for some of the miRNAs under investigation. We compared the total reads across 452 subjects for a canonical miRNA and its isoforms in the 1000 Genomes sRNA-seq dataset for miRNAs with at least 5 subjects having 20 or more sequence reads. Non-canonical isomiRs were more abundant in 52% of the miRNAs. However, after considering the impact of 3’-adaptor trimming by grouping isomiRs based on sequence variations at the 5’-end, we observed that the frequency of miRNAs in non-canonical isomiR categories was 11% of the total miRNAs. These findings imply that at least some non-canonical isomiRs might have important roles in miRNA regulation.
3.3. Genetic associations
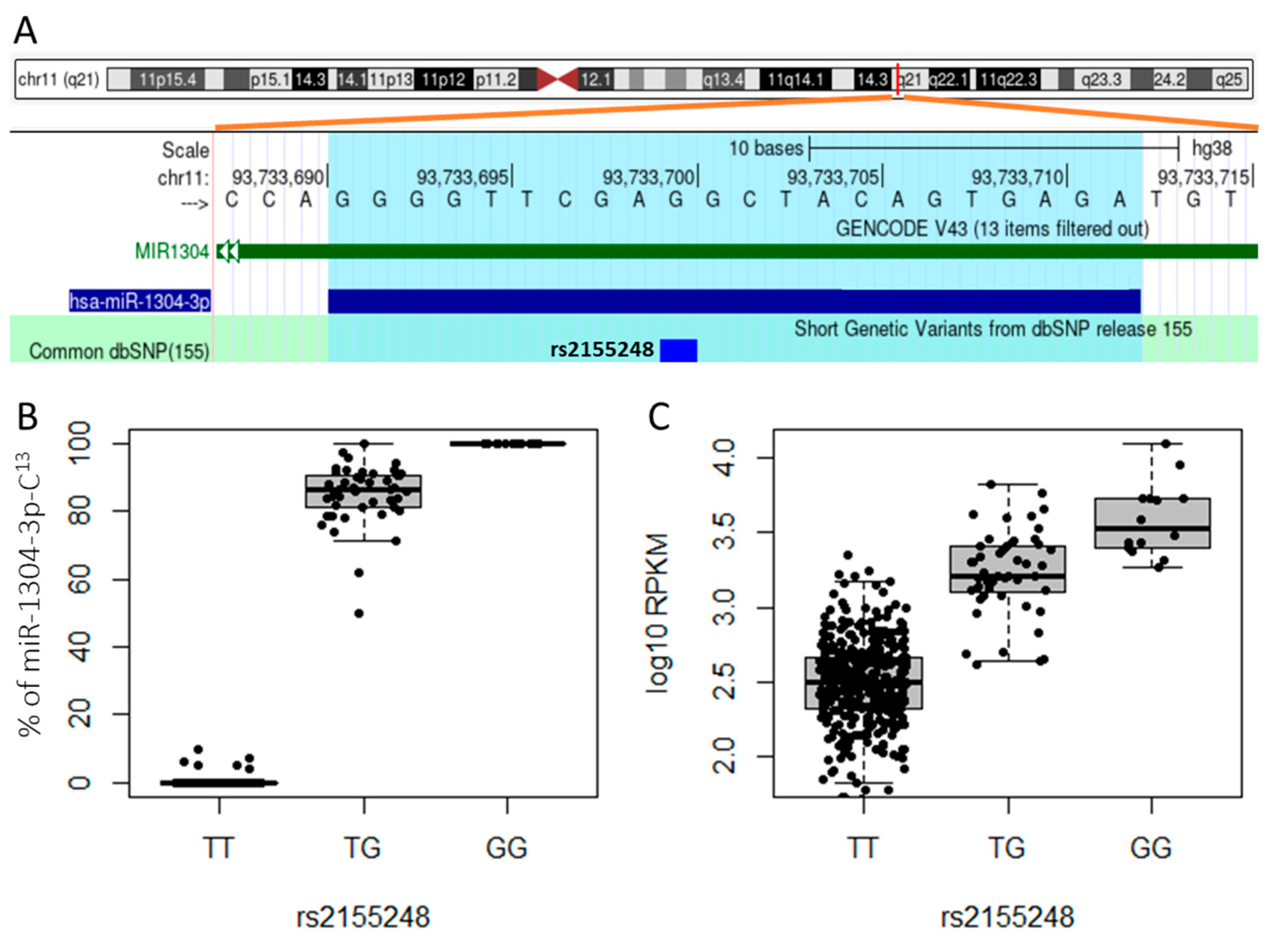
Next, we asked whether cis-acting genetic variants impacted the frequency of isomiR subtypes. To address this question, we queried genotype data from the 1000 Genomes Project for SNPs located in DNA regions encoding precursor miRNA transcripts. We identified 4,478 variants, from which we selected 481 bi-allelic SNPs with a minor allele frequency (MAF) greater than 1% in 435 individuals with both genotype and sRNA-seq data. We then used customized sequences with reference and alternative alleles for those SNPs to identify isomiRs transcribed from either allele. Our personalized references method also revealed allele-specific expression of miRNAs. As an example, the DNA sequence of hsa-miR-1304-3p has a SNP (rs2155248, T/G) at the 13th base (
Figure 2A). Despite the T allele being the major allele among 435 individuals, we observed a higher number of miRNA reads with a C at the 13th nucleotide that were transcribed on the reverse strand of the G allele. This intriguing finding can be explained by the fact that cells heterozygous for rs2155248 (T/G) predominantly expressed the C allele isomiRs, while cells homozygous for T/T transcribed hsa-miR-1304-3p at very low levels (
Figure 2B,C). In addition, allele-specific expression of miRNAs was commonly observed in the human lymphoblastoid cell lines where miRNAs containing alleles different from those annotated in miRBase were transcribed at lower levels compared to canonical miRNAs.
To investigate the genetic association of isomiR variants, we initially utilized the data from all study populations, and conducted 839 associations between SNPs and different 5’-isomiRs. To account for population stratification, we conducted separate association studies with subjects from European or African ancestry populations (supplemental
Figure 1). We set a criterion that the findings from all populations should be significant in either the European or African population study. Ultimately, we identified a total of 7, 51, 28, and 9 SNP-isomiR pairs that exhibited significance for 5’-substitution, -trimming, -extension, or -addition, respectively, using a threshold of false discovery rate (FDR) < 0.05 (Supplementary
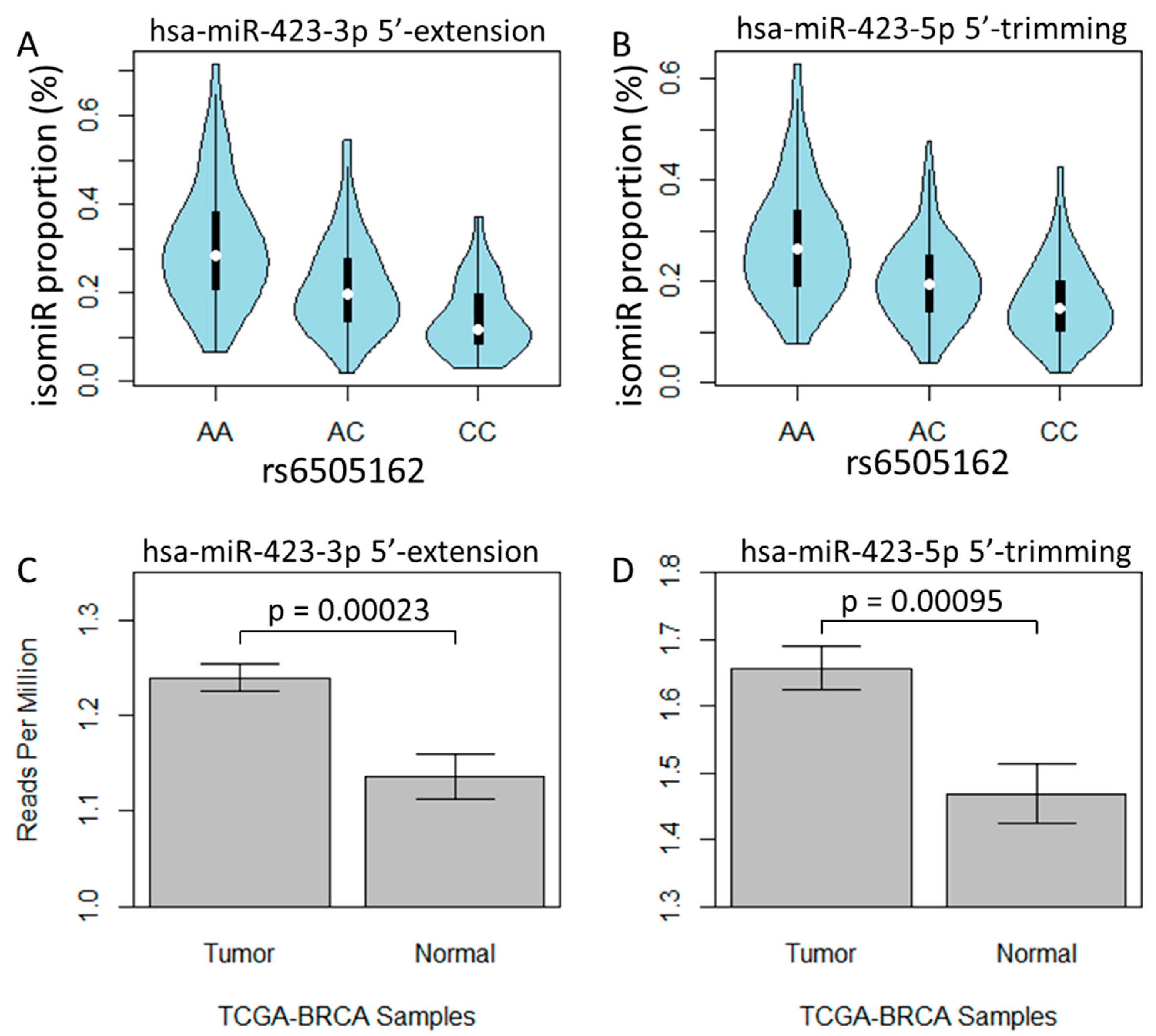
Table 1). We found rs6505162 (A/C) was associated with a two-base 5’-extension isomiR of hsa-miR-423-3p (FDR = 3.0 x 10
-21) and a two-base 5’-trimming isomiR of hsa-miR-423-5p (FDR = 2.4 x 10
-17), where the C allele was linked to a decrease in the expression of both isomiRs (
Table 1 and
Figure 3A,B). Interestingly, rs6505162 has been reported to have a high frequency of somatic mutation in breast cancer cell lines and tumor tissues [
27], and miR-423 activities were increased in breast cancer cells [
28]. To investigate the association between the hsa-miR-423 isomiRs and breast cancer pathology, we compared expression of these isomiRs between tumor and normal samples in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) breast cancer (BRCA) dataset. We found that expression of the two-base 5’-extension isomiR of hsa-miR-423-3p was significantly higher in tumor compared to normal tissue (p = 0.00023,
Figure 3C). This finding is consistent with a prior study that reported that miR-423-3p, as compared to miR-423-5p, promoted cell proliferation and tumorigenesis in breast cancer [
27]; although, we also observed higher expression of the 5’-trimming isomiR of hsa-miR-423-5p in the tumor (p = 0.00095,
Figure 3D). To investigate whether the hsa-miR-423-3p two-base 5’-extension isomiR was associated with other cancers, we repeated our analysis using the TCGA kidney renal clear cell carcinoma (TCGA-KIRC) dataset. We observed a similar finding that this isomiR was expressed at higher levels in tumors compared to normal tissues (p=0.00096, supplemental
Figure 2A), while a trend of high expression in tumors was also observed for hsa-miR-423-5p 5’-trimming isomiRs (p=0.064, supplemental
Figure 2B).
4. Discussion
The discovery of miRNA and other small non-coding RNAs has expanded our vision of the gene regulation network remarkably. The potential to regulate hundreds of genes by one miRNA provides the control of multiple pathways at once. In fact, increasing evidence supports the notion that miRNAs play critical roles in diverse aspects of biological processes, and dysfunction or aberrant expression of miRNAs and their isoforms may trigger disease pathogenesis. A SNP located in a precursor or mature miRNA may influence the biogenesis, maturation, expression, or target recognitions of that miRNA by altering the secondary structure of the miRNA hairpin and subsequent enzyme cleavage or transcript editing of its isomiRs. In this way, miR-SNPs may play important roles in signaling pathways that are essential to cellular homeostasis and contribute to disease progression. In this study, we investigated isomiR expression profiles and the cis-regulation of isomiR biogenesis in human lymphoblastoid cell lines. We found that numerous SNPs were significantly associated with the frequency of 5’-end isomiRs including base substitution, trimming, extension, and addition. Empirical evidence was observed to support the premise that genetic variants contribute to the composition of 5’-end isomiRs by altering the sequence of precursor miRNA. Our study reported 95 significant associations between miR-SNPs and the composition of 5’-isomiRs at an FDR less than 0.05 across 435 available subjects, and in a subset of either European or African populations.
The SNP rs6505162 is located in the transcribed region of precursor hsa-mir-423, but outside of the mature miRNAs. The pathologic risk of the rs6505162 polymorphism has been evaluated in a wide range of cancers and diseases including esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, ovarian cancer, colorectal cancer, non-small cell lung cancer and others [
28,
29,
30,
31]. In breast cancer, studies reporting the association between rs6505162 and cancer risk have come to contradictory conclusions. Smith et. al. showed that the CC genotype was linked to a reduced risk of breast cancer in Caucasian women (Odds Ratio, OR = 0.50; p = 0.03) [
32], and the A allele was reported as a risk factor in the pathogenesis of breast cancer among the Egyptian population (OR = 3.28, p= 0.002; OR = 2.11, p= 0.011, for AA and CA against CC patients respectively) [
33]. In contrast, the CC genotype of rs6506162 was reported to be associated with an increased risk of breast cancer in Iranian women (OR = 2.37; p = 0.0023) [
34]. While this miR-SNP was not predicted to affect the hsa-mir-423 precursor RNA secondary structure [
27,
28], it is possible that it could influence the processing efficiency and maturation of the miRNA, and thereby affect breast cancer susceptibility. However, it is largely unknown how hsa-mir-423 isomiRs are involved in the genetic association of rs6505162 with breast cancer. In our study, we found that rs6505162 was significantly associated with hsa-miR-423-3p and hsa-miR-423-5p isomiR compositions and that the C allele was associated with lower expression of these isomiRs. The corresponding isomiRs were found to be highly expressed in tumor compared to normal samples in TCGA-BRCA and -KIRC datasets, which infers that the C allele may have a protective effect in tumorigenesis. This conclusion is consistent with the fact that cells with a C allele expressing the pre-miR-423 had a lower proliferation efficacy than cells with the A allele [
27]. Zhao et al also reported that although rs6505162 regulated both -3p and -5p miRNAs, miR-423-3p was the only molecule promoting breast cell proliferation [
27]. Because this SNP is located outside of the mature miRNA, it would not be expected to affect miR-423 binding with its targets, but rather could affect the expression of miR-423-3p isomiRs. Additionally, the 5’-extension isomiRs could potentially be involved in regulating the canonical hsa-miR-423-3p’s target recognition, degradation, or binding to new targets implicated in breast cancer pathogenesis.
In addition, multiple complex disease-associated SNPs from previous reports were found associated with isomiR compositions in the human lymphoblastoid cell lines [
35,
36,
37,
38]. Rs2273626 is located in the seed region of miR-4707 and is associated with primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) independently of the canonical miRNA expression levels [
36]. This SNP was significantly positively associated with the composition of a 5’-extension isomiR of miR-4707-3p, which could play a role in regulating the biological function of the canonical miRNA. Rs2168518, which is associated with blood pressure, triglycerides, total cholesterol, fasting glucose levels, and risk of diabetes mellitus [
35], was found associated with 5’-addition isomiRs of hsa-miR-4513 in our study.
One limitation of our study is that by using the default alignment settings for isomiRID and only considering one-base substitutions in the sequence, not all possible isomiR variations have been captured. Another limitation is that the trimming of the 3’-adaptor from the sRNA-seq reads made it difficult to accurately estimate the variations in 3’-isomiRs. Additionally, the associations between SNPs and isomiR compositions identified in our study are not yet supported by experimental validation, and the relationship between 5’-end base substitution isomiRs and miRNA half-lives requires further investigation in a large dataset. Despite these limitations, this study provides new insights into the genetic regulation of isomiR biogenesis in human cells and has potential implications for regulating miRNA expression and for generating new targeted therapies.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this study investigated the cis-regulation of isomiR biogenesis in human lymphoblastoid cell lines and found significant associations between SNPs and 5'-isomiRs. Our findings, particularly the identified association between rs6505162 and isomiR alterations of hsa-miR-423-3p and hsa-miR-423-5p, shed light on the genetic aspects of breast cancer tumorigenesis. Additionally, our study revealed the prevalence of non-canonical miRNAs and allele-specific expression of miRNAs, highlighting their roles in biological processes and the influence of genetic variants on miRNA regulation. These insights contribute to our understanding of the intricate mechanisms governing isomiR biogenesis and its implications in disease.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, Y.L., Y.W. and G.J.; writing—original draft preparation, G.J and Y.L; formal analysis, visualization, G.J.; resource, data curation, C.D., F.F. and Z.J.; writing—review and editing, G.J., J.L.R., Y.L., Y.W., Z.J., F.F.; supervision, Y.L. and J.L.R.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data analyzed in this study were a re-analysis of existing data, which are openly available at locations cited in the reference section.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.-H.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardekani, A.M.; Naeini, M.M. The Role of MicroRNAs in Human Diseases. Avicenna J. Med Biotechnol. 2010, 2, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Kowdley, K.V. MicroRNAs in Common Human Diseases. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2012, 10, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dweep, H.; et al. miRWalk--database: prediction of possible miRNA binding sites by "walking" the genes of three genomes. J Biomed Inform 2011, 44, 839–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.W.; Mendell, J.T. MicroRNAs in cell proliferation, cell death, and tumorigenesis. Br J Cancer 2006, 94, 776–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, J.; Hossain, G.S.; Kocerha, J. The Potential for microRNA Therapeutics and Clinical Research. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambros, V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telonis, A.G.; Magee, R.; Loher, P.; Chervoneva, I.; Londin, E.; Rigoutsos, I. Knowledge about the presence or absence of miRNA isoforms (isomiRs) can successfully discriminate amongst 32 TCGA cancer types. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 2973–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.W.; Zhang, S.; Etheridge, A.; Ma, L.; Martin, D.; Galas, D.; Wang, K. Complexity of the microRNA repertoire revealed by next-generation sequencing. RNA 2010, 16, 2170–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desvignes, T.; Batzel, P.; Berezikov, E.; Eilbeck, K.; Eppig, J.T.; McAndrews, M.S.; Singer, A.; Postlethwait, J.H. miRNA Nomenclature: A View Incorporating Genetic Origins, Biosynthetic Pathways, and Sequence Variants. Trends Genet. 2015, 31, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Kwast, R.; et al. , MicroRNA-411 and Its 5'-IsomiR Have Distinct Targets and Functions and Are Differentially Regulated in the Vasculature under Ischemia. Mol Ther 2020, 28, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starega-Roslan, J.; Krol, J.; Koscianska, E.; Kozlowski, P.; Szlachcic, W.J.; Sobczak, K.; Krzyzosiak, W.J. Structural basis of microRNA length variety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 39, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphreys, D.T.; Hynes, C.J.; Patel, H.R.; Wei, G.H.; Cannon, L.; Fatkin, D.; Suter, C.M.; Clancy, J.L.; Preiss, T. Complexity of Murine Cardiomyocyte miRNA Biogenesis, Sequence Variant Expression and Function. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juvvuna, P.K. Argonaute identity defines the length of mature mammalian microRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res, 2012; 40, 6808–6820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borel, C.; Deutsch, S.; Letourneau, A.; Migliavacca, E.; Montgomery, S.B.; Dimas, A.S.; Vejnar, C.E.; Attar, H.; Gagnebin, M.; Gehrig, C.; et al. Identification of cis- and trans-regulatory variation modulating microRNA expression levels in human fibroblasts. Genome Res. 2010, 21, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappalainen, T.; Sammeth, M.; Friedländer, M.R.; ‘t Hoen, P.A.C.; Monlong, J.; Rivas, M.A.; Gonzàlez-Porta, M.; Kurbatova, N.; Griebel, T.; Ferreira, P.G.; et al. Transcriptome and genome sequencing uncovers functional variation in humans. Nature 2013, 501, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budach, S.; Heinig, M.; Marsico, A. Principles of microRNA Regulation Revealed Through Modeling microRNA Expression Quantitative Trait Loci. Genetics 2016, 203, 1629–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, T.; Rong, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X.; Tanriverdi, K.; Joehanes, R.; Chen, B.H.; Murabito, J.M.; Yao, C.; Courchesne, P.; et al. Genome-wide identification of microRNA expression quantitative trait loci. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraoni, I.; Antonetti, F.R.; Cardone, J.; Bonmassar, E. miR-155 gene: A typical multifunctional microRNA. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Mol. Basis Dis. 2009, 1792, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldemariam, N.T.; Agafonov, O.; Høyheim, B.; Houston, R.D.; Taggart, J.B.; Andreassen, R. Expanding the miRNA Repertoire in Atlantic Salmon; Discovery of IsomiRs and miRNAs Highly Expressed in Different Tissues and Developmental Stages. Cells 2019, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neilsen, C.T.; Goodall, G.J.; Bracken, C.P. IsomiRs – the overlooked repertoire in the dynamic microRNAome. Trends Genet. 2012, 28, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kai, Z.S.; E Pasquinelli, A. MicroRNA assassins: factors that regulate the disappearance of miRNAs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Mei, J.; Ren, G. Plant microRNAs: Biogenesis, Homeostasis, and Degradation. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; et al. , Importance of miRNA stability and alternative primary miRNA isoforms in gene regulation during Drosophila development. Elife 2018, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Singh, H.; Trinidad, C.M.; Albarracin, C.T.; Hunt, K.K.; Bedrosian, I. The isomiR-140-3p-regulated mevalonic acid pathway as a potential target for prevention of triple negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2018, 20, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Gao, A.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, R.; Luo, A.; Li, M.; Zhao, D.; Fu, L.; Fu, L.; Dong, J.-T.; et al. Genetic analysis and preliminary function study of miR-423 in breast cancer. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 4763–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontorovich, T.; Levy, A.; Korostishevsky, M.; Nir, U.; Friedman, E. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in miRNA binding sites and miRNA genes as breast/ovarian cancer risk modifiers in Jewish high-risk women. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; et al. Genetic variations in microRNA-related genes are novel susceptibility loci for esophageal cancer risk. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2008, 1, 460–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; et al. Genetic polymorphisms in pre-microRNA genes as prognostic markers of colorectal cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2012, 21, 217–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Chen, J.; Tian, T.; Zhou, X.; Gu, H.; Xu, L.; Zeng, Y.; Miao, R.; Jin, G.; Ma, H.; et al. Genetic variants of miRNA sequences and non–small cell lung cancer survival. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 2600–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Smith, R.; Jedlinski, M.J.; Gabrovska, P.N.; Weinstein, S.R.; Haupt, L.M.; Griffiths, L.R. A genetic variant located in miR-423 is associated with reduced breast cancer risk. Cancer Genom. - Proteom. 2012, 9. [Google Scholar]
- El-Ashry, A.H.; Albeltagy, A.M.G.; Ramez, A.M.; Hendawy, S.R. Influence of Micro-RNA-423 Gene Variation on Risk and Characteristics of Breast Cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2022, 23, 3771–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourmoshir, N., G. H. Motalleb, and S. Vallian, hsa-miR-423 rs6505162 Is Associated with The Increased Risk of Breast Cancer in Isfahan Central Province of Iran. Cell J 2020, 22 (Suppl 1), 110–116. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; et al. Influence of microRNA-related polymorphisms on clinical outcomes in coronary artery disease. Am J Transl Res 2015, 7, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ghanbari, M.; et al. A Genome-Wide Scan for MicroRNA-Related Genetic Variants Associated With Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2017, 58, 5368–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Du, M.; Chen, W.; Zhu, L.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M.; Chu, H.; Gu, D.; Chen, J. Polymorphism rs2682818 in miR-618 is associated with colorectal cancer susceptibility in a Han Chinese population. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 1194–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; et al. . Polymorphisms in MicroRNAs are associated with survival in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2014, 23, 2503–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsel, D.; Vilcinskas, A.; Billion, A. Evaluation of high-throughput isomiR identification tools: illuminating the early isomiRome of Tribolium castaneum. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, L.F.V.; Christoff, A.P.; Margis, R. isomiRID: a framework to identify microRNA isoforms. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2521–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, B.P.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Conserved Seed Pairing, Often Flanked by Adenosines, Indicates that Thousands of Human Genes are MicroRNA Targets. Cell 2005, 120, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degner, J.F.; Marioni, J.C.; Pai, A.A.; Pickrell, J.K.; Nkadori, E.; Gilad, Y.; Pritchard, J.K. Effect of read-mapping biases on detecting allele-specific expression from RNA-sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 3207–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendall, M.G. A new measure of rank correlation. Biometrika 1938, 30, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).