Submitted:
14 July 2023
Posted:
17 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. General, and epidemiological profiles
1.2. Pathology
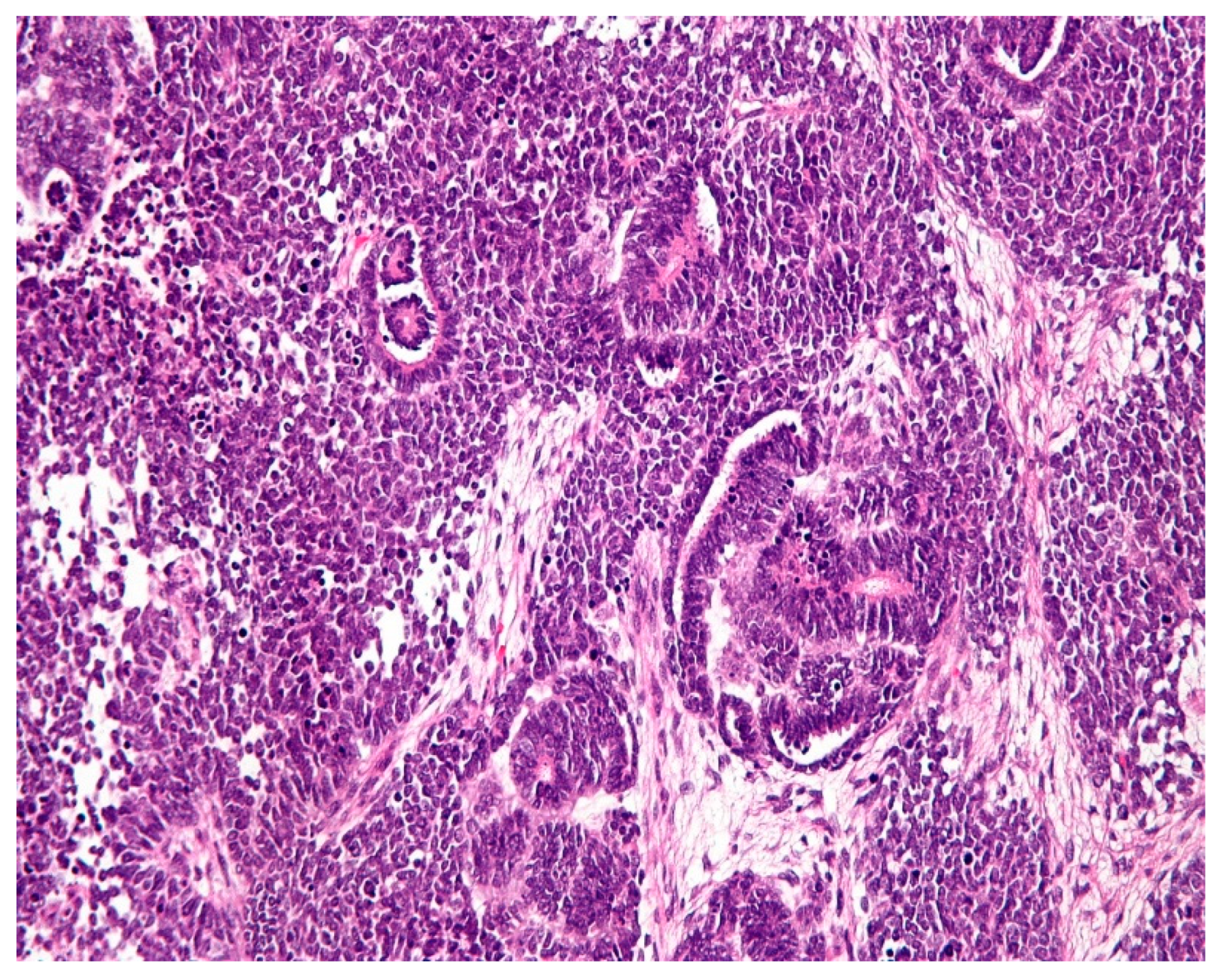
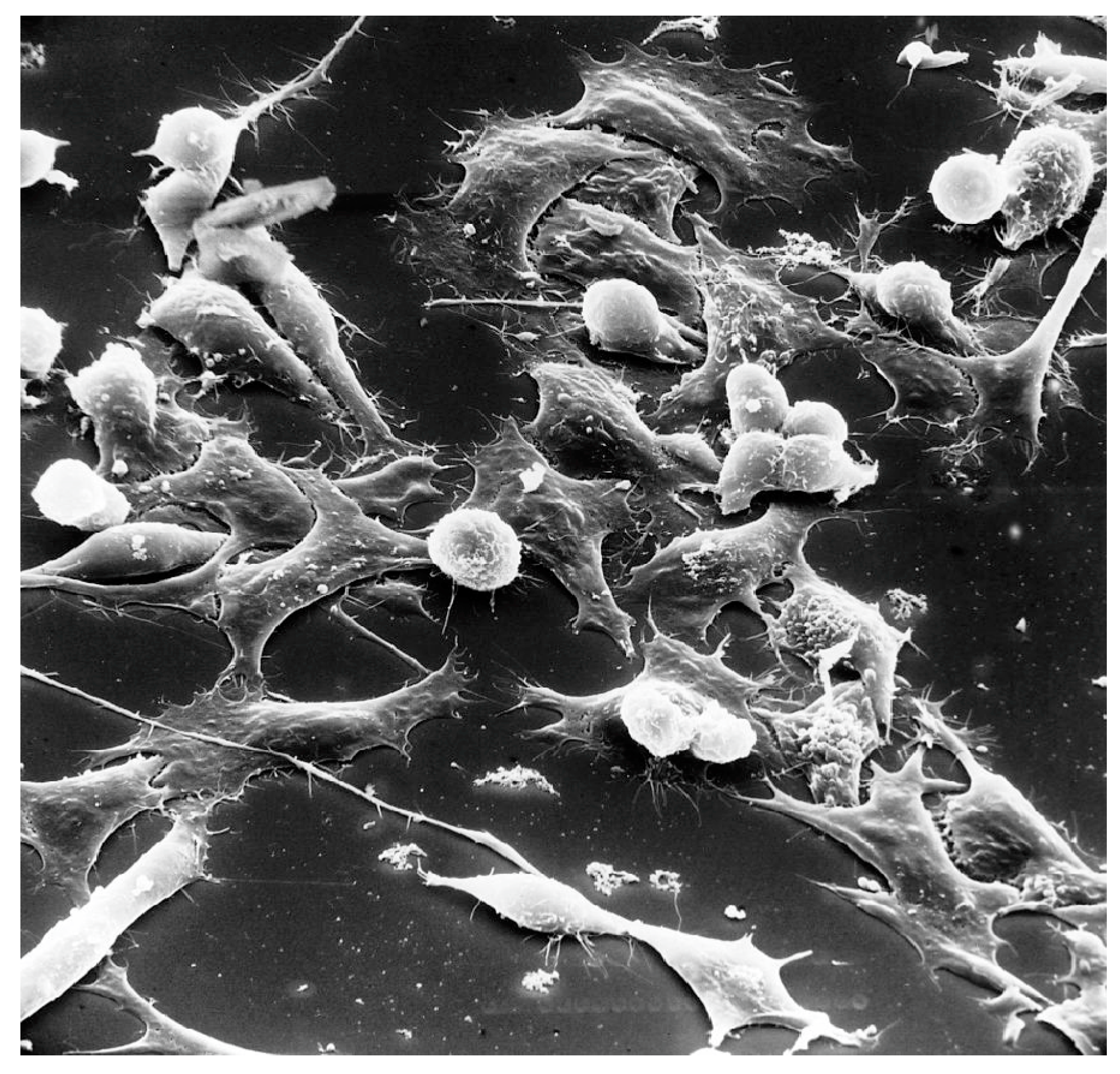
1.3. Clinical profiles
1.4. Aim
2. Materials and method
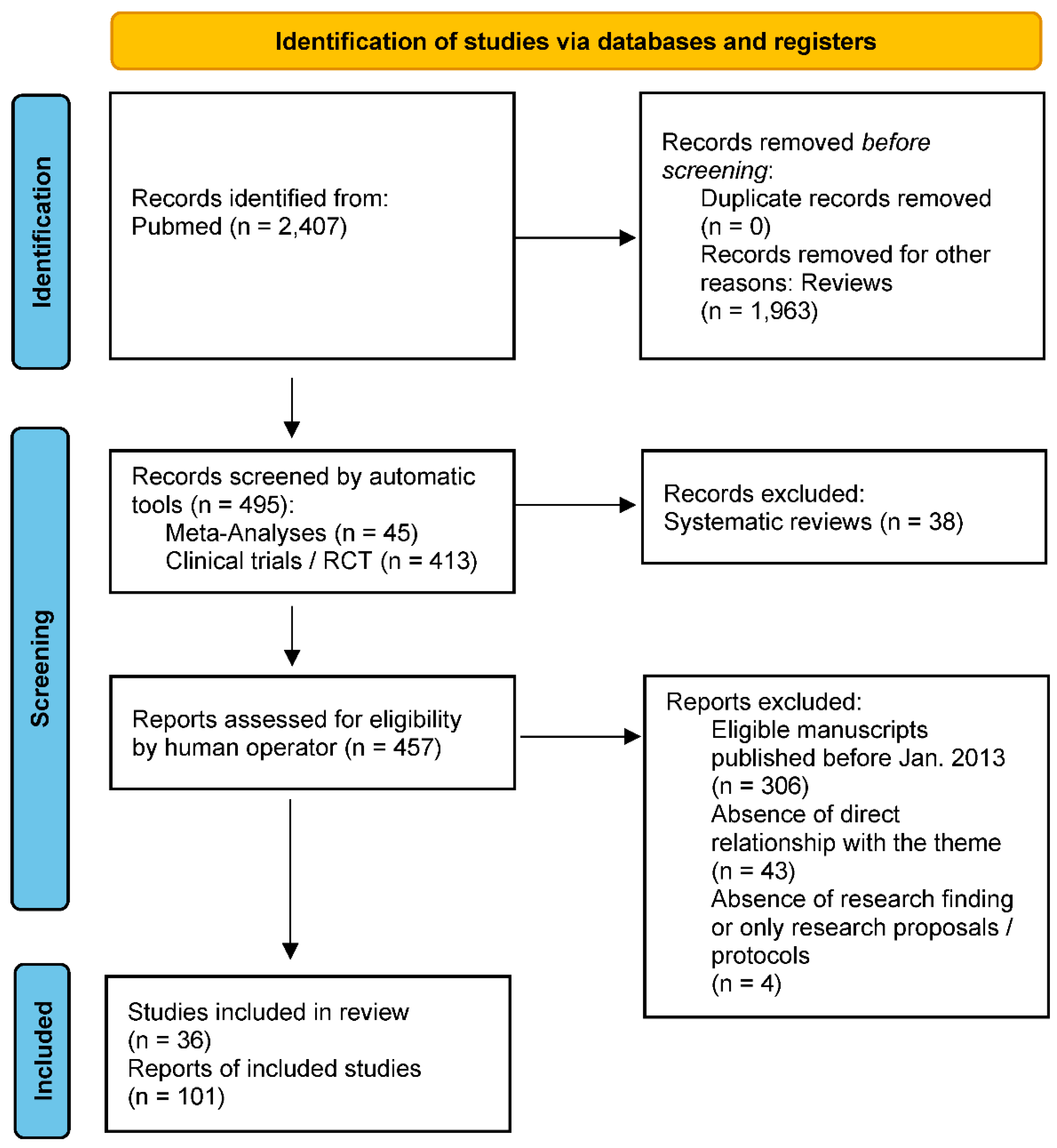
3. Results
3.1. Etiology
3.2. Diagnosis
3.3. Therapy
3.4. Prognosis
3.5. Nutritional implications
3.6. Psychological implications
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spreafico, F.; Bellani, F.F. Wilms' tumor: past, present and (possibly) future. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 2006, 6, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welter, N.; Brzezinski, J.; Treece, A.; Chintagumpala, M.; Young, M.D.; Perotti, D.; Kieran, K.; Jongmans, M.C.J.; Murphy, A.J. The pathophysiology of bilateral and multifocal Wilms tumors: What we can learn from the study of predisposition syndromes. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2022, 70, e29984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vujanic, G.M.; Parsons, L.N.; D’Hooghe, E.; Treece, A.L.; Collini, P.; Perlman, E.J. Pathology of Wilms' tumour in International Society of Paediatric Oncology (SIOP) and Children's oncology group (COG) renal tumour studies: Similarities and differences. Histopathology 2022, 80, 1026–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Perdomo, H.A.; González-Arboleda, A.A.; Fernandez, N. Genitourinary Tract Tumors in Children: An Update. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekenze, S.O.; Okafor, O.C.; Obasi, A.A.; Okafor, D.C.; Nnabugwu, I.I. Wilms tumor in Africa: A systematic review of management challenges and outcome in two decades (2000-2019). Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2020, 67, e28695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, M.V.; Koenig, C.; Armstrong, A.E.; Brok, J.; de Camargo, B.; Mavinkurve-Groothuis, A.M.C. Advances in the clinical management of high-risk Wilms tumors. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2023, 70, e30153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libes, J.; Hol, J.; Vallance, K.L.; van Tinteren, H.; Benedetti, D.J.; Ramirez Villar, G.L. Pediatric renal tumor epidemiology: Global perspectives, progress, and challenges. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2023, 70, e30006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd, A.B.; A Ghannam, R.; Mohd, O.B.; Elayan, R.; Albakri, K.; Huneiti, N.; Daraghmeh, F.; Al-Khatatbeh, E.; Al-Thnaibat, M. Etiologies, Gross Appearance, Histopathological Patterns, Prognosis, and Best Treatments for Subtypes of Renal Carcinoma: An Educational Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e32338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, R.; Asanuma, H.; Mizuno, R.; Oya, M. Current clinical perspective of urological oncology in the adolescent and young adult generation. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 28, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrotta, G. Port-Site Metastasis (PSM): Definition, clinical contexts and possible preventive actions to reduce risk. J Surg Surgical Res 2021, 7, 088–092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarello, P.; Carli, D.; Biasoni, D.; Nappo, S.G.; Morosi, C.; Cotti, R.; Garelli, E.; Zucchetti, G.; Spadea, M.; Tirtei, E.; et al. Implications of an Underlying Beckwith–Wiedemann Syndrome for Wilms Tumor Treatment Strategies. Cancers 2023, 15, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craver, R.; Stark, M.; Moss, S.; Long, S.; Prasad, P.; Roth, C.C. WAGR, Sex Reversal, Bilateral Gonadoblastomas, and Intralobar Nephrogenic Rests: Uncertainties of Pre-Biopsy Chemotherapy in a High Risk Syndrome for Nephroblastoma. Fetal Pediatr. Pathol. 2022, 42, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhutani, N.; Kajal, P.; Sharma, U. Many faces of Wilms Tumor: Recent advances and future directions. Ann. Med. Surg. 2021, 64, 102202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, C.N.; Rhee, D.; Tracy, E.T.; Aldrink, J.H.; Baertschiger, R.M.; Lautz, T.B.; Glick, R.D.; Rodeberg, D.A.; Ehrlich, P.F.; Christison-Lagay, E. Pediatric solid tumors and associated cancer predisposition syndromes: Workup, management, and surveillance. A summary from the APSA Cancer Committee. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2021, 57, 430–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Xiong, Q.-W.; Wang, J.-H.; Peng, W.-X. Roles of lncRNAs in childhood cancer: Current landscape and future perspectives. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1060107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hont, A.B.; Dumont, B.; Sutton, K.S.; Anderson, J.; Kentsis, A.; Drost, J.; Hong, A.L.; Verschuur, A. The tumor microenvironment and immune targeting therapy in pediatric renal tumors. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2022, 70, e30110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bánki, T.; Drost, J.; Heuvel-Eibrink, M.M.v.D.; Mavinkurve-Groothuis, A.M.C.; de Krijger, R.R. Somatic, Genetic and Epigenetic Changes in Nephrogenic Rests and Their Role in the Transformation to Wilms Tumors, a Systematic Review. Cancers 2023, 15, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Q.; He, H.; Fan, D.; Lyu, J.; Pan, Z.; You, H. Association between loss of heterozygosity of chromosome 16q and survival in Wilms’ tumor: A meta-analysis. Pathol. - Res. Pr. 2018, 214, 1772–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizhi, L.; Rongdong, H.; Shaohua, H.; Yingquan, K.; Huihuang, X.; Shan, L.; Kunbin, T.; Di, X. Association Between TP53 Mutation and Prognosis in Wilms Tumor: A Meta-Analysis. Fetal Pediatr. Pathol. 2020, 40, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhuo, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, H.; He, J.; Li, P. HMGA2 gene polymorphisms and Wilms tumor susceptibility in Chinese children: a four-center case-control study. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2019, 67, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Feulefack, J.; Sergi, C. Exposure to pesticides and pediatric Wilms’ tumor. A meta-analysis on pre-conception and pregnancy parental exposure with an IARC/WHO commentary. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2022, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doganis, D.; Katsimpris, A.; Panagopoulou, P.; Bouka, P.; Bouka, E.; Moschovi, M.; Polychronopoulou, S.; Papakonstantinou, E.; Tragiannidis, A.; Katzilakis, N.; et al. Maternal lifestyle characteristics and Wilms tumor risk in the offspring: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiology 2020, 67, 101769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welter, N.; Furtwangler, R.; Schneider, G.; Graf, N.; Schenk, J-P. Tumor predisposition syndromes and nephroblastoma: early diagnosis with imaging. Radiologie (Heidelb) 2022, 62, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedrzejewski, G.; Wozniak, M.M.; Pawelec, A.; Matera, A.; Kunach, M.; Madej, T.; Wieczorek, A.P.; Nowakowska, K. Ultrasound screening for neoplasms in children up to 6 years old. Medicine 2016, 95, e5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Beek, J.N.; Artunduaga, M.; Schenk, J.; Eklund, M.J.; Smith, E.A.; Lederman, H.M.; Warwick, A.B.; Littooij, A.S.; Khanna, G. Similarities and controversies in imaging of pediatric renal tumors: A SIOP-RTSG and COG collaboration. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2022, 70, e30080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uslu, L.; Donig, J.; Link, M.; Rosenberg, J.; Quon, A.; Daldrup-Link, H.E. Value of 18F-FDG PET and PET/CT for Evaluation of Pediatric Malignancies. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madanat-Harjuoja, L.M.; Renfro, L.A.; Klega, K.; Tornwall, B.; Thorner, A.R.; Nag, A. Circulating Tumor DNA as a Biomarker in Patients With Stage III and IV Wilms Tumor: Analysis From a Children's Oncology Group Trial, AREN0533. J Clin Oncol 2022, 40, 3047–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walz, A.L.; Maschietto, M.; Crompton, B.; Evageliou, N.; Dix, D.; Tytgat, G.; Gessler, M.; Gisselsson, D.; Daw, N.C.; Wegert, J. Tumor biology, biomarkers, and liquid biopsy in pediatric renal tumors. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2023, 70, e30130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Dai, R.; Li, X.; Liu, F. Genetic variation frequencies in Wilms' tumor: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagtai, T.; Zill, C.; Dainese, L.; Wegert, J.; Savola, S.; Popov, S. Gain of 1q As a Prognostic Biomarker in Wilms Tumors (WTs) Treated With Preoperative Chemotherapy in the International Society of Paediatric Oncology (SIOP) WT 2001 Trial: A SIOP Renal Tumours Biology Consortium Study. J Clin Oncol 2016, 34, 3195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute (NIH). Wilms Tumor and Other Childhood Kidney Tumors Treatment (PDQ®)–Patient Version. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/types/kidney/patient/wilms-treatment-pdq#section/_29.
- Palmisani, F.; Kovar, H.; Kager, L.; Amann, G.; Metzelder, M.; Bergmann, M. Systematic review of the immunological landscape of Wilms tumors. Mol. Ther. - Oncolytics 2021, 22, 454–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhafeez, A.H.; Reljic, T.; Kumar, A.; Banu, T.; Cox, S.; Davidoff, A.M.; Elgendy, A.; Ghandour, K.; Gerstle, J.T.; Karpelowsky, J.; et al. Evidence-based surgical guidelines for treating children with Wilms tumor in low-resource settings. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2022, 69, e29906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sforza, S.; Palmieri, V.E.; Raspollini, M.R.; Roviello, G.; Mantovani, A.; Basso, U.; Affinita, M.C.; D'Angelo, A.; Antonuzzo, L.; Carini, M.; et al. Robotic approach with neoadjuvant chemotherapy in adult Wilms’ tumor: A feasibility study report and a systematic review of the literature. Asian J. Urol. 2023, 10, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, M.M.; Behr, C.A.; Aldrink, J.H.; Dasgupta, R.; Heaton, T.E.; Gehred, A.; Lautz, T.B.; Baertschiger, R.M.; Christison-Lagay, E.R.; Tracy, E.T.; et al. Minimally invasive surgery for pediatric renal tumors: A systematic review by the APSA Cancer Committee. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2020, 55, 2251–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.; Li, K.; Dong, K.; Xiao, X.; Yao, W.; Liu, G. Clinical features, treatment, and outcomes of bilateral Wilms' tumor: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2018, 53, 2465–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, J.; Irtan, S.; Bergeron, C.; Pritchard-Jones, K. Bilateral Wilms tumour: a review of clinical and molecular features. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2017, 19, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, P.; Chi, Y.Y.; Chintagumpala, M.M.; Hoffer, F.A.; Perlman, E.J.; Kalapurakal, J.A. Results of the First Prospective Multi-institutional Treatment Study in Children With Bilateral Wilms Tumor (AREN0534): A Report From the Children's Oncology Group. Ann Surg 2017, 266, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, M.; Curigliano, G.; Dieras, V.; Kuemmel, S.; Kunz, G.; Fasching, P.A.; Campone, M.; Bachelot, T.; Krivorotko, P.; Chan, S.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of neoadjuvant treatment using WT1-immunotherapeutic in combination with standard therapy in patients with WT1-positive Stage II/III breast cancer: a randomized Phase I study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 162, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, F.M.; Patel, P.A.; Stuart, S.; Roebuck, D.J. Systematic review of ablation techniques for the treatment of malignant or aggressive benign lesions in children. Pediatr. Radiol. 2014, 44, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Heuvel-Eibrink, M.M.; Hol, J.A.; Pritchard-Jones, K.; van Tinteren, H.; Furtwängler, R.; Verschuur, A.C.; Vujanic, G.M.; Leuschner, I.; Brok, J.; Rübe, C.; et al. Rationale for the treatment of Wilms tumour in the UMBRELLA SIOP–RTSG 2016 protocol. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2017, 14, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pater, L.; Melchior, P.; Rube, C.; Cooper, B.T.; McAleer, M.F.; Kalapurakal, J.A.; Paulino, A.C. Wilms tumor. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2021, 68, e28257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malogolowkin, M.; Spreafico, F.; Dome, J.S.; van Tinteren, H.; Pritchard-Jones, K.; van den Heuvel-Eibrink, M.; Bergeron, C.; de Kraker, J.; Graf, N. ; On behalf of the COG Renal Tumors Committee and the SIOP Renal Tumor Study Group Incidence and outcomes of patients with late recurrence of Wilms' tumor. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2013, 60, 1612–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrotta, G. The acceptance in the elaboration of mourning in oncological diseases: definition, theoretical models, and practical applications. Needs analysis and subjective oncological reality. Biomed J Sci & Tech Res 2019, 21, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geets, E.; Meuwissen, M.; Van Hul, W. Clinical, molecular genetics and therapeutic aspects of syndromic obesity. Clin. Genet. 2018, 95, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H-Y. Wilms' tumor management. Curr Opin Urol 2005, 15, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.K.; Suson, K.D. Syndromic Wilms tumor: a review of predisposing conditions, surveillance and treatment. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2020, 9, 2370–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrotta, G. Anxiety disorders: definitions, contexts, neural correlates and strategic therapy. J Neur Neurosci 2019, 6, 046. [Google Scholar]
- Perrotta, G. Post-traumatic stress disorder: Definition, contexts, neural correlations and cognitive-behavioural therapy. J Pub Health Catalog 2019, 2, 40–7. [Google Scholar]
- Perrotta, G. Depressive disorders: Defi nitions, contexts, differential diagnosis, neural correlates and clinical strategies. Arch. Depression Anxiety 2019, 5, 009–033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrotta, G. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: definition, contexts, neural correlates and clinical strategies. J. Neurol. 2019, 2019, 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- Perrotta, G. Bipolar disorder: definition, differential diagnosis, clinical contexts and therapeutic approaches. Neurosci. Neurol. Surg. 2019, 5, 01–06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrotta, G. Psychological trauma: definition, clinical contexts, neural correlations and therapeutic approaches. Curr Res Psychiatry Brain Disord 2020, CRPBD-100006. [Google Scholar]
- Perrotta, G. The reality plan and the subjective construction of one's perception: the strategic theoretical model among sensations, perceptions, defence mechanisms, needs, personal constructs, beliefs system, social influences and systematic errors. J Clin. Res. Rep. 2019, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouty, A.; Blanc, T.; Leclair, M.D.; Lavrand, F.; Faure, A.; Binet, A.; Rod, J.; O'Brien, M.; Sarnacki, S.; Nightingale, M.; et al. Minimally invasive surgery for unilateral Wilms tumors: Multicenter retrospective analysis of 50 transperitoneal laparoscopic total nephrectomies. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2020, 67, e28212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavens, E.; Arul, G.S.; Pachl, M. A single centre matched pair series comparing minimally invasive and open surgery for the resection of pediatric renal tumours. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 35, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dix, D.B.; Seibel, N.L.; Chi, Y.-Y.; Khanna, G.; Gratias, E.; Anderson, J.R.; Mullen, E.A.; Geller, J.I.; Kalapurakal, J.A.; Paulino, A.C.; et al. Treatment of Stage IV Favorable Histology Wilms Tumor With Lung Metastases: A Report From the Children’s Oncology Group AREN0533 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1564–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irtan, S.; Messahel, B.; Moroz, V.; Taylor, R.E.; Grundy, R.; Kelsey, A.; Vujanic, G.; Pritchard-Jones, K. Outcomes of non-anaplastic stage III and ‘inoperable’ Wilms tumour treated in the UKW3 trial. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 131, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujanic, G.M.; D’Hooghe, E.; Popov, S.D.; Sebire, N.J.; Kelsey, A. The effect of preoperative chemotherapy on histological subtyping and staging of Wilms tumors: The United Kingdom Children's Cancer Study Group (UKCCSG) Wilms tumor trial 3 (UKW3) experience. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2019, 66, e27549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joannon, P.; Becker, A.; Kabalan, P.; Concha, E.; Beresi, V.; Salgado, C.; Martínez, P.; Olate, P.; Arriagada, M.; Espinoza, F.; et al. Results of Therapy for Wilms Tumor and Other Malignant Kidney Tumors: A Report From the Chilean Pediatric National Cancer Program (PINDA). J. Pediatr. Hematol. 2016, 38, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigel, B.; Malempati, S.; Reid, J.M.; Voss, S.D.; Cho, S.Y.; Chen, H.X. Phase 2 trial of cixutumumab in children, adolescents, and young adults with refractory solid tumors: a report from the Children's Oncology Group. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2014, 61, 452–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hol, J.A.; Heuvel-Eibrink, M.M.V.D.; Graf, N.; Pritchard-Jones, K.; Brok, J.; Van Tinteren, H.; Howell, L.; Verschuur, A.; Bergeron, C.; Kager, L.; et al. Irinotecan for relapsed Wilms tumor in pediatric patients: SIOP experience and review of the literature-A report from the SIOP Renal Tumor Study Group. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2017, 65, e26849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Widemann, B.C.; Krailo, M.; Jayaprakash, N.; Fox, E.; Weigel, B. Phase 2 trial of sorafenib in children and young adults with refractory solid tumors: A report from the Children's Oncology Group. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2015, 62, 1562–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, N.; Tsuboi, A.; Kagawa, N.; Chiba, Y.; Izumoto, S.; Kinoshita, M.; Kijima, N.; Oka, Y.; Morimoto, S.; Nakajima, H.; et al. Wilms tumor 1 peptide vaccination combined with temozolomide against newly diagnosed glioblastoma: safety and impact on immunological response. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2015, 64, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koido, S.; Homma, S.; Okamoto, M.; Takakura, K.; Mori, M.; Yoshizaki, S. Treatment with chemotherapy and dendritic cells pulsed with multiple Wilms' tumor 1 (WT1)-specific MHC class I/II-restricted epitopes for pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2014, 20, 4228–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrovic, M.; Kostic, T.; Virijevic, M.; Karan-Djurasevic, T.; Vukovic, N.S.; Pavlovic, S.; Tosic, N. The influence of Wilms' tumor 1 gene expression level on prognosis and risk stratification of acute promyelocytic leukemia patients. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2019, 42, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsohn, D.A.; Loken, M.R.; Fei, M.; Adams, A.; Brodersen, L.E.; Logan, B.R.; Ahn, K.W.; Shaw, B.E.; Kletzel, M.; Olszewski, M.; et al. Outcomes of Measurable Residual Disease in Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia before and after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant: Validation of Difference from Normal Flow Cytometry with Chimerism Studies and Wilms Tumor 1 Gene Expression. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018, 24, 2040–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibasaki, Y.; Seki, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Miyakoshi, S.; Fuse, K.; Kozakai, T.; Kobayashi, H.; Ushiki, T.; Abe, T.; Yano, T.; et al. The association of level of reduction of Wilms’ tumor gene 1 mRNA transcript in bone marrow and outcome in acute myeloid leukemia patients. Leuk. Res. 2015, 39, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogasawara, M.; Miyashita, M.; Yamagishi, Y.; Ota, S. Phase I/II Pilot Study of Wilms' Tumor 1 Peptide-Pulsed Dendritic Cell Vaccination Combined With Conventional Chemotherapy in Patients With Head and Neck Cancer. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2019, 23, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreutmair, S.; Pfeifer, D.; Waterhouse, M.; Takács, F.; Graessel, L.; Döhner, K.; Duyster, J.; Illert, A.L.; Frey, A.-V.; Schmitt, M.; et al. First-in-human study of WT1 recombinant protein vaccination in elderly patients with AML in remission: a single-center experience. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2022, 71, 2913–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, K.; Shimodaira, S.; Maejima, S.; Udagawa, N.; Sano, K.; Higuchi, Y.; Koya, T.; Ochiai, T.; Koide, M.; Uehara, S.; et al. Dendritic cell–based immunotherapy targeting Wilms’ tumor 1 in patients with recurrent malignant glioma. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 123, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Fang, S.; Dai, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhu, W.; Wang, S. The Wilms Tumor-1 (WT1) rs16754 polymorphism is a prognostic factor in acute myeloid leukemia (AML): a meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 32079–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, S.; Koido, S.; Takeda, Y.; Homma, S.; Komita, H.; Takahara, A.; Morita, S.; Ito, T.; Morimoto, S.; Hara, K.; et al. Wilms Tumor Gene (WT1) Peptide–based Cancer Vaccine Combined With Gemcitabine for Patients With Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. J. Immunother. 2014, 37, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, S.; Yanagisawa, R.; Yoshikawa, K.; Higuchi, Y.; Koya, T.; Yoshizawa, K.; Tanaka, M.; Sakashita, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Kurata, T.; et al. Safety and tolerability of allogeneic dendritic cell vaccination with induction of Wilms tumor 1–specific T cells in a pediatric donor and pediatric patient with relapsed leukemia: a case report and review of the literature. Cytotherapy 2014, 17, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuboi, A.; Hashimoto, N.; Fujiki, F.; Morimoto, S.; Kagawa, N.; Nakajima, H.; Hosen, N.; Nishida, S.; Nakata, J.; Morita, S.; et al. A phase I clinical study of a cocktail vaccine of Wilms’ tumor 1 (WT1) HLA class I and II peptides for recurrent malignant glioma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2018, 68, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, M.; Ogawa, C.; Iehara, T.; Aoki-Nogami, Y.; Ishibashi, E.; Imai, M.; Kimura, T.; Nagata, M.; Yasuhara, M.; Masutani, M.; et al. First phase 1 clinical study of olaparib in pediatric patients with refractory solid tumors. Cancer 2022, 128, 2949–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirabayashi, K.; Yanagisawa, R.; Saito, S.; Higuchi, Y.; Koya, T.; Sano, K.; Koido, S.; Okamoto, M.; Sugiyama, H.; Nakazawa, Y.; et al. Feasibility and Immune Response of WT1 Peptide Vaccination in Combination with OK-432 for Paediatric Solid Tumors. Anticancer. Res. 2018, 38, 2227–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, R.; Koizumi, T.; Koya, T.; Sano, K.; Koido, S.; Nagai, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Okamoto, M.; Sugiyama, H.; Shimodaira, S. WT1-pulsed Dendritic Cell Vaccine Combined with Chemotherapy for Resected Pancreatic Cancer in a Phase I Study. Anticancer. Res. 2018, 38, 2217–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lu, X.; Cui, P.; Piao, C.; Xiao, M.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, L. Phase I/II clinical trial of a Wilms’ tumor 1-targeted dendritic cell vaccination-based immunotherapy in patients with advanced cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2018, 68, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayanagi, S.; Kitago, M.; Sakurai, T.; Matsuda, T.; Fujita, T.; Higuchi, H.; Taguchi, J.; Takeuchi, H.; Itano, O.; Aiura, K.; et al. Phase I pilot study of Wilms tumor gene 1 peptide-pulsed dendritic cell vaccination combined with gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brayer, J.; Lancet, J.E.; Powers, J.; List, A.; Balducci, L.; Komrokji, R.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J. WT1 vaccination in AML and MDS: A pilot trial with synthetic analog peptides. Am. J. Hematol. 2015, 90, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, S.; Miyashita, M.; Yamagishi, Y.; Ogasawara, M. Baseline immunity predicts prognosis of pancreatic cancer patients treated with WT1 and/or MUC1 peptide-loaded dendritic cell vaccination and a standard chemotherapy. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2021, 17, 5563–5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Z.; Kan, S.; Bito, T.; Horiuchi, S.; Akasu, T.; Yoshida, S.; Kajihara, M.; Hokari, A.; Saruta, M.; Yoshida, N.; et al. Predicted Markers of Overall Survival in Pancreatic Cancer Patients Receiving Dendritic Cell Vaccinations Targeting WT1. Oncology 2019, 97, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyi, C.; Doubrovina, E.; Zhou, Q.; Kravetz, S.; Iasonos, A.; Aghajanian, C.; Sabbatini, P.; Spriggs, D.; O'Reilly, R.J.; E O’cearbhaill, R. Phase I dose escalation safety and feasibility study of autologous WT1-sensitized T cells for the treatment of patients with recurrent ovarian cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, K.; Funakoshi, T.; Sakurai, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Mori, M.; Tanese, K.; Tanikawa, A.; Taguchi, J.; Fujita, T.; Okamoto, M.; et al. Peptide-pulsed dendritic cell vaccine in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel chemotherapy for stage IV melanoma. Melanoma Res. 2017, 27, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, D.M.; Lange, J.M.; Qu, A.; Peterson, S.M.; Kalapurakal, J.A.; Stokes, D.C.; Grigoriev, Y.A.; Takashima, J.R.; Norkool, P.; Friedman, D.L.; et al. Pulmonary disease after treatment for wilms tumor: A report from the national wilms tumor long-term follow-up study. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2013, 60, 1721–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maslak, P.G.; Dao, T.; Bernal, Y.; Chanel, S.M.; Zhang, R.; Frattini, M.; Rosenblat, T.; Jurcic, J.G.; Brentjens, R.J.; Arcila, M.E.; et al. Phase 2 trial of a multivalent WT1 peptide vaccine (galinpepimut-S) in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coosemans, A.; Vanderstraeten, A.; Tuyaerts, S.; Verschuere, T.; Moerman, P.; Berneman, Z.; Vergote, I.; Amant, F.; Van Gool, S.W. Wilms' Tumor Gene 1 (WT1)--loaded dendritic cell immunotherapy in patients with uterine tumors: a phase I/II clinical trial. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Nishida, S.; Ishikawa, T.; Egawa, S.; Koido, S.; Yanagimoto, H.; Ishii, J.; Kanno, Y.; Kokura, S.; Yasuda, H.; Oba, M.S.; et al. Combination Gemcitabine and WT1 Peptide Vaccination Improves Progression-Free Survival in Advanced Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: A Phase II Randomized Study. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 6, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oji, Y.; Hashimoto, N.; Tsuboi, A.; Murakami, Y.; Iwai, M.; Kagawa, N.; Chiba, Y.; Izumoto, S.; Elisseeva, O.; Ichinohasama, R.; et al. Association of WT1 IgG antibody against WT1 peptide with prolonged survival in glioblastoma multiforme patients vaccinated with WT1 peptide. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, J.; Nakae, Y.; Kawakami, M.; Morimoto, S.; Motooka, D.; Hosen, N.; Fujiki, F.; Nakajima, H.; Hasegawa, K.; Nishida, S.; et al. Wilms tumour 1 peptide vaccine as a cure-oriented post-chemotherapy strategy for patients with acute myeloid leukaemia at high risk of relapse. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 182, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uttenthal, B.; Martinez-Davila, I.; Ivey, A.; Craddock, C.; Chen, F.; Virchis, A.; Kottaridis, P.; Grimwade, D.; Khwaja, A.; Stauss, H.; et al. Wilms’ Tumour 1 (WT1) peptide vaccination in patients with acute myeloid leukaemia induces short-livedWT1-specific immune responses. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 164, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Gu, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhong, H.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Z. Wilms' tumor 1 (WT1) as a prognosis factor in gynecological cancers: A meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2018, 97, e11485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, Y.; Ogura, M.; Miyakoshi, S.; Suzuki, T.; Heike, Y.; Tagashira, S. Phase 1/2 study of the WT1 peptide cancer vaccine WT4869 in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Cancer Sci 2017, 108, 2445–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israyelyan, A.; Goldstein, L.; Tsai, W.; Aquino, L.; Forman, S.J.; Nakamura, R.; Diamond, D.J. Real-time assessment of relapse risk based on the WT1 marker in acute leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome patients after hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014, 50, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, K.; Hu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Fu, W.; Liu, G.-C. Meta-analysis of the effect of preoperative chemotherapy on Wilms' tumor. J. B.U.ON. : Off. J. Balk. Union Oncol. 2018, 23, 211–217. [Google Scholar]
- Koshinaga, T.; Takimoto, T.; Okita, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Inoue, E.; Oue, T. Blastemal predominant type Wilms tumor in Japan: Japan Children's Cancer Group. Pediatr Int 2019, 61, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trink, A.; Kanter, I.; Pode-Shakked, N.; Urbach, A.; Dekel, B.; Kalisky, T. Geometry of Gene Expression Space of Wilms' Tumors From Human Patients. Neoplasia 2018, 20, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, A.; Pluijm, S.M.; Wijnen, M.; Neggers, S.J.; Clemens, E.; Pieters, R.; Heuvel-Eibrink, M.M.v.D. Health-related fitness in very long-term survivors of childhood cancer: A cross-sectional study. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2017, 65, e26907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Cao, H.; Zou, H. Influence of psychological nursing intervention in the recovery of children with Wilms' tumor. Minerva Pediatr. 2019, 71, 545–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrotta, G. The intestinal microbiota: Towards a multifactorial integrative model. Eubiosis and dysbiosis in morbid physical and psychological conditions. Arch Clin Gastroenterol 2021, 7, 024–035. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




