1. Introduction
Point-of-care applications are moving toward more decentralized clinical diagnostic methods and approaches that are portable, selective, sensitive, highly effective, and producing accurate analytical results in a timely manner when compared to traditional laboratory testing, hence they are attracting a lot of attention in the biomedical field [
1,
2,
3]. Over the past several years, the number of point-of-care testing platforms has steadily increased, aiding in their application in emergency and accident cases. There are many ways to identify illnesses and keep track of a patient's health, however, biosensors proved to play a crucial part in prognostics and diagnostics [
4,
5].
Particularly, electrochemical biosensors for DNA detection are analytical devices that use electrochemical principles to detect the presence and quantity of DNA molecules in a sample. These biosensors have emerged as a powerful tool for DNA analysis due to their high sensitivity, specificity, and rapid response time [
6]. These devices have potential applications in a wide range of fields, including medical diagnosis, environmental monitoring, food safety, and forensic analysis [
7,
8,
9,
10]. As research in this field continues, the development of new and improved electrochemical biosensors for DNA detection is likely to accelerate, providing new opportunities for DNA analysis and other biomedical applications.
Graphene and graphene-based nanomaterials have been showing the greatest promise among the nanomaterials applied in biosensors fabrication, due to their outstanding properties like high surface area, excellent conductivity, chemical stability [
12,
13,
14] and high biocompatibility with a wide range of biomolecules, including antibodies, enzymes, DNA, cells, and proteins [
15,
16,
17,
18]. Biosensors based on graphene have been applied in the detection of multiple analytes, from small molecules to biomolecules, and even cells [
19,
20]. In particular, graphene-based biosensors have been extensively studied and optimized for selective detection and analysis of different DNA forms, enabling diverse applications in genomics, diagnostics, and DNA-based research [
21,
22]. Besides graphene, other nanomaterials have been employed for DNA detection to increase the assay sensitivity. Gold nanostructures are excellent options among these nanomaterials because of their outstanding optical and mechanical characteristics, as well as their high chemical stability [
23]. The synthesis of Au nanostructures can be achieved in a number of ways. Among these, the electrochemical synthesis of Au nanostructures has been widely employed because it offers several advantages over chemical synthesis, including the ability to control size, shape, morphology, and growth rate by modulating the applied potential or current, and via the electrolyte concentration [
24,
25,
26]. Several studies have demonstrated that single-stranded (ss) oligonucleotides possess a more pronounced affinity for gold nanoparticles than their corresponding double-stranded (ds) helix [
27,
28]. Li and Rothberg mentioned underlying adsorption mechanism of ssDNA on gold is electrostatic, and exploited the difference in the electrostatic properties of ssDNA and dsDNA in DNA detection by a colorimetric assay [
27].
In this work, we aim to develop an electrochemical detection platform for DNA hybridization based on screen printed carbon electrodes (SPCEs) modified with reduced graphene oxide (RGO) and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). A protocol previously established by our group was employed for the preparation of RGO/SPCEs modified electrodes [
29], and then, the functionalization of RGO with AuNPs was performed by the electrochemical reduction of chloroauric acid. The modified electrodes were extensively characterized before further modifications. Finally, the detection platform was obtained by the immobilization of the ssDNA probe (DNAp) at the AuNPs/RGO/SPCEs by simple physical adsorption and the hybridization event between ssDNA probe and ssDNA target (DNAt) was detected electrochemically. Cyclic voltammetry (CV), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and chronocoulometry were the electrochemical characterization and detection techniques, while the morphology of the films deposited at electrodes was determined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The results show a successful detection of DNA target for concentrations as low as 1 nM, while the specificity of the biosensor is demonstrated by control experiments using a non-complimentary oligonucleotide (ncDNA).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
Graphene oxide (GO) dispersion in water (2 mg/mL), HCl, KCl, HNa2O4P, H2NaO4P, H2SO4 and HAuCl4 were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Potassium ferricyanide (K3[Fe(CN)6]) and potassium ferrocyanide (K4[Fe(CN)6] x 3H2O) were acquired from Merck Co., (Darmstadt, Germany). Single stranded DNA probe (5’ - TTT CAA CAT CAG TCT GAT AAG CTA TCT CCC-3’), complementary single stranded DNA target (DNAt, 5’ - GGG AGA TAG CTT ATC AGA CTG ATG TTG AAA-3’), and 10 mM Tris, 0.1 mM EDTA (IDTE) buffer were supplied from Integrated DNA Technologies, Inc (Coralville, IA, USA). Screen printed carbon electrodes (SPCE-DRP 110) were purchased from Metrohm DropSens, Spain and consisted of a 4 mm diameter working electrode (WE), a silver pseudo-reference electrode (RE), and a carbon counter electrode (CE). The electrodes were washed with ultrapure water (Adrona Crystal EX water purification system, 18.2 MΩ x cm resistivity) after each stage of the modification.
2.2. Procedures
2.2.1. Morphological Characterization
A FEI’s high-resolution focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy (FIB-SEM) system model Versa 3D DualBeam (FEI Company, Hillsboro, USA) equipped with a TEAM EDS Analysis System (EDAX Inc., USA) were used to characterize the selected sample series. The plane view (0° tilt) samples surface morphology were investigated by detecting the secondary electrons (SE) signals in High-Vacuum operation mode (6.1x10-4 Pa) at a working distance of 10 mm, using 10 kV as accelerating voltage and a spot size of 4.5. Moreover, the SmartSCAN scanning strategy and DCFI drift suppression features of Versa 3D DualBeam tool were involved to fully ensure the imaging stability.
2.2.2. Electrochemical Characterization
Each step of electrode modification was studied by CV and EIS, that were performed at room temperature, using the potentiostat/galvanostat Autolab with PGSTAT 204 model (Metrohm Autolab, Netherlands) controlled by NOVA 2.1 software. The SPCE was attached to a connector (DSC) device from Metrohm Dropsens, functioning as an interface between the electrode and the potentiostat. The electrochemical measurements were recorded by adding 100 µL 0.1 M KCl electrolyte solution containing 1 mM K3[Fe(CN)6]/K4[Fe(CN)6] (1:1) redox probe on the SPCE. CV curves were recorded by scanning the potential from -0.2 V to +0.6 V, at a scan rate of 0.05 V/s (unless stated otherwise). The impedance spectra were recorded in the frequency range of 0.01-105 Hz, with 10 mV AC amplitude at the formal potential of the redox probes.
2.2.3. Electrode Functionalization Procedure
Before any modification, the SPCEs were washed with ultrapure water then underwent an electrochemical pretreatment meant to improve their electrochemical properties and to increase the hydrophilicity of the WE. Therefore, 5 CV cycles were performed first in 0.1 M HCl, between +0.5 V and -1.5 V at a sweep rate of 0.05 V/s, then other 5 voltammetric cycles were applied in 0.1 M phosphate buffer solution (PBS), pH 7, from 0 to +2 V, at a scan rate of 0.05 V/s. The next step consisted in depositing on the WE 3 µL PBS, then the electrodes were washed after 10 minutes and dried in the oven at 60°C. This stage modified the wettability properties of the electrode surface and ensures a reproducible modification with graphene.
After the electrodes were washed and dried, a volume of 3 µL GO dispersion (0.3 mg/mL) was added on the electrodes with a micropipette, which were dried at 60°C for 2 hours then at room temperature overnight. Next, the GO modified electrodes were electrochemically reduced in 0.5 M KCl applying 10 CV cycles between 0 and -1.5 V at a scan rate of 0.1 V/s.
The functionalization procedure of RGO/SPCEs with AuNPs consisted in performing 5 CV cycles in a potential range from +1 and -1 V, at a sweep rate of 0.05 V/s, in a solution containing various concentrations (1, 5, 10, or 15 mM) of HAuCl4 in 0.5 mM H2SO4. The SPCEs were modified at the same time, and at least 3 samples have been used for each test, in order to attest the reproducibility and the validity of the results.
2.2.4. The Fabrication and Testing Procedure of the DNA Biosensor
The bioreceptor consisting in ssDNA probe was immobilized at AuNPs-RGO/SPCEs through non-covalent bonding (physical adsorption) by incubating the electrodes with 10 µL of 500 nM DNA solution, overnight, at room temperature. The ssDNA/AuNPs-RGO/SPCEs biosensor, fabricated as previously described, was then tested by measuring the electrochemical changes that occurred after the hybridization with complementary ssDNA target. The hybridization was performed by incubating the sensor with DNA target solution for 3 hours at 42°C. The specificity of the biosensor was tested by incubating it with non-complimentary DNA in the exact same conditions used for the hybridization with DNA target (3 hours at 42°C).
2.2.5. Chronocoulometric Tests
Chronocoulometry has been used to estimate the DNA surface coverage before and after the target DNA addition as indicative of the hybridization process, by measuring the reduction charge of the accumulated cationic Ru(NH
3)
63+ redox species with the negatively charged backbone of the surface-bound oligonucleotides. The applied two step chronocoulometric procedure consisted in stepping from 0 to −0.400 V to 0 V vs Ag/AgCl, with a pulse period of 0.250 s. In this regard, the electrode is immersed in a deaerated low ionic strength buffer solution (TRIS 10 mM, pH = 7.4), and maintained 10 minutes under stirring, for equilibration, before performing the chronocoulometric test. The same procedure is then applied by addition of 100 μM Ru(NH
3)
63+ to the buffer solution. The DNA surface coverages were calculated using a previously established method based on the integrated Cottrell expression [
30]. Thus, the redox marker surface excess (Γ
0) is determined from the difference in chronocoulometric intercepts in the representation of the total charge (Q) as a function of the square root of time (t
1/2) for the identical experiment in the presence and absence of redox marker: Γ
0 = ∆Q/nFA, with n = 1, the number of electrons transferred, F = 96485 C mol
-1, Faraday constant, and A the electrode area in cm
2. Then Γ
DNA, the probe surface density in molecules/cm
2, can be calculated as Γ
DNA = Γ
0 z / m, with m = the number of bases in the probe DNA, and z the charge of the redox molecule.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Morphological Characterization
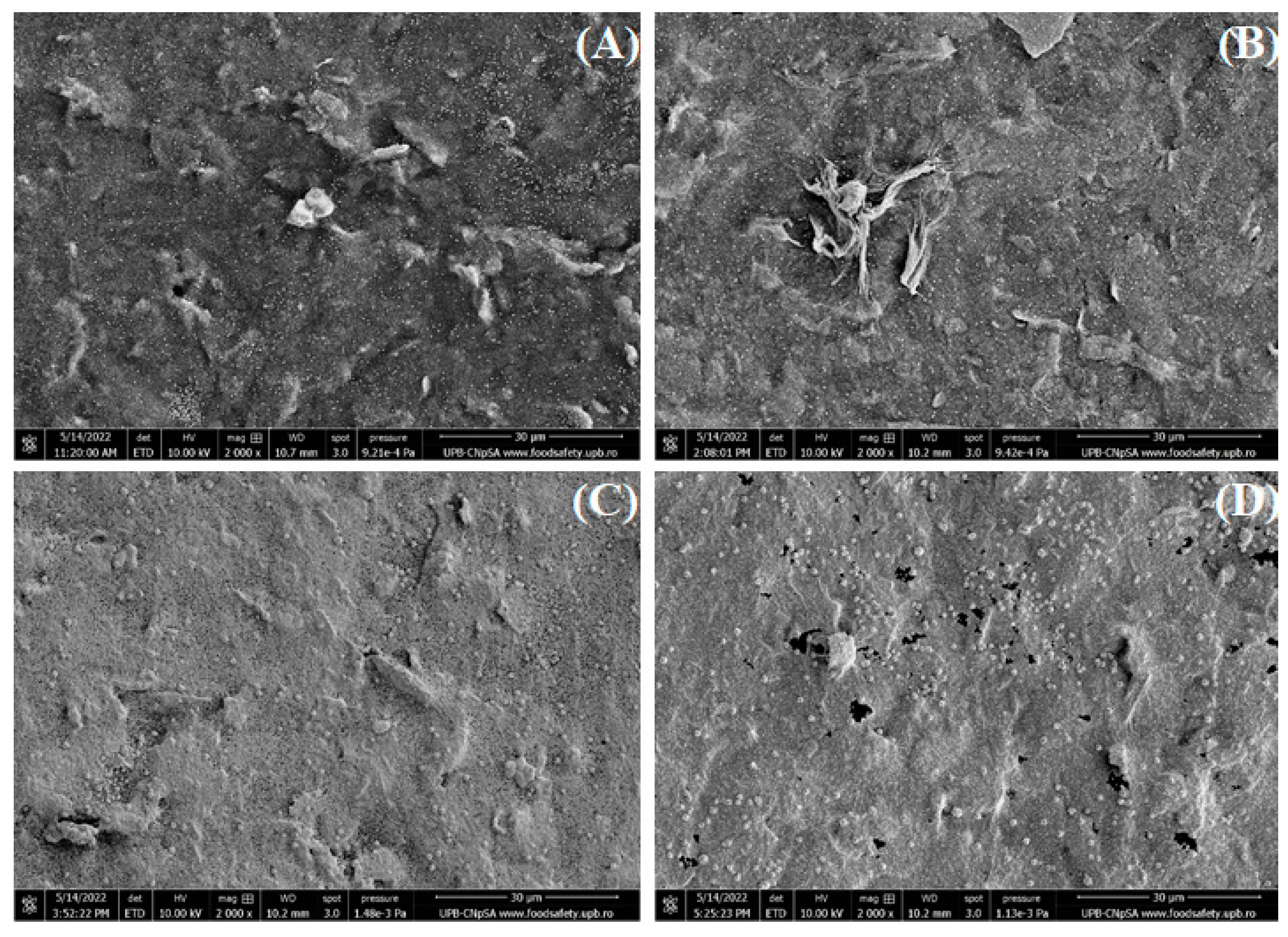
The morphology of the electrodes modified with graphene and different concentrations of gold nanoparticles was investigated by SEM to determine the influence of increasing AuNPs concentration. Several images were recorded at different magnifications and the most representative ones are shown below. First of all, the images are presented at 2000 X magnification (
Figure 1) to observe the coverage of RGO/SPCE with gold nanoparticles. It is easily noticeable that the modified electrode surface is covered with a moderate quantity of 1 mM AuNPs (
Figure 1A) and the RGO sheet can still be observed. When 5 mM HAuCl
4 was used for SPCE modification, more nanoparticles formed on the graphene electrode and are uniformly dispersed on the entire surface (
Figure 1B), while increasing the concentration to 10 mM determined the whole electrode surface to be covered with AuNPs that also show a small tendency for agglomeration (
Figure 1C). Finally, at 15 mM HAuCl
4 the RGO surface is also entirely covered with AuNPs, while small dark patches can also be observed, that seem to be material stripped off the carbon substrate (
Figure 1D).
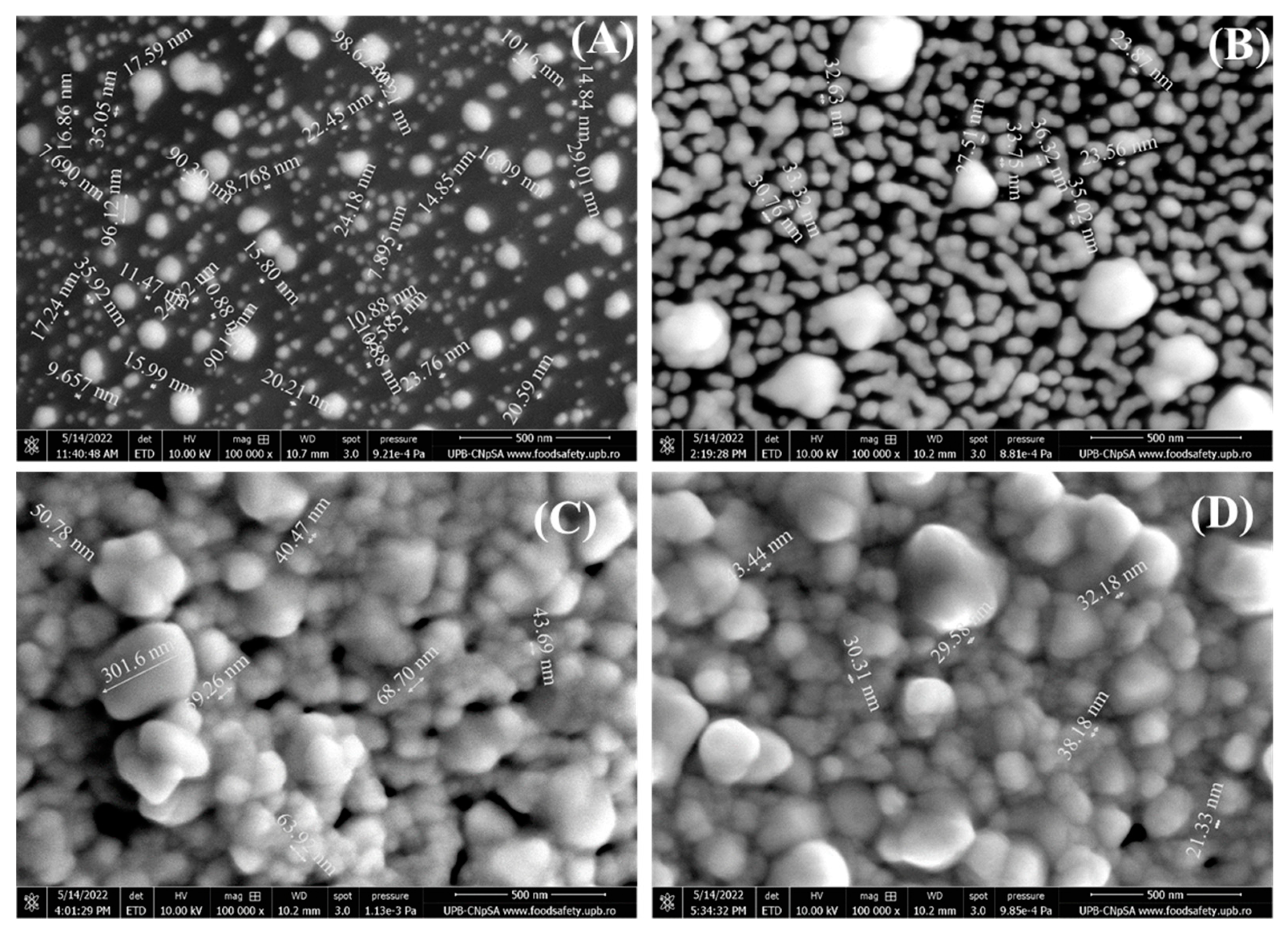
Secondly, the SEM images are also presented at 100000 X magnification (
Figure 2) to better observe the morphology and size of the gold nanoparticles.
Figure 2A shows the SPCE functionalized with 1 mM HAuCl
4 and it is revealed that the RGO substrate is covered with AuNPs between 7 and 90 nm in size. Increasing the concentration to 5 mM (
Figure 2B), the number of nanoparticles increased covering more of the electrode surface and showing nanoparticles of 23-33 nm, but also a few agglomerated ones. At 10 mM (
Figure 2C) and 15 mM (
Figure 2D) the SEM images are very similar, showing that AuNPs covered the entire SPCE surface and that the nanoparticles increase in size (up to 300 nm) and have a higher tendency of agglomeration.
3.2. Structural Characterization
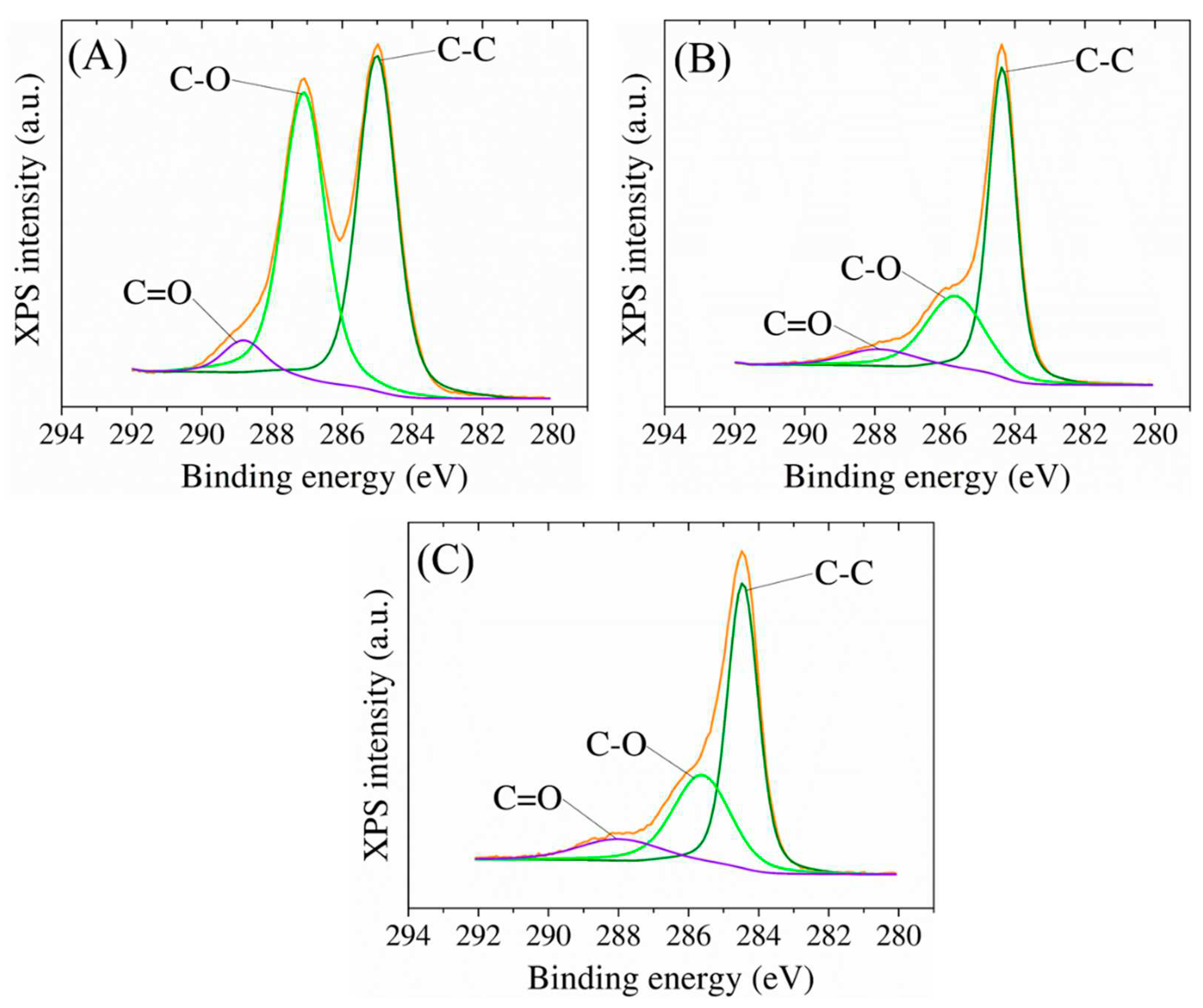
XPS was used to conduct a comprehensive analysis of the elemental composition of the surface of the modified electrodes (
Figure 3). The survey spectra of GO-modified SPCE indicated the presence of carbon and oxygen species, with small amounts of nitrogen detected due to process contamination. The C to O atomic ratio from the XPS survey spectra was used as a reference to assess the presence of oxygenated functional groups in the GO sheets. The assessment revealed that the GO samples had a high percentage of oxygen atoms, as indicated by a C:O ratio value of 2.7. Upon electrochemical reduction, the signals for oxygen-containing functional groups decreased significantly, indicating efficient reduction of GO to RGO. The C:O atomic ratio increased to 6.2 in the RGO samples, indicating that the delocalized π conjugation was partially restored as the relatively low intensity of the C-O peak from 286 eV (
Figure 3A,B) suggests, compared to that obtained from the GO surfaces, which is also consistent with the C:O ratio. Moreover, the addition of gold nanoparticles is confirmed by this characterization technique which shows a content of approximately 10.4% Au on the surface of the electrode and a decrease of the C:O ratio to 5.3 offering an insight about the C:O:Au atomic distribution upon the modified electrode surface.In case of the presence of gold nanoparticles, only a slight shift towards lower binding energies is observed, due to an electropositive electron interaction between RGO and Au as it is translated in the C-C secondary peak position (
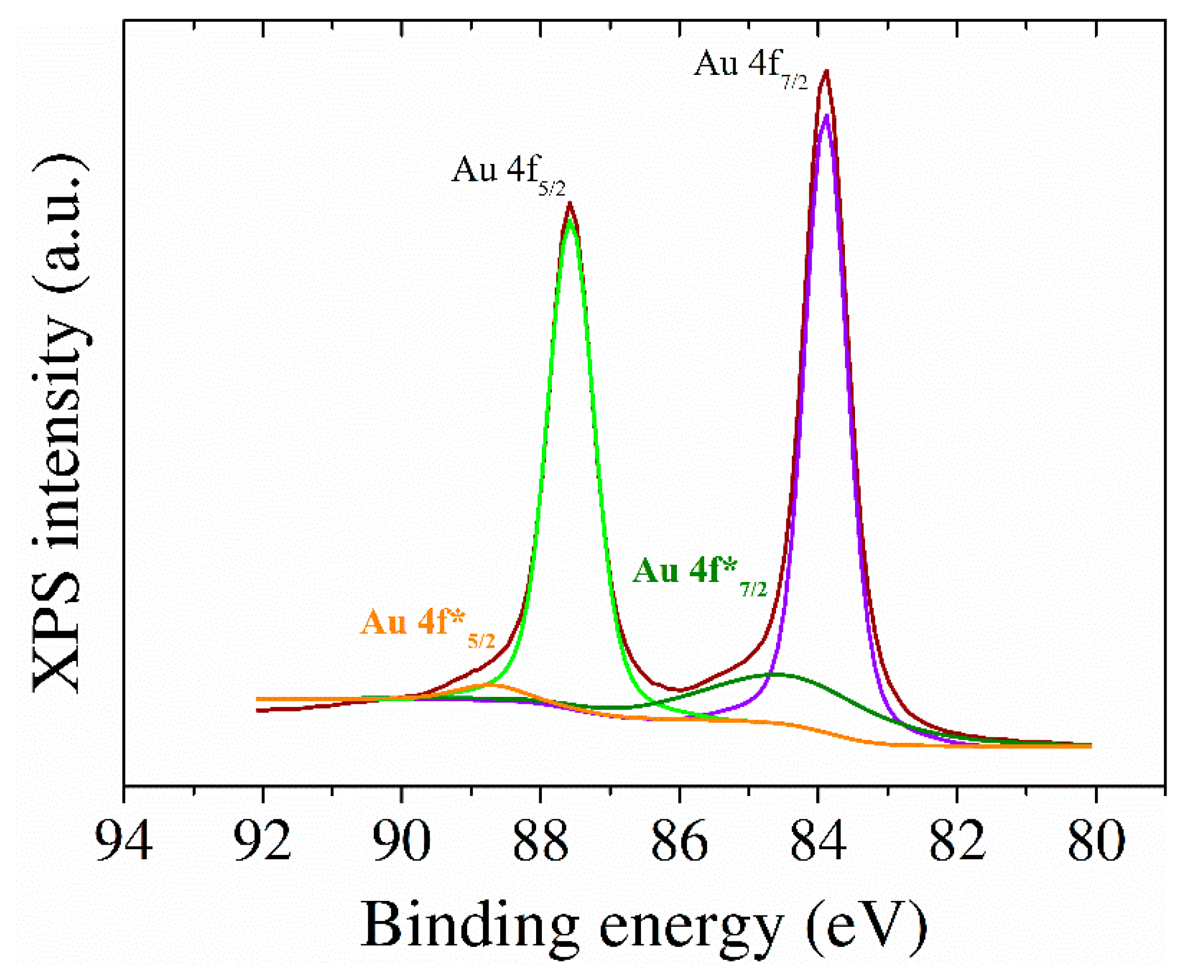
Figure 3C). According to Moulder [
31], the secondary peaks for Au nanoparticles can be assigned to elemental Au 4f energy levels as well as a small part of these Au species were noticed to interact with the aromatic structure of RGO, translated as the Au* 4f shifted bands (
Figure 4).
3.3. Electrochemical Characterization
3.3.1. AuNPs-RGO Functionalized SPCEs
The RGO/SPCEs functionalized with AuNPs, fabricated from HAuCl
4 solutions of different concentrations, have been also investigated electrochemically using cyclic voltammetry (
Figure 5A) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy techniques in the presence of 1 mM [Fe(CN)
6]
3-/4 redox species in 0.1 M KCl solution (
Figure 5B). The CV studies indicate a slight increase in the characteristic peak current intensity for an increase of the HAuCl
4 concentration in the synthesis solution up to 10 mM. As displayed in
Figure 5A, for the electrodes fabricated with 10 and 15 mM HAuCl
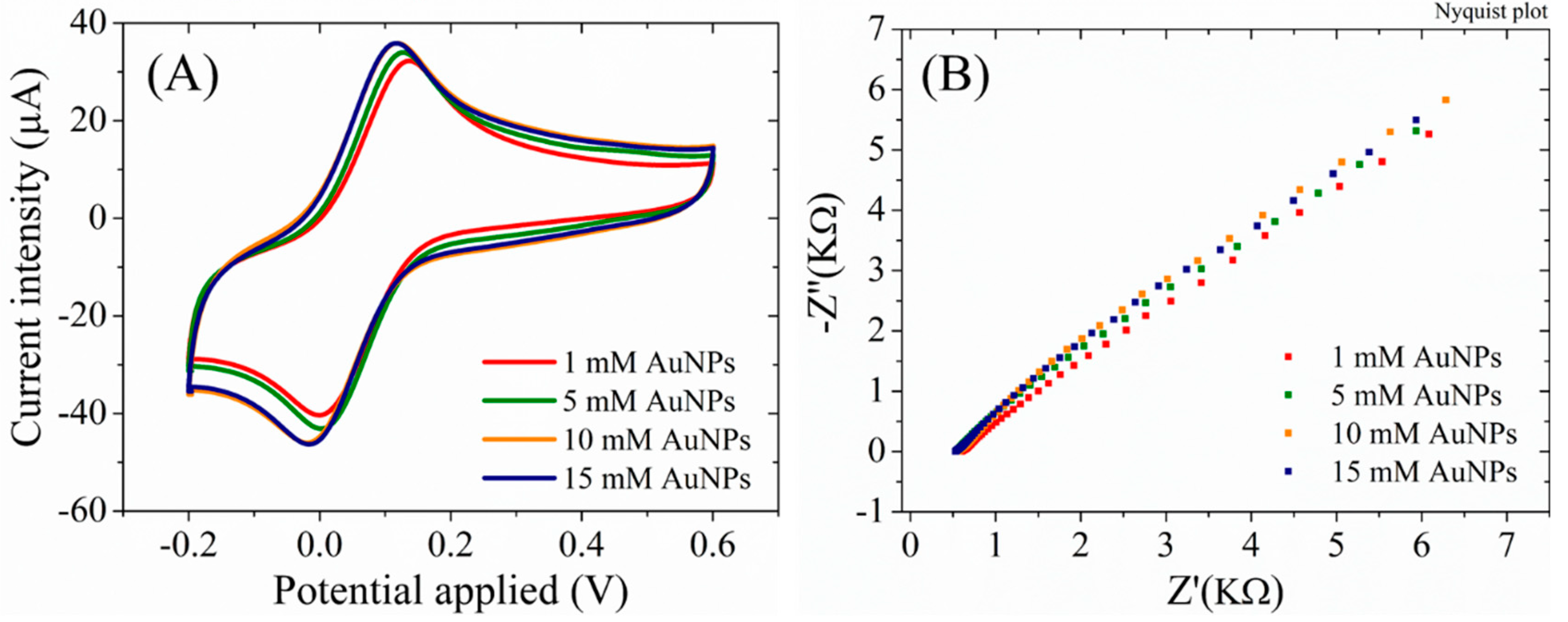
4 the CVs overlap, confirming the SEM results, that indicated a surface completely covered with AuNPs at 10mM, and no further change in the surface properties for higher concentrations. Similarly, the EIS measurements support these results, displaying an absence of the semicircle in the Nyquist plot, indicative of a very low charge transfer resistance (Rct) for all AuNPs-RGO/SPCEs.
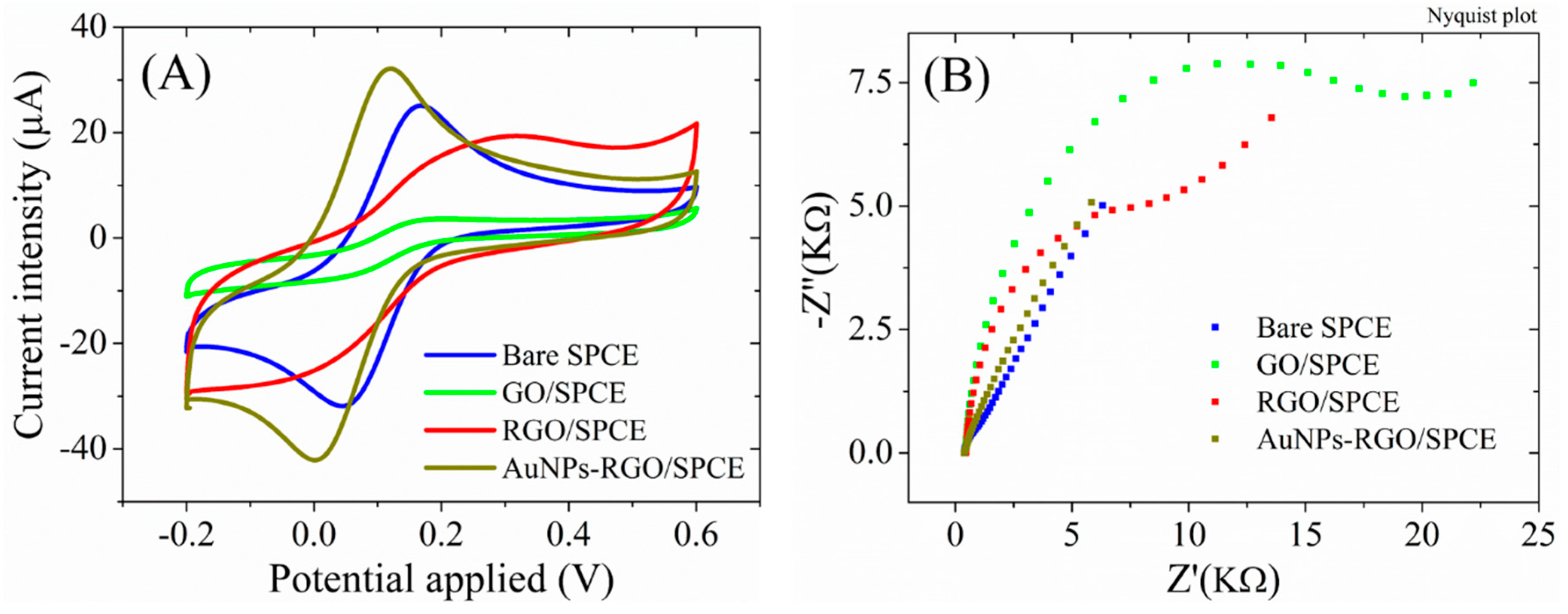
The electrochemical properties were also recorded for each stage of SPCE functionalization. In
Figure 6 we present the typical voltammograms recorded for the tested samples after each modification step. The CV measurements for the bare SPCE in presence of 1mM Fe(CN
6)
3-/4- redox species (
Figure 6A) display well-defined redox peaks with a current intensity of 26.05±0.39 µA and peak-to-peak separation (ΔEp) below 100mV, indicating a good electrical conductivity for this substrate. Deposition of the low conductive GO dispersion induced a substantial change of the CVs, the intensity of the peak currents decreasing down to 3.75±0.16 µA. After the electrochemical reduction of GO, the peak current intensity increases up to 21.11±0.61 µA, while the CVs displayed higher capacitive currents, as expected for electrodes with an increased electrochemical active surface area. Finally, the modification of the RGO surface with gold nanoparticles induced a significant change of the CV shape, with more defined peaks, increased redox signals (reaching 32.61±0.97 µA), and a lower ΔE These characteristics suggest an improved conductivity of the AuNPs-RGO/SPCE modified electrode.
The impedimetric results (
Figure 6B) are in accordance with the CV measurements. While the Nyquist spectrum for the bare SPCE is defined by the presence of Warburg line and a low charge transfer resistance, the electrode modification with GO caused the formation of a large semicircle indicative of a high Rct (15.2±1.8 KΩ), that decreased after the GO electrochemical reduction to 7.7±0.7 KΩ, as a result of the better conductivity of RGO compared to GO. The completely disappearance of the semicircle and the presence of the simple diffusion line for AuNPs-RGO/SPCE, confirms the superior conductivity of the complex graphene-gold nanoparticles.
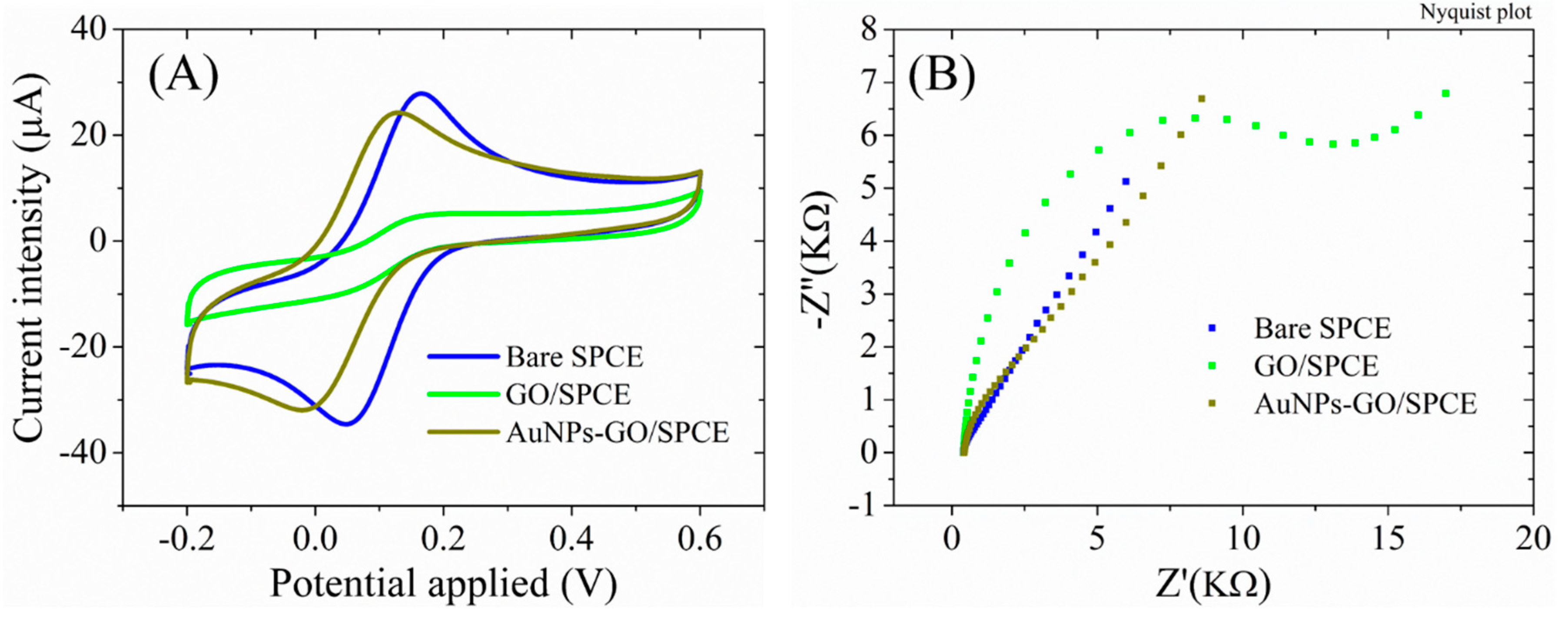
The necessity of GO electrochemical reduction before AuNPs functionalization is revealed by the electrochemical properties of the SPCEs modified with GO dispersion and AuNPs in comparison with AuNPs-RGO/SPCEs. Accordingly, the AuNPs-GO/SPCE system displayed lower peak currents (
Figure 7A), of only 25±0.98 µA, compared to 32.61±0.97 µA previously obtained for AuNPs-RGO/SPCEs. Moreover, a higher impedance was observed for AuNPs-GO/SPCE system in EIS measurements (
Figure 7B), despite the same increase in Rct after modification of bare SPCEs with GO, and the disappearance of the semicircle in the Nyquist plot after the modification with AuNPs (indicating the conductivity improvement).
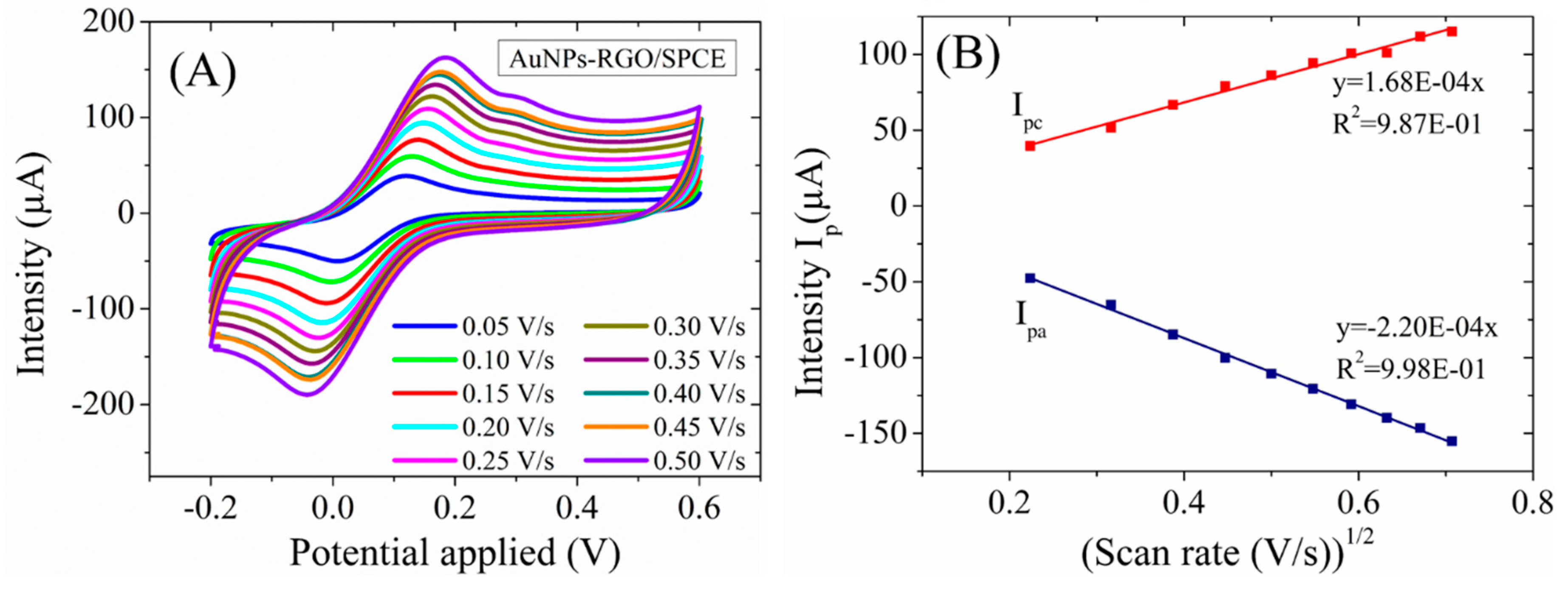
A study of the kinetics of the [Fe(CN)
6]
3-/4- redox probe at the fabricated AuNPs-RGO/SPCE electrodes was also performed. To this end, CV has been performed at various scan rates, ranging from 0.05 to 0.5 V/s (
Figure 8A), and the expected linear relationship with the square root of scan rate is observed (
Figure 8B). This implies a diffusion-controlled oxido-reduction process at the electrode surface, in agreement with the Randles-Sevcik equation for quasi-reversible one-electron transfer processes. The use of Randles-Ševčík equation to accurately determine the real surface area for the electrodes modified with nanomaterials from CV experiments is required to be considered with care [
32,
33], therefore we emphasize that the surface area of AuNPs-GO/SPCE modified electrode determined here to be on average 0.21 cm
2, based on this equation, is only an estimation.
3.3.2. The Characterization and Testing of DNAp/AuNPs-RGO/SPCE Sensing Platform
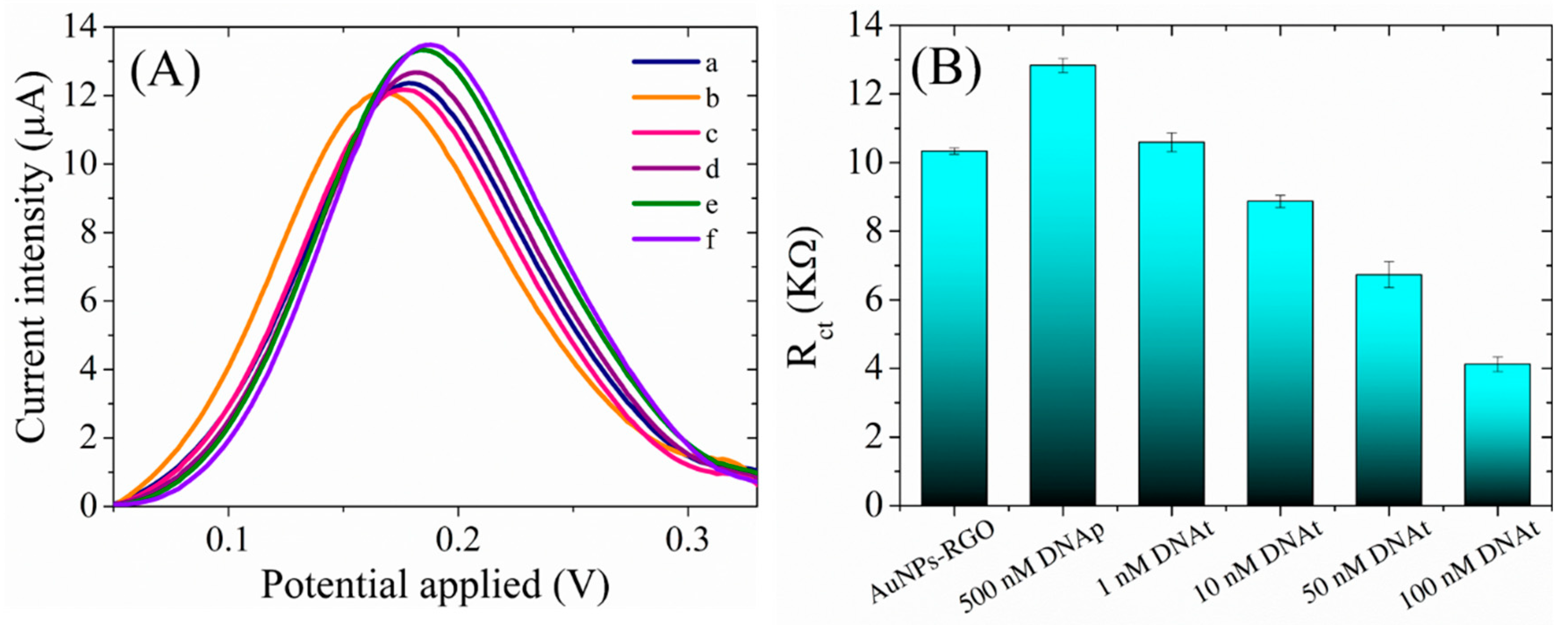
The preparation of the biosensor by the immobilization of the ssDNA probe, as bioreceptor, at the detection interface consisted in the incubation of the AuNPs-RGO/SPCEs with 500 nM ssDNA probe at room temperature, overnight. The hybridization tests, in the presence of the complementary DNA target, were performed by incubating the newly prepared DNAp/AuNPs-RGO/SPCE sensor with different concentrations of DNA target (1 nM – 100 nm) at 42°C for 3 hours.
Figure 9 displays the change in the electrochemical properties of the interface after each step in the preparation and testing of the final sensor, tested in a solution containing 1 mM [Fe(CN)
6]
3-/4- redox species in 0.1M KCl. Accordingly, a first decrease in the oxidation peak current was observed after DNA probe immobilization, which is to be expected due to the fact that the oligonucleotide is a large molecule that blocks the electron transfer between the electrolyte solution and electrode surface (
Figure 9A). Next, the incubations of the sensor with 1 nM, 10 nM, 50 nM, and 100 nM DNA target determined successive increase in current intensity, that can be explained by the formation of dsDNA with each addition of DNA target. In agreement with the previous findings [
34], we may assume that the newly formed dsDNA easily detaches from the surface, by this favoring the redox process of [Fe(CN)
6]
3-/4- species. The impedimetric measurements (
Figure 9B) were in agreement with the CV results, and showed an increase in Rct following the adsorption of the DNA probe at AuNPs-RGO/SPCE interface, that impede the redox process of the negatively charged [Fe(CN)
6]
3-/4-. Moreover, as expected from the CV results, the hybridization with DNA target determined a decrease in Rct for each successive addition up to 100 nM. Both the increase in the anodic oxidation current, and the decrease of the charge transfer resistance imply changes in the heterogeneous electron transfer of [Fe(CN)
6]
3-/4- at the sensing interface as a result of the hybridization process, that can be exploited in DNA detection.
The specificity of the biosensor was also demonstrated by control experiments using a non-complimentary oligonucleotide. Thus the incubation of DNAp-AuNPs-RGO/SPCE with non-complementary DNA induced negligible change in the electrochemical signal, both in CV (0.3 μA increase in current intensity for ncDNA, in comparison with 4.4 μA for DNAt) and EIS (0.32 kΩ for ncDNA, in comparison with 8.26 kΩ for DNAt) for 100 nM concentration of DNA. The subsequently addition, in the same experiment, of the complementary DNA target, determined a predictable increase in the current intensity in CV, and Rct decrease in EIS, suggesting that the detection platform can discriminate between specific DNA sequences.
3.3.3. Chronoculometry Measurements
The surface density of DNA modified electrodes can be quantified using chronocoulometry, by taking advantage of the electrostatic attraction between specific redox cations added in the test solution, and the nucleotide phosphate backbone of DNA. Redox molecules can interact with DNA through either electrostatic attraction or intercalation, and the nature of the interaction is often influenced by the ionic strength and molecular structure of the redox molecule [
30]. Therefore, in order to perform the measurement, the DNA-modified electrodes were placed in a low-ionic-strength electrolyte solution (TRIS 10 mM, pH = 7.4) containing 100 μM Ru(NH
3)
63+ cationic redox marker. The redox cations in the solution replace the native counterions that are associated with the nucleotide phosphate residues of the DNA probe, and the amount of redox marker that attaches electrostatically to the DNA-modified electrode is then determined using chronocoulometry. When the redox marker reaches saturation coverage, the surface density of the DNA probe is calculated by assuming that the DNA phosphate residues are completely compensated by the redox cations. This approach is advantageous because it is insensitive to variations in base composition and chain order (single-stranded versus duplex), unlike other non-covalent labeling techniques [
35]. The system is observed under equilibrium conditions, so that the electrodes have been immersed in the deaerated buffer solution, and maintained 10 minutes under stirring, for equilibration, before performing the chronocoulometric test. The DNA surface coverages were calculated using the established method reported by Steel et al. [
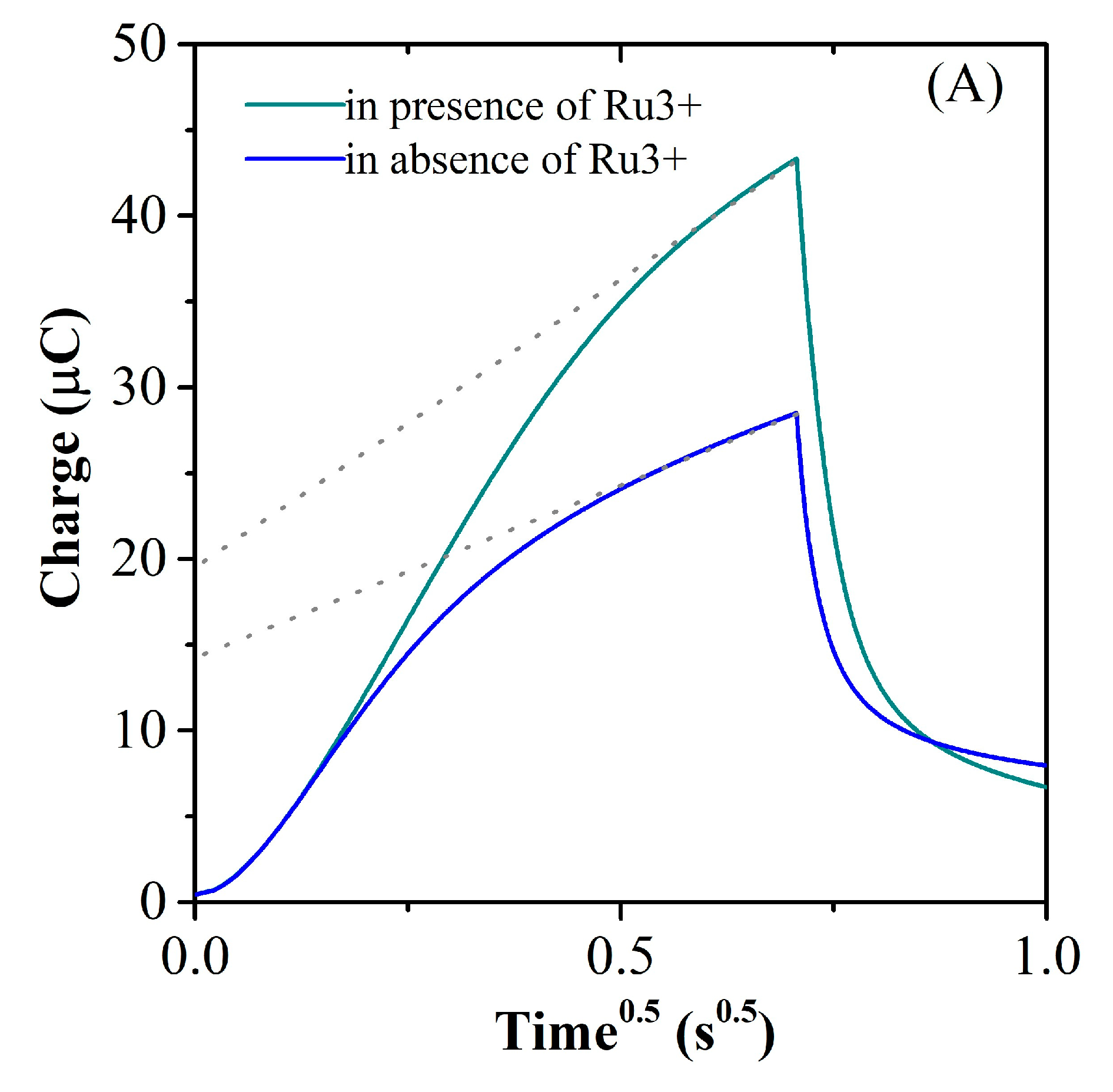
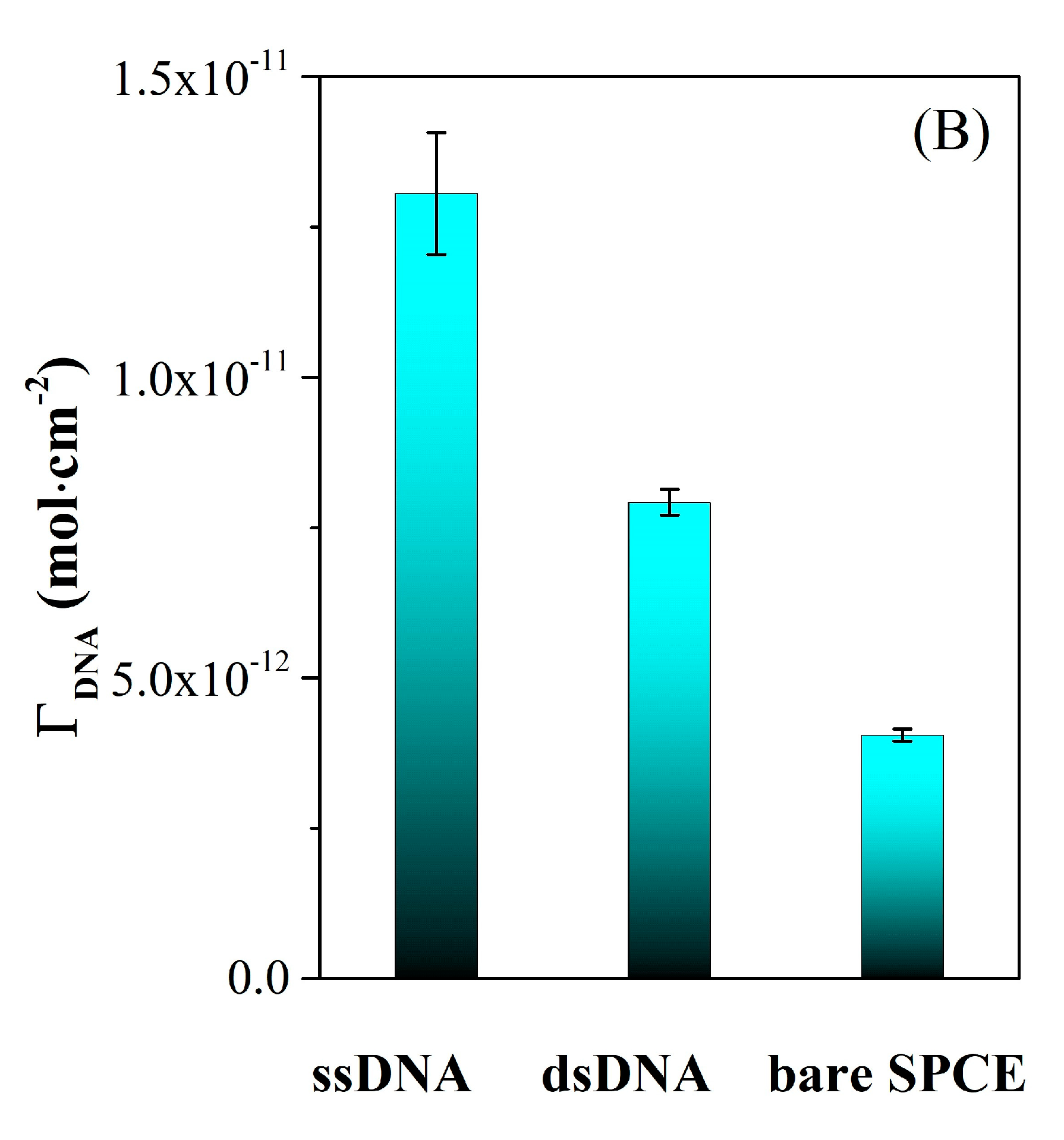
30]. Thus, in
Figure 10A is presented the typical chronocoulometric response that affords the calculation of the surface concentration of the oligonucleotide present at the electrode from the difference in chronocoulometric intercepts (nFAΓ
0), assuming that for the measurements performed both in absence and in presence of Ru(NH
3)
63+ the double layer capacitance has the same value. Considering a complete charge compensation of DNA by redox marker, the conversion of the calculated Γ
0 to DNA surface density (Γ
DNA) was made as indicated in the Experimental part, and the Γ
DNA values before (ssDNA), and after hybridization with 100nM DNAt (dsDNA) are presented in
Figure 10B. The results correlate well with the CV and EIS data presented previously, and demonstrate the removal from the electrode surface of the hybridized dsDNA after DNA target addition.
4. Conclusions
A simple, cost-effective biosensor employing AuNPs-RGO nanocomposite as transducing interface was developed for the direct detection of DNA hybridization. The electrochemical platform has a good sensitivity, being able to detect DNA molecules as low as 1 nM, and can also discriminate between complementary and non-complementary DNA. The detection of DNA hybridization was demonstrated by several electrochemical techniques, such as CV, EIS, and chronocoulometry. The results obtained in this work can pave the way towards fabrication of DNA biosensors at industrial scale with applicability in various medical applications due to the high biocompatibility and stability of graphene functionalized with gold nanoparticles.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.A.C. and L.P.; methodology, E.A.C. and L.P.; validation, M.I. and L.P.; formal analysis, E.A.C, C.M.D., and L.P.; investigation, E.A.C., L.P. and C.M.D.; resources, M.I.; writing—original draft preparation, E.A.C.; writing—review and editing, L.P.; supervision, M.I.; project administration, M.I.; funding acquisition, M.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant of the Ministry of Research, Innovation and Digitization, Executive Agency for Higher Education, Research, Development and Innovation, project number PCE 103/2022 (REOSTEOKIT) and by Ministry of Research and Innovation, Operational Program Competitiveness Axis 1 - Section E, Program co-financed from European Regional Development Fund "Investments for your future" under the project number 154/25.11.2016, P_37_221/2015, “A novel graphene biosensor testing osteogenic potency; capturing best stem cell performance for regenerative medicine” (GRABTOP).
Acknowledgments
Elena Alina Chiticaru acknowledges the financial support from Project SMART (13530/16.06.2022 - SMIS code: 153734).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Roy, L.; Buragohain, P.; Borse, V. Strategies for sensitivity enhancement of point-of-care devices. Biosens. Bioelectron.:X 2022, 10, 100098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stranieri, A.; Venkatraman, S.; Minicz, J.; Zarnegar, A.; Firmin, S.; Balasubramanian, V.; Jelinek, H.F. Emerging point of care devices and artificial intelligence: Prospects and challenges for public health. Smart Health 2022, 24, 100279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, L.C.; Santos, A.; Bueno, P.R. An outlook on electrochemical approaches for molecular diagnostics assays and discussions on the limitations of miniaturized technologies for point-of-care devices. Sensors and Actuators Reports 2022, 4, 100087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lino, C.; Barrias, S.; Chaves, R.; Adega, F.; Martins-Lopes, P.; Fernandes, J.R. Biosensors as diagnostic tools in clinical applications. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Cancer 2022, 1877, 188726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahshid, S.S. Electrochemical Immuno-Biosensors on Nanostructured Electrodes for Rapid Sensitive Detection of Disease Biomarkers. ECS Meet. Abstr. MA 2021, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Su, W.; Liu, S.; Huang, C.; Ghalandari, B.; Divsalar, A.; Ding, X. Recent Progresses in Electrochemical DNA Biosensors for MicroRNA Detection. Phenomics 2022, 2, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Shang, D.; Gao, S.; Wang, B.; Kong, H.; Yang, G.; Shu, W.; Xu, P.; Wei, G. Two-Dimensional Material-Based Electrochemical Sensors/Biosensors for Food Safety and Biomolecular Detection. Biosensors 2022, 12, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.S.; et al. Perspectives and trends in advanced DNA biosensors for the recognition of single nucleotide polymorphisms. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 441, 135988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, Q.u.A.; Fang, X.; Luo, Z.; Ullah, S.; Fatima, S.; Batool, S.; Qiu, B.; Shahzad, F. Graphene Based Nanohybrid Aptasensors in Environmental Monitoring: Concepts, Design and Future Outlook. Crit Rev Anal Chem 2022, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilge, S.; Dogan-Topal, B.; Gürbüz, M.M.; Yücel, A.; Sınağ, A.; Ozkan, S.A. Recent advances in electrochemical sensing of cocaine: A review. Trends Analyt Chem 2022, 157, 116768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amărandi, R.-M.; Becheru, D.F.; Vlăsceanu, G.M.; Ioniță, M.; Burns, J.S. Advantages of Graphene Biosensors for Human Stem Cell Therapy Potency Assays. Biomed Res Int 2018, 2018, 1676851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Narváez, E.; Baptista-Pires, L.; Zamora-Gálvez, A.; Merkoçi, A. Graphene-Based Biosensors: Going Simple. Adv Mater 2017, 29, 1604905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, N.; Maekawa, T.; Kumar, D.N.S. Graphene based biosensors—Accelerating medical diagnostics to new-dimensions. J. Mater. Res. 2017, 32, 2860–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janegitz, B.C.; Silva, T.A.; Wong, A.; Ribovski, L.; Vicentini, F.C.; Taboada Sotomayor, M.d.P.; Fatibello-Filho, O. The application of graphene for in vitro and in vivo electrochemical biosensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriakides, T.R.; Raj, A.; Tseng, T.H.; Xiao, H.; Nguyen, R.; Mohammed, F.S.; Halder, S.; Xu, M.; Wu, M.J.; Bao, S.; et al. Biocompatibility of nanomaterials and their immunological properties. Biomed Mater 2021, 16, 042005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucherenko, I.S.; Soldatkin, O.O.; Kucherenko, D.Y.; Soldatkina, O.V.; Dzyadevych, S.V. Advances in nanomaterial application in enzyme-based electrochemical biosensors: a review. Nanoscale Adv 2019, 1, 4560–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolson, F.; Ali, A.; Kircher, M. F.; Pal, S. DNA Nanostructures and DNA-Functionalized Nanoparticles for Cancer Theranostics. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2001669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamalipour Soufi, G.; Iravani, S. Eco-friendly and sustainable synthesis of biocompatible nanomaterials for diagnostic imaging: current challenges and future perspectives. Green Chem 2020, 22, 2662–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Lin, Y. Graphene and graphene oxide: biofunctionalization and applications in biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol 2011, 29, 205–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tang, J.; Gooding, J.J. Strategies for chemical modification of graphene and applications of chemically modified graphene. J. Mater. Chem 2012, 22, 12435–12452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Goo, N.-I.; Kim, D.-E. Mechanism of DNA Adsorption and Desorption on Graphene Oxide. Langmuir 2014, 30, 12587–12595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferapontova, EE. DNA Electrochemistry and Electrochemical Sensors for Nucleic Acids. Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto Calif). 2018, 11, 197–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ielo, I.; Rando, G.; Giacobello, F.; Sfameni, S.; Castellano, A.; Galletta, M.; Drommi, D.; Rosace, G.; Plutino, M.R. Synthesis, Chemical–Physical Characterization, and Biomedical Applications of Functional Gold Nanoparticles: A Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, T.; Huang, J.; Wang, D.; Meng, T.; Yang, X. Au and Au-Based nanomaterials: Synthesis and recent progress in electrochemical sensor applications. Talanta 2020, 206, 120210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evers, M.V.; Bernal, M.; Roldan Cuenya, B.; Tschulik, K. Piece by Piece—Electrochemical Synthesis of Individual Nanoparticles and their Performance in ORR Electrocatalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 8221–8225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsabadi, A.S.; Tavanai, H.; Ranjbar, M.; Farnood, A.; Bazarganipour, M. Electrochemical non-enzymatic sensing of glucose by gold nanoparticles incorporated graphene nanofibers. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 24, 100963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Rothberg, L. Colorimetric detection of DNA sequences based on electrostatic interactions with unmodified gold nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2004, 101, 14036–14039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbunova, E.A.; Epanchintseva, A.V.; Pyshnyi, D.V.; Pyshnaya, I.A. Noncovalent Adsorption of Single-Stranded and Double-Stranded DNA on the Surface of Gold Nanoparticles. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiticaru, E.A.; Pilan, L.; Damian, C.-M.; Vasile, E.; Burns, J.S.; Ioniţă, M. Influence of Graphene Oxide Concentration when Fabricating an Electrochemical Biosensor for DNA Detection. Biosensors 2019, 9, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, A.B.; Herne, T.M.; Tarlov, M.J. Electrochemical Quantitation of DNA Immobilized on Gold. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 4670–4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulder, J.F.; Stickle, W.F.; Sobol, W.M.; Bomben, K.D. Handbook of X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy. 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Bogdanowicz, R.; Ficek, M.; Malinowska, N.; Gupta, S.; Meek, R.; Niedziałkowski, P.; Rycewicz, M.; Sawczak, M.; Ryl, J.; Ossowski, T. Electrochemical performance of thin free-standing boron-doped diamond nanosheet electrodes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 862, 114016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paixão, T.R.L.C. Measuring Electrochemical Surface Area of Nanomaterials versus the Randles−Ševčík Equation. ChemElectroChem 2020, 7, 3414–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbunova, E.A.; Epanchintseva, A.V.; Pyshnyi, D.V.; Pyshnaya, I.A. Noncovalent Adsorption of Single-Stranded and Double-Stranded DNA on the Surface of Gold Nanoparticles. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piehler, J.; Brecht, A.; Gauglitz, G.; Zerlin, M.; Maul, C.; Thiericke, R.; Grabley, S. Label-Free Monitoring of DNA–Ligand Interactions. Anal. Biochem. 1997, 249, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
SEM images recorded at 2 kX magnification for RGO/SPCEs functionalized with AuNPs from (A) 1 mM, (B) 5 mM, (C) 10 mM, and (D) 15 mM HAuCl4 solutions in 0.5 mM H2SO4.
Figure 1.
SEM images recorded at 2 kX magnification for RGO/SPCEs functionalized with AuNPs from (A) 1 mM, (B) 5 mM, (C) 10 mM, and (D) 15 mM HAuCl4 solutions in 0.5 mM H2SO4.
Figure 2.
SEM images recorded at 100 kX magnification for RGO/SPCEs functionalized with AuNPs from (A) 1 mM, (B) 5 mM, (C) 10 mM, and (D) 15 mM HAuCl4 solutions in 0.5 mM H2SO4.
Figure 2.
SEM images recorded at 100 kX magnification for RGO/SPCEs functionalized with AuNPs from (A) 1 mM, (B) 5 mM, (C) 10 mM, and (D) 15 mM HAuCl4 solutions in 0.5 mM H2SO4.
Figure 3.
High-resolution C1 XPS spectra of bare SPCE modified with (A) GO, (B) RGO, and (C) AuNPs.
Figure 3.
High-resolution C1 XPS spectra of bare SPCE modified with (A) GO, (B) RGO, and (C) AuNPs.
Figure 4.
High resolution XPS Au 4f spectra of SPCE modified with RGO and AuNPS.
Figure 4.
High resolution XPS Au 4f spectra of SPCE modified with RGO and AuNPS.
Figure 5.
(A) CV and (B) EIS Nyquist plot recorded in 1 mM [Fe(CN)6]3-/4-, 0.1M KCl, for RGO/SPCE functionalized with AuNPs from 1 mM, 5 mM, 10 mM, and 15 mM HAuCl4 solutions in 0.5 mM H2SO4.
Figure 5.
(A) CV and (B) EIS Nyquist plot recorded in 1 mM [Fe(CN)6]3-/4-, 0.1M KCl, for RGO/SPCE functionalized with AuNPs from 1 mM, 5 mM, 10 mM, and 15 mM HAuCl4 solutions in 0.5 mM H2SO4.
Figure 6.
(A) CV and (B) EIS Nyquist plot recorded in 1 mM [Fe(CN)6]3-/4-, 0.1M KCl, for bare SPCE, GO/SPCE, RGO/SPCE, and AuNPs-RGO/SPCE.
Figure 6.
(A) CV and (B) EIS Nyquist plot recorded in 1 mM [Fe(CN)6]3-/4-, 0.1M KCl, for bare SPCE, GO/SPCE, RGO/SPCE, and AuNPs-RGO/SPCE.
Figure 7.
(A) CV and (B) EIS Nyquist plot recorded in 1 mM [Fe(CN)6]3-/4-, 0.1M KCl, for bare SPCE, GO/SPCE, and AuNPs-GO/SPCE.
Figure 7.
(A) CV and (B) EIS Nyquist plot recorded in 1 mM [Fe(CN)6]3-/4-, 0.1M KCl, for bare SPCE, GO/SPCE, and AuNPs-GO/SPCE.
Figure 8.
(A) CV curves of AuNPs-RGO/SPCE at different scan rates in 1mM [Fe(CN)6]3-/4- solution with 0.1M KCl. (B) Plot of anodic and cathodic peaks current vs. square root of scan rates.
Figure 8.
(A) CV curves of AuNPs-RGO/SPCE at different scan rates in 1mM [Fe(CN)6]3-/4- solution with 0.1M KCl. (B) Plot of anodic and cathodic peaks current vs. square root of scan rates.
Figure 9.
(A) Anodic peaks in CV (after baseline correction) recorded in 1 mM [Fe(CN)6]3-/4-, 0.1M KCl, for (a) AuNPs-RGO/SPCE modified with (b) 500 nM DNA probe and hybridized with (c)1 nM, (d) 10 nM, (e) 50 and (f) 100 nM DNA target. (B) Charge transfer resistance recorded by EIS in 1 mM [Fe(CN)6]3-/4-, 0.1M KCl, for AuNPs-RGO/SPCE modified with 500 nM DNA probe and hybridized with 1 nM, 10 nM, 50 and 100 nM DNA target.
Figure 9.
(A) Anodic peaks in CV (after baseline correction) recorded in 1 mM [Fe(CN)6]3-/4-, 0.1M KCl, for (a) AuNPs-RGO/SPCE modified with (b) 500 nM DNA probe and hybridized with (c)1 nM, (d) 10 nM, (e) 50 and (f) 100 nM DNA target. (B) Charge transfer resistance recorded by EIS in 1 mM [Fe(CN)6]3-/4-, 0.1M KCl, for AuNPs-RGO/SPCE modified with 500 nM DNA probe and hybridized with 1 nM, 10 nM, 50 and 100 nM DNA target.
Figure 10.
(A) Typical chronocoulometric curves illustrated for dsDNA/AuNPs-RGO/SPCE electrodes using 100 μM Ru(NH3)3+ as redox indicator. (B) The calculated oligonucleotides surface density before (ssDNA), and after hybridization with 100 nM DNAt (dsDNA) suggesting the formation of dsDNA after DNA target addition, with lower affinity for the modified SPCE surface.
Figure 10.
(A) Typical chronocoulometric curves illustrated for dsDNA/AuNPs-RGO/SPCE electrodes using 100 μM Ru(NH3)3+ as redox indicator. (B) The calculated oligonucleotides surface density before (ssDNA), and after hybridization with 100 nM DNAt (dsDNA) suggesting the formation of dsDNA after DNA target addition, with lower affinity for the modified SPCE surface.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).