1. Introduction
Graphs are commonly used to model networks of any kind; a node in a graph may represent a protein in a protein interface network with interactions represented by edges, a router in a computer network with edges showing the links between the routers, a person in a social network with edges displaying friendships or a node may show a Web page with edges assigned as hyperlinks between the pages.
Biological networks have genes, proteins, DNA, RNA and metaboltites as their nodes and the edges show interactions such as biochemical reactions between the nodes in such networks. At a coarser level, a brain functional network is modeled by a graph showing the interactions between functional regions of he brain. The biological networks at moleculer level are large, consisting of thousands of nodes and tens of thousands of edges between the nodes, and are considered as a class of networks called complex networks. These networks exhibit some interesting properties: they have few nodes with many connections to other nodes where the rest of the nodes have very few connections. This so called scale-free networks also have small diameters with a reatively small number of hops between two farthest nodes and are called small-world networks for this reason . Contemporary areas of research studies in biological networks may be classified as follows:
Topological Analysis: This analysis is based on topological properties of the network providing information to be used in further analysis decsribed in the next sections.
Clustering: This is the process of discovering dense regions of a biological network which may indicate important activity for the survival of the organism or sometimes disease states.
Network Motifs: These are frequently repeating subgraph patterns in biological networks which may indicate some specific function performed by them.
Network Alignment: The alignment of two networks shows the similarity between them which may be used to deduce hereditary relationships. This affinity may help to discover comserved regions in organisms to aid understanding the evolutionary process.
Analysis of biological networks is imperative for a number of reasons; firstly, it may provide insight to the functioning of organisms to aid understanding life better. Finding cures for diseases, designing drug therapies all need data obtained from these analyses. Graphs are increasingly used for qualitative analysis of biological networks and many results from graph theory and graph algorithms can be conveniently used to obtain imperative results for the mainstream problems in medicine to help provide better and healthy life. In this survey, we review the research studies by first reviewing the backgrounds of three distinct areas of graph-theoretic analysis of biological networks outlined above; graph clustering, network motif search and network alignment.
2. Biological Networks
Biological processes may be conveniently modeled by networks with nodes representing biological entities and the connections between the nodes showing the interactions between the entities. Analysis of these networks provides insight to their structure which may help develop therapeutic treatment procedures for complex diseaeses such as cancer [
66], schizophrenia [
10,
36] and Parkinson’s disease. Biological networks are basically of two kinds: networks in the cell and networks outside the cell, the latter comprising diverse examples of such networks.
Biological networks are dynamic, changing and evolving with time, which makes their analysis difficult. These networks are very large preventing their precise analysis as a whole network in general.
Random sampling is commonly used to analyse samples obtained from a large network and estimate its approximate structure and functionality based on these samples [
15].
2.1. Networks In the Cell
The main networks in the cell can be classified as follows.
Protein Networks: Proteins are the workhorses of the cell performing vital functions of organisms. A protein is basically a sequence of amino acids contsructed by the code in a gene which is part of the DNA. The 3-D structure of a protein plays an important role in its function which various drug treatment methods use this property to disable functioning of a disease causing virus such as the HIV. A protein interacts with various other proteins through bio-chemical reactions forming a protein-protein-interaction (PPI) network. Nodes with high degrees in a PPI network has fundamental functions in the cell [
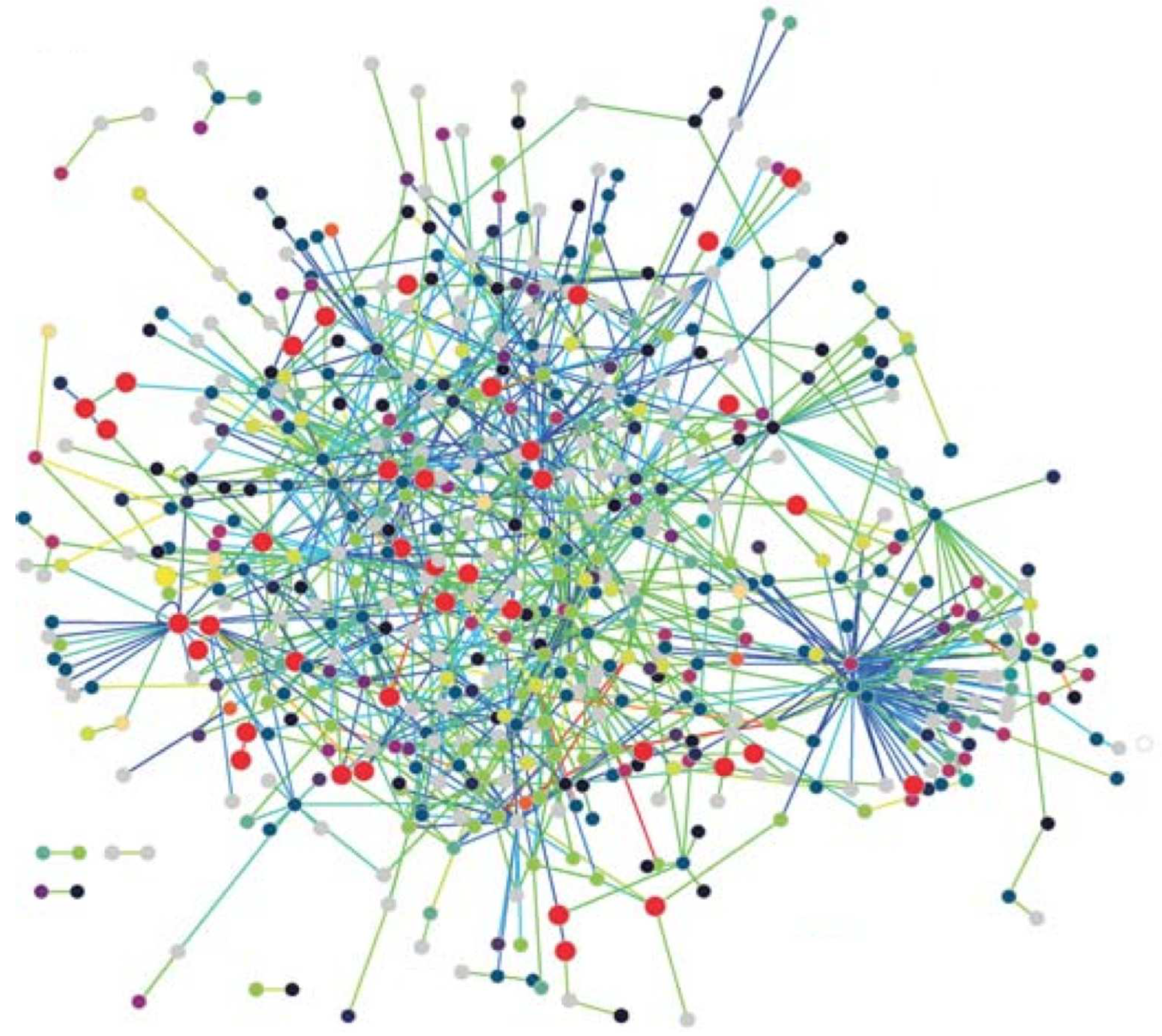
23]. The PPI network of T. pallidum is depicted in
Figure 1 where proteins involved in DNA metabolism are shown as enlarged red circles.
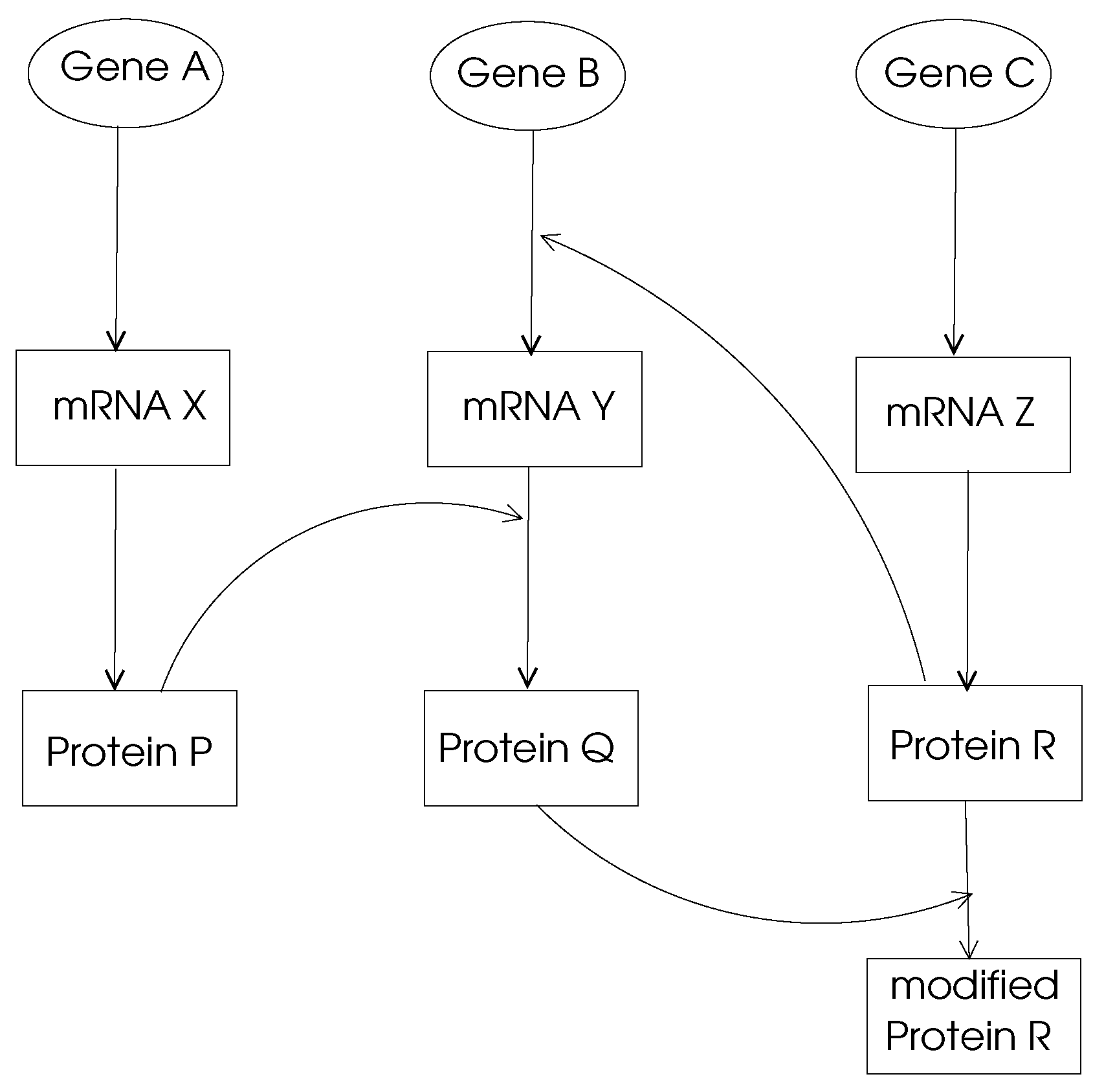
Gene Regulation Networks:The main function of a gene in DNA is to provide the code to be used through transcription and translation processes to produce a protein. This process is called
gene expression and the mechanism of a specific gene expression is controlled and affected by proteins coded by other genes denoted
regularity interactions. For example, gene
X regulates gene
Y if a change in expression of gene
X results in a change in the expression of gene
Y. A gene regulation network (GRN) is made of genes, proteins and various other molecules which may be modeled by a directed graph with nodes representing these entities and the edges showing their biochemical interactions leading to regulations as shown in
Figure 2. Typically, a GRN is a sparse graph with small world and power-law properties, which means there are only few nodes that have very high out-degrees which regulate other gene expressions. Moreover, the distance between any two nodes in a GRN network is small compared to the size of the network as consistent with small-world properties.
Metabolic Pathways: The main ingredients of the cell such as sugars, amino acids and lipids are produced by the basic chemical system called
metabolism that work on ingedients called
metabolites. The biochemical reactions in the cell that result in metabolisms can be modeled by directed or undirected graphs with nodes representing metabolites and edges showing biochemical reactions which transform one metabolite to another one [
22,
60,
64]. An edge in such a graph may also represent an enzyme that catalyzes a biochemical reaction. An undirected edge in the graph model denotes a reversible reaction where a directed edge means an irreversible one. A
metabolic pathway is a sequence of biochemical reactions to perform a specific metabolic function. An example of a metabolic function is glycolysis in which a glucose molecule is divided into two sugars which generate adenosine triphosphates (ATPs) to produce energy. Graphs representing metabolic pathways have the small-world and scale-free properties. Study of metabolic pathways may provide insight into pathogens causing infections in search of cures for diseases [
26].
2.2. Networks Outside the Cell
Biological networks outside the cell are of following types.
Brain Networks: We can analyse brain networks at cell (neuron) level or at a coarser functional level. A neuron in the brain fires when the sum of its input signal strengths exceeds a thershold. A neural network made of neurons performs various cognitive tasks such as problem solving, reasoning and image processing. The artificial neural networks function similar to biological neural networks and have been used widely to implement various tasks in deep learning which is a component of machine learning to be used for artificial intelligence tasks. At a coarser level, we can investigate the functions performed by the brain using
brain structural networks (BSNs) or
brain functional networks (BFNs). A BSN basically reflects the structures of neural connections whereas a BFN models the connnectedness of the functional regions of the brain. Studies of BFNs have shown that these networks are also small-world and scale-free networks like most of the biological networks [
62].
Phylogenetic Networks: A phylogenetic tree shows evolutionary relationships among organisms with leaves representing living organisms and the intermediate nodes their common ancestors. A phylogenetic network is the general form of a phylogenetic tree where a node may have more than one parent.
The Food Chain: Living organisms rely on food for survival. The food chain directed graph shows the relationships between the predators and preys where the direction of an edge is from the predator to the prey.
3. Large Graph Analysis
Large graphs representing biological networks can be analysed using their local properties focusing on nodes and their neighbors or global properties which consider the network as a whole. We will investigate some useful local properties of large graphs and use them to arrive at global properties in this section.
3.1. Degree Distribution
The degree distribution of a graph displays the percentage of vertices with a given degree which may give an insight to the structure of the graph.
Definition 1 (degree distribution). The degree distribution of a given degree k in a graph G is the ratio of the number of vertices with degree k to the total number of vertices.
The degree distribution displays the probability of a randomly selected vertex to have a degree
k. Formally,
where
is the number of vertices with degree
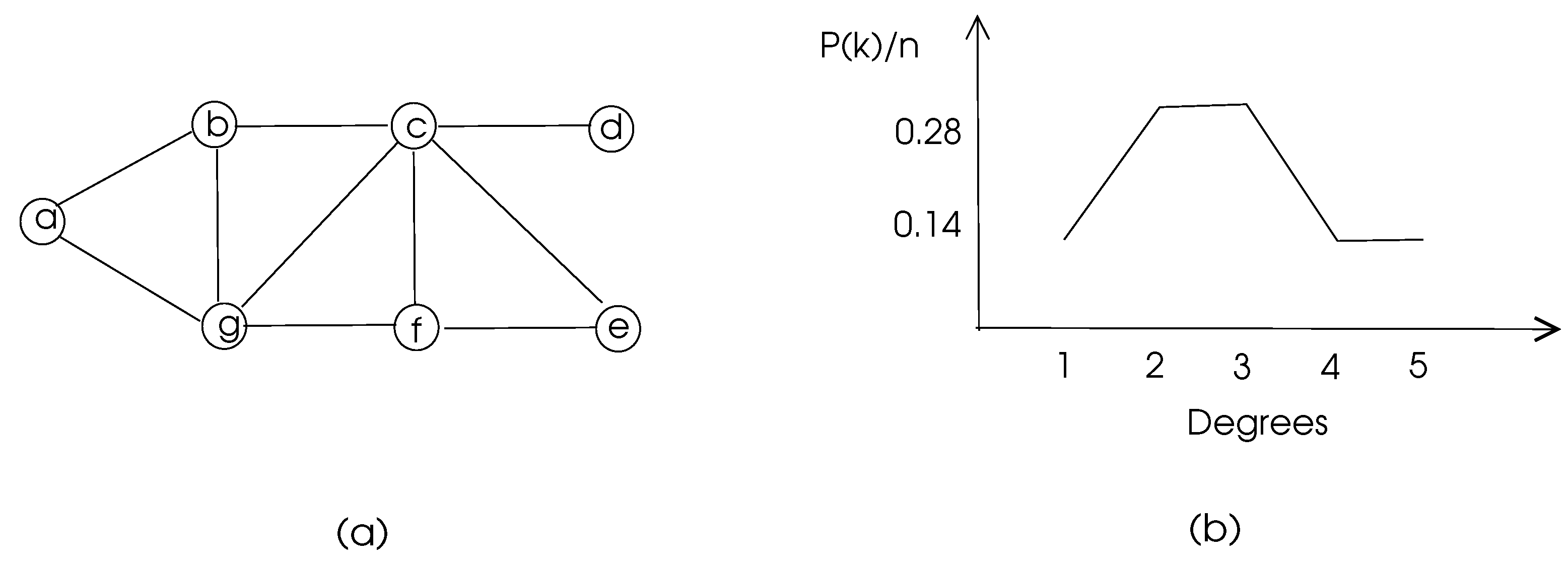
k. Degree distribution of a graph is depicted in
Figure 3.
3.2. Density
The density of a graph provides general information about its structure, basically, it shows how well it is connected. Note that a sparse graph with few connections between its vertices may be represented by an adjacency list whereas a dense graph is commonly represented by an adjacency matrix. There is no strict definition of a sparse or a dense graph, however, a general assumption is that the number of edges in a sparse graph grows as whereas a dense graph has edges in the order of .
Definition 2 (graph density).
The density of a graph G shown by is the ratio of the number of its edges to the maximum possible number of edges in G as follows.
Note that
is between 0 and 1. The density of the graph in
Figure 3 is 10/21=0.48. The sum of degrees in an undirected graph
G is
and thus, the average degree of
G,
, is
. Equation (
2) can now be modified as follows.
3.3. Clustering Coefficient
The clustering coefficient of a vertex in a graph displays how well its neighbors are connected. For example, a person with high clustering coefficient in a social network means having closely related friends for that person.
Definition 3 (clustering coefficient). The clustering coefficient of a node v is the ratio of total number of edges between the neighbors of v to the maximum number of edges possible between these neighbors.
If
k denotes the number of neighbors of a node
v in a graph
G, then the maximum possible number of edges connecting vertices in the neighbor set
of
v is
. Thus, the clustering coefficient
of
v can be expressed as below:
where
r denotes the number of connections between the neighbor vertices of
v. The average clustering coefficient of a graph
G,
, is calculated as the mean value of all of the clustering coefficients of nodes as below:
The clustering coefficients of the nodes
of the graph of
Figure 3 are 1, 0.67, 0.5, 0, 1, 0.67, 0.5 respectively and the average clustering coefficient of this graph is 0.48.
3.4. Matching Index
The matching index of two nodes in a graph relates them by comparing their common neighbors with all of their neighbors. This parameter basically shows the similarity of two nodes in a graph, a high number of common neighbors means these nodes have similar properties. As an example, two persons in a social network with many common friends may have similar personalities.
Definition 4 (matching index). The matching index of two nodes u and v in a graph is the ratio of the number of their common neighbors to the number of the union of all of their neighbors.
For example, nodes
c and
g in
Figure 3 have two common neighbors
b and
f and the total number of their neighbors is 6. Thus, matching index of
c and
g is 0.33. In a biological network, a high matching index of two nodes may mean similar functionality of these nodes.
3.5. Centrality
Centrality is yet another measure to determine the importance of nodes or edges in a complex network. This parameter is evaluated by calculating shortest paths over the nodes.
3.5.1. Closeness Centrality
The
closeness centrality of a node
v in a graph is calculated by summing distances from
v to all other nodes and then taking the reciprocal of this sum as shown below.
with
showing the distance between vertices
u and
v. Distances in an unweighted graph may be found using the breadth-first-search algorithm and distences in a weighted graph may be calculated using Dijkstra’s shortest path algorithm or Bellman-Ford algorithm [
15]. This parameter is used to determine how central a node in a graph is, since a node with a high closeness centrality means that node is close to all other nodes. The closeness centrality for node
a in the graph of
Figure 3 is 0.08 whereas node
c has 0.14 for this parameter which shows
c is more central than
a as can be visually detected.
3.5.2. Vertex Betweenness Centrality
Vertex betweenness centrality of a node
v,
, is used to determine the importance of node
v in a graph by claculating the number of shortest paths through node
v and dividing this number by the total number of shortest paths in the graph as shown below.
where
shows the number of shortest paths between all nodes
s and
t other than node
v, and
is the number of shortest paths through node
v.
3.5.3. Edge Betweenness Centrality
Edge betweenness centrality is similar to vertex betweenness centrality but the shortest paths through an edge is calculated instead of a vertex. This parameter may be used for clustering in biological networks as we will see in the next sections. Edge betweeness
of an edge
e may be stated as below.
4. Large Network Models
Analysis of the topological properties of biological networks reveal that these networks have small diameters allowing reaching any node from any other node in only few hops. Moreover, these networks have very few nodes with very high degrees called hubs where the majority of nodes have low degrees. They can be classified as random networks, small-world networks and scale-free networks based on these properties.
Random networks: This type of networks, proposed by Erdos and Renyi, assumes that an edge
between the vertices
u and
v is formed with the probability
. The degree distribution in random networks is Binomial following Poission distribution. A random network has a short average path length and has a clustering coefficient inversely proprortional to the size of the network [
15].
Small-world networks: This type of networks are characterized by low average path lengths and short diameters. Biological networks such as PPI networks, GRNs and metabolic pathways, and other complex networks such as social networks and the Internet exhibit this property. The diameter of a small-world network is proportional to where n is the number of nodes in the network.
-
Scale-free networks: Most biological networks have few high-degree nodes with many low-degree ones. The PPI network of T. pallidum in
Figure 1 exhibits small-world and scale-free network properties as can be seen. These networks, along with various other complex networks, obey power-law degree distribution shown by the following equation,
where
is known as the power-law exponent. These networks are called scale-free networks The PPI networks of E. coli, D. melanogaster, C. elegans and H. Pylori were shown to be scale-free. Barabasi and Albert provided a method to form a scale-free network with the following steps [
4]:
- 1.
Growth: A new node is added to the network at each discrete time t.
- 2.
Preferential Attachment: A new node u is attached to any node v in the network with a probability proportional to the degree of v which means higher degree nodes tend to have more neighbors at each attachment.
Hierarchical Networks: Study of biological networks show that the clustering coefficients of nodes are inversely proportional to their degrees. This unexpected result means lower degree nodes in these networks have higher clustering coefficents than the hubs. A hierarchical network model of a biological network captures all observed properties such as small-world and scale-free with an additional property that is exhibited by dense clusters of low-degree nodes connected by high-degree hubs.
5. Cluster Discovery in Biological Networks
Graph clustering aims at finding dense regions of a graph which have many connections among the nodes in that region. In the extreme case, this problem may be viewed as finding cliques of a graph which is an NP-Hard problem. Finding clusters in biological networks may provide insight into intense activities in these regions to understand health and disease states of organisms. Quality of the discovered clusters may be evaluated using its
modularity Q of a detected cluster set
which is defined using the following formula [
42,
43]:
where
is the percentages of edges in
, and
is the percentage of edges with at least one edge in
. This parameter shows the sum of the differences of probabilities of an edge being in
and a random edge that would exist in
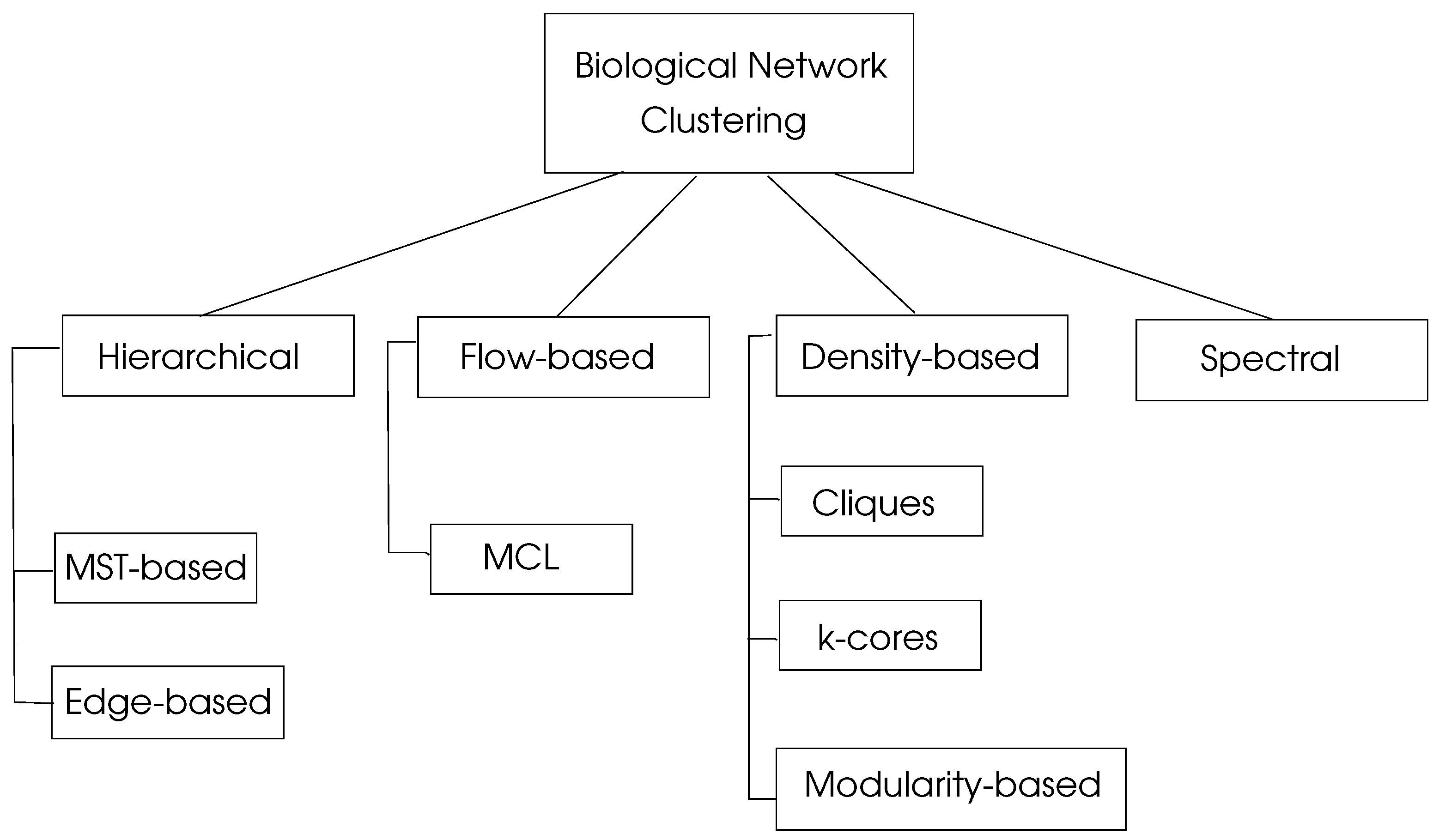
with a maximum value of unity. Graph clustering algorithms may be classified in four basic types as hierarchical, density-based, flow-based, and spectral algorithms as depicted in
Figure 4.
5.1. Hierarchical Clustering
Hierarchical clustering algorithms build clusters iteratively, commonly starting by initializing each vertex as a cluster and then merging close clusters to form new clusters at each step. Alternatively, the whole graph may be considered as a cluster and then separation of remotely related regions provide clusters [
15].
Minimum spanning tree (MST) based clustering assumes an MST
T of a weighted graph is constructed beforehand and the heaviest edge is removed from
T at each step to form clusters. The basic idea of this algorithm is to assume that the nodes that are far apart should be in different clusters. Removal of
heaviest edges are needed to form
k clusters. Instead of removing a single edge at each iteration, edges that have weights larger than a threshold
may be removed at each step resulting in a number of edges deleted from the MST. Then, the quality
Q of the clusters may be assesed and this process continues until a target quality is achieved. Clustering through MST in parallel (CLUMP) is an MST-based parallel clustering method designed to detect dense regions of biological data [
44] and parallel MST construction algorithms are reviewed in [
41].
The edge betweenness based clustering method takes a similar approach by calculating edge betweenness values of all edges in the graph and then removing the high valued edges to form clusters [
19]. The basic idea in this algorithm is that the edges with high betweenness values have a high probability of joining clusters as many shortest paths run through them as a bridge in a graph. Yang and Lonardi provided a parallel implementation of this algorithm and showed that a linear speedup is achieved up to 32 processors [
71].
5.2. Density-based Clustering
In the extreme case, a clique of a graph is a perfect cluster with every node connected to every other node in this structure. Finding the maximum clique of a graph is a NP-Hard problem, moreover, cliques in biological networks are rare due to the dynamicity of these networks with frequent edge deletions. However, clique-like structures which have less connections than cliques that still exhibit a dense region in a graph may be sought in polynomial time.
Bron and Kerbosch provided a recursive backtracking algorithm [
7] to find cliques of a graph with a time complexity off
. A scalable parallel implementation of Bron and Kerbosch algorithm on a Cray XT supercomputer was reported in [
59]. Mohseni-Zadeh et al. provided an algorithm to cluster protein sequences using the extraction of maximal cliques [
39] and Jaber et al. proposed a parallel version of this algorithm using Message Passing Interface [
25].
A
k-core of a graph
G is a subgraph
of
G with each vertex in
having a minimum degree of
k. Thus, finding
k-cores of a graph may provide dense regions which are clusters of the graph. Batagelj and Zaversnik provided an algorithm that finds
k-cores in
time in a connected graph [
5]. The Molecular Complex Detection (MCODE) Algorithm based on
k-cores is used to detect protein complexes in large PPI networks [
3] and a distributed
k-core algorithm for large networks is proposed in [
40].
Girvan and Newman proposed a modularity based algorithm that works iteratively by considering each node of the graph as a cluster initially and then joining two clusters that will increase the modularity parameter
Q best. The algorithm stops when any merge operation decreases the
Q parameter [
43]. A modularity-based distributed clustering algorithm was proposed by Gehweiler et al. [
18] and Reidy et al. provided a scalable parallel modularity-based clustering algorithm for social networks [
53].
5.3. Flow-Based Clustering
Flow-based clustering algorithms make use of the water distribution network model in which the pumped water will be collected at storage points with many pipe connections. The nodes of the graph correspond to storage places and the edges represent the pipes in this model. Markov Clustering Algorithm takes this approach by considering random walks from a node
u and assuming such a walk will end in the same cluster as the node
u [
13]. This algorithm is successfully used to find clusters in biological networks [
6,
65] and parallel versions of Markov Clustering Algorithm are presented in [
8,
9]
5.4. Spectral Clustering
Spectral clustering algorithms use the algebraic properties of a graph to detect dense regions in the graph. The Laplacian matrix of a graph is defined as
where
D is a diagonal matrix with each diagonal element
denoting the degree of vertex
i and
A is its adjacency matrix. In normalized form,
. The eigenvalues of
L are real since
L is real and symmetric. The second eigenvalue called the
Fiedler value and its eigenvector called the
Fiedler vector F[
17] can be used to form clusters of the graph
G as follows. Spectral bisection algorithms work by testing each entry
and if it is larger than a constant value, commonly 0, it is placed in one cluster; otherwise in the other cluster. This algorithm may be invoked recursively to find any required number of clusters. A parallel version of the spectral clustering algorithm was proposed by Chen et al. [
11].
6. Network Motifs
A network motif is a frqeuently repeating subgraph in a graph which represents a biological network. A motif with high occurences may indicate a basic function that is carried out by that motif in the network which may lead to determining the function performed. Moreover, discovering similar motifs in two or more organisms may provide insight to their genetic affinity and thus to the evolutionary process. Unfortunately, detection of a subgraph with a given number of nodes in a graph is an NP-Hard problem which means heuristic solutions are the only possible choices in most cases.
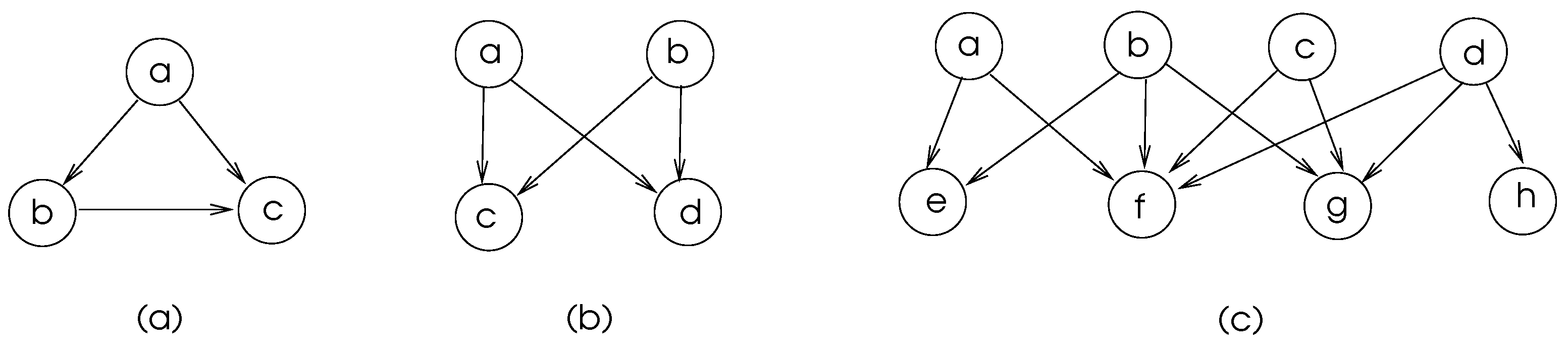
Some commonly found motifs in biological networks are depicted in
Figure 5. The motifs in (a) and (b) of this figure are frequent in transcriptional regulatory networks and neuronal connectivity networks [
15]. The feed-forward-loop ensures that the signal sent fron node
a is delivered to node
c and node
c discards the second arrival of signal from node
a which shows that there is some level of fault tolerance in these network structures.
6.1. Motif Discovery
There exists two basic methods of motif search in a biological network; all subgraph of given order k are searched in network-centric motif search, alternatively, a distinct motif may be searched in G in the motif-centric method. The following steps are commonly performed to discover a motif of order k in a graph G representing a biological network.
- 1.
Detection of in G may be performed by exact counting that involves enumeration of all subgraphs of order k. This method evidently has a high time complexity, alternatively, sampling based methods which work in a representative sample of the graph may provide approximate solutions.
- 2.
Isomorphic classes of the discovered motifs should be determined since various motifs may be isomorphic to each other.
- 3.
Statistical significance of the discovered motifs in G should be determined. Commonly, a similar structured set H of random graphs are generated and motifs are searched in these graphs. If motifs found in G are statistically higher in number than the ones found in the graphs of set H, we can conclude that they do represent some biological function in the network represented by G.
6.2. Background
Finding motifs in a graph is closely related to the graph isomorphism problem. Two graphs and are isomorphic if there is a one-to-one and onto function such that . The number of motifs found in a graph is called its frequency which can be evaluated in three different ways denoted by , and . is computed by discovering all motifs of a given size with overlapping nodes and edges whereas shows edge disjoint motifs with node overlaps only and the frequency shows the number of edge and vertex disjoint motifs.
The goodness of a motif search algorithm is commonly decided by generating a set of n random graphs, applying the algorithm on these graphs and comparing the results by statistical evaluation. Three statistical methods to evaluate a motif discovery algorithm are as follows.
P-value: This parameter is calculated by finding the number of elements of the randomly generated set
that have more frequency of motif
m than in the target graph
G. A motif
m is considered a significant motif if
P-value of
m,
given below, is less than 0.01.
where
is 1 if the occurrence of motif
m in the random network
is higher and 0 if lower than found in the target graph
G.
Z-score: The Z-score of a motif
m,
, in a graph
G is evaluated by the following formula:
where
is the number of discovered motifs
m in
G, and
and
are the mean and variance frequencies of
m in a set of random networks. A motif m is significant if
[
27].
Motif significance profile: The motif significance profile vector SP is structured with elements as
Z-scores of motifs
and normalized to unity as below. Various graphs may then be compared for any common motifs contained in them.
6.3. Review of Motif Searching Algorithms
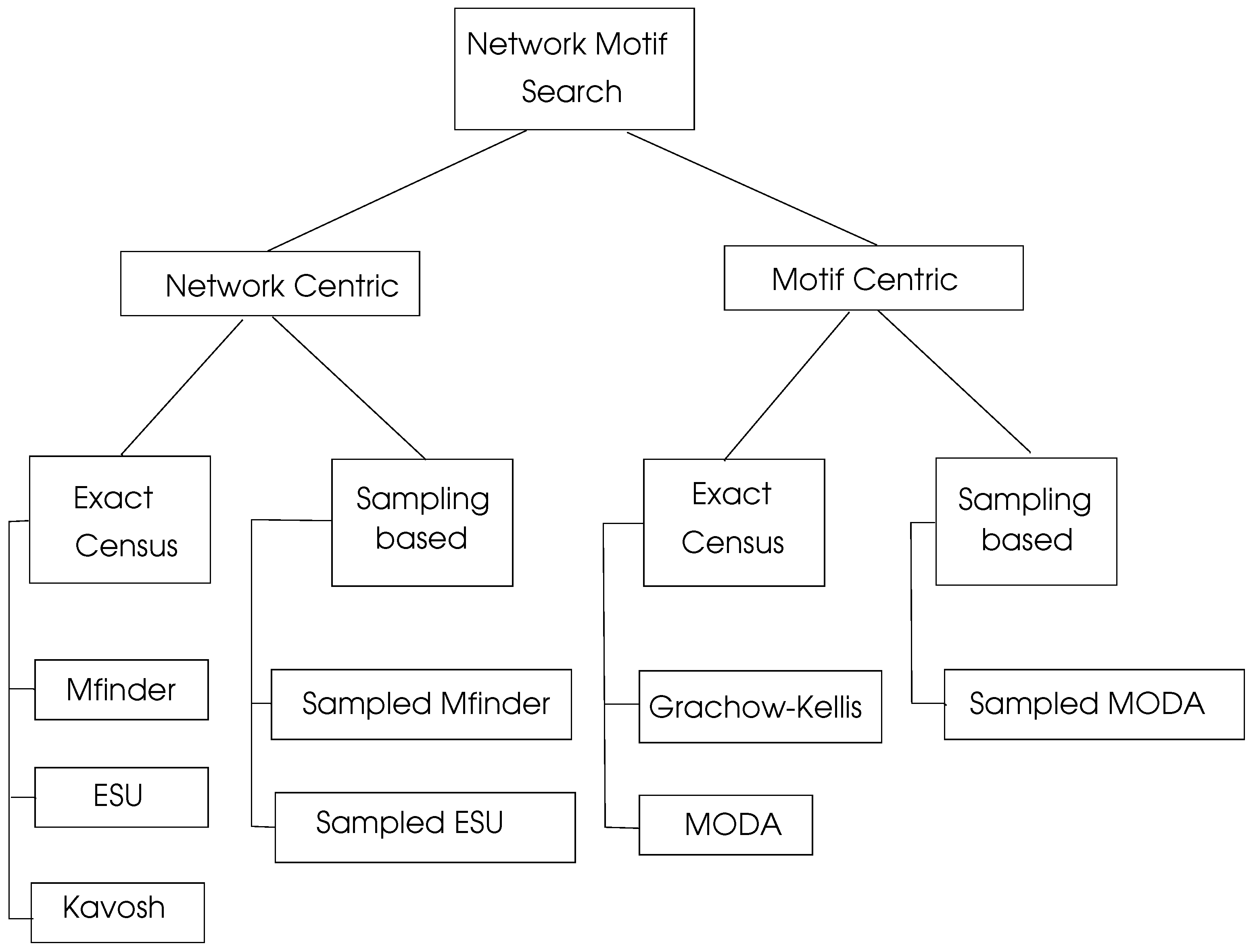
There is a significant research on motif searching algorithms which can be viewed as network centric and motif centric as shown in
Figure 6. Exact census refers to exact numbering of motifs whereas sampling methods work by selecting a representive sample of the network under consideration and then projecting the computed results to the whole network.
6.3.1. Network Centric Search Algorithms
proposed by Milo et al. [
27,
37] uses F1 frequency concept and can be applied to both directed and undirected graphs. It starts with an edge
in the target graph
G and enumerates all subgraphs of order
k that contain
. Due to its high memory space requirement and high run-time, it can be used only up to motif size of five. The sampled version of
called
Edge Sampling Algorithm (ESA) selects an edge
and its adjacent edges randomly to form a motif of size
k [
28].
Enumerate Subgraph (ESU) Algorithm [
68,
69] is an efficient motif search algorithm implemented using both exat census and sampling-based approaches. The randomized version of this algorithm (RAND-ESU) was compared with
algorithm in finding motifs of transcriptional network of E. Coli [
57], transcriptional network of S. Cereviciae [
38], neuronal network of Caenorhabditis Elegans [
28] and food web of the YTHAN estuary [
70]. The authors concluded that RAND-ESU has a much better performance than sampling-based
for graphs with sizes larger than five.
which consists of steps enumeration, classification, random graph generation, and motif identification is a network motif discovery tool designed for directed and undirected graphs [
29].
6.3.2. Motif Centric Search Algorithms
These algorithms may input a single motif structure or simply the size
k of a motif to search. They are commonly used in cases when
k or the structure of a motif is known before the search.
Grachow-Kellis algorithm uses a symmetry breaking method to prevent subgraph isomorphism tests which results in better performance when compared to other algorithms [
20]. This algorithm was implemented in a PPI network [
21] and a transcription network of S. cerevisiae [
12], and was compared with other methods of motif discovery. It was shown that Grachow-Kellis algorithm provides an exponential time improvement compared to Mfinder when subgraphs up to size 7 are considered. MODA is a motif search algorithm that uses the expansion tree approach to employ pereviously searched queries [
45]. The sampling version of MODA provides faster motif searches by sampling nodes with probabilities related to their degrees [
45].
6.3.3. Parallel Motif Search Algorithms
As motif search problem is time consuming in general, various studies aim to parallelize this process. The three steps of motif finding are subgraph enumeration, detecting subgraph isomorphisms and evaluating statistical significance as outlined and there is potential at each step for parallel processing. The graph under consideration may be partitioned and the first two steps may be carried in these partitions considering border vertices carefully. The third step can be conveniently performed in parallel by assigning elements of the randomly generated graph set to the processors.
Parallel exact motif discover is performed by searching the motifs in the neighborhoods of nodes in parallel in [
67] and a distributed version of Grochow–Kellis algorithm by query parallelization and network partitioning is presented in [
58]. A parallel version of a motif centric algorithm that attempts to find a set of input motifs instead of a single one was proposed in [
50] and a parallelized version of the ESU algorithm was presented in [
51]. An extended and generalized parallel motif search based on ESU algorithm is presented in [
52]. Recently, Ruzgar et al. provided an efficient parallelization of the ESU algorithm [
54]. A more recent review of network motif search algorithms can be found in [
46].
7. Network Alignment
Network alignment aims at finding similarities between two or more biological networks which helps to deduce phylogenetic relationships between them to predict future organism structures and also to investigate evolutionary process. Moreover, finding conserved regions in two or more organisms may indicate shared functional modules within them. Global alignment methods compare two or more networks as a whole whereas local alignment procedures attempt to find similar subgraphs in the graphs representing the networks. Pairwise alignment is between two networks and multiple alignment is performed over a set of networks. Comparing biological networks of diverse organisms using global alignment is not usuallly preferred, the local alignment is the reasonable choice in these cases.
7.1. Background
Subgraph isomorphism is the process of searching for a smaller graph in a larger graph with the maximal size that is isomorphic to the smaller graph. Network alignment is the more general form of subgraph isomorphism in which we search for a set of subgraphs in the larger graph, thus, this process is NP-Hard as the subgraph isomorphism problem which means approximation algorithms or more frequently, heuristic algorithms are commonly used for this purpose.
A matching of a graph is defined as a subset of its disjoint edges, in other words, these edges do not share any endpoints. A maximal matching of an unweighted graph G can not be embedded in any other matching of the graph and a maximum matching (MaxM) of an unweighted graph G has the maximum size among all matchings of G. When a graph G is weighted, MM and MAxM of G is its matchings with the maximal and maximum weights of G respectively. We can use maximal weighted matching of a complete bipartite graph for network alignment with the following reasoning. Let a bipartite graph represent two networks with as the nodes of the first network and as the nodes of the second network . Let us further assign weights proportional to the similarities of nodes to the edges between and . Then, a maximal weighted matching in G will exhibit how similar these two networks and are. The main steps in a global network alignment algorithm based on this approach may be stated as follows.
- 1.
Form the similarity matrix R with entry showing the similarity score of the nodes and in input networks and respectively.
- 2.
Implement a weighted matching algorithm to asses the similarity of the networks and .
7.2. Alignment Quality
Topological similarity of two networks displays the similarity of the structures they exhibit whereas
node similarity is a measure of the affinity of the node structures, for example, the amino acid sequence in a protein node of a PPI network. Edge correctness (EC) parameter shown below is one measure of similarity between two graphs
to
. [
61].
with
f as an edge mapping function from graph
to
. This parameter evaluates the correctness of the alignment by testing the percentage of the correctly aligned edges. The induced conserved structure (ICS) based on EC attempts to map the sparse regions or the dense regions of the two graphs [
47]. The size of the largest connected component (LCC) shared by the input graphs is another parameter to estimate the similarity of two graphs with a larger LCC exhibiting a greater similarity. As with the network motif search algorithms, a random set of graphs may be generated and the quality of the alignment of two input graphs may be compared with these random networks statistically [
49]. We can now classify network alignment algorithms as pairwise or multiple; local or global; and using node and/or topological similarity. Frequently, node and topological similarity are both used with assigned weights to each method. In PPI networks, node similarity may be evaluated using biol ogical sequence alignment tools such as Basic Local Alignment Search Tool BLAST [
2].
7.3. Review of Network Alignment Algorithms
The PathBLAST tool provides network alignment for PPI networks to discover protein pathways and complexes [
30]. The IsoRank algorithm based on the PageRank algorithm finds global network alignment between two PPI networks using both node similarity and local connectivity structure [
61]. Maximum-weight-induced subgraph (MaWIsh) is a pairwise local alignment algorithm for PPI networks [
32]. Natalie [
14] is a tool for pairwise global network alignment and uses the Lagrangian relaxation method proposed by Klau [
31]. A global alignment algorithm Graph Aligner (GRAAL) uses topological data to discover similarity of networks [
33]. Scalable Protein Interaction Network Alignment (SPINAL) is a two-phase global alignemnt algorithm with coarse-grained alignment in the first phase and a fine-grained alignment in the second [
1].
The two main steps of network alignment are the formation of the similarity matrix R and then the maximal weighted matching step. A simple algorithm for this task picks the heaviest edge incident at a randomly selected node and deletes the node and all adjacent edges at each step until no more edges left [
48] with a time complexity of
and an approximation ratio of 0.5. A distributed version of this algorithm [
24] and then its parallel version was proposed in [
34]. A parallel maximal weighted matching algorithm based on auctions was proposed in [
56] and a recent study finds weighted matching of a bipartite graph by partitioning the adjacency matrix of the graph to processors with significant speedups [
55] and a survey of network alignment methods is provided in [
35]
8. Discussion
Graph theory is a rich and dynamic branch of mathematics studied extensively by researchers with numerous results, both theoretically and with discovered algorithms applied to many diverse applications. Biological networks can be represented by graphs and analysis of these networks can be performed conveniently using the results of graph theory. In this survey, we outlined basic large graph analysis methods, classified large biological networks and turned our attention to three main problems in the analysis of biological networks which are clustering, network motif search and network alignment. All of these problems are NP-Hard defying solutions in polynomial time which means approximation algorithms or suitable heuristics are the only solutions in most cases.
Graph clustering aims at finding closely related regions of graphs representing biological networks and these zones may indicate high activities and disease states of an organisms. Data and graph clustering remains one of the most studied topics in Computer Science and various other disciplines such as Statistics. We reviewed basic methods of clustering as hierarchical, dense and spectral clustering. Network motif search identifies repeating subgraphs in a graph of a biological network to investigate the functions performed by these subgraphs. We reviewed basic approaches and algorithms that aim efficient motif search globally or locally. Network alignment addressed by various researchers is another basic problem in biological networks targeting to find similarities between networks to detect basic functions peformed by them and to deduce ancestral relationships.
Although there are various algorithms and methods for these three distinct problems, efficient implementations are required due to the large size of biological networks. A basic approach for effective algorithms for this purpose is to parallelize the steps of the sequential algorithms. In network motif search, we described ways of parallel implementation steps, namely, detection of a motif, finding its isomorphic class and evaluating statistical significance of the results. The two main steps of network alignment which are forming the similarity matrix and applying maximal weighted matching in this matrix can also be performed in parallel. Algebraic graph analysis is the method of analyzing algebraic properties of graph matrices and deducing graph structure using these results. This approach is relatively more recent than classical graph analysis, and may be conveniently used in various applications since parallel matix operations are already available. Basic algebraic graph algorithms using Python are reviewed in [
16].
References
- Aladag AE, Erten C. (2013) SPINAL: scalable protein interaction network alignment. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 917–924. [CrossRef]
- Altschul S.; Gish W.; Miller W.; Myers E.; Lipman D. (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 1990, 215, 403–410. [CrossRef]
- Bader G.D.; Hogue C.W.V. An automated method for finding molecular complexes in0 large protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinform 2003, 4, 1–27. [CrossRef]
- Albert, R.; Barabasi, A. The statistical mechanics of complex networks. Rev Mod Phys, 2002, 74, 47–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batagelj V.; Zaversnik M. An O(m) algorithm for cores decomposition of networks. CoRR (Computing Research Repository) arXiv:0310049.
- Brohee, S.; van Helden, J. Evaluation of clustering algorithms for protein-protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinform 2006, 7, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bron, C.; Kerbosch, J. Algorithm 457: finding all cliques of an undirected graph. Commun ACM 1973, 16, 575–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamam, A.; Sehgal, M.S.; Hamilton, N.; Wong, S.; Ragan, M.A.; Burrage, K. An efficient parallel implementation of Markov clustering algorithm for large-scale protein-protein interaction networks that uses MPI. In Proceedings of the fifth IMT-GT international conference mathematics, statistics, and their applications (ICMSA), Sumatra Barat, Indonesia, 09 06 2009,pp 94-101.
- Bustamam A, Burrage K; Hamilton N.A. (2012) Fast parallel Markov clustering in bioinformatics using massively parallel computing on GPU with CUDA and ELLPACK-R sparse format. IEEE/ACM Trans Comp Biol Bioinform 2012, 9, 679–691. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pablo Carbonell P.; Anne-Galle Planson A-G.; Davide Fichera D.; Jean-Loup Faulon J-P. A retrosynthetic biology approach to metabolic pathway design for therapeutic production. BMC Syst Biol 2011, 5, 1–18. [CrossRef]
- Chen W-Y.; Song Y.; Bai H., Lin C-J.; Chang E.Y. Parallel spectral clustering in distributed systems. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 2010, 33, 568–586. [CrossRef]
- Costanzo M.C.; Crawford M.E.; Hirschman J.E.; Kranz J.E.; Olsen P.; Robertson L.S.; Skrzypek M.S.; Braun B.R.; Hopkins K.L.; Kondu P.; Lengieza C.; Lew-Smith J.E.; Tillberg M., Garrels J.I. Ypd(tm), pombepd(tm), and wormpd(tm): model organism volumes of the bioknowledge(tm) library, an integrated resource for protein information. Nucleic Acids Res, 2001, 29, 75–79. [PubMed]
- Dongen, S.V. Graph clustering by flow simulation. PhD Thesis, University of Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- El-Kebir M, Heringa J,KlauGW(2011) Lagrangian relaxation applied to sparse global network alignment. Proceedings of 6th IAPR international conference on pattern recognition in bioinformatics (PRIB’11), Delft, The Netherlands, 02 11 2011, 225-236.
- Erciyes, K. Distributed and Sequential Algorithms for Bioinformatics, Springer Computational Biology Series, Switzerland, chapters 10, 11, 12, 13, 2013.
- Erciyes, K. Algebraic Graph Algorithms, A Practical Approach Using Python. Springer Undergraduate Topics in Computer Science Series, Switzerland, 2021.
- Fiedler, M. Laplacian of graphs and algebraic connectivity. Comb Graph Theory 1989, 25, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehweiler, J.; Meyerhenke, H. A distributed diffusive heuristic for clustering a virtual P2P supercomputer. In Proceedings of the 7th high-performance grid computing workshop (HGCW10) in conjunction with 24th international parallel and distributed processing symposium (IPDPS10), Atlanta, USA, 19 04 2010.
- Girvan M, Newman M.E.J. Community structure in social and biological networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002, 99, 7821–7826. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grochow, J.; Kellis, M. Network motif discovery using subgraph enumeration and symmetry-breaking. Proceedings of 11th annual international conference research in computational molecular biology (RECOMB’07), Oakland, USA, 21 04 2007, 92-106.
- Han J-D.J.; Bertin N., Hao T.; Goldberg D.S.; Berriz G.F.; Zhang L.V.; Dupuy D.; Walhout A.J.M.; Cusick M.E.; Roth F.P.; Vidal M. Evidence for dynamically organized modularity in the yeast protein-protein interaction network. Nature 2004, 430, 88–93. [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Chen, Z.; Evans, A. Structural insights into aberrant topological patterns of largescale cortical networks in Alzheimers disease. J Neurosci 2008, 28, 4756–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong H.; Mason S.P.; Barabási A-L.; Oltvai Z.N. Lethality and centrality in protein networks. Nature 2011, 411, 41–42. [CrossRef]
- Hoepman, J.H. Simple distributed weighted matchings. 2004, arXiv:cs/0410047v1.
- Jaber, K.; Rashid, N.A.; Abdullah, R. The parallel maximal cliques algorithm for protein sequence clustering. Am J Appl Sci 2009, 6, 1368–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junker, B. Analysis of biological networks. Chap. 9. Wiley, Chapter 9, 2008.
- Kashtan N; Itzkovitz S; Milo R; Alon U. Mfinder tool guide. Technical report, Department of Molecular Cell Biology and Computer Science and Applied Mathematics, Weizman Institute of Science, 2002.
- Kashtan, N.; Itzkovitz, S.; Milo, R.; Alon, U. Efficient sampling algorithm for estimating sub-graph concentrations and detecting network motifs. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 1746–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashani, Z.R.; Ahrabian, H.; Elahi, E.; Nowzari-Dalini, A.; Ansari, E.S.; Asadi, S.; Mohammadi, S.; Schreiber, F.; Masoudi-Nejad, A. Kavosh: a new algorithm for finding network motifs. BMC Bioinform 2009, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley B.P.; Sharan R.; Karp R.M.; Sittler T.; Root D.E.; Stockwell B.R.; Ideker T. Conserved pathways within bacteria and yeast as revealed by global protein network alignment. Proc PNAS 2003, 100, 11394–11399. [CrossRef]
- Klau, G.W. A new graph-based method for pairwise global network alignment. BMC Bioinform 2009, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyuturk, M.; Kim, Y.; Topkara, U.; Subramaniam, S.; Szpankowski, W.; Grama, A. Pairwise alignment of protein interaction networks. J Comput Biol 2006, 13, 182–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchaiev, O.; Milenkovic, T.; Memisevic, V.; Hayes, W.; Przulj, N. Topological network alignment uncovers biological function and phylogeny. J Royal Soc Interface 2010, 7, 1341–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manne F, Bisseling RH, A parallel approximation algorithm for the weighted maximum matching problem. In: Wyrzykowski R, Karczewski K, Dongarra J, Wasniewski J (eds). Proceedings of seventh international conference on parallel processing and applied mathematics (PPAM 2007), Lecture notes in computer science, Gdansk, Poland, 09 09 2007, 708-717.
- S. Maskey and Y. -R. Cho, "Survey of biological network alignment: cross-species analysis of conserved systems,". 2019 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), San Diego, USA, 18 11 2019, 2090-2096.
- Mason, O.; Verwoerd, M. Graph theory and networks in biology. IET Syst Biol 2007, 1(2), 89–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mfinder. Available online: http://www.weizmann.ac.il/mcb/UriAlon/index.
- Milo, R.; Shen-Orr, S.; Itzkovitz, S.; Kashtan, N.; Chklovskii, D.; Alon, U. Network motifs: simple building blocks of complex networks. Science 2004, 298, 824–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohseni-Zadeh, S.; Brezelec, P.; Risler, J.L. Cluster-C, an algorithm for the large-scale clustering of protein sequences based on the extraction of maximal cliques. Comput Biol Chem 2004, 28, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montresor, A.; Pellegrini, F.D.; Miorandi, D. Distributed k-Core decomposition. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 2013, 24(2), 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtagh, F. Clustering in massive data sets. In Handbook of massive data sets; 2002; pp. 501–543. [Google Scholar]
- Newman MEJ (2004) Fast algorithm for detecting community structure in networks. Phys Rev E 2004, 69, 66133. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, M.E.J.; Girvan, M. Finding and evaluating community structure in networks. Phys Rev E 2004, 69, 026113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olman, V.; Mao, F.; Wu, H.; Xu, Y. Parallel clustering algorithm for large data sets with applications in bioinformatics. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform 2009, 6, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidi, S.; Schreiber, F.; Masoudi-Nejad, A. MODA: an efficient algorithm for network motif discovery in biological networks. Genes Genet Syst 2009, 84, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, S.; Mohapatra, A. ; Review of tools and algorithms for network motif discovery in biological networks. IET Systems Biology 2020, 14, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patro, R.; Kingsford, C. Global network alignment using multiscale spectral signatures. Bioinformatics 2012, 28(23), 3105–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preis, R. Linear time 2-approximation algorithm for maximum weighted matching in general graphs. C. Meinel, S. Tison (eds) STACS99 Proceeedings 16th annual conference theoretical aspects of computer science, Lecture notes in computer science, Trier, Germany, 04 04 1999, 259-269.
- Przulj N (2005) Graph theory analysis of protein-protein interactions. In Igor J, Dennis W (eds) A chapter in knowledge discovery in proteomics; CRC Press.
- Ribeiro, P. Efficient and scalable algorithms for network motifs discovery. Ph.D. Thesis, Doctoral Programme in Computer Science. Faculty of Science of the University of Porto, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro P, Silva F, Lopes L (2010) A parallel algorithm for counting subgraphs in complex networks. 3rd international conference on biomedical engineering systems and technologies, Valencia, Spain, 20 01 2010, 380-393.
- Ribeiro, P.; Silva, F.; Lopes, L. Parallel discovery of network motifs. J Parallel Distrib Comput 2012, 72, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedy J, Bader DA, Meyerhenke H (2012) Scalable multi-threaded community detection in social networks. Proceedings of IEEE 26th international parallel and distributed processing symposium workshops and PhD forum (IPDPSW), IEEE, Shanghai, China, 21 05 2012, 1619-1628.
- Ruzgar, E.; Erciyes, K.; Dalkilic, M.E. Parallelization of network motif discovery using star contraction. Parallel Computing 2021, 101, 102734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saribatir MB, Erciyes K, A Parallel Network Alignment Algorithm for Biological Networks. IEEE 3rd International Informatics and Software Engineering Conference (IISEC), Ankara, Turkey, 15 12 2022.
- Sathe, M.; Schenk, O.; Burkhart, H. An auction-based weighted matching implementation on massively parallel architectures. Parallel Comput 2012, 38, 595–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen-Orr, S.S.; Milo, R.; Mangan, S.; Alon, U. Network motifs in the transcriptional regulation network of Escherichia Coli. Nat Gen 2002, 31, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schatz, M.; Cooper-Balis, E.; Bazinet, A. Parallel network motif finding. Techinical report, University of Maryland Insitute for Advanced Computer Studies, 2008.
- Schmidt M.C.; Samatova N.F.; Thomas K.; Park B-H. A scalable, parallel algorithm for maximal clique enumeration. J Parallel Distrib Comput 2009, 69, 417–428. [CrossRef]
- Schuster, S.; Fell, D.A.; Dandekar, T. A general definition of metabolic pathways useful for systematic organization and analysis of complex metabolic networks. Nat Biotechnol 2000, 18, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Xu, J.; Berger, B. Pairwise global alignment of protein interaction networks by matching neighborhood topology. Research in computational molecular biology, Springer, 16-31.
- Sporns, O. Networks of the Brain; MIT Press: USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Titz, B.; Rajagopala, S.V.; Goll, J.; Hauser, R.; McKevitt, M.T.; Palzkill, T.; Uetz, P. The binary protein interactome of Treponema pallidum, the syphilis spirochete. PLoS one 2008, 3(5), e2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal M.; Cusick M.E.; Barabasi A.L. Interactome networks and human disease. Cell 2011, 144, 986–998. [CrossRef]
- Vlasblom, J.; Wodak, S.J. Markov clustering versus affinity propagation for the partitioning of protein interaction graphs. BMC Bioinform 2009, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelstein, B.; Lane, D.; Levine, A. Surfing the p53 network. Nature 2000, 408, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Touchman, J.W.; Zhang, W.; Suh, E.B.; Xue, G. A parallel algorithm for extracting transcription regulatory network motifs. In Proceedings of the IEEE international symposium on bioinformatics and bioengineering, IEEE Computer Society Press, Minneapolis, USA, 09 10 2005, 193-200.
- Wernicke, S. Wernicke S. Efficient detection of network motifs. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform 2006, 3, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernicke, S.; Rasche, F. FANMOD: a tool for fast network motif detection. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1152–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.J.; Martinez, N.D. Simple rules yield complex food webs. Nature 2000, 404, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Lonardi, S. A parallel edge-betweenness clustering tool for protein-protein interaction networks. Int J Data Min Bioinform (IJDMB) 2007, 1, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).