Submitted:
13 July 2023
Posted:
13 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Neuropsychological testing
2.2. Recording parameters
2.3. Statistical analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gelžinienė G, Jurkevičienė G, Marmienė V, Adomaitienė V, Endzinienė M. Executive functions in adolescents with idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Medicina (Kaunas) 2011, 47, 313–319.
- Aarts JHP, Binnie CD, Smith AM, Wilkins AJ. Selective cognitive impairment during focal and generalised epileptiform EEG activity. Brain. 1984, 107, 293–308. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca LC, Tedrus GM, Lalloni DT, Tella LM, Maluf P, Sousa VD. [Transient cognitive impairment during generalized or diffuse epileptiform EEG discharges]. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2005, 63, 817–24.
- Mataró, M.; Junqué, C.; Viñas, J.; Escartín, A. Learning and memory skills in patients with cryptogenic epilepsy. Neurologia 1996, 11, 280–6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meador, K.J. Cognitive outcomes and predictive factors in epilepsy. Neurology 2002, 58, S21–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulteau C, Jambaque I, Viguier D, Kieer V, Dellatolas G, Dulac O. Epileptic syndromes, cognitive assessment and school placement: a study of 251 children. Dev Med Child Neurol 2000, 42, 319–27. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kälviäinen, R.; Äikiä, M.; Helkala, E.-L.; Mervaala, E.; Riekkinen, P.J. Memory and attention in newly diagnosed epileptic seizure disorder. Seizure 1992, 1, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, M.-C.; Tsai, J.-J. Is Cognitive Reserve Applicable to Epilepsy? The Effect of Educational Level on the Cognitive Decline After Onset of Epilepsy. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-W.; Hsieh, Y.-J.; Tsai, J.-J.; Pai, M.-C. Cognitive performance in cryptogenic epilepsy. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2005, 112, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotloski, R.; Lynch, M.; Lauersdorf, S.; Sutula, T. Repeated brief seizures induce progressive hippocampal neuron loss and memory deficits. Prog Brain Res 2002, 135, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuerst D, Shah J, Kupsky W et al. Is hippocampal sclerosis a progressive disorder? A volumetric MRI, pathological and neuropsychological study. Neurology 2001, 57, 184–8. [CrossRef]
- Petrucco L., Pracucci E., Brondi M., Ratto G. M., Landi S. Epileptiform activity in the mouse visual cortex interferes with cortical processing in connected areas. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40054. [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, E. , Bagshaw A. P., Jansen A., Andermann F., Andermann E., Gotman J., et al. Intrinsic epileptogenicity in polymicrogyric cortex suggested by EEG-fMRI BOLD responses. Neurology. 2005, 64, 1263–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ung, H.; Cazares, C.; Nanivadekar, A.; Kini, L.; Wagenaar, J.; Becker, D.; Krieger, A.; Lucas, T.; Litt, B.; Davis, K.A. Interictal epileptiform activity outside the seizure onset zone impacts cognition. Brain 2017, 140, 2157–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landi, S.; Petrucco, L.; Sicca, F.; Ratto, G.M. Transient Cognitive Impairment in Epilepsy. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 11, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artemiadis, A.K.; Fili, M.; Papadopoulos, G.; Christidi, F.; Gatzonis, S.; Zalonis, I.; Nikolaou, G.; Triantafyllou, N. Auditory event-related potentials (P300) and mesial temporal sclerosis in temporal lobe epilepsy patients. Epileptic Disord. 2014, 16, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.; Li, M.; Chen, Q.; Li, J.; Li, G.; Lin, W. The P300 Event-Related Potential Component and Cognitive Impairment in Epilepsy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polich, J. Updating P300: An integrative theory of P3a and P3b. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2007, 118, 2128–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dien, J.; Spencer, K.M.; Donchin, E. Localization of the event-related potential novelty response as defined by principal components analysis. Cogn. Brain Res. 2003, 17, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratton, G.; Bosco, C.M.; Kramer, A.F.; Coles, M.G.; Wickens, C.D.; Donchin, E. Event-related brain potentials as indices of information extraction and response priming. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1990, 75, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner GZ, Barry RJ, Gonsalvez CJ. Can working memory predict target-to-target interval effects in the P300? Int J Psychophysiol. 2013, 89, 399–408. [CrossRef]
- van Dinteren, R.; Arns, M.; Jongsma, M.L.A.; Kessels, R.P.C. P300 Development across the Lifespan: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e87347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, M.; Helmstaedter, C. EpiTrack: Tracking cognitive side effects of medication on attention and executive functions in patients with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2005, 7, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papaliagkas, V.; Kimiskidis, V.; Tsolaki, M.; Anogianakis, G. Usefulness of event-related potentials in the assessment of mild cognitive impairment. BMC Neurosci. 2008, 9, 107–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deckers, C.L.P.; Hekster, Y.A.; Keyser, A.; Meinardi, H.; Renier, W.O. Reappraisal of polytherapy in epilepsy: a critical review of drug load and adverse effects. Epilepsia 1997, 38, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, J.-A.; Elger, C.E.; Helmstaedter, C. Adverse cognitive effects of antiepileptic pharmacotherapy: Each additional drug matters. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015, 25, 1954–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.-C.; Tsai, S.-Y.; Chang, Y.-C.; Liou, H.-H. Seizure frequency affects event-related potentials(P300) in epilepsy. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2001, 8, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-P.; Kwon, S.-H. Cognitive Effects of Antiepileptic Drugs. J. Clin. Neurol. 2008, 4, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moavero, R.; Santarone, M.E.; Galasso, C.; Curatolo, P. Cognitive and behavioral effects of new antiepileptic drugs in pediatric epilepsy. Brain Dev. 2017, 39, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brückner, K. E. (2020). Cognitive and Psychological Side Effects of Antiepileptic Drugs. In Epilepsy-Update on Classification, Etiologies, Instrumental Diagnosis and Treatment. IntechOpen.
- van Rijckevorsel-Harmant, K.; Flahaut, D.; Harman, J.; de Barsy, T. Event-Related Potentials and Cognitive Functions in Epileptic Treated Patients. Clin. Electroencephalogr. 1990, 21, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naganuma, Y.; Konishi, T.; Hongou, K.; Murakami, M.; Yamatani, M.; Yagi, S.; Okada, T. Auditory Event-related Potentials in Benign Childhood Epilepsy with Centrotemporal Spike: The Effects of Carbamazepine. Clin. Electroencephalogr. 1994, 25, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naganuma, Y.; Konishi, T.; Matsui, M.; Hongou, K.; Murakami, M.; Yamatani, M.; Okada, T. [The relationship between P300 latencies, and WISC-R and Wechsler memory scale results in epileptic children]. No hattatsu. Brain Dev. 1993, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Helmstaedter C, Witt JA. Epilepsy and cognition - A bidirectional relationship? Seizure 2017, 49, 83–89. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soysal, A.; Atakli, D.; Atay, T.; Altintas, H.; Baybas, S.; ArpacI, B. Auditory event-related potentials (P300) in partial and generalized epileptic patients. Seizure 1999, 8, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlooswijk, M.C.G.; Jansen, J.F.A.; Jeukens, C.R.L.P.N.; Majoie, H.J.M.; Hofman, P.A.M.; de Krom, M.C.T.F.M.; Aldenkamp, A.P.; Backes, W.H. Memory processes and prefrontal network dysfunction in cryptogenic epilepsy. Epilepsia 2011, 52, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funahashi, S. Working Memory in the Prefrontal Cortex. Brain Sci. 2017, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niedermeyer, E. Frontal Lobe Epilepsy: The Next Frontier. Clin. Electroencephalogr. 1998, 29, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddeley, A. D. Baddeley, A. D., & Hitch, G. (1974). Working memory. In Psychology of learning and motivation (Vol. 8, pp. 47-89); Academic press.
- Patrikelis, P.; Lucci, G.; Fasilis, T.; Korfias, S.; Messinis, L.; Kosmidis, M.H.; Lagogianni, C.; Konstantakopoulos, G.; Manolia, S.; Sakas, D.; et al. Selective impairment of auditory attention processing in idiopathic generalized epilepsies: Implications for their cognitive pathophysiology. Appl. Neuropsychol. Adult 2020, 29, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, A.; Vizjak, K.; Rakusa, M. Cognitive Impairment in People with Epilepsy. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, T.M.; Mason, C.A.; Seidenberg, M.; Jones, J.; Hermann, B. The impact of processing speed on cognition in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2021, 122, 108203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luria, A. R. (1976). The working brain: An introduction to neuropsychology.
- Binnie, C.; Trenité, D.K.-N.; Smit, A.; Wilkins, A. Interactions of epileptiform EEG discharges and cognition. Epilepsy Res. 1987, 1, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binnie, CD. Cognitive impairment during epileptiform discharges: is it ever justifiable to treat the EEG? Lancet Neurol. 2003, 2, 725–730 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
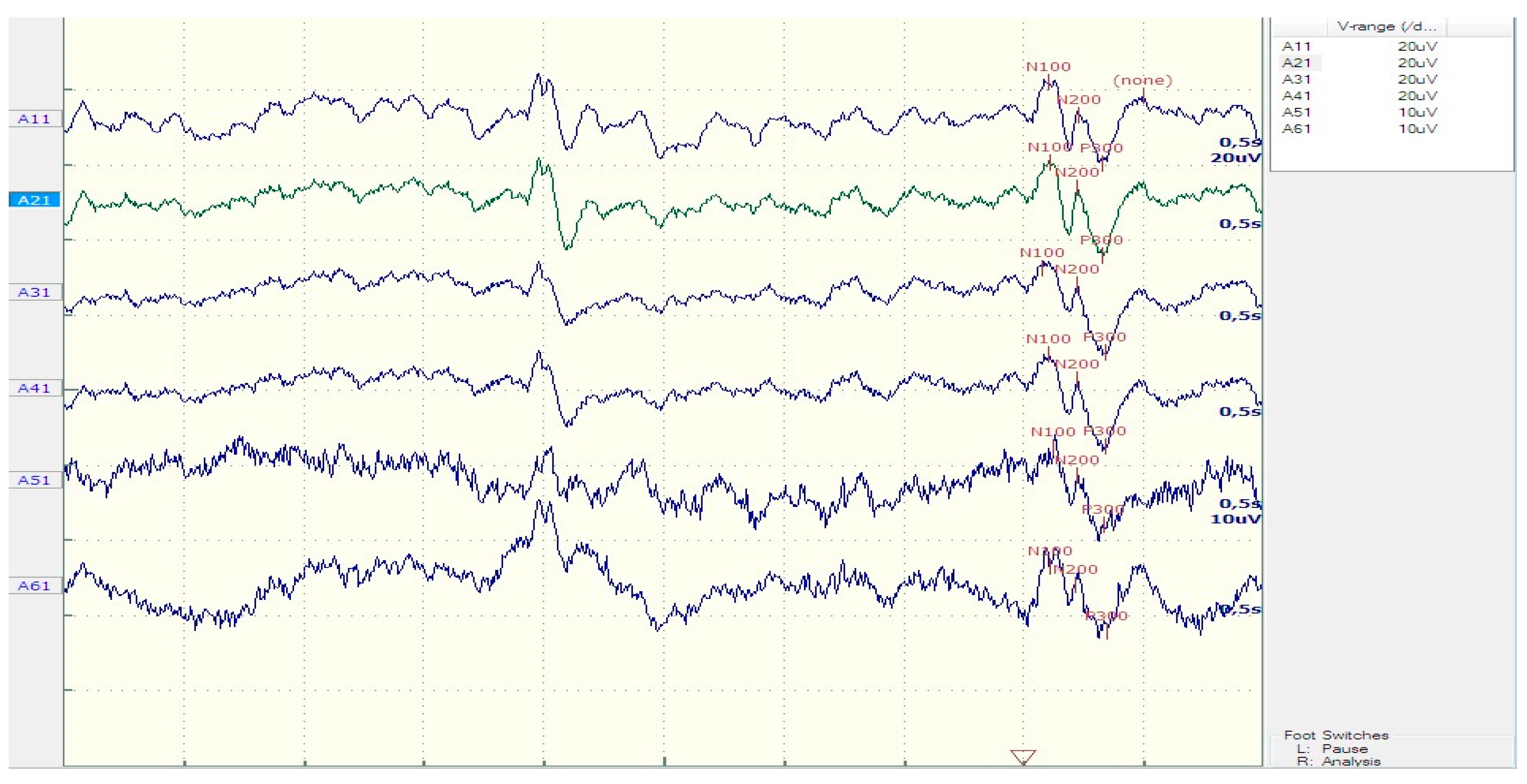
| Patients | Controls | t-test (P) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 30.3 ± 12.56 | 24.22 ± 15.39 | 0.07 |
| N200 latency (ms) | 223.75 ± 26.9 | 212.5 ± 18.3 | 0.23 |
| P300 latency (ms) | 359.73 ± 39.1 | 318.13 ± 23 | 0.005* |
| Sw latency (ms) | 492.36 ± 50.72 | 451.25 ± 41.1 | 0.05* |
| N200 amplitude (μV) | 8.64 ±3.8 | 7.83 ±1.85 | 0.52 |
| P300 amplitude (μV) | 16.12 ±7.45 | 17.86 ±7.02 | 0.59 |
| Reaction time (ms) | 900.25 ± 206.9 | 833.38 ± 94 | 0.59 |
| Patients | Controls | t-test (P) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Score | 26.94± 3.77 | 29.87± 2.16 | 0.055 |
| Interference | 5.44± 1.03 | 5.75± 0.7 | 0.62 |
| Trail A | 5.31 ± 0.79 | 6 ± 0.53 | 0.038* |
| Trail B | 5.31 ± 1.01 | 6.12 ± 0.35 | 0.040* |
| Maze | 5.68±1.19 | 6.37 ±0.51 | 0.137 |
| Verbal fluency test | 5.06 ±0.85 | 5.62 ±0.74 | 0.128 |
| ASM load | 2.54 ±1.70 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





