Submitted:
08 July 2023
Posted:
11 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strain, media and growth conditions
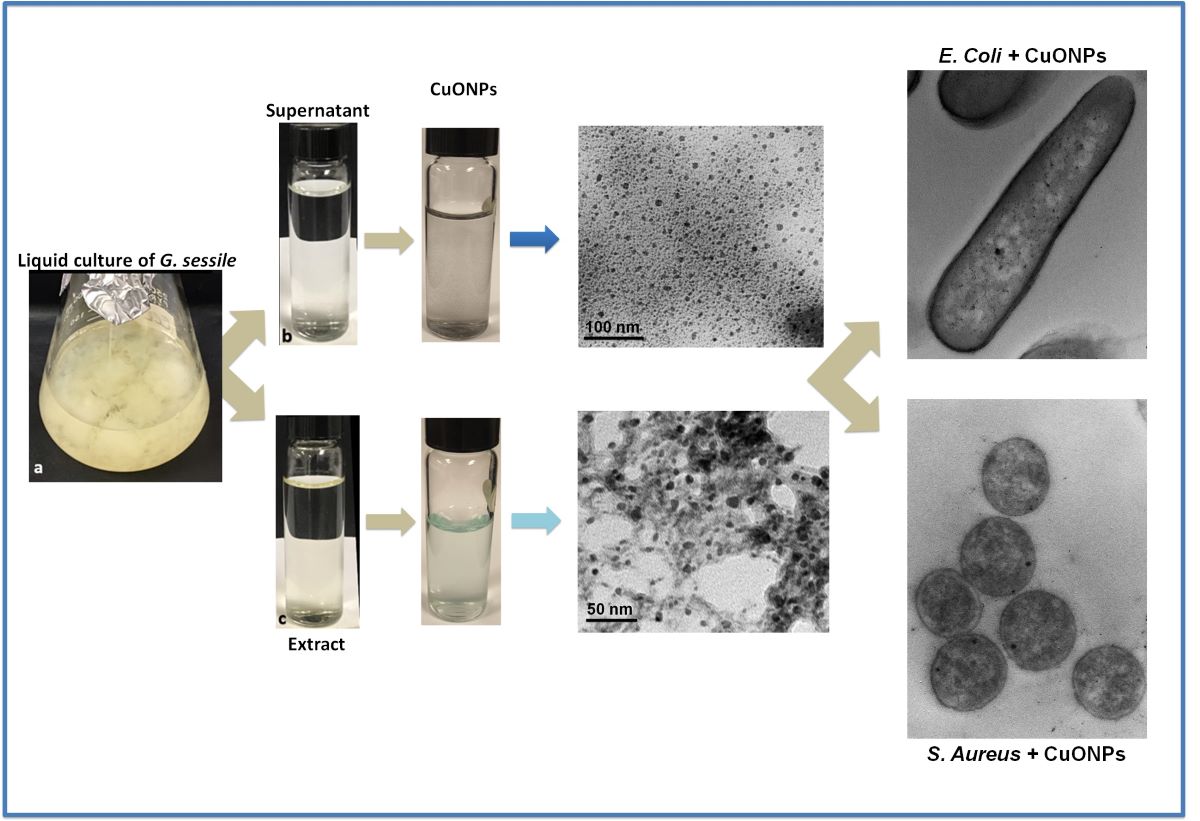
2.2. Obtention of fungal supernatant and extract
2.3 Biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles (CuONPs)
2.4 Characterization of CuONPs
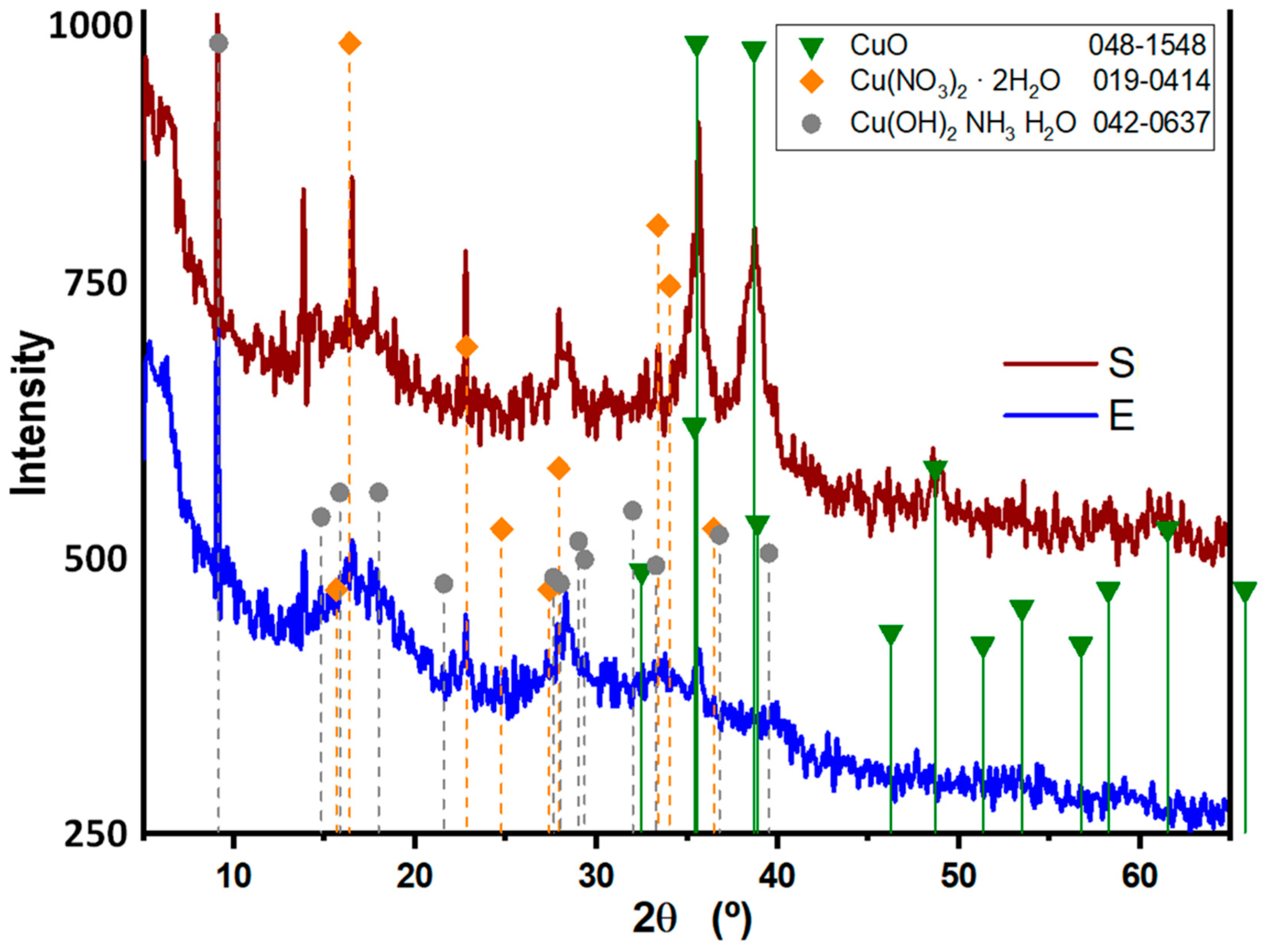
2.5. X-ray diffraction (XRD) Analysis of Synthesized CuONPs
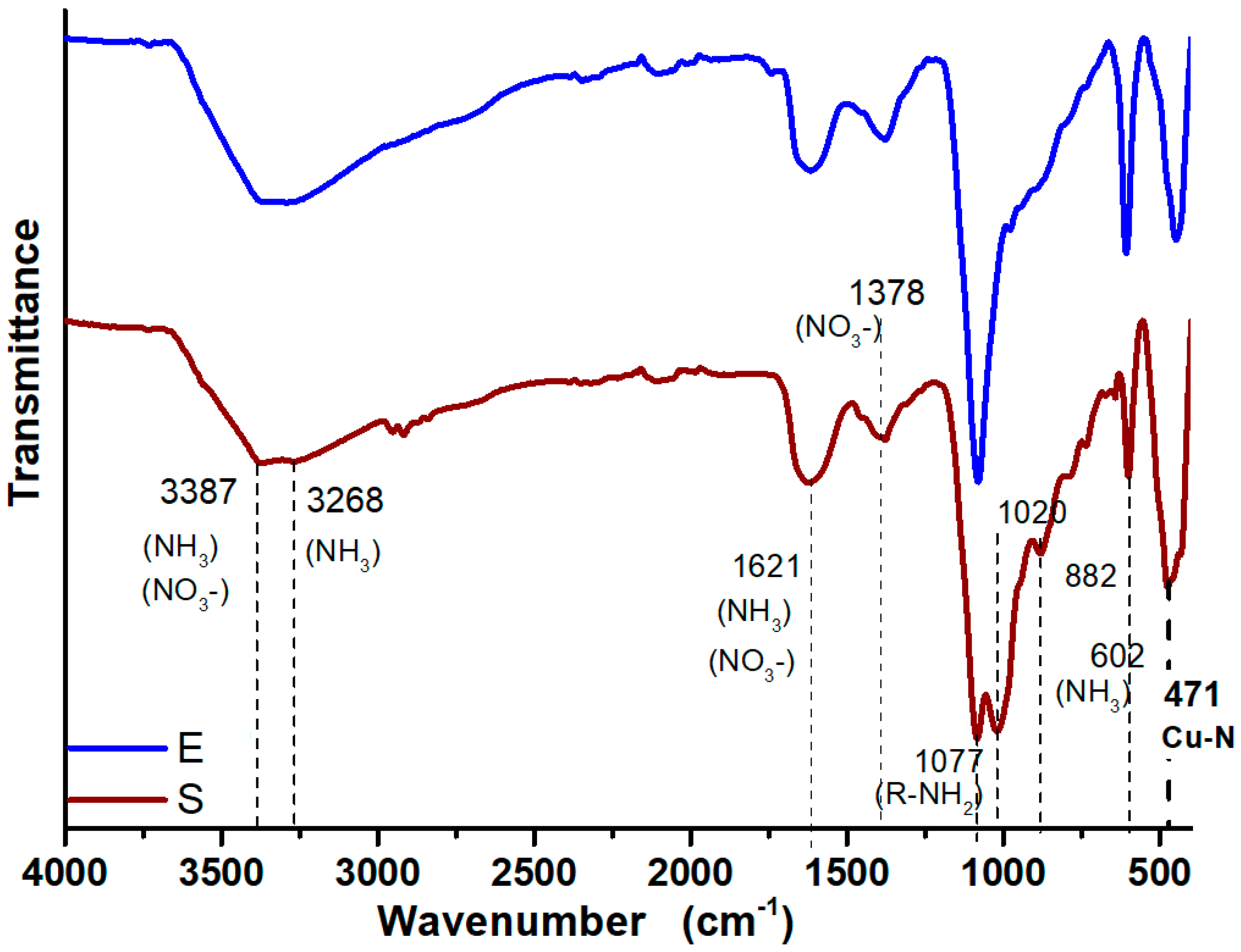
2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopic (FTIR) Analysis of Synthesized CuONPs
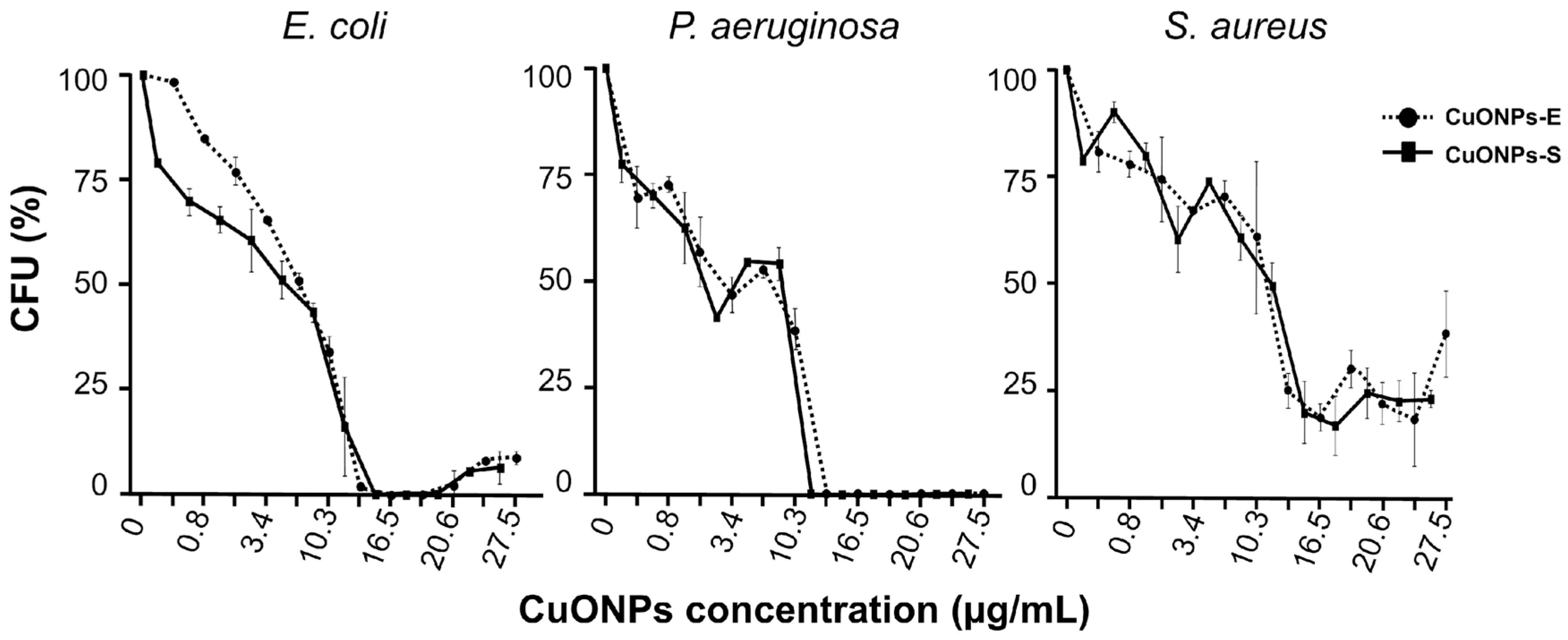
2.7. Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity
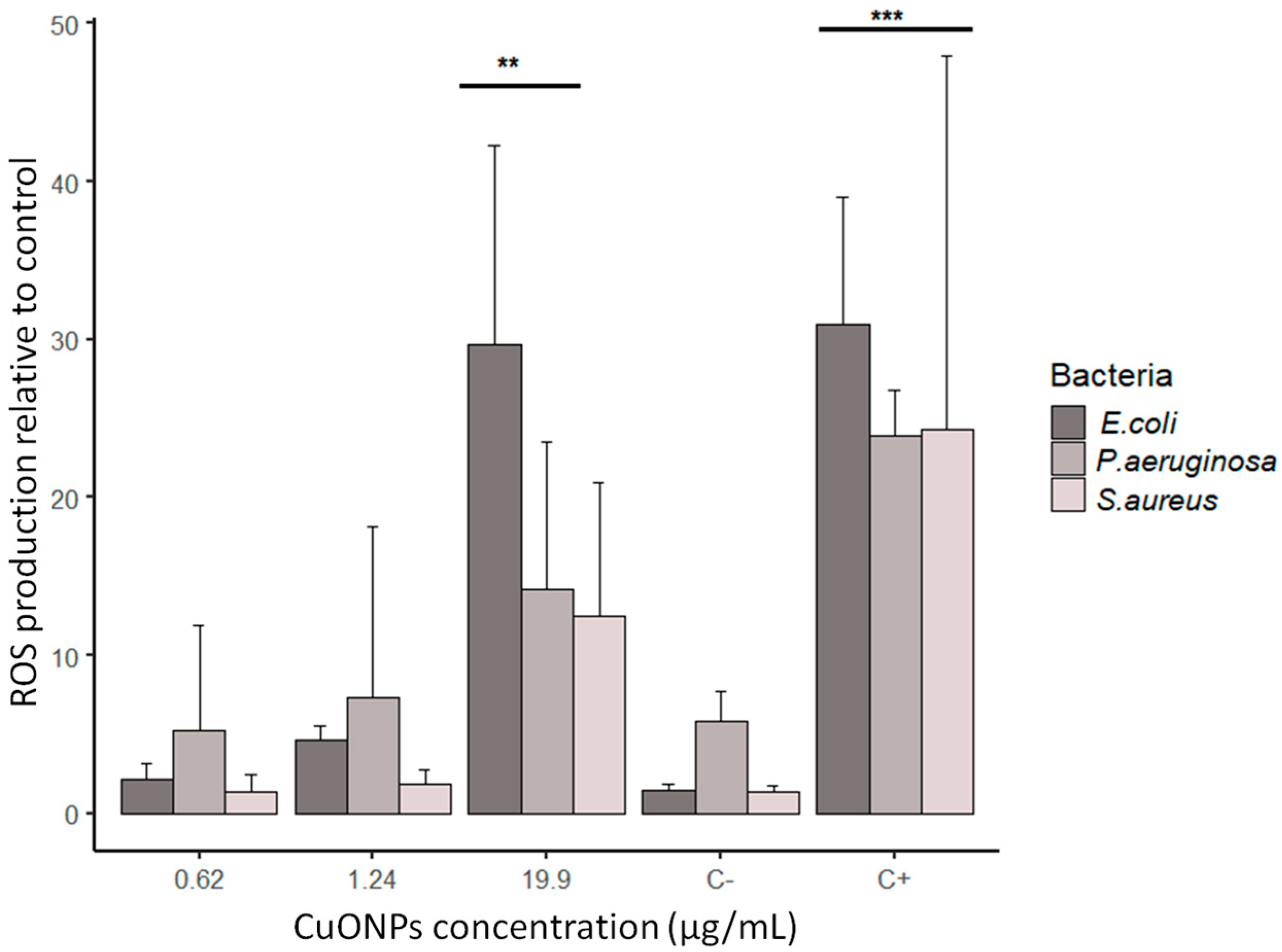
2.8. ROS production in bacteria
2.9. Ultrastructural analysis of bacteria
2.10. Effect of CuONPs in mammalian cell lines
2.11. Statistical analysis
3. Results
3.1. Nanoparticle characterization
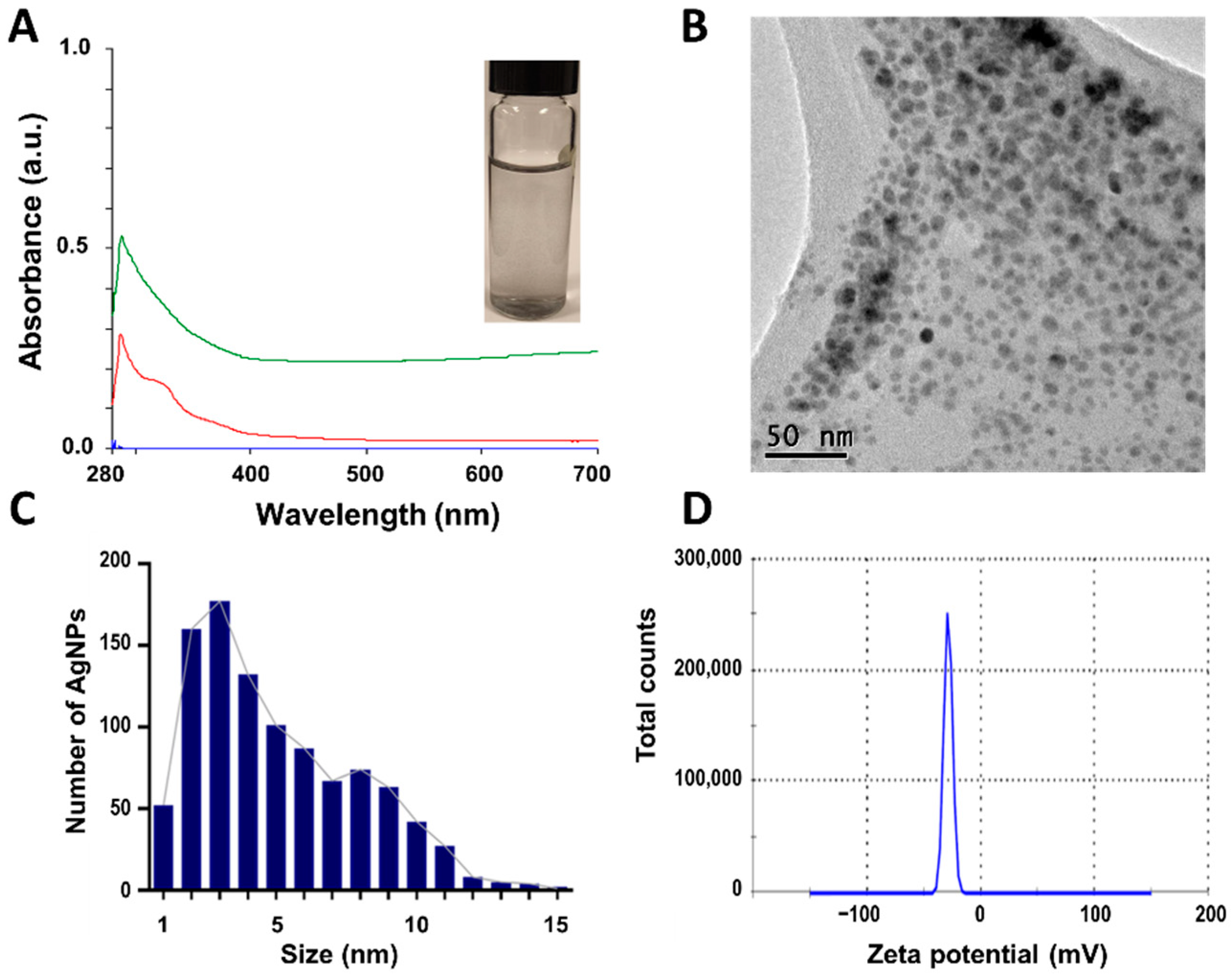
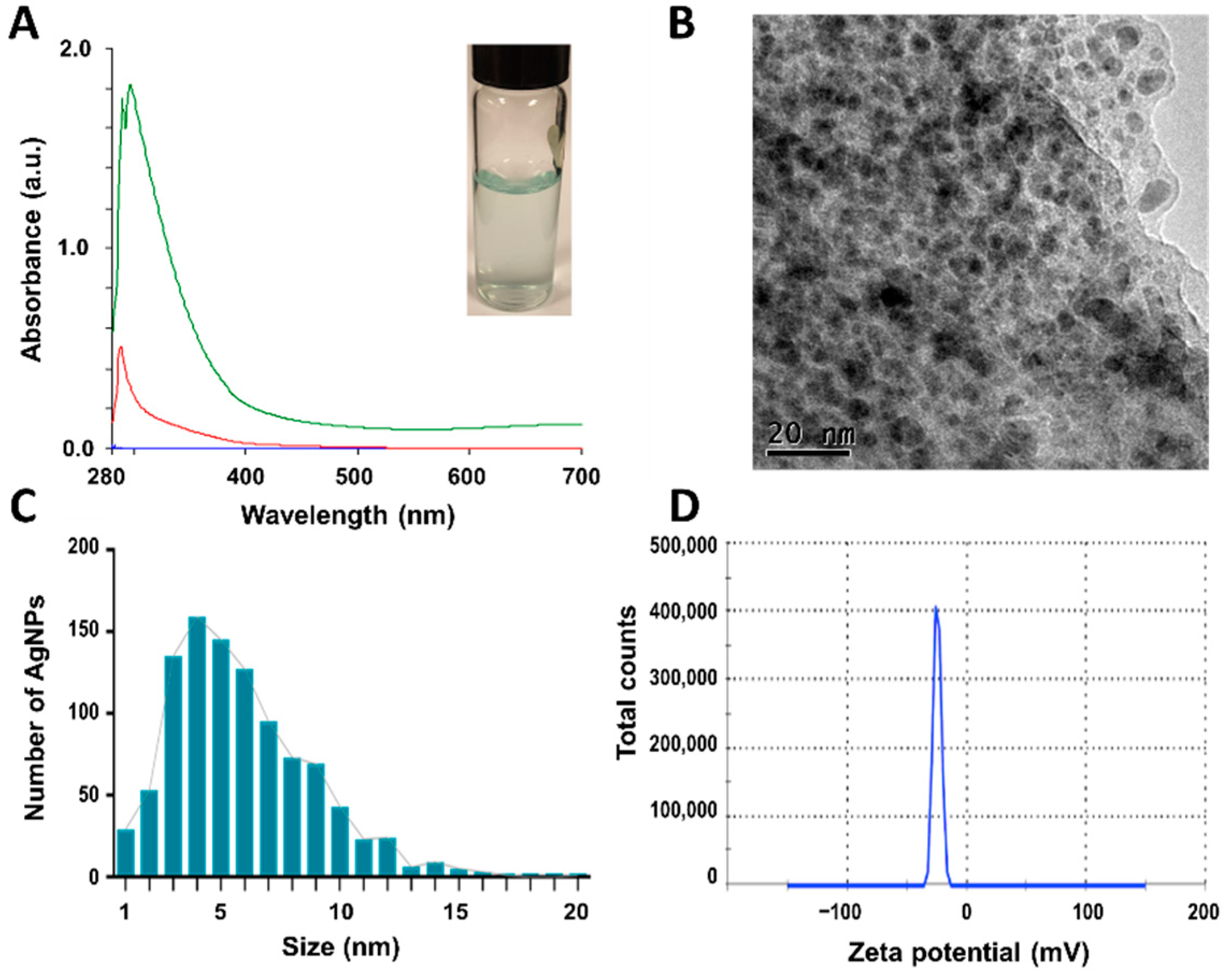
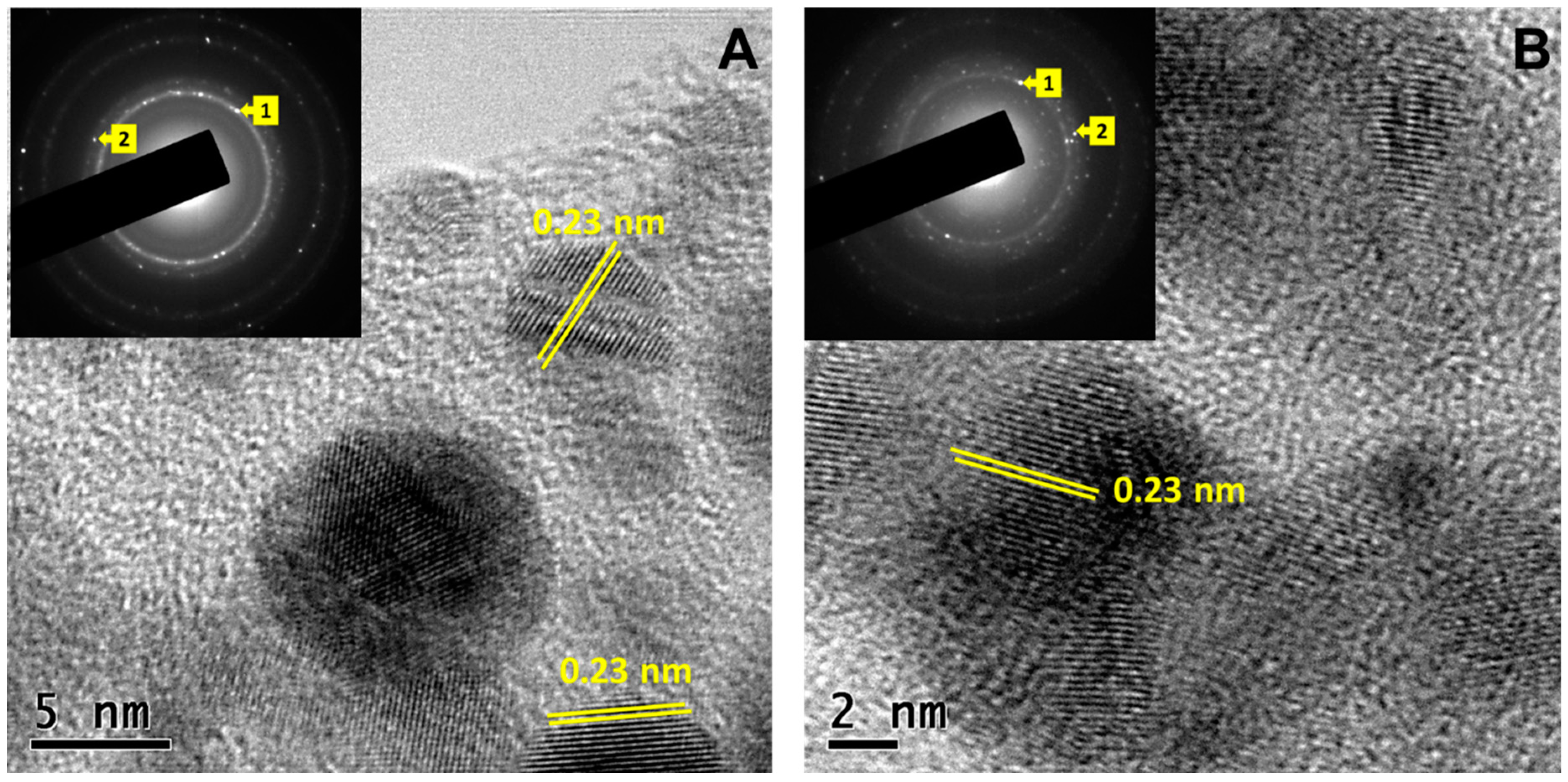
3.2. X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of Synthesized CuONPs
3.3. FTIR Analysis of Synthesized CuONPs
3.4. Antibacterial capacity
| NPs | Physicochemical characteristics | Antimicrobial effect | Toxicity | ||||||||||
| TEM | PDI | ZP (mV) |
Bacteria (µg/mL) |
Cell lines | |||||||||
|
Size (nm) |
Shape | E. coli | P. aeruginosa | S. aureus | AML-12 | RAW-264.7 | MDCK | ||||||
| MIC | IC50 | MIC | IC50 | MIC | IC50 | IC50 | IC50 | IC50 | |||||
| CuONPs-S | 4.5 ± 1.9 |
QS | 0.619 | -28.7 | 15.9 | 8.0 | 13.7 | 4.1 | 15.9 | 8.8 | 3.6 | 7.3 | 7.3 |
| CuONPs-E | 5.2 ± 2.1 |
QS | 0.674 | -24.8 | 16.5 | 8.5 | 16.5 | 3.4 | 16.5 | 10.2 | 14.7 | 29.5 | 29.5 |
3.3. ROS production in bacteria
3.4. Ultrastructural analysis of bacteria
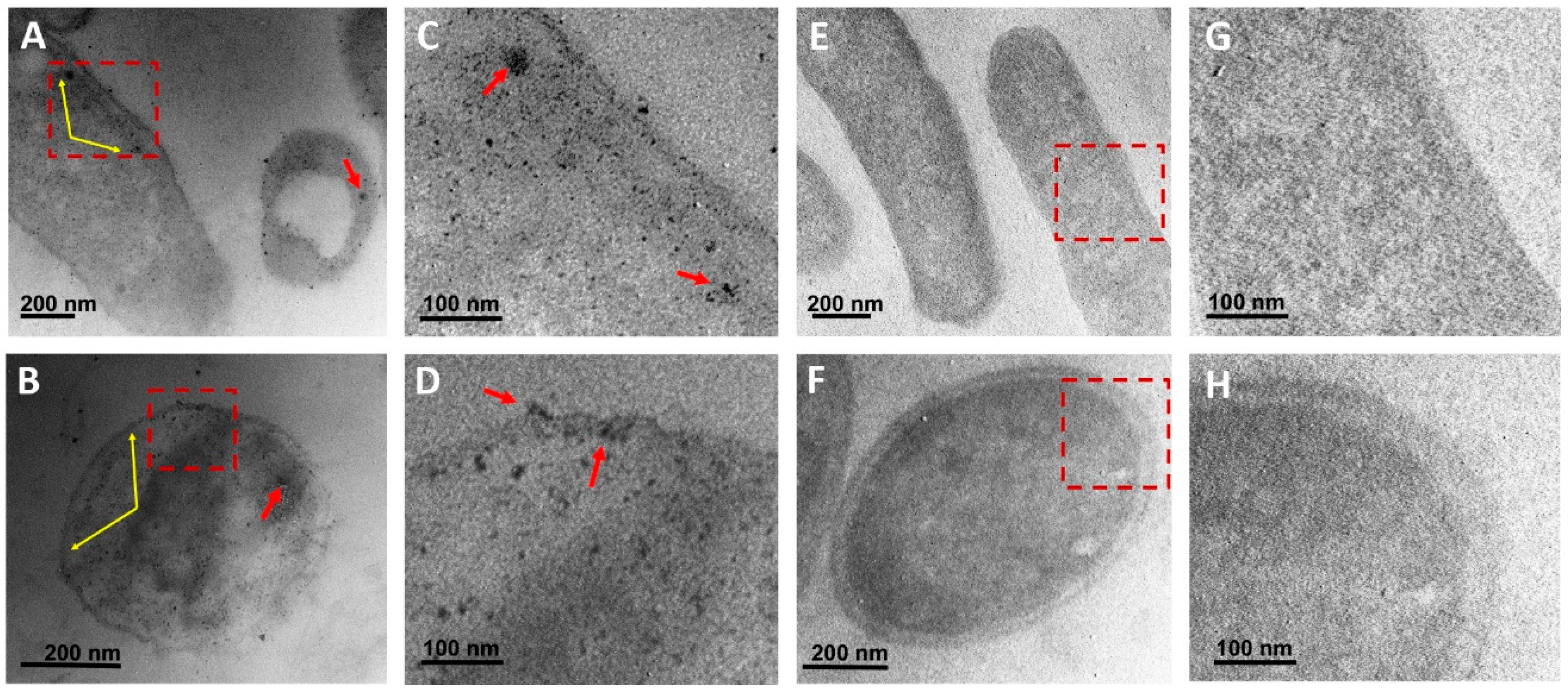
3.5. Toxicity of CuONPs in Mammalian Cell Lines
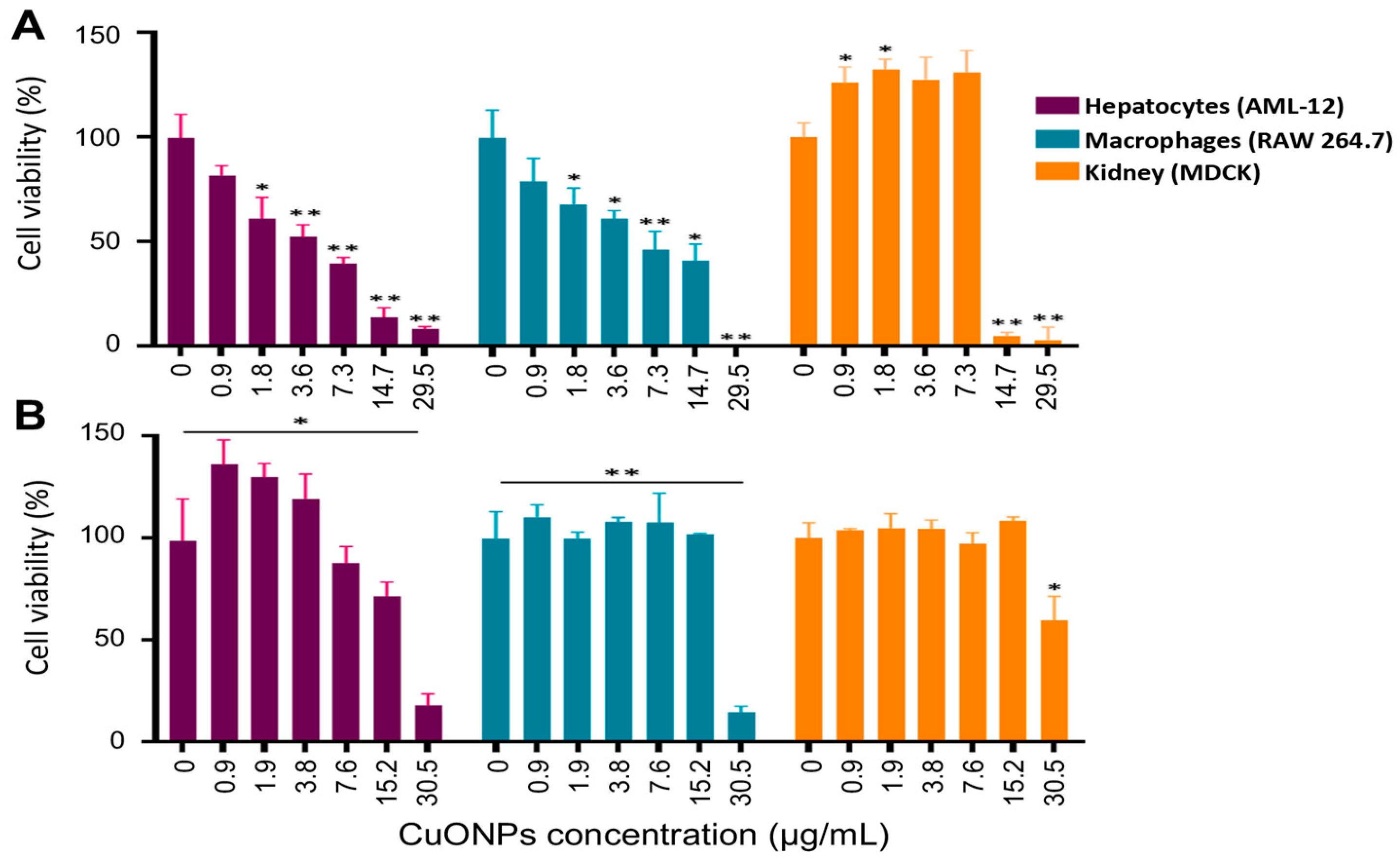

4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blecher, K., Nasir, A., Friedman, A. 2011. The growing role of nanotechnology in combating infectious disease. Virulence, 2(5), 395–401. [CrossRef]
- Farokhzad, O. C., Langer, R. 2009. Impact of nanotechnology on drug delivery. ACS Nano, 3(1), 16–20. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn900002m. [CrossRef]
- Kaweeteerawat, C., Na Ubol, P., Sangmuang, S., Aueviriyavit, S., Maniratanachote, R. 2017. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in bacteria mediated by silver nanoparticles. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health - Part A: Current Issues, 80(23–24), 1276–1289. https://doi.org/10.1080/15287394.2017.1376727. [CrossRef]
- Pelgrift, R. Y., Friedman, A. J. 2013. Nanotechnology as a therapeutic tool to combat microbial resistance. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 65(13–14), 1803–1815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2013.07.011. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L., Gu, F., Chan, J., Wang, A., Langer, R., Farokhzad, O. 2007. Therapeutic, Nanoparticles in Medicine: Applications and Developments. Education Policy Analysis Archives, 8(5), 761–769. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.clp. [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, S., Seyedalipour, B., Shafieyan, S., Kheime, A., Mohammadi, P., Aghdami, N. 2019. Copper nanoparticles promote rapid wound healing in acute full thickness defect via acceleration of skin cell migration, proliferation, and neovascularization. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 517(4), 684–690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.07.110. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y., Lihua, L., Zhu, Y., Wang, X., Li, M., Zefeng, L., Xiaoming, H., Zhang, Y., Qingshiu, Y., Chuanbin, M. 2018. Multifunctional copper-containing carboxymethyl chitosan/alginate scaffolds for eradicating clinical bacterial infection and promoting bone formation. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 10(1), 127–138. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b13750. [CrossRef]
- Norambuena, G. A., Patel, R., Karau, M., Wyles, C. C., Jannetto, P. J., Bennet, K. E., Hanssen, A. D., Sierra, R. J. 2017. Antibacterial and Biocompatible Titanium-Copper Oxide Coating May Be a Potential Strategy to Reduce Periprosthetic Infection: An In Vitro Study. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, 475(3), 722–732. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-016-4713-7. [CrossRef]
- Rajeshkumar, S., Menon, S., Venkat Kumar, S., Tambuwala, M. M., Bakshi, H. A., Mehta, M., Satija, S., Gupta, G., Chellappan, D. K., Thangavelu, L., Dua, K. 2019. Antibacterial and antioxidant potential of biosynthesized copper nanoparticles mediated through Cissus arnotiana plant extract. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology, 197(May). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.111531. [CrossRef]
- 10. Lee J, Choi KH, Min J, Kim HJ, Jee JP, Park BJ. 2017. Functionalized ZnO nanoparticles with gallic acid for antioxidant and antibacterial activity against methicillin resistant S. Aureus. Nanomaterials 7(11):365. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7110365. [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi KR, Sri Venkata NP, Girija SG, Veerabhadra SP, Venkata RMK. 2019. A review on anti-bacterials to combat resistance: from ancient era of plants and metals to present and future perspectives of green nano technological combinations. Asian J Pharm Sci.7:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajps.2019.03.002. [CrossRef]
- Henson, T. E., Navratilova, J., Tennant, A. H., Bradham, K. D., Rogers, K. R., Hughes, M. F. 2019. In vitro intestinal toxicity of copper oxide nanoparticles in rat and human cell models. Nanotoxicology, 13(6), 795–811. https://doi.org/10.1080/17435390.2019.1578428. [CrossRef]
- Midander, K., Cronholm, P., Karlsson, H. L., Elihn, K., Möller, L., Leygraf, C., Wallinder, I. O. 2009. Surface characteristics, copper release, and toxicity of nano- and micrometer-sized copper and copper(ll) oxide particles: A cross-disciplinary study. Small, 5(3), 389–399. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.200801220. [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, M., Anbuvannan, M., & Viruthagiri, G. J. S. A. P. A. M. (2015). Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Solanum nigrum leaf extract and their antibacterial activity. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 136, 864-870. [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, V., Samal, S. K., Mohanty, S., Nayak, S. K. 2019. Recent advancements in biopolymer and metal nanoparticle-based materials in diabetic wound healing management. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 122, 137–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.10.120. [CrossRef]
- Oskam, G. (2006). Metal oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and application. Journal of sol-gel science and technology, 37, 161-164. [CrossRef]
- Gour, A., Jain, N. K. 2019. Advances in green synthesis of nanoparticles. Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine and Biotechnology, 47(1), 844–851. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2019.1577878. [CrossRef]
- Andra, S., Balu, S. K., Jeevanandham, J., Muthalagu, M., Vidyavathy, M., Chan, Y. S., & Danquah, M. K. (2019). Phytosynthesized metal oxide nanoparticles for pharmaceutical applications. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s archives of pharmacology, 392, 755-771. [CrossRef]
- Hussain, I., Singh, N. B., Singh, A., Singh, H., Singh, S. C. 2016. Green synthesis of nanoparticles and its potential application. Biotechnology Letters, 38(4), 545–560. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-2026-7. [CrossRef]
- Kharissova, O. V., Dias, H. V. R., Kharisov, B. I., Pérez, B. O., Pérez, V. M. J. 2013. The greener synthesis of nanoparticles. Trends in Biotechnology, 31(4), 240–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2013.01.003. [CrossRef]
- Shafey, A. M. E. (2020). Green synthesis of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles from plant leaf extracts and their applications: A review. Green Processing and Synthesis, 9(1), 304-339. [CrossRef]
- Castro-Longoria, E. 2016. Fungal Biosynthesis of Nanoparticles, a Cleaner Alternative. In Fungal Applications in Sustainable Environmental Biotechnology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, pp. 323–351. [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Wareth, M. T. A. 2017. Fungal applications in sustainable environmental biotechnology. En International Journal of Environmental Studies. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207233.2017.1363570. [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, G. S., Brar, S. K., Kaur, S., Verma, M. 2012. Green approach for nanoparticle biosynthesis by fungi: Current trends and applications. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 32(1), 49–73. https://doi.org/10.3109/07388551.2010.550568. [CrossRef]
- Vetchinkina, E., Loshchinina, E., Kupryashina, M., Burov, A., Pylaev, T., Nikitina, V. 2018. Green synthesis of nanoparticles with extracellular and intracellular extracts of basidiomycetes. PeerJ, 2018(7). https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.5237. [CrossRef]
- Murillo-Rábago, E. I., Vilchis-Nestor, A. R., Juarez-Moreno, K., Garcia-Marin, L. E., Quester, K., & Castro-Longoria, E. (2022). Optimized synthesis of small and stable silver nanoparticles using intracellular and extracellular components of fungi: An alternative for bacterial inhibition. Antibiotics, 11(6), 800. [CrossRef]
- Bezza, F. A., Tichapondwa, S. M., & Chirwa, E. M. (2020). Fabrication of monodispersed copper oxide nanoparticles with potential application as antimicrobial agents. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 16680. [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, N., Ahmad, F., Da-Wei, L., Zhou, R. Bin, Feng-Li, H., Yin, D. C. 2019. Iron/iron oxide nanoparticles: advances in microbial fabrication, mechanism study, biomedical, and environmental applications. Critical Reviews in Microbiology, 45(3), 278–300. https://doi.org/10.1080/1040841X.2019.1593101. [CrossRef]
- Dadfar, S. M., Roemhild, K., Drude, N. I., von Stillfried, S., Knüchel, R., Kiessling, F., Lammers, T. 2019. Iron oxide nanoparticles: Diagnostic, therapeutic and theranostic applications. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 138, 302–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2019.01.005. [CrossRef]
- Jamdagni, P., Khatri, P., Rana, J. S. 2018. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using flower extract of Nyctanthes arbor-tristis and their antifungal activity. Journal of King Saud University - Science, 30(2), 168–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2016.10.002. [CrossRef]
- Noor, S., Shah, Z., Javed, A., Ali, A., Hussain, S. B., Zafar, S., Ali, H., Muhammad, S. A. 2020. A fungal based synthesis method for copper nanoparticles with the determination of anticancer, antidiabetic and antibacterial activities. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 174(March), 105966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2020.105966. [CrossRef]
- Erci, F., Cakir-Koc, R., Yontem, M., Torlak, E. 2020. Synthesis of biologically active copper oxide nanoparticles as promising novel antibacterial-antibiofilm agents. Preparative Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 6068. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2019.1711393. [CrossRef]
- Nikolova, M. P., & Chavali, M. S. (2020). Metal oxide nanoparticles as biomedical materials. Biomimetics, 5(2), 27. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, Purva, Tulsawani, R. 2020. Ganoderma lucidum aqueous extract prevents hypobaric hypoxia induced memory deficit by modulating neurotransmission, neuroplasticity and maintaining redox homeostasis. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-65812-5. [CrossRef]
- Vetchinkina, E., Shirokov, A., Bucharskaya, A., Navolokin, N., Prilepskii, A., Burov, A., Maslyakova, G., Nikitina, V. 2016. Antitumor activity of extracts from medicinal basidiomycetes mushrooms. International Journal of Medicinal Mushrooms, 18(11), 955–964. https://doi.org/10.1615/IntJMedMushrooms.v18.i11.10. [CrossRef]
- CLSI. 2012. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically; Approved Standard—Ninth Edition (CLSI docum, Vol. 32). Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA.
- Wiegand, I., Hilpert, K., & Hancock, R. E. (2008). Agar and broth dilution methods to determine the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antimicrobial substances. Nature protocols, 3(2), 163-175. [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Muñoz, R., Avalos-Borja, M., & Castro-Longoria, E. (2014). Ultrastructural analysis of Candida albicans when exposed to silver nanoparticles. PloS one, 9(10), e108876. [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, K. (2009). Infrared and Raman spectra of inorganic and coordination compounds, part B: applications in coordination, organometallic, and bioinorganic chemistry. John Wiley & Sons, 6th edition.
- Skoog, D. A., Holler, F. J., & Crouch, S. R. (2017). Principles of instrumental analysis. Cengage learning.
- Hathaway, B. J., & Tomlinson, A. A. G. (1970). Copper (II) ammonia complexes. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 5(1), 1-43.
- Quester, K., Avalos-Borja, M., & Castro-Longoria, E. (2013). Biosynthesis and microscopic study of metallic nanoparticles. Micron, 54, 1-27. [CrossRef]
- Naz, S., Gul, A., & Zia, M. (2020). Toxicity of copper oxide nanoparticles: a review study. IET nanobiotechnology, 14(1), 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Mali, S. C., Dhaka, A., Githala, C. K., Trivedi, R. 2020. Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles using Celastrus paniculatus Willd. leaf extract and their photocatalytic and antifungal properties. Biotechnology Reports, 27, e00518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2020.e00518. [CrossRef]
- Maruthupandy, M., Zuo, Y., Chen, J. S., Song, J. M., Niu, H. L., Mao, C. J., Zhang, S. Y., Shen, Y. H. 2017. Synthesis of metal oxide nanoparticles (CuO and ZnO NPs) via biological template and their optical sensor applications. Applied Surface Science, 397, 167–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.11.118. [CrossRef]
- Sivaraj, R., Rahman, P. K. S. M., Rajiv, P., Salam, H. A., Venckatesh, R. 2014. Biogenic copper oxide nanoparticles synthesis using Tabernaemontana divaricate leaf extract and its antibacterial activity against urinary tract pathogen. Spectrochimica Acta - Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 133, 178–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.05.048. [CrossRef]
- Scheiber, I. F., Mercer, J. F. B., Dringen, R. 2014. Metabolism and functions of copper in brain. Progress in Neurobiology, 116, 33–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2014.01.002. [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, L. M., Libedinsky, A., & Elorza, A. A. (2021). Role of copper on mitochondrial function and metabolism. Frontiers in molecular biosciences, 8, 711227. [CrossRef]
- Barber, R. G., Grenier, Z. A., & Burkhead, J. L. (2021). Copper toxicity is not just oxidative damage: Zinc systems and insight from Wilson disease. Biomedicines, 9(3), 316. [CrossRef]
- El-Batal, A. I., Al-Hazmi, N. E., Mosallam, F. M., El-Sayyad, G. S. 2018. Biogenic synthesis of copper nanoparticles by natural polysaccharides and Pleurotus ostreatus fermented fenugreek using gamma rays with antioxidant and antimicrobial potential towards some wound pathogens. Microbial Pathogenesis, 118, 159–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2018.03.013. [CrossRef]
- Honary, S., Barabadi, H., Gharaei-Fathabad, E., Naghibi, F. 2012. Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Penicillium aurantiogriseum, Penicillium citrinum and Penicillium waksmanii. Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures, 7(3), 999–1005.
- Bishop, K.S.; Kao, C.H.; Xu, Y.; Glucina, M.P.; Paterson, R.R.M.; Ferguson, L.R. From 2000 years of Ganoderma lucidum to recent developments in nutraceuticals. Phytochemistry 2015, 114, 56–65. [CrossRef]
- Consolo, V. F., Torres-Nicolini, A., Alvarez, V. A. 2020. Mycosinthetized Ag, CuO and ZnO nanoparticles from a promising Trichoderma harzianum strain and their antifungal potential against important phytopathogens. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-77294-6. [CrossRef]
- Oza, G., Calzadilla-Avila, A. I., Reyes-Calderón, A., Anna, K. K., Ramírez-Bon, R., Tapia-Ramirez, J., Sharma, A. 2020. pH-dependent biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Galphimia glauca for their cytocompatibility evaluation. Applied Nanoscience (Switzerland), 10(2), 541–550. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01159-2. [CrossRef]
- Ruparelia, J. P., Chatterjee, A. K., Duttagupta, S. P., & Mukherji, S. (2008). Strain specificity in antimicrobial activity of silver and copper nanoparticles. Acta biomaterialia, 4(3), 707-716. [CrossRef]
- Ameh, T., Sayes, C. M. 2019. The potential exposure and hazards of copper nanoparticles: A review. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 71(June), 103220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2019.103220. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P., Goyal, D., & Chudasama, B. (2022). Antibacterial activity of colloidal copper nanoparticles against Gram-negative (Escherichia coli and Proteus vulgaris) bacteria. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 74(5), 695-706. [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A. K., Chakraborty, R., & Basu, T. (2014). Mechanism of antibacterial activity of copper nanoparticles. Nanotechnology, 25(13), 135101. [CrossRef]
- Choi, O., & Hu, Z. (2008). Size dependent and reactive oxygen species related nanosilver toxicity to nitrifying bacteria. Environmental Science & Technology, 42(12), 4583–4588. https://doi.org/10.1021/es703238h . [CrossRef]
- Quinteros, M. A., Cano Aristizábal, V., Dalmasso, P. R., Paraje, M. G., & Páez, P. L. (2016). Oxidative stress generation of silver nanoparticles in three bacterial genera and its relationship with the antimicrobial activity. Toxicology in Vitro, 36, 216–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2016.08.007. [CrossRef]
- Ameh, T., Gibb, M., Stevens, D., Pradhan, S. H., Braswell, E., & Sayes, C. M. (2022). Silver and copper nanoparticles induce oxidative stress in bacteria and mammalian cells. Nanomaterials, 12(14), 2402. [CrossRef]
- Peetla, C., Stine, A., & Labhasetwar, V. (2009). Biophysical interactions with model lipid membranes: Applications in drug discovery and drug delivery. Molecular Pharmaceutics, 6(5), 1264–1276. https://doi.org/10.1021/mp9000662. [CrossRef]
- Le-Deygen, I. M., Safronova, A. S., Mamaeva, P. V., Kolmogorov, I. M., Skuredina, A. A., & Kudryashova, E. V. (2022). Drug–membrane interaction as revealed by spectroscopic methods: The role of drug structure in the example of rifampicin, levofloxacin and rapamycin. Biophysica, 2(4), 353–365. https://doi.org/10.3390/biophysica2040032. [CrossRef]
- Singh, P., Kim, Y.-J., Zhang, D., & Yang, D.-C. (2016). Biological synthesis of nanoparticles from plants and microorganisms. Trends in Biotechnology, 34(7), 588–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2016.02.006. [CrossRef]
- Azam, A., Ahmed, A. S., Oves, M., Khan, M. S., Habib, S. S., & Memic, A. (2012). Antimicrobial activity of metal oxide nanoparticles against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria: a comparative study. International journal of nanomedicine, 6003-6009.
- Bondarenko, O., Juganson, K., Ivask, A., Kasemets, K., Mortimer, M., & Kahru, A. (2013). Toxicity of Ag, CuO and ZnO nanoparticles to selected environmentally relevant test organisms and mammalian cells in vitro: a critical review. Archives of toxicology, 87, 1181-1200. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z., Li, Q., Wang, J., Yu, Y., Wang, Y., Zhou, Q., Li, P. 2020. Reactive Oxygen Species-Related Nanoparticle Toxicity in the Biomedical Field. Nanoscale Research Letters, 15(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-020-03344-7. [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, H. 2014. Self-disinfecting and microbiocide-impregnated surfaces and fabrics: What potential in interrupting the spread of healthcare-associated infection? Clinical Infectious Diseases, 58(6), 848–853. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/cit765. [CrossRef]
- Mitra, D., Kang, E. T., Neoh, K. G. 2020. Antimicrobial Copper-Based Materials and Coatings: Potential Multifaceted Biomedical Applications. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 12(19), 21159–21182. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b17815. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. (2021). A global overview of national regulations and standards for drinking-water quality.
- Liu, H.; Guo, H.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.;Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Copper Induces Hepatic Inflammatory Responses by Activation of MAPKs and NF-KB Signalling Pathways in the Mouse. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 201, 110806. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





