Submitted:
08 July 2023
Posted:
11 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
- Introduction
- Etiology
- COVID-19 variants and their characteristics
- Variants Being Monitored (VBM)
- Variant of Concern (VOC)
- Variants of Interest (VOI)
- Variants of High Consequence (VOHC)
- Alpha variant
- Beta variant
- Delta variant
- Delta AY.4.2
- Omicron variant
- A brief history of the Origins
- Introduction via intermediate host followed by zoonotic transmission
- Direct zoonotic spread
- Introduction through the cold/food chain
- Introduction through a laboratory incident
- Economic Burden of COVID-19
- Lockdown Cost
- Pre-Vaccination Cost
- Direct Healthcare Cost
- Testing
- Indirect cost (Loss of revenue and productivity)
- Vaccination cost (Development, production, and administration)
- Age, Gender, and Racial Disparities
- COVID-19 Pathophysiology
- Early infection phase (Stage 1)
- Pulmonary phase (Stage 2)
- Hyperinflammation phase (Stage 3)
- Histopathology
- Respiratory system
- Gastrointestinal system
- Liver
- Gastrointestinal tract
- Urinary and Reproductive System
- Kidneys
- Testes
- Nervous System
- Brain
- Cardiovascular System
- Heart
- Skin
- Organ System Manifestations
- Ocular manifestations:
- COVID-19-associated Endocrinopathies
- Thyroid:
- Pituitary:
- Adrenal:
- Reproductive:
- Pancreas:
- Obesity:
- Recent Trends of Severity Compared to The Beginning
- Evaluation
- Nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT)
- Antigen testing
- Antibody or serologic testing
- Therapeutics
- Importance of data sharing
- COVID-19 trial challenges
- COVID-19 trials overview
- Prevention trials: To evaluate vaccines or other interventions designed to prevent people from getting infected with SARS-CoV-2. These trials typically involve healthy individuals.
- Treatment trials: Testing treatments for people who have already been diagnosed with COVID-19. Treatments may include drugs, monoclonal antibodies, or other therapies.
- Diagnostic trials: Testing new diagnostic tests or procedures for COVID-19. These tests can help diagnose early infection and identify individuals who may be asymptomatic carriers of the virus.
- Prognostic trials: To identify predictors of disease severity, or outcome. They can help identify patients at high risk for severe disease or complications.
- Observational studies: These studies gather data on patients with COVID-19 and help researchers understand how the disease progresses, how different patient populations are affected, long-term complications from the disease, and which treatments are most effective.
- Importance of ongoing trials to fight COVID-19
- Medications
- Antivirals
- Antibody Products
- Immunomodulators
- Management of Respiratory Failure in COVID-19
- Monitoring Oxygenation
- Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure
- High-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) oxygen therapy
- Non-invasive Ventilation
- Prone Positioning
- Mechanical Ventilation
- Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO)
- Vaccinations
- COVID-19 in special circumstances
- Immunocompromised state
- Pregnancy
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus/Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (HIV/AIDS)
- COVID-19 and mental health
- Long-term Effects, Complications, and Mortality
- Myths associated with COVID-19
- Conclusion
References
- Fauci AS, Lane HC, Redfield RR. Covid-19 — Navigating the Uncharted. N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 26;382(13):1268–9. [CrossRef]
- Phan DHB, Narayan PK. Country Responses and the Reaction of the Stock Market to COVID-19—a Preliminary Exposition. Emerg Mark Finance Trade. 2020 Aug 8;56(10):2138–50. [CrossRef]
- Statista [Internet]. [cited 2023 Apr 18]. Coronavirus (COVID-19) cases by country worldwide 2023. Available from: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1043366/novel-coronavirus-2019ncov-cases-worldwide-by-country/.
- Kaye AD, Okeagu CN, Pham AD, Silva RA, Hurley JJ, Arron BL, et al. Economic impact of COVID-19 pandemic on healthcare facilities and systems: International perspectives. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2021 Oct 1;35(3):293–306. [CrossRef]
- Mehta OP, Bhandari P, Raut A, Kacimi SEO, Huy NT. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): Comprehensive Review of Clinical Presentation. Front Public Health [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 Apr 18];8. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2020.582932. [CrossRef]
- COVID - Coronavirus Statistics - Worldometer [Internet]. [cited 2023 Apr 18]. Available from: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/.
- Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song J, et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 2020 Feb 20;382(8):727–33. [CrossRef]
- Lei J, Kusov Y, Hilgenfeld R. Nsp3 of coronaviruses: Structures and functions of a large multi-domain protein. Antiviral Res. 2018 Jan;149:58–74. [CrossRef]
- Haque SM, Ashwaq O, Sarief A, Azad John Mohamed AK. A comprehensive review about SARS-CoV-2. Future Virol. 2020 Sep;15(9):625–48. [CrossRef]
- Malik, YA. Malik YA. Properties of Coronavirus and SARS-CoV-2. Malays J Pathol. 2020 Apr;42(1):3–11.
- Chin AWH, Chu JTS, Perera MRA, Hui KPY, Yen HL, Chan MCW, et al. Stability of SARS-CoV-2 in different environmental conditions. Lancet Microbe. 2020 May;1(1):e10. [CrossRef]
- Zhou H, Ji J, Chen X, Bi Y, Li J, Wang Q, et al. Identification of novel bat coronaviruses sheds light on the evolutionary origins of SARS-CoV-2 and related viruses. Cell. 2021 Aug 19;184(17):4380-4391.e14. [CrossRef]
- Pagani I, Ghezzi S, Alberti S, Poli G, Vicenzi E. Origin and evolution of SARS-CoV-2. Eur Phys J Plus. 2023;138(2):157.
- Virological [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 Apr 1]. Early appearance of two distinct genomic lineages of SARS-CoV-2 in different Wuhan wildlife markets suggests SARS-CoV-2 has a natural origin. Available from: https://virological.org/t/early-appearance-of-two-distinct-genomic-lineages-of-sars-cov-2-in-different-wuhan-wildlife-markets-suggests-sars-cov-2-has-a-natural-origin/691.
- Oreshkova N, Molenaar RJ, Vreman S, Harders F, Oude Munnink BB, Hakze-van der Honing RW, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection in farmed minks, the Netherlands, April and May 2020. Eurosurveillance. 2020 Jun 11;25(23):2001005.
- Patterson EI, Elia G, Grassi A, Giordano A, Desario C, Medardo M, et al. Evidence of exposure to SARS-CoV-2 in cats and dogs from households in Italy. Nat Commun. 2020 Dec 4;11:6231. [CrossRef]
- McAloose D, Laverack M, Wang L, Killian ML, Caserta LC, Yuan F, et al. From People to Panthera: Natural SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Tigers and Lions at the Bronx Zoo. mBio. 2020 Oct 13;11(5):e02220-20. [CrossRef]
- Graham RL, Baric RS. Recombination, Reservoirs, and the Modular Spike: Mechanisms of Coronavirus Cross-Species Transmission. J Virol. 2010 Apr;84(7):3134–46. [CrossRef]
- Giovanetti M, Benedetti F, Campisi G, Ciccozzi A, Fabris S, Ceccarelli G, et al. Evolution patterns of SARS-CoV-2: Snapshot on its genome variants. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 Jan 29;538:88–91. [CrossRef]
- Rahimi A, Mirzazadeh A, Tavakolpour S. Genetics and genomics of SARS-CoV-2: A review of the literature with the special focus on genetic diversity and SARS-CoV-2 genome detection. Genomics. 2021 Jan 1;113(1, Part 2):1221–32. [CrossRef]
- WHO. Tracking SARS-CoV-2 variants [Internet]. [cited 2023 Mar 22]. Available from: https://www.who.int/activities/tracking-SARS-CoV-2-variants.
- CDC. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2020 [cited 2023 Mar 22]. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Variants of the Virus. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/variants/index.html.
- Gaymard A, Bosetti P, Feri A, Destras G, Enouf V, Andronico A, et al. Early assessment of diffusion and possible expansion of SARS-CoV-2 Lineage 20I/501Y.V1 (B.1.1.7, variant of concern 202012/01) in France, January to March 2021. Eurosurveillance. 2021 Mar 4;26(9):2100133.
- Davies NG, Abbott S, Barnard RC, Jarvis CI, Kucharski AJ, Munday JD, et al. Estimated transmissibility and impact of SARS-CoV-2 lineage B.1.1.7 in England. Science. 2021 Apr 9;372(6538):eabg3055. [CrossRef]
- UK Govt. GOV.UK. [cited 2023 Mar 22]. NERVTAG paper on COVID-19 variant of concern B.1.1.7. Available from: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/nervtag-paper-on-covid-19-variant-of-concern-b117.
- Zeng B, Gao L, Zhou Q, Yu K, Sun F. Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2022 May 23;20(1):200. [CrossRef]
- Jacobs JL, Haidar G, Mellors JW. COVID-19: Challenges of Viral Variants. Annu Rev Med. 2023;74(1):31–53. [CrossRef]
- Madhi SA, Baillie V, Cutland CL, Voysey M, Koen AL, Fairlie L, et al. Efficacy of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Covid-19 Vaccine against the B.1.351 Variant. N Engl J Med. 2021 May 20;384(20):1885–98. [CrossRef]
- Duong, D. Duong D. Alpha, Beta, Delta, Gamma: What’s important to know about SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern? CMAJ. 2021 Jul 12;193(27):E1059–60. [CrossRef]
- Abu-Raddad LJ, Chemaitelly H, Ayoub HH, Yassine HM, Benslimane FM, Al Khatib HA, et al. Severity, Criticality, and Fatality of the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Beta Variant. Clin Infect Dis. 2022 Jul 1;75(1):e1188–91. [CrossRef]
- Lin L, Liu Y, Tang X, He D. The Disease Severity and Clinical Outcomes of the SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern. Front Public Health [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 Mar 22];9. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2021.775224. [CrossRef]
- EU CDC. Threat Assessment Brief: Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617 variants in India and situation in the EU/EEA [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 Mar 22]. Available from: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/threat-assessment-emergence-sars-cov-2-b1617-variants.
- Allen H, Vusirikala A, Flannagan J, Twohig KA, Zaidi A, Chudasama D, et al. Household transmission of COVID-19 cases associated with SARS-CoV-2 delta variant (B.1.617.2): national case-control study. Lancet Reg Health - Eur. 2022 Jan 1;12:100252. [CrossRef]
- Bolze A, Luo S, White S, Cirulli ET, Wyman D, Rossi AD, et al. SARS-CoV-2 variant Delta rapidly displaced variant Alpha in the United States and led to higher viral loads. Cell Rep Med [Internet]. 2022 Mar 15 [cited 2023 Mar 22];3(3). Available from: https://www.cell.com/cell-reports-medicine/abstract/S2666-3791(22)00071-4.
- Twohig KA, Nyberg T, Zaidi A, Thelwall S, Sinnathamby MA, Aliabadi S, et al. Hospital admission and emergency care attendance risk for SARS-CoV-2 delta (B.1.617.2) compared with alpha (B.1.1.7) variants of concern: a cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2022 Jan 1;22(1):35–42. [CrossRef]
- Delta variant : what we know about the science [Internet]. [cited 2023 May 3]. Available from: https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/108671.
- Khandia R, Singhal S, Alqahtani T, Kamal MA, El-Shall NA, Nainu F, et al. Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron (B.1.1.529) variant, salient features, high global health concerns and strategies to counter it amid ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. Environ Res. 2022 Jun 1;209:112816. [CrossRef]
- Arora S, Grover V, Saluja P, Algarni YA, Saquib SA, Asif SM, et al. Literature Review of Omicron: A Grim Reality Amidst COVID-19. Microorganisms. 2022 Feb;10(2):451. [CrossRef]
- Lubin JH, Markosian C, Balamurugan D, Pasqualini R, Arap W, Burley SK, et al. Structural models of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant in complex with ACE2 receptor or antibodies suggest altered binding interfaces [Internet]. bioRxiv; 2021 [cited 2023 Mar 22]. p. 2021.12.12.472313. Available from: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.12.12.472313v1.
- Christie, B. Christie B. Covid-19: Early studies give hope omicron is milder than other variants. BMJ. 2021 Dec 23;375:n3144. [CrossRef]
- Hui KPY, Ho JCW, Cheung M chun, Ng K chun, Ching RHH, Lai K ling, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant replication in human bronchus and lung ex vivo. Nature. 2022 Mar;603(7902):715–20. [CrossRef]
- Parums DV. Editorial: The XBB.1.5 (‘Kraken’) Subvariant of Omicron SARS-CoV-2 and its Rapid Global Spread. Med Sci Monit [Internet]. 2023 Feb 1 [cited 2023 Mar 22];29. Available from: https://medscimonit.com/abstract/full/idArt/939580.
- Andersen KG, Rambaut A, Lipkin WI, Holmes EC, Garry RF. The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2. Nat Med. 2020 Apr;26(4):450–2. [CrossRef]
- Holmes EC, Goldstein SA, Rasmussen AL, Robertson DL, Crits-Christoph A, Wertheim JO, et al. The origins of SARS-CoV-2: A critical review. Cell. 2021 Sep;184(19):4848–56.
- NCBI [Internet]. [cited 2023 May 2]. News: What does the science say about the.. (NPR News) - Behind the headlines - NLM. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/search/research-news/18331.
- Zhu H, Wei L, Niu P. The novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China. Glob Health Res Policy. 2020 Mar 2;5(1):6. [CrossRef]
- Team TNCPERE. The Epidemiological Characteristics of an Outbreak of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Diseases (COVID-19) — China, 2020. China CDC Wkly. 2020 Feb 1;2(8):113–22.
- Worobey M, Levy JI, Malpica Serrano L, Crits-Christoph A, Pekar JE, Goldstein SA, et al. The Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market in Wuhan was the early epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic. Science. 2022 Aug 26;377(6609):951–9. [CrossRef]
- Mallapaty S. WHO abandons plans for crucial second phase of COVID-origins investigation. Nature [Internet]. 2023 Feb 14 [cited 2023 May 2]; Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-023-00283-y. [CrossRef]
- WHO-convened global study of origins of SARS-CoV-2: China Part [Internet]. [cited 2023 May 2]. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/who-convened-global-study-of-origins-of-sars-cov-2-china-part.
- A Lab Leak in China Most Likely Origin of Covid Pandemic, Energy Department Says - WSJ [Internet]. [cited 2023 May 2]. Available from: https://www.wsj.com/articles/covid-origin-china-lab-leak-807b7b0a.
- Richards F, Kodjamanova P, Chen X, Li N, Atanasov P, Bennetts L, et al. Economic Burden of COVID-19: A Systematic Review. Clin Outcomes Res CEOR. 2022;14:293–307. [CrossRef]
- Kohli M, Maschio M, Becker D, Weinstein MC. The potential public health and economic value of a hypothetical COVID-19 vaccine in the United States: Use of cost-effectiveness modeling to inform vaccination prioritization. Vaccine. 2021 Feb 12;39(7):1157–64. [CrossRef]
- Athanasakis K, Nomikos N, Souliotis K, Kyriopoulos J. PNS21 From Disease Burden to Healthcare Cost: Highlighting the Health Economics Aspects of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Value Health. 2020 Dec 1;23:S647. [CrossRef]
- Miethke-Morais A, Cassenote A, Piva H, Tokunaga E, Cobello V, Rodrigues Gonçalves FA, et al. COVID-19-related hospital cost-outcome analysis: The impact of clinical and demographic factors. Braz J Infect Dis Off Publ Braz Soc Infect Dis. 2021;25(4):101609. [CrossRef]
- Miles DK, Stedman M, Heald AH. “Stay at Home, Protect the National Health Service, Save Lives”: A cost benefit analysis of the lockdown in the United Kingdom. Int J Clin Pract. 2021;75(3):e13674. [CrossRef]
- Hafner M, Yerushalmi E, Fays C, Dufresne E, Van Stolk C. COVID-19 and the cost of vaccine nationalism [Internet]. RAND Corporation; 2020 [cited 2023 May 2]. Available from: https://www.rand.org/pubs/research_reports/RRA769-1.html.
- The Potential Health Care Costs And Resource Use Associated With COVID-19 In The United States | Health Affairs [Internet]. [cited 2023 May 2]. Available from: https://www.healthaffairs.org/doi/10.1377/hlthaff.2020.00426. [CrossRef]
- Nakhaei K, Jalilian H, Arab-Zozani M, Heydari S, Torkzadeh L, Taji M. Direct and indirect cost of COVID-19 patients in Iran. Health Policy Technol. 2021 Dec;10(4):100572. [CrossRef]
- Gedik H. The cost analysis of inpatients with COVID-19. Acta Medica Mediterr. 2020 Dec 1;(6):3289–92.
- Yigezu A, Zewdie SA, Mirkuzie AH, Abera A, Hailu A, Agachew M, et al. Cost-analysis of COVID-19 sample collection, diagnosis, and contact tracing in low resource setting: The case of Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. PLOS ONE. 2022 Jun 9;17(6):e0269458. [CrossRef]
- Hashmi P, Fahad S, Naqi Khan H, Zahid M, Sadruddin A, Noordin S. Covid-19 pandemic: Economic burden on patients with musculoskeletal injuries in a tertiary care hospital of LMIC; retrospective cross sectional study. Ann Med Surg 2012. 2020 Dec;60:5–8. [CrossRef]
- US Taxpayers Heavily Funded the Discovery of COVID-19 Vaccines - PMC [Internet]. [cited 2023 Jun 6]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8426978/.
- Nonvignon J, Owusu R, Asare B, Adjagba A, Aun YW, Yeung KHT, et al. Estimating the cost of COVID-19 vaccine deployment and introduction in Ghana using the CVIC tool. Vaccine. 2022 Mar 15;40(12):1879–87. [CrossRef]
- Williamson EJ, Walker AJ, Bhaskaran K, Bacon S, Bates C, Morton CE, et al. Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY. Nature. 2020 Aug;584(7821):430–6. [CrossRef]
- Gallo Marin B, Aghagoli G, Lavine K, Yang L, Siff EJ, Chiang SS, et al. Predictors of COVID-19 severity: A literature review. Rev Med Virol. 2021 Jan;31(1):1–10. [CrossRef]
- CDC. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2020 [cited 2023 May 2]. COVID Data Tracker. Available from: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2023 May 3]. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/variants/index.html.
- Carethers, JM. Carethers JM. Insights into disparities observed with COVID-19. J Intern Med. 2021 Apr;289(4):463–73. [CrossRef]
- Pivonello R, Auriemma RS, Pivonello C, Isidori AM, Corona G, Colao A, et al. Sex Disparities in COVID-19 Severity and Outcome: Are Men Weaker or Women Stronger? Neuroendocrinology. 2021;111(11):1066–85. [CrossRef]
- Mackey K, Ayers CK, Kondo KK, Saha S, Advani SM, Young S, et al. Racial and Ethnic Disparities in COVID-19-Related Infections, Hospitalizations, and Deaths : A Systematic Review. Ann Intern Med. 2021 Mar;174(3):362–73. [CrossRef]
- Magesh S, John D, Li WT, Li Y, Mattingly-App A, Jain S, et al. Disparities in COVID-19 Outcomes by Race, Ethnicity, and Socioeconomic Status: A Systematic-Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Nov 1;4(11):e2134147. [CrossRef]
- Su S, Wong G, Shi W, Liu J, Lai ACK, Zhou J, et al. Epidemiology, Genetic Recombination, and Pathogenesis of Coronaviruses. Trends Microbiol. 2016 Jun 1;24(6):490–502. [CrossRef]
- Wiersinga WJ, Rhodes A, Cheng AC, Peacock SJ, Prescott HC. Pathophysiology, Transmission, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review. JAMA. 2020 Aug 25;324(8):782–93. [CrossRef]
- Yang H, Rao Z. Structural biology of SARS-CoV-2 and implications for therapeutic development. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2021 Nov;19(11):685–700. [CrossRef]
- Lamers MM, Haagmans BL. SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2022 May;20(5):270–84. [CrossRef]
- Marik PE, Iglesias J, Varon J, Kory P. A scoping review of the pathophysiology of COVID-19. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 26;35:20587384211048024. [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi HK, Mehra MR. COVID-19 illness in native and immunosuppressed states: A clinical–therapeutic staging proposal. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2020 May 1;39(5):405–7. [CrossRef]
- Teuwen LA, Geldhof V, Pasut A, Carmeliet P. COVID-19: the vasculature unleashed. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020;20(7):389–91. [CrossRef]
- Azkur AK, Akdis M, Azkur D, Sokolowska M, van de Veen W, Brüggen M, et al. Immune response to SARS-CoV-2 and mechanisms of immunopathological changes in COVID-19. Allergy. 2020 Jul;75(7):1564–81. [CrossRef]
- Cascella M, Montomoli J, Bellini V, Bignami E. Evaluating the Feasibility of ChatGPT in Healthcare: An Analysis of Multiple Clinical and Research Scenarios. J Med Syst. 2023;47(1):33. [CrossRef]
- Ackermann M, Verleden SE, Kuehnel M, Haverich A, Welte T, Laenger F, et al. Pulmonary Vascular Endothelialitis, Thrombosis, and Angiogenesis in Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020 Jul 9;383(2):120–8. [CrossRef]
- Conti P, Ronconi G, Caraffa A, Gallenga C, Ross R, Frydas I, et al. Induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1 and IL-6) and lung inflammation by Coronavirus-19 (COVI-19 or SARS-CoV-2): anti-inflammatory strategies. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020 Apr;34(2):327–31.
- Kornowski R, Witberg G. Acute myocarditis caused by COVID-19 disease and following COVID-19 vaccination. Open Heart. 2022 Mar 1;9(1):e001957. [CrossRef]
- Mehta P, McAuley DF, Brown M, Sanchez E, Tattersall RS, Manson JJ. COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. The Lancet. 2020 Mar 28;395(10229):1033–4. [CrossRef]
- Tian S, Xiong Y, Liu H, Niu L, Guo J, Liao M, et al. Pathological Study of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) through Post-Mortem Core Biopsies. 2020 Mar 20 [cited 2023 Mar 22]; Available from: https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202003.0311/v1.
- Borczuk AC, Salvatore SP, Seshan SV, Patel SS, Bussel JB, Mostyka M, et al. COVID-19 pulmonary pathology: a multi-institutional autopsy cohort from Italy and New York City. Mod Pathol. 2020 Nov;33(11):2156–68. [CrossRef]
- Hanley B, Naresh KN, Roufosse C, Nicholson AG, Weir J, Cooke GS, et al. Histopathological findings and viral tropism in UK patients with severe fatal COVID-19: a post-mortem study. Lancet Microbe. 2020 Oct;1(6):e245–53. [CrossRef]
- Xiao F, Tang M, Zheng X, Liu Y, Li X, Shan H. Evidence for Gastrointestinal Infection of SARS-CoV-2. Gastroenterology. 2020 May 1;158(6):1831-1833.e3.
- Su H, Yang M, Wan C, Yi LX, Tang F, Zhu HY, et al. Renal histopathological analysis of 26 postmortem findings of patients with COVID-19 in China. Kidney Int. 2020 Jul;98(1):219–27. [CrossRef]
- Duarte-Neto AN, Teixeira TA, Caldini EG, Kanamura CT, Gomes-Gouvêa MS, dos Santos ABG, et al. Testicular pathology in fatal COVID-19: A descriptive autopsy study. Andrology. 2022 Jan;10(1):13–23. [CrossRef]
- Solomon IH, Normandin E, Bhattacharyya S, Mukerji SS, Keller K, Ali AS, et al. Neuropathological Features of Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020 Jun 12;NEJMc2019373. [CrossRef]
- Escher F, Pietsch H, Aleshcheva G, Bock T, Baumeier C, Elsaesser A, et al. Detection of viral SARS-CoV-2 genomes and histopathological changes in endomyocardial biopsies. ESC Heart Fail. 2020 Jun 12;7(5):2440–7. [CrossRef]
- Gianotti R, Zerbi P, Dodiuk-Gad RP. Clinical and histopathological study of skin dermatoses in patients affected by COVID-19 infection in the Northern part of Italy. J Dermatol Sci. 2020 May;98(2):141–3. [CrossRef]
- Cazzato, G. Cazzato G. Cutaneous Manifestations of SARS-CoV-2, Cutaneous Adverse Reactions to Vaccines Anti-SARS-CoV-2 and Clinical/Dermoscopical Findings: Where We Are and Where We Will Go. Vaccines. 2023 Jan 10;11(1):152. [CrossRef]
- Kumar P, Radha G, Muthukrishnan M, Chandrasekaran B, Subbiah P, Raman J. Cutaneous Manifestations Associated with COVID-19 Infection in a COVID-Designated Hospital in North Chennai – A Descriptive Cross-Sectional Study. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2022 Dec 29;14(1):67–71. [CrossRef]
- Rajan M B, Kumar-M P, Bhardwaj A. The trend of cutaneous lesions during COVID-19 pandemic: lessons from a meta-analysis and systematic review. Int J Dermatol. 2020 Nov;59(11):1358–70. [CrossRef]
- Afrisham R, Jadidi Y, Davoudi M, Moayedi K, Karami S, Sadegh-Nejadi S, et al. Renal, Cardiac, Neurological, Cutaneous and Coagulopathic Long-term Manifestations of COVID-19 after Recovery; A review. Epidemiol Infect. 2022 Sep 21;1–29. [CrossRef]
- Lin L, Chen Y, Han D, Yang A, Wang AY, Qi W. Cardiorenal Syndrome in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Jun 28;9:915533. [CrossRef]
- Crosier R, Kafil TS, Paterson DI. Imaging for Cardiovascular Complications of COVID-19: Cardiac Manifestations in Context. Can J Cardiol. 2023 Jan 31;S0828-282X(23)00068-5. [CrossRef]
- Dommaraju S, Avula S, Buch T, Kela K, Babic M. Brugada pattern unmasked by covid19 infection complicated by cardiogenic shock. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021 May 11;77(18_Supplement_1):2020–2020. [CrossRef]
- Dubey L, Dorosh O, Dubey N, Doan S, Kozishkurt O, Duzenko O, et al. COVID-19-induced coagulopathy: Experience, achievements, prospects. Cardiol J. 2023 Jan 2; [CrossRef]
- Kobusiak-Prokopowicz M, Fułek K, Fułek M, Kaaz K, Mysiak A, Kurpas D, et al. Cardiovascular, Pulmonary, and Neuropsychiatric Short- and Long-Term Complications of COVID-19. Cells. 2022 Dec 1;11(23):3882. [CrossRef]
- Molina G, Contreras R, Coombes K, Walgamage T, Perozo MA, DesBiens MT. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Following COVID-19 Infection. Cureus. 15(1):e34307. [CrossRef]
- Iskander P, Zheng J, Zaidi SMH, Iskander A. A coagulopathic conundrum of COVID-19. Univ Tor Med J [Internet]. 2023 Feb 28 [cited 2023 Jun 27];100(1). Available from: https://jps.library.utoronto.ca/index.php/utmj/article/view/39018.
- Kalita P, Dey B, Mishra J, Tiewsoh I, Raphael V. Immunoglobulin A Nephropathy in a SARS-CoV-2-Positive Patient With Coexistent Metabolic Syndrome. Cureus. 14(9):e28719. [CrossRef]
- Malgaj Vrečko M, Aleš Rigler A, Večerić-Haler Ž. Coronavirus Disease 2019-Associated Thrombotic Microangiopathy: Literature Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 25;23(19):11307. [CrossRef]
- Janbazi Roudsari H, Negaresh M, Shirzadeh V, Mohammadzadeh Germi B, Mirzaei A. Renal vein thrombosis after COVID-19: A case report. Clin Case Rep. 2022 Dec 26;10(12):e6778. [CrossRef]
- Flores VAG, Chicano S, Resontoc LP, Aragon EE. Diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis in a patient with COVID-19 infection. BMJ Case Rep CP. 2023 Jan 1;16(1):e251962. [CrossRef]
- El-Kassas M, Alboraie M, Elbadry M, El Sheemy R, Abdellah M, Afify S, et al. Non-pulmonary involvement in COVID-19: A systemic disease rather than a pure respiratory infection. World J Clin Cases. 2023 Jan 26;11(3):493–505. [CrossRef]
- Radovic S, Meng W, Chen L, Paniz Mondolfi AE, Bryce C, Grimes Z, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection of kidney tissues from severe COVID-19 patients. J Med Virol. 2023 Feb;95(2):e28566. [CrossRef]
- Jayadi, Airlangga PS, Kusuma E, Waloejo CS, Salinding A, Lestari P. Correlation between serum surfactant protein-D level with respiratory compliance and acute respiratory distress syndrome in critically ill COVID-19 Patients: A retrospective observational study. Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci. 2022;12(4):204–10. [CrossRef]
- Vangara A, Rahmlow TH, Gullapalli D, Kommineni SS, Haroon M, Ganti SS, et al. COVID-19 and Cavitary Lesion in Lung. Cureus [Internet]. 2023 Jan 23 [cited 2023 Jun 28];15(1). Available from: https://www.cureus.com/articles/126856-covid-19-and-cavitary-lesion-in-lung.
- Ekanem E, Podder S, Donthi N, Bakhshi H, Stodghill J, Khandhar S, et al. Spontaneous pneumothorax: An emerging complication of COVID-19 pneumonia. Heart Lung J Crit Care. 2021;50(3):437–40. [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam S, Arora H, Gunasekaran K, Muruganandam M, Nagaraju S. A Unique Case of Spontaneous Pneumomediastinum in a Patient With COVID-19 and Influenza Coinfection. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2021;9:23247096211016228. [CrossRef]
- Del Nonno F, Colombo D, Nardacci R, Falasca L. Fatal pulmonary arterial thrombosis in a COVID-19 patient, with asymptomatic history, occurred after swab negativization. Thromb J. 2021 Jan 6;19(1):1. [CrossRef]
- Poissy J, Goutay J, Caplan M, Parmentier E, Duburcq T, Lassalle F, et al. Pulmonary Embolism in Patients With COVID-19: Awareness of an Increased Prevalence. Circulation. 2020 Jul 14;142(2):184–6. [CrossRef]
- Malas MB, Naazie IN, Elsayed N, Mathlouthi A, Marmor R, Clary B. Thromboembolism risk of COVID-19 is high and associated with a higher risk of mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. EClinicalMedicine. 2020 Dec;29:100639. [CrossRef]
- Aquino-Matus J, Uribe M, Chavez-Tapia N. COVID-19: Current Status in Gastrointestinal, Hepatic, and Pancreatic Diseases—A Concise Review. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2022 Aug 16;7(8):187. [CrossRef]
- Schmulson M, Dávalos MF, Berumen J. Beware: Gastrointestinal symptoms can be a manifestation of COVID-19. Rev Gastroenterol Mex Engl. 2020;85(3):282–7. [CrossRef]
- Liang W, Feng Z, Rao S, Xiao C, Xue X, Lin Z, et al. Diarrhoea may be underestimated: a missing link in 2019 novel coronavirus. Gut. 2020 Jun 1;69(6):1141–3. [CrossRef]
- Groff A, Kavanaugh M, Ramgobin D, McClafferty B, Aggarwal CS, Golamari R, et al. Gastrointestinal Manifestations of COVID-19: A Review of What We Know. Ochsner J. 2021;21(2):177–80. [CrossRef]
- Ma C, Cong Y, Zhang H. COVID-19 and the Digestive System. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020 Jul;115(7):1003–6.
- Galanopoulos M, Gkeros F, Doukatas A, Karianakis G, Pontas C, Tsoukalas N, et al. COVID-19 pandemic: Pathophysiology and manifestations from the gastrointestinal tract. World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Aug 21;26(31):4579–88. [CrossRef]
- Mohamed DZ, Ghoneim MES, Abu-Risha SES, Abdelsalam RA, Farag MA. Gastrointestinal and hepatic diseases during the COVID-19 pandemic: Manifestations, mechanism and management. World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Jul 28;27(28):4504–35. [CrossRef]
- Keshavarz P, Rafiee F, Kavandi H, Goudarzi S, Heidari F, Gholamrezanezhad A. Ischemic gastrointestinal complications of COVID-19: a systematic review on imaging presentation. Clin Imaging. 2021 May;73:86–95. [CrossRef]
- Uhlenhopp DJ, Ramachandran R, Then E, Parvataneni S, Grantham T, Gaduputi V. COVID-19-Associated Ischemic Colitis: A Rare Manifestation of COVID-19 Infection—Case Report and Review. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2022 Mar 28;10:23247096211065624. [CrossRef]
- Kukla M, Skonieczna-Żydecka K, Kotfis K, Maciejewska D, Łoniewski I, Lara LuisF, et al. COVID-19, MERS and SARS with Concomitant Liver Injury—Systematic Review of the Existing Literature. J Clin Med. 2020 May 11;9(5):1420. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira RJO, Welsing PMJ, Jacobs JWG, Gossec L, Ndosi M, Machado PM, et al. Revisiting the use of remission criteria for rheumatoid arthritis by excluding patient global assessment: an individual meta-analysis of 5792 patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021 Mar;80(3):293–303. [CrossRef]
- Nardo AD, Schneeweiss-Gleixner M, Bakail M, Dixon ED, Lax SF, Trauner M. Pathophysiological mechanisms of liver injury in COVID-19. Liver Int Off J Int Assoc Study Liver. 2021 Jan;41(1):20–32. [CrossRef]
- Hamid S, Alvares da Silva MR, Burak KW, Chen T, Drenth JPH, Esmat G, et al. WGO Guidance for the Care of Patients With COVID-19 and Liver Disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2021 Jan;55(1):1–11. [CrossRef]
- Lagana SM, Kudose S, Iuga AC, Lee MJ, Fazlollahi L, Remotti HE, et al. Hepatic pathology in patients dying of COVID-19: a series of 40 cases including clinical, histologic, and virologic data. Mod Pathol Off J U S Can Acad Pathol Inc. 2020 Nov;33(11):2147–55. [CrossRef]
- Horvatits T, Drolz A, Trauner M, Fuhrmann V. Liver Injury and Failure in Critical Illness. Hepatol Baltim Md. 2019 Dec;70(6):2204–15. [CrossRef]
- Taquet M, Geddes JR, Husain M, Luciano S, Harrison PJ. 6-month neurological and psychiatric outcomes in 236 379 survivors of COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study using electronic health records. Lancet Psychiatry. 2021 May 1;8(5):416–27. [CrossRef]
- Mao L, Jin H, Wang M, Hu Y, Chen S, He Q, et al. Neurologic Manifestations of Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Wuhan, China. JAMA Neurol. 2020 Jun 1;77(6):683–90. [CrossRef]
- Tan YK, Goh C, Leow AST, Tambyah PA, Ang A, Yap ES, et al. COVID-19 and ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-summary of the literature. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2020 Oct;50(3):587–95. [CrossRef]
- Morassi M, Bagatto D, Cobelli M, D’Agostini S, Gigli GL, Bnà C, et al. Stroke in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: case series. J Neurol. 2020 Aug;267(8):2185–92. [CrossRef]
- Oxley TJ, Mocco J, Majidi S, Kellner CP, Shoirah H, Singh IP, et al. Large-Vessel Stroke as a Presenting Feature of Covid-19 in the Young. N Engl J Med. 2020 May 14;382(20):e60. [CrossRef]
- Vogrig A, Gigli GL, Bnà C, Morassi M. Stroke in patients with COVID-19: Clinical and neuroimaging characteristics. Neurosci Lett. 2021 Jan 19;743:135564. [CrossRef]
- Xie Z, Hui H, Zhao Z, Yu W, Wu R, Zhu Y, et al. Nervous system manifestations related to COVID-19 and their possible mechanisms. Brain Res Bull. 2022 Sep;187:63–74. [CrossRef]
- Kirschenbaum D, Imbach LL, Rushing EJ, Frauenknecht KBM, Gascho D, Ineichen BV, et al. Intracerebral endotheliitis and microbleeds are neuropathological features of COVID-19. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2021 Apr;47(3):454–9. [CrossRef]
- Kow CS, Zaihan AF, Hasan SS. Anticoagulant approach in COVID-19 patients with cerebral venous thrombosis. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020 Dec;29(12):105222. [CrossRef]
- Thachil J, Tang N, Gando S, Falanga A, Cattaneo M, Levi M, et al. ISTH interim guidance on recognition and management of coagulopathy in COVID-19. J Thromb Haemost JTH. 2020 May;18(5):1023–6. [CrossRef]
- Wysocki J, Ye M, Rodriguez E, González-Pacheco FR, Barrios C, Evora K, et al. Targeting the Degradation of Angiotensin II with Recombinant ACE2: Prevention of Angiotensin II-dependent Hypertension. Hypertension. 2010 Jan;55(1):90–8. [CrossRef]
- Soltani Zangbar H, Gorji A, Ghadiri T. A Review on the Neurological Manifestations of COVID-19 Infection: a Mechanistic View. Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Feb;58(2):536–49. [CrossRef]
- Virhammar J, Kumlien E, Fällmar D, Frithiof R, Jackmann S, Sköld MK, et al. Acute necrotizing encephalopathy with SARS-CoV-2 RNA confirmed in cerebrospinal fluid. Neurology. 2020 Sep 8;95(10):445–9. [CrossRef]
- Radmanesh A, Derman A, Ishida K. COVID-19-associated delayed posthypoxic necrotizing leukoencephalopathy. J Neurol Sci. 2020 Aug 15;415:116945. [CrossRef]
- Poyiadji N, Shahin G, Noujaim D, Stone M, Patel S, Griffith B. COVID-19-associated Acute Hemorrhagic Necrotizing Encephalopathy: Imaging Features. Radiology. 2020 Aug;296(2):E119–20. [CrossRef]
- Gupta A, Paliwal VK, Garg RK. Is COVID-19-related Guillain-Barré syndrome different? Brain Behav Immun. 2020 Jul;87:177–8. [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam S, Arora H, Lewis S, Gunasekaran K, Muruganandam M, Nagaraju S, et al. COVID-19 vaccine-induced cellulitis and myositis. Cleve Clin J Med. 2021 Dec 2;88(12):648–50. [CrossRef]
- Wang F, Kream RM, Stefano GB. Long-Term Respiratory and Neurological Sequelae of COVID-19. Med Sci Monit Int Med J Exp Clin Res. 2020 Nov 1;26:e928996. [CrossRef]
- Vollono C, Rollo E, Romozzi M, Frisullo G, Servidei S, Borghetti A, et al. Focal status epilepticus as unique clinical feature of COVID-19: A case report. Seizure. 2020 May;78:109–12. [CrossRef]
- Hepburn M, Mullaguri N, George P, Hantus S, Punia V, Bhimraj A, et al. Acute Symptomatic Seizures in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19: Is There an Association? Neurocrit Care. 2021 Feb;34(1):139–43. [CrossRef]
- Scullen T, Keen J, Mathkour M, Dumont AS, Kahn L. Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19)–Associated Encephalopathies and Cerebrovascular Disease: The New Orleans Experience. World Neurosurg. 2020 Sep;141:e437–46. [CrossRef]
- Shehata GA, Lord KC, Grudzinski MC, Elsayed M, Abdelnaby R, Elshabrawy HA. Neurological Complications of COVID-19: Underlying Mechanisms and Management. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 15;22(8):4081. [CrossRef]
- Bo HX, Li W, Yang Y, Wang Y, Zhang Q, Cheung T, et al. Posttraumatic stress symptoms and attitude toward crisis mental health services among clinically stable patients with COVID-19 in China. Psychol Med. 2021 Apr;51(6):1052–3. [CrossRef]
- De Boni RB, Balanzá-Martínez V, Mota JC, Cardoso TDA, Ballester P, Atienza-Carbonell B, et al. Depression, Anxiety, and Lifestyle Among Essential Workers: A Web Survey From Brazil and Spain During the COVID-19 Pandemic. J Med Internet Res. 2020 Oct 30;22(10):e22835. [CrossRef]
- Czeisler MÉ, Lane RI, Petrosky E, Wiley JF, Christensen A, Njai R, et al. Mental Health, Substance Use, and Suicidal Ideation During the COVID-19 Pandemic - United States, June 24-30, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020 Aug 14;69(32):1049–57. [CrossRef]
- Leven Y, Bösel J. Neurological manifestations of COVID-19 - an approach to categories of pathology. Neurol Res Pract. 2021 Jul 26;3(1):39. [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili M, Abdi F, Shafiee G, Asayesh H, Abdar ZE, Baygi F, et al. Olfactory and Gustatory Dysfunction in 2019 Novel Coronavirus: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Int J Prev Med. 2021 Dec 14;12:170. [CrossRef]
- Boscolo-Rizzo P, Borsetto D, Fabbris C, Spinato G, Frezza D, Menegaldo A, et al. Evolution of Altered Sense of Smell or Taste in Patients With Mildly Symptomatic COVID-19. JAMA Otolaryngol-- Head Neck Surg. 2020 Aug 1;146(8):729–32. [CrossRef]
- Fodoulian L, Tuberosa J, Rossier D, Boillat M, Kan C, Pauli V, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Receptors and Entry Genes Are Expressed in the Human Olfactory Neuroepithelium and Brain. iScience. 2020 Nov 25;23(12):101839.
- Xu W, Sunavala-Dossabhoy G, Spielman AI. Chemosensory loss in COVID-19. Oral Dis. 2022 Nov;28 Suppl 2:2337–46. [CrossRef]
- Butowt R, von Bartheld CS. Anosmia in COVID-19: Underlying Mechanisms and Assessment of an Olfactory Route to Brain Infection. Neurosci Rev J Bringing Neurobiol Neurol Psychiatry. 2021 Dec;27(6):582–603. [CrossRef]
- Danesh-Meyer HV, McGhee CNJ. Implications of COVID-19 for Ophthalmologists. Am J Ophthalmol. 2021 Mar;223:108–18. [CrossRef]
- Cheema M, Aghazadeh H, Nazarali S, Ting A, Hodges J, McFarlane A, et al. Keratoconjunctivitis as the initial medical presentation of the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Can J Ophthalmol J Can Ophtalmol. 2020 Aug;55(4):e125–9. [CrossRef]
- Navel V, Chiambaretta F, Dutheil F. Haemorrhagic conjunctivitis with pseudomembranous related to SARS-CoV-2. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2020 May 6;19:100735. [CrossRef]
- Update on overview of ocular manifestations of COVID-19 - PMC [Internet]. [cited 2023 May 3]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9513125/.
- Invernizzi A, Pellegrini M, Messenio D, Cereda M, Olivieri P, Brambilla AM, et al. Impending Central Retinal Vein Occlusion in a Patient with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2020 Nov 16;28(8):1290–2. [CrossRef]
- Walinjkar JA, Makhija SC, Sharma HR, Morekar SR, Natarajan S. Central retinal vein occlusion with COVID-19 infection as the presumptive etiology. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2020 Nov;68(11):2572–4. [CrossRef]
- Sheth JU, Narayanan R, Goyal J, Goyal V. Retinal vein occlusion in COVID-19: A novel entity. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2020 Oct;68(10):2291–3. [CrossRef]
- Sarkar S, Gokhale T, Choudhury SS, Deb AK. COVID-19 and orbital mucormycosis. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2021 Apr;69(4):1002–4. [CrossRef]
- Sen M, Lahane S, Lahane TP, Parekh R, Honavar SG. Mucor in a Viral Land: A Tale of Two Pathogens. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2021 Feb;69(2):244–52. [CrossRef]
- Brix TH, Hegedüs L, Hallas J, Lund LC. Risk and course of SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients treated for hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021 Apr;9(4):197–9.
- Chen M, Zhou W, Xu W. Thyroid Function Analysis in 50 Patients with COVID-19: A Retrospective Study. Thyroid®. 2021 Jan;31(1):8–11. [CrossRef]
- Peeters RP, Wouters PJ, van Toor H, Kaptein E, Visser TJ, Van den Berghe G. Serum 3,3′,5′-Triiodothyronine (rT3) and 3,5,3′-Triiodothyronine/rT3 Are Prognostic Markers in Critically Ill Patients and Are Associated with Postmortem Tissue Deiodinase Activities. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005 Aug 1;90(8):4559–65. [CrossRef]
- Chen Y, Li X, Dai Y, Zhang J. The Association Between COVID-19 and Thyroxine Levels: A Meta-Analysis. Front Endocrinol. 2021;12:779692. [CrossRef]
- Lui DTW, Lee CH, Chow WS, Lee ACH, Tam AR, Fong CHY, et al. Role of non-thyroidal illness syndrome in predicting adverse outcomes in COVID-19 patients predominantly of mild-to-moderate severity. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2021 Sep;95(3):469–77. [CrossRef]
- Clarke SA, Phylactou M, Patel B, Mills EG, Muzi B, Izzi-Engbeaya C, et al. Normal Adrenal and Thyroid Function in Patients Who Survive COVID-19 Infection. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Jul 13;106(8):2208–20. [CrossRef]
- Barkhoudarian G, Kelly DF. Pituitary Apoplexy. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2019 Oct;30(4):457–63.
- Chigr F, Merzouki M, Najimi M. Autonomic Brain Centers and Pathophysiology of COVID-19. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020 Jun 3;11(11):1520–2. [CrossRef]
- Christ-Crain M, Hoorn EJ, Sherlock M, Thompson CJ, Wass JAH. ENDOCRINOLOGY IN THE TIME OF COVID-19: Management of diabetes insipidus and hyponatraemia. Eur J Endocrinol. 2020 Jul;183(1):G9–15.
- Frara S, Rodriguez-Carnero G, Formenti AM, Martinez-Olmos MA, Giustina A, Casanueva FF. Pituitary Tumors Centers of Excellence. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2020 Sep;49(3):553–64. [CrossRef]
- Leyendecker P, Ritter S, Riou M, Wackenthaler A, Meziani F, Roy C, et al. Acute adrenal infarction as an incidental CT finding and a potential prognosis factor in severe SARS-CoV-2 infection: a retrospective cohort analysis on 219 patients. Eur Radiol. 2021;31(2):895–900. [CrossRef]
- Amiri-Dashatan N, Koushki M, Parsamanesh N, Chiti H. Serum cortisol concentration and COVID-19 severity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Investig Med Off Publ Am Fed Clin Res. 2022 Mar;70(3):766–72. [CrossRef]
- Tan T, Khoo B, Mills EG, Phylactou M, Patel B, Eng PC, et al. Association between high serum total cortisol concentrations and mortality from COVID-19. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020 Aug;8(8):659–60. [CrossRef]
- Kanczkowski W, Evert K, Stadtmüller M, Haberecker M, Laks L, Chen LS, et al. COVID-19 targets human adrenal glands. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022 Jan;10(1):13–6. [CrossRef]
- Tresoldi AS, Sumilo D, Perrins M, Toulis KA, Prete A, Reddy N, et al. Increased Infection Risk in Addison’s Disease and Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Feb 1;105(2):418–29. [CrossRef]
- Quinkler M, Ekman B, Zhang P, Isidori AM, Murray RD, EU-AIR Investigators. Mortality data from the European Adrenal Insufficiency Registry-Patient characterization and associations. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2018 Jul;89(1):30–5. [CrossRef]
- Peckham H, de Gruijter NM, Raine C, Radziszewska A, Ciurtin C, Wedderburn LR, et al. Male sex identified by global COVID-19 meta-analysis as a risk factor for death and ITU admission. Nat Commun. 2020 Dec 9;11(1):6317. [CrossRef]
- Li K, Chen G, Hou H, Liao Q, Chen J, Bai H, et al. Analysis of sex hormones and menstruation in COVID-19 women of child-bearing age. Reprod Biomed Online. 2021 Jan;42(1):260–7. [CrossRef]
- F C, S Z, Z D, L H, C L, Q G, et al. Effects of COVID-19 and mRNA vaccines on human fertility. Hum Reprod Oxf Engl [Internet]. 2021 Dec 27 [cited 2023 Jun 26];37(1). Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34734259/.
- Li D, Jin M, Bao P, Zhao W, Zhang S. Clinical Characteristics and Results of Semen Tests Among Men With Coronavirus Disease 2019. JAMA Netw Open. 2020 May 7;3(5):e208292. [CrossRef]
- Dhindsa S, Zhang N, McPhaul MJ, Wu Z, Ghoshal AK, Erlich EC, et al. Association of Circulating Sex Hormones With Inflammation and Disease Severity in Patients With COVID-19. JAMA Netw Open. 2021 May 25;4(5):e2111398. [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi L, Bertacca C, Centenari C, Merusi I, Parolo E, Ragazzo V, et al. Orchiepididymitis in a Boy With COVID-19. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2020 Aug;39(8):e200–2. [CrossRef]
- Clarke SA, Abbara A, Dhillo WS. Impact of COVID-19 on the Endocrine System: A Mini-review. Endocrinology. 2022 Jan 1;163(1):bqab203. [CrossRef]
- Chen L, Huang X, Yi Z, Deng Q, Jiang N, Feng C, et al. Ultrasound Imaging Findings of Acute Testicular Infection in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Single-Center-Based Study in Wuhan, China. J Ultrasound Med Off J Am Inst Ultrasound Med. 2021 Sep;40(9):1787–94. [CrossRef]
- Ruan Y, Hu B, Liu Z, Liu K, Jiang H, Li H, et al. No detection of SARS-CoV-2 from urine, expressed prostatic secretions, and semen in 74 recovered COVID-19 male patients: A perspective and urogenital evaluation. Andrology. 2021 Jan;9(1):99–106. [CrossRef]
- Jamieson DJ, Rasmussen SA. An update on COVID-19 and pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022 Feb;226(2):177–86. [CrossRef]
- Villar J, Ariff S, Gunier RB, Thiruvengadam R, Rauch S, Kholin A, et al. Maternal and Neonatal Morbidity and Mortality Among Pregnant Women With and Without COVID-19 Infection: The INTERCOVID Multinational Cohort Study. JAMA Pediatr. 2021 Aug 1;175(8):817–26.
- Chmielewska B, Barratt I, Townsend R, Kalafat E, Meulen J van der, Gurol-Urganci I, et al. Effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on maternal and perinatal outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2021 Jun 1;9(6):e759–72. [CrossRef]
- Fenizia C, Biasin M, Cetin I, Vergani P, Mileto D, Spinillo A, et al. Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 vertical transmission during pregnancy. Nat Commun. 2020 Oct 12;11(1):5128. [CrossRef]
- Yang JK, Lin SS, Ji XJ, Guo LM. Binding of SARS coronavirus to its receptor damages islets and causes acute diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 2010 Sep;47(3):193–9. [CrossRef]
- Chee YJ, Ng SJH, Yeoh E. Diabetic ketoacidosis precipitated by Covid-19 in a patient with newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020 Jun;164:108166. [CrossRef]
- Müller JA, Groß R, Conzelmann C, Krüger J, Merle U, Steinhart J, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infects and replicates in cells of the human endocrine and exocrine pancreas. Nat Metab. 2021 Feb;3(2):149–65. [CrossRef]
- Kusmartseva I, Wu W, Syed F, Van Der Heide V, Jorgensen M, Joseph P, et al. Expression of SARS-CoV-2 Entry Factors in the Pancreas of Normal Organ Donors and Individuals with COVID-19. Cell Metab. 2020 Dec 1;32(6):1041-1051.e6. [CrossRef]
- Marchand L, Pecquet M, Luyton C. Type 1 diabetes onset triggered by COVID-19. Acta Diabetol. 2020;57(10):1265–6. [CrossRef]
- Hollstein T, Schulte DM, Schulz J, Glück A, Ziegler AG, Bonifacio E, et al. Autoantibody-negative insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus after SARS-CoV-2 infection: a case report. Nat Metab. 2020 Oct;2(10):1021–4. [CrossRef]
- Armeni E, Aziz U, Qamar S, Nasir S, Nethaji C, Negus R, et al. Protracted ketonaemia in hyperglycaemic emergencies in COVID-19: a retrospective case series. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020 Aug;8(8):660–3. [CrossRef]
- Li J, Wang X, Chen J, Zuo X, Zhang H, Deng A. COVID-19 infection may cause ketosis and ketoacidosis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020 Oct;22(10):1935–41. [CrossRef]
- Anderson MR, Shashaty MGS. Impact of Obesity in Critical Illness. Chest. 2021 Dec;160(6):2135–45. [CrossRef]
- COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative. Mapping the human genetic architecture of COVID-19. Nature. 2021 Dec;600(7889):472–7.
- Földi M, Farkas N, Kiss S, Dembrovszky F, Szakács Z, Balaskó M, et al. Visceral Adiposity Elevates the Risk of Critical Condition in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes Silver Spring Md. 2021 Mar;29(3):521–8. [CrossRef]
- Oguz SH, Koca M, Yildiz BO. Aging versus youth: Endocrine aspects of vulnerability for COVID-19. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2022;23(2):185. [CrossRef]
- Wolter N, Jassat W, Walaza S, Welch R, Moultrie H, Groome M, et al. Early assessment of the clinical severity of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant in South Africa [Internet]. medRxiv; 2021 [cited 2023 May 3]. p. 2021.12.21.21268116. Available from: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.12.21.21268116v1.
- Lewnard JA, Hong VX, Patel MM, Kahn R, Lipsitch M, Tartof SY. Clinical outcomes among patients infected with Omicron (B.1.1.529) SARS-CoV-2 variant in southern California [Internet]. medRxiv; 2022 [cited 2023 May 3]. p. 2022.01.11.22269045. Available from: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.01.11.22269045v1.
- COVID-19 Incidence and Death Rates Among Unvaccinated and Fully Vaccinated Adults with and Without Booster Doses During Periods of Delta and Omicron Variant Emergence — 25 U.S. Jurisdictions, April 4–December 25, 2021 | MMWR [Internet]. [cited 2023 May 3]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/71/wr/mm7104e2.htm?s_cid=mm7104e2_w.%20https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7104e2. [CrossRef]
- Abdullah F, Myers J, Basu D, Tintinger G, Ueckermann V, Mathebula M, et al. Decreased severity of disease during the first global omicron variant covid-19 outbreak in a large hospital in tshwane, south africa. Int J Infect Dis IJID Off Publ Int Soc Infect Dis. 2022 Mar;116:38–42. [CrossRef]
- Diamond M, Halfmann P, Maemura T, Iwatsuki-Horimoto K, Iida S, Kiso M, et al. The SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus causes attenuated infection and disease in mice and hamsters. Res Sq. 2021 Dec 29;rs.3.rs-1211792.
- León TM. COVID-19 Cases and Hospitalizations by COVID-19 Vaccination Status and Previous COVID-19 Diagnosis — California and New York, May–November 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 May 3];71. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/71/wr/mm7104e1.htm.
- publisher, E. publisher E. World Health Organization - Regional Office for the Eastern Mediterranean. [cited 2023 Jun 29]. Information note on new COVID-19 Omicron subvariant XBB.1.5. Available from: http://www.emro.who.int/media/news/information-note-on-new-covid-19-omicron-subvariant-xbb15.html.
- Mahase, E. Mahase E. Covid-19: What do we know about XBB.1.5 and should we be worried? BMJ. 2023 Jan 19;380:p153. [CrossRef]
- Xiao AT, Tong YX, Zhang S. Profile of RT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2: A Preliminary Study From 56 COVID-19 Patients. Clin Infect Dis Off Publ Infect Dis Soc Am. 2020 Apr 19;71(16):2249–51. [CrossRef]
- CDC. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2020 [cited 2023 Apr 17]. Healthcare Workers. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/duration-isolation.html.
- NIH COVID-19 Research [Internet]. [cited 2023 May 3]. Home. Available from: https://covid19.nih.gov/homepage.
- EMA. European Medicines Agency. 2021 [cited 2023 May 3]. EMA and Health Canada publish clinical data used to support their authorisations of the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine. Available from: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/ema-health-canada-publish-clinical-data-used-support-their-authorisations-moderna-covid-19-vaccine.
- ClinicalStudyDataRequest.com [Internet]. [cited 2023 May 4]. Available from: https://www.clinicalstudydatarequest.com/.
- The YODA Project | Trials By Generic Name [Internet]. [cited 2023 May 4]. Available from: https://yoda.yale.edu/browsetrials/generic-name.
- Home – GREI - Vivli [Internet]. [cited 2023 May 3]. Available from: https://vivli.org/. https://vivli.org/.
- Bugin K, Woodcock J. Trends in COVID-19 therapeutic clinical trials. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021 Apr;20(4):254–5. [CrossRef]
- Palm ME, Lindsell CJ, Selker HP. Sharing data among clinical trials of therapeutics in COVID-19: Barriers and facilitators to collaborating in a crisis. J Clin Transl Sci. 6(1):e52. [CrossRef]
- Janiaud P, Hemkens LG, Ioannidis JPA. Challenges and Lessons Learned From COVID-19 Trials: Should We Be Doing Clinical Trials Differently? Can J Cardiol. 2021 Sep;37(9):1353–64.
- Negi K, Agarwal M, Pahuja I, Bhardwaj B, Rawat M, Bhaskar A, et al. Combating the challenges of COVID-19 pandemic: Insights into molecular mechanisms, immune responses and therapeutics against SARS-CoV-2. Oxf Open Immunol. 2023 Jan 1;4(1):iqad001. [CrossRef]
- Recovery protocol [Internet]. [cited 2023 May 3]. Available from: https://www.recoverytrial.net/files/recovery-protocol-v12-1-2020-12-16.pdf.
- Demotes-Mainard J. [ECRIN (European clinical research infrastructures network), a pan-European infrastructure for clinical research]. Bull Acad Natl Med. 2010 Dec;194(9):1683–94.
- Horby PW, Mafham M, Bell JL, Linsell L, Staplin N, Emberson J, et al. Lopinavir–ritonavir in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial. The Lancet. 2020 Oct 24;396(10259):1345–52. [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID). A Multicenter, Adaptive, Randomized Blinded Controlled Trial of the Safety and Efficacy of Investigational Therapeutics for the Treatment of COVID-19 in Hospitalized Adults [Internet]. clinicaltrials.gov; 2022 Mar [cited 2023 May 2]. Report No.: NCT04280705. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04280705.
- Hospital do Coracao. An Open-label, Randomized Controlled Trial of Hydroxychloroquine and Azithromycin for COVID-19 Infection on Hospitalized, Noncritical Patients [Internet]. clinicaltrials.gov; 2022 Apr [cited 2023 May 2]. Report No.: results/NCT04322123. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/results/NCT04322123.
- Remdesivir and three other drugs for hospitalised patients with COVID-19: final results of the WHO Solidarity randomised trial and updated meta-analyses. The Lancet. 2022 May 21;399(10339):1941–53. [CrossRef]
- RECOVERY Collaborative Group, Horby P, Lim WS, Emberson JR, Mafham M, Bell JL, et al. Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021 Feb 25;384(8):693–704. [CrossRef]
- INSPIRATION Investigators, Sadeghipour P, Talasaz AH, Rashidi F, Sharif-Kashani B, Beigmohammadi MT, et al. Effect of Intermediate-Dose vs Standard-Dose Prophylactic Anticoagulation on Thrombotic Events, Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Treatment, or Mortality Among Patients With COVID-19 Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit: The INSPIRATION Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2021 Apr 27;325(16):1620–30.
- Rosas IO, Diaz G, Gottlieb RL, Lobo SM, Robinson P, Hunter BD, et al. Tocilizumab and remdesivir in hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia: a randomized clinical trial. Intensive Care Med. 2021 Nov 1;47(11):1258–70. [CrossRef]
- REMAP-CAP Investigators, ACTIV-4a Investigators, ATTACC Investigators, Goligher EC, Bradbury CA, McVerry BJ, et al. Therapeutic Anticoagulation with Heparin in Critically Ill Patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021 Aug 26;385(9):777–89. [CrossRef]
- Barbaro RP, MacLaren G, Boonstra PS, Combes A, Agerstrand C, Annich G, et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for COVID-19: evolving outcomes from the international Extracorporeal Life Support Organization Registry. The Lancet. 2021 Oct;398(10307):1230–8. [CrossRef]
- Ader F, Bouscambert-Duchamp M, Hites M, Peiffer-Smadja N, Poissy J, Belhadi D, et al. Remdesivir plus standard of care versus standard of care alone for the treatment of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (DisCoVeRy): a phase 3, randomised, controlled, open-label trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2022 Feb 1;22(2):209–21. [CrossRef]
- RECOVERY Collaborative Group. Aspirin in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial. Lancet Lond Engl. 2022 Jan 8;399(10320):143–51. [CrossRef]
- Fralick M, Colacci M, Munshi L, Venus K, Fidler L, Hussein H, et al. Prone positioning of patients with moderate hypoxaemia due to covid-19: multicentre pragmatic randomised trial (COVID-PRONE). BMJ. 2022 Mar 23;376:e068585. [CrossRef]
- Perkins GD, Ji C, Connolly BA, Couper K, Lall R, Baillie JK, et al. An adaptive randomized controlled trial of non-invasive respiratory strategies in acute respiratory failure patients with COVID-19 [Internet]. medRxiv; 2021 [cited 2023 May 8]. p. 2021.08.02.21261379. Available from: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.08.02.21261379v1.
- Reis G, Silva EASM, Silva DCM, Thabane L, Milagres AC, Ferreira TS, et al. Effect of Early Treatment with Ivermectin among Patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2022 May 5;386(18):1721–31. [CrossRef]
- Eikelboom JW, Jolly SS, Belley-Cote EP, Whitlock RP, Rangarajan S, Xu L, et al. Colchicine and the combination of rivaroxaban and aspirin in patients hospitalised with COVID-19 (ACT): an open-label, factorial, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2022 Dec;10(12):1169–77. [CrossRef]
- Hammond J, Leister-Tebbe H, Gardner A, Abreu P, Bao W, Wisemandle W, et al. Oral Nirmatrelvir for High-Risk, Nonhospitalized Adults with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2022 Apr 14;386(15):1397–408. [CrossRef]
- Xie Y, Xu E, Bowe B, Al-Aly Z. Long-term cardiovascular outcomes of COVID-19. Nat Med. 2022 Mar;28(3):583–90. [CrossRef]
- Writing Committee for the REMAP-CAP Investigators. Long-term (180-Day) Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19 in the REMAP-CAP Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2023 Jan 3;329(1):39–51.
- Schwartz KL, Wang J, Tadrous M, Langford BJ, Daneman N, Leung V, et al. Population-based evaluation of the effectiveness of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir for reducing hospital admissions and mortality from COVID-19. CMAJ Can Med Assoc J J Assoc Medicale Can. 2023 Feb 13;195(6):E220–6. [CrossRef]
- Dougan M, Azizad M, Chen P, Feldman B, Frieman M, Igbinadolor A, et al. Bebtelovimab, alone or together with bamlanivimab and etesevimab, as a broadly neutralizing monoclonal antibody treatment for mild to moderate, ambulatory COVID-19 [Internet]. medRxiv; 2022 [cited 2023 Mar 2]. p. 2022.03.10.22272100. Available from: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.03.10.22272100v1.
- Weinreich DM, Sivapalasingam S, Norton T, Ali S, Gao H, Bhore R, et al. REGEN-COV Antibody Combination and Outcomes in Outpatients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021 Dec 2;385(23):e81. [CrossRef]
- Polack FP, Thomas SJ, Kitchin N, Absalon J, Gurtman A, Lockhart S, et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2020 Dec 31;383(27):2603–15. [CrossRef]
- Voysey M, Clemens SAC, Madhi SA, Weckx LY, Folegatti PM, Aley PK, et al. Safety and efficacy of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine (AZD1222) against SARS-CoV-2: an interim analysis of four randomised controlled trials in Brazil, South Africa, and the UK. Lancet Lond Engl. 2021 Jan 9;397(10269):99–111. [CrossRef]
- Baden LR, El Sahly HM, Essink B, Kotloff K, Frey S, Novak R, et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2021 Feb 4;384(5):403–16.
- Sadoff J, Gray G, Vandebosch A, Cárdenas V, Shukarev G, Grinsztejn B, et al. Safety and Efficacy of Single-Dose Ad26.COV2.S Vaccine against Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021 Jun 10;384(23):2187–201. [CrossRef]
- Dunkle LM, Kotloff KL, Gay CL, Áñez G, Adelglass JM, Barrat Hernández AQ, et al. Efficacy and Safety of NVX-CoV2373 in Adults in the United States and Mexico. N Engl J Med. 2022 Feb 10;386(6):531–43. [CrossRef]
- Kwan AC, Ebinger JE, Botting P, Navarrette J, Claggett B, Cheng S. Association of COVID-19 Vaccination With Risk for Incident Diabetes After COVID-19 Infection. JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Feb 14;6(2):e2255965. [CrossRef]
- Robinson PC, Liew DFL, Tanner HL, Grainger JR, Dwek RA, Reisler RB, et al. COVID-19 therapeutics: Challenges and directions for the future. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Apr 12;119(15):e2119893119. [CrossRef]
- Wang M, Cao R, Zhang L, Yang X, Liu J, Xu M, et al. Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro. Cell Res. 2020 Mar;30(3):269–71. [CrossRef]
- Beigel JH, Tomashek KM, Dodd LE, Mehta AK, Zingman BS, Kalil AC, et al. Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19 — Final Report. N Engl J Med. 2020 Nov 5;383(19):1813–26. [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb RL, Vaca CE, Paredes R, Mera J, Webb BJ, Perez G, et al. Early Remdesivir to Prevent Progression to Severe Covid-19 in Outpatients. N Engl J Med. 2022 Jan 27;386(4):305–15. [CrossRef]
- Owen DR, Allerton CMN, Anderson AS, Aschenbrenner L, Avery M, Berritt S, et al. An oral SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19. Science. 2021 Dec 24;374(6575):1586–93. [CrossRef]
- The Food and Drug Administration (FDA). FDA Paxlovid [Internet]. [cited 2023 Mar 2]. Available from: https://www.fda.gov/media/155050/download.
- Fischer WA, Eron JJ, Holman W, Cohen MS, Fang L, Szewczyk LJ, et al. A phase 2a clinical trial of molnupiravir in patients with COVID-19 shows accelerated SARS-CoV-2 RNA clearance and elimination of infectious virus. Sci Transl Med. 2022 Jan 19;14(628):eabl7430. [CrossRef]
- Benaicha K, Khenhrani RR, Veer M, Devi S, Shahbaz U, Salah QM, et al. Efficacy of Molnupiravir for the Treatment of Mild or Moderate COVID-19 in Adults: A Meta-Analysis. Cureus [Internet]. 2023 May 5 [cited 2023 Jun 27]; Available from: https://www.cureus.com/articles/155447-efficacy-of-molnupiravir-for-the-treatment-of-mild-or-moderate-covid-19-in-adults-a-meta-analysis.
- Alavi Darazam I, Hatami F, Mahdi Rabiei M, Amin Pourhoseingholi M, Shabani M, Shokouhi S, et al. An investigation into the beneficial effects of high-dose interferon beta 1-a, compared to low-dose interferon beta 1-a in severe COVID-19: The COVIFERON II randomized controlled trial. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Oct;99:107916.
- Rahmani H, Davoudi-Monfared E, Nourian A, Khalili H, Hajizadeh N, Jalalabadi NZ, et al. Interferon β-1b in treatment of severe COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Nov;88:106903. [CrossRef]
- Hung IFN, Lung KC, Tso EYK, Liu R, Chung TWH, Chu MY, et al. Triple combination of interferon beta-1b, lopinavir–ritonavir, and ribavirin in the treatment of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19: an open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet Lond Engl. 2020;395(10238):1695–704. [CrossRef]
- Kalil AC, Mehta AK, Patterson TF, Erdmann N, Gomez CA, Jain MK, et al. Efficacy of interferon beta-1a plus remdesivir compared with remdesivir alone in hospitalised adults with COVID-19: a double-bind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2021 Dec;9(12):1365–76. [CrossRef]
- WHO Solidarity Trial Consortium, Pan H, Peto R, Henao-Restrepo AM, Preziosi MP, Sathiyamoorthy V, et al. Repurposed Antiviral Drugs for Covid-19 - Interim WHO Solidarity Trial Results. N Engl J Med. 2021 Feb 11;384(6):497–511. [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb RL, Nirula A, Chen P, Boscia J, Heller B, Morris J, et al. Effect of Bamlanivimab as Monotherapy or in Combination With Etesevimab on Viral Load in Patients With Mild to Moderate COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2021 Feb 16;325(7):632–44.
- Dougan M, Azizad M, Mocherla B, Gottlieb RL, Chen P, Hebert C, et al. A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial of Bamlanivimab and Etesevimab Together in High-Risk Ambulatory Patients With COVID-19 and Validation of the Prognostic Value of Persistently High Viral Load. Clin Infect Dis. 2022 Jul 1;75(1):e440–9. [CrossRef]
- Westendorf K, Žentelis S, Wang L, Foster D, Vaillancourt P, Wiggin M, et al. LY-CoV1404 (bebtelovimab) potently neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 variants [Internet]. bioRxiv; 2022 [cited 2023 Mar 2]. p. 2021.04.30.442182. Available from: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.04.30.442182v6.
- Gupta A, Gonzalez-Rojas Y, Juarez E, Crespo Casal M, Moya J, Rodrigues Falci D, et al. Effect of Sotrovimab on Hospitalization or Death Among High-risk Patients With Mild to Moderate COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2022 Apr 5;327(13):1236–46. [CrossRef]
- Tixagevimab and Cilgavimab (Evusheld) for Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis of COVID-19. JAMA. 2022 Jan 25;327(4):384–5. [CrossRef]
- Bégin P, Callum J, Jamula E, Cook R, Heddle NM, Tinmouth A, et al. Convalescent plasma for hospitalized patients with COVID-19: an open-label, randomized controlled trial. Nat Med. 2021 Nov;27(11):2012–24. [CrossRef]
- Convalescent plasma in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised controlled, open-label, platform trial. The Lancet. 2021 May 29;397(10289):2049–59. [CrossRef]
- Writing Committee for the REMAP-CAP Investigators. Effect of Convalescent Plasma on Organ Support–Free Days in Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2021 Nov 2;326(17):1690–702.
- Denkinger CM, Janssen M, Schäkel U, Gall J, Leo A, Stelmach P, et al. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody-containing plasma improves outcome in patients with hematologic or solid cancer and severe COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial. Nat Cancer. 2023 Jan;4(1):96–107. [CrossRef]
- Senefeld JW, Franchini M, Mengoli C, Cruciani M, Zani M, Gorman EK, et al. COVID-19 Convalescent Plasma for the Treatment of Immunocompromised Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Jan 12;6(1):e2250647. [CrossRef]
- WHO Rapid Evidence Appraisal for COVID-19 Therapies (REACT) Working Group, Sterne JAC, Murthy S, Diaz JV, Slutsky AS, Villar J, et al. Association Between Administration of Systemic Corticosteroids and Mortality Among Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19: A Meta-analysis. JAMA. 2020 Oct 6;324(13):1330–41. [CrossRef]
- Li H, Yan B, Gao R, Ren J, Yang J. Effectiveness of corticosteroids to treat severe COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Nov;100:108121. [CrossRef]
- Crothers K, DeFaccio R, Tate J, Alba PR, Goetz MB, Jones B, et al. Dexamethasone in hospitalised COVID-19 patients not on intensive respiratory support. Eur Respir J. 2022 Jul 14;60(1):2102532. [CrossRef]
- Yu LM, Bafadhel M, Dorward J, Hayward G, Saville BR, Gbinigie O, et al. Inhaled budesonide for COVID-19 in people at high risk of complications in the community in the UK (PRINCIPLE): a randomised, controlled, open-label, adaptive platform trial. Lancet Lond Engl. 2021 Sep 4;398(10303):843–55. [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan S, Nicolau DV, Langford B, Mahdi M, Jeffers H, Mwasuku C, et al. Inhaled budesonide in the treatment of early COVID-19 (STOIC): a phase 2, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2021 Jul;9(7):763–72. [CrossRef]
- Clemency BM, Varughese R, Gonzalez-Rojas Y, Morse CG, Phipatanakul W, Koster DJ, et al. Efficacy of Inhaled Ciclesonide for Outpatient Treatment of Adolescents and Adults With Symptomatic COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2022 Jan 1;182(1):42–9. [CrossRef]
- Ezer N, Belga S, Daneman N, Chan A, Smith BM, Daniels SA, et al. Inhaled and intranasal ciclesonide for the treatment of covid-19 in adult outpatients: CONTAIN phase II randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2021 Nov 2;375:e068060. [CrossRef]
- Wang Z, Yang B, Li Q, Wen L, Zhang R. Clinical Features of 69 Cases With Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Wuhan, China. Clin Infect Dis Off Publ Infect Dis Soc Am. 2020 Jul 28;71(15):769–77. [CrossRef]
- Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, Fan G, Liu Y, Liu Z, et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Lond Engl. 2020 Mar 28;395(10229):1054–62.
- Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial. The Lancet. 2021 May 1;397(10285):1637–45. [CrossRef]
- REMAP-CAP Investigators, Gordon AC, Mouncey PR, Al-Beidh F, Rowan KM, Nichol AD, et al. Interleukin-6 Receptor Antagonists in Critically Ill Patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021 Apr 22;384(16):1491–502. [CrossRef]
- Lescure FX, Honda H, Fowler RA, Lazar JS, Shi G, Wung P, et al. Sarilumab in patients admitted to hospital with severe or critical COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2021 May;9(5):522–32. [CrossRef]
- Babon JJ, Lucet IS, Murphy JM, Nicola NA, Varghese LN. The molecular regulation of Janus kinase (JAK) activation. Biochem J. 2014 Aug 15;462(1):1–13. [CrossRef]
- Zhang W, Zhao Y, Zhang F, Wang Q, Li T, Liu Z, et al. The use of anti-inflammatory drugs in the treatment of people with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): The Perspectives of clinical immunologists from China. Clin Immunol Orlando Fla. 2020 May;214:108393. [CrossRef]
- Richardson P, Griffin I, Tucker C, Smith D, Oechsle O, Phelan A, et al. Baricitinib as potential treatment for 2019-nCoV acute respiratory disease. Lancet Lond Engl. 2020 Feb 15;395(10223):e30–1. [CrossRef]
- Baricitinib in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial and updated meta-analysis. Lancet Lond Engl. 2022 Jul 30;400(10349):359–68.
- Marconi VC, Ramanan AV, de Bono S, Kartman CE, Krishnan V, Liao R, et al. Efficacy and safety of baricitinib for the treatment of hospitalised adults with COVID-19 (COV-BARRIER): a randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2021 Dec;9(12):1407–18. [CrossRef]
- Kalil AC, Patterson TF, Mehta AK, Tomashek KM, Wolfe CR, Ghazaryan V, et al. Baricitinib plus Remdesivir for Hospitalized Adults with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021 Mar 4;384(9):795–807. [CrossRef]
- Wolfe CR, Tomashek KM, Patterson TF, Gomez CA, Marconi VC, Jain MK, et al. Baricitinib versus dexamethasone for adults hospitalised with COVID-19 (ACTT-4): a randomised, double-blind, double placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2022 Sep;10(9):888–99. [CrossRef]
- Ely EW, Ramanan AV, Kartman CE, de Bono S, Liao R, Piruzeli MLB, et al. Efficacy and safety of baricitinib plus standard of care for the treatment of critically ill hospitalised adults with COVID-19 on invasive mechanical ventilation or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: an exploratory, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2022 Apr;10(4):327–36. [CrossRef]
- Jimenez D, Rali P, Doerschug K. COUNTERPOINT: Should Therapeutic Heparin Be Administered to Acutely Ill Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19? No. CHEST. 2022 Jun 1;161(6):1448–51. [CrossRef]
- Lopes RD, de Barros E Silva PGM, Furtado RHM, Macedo AVS, Bronhara B, Damiani LP, et al. Therapeutic versus prophylactic anticoagulation for patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 and elevated D-dimer concentration (ACTION): an open-label, multicentre, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Lond Engl. 2021 Jun 12;397(10291):2253–63. [CrossRef]
- Sholzberg M, Tang GH, Rahhal H, AlHamzah M, Kreuziger LB, Áinle FN, et al. Effectiveness of therapeutic heparin versus prophylactic heparin on death, mechanical ventilation, or intensive care unit admission in moderately ill patients with covid-19 admitted to hospital: RAPID randomised clinical trial. BMJ. 2021 Oct 14;375:n2400. [CrossRef]
- Spyropoulos AC, Goldin M, Giannis D, Diab W, Wang J, Khanijo S, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Therapeutic-Dose Heparin vs Standard Prophylactic or Intermediate-Dose Heparins for Thromboprophylaxis in High-risk Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19: The HEP-COVID Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2021 Dec 1;181(12):1612–20. [CrossRef]
- Berger JS, Kornblith LZ, Gong MN, Reynolds HR, Cushman M, Cheng Y, et al. Effect of P2Y12 Inhibitors on Survival Free of Organ Support Among Non-Critically Ill Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2022 Jan 18;327(3):227–36. [CrossRef]
- Tardif JC, Bouabdallaoui N, L’Allier PL, Gaudet D, Shah B, Pillinger MH, et al. Colchicine for community-treated patients with COVID-19 (COLCORONA): a phase 3, randomised, double-blinded, adaptive, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2021 Aug;9(8):924–32. [CrossRef]
- Mw M, S N, Dr B, Cj L, Tg S, Gm F, et al. Effect of Fluvoxamine vs Placebo on Time to Sustained Recovery in Outpatients With Mild to Moderate COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2023 Jan 1;329(4):296–305. [CrossRef]
- Thomas S, Patel D, Bittel B, Wolski K, Wang Q, Kumar A, et al. Effect of High-Dose Zinc and Ascorbic Acid Supplementation vs Usual Care on Symptom Length and Reduction Among Ambulatory Patients With SARS-CoV-2 Infection: The COVID A to Z Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Feb 1;4(2):e210369. [CrossRef]
- Alhazzani W, Møller MH, Arabi YM, Loeb M, Gong MN, Fan E, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: guidelines on the management of critically ill adults with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Intensive Care Med. 2020 May;46(5):854–87. [CrossRef]
- Chu DK, Kim LHY, Young PJ, Zamiri N, Almenawer SA, Jaeschke R, et al. Mortality and morbidity in acutely ill adults treated with liberal versus conservative oxygen therapy (IOTA): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Lond Engl. 2018 Apr 28;391(10131):1693–705. [CrossRef]
- Barrot L, Asfar P, Mauny F, Winiszewski H, Montini F, Badie J, et al. Liberal or Conservative Oxygen Therapy for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 12;382(11):999–1008. [CrossRef]
- Valbuena VSM, Seelye S, Sjoding MW, Valley TS, Dickson RP, Gay SE, et al. Racial bias and reproducibility in pulse oximetry among medical and surgical inpatients in general care in the Veterans Health Administration 2013-19: multicenter, retrospective cohort study. The BMJ. 2022 Jul 6;378:e069775. [CrossRef]
- Mauri T, Turrini C, Eronia N, Grasselli G, Volta CA, Bellani G, et al. Physiologic Effects of High-Flow Nasal Cannula in Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017 May;195(9):1207–15. [CrossRef]
- Frat JP, Thille AW, Mercat A, Girault C, Ragot S, Perbet S, et al. High-flow oxygen through nasal cannula in acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. N Engl J Med. 2015 Jun 4;372(23):2185–96. [CrossRef]
- Ni YN, Luo J, Yu H, Liu D, Liang BM, Liang ZA. The effect of high-flow nasal cannula in reducing the mortality and the rate of endotracheal intubation when used before mechanical ventilation compared with conventional oxygen therapy and noninvasive positive pressure ventilation. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Emerg Med. 2018 Feb;36(2):226–33. [CrossRef]
- Ospina-Tascón GA, Calderón-Tapia LE, García AF, Zarama V, Gómez-Álvarez F, Álvarez-Saa T, et al. Effect of High-Flow Oxygen Therapy vs Conventional Oxygen Therapy on Invasive Mechanical Ventilation and Clinical Recovery in Patients With Severe COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2021 Dec 7;326(21):2161–71. [CrossRef]
- Tran K, Cimon K, Severn M, Pessoa-Silva CL, Conly J. Aerosol generating procedures and risk of transmission of acute respiratory infections to healthcare workers: a systematic review. PloS One. 2012;7(4):e35797. [CrossRef]
- Grieco DL, Menga LS, Cesarano M, Rosà T, Spadaro S, Bitondo MM, et al. Effect of Helmet Noninvasive Ventilation vs High-Flow Nasal Oxygen on Days Free of Respiratory Support in Patients With COVID-19 and Moderate to Severe Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure: The HENIVOT Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2021 May 4;325(17):1731–43. [CrossRef]
- Perkins GD, Ji C, Connolly BA, Couper K, Lall R, Baillie JK, et al. Effect of Noninvasive Respiratory Strategies on Intubation or Mortality Among Patients With Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure and COVID-19: The RECOVERY-RS Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2022 Feb 8;327(6):546–58. [CrossRef]
- Guérin C, Reignier J, Richard JC, Beuret P, Gacouin A, Boulain T, et al. Prone positioning in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2013 Jun 6;368(23):2159–68. [CrossRef]
- Sun Q, Qiu H, Huang M, Yang Y. Lower mortality of COVID-19 by early recognition and intervention: experience from Jiangsu Province. Ann Intensive Care. 2020 Mar 18;10:33. [CrossRef]
- Sartini C, Tresoldi M, Scarpellini P, Tettamanti A, Carcò F, Landoni G, et al. Respiratory Parameters in Patients With COVID-19 After Using Noninvasive Ventilation in the Prone Position Outside the Intensive Care Unit. JAMA. 2020 Jun 9;323(22):2338–40. [CrossRef]
- Ehrmann S, Li J, Ibarra-Estrada M, Perez Y, Pavlov I, McNicholas B, et al. Awake prone positioning for COVID-19 acute hypoxaemic respiratory failure: a randomised, controlled, multinational, open-label meta-trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2021 Dec;9(12):1387–95. [CrossRef]
- Munshi L, Del Sorbo L, Adhikari NKJ, Hodgson CL, Wunsch H, Meade MO, et al. Prone Position for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017 Oct;14(Supplement_4):S280–8. [CrossRef]
- Briel M, Meade M, Mercat A, Brower RG, Talmor D, Walter SD, et al. Higher vs lower positive end-expiratory pressure in patients with acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome: systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2010 Mar 3;303(9):865–73.
- Tsolaki V, Siempos I, Magira E, Kokkoris S, Zakynthinos GE, Zakynthinos S. PEEP levels in COVID-19 pneumonia. Crit Care Lond Engl. 2020 Jun 6;24(1):303. [CrossRef]
- Schmidt M, Tachon G, Devilliers C, Muller G, Hekimian G, Bréchot N, et al. Blood oxygenation and decarboxylation determinants during venovenous ECMO for respiratory failure in adults. Intensive Care Med. 2013 May;39(5):838–46. [CrossRef]
- Makdisi G, Wang I wen. Extra Corporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) review of a lifesaving technology. J Thorac Dis. 2015 Jul;7(7):E166–76.
- Pham T, Combes A, Rozé H, Chevret S, Mercat A, Roch A, et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for pandemic influenza A(H1N1)-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome: a cohort study and propensity-matched analysis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013 Feb 1;187(3):276–85.
- Combes A, Hajage D, Capellier G, Demoule A, Lavoué S, Guervilly C, et al. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2018 May 24;378(21):1965–75. [CrossRef]
- Goldman JD, Robinson PC, Uldrick TS, Ljungman P. COVID-19 in immunocompromised populations: implications for prognosis and repurposing of immunotherapies. J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Jun;9(6):e002630. [CrossRef]
- Stainer A, Amati F, Suigo G, Simonetta E, Gramegna A, Voza A, et al. COVID-19 in Immunocompromised Patients: A Systematic Review. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2021 Dec;42(6):839–58. [CrossRef]
- Shoham S, Batista C, Ben Amor Y, Ergonul O, Hassanain M, Hotez P, et al. Vaccines and therapeutics for immunocompromised patients with COVID-19. EClinicalMedicine. 2023 May;59:101965. [CrossRef]
- Zambrano LD, Ellington S, Strid P, Galang RR, Oduyebo T, Tong VT, et al. Update: Characteristics of Symptomatic Women of Reproductive Age with Laboratory-Confirmed SARS-CoV-2 Infection by Pregnancy Status - United States, January 22-October 3, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020 Nov 6;69(44):1641–7.
- Metz TD, Clifton RG, Hughes BL, Sandoval G, Saade GR, Grobman WA, et al. Disease Severity and Perinatal Outcomes of Pregnant Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Obstet Gynecol. 2021 Apr 1;137(4):571–80.
- Allotey J, Stallings E, Bonet M, Yap M, Chatterjee S, Kew T, et al. Clinical manifestations, risk factors, and maternal and perinatal outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019 in pregnancy: living systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2020 Sep 1;370:m3320.
- Smith ER, Oakley E, Grandner GW, Rukundo G, Farooq F, Ferguson K, et al. Clinical risk factors of adverse outcomes among women with COVID-19 in the pregnancy and postpartum period: a sequential, prospective meta-analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2023 Feb;228(2):161–77. [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Portilla RJ, Sotiriadis A, Chatzakis C, Torres-Torres J, Espino Y Sosa S, Sandoval-Mandujano K, et al. Pregnant women with SARS-CoV-2 infection are at higher risk of death and pneumonia: propensity score matched analysis of a nationwide prospective cohort (COV19Mx). Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol Off J Int Soc Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2021 Feb;57(2):224–31. [CrossRef]
- Molina RL, Tsai TC, Dai D, Soto M, Rosenthal N, Orav EJ, et al. Comparison of Pregnancy and Birth Outcomes Before vs During the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Netw Open. 2022 Aug 12;5(8):e2226531. [CrossRef]
- Hecht JL, Quade B, Deshpande V, Mino-Kenudson M, Ting DT, Desai N, et al. SARS-CoV-2 can infect the placenta and is not associated with specific placental histopathology: a series of 19 placentas from COVID-19-positive mothers. Mod Pathol Off J U S Can Acad Pathol Inc. 2020 Nov;33(11):2092–103.
- Conde-Agudelo A, Romero R. SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy and risk of preeclampsia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022 Jan;226(1):68-89.e3.
- Shah PS, Ye XY, Yang J, Campitelli MA. Preterm birth and stillbirth rates during the COVID-19 pandemic: a population-based cohort study. CMAJ. 2021 Aug 3;193(30):E1164–72. [CrossRef]
- DeSisto CL, Wallace B, Simeone RM, Polen K, Ko JY, Meaney-Delman D, et al. Risk for Stillbirth Among Women With and Without COVID-19 at Delivery Hospitalization - United States, March 2020-September 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021 Nov 26;70(47):1640–5. [CrossRef]
- Karmen-Tuohy S, Carlucci PM, Zervou FN, Zacharioudakis IM, Rebick G, Klein E, et al. Outcomes Among HIV-Positive Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 1999. 2020 Sep 1;85(1):6–10. [CrossRef]
- Gervasoni C, Meraviglia P, Riva A, Giacomelli A, Oreni L, Minisci D, et al. Clinical features and outcomes of HIV patients with coronavirus disease 2019. Clin Infect Dis Off Publ Infect Dis Soc Am. 2020 May 14;ciaa579. [CrossRef]
- Dandachi D, Geiger G, Montgomery MW, Karmen-Tuohy S, Golzy M, Antar AAR, et al. Characteristics, Comorbidities, and Outcomes in a Multicenter Registry of Patients With Human Immunodeficiency Virus and Coronavirus Disease 2019. Clin Infect Dis Off Publ Infect Dis Soc Am. 2021 Oct 5;73(7):e1964–72. [CrossRef]
- Yang X, Sun J, Patel RC, Zhang J, Guo S, Zheng Q, et al. Associations between HIV infection and clinical spectrum of COVID-19: a population level analysis based on US National COVID Cohort Collaborative (N3C) data. Lancet HIV. 2021 Nov;8(11):e690–700. [CrossRef]
- COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines [Internet]. [cited 2023 Jun 3]. HIV. Available from: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/special-populations/hiv/.
- Beaglehole B, Mulder RT, Frampton CM, Boden JM, Newton-Howes G, Bell CJ. Psychological distress and psychiatric disorder after natural disasters: systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Psychiatry J Ment Sci. 2018 Dec;213(6):716–22. [CrossRef]
- Chaves C, Castellanos T, Abrams M, Vazquez C. The impact of economic recessions on depression and individual and social well-being: the case of Spain (2006-2013). Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2018 Sep;53(9):977–86. [CrossRef]
- Hossain MM, Tasnim S, Sultana A, Faizah F, Mazumder H, Zou L, et al. Epidemiology of mental health problems in COVID-19: a review. F1000Research. 2020 Jun 23;9:636. [CrossRef]
- Lu W, Wang H, Lin Y, Li L. Psychological status of medical workforce during the COVID-19 pandemic: A cross-sectional study. Psychiatry Res. 2020 Jun;288:112936. [CrossRef]
- Xie Y, Xu E, Al-Aly Z. Risks of mental health outcomes in people with covid-19: cohort study. BMJ. 2022 Feb 16;376:e068993. [CrossRef]
- Tessler H, Choi M, Kao G. The Anxiety of Being Asian American: Hate Crimes and Negative Biases During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Am J Crim Justice. 2020;45(4):636–46. [CrossRef]
- Grover S, Sahoo S, Mehra A, Avasthi A, Tripathi A, Subramanyan A, et al. Psychological impact of COVID-19 lockdown: An online survey from India. Indian J Psychiatry. 2020;62(4):354–62. [CrossRef]
- Chippa V, Aleem A, Anjum F. Post Acute Coronavirus (COVID-19) Syndrome. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 [cited 2023 May 3]. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK570608/.
- Yong, SJ. Yong SJ. Long COVID or post-COVID-19 syndrome: putative pathophysiology, risk factors, and treatments. Infect Dis Lond Engl. 2021 Oct;53(10):737–54. [CrossRef]
- Pintos-Pascual I, Moreno-Torres V, Ibánez-Estéllez F, Corrales-Rodriguez P, Treviño A, Corpas M, et al. Is SARS-CoV-2 the only cause of long-COVID? AIDS Rev. 2022 Dec 28;24(4):183–96. [CrossRef]
- Aiyegbusi OL, Hughes SE, Turner G, Rivera SC, McMullan C, Chandan JS, et al. Symptoms, complications and management of long COVID: a review. J R Soc Med. 2021 Sep;114(9):428–42. [CrossRef]
- Tosato M, Carfì A, Martis I, Pais C, Ciciarello F, Rota E, et al. Prevalence and Predictors of Persistence of COVID-19 Symptoms in Older Adults: A Single-Center Study. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2021 Sep;22(9):1840–4. [CrossRef]
- Borch L, Holm M, Knudsen M, Ellermann-Eriksen S, Hagstroem S. Long COVID symptoms and duration in SARS-CoV-2 positive children - a nationwide cohort study. Eur J Pediatr. 2022 Apr;181(4):1597–607.
- Ramakrishnan RK, Kashour T, Hamid Q, Halwani R, Tleyjeh IM. Unraveling the Mystery Surrounding Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19. Front Immunol. 2021;12:686029. [CrossRef]
- Yao XH, He ZC, Li TY, Zhang HR, Wang Y, Mou H, et al. Pathological evidence for residual SARS-CoV-2 in pulmonary tissues of a ready-for-discharge patient. Cell Res. 2020 Jun;30(6):541–3. [CrossRef]
- Wang J, Mei F, Bai L, Zhou S, Liu D, Yao L, et al. Serum nitrite and nitrate: A potential biomarker for post-covid-19 complications? Free Radic Biol Med. 2021 Nov 1;175:216–25.
- Ahmad MS, Shaik RA, Ahmad RK, Yusuf M, Khan M, Almutairi AB, et al. “LONG COVID”: an insight. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021 Sep;25(17):5561–77. [CrossRef]
- More than 50 Long-term effects of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis - PubMed [Internet]. [cited 2023 Jun 2]. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33532785/.
- Rao S, Benzouak T, Gunpat S, Burns RJ, Tahir TA, Jolles S, et al. Fatigue Symptoms Associated With COVID-19 in Convalescent or Recovered COVID-19 Patients; a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann Behav Med Publ Soc Behav Med. 2022 Mar 1;56(3):219–34. [CrossRef]
- Ali SS, Mumtaz A, Qamar MA, Tebha SS, Parhin A, Butt M, et al. New-onset Parkinsonism as a Covid-19 infection sequela: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Med Surg 2012. 2022 Aug;80:104281. [CrossRef]
- Maury A, Lyoubi A, Peiffer-Smadja N, de Broucker T, Meppiel E. Neurological manifestations associated with SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses: A narrative review for clinicians. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2021;177(1–2):51–64. [CrossRef]
- Zeng N, Zhao YM, Yan W, Li C, Lu QD, Liu L, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of long term physical and mental sequelae of COVID-19 pandemic: call for research priority and action. Mol Psychiatry. 2023 Jan;28(1):423–33. [CrossRef]
- Silva Andrade B, Siqueira S, de Assis Soares WR, de Souza Rangel F, Santos NO, Dos Santos Freitas A, et al. Long-COVID and Post-COVID Health Complications: An Up-to-Date Review on Clinical Conditions and Their Possible Molecular Mechanisms. Viruses. 2021 Apr 18;13(4):700.
- Joshee S, Vatti N, Chang C. Long-Term Effects of COVID-19. Mayo Clin Proc. 2022 Mar;97(3):579–99. [CrossRef]
- Pulmonary long-term consequences of COVID-19 infections after hospital discharge - PMC [Internet]. [cited 2023 Jun 2]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7920814/.
- Akbarialiabad H, Taghrir MH, Abdollahi A, Ghahramani N, Kumar M, Paydar S, et al. Long COVID, a comprehensive systematic scoping review. Infection. 2021 Dec;49(6):1163–86. [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry ZS, Nellessen N, Reis C, Sharip A. The development of inflammatory arthritis following SARS-CoV-2 infection: a systematic review of the literature. Fam Pract. 2022 Nov 22;39(6):1116–34. [CrossRef]
- Disser NP, De Micheli AJ, Schonk MM, Konnaris MA, Piacentini AN, Edon DL, et al. Musculoskeletal Consequences of COVID-19. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020 Jul 15;102(14):1197–204. [CrossRef]
- Koutalos AA, Stefanou N, Malizos KN. Postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Osteonecrosis must not be overlooked. Int J Infect Dis IJID Off Publ Int Soc Infect Dis. 2022 Aug;121:11–3. [CrossRef]
- Kordyukova LV, Shanko AV. COVID-19: Myths and Reality. Biochem Biokhimiia. 2021;86(7):800–17. [CrossRef]
- Poutoglidou F, Saitis A, Kouvelas D. Ibuprofen and COVID-19 disease: separating the myths from facts. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2021 Aug;15(8):979–83. [CrossRef]
- Tang JW, Bahnfleth WP, Bluyssen PM, Buonanno G, Jimenez JL, Kurnitski J, et al. Dismantling myths on the airborne transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2). J Hosp Infect. 2021 Apr;110:89–96.
- Sahoo S, Padhy SK, Ipsita J, Mehra A, Grover S. Demystifying the myths about COVID-19 infection and its societal importance. Asian J Psychiatry. 2020 Dec;54:102244. [CrossRef]
- Challenger A, Sumner P, Bott L. COVID-19 myth-busting: an experimental study. BMC Public Health. 2022 Jan 19;22(1):131. [CrossRef]
- Roy, S. Roy S. COVID-19 Reinfection: Myth or Truth? SN Compr Clin Med. 2020;2(6):710–3.
- Fowler AA III, Truwit JD, Hite RD, Morris PE, DeWilde C, Priday A, et al. Effect of Vitamin C Infusion on Organ Failure and Biomarkers of Inflammation and Vascular Injury in Patients With Sepsis and Severe Acute Respiratory Failure: The CITRIS-ALI Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2019 Oct 1;322(13):1261–70.
- Adams KK, Baker WL, Sobieraj DM. Myth Busters: Dietary Supplements and COVID-19. Ann Pharmacother. 2020 Aug;54(8):820–6. [CrossRef]
- Kumar S, Sil A, Das A. Hydroxychloroquine for COVID-19: Myths vs facts. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33(6):e13857.
- Al-Bari, AA. Al-Bari AA. Facts and Myths: Efficacies of Repurposing Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine for the Treatment of COVID-19. Curr Drug Targets. 2020;21(16):1703–21. [CrossRef]
- Mercurio AM, Gianakos AL, Mulcahey MK, Sutton KM. Five Myths of COVID-19 for the Team Physician. HSS J Musculoskelet J Hosp Spec Surg. 2020 Nov;16(Suppl 1):173–8. [CrossRef]
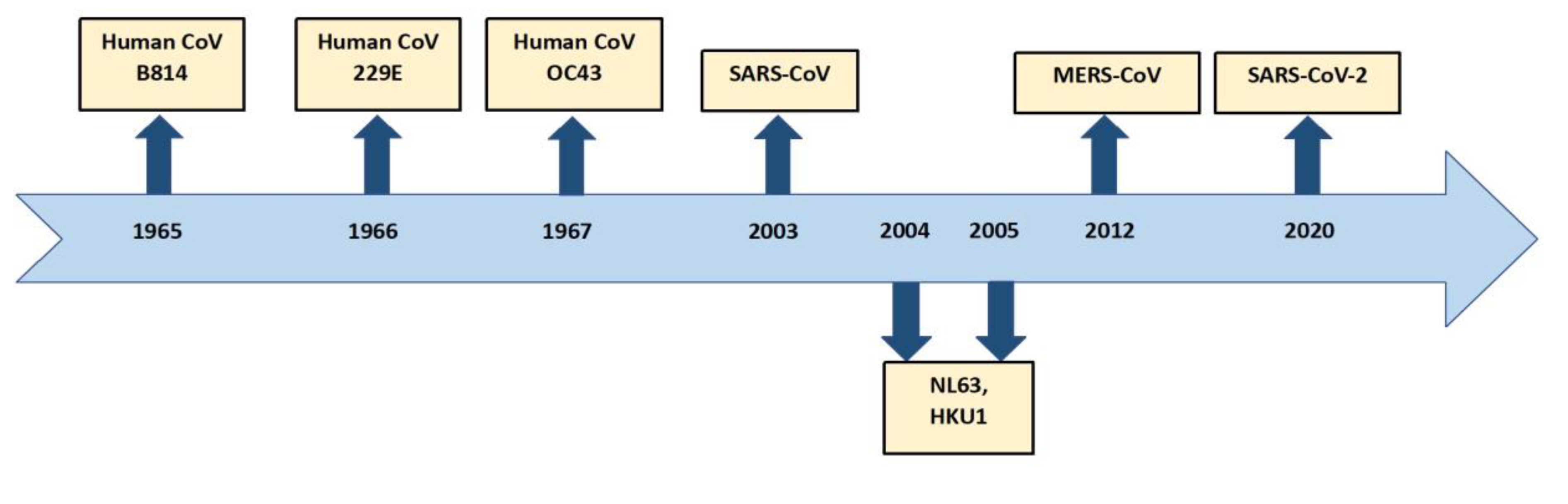
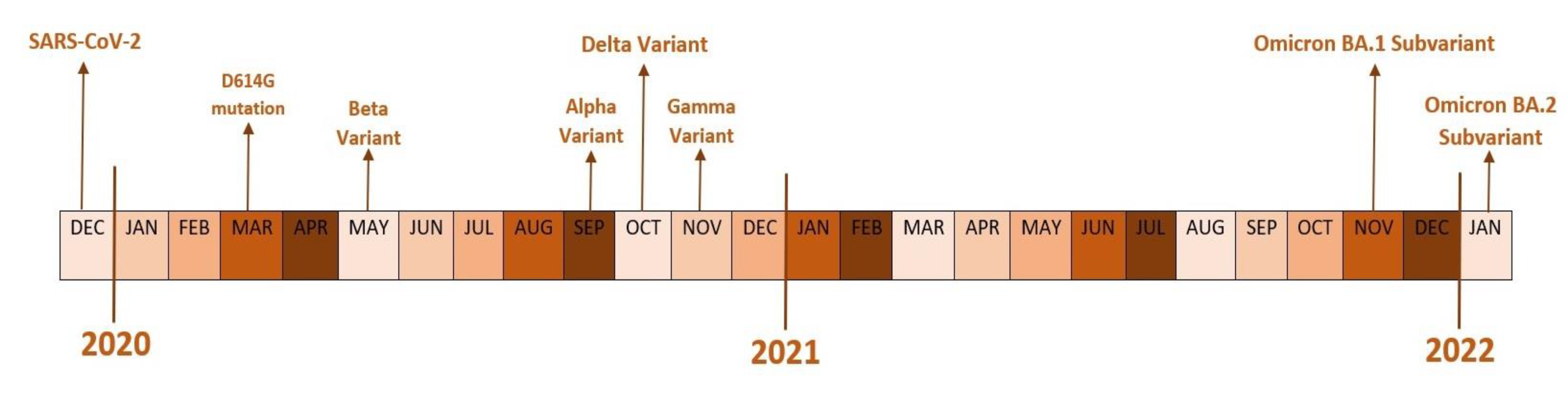
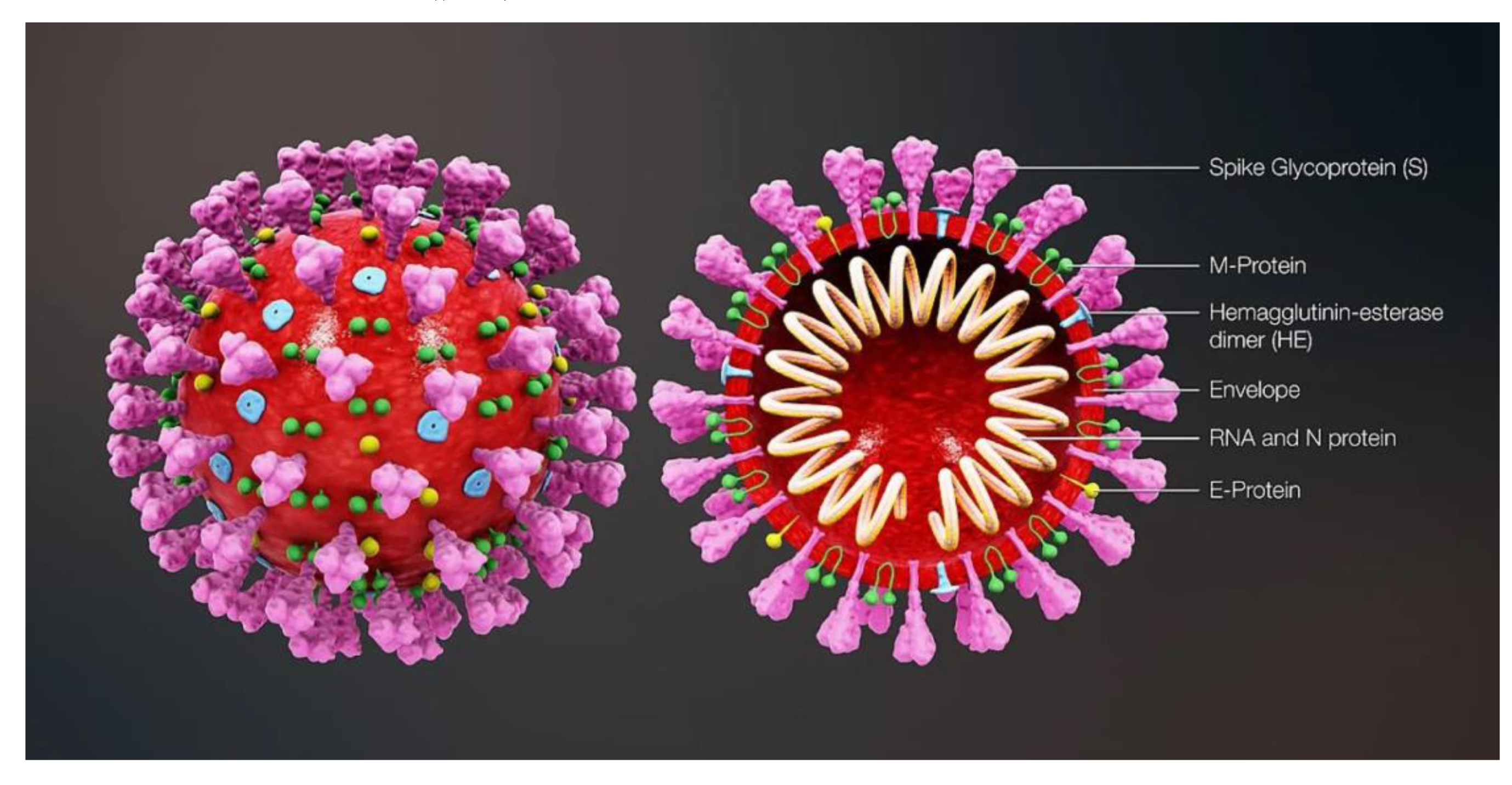
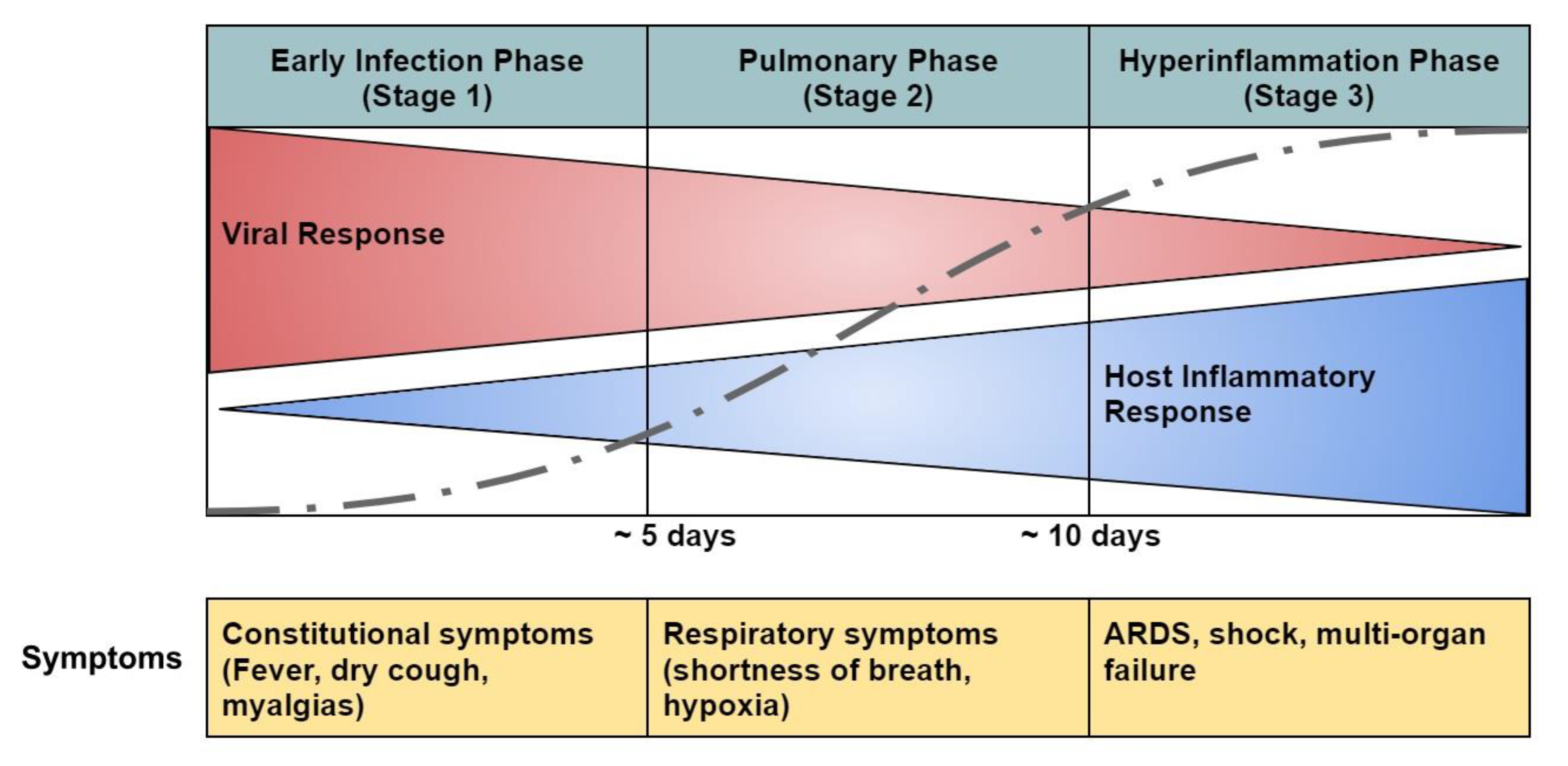
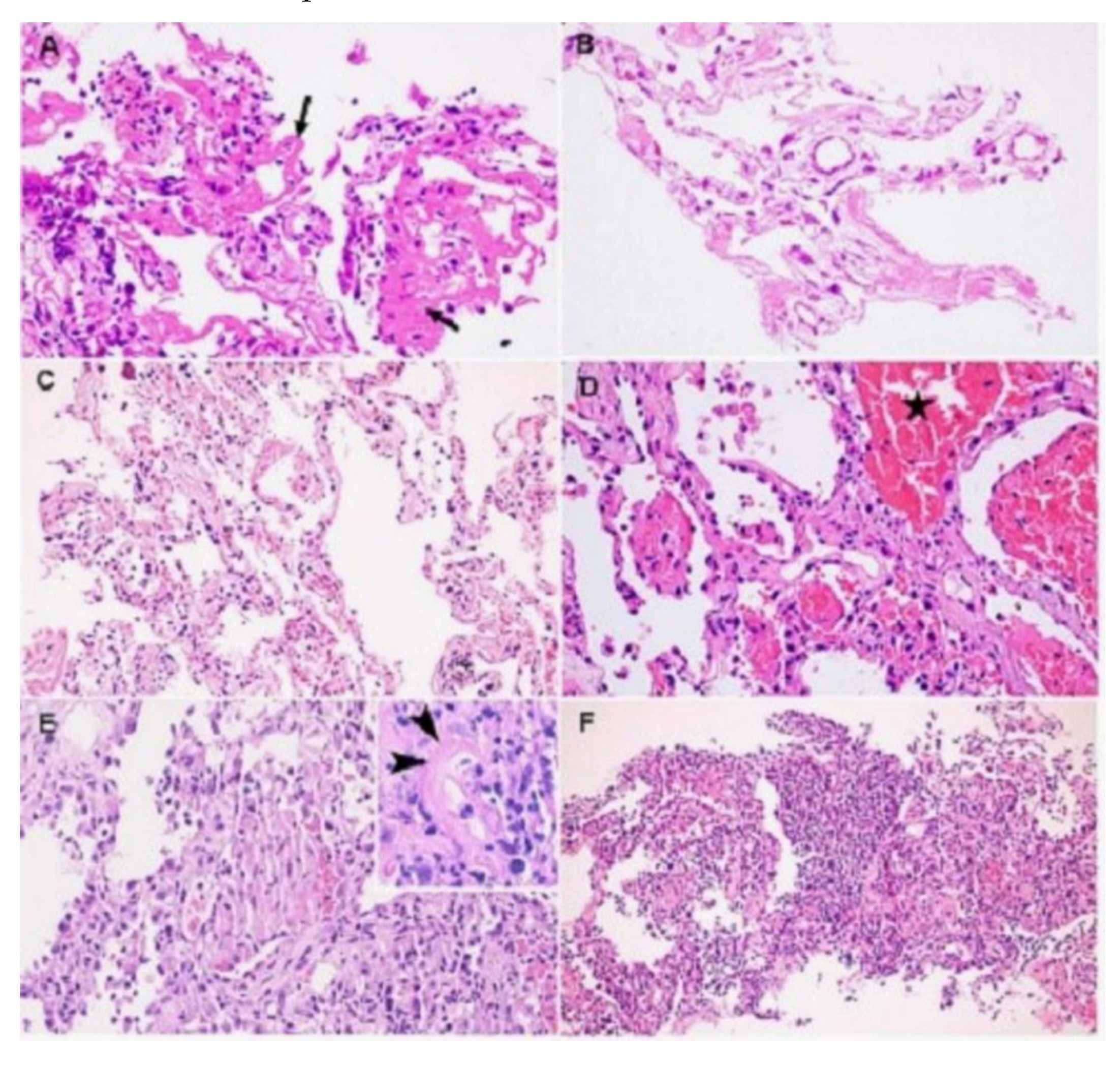
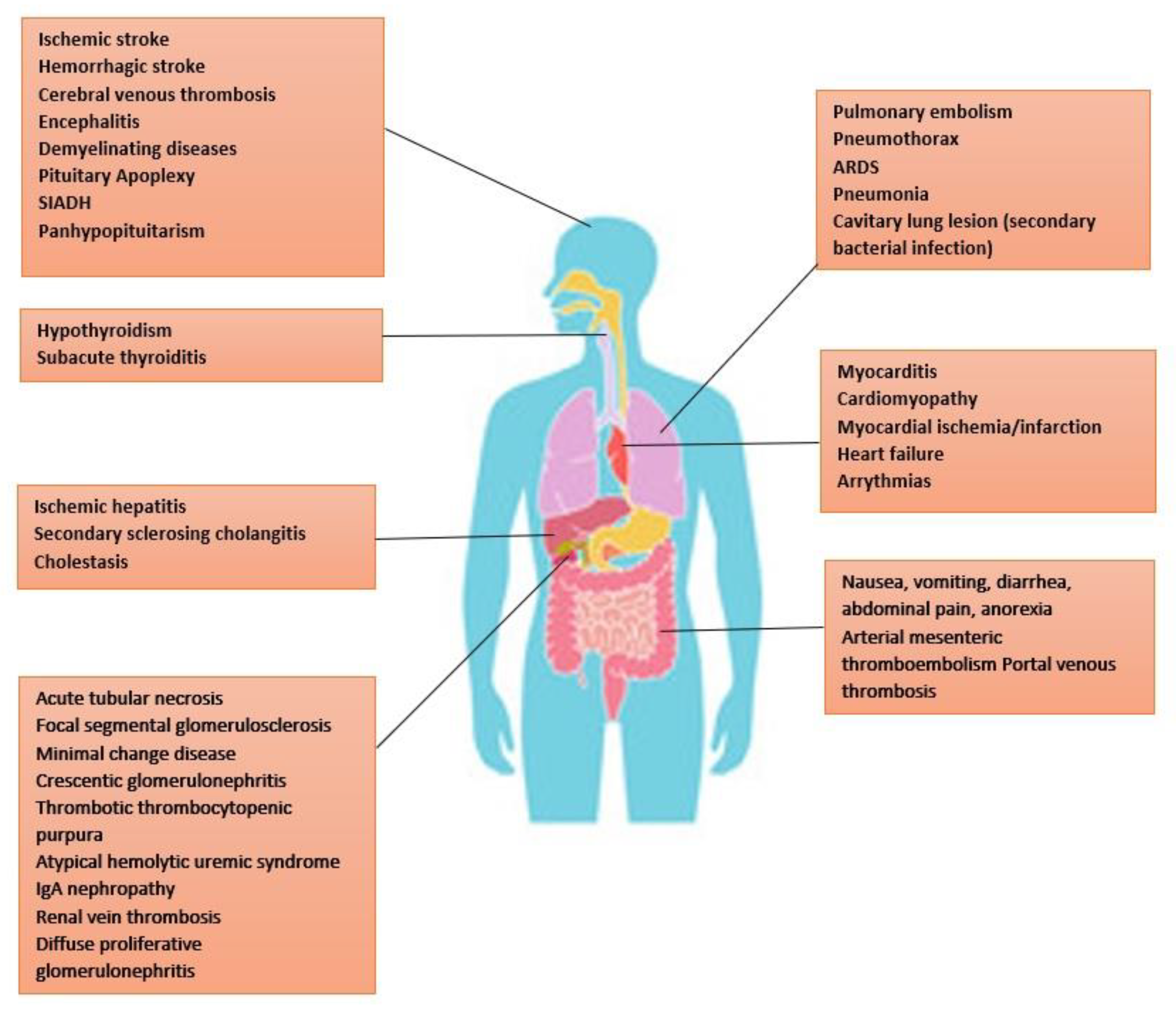
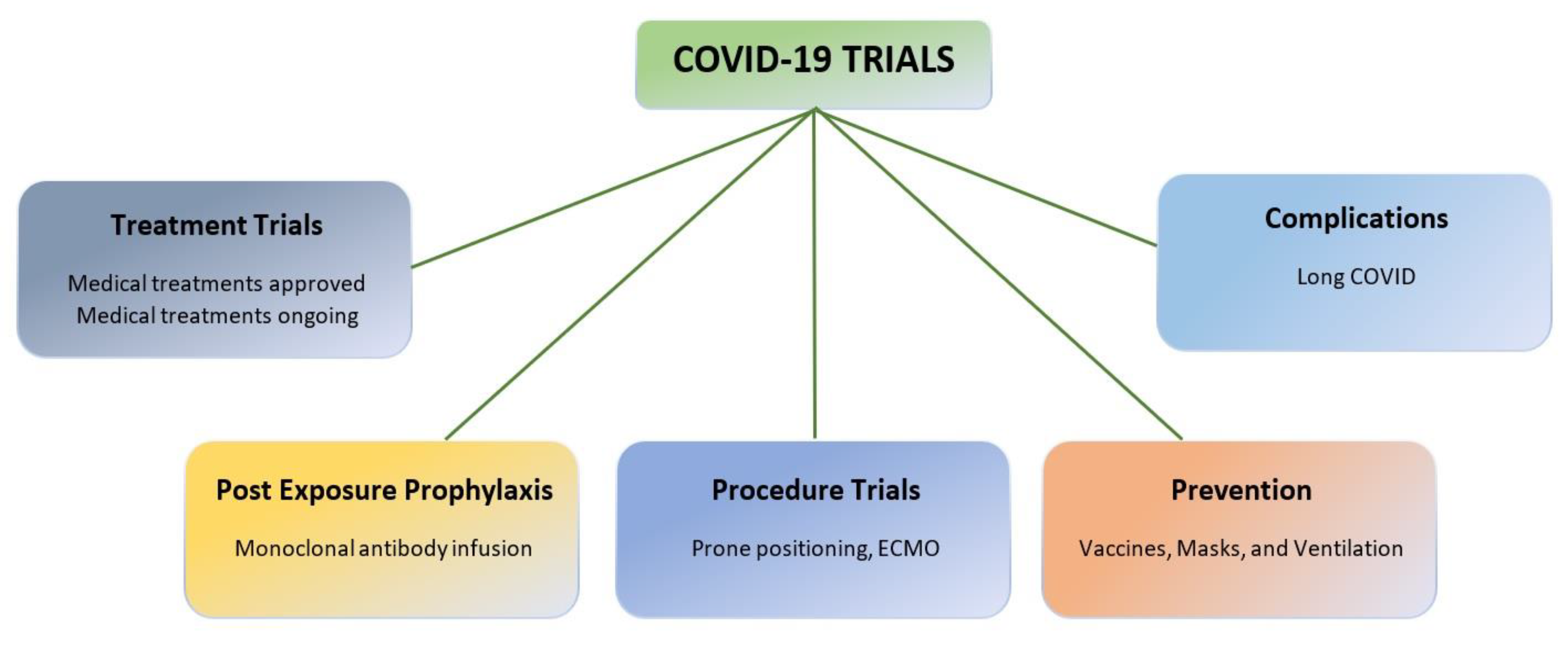
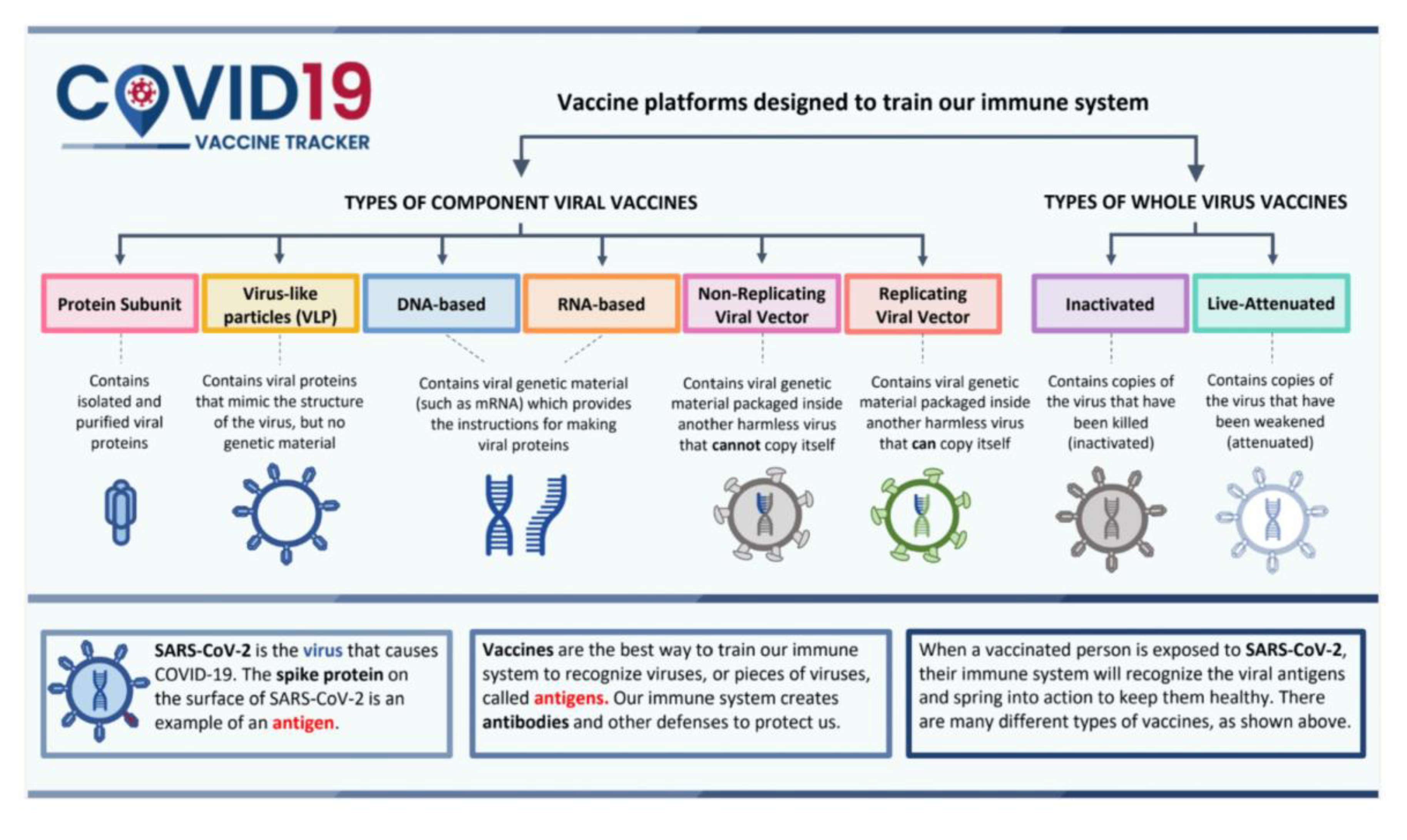
| WHO Nomenclature | Lineage | Emergence |
|---|---|---|
| Alpha | B.1.1.7 | Great Britain |
| Beta | B.1.351 | South Africa |
| Delta | B.1.617.2 | India |
| Gamma | P.1 | Brazil |
| Epsilon | B.1.427 | USA |
| Eta | B.1.525 | USA |
| Iota | B.1.526 | USA |
| Kappa | B.1.617.1 | India |
| Mu | B.1.621 | Columbia |
| Zeta | P.2 | Brazil |
| Omicron | B.1.1.529 | South Africa |
| Treatments | |||||||
| Study/Year | Treatment (Interventions) |
Study Design | Stratification Methods | No of Participants (n) | Outcomes | Limitations | Other events/observations |
| COVID-19 Convalescent Plasma - September 2020 | Convalescent Plasma | FDA-initiated, national, multicenter, open-label to evaluate the safety of convalescent plasma for patients at high risk of progression to) severe or life-threatening COVID | Open-label | 20,000 | Convalescent plasma was safe and likely to reduce mortality | Convalescent plasma therapy had to be given early in the course of the disease | Subsequent trials found no consistent evidence of benefit |
| RECOVERY (236) - October 2020 | Lopinavir 400 mg plus ritonavir 100 mg by mouth every 12 h for 10 days or until discharge |
Randomized controlled, Open-label | 2:1:1 Standard of care alone or usual standard of care plus lopinavir–ritonavir (400 mg and 100 mg, respectively) by mouth for 10 days or until discharge (or one of the other RECOVERY treatment groups: hydroxychloroquine, dexamethasone, or azithromycin | 1616 | Lopinavir–ritonavir was not effective | Open-label, very few patients on ventilator were enrolled | It is unclear whether the dose of lopinavir–ritonavir we used achieved adequate SARS-CoV-2 inhibitory concentrations in the lungs |
| Remdesivir - ACTT-1 (237) - November 2020 | Remdesivir vs placebo | Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial | 1:1 ratio to receive Remdesivir (200 mg loading dose on day 1, followed by 100 mg daily for up to 9 additional days) or placebo for up to 10 days. |
1062 | Remdesivir was superior to placebo in shortening the time to recovery in adults who were hospitalized with COVID-19 | Data on 4.8% of the study were unblinded to provide data to the sponsor, Study had a crossover during this early phase of COVID. | The primary outcome of the current trial was changed early in the trial, from a comparison of outcomes on day 15 to a comparison of time to recovery up to day 29. |
| Coalition I (238) - November 2020 | Hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin or standard of care | Open-label three group RCT | Randomly assigned in a 1:1:1 ratio to receive standard care, standard care plus hydroxychloroquine, or standard care plus hydroxychloroquine at a dose of 400 mg twice daily plus azithromycin for 7 days for Mild-to-Moderate COVID-19 | 667 | Did not improve clinical status at 15 days | Could not rule out either a substantial benefit or substantial harm. | Other trials did not show benefit for post-exposure prophylaxis in mild COVID |
|
SOLIDARITY trial (239) - January 2021 |
Remdesivir, lopinavir/ritonavir combined with interferon-beta, and hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine. | Open-label phase III-IV clinical trial organized by the World Health Organization (WHO), Participants were randomly allocated to get one of the 4 therapies | Random assignment to receive one of the 4 treatments | 14,304 | Hospitalized patients with COVID-19 treated with remdesivir had lower death rates and reduced need for oxygen, but no difference in patients already on mechanical ventilation | Trial period had outbreaks due to different strains, delta, and omicron variants. Vaccinations also became more widespread during the trial. Mechanical ventilators were available in resource-limited countries. |
WHO suspended the hydroxychloroquine arm of the Solidarity trial in late May 2020 |
| RECOVERY (240) - February 2021 | Usual standard of care alone or the usual standard of care plus oral or intravenous dexamethasone (at a dose of 6 mg once daily) for up to 10 days or until hospital discharge |
Randomized controlled, Open-label | 2:1 ratio randomization to receive usual care alone or usual standard of care plus oral or intravenous dexamethasone |
2104 | Lower 28-day mortality among those on invasive mechanical ventilation or oxygen |
Open-label, the standard of care varied during the trial period | Patients in the dexamethasone group had a shorter duration of hospitalization than those in the usual care group |
| INSPIRATION (241) - March 2021 | Intermediate vs standard prophylactic dose Enoxaparin | RCT, 10 academic centers in Iran | Intermediate-dose (enoxaparin, 1 mg/kg daily) vs standard prophylactic anticoagulation (enoxaparin, 40 mg daily), with modification according to body weight and creatinine clearance. The assigned treatments were planned to be continued until the completion of the 30-day follow-up. | 600 | No differences in venous or arterial thrombus, treatment with ECMO or mortality within 30 days | Open-label, enrolled ICU patients but not severely ill patients requiring ECMO, lack of systematic screening for venous thromboembolism, only 4 patients were >120kg | increased risk of bleeding (2.5%) in intermediate dose group which did not meet non -inferiority criteria, severe thrombocytopenia only occurred in intermediate dose group. |
| COVACTA (242) - May 2021 | Standard of care alone versus usual standard of care plus tocilizumab at a dose of 400 mg–800 mg | Open-label | 21,550 patients enrolled into the RECOVERY trial were included in the assessment of tocilizumab | 4116 | Tocilizumab improved survival | Duration of hospitalization beyond 28 days was not recorded | 16% of patients in the tocilizumab group did not receive this treatment and the reasons for this were not recorded |
| Heparin (243) - August 2021 | Therapeutic-dose anticoagulation with heparin vs pharmaco- logic thromboprophylaxis |
Open-label RCT, critically ill patients with severe COVID-19 |
1:1 randomization to therapeutic-dose anticoagulation with heparin vs pharmaco- logic thromboprophylaxis in accordance with local usual care | 1098 | No differences in of survival to hospital discharge or a greater number of days free of cardiovascular or respiratory organ support | Open-label, most patients were from the United Kingdom, practice guideline changed during the trial period and majority received intermediate dose anticoagulation in the control group | Incidence of major bleeding was 3.8% in the treatment group |
| ECMO (244) - September 2021 | Outcomes after ECMO in COVID | Analysis of the Extracorporeal Life Support Organization Registry and COVID-19 for between group comparison of ECMO-supported patients with COVID-19 | Retrospective analysis of ECMO registries | 4812 | Mortality for ECMO-supported patients with COVID-19 worsened worldwide over the course of the pandemic, and duration of ECMO support increased. |
Not an RCT, did not give insight about which patients need ECMO support | Mortality ranged between 38 to 59% |
| Remdesivir plus standard of care - DISCOVERY (245) - September 2021 | Remdesivir plus standard of care | Phase 3, open-label, adaptive, multicenter, randomized, controlled trial conducted in 48 sites in Europe (France, Belgium, Austria, Portugal, Luxembourg), between March 22, 2020, and Jan 21, 2021, |
1:1 randomization, Remdesivir was administered intravenously at a loading dose of 200 mg on day 1 followed by a 100 mg, for a total duration of 10 days. Its cessation was allowed after 5 days if the participant was discharged from the hospital. |
857 | No clinical benefit was observed from the use of remdesivir in symptomatic patients for more than 7 days and required oxygen support. | Open-label, several treatments were concomitantly evaluated during the trial period, no viral load assessment was available at any time point | Among the subset of participants without mechanical ventilation or ECMO at randomization, remdesivir significantly delayed the need for new mechanical ventilation or ECMO, or death, consistent with what was reported in ACTT-1.9 |
| Aspirin- RECOVERY (246) - November 2021 | Aspirin | Open-label RCT, 177 hospitals in the UK, two hospitals in Indonesia, and two hospitals in Nepal, Nov 1, 2020, and March 21, 2021 | 1:1 ratio to either the usual standard of care plus 150 mg aspirin once per day until discharge or the usual standard of care alone | 14892 | No reduction in 28-day mortality, mechanical ventilation, or death, a small increase of 1 median day of being discharged alive. | Open-label, only hospitalized patients were studied, radiological information was not collected, | The effects of Aspirin were like other trials of patients with cardiovascular disease |
| COVID-PRONE (247) - January 2022 | Proning in patient requiring up to 50% fraction of inspired oxygen but not critically ill |
Randomized 1:1 to prone positioning | Patients were randomized 1:1 to prone positioning (That is, instructing a patient to lie on their stomach while they are in bed) or standard of care |
570 | Prone positioning did not improve outcomes in hospitalized hypoxemic patients | Adherence to prone positioning was poor, despite multiple efforts to increase it, time spent prone was self-reported and thus at risk of recall bias, | The median total time spent in prone position up to the first 72 hours was 6 hours |
| CPAP - RECOVERY-RS (248) - January 2022 | CPAP vs conventional oxygen | Parallel group, adaptive, randomized clinical trial from April 6, 2020, and May 3, 2021, across 48 acute care hospitals in the UK and Jersey | 1:1 randomization | 1273 | Initial strategy of CPAP significantly reduced the risk of tracheal intubation or mortality compared with conventional oxygen therapy | Cross over occurred | Treatment crossover occurred in 17.1% of participants. |
| Early treatment with Ivermectin (249) - March 2022 | Ivermectin | Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, adaptive platform trial, 12 public health clinics in Brazil. |
Patients were randomized to receive ivermectin (679 patients), placebo (679), or another intervention (2157)., ivermectin (400 μg per kilogram of body weight) once daily for 3 days or placebo. | 3515 | Did not result in a lower incidence of medical admission to a hospital due to the progression of disease among outpatients with an early diagnosis of COVID-19. | Enrolled patients only in Brazil, although 3515 patients were enrolled, ivermectin vs placebo was compared only in 679 patients | There was no evidence of a treatment effect with ivermectin as compared with placebo in subgroups defined according to patient age, body-mass index, status of having cardiovascular disease or lung disease, sex, smoking status, or time since symptom onset |
| Colchicine and Rivaroxaban- Anti-Coronavirus Therapies (ACT) Trial (250) - October 2022 | Colchicine and Rivaroxaban + Aspirin | Open-label RCT, 62 clinical centers in 11 countries between Oct 2, 2020, and Feb 10, 2022 | colchicine 1·2 mg followed by 0·6 mg 2 h later within 72 hours of hospitalization and then 0·6 mg twice daily for 28 days versus usual care; and in a second (1:1) randomization, to the combination of rivaroxaban 2·5 mg twice daily plus aspirin 100 mg once daily for 28 days versus usual care | 2749 | No prevention of disease progression or death | Open-label, the trial was done over 18 months and different therapies were used, different strains emerged, vaccinations increased as the trial progressed | 56 to 65% of patients were unvaccinated. |
| Nirmatrelvir and Ritonavir EPIC-HR (251) - February 2022 | 300 mg of nirmatrelvir plus 100 mg of ritonavir vs placebo | Phase 2–3 double-blind, randomized, controlled trial | 1:1 ratio to receive either 300 mg of nirmatrelvir plus 100 mg of ritonavir for 5 days | 2246 | The risk of progression to severe COVID-19 was 89% lower than the risk with a placebo | The median age was only 45 years and the predominantly white population | The trial was restricted to unvaccinated persons |
| Long-term cardiovascular outcomes of COVID-19 (252) - March 2022 | Prospective cohort | Data was reported from the US Department of Veterans Affairs national healthcare databases |
The healthcare database was used to build a cohort and then followed longitudinally to estimate the risks and 12-month burdens of pre-specified incident cardiovascular outcomes | 153,760 | risk and 12-month burden of ischemic and non-ischemic heart disease, dysrhythmias increased post COVID | Majority were males | Increased risk of myocarditis and pericarditis reported in this study is significant in people who were not vaccinated and is evident regardless of vaccination status. |
| Long-term (180-Day) Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19 - REMAP-CAP (253) - December 2022 |
Follow-up study | Randomized to receive 1 or more interventions within 6 treatment domains: immune modulators, convalescent plasma, antiplatelet therapy (n = 1557), anticoagulation, antivirals, and corticosteroids | 4869 | IL-6 receptor antagonist had a greater than 99.9% probability of improved 180-day mortality |
Open-label, not all centers collected quality of life and disability scores | 1 in 3 patients had at least moderate disability that persisted through 6 months | |
| Nirmatrelvir–ritonavir (254) - February 2023 | nirmatrelvir–ritonavir for reducing hospital admissions and mortality from COVID-19 |
Population-based cohort study | Population-based follow-up study | 177,545 | Significantly reduced odds of hospital admission and death from COVID-19, | Study tracked prescriptions, could not confirm adherence | Number needed to treat= 62. |
| Prevention | |||||||
| Phase 3 of BLAZE-1 trial, Bamlanivimab plus Etesevimab (255) - July 2021 | 2800 mg of Bamlanivimab and 2800 mg of Etesevimab within 3 days of in Mild or Moderate COVID-19 | Double-blind, placebo-controlled, RCT, single-dose trial conducted in the United States | Ambulatory patients with mild or moderate COVID-19, who were at high risk for progression to severe disease were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive a single intravenous infusion of either a neutralizing monoclonal-antibody combination agent (2800 mg of bamlanivimab and 2800 mg of etesevimab, administered together) or placebo within 3 days after a laboratory diagnosis. The primary outcome was the overall clinical status of the patients, defined as COVID-19–related hospitalization or death from any cause by day 29. |
1035 | Bamlanivimab plus etesevimab resulted in more rapid resolution of symptoms within 4 days after the initiation of treatment, less hospitalization and death compared to placebo, and accelerated decline in the SARS-CoV-2 viral load. | 12.6% were whites, conduction only in the United States with very few adolescents, emergency use authorization for bamlanivimab plus etesevimab is for administration within 10 days but was administered within 3 days in the study | On 16 April 2021, the FDA revoked the emergency use authorization (EUA) for the investigational monoclonal antibody therapy bamlanivimab to be used alone |
| REGEN-COV (256) - September 2021 | combination of the monoclonal antibodies casirivimab and imdevimab, REGEN-COV 2400-mg vs placebo | Phase 3, randomized controlled trial | 1:1:1 ratio to receive intravenous REGEN-COV at a dose of 2400 mg (1200 mg each of casirivimab and im- devimab) or 8000 mg (4000 mg of each anti- body) or intravenous placebo |
2696 | REGEN-COV reduced the risk of COVID-19–related hospitalization or death from any | Efficacy against other strains was not studied | FDA has revised the EUAs for Bamlanivimab/etesevimab and casirivimab/imdevimab (REGEN-COV) and are currently not authorized for use due to inactivity against the omicron variant |
| Vaccines | |||||||
| Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine(Pfizer) (257) - December 2020 | BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine vs placebo | Randomized placebo-controlled, observer-blinded | 1:1 ratio to receive two doses, 21 days apart, of either placebo or the BNT162b2 vaccine |
43,548 | cause, and it resolved symptoms and reduced the SARS-CoV-2 viral load more rap- | The endpoints in protocols for different vaccines are different, difficult to compare efficacy across different vaccine groups | Further studies showed that the bivalent vaccine was 58.7% effective against hospitalization compared to 25% for the monovalent one that preceded it |
| Astrazeneca COVID vaccine AZD1222 against SARS-CoV-2 (258) January 2021 | ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine (AZD1222) | Randomized, blinded, controlled trials done across three countries: COV001 (phase 1/2; UK), COV002 (phase 2/3; UK), COV003 (phase 3; Brazil), and COV005 (phase 1/2; South Africa) between April 23 and Nov 4, 2020 | Two standard doses vs one low dose followed by standard dose | 23,848 | idly than placebo. | The endpoints in protocols for different vaccines are different, difficult to compare efficacy across different vaccine groups | |
| Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 Vaccine (Moderna) (259) - February 2021 | mRNA-1273 vaccine vs placebo | Phase 3 randomized, observer-blinded, placebo-controlled trial | 1:1 ratio to receive two intra- muscular injections of mRNA-1273 (100 μg) or a placebo 28 days apart. |
30,420 | 94.1% efficacy at preventing COVID-19 illness, including severe disease |
The endpoints in protocols for different vaccines are different, difficult to compare efficacy across different vaccine groups | Further studies showed effectiveness against the XBB strains varied by age: in ages 18 to 49, it was 49% against the XBB strains versus 52% against the BA.5 viruses; in ages 50 to 64, it was 40% compared to 43% for BA.5; and in people 65 and older, 43%, compared to 37% for the BA.5 viruses. |
| ENSEMBLE trial-Johnson and Johnson vaccine (260) - April 2021 | Ad26.COV2.S vaccine against COVID-19 | Randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial | 1:1 ratio to receive a single dose of Ad26.COV2.S (5×1010 viral particles) or placebo. |
39,321 | Safety appeared to be similar to that in other phase 3 trials of COVID-19 vaccines. | The endpoints in protocols for different vaccines are different, difficult to compare efficacy across different vaccine groups | |
| Efficacy and Safety of NVX-CoV2373 (Novavax) (261) - February 2022 | NVX-CoV2373 vaccine vs placebo | Phase 3, randomized, observer-blinded, placebo-controlled trial at 113 clinical sites | 2:1 ratio to receive two doses of NVX-CoV2373 or placebo 21 days apart | 29,949 | Two doses of NVX-CoV2373 were safe | The endpoints in protocols for different vaccines are different, difficult to compare efficacy across different vaccine groups | Had a blinded crossover approximately 3 to 4 months after the first vaccination series to allow all trial participants to receive NVX-CoV2373, after vaccine efficacy and required safety had been established and reviewed |
| COVID and risk of incident diabetes (262) - December 2022 | COVID vaccine | Self-controlled crossover observational cohort, Cedars-Sinai Health System in Los Angeles, California from March 2020 to June 2022 | 23,709 | The risk of type 2 diabetes after COVID infection was higher in unvaccinated individuals compared to vaccinated individuals | |||
| Ongoing trials | |||||||
| COVERAGE-A Early Treatment of Vulnerable Individuals with Non-Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection - Full - Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov | Early treatment of vulnerable individuals with non-severe SARS-CoV-2 | ||||||
| SOLIDARITY PLUS SOLIDARITY Finland Plus Long-COVID - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov | Enroll hospitalized patients to test artesunate, imatinib and infliximab. | ||||||
| HALT-COVID-19 Inhalation of Ciclesonide for Patients With COVID-19: A Randomized Open Treatment Study (HALT COVID-19) - No Study Results Posted - ClinicalTrials.gov | Inhaled Ciclesonide |
|

| Vaccine | Vaccine Type | Vaccine Platform | Approved Countries | No of Trials | WHO EUL recommendation | Age indication | Shelf life | EUL Holder | Approval Source | Trials Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COVOVAX | SARS-CoV-2 rS Protein Nanoparticle [Recombinant] | Protein subunit | 6 | 7 | 17 December 2021 | 12 years and older | 9 months Storage temperature: 2°C to 8°C | Serum Institute of India Pvt. Ltd. (SIIPL) | COVOVAX | WHO - Prequalification of Medical Products (IVDs, Medicines, Vaccines, and Immunization Devices, Vector Control) | Serum Institute of India: COVOVAX (Novavax formulation) – COVID19 Vaccine Tracker |
| NOVAVAX | SARS-CoV-2 rS [Recombinant, adjuvanted] | Protein subunit | 40 | 22 | 20 December 2021 | 12 years and older | 9 months Storage temperature: 2°C to 8°C | Serum Institute of India Pvt. Ltd. (SIIPL) | NUVAXOVID | WHO - Prequalification of Medical Products (IVDs, Medicines, Vaccines, and Immunization Devices, Vector Control) | Novavax: Nuvaxovid – COVID19 Vaccine Tracker |
| MODERNA | COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine (nucleoside modified) | RNA | 88 | 70 | 30 April 2021 | 6 years and older | 9 months Storage temperature: -20°C ± 5°C | Moderna Biotech | COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine (nucleoside modified) | Moderna: Spikevax – COVID19 Vaccine Tracker |
| Pfizer/BioNTech | COVID-19 mRNA vaccine (nucleoside modified) | RNA | 149 | 100 | 31 December 2020 | 6 months and older | 9 months Storage temperature: - 90°C to - 60°C | BioNTech Manufacturing GmbH | WHO recommendation BioNtech Tozinameran – COVID-19 mRNA vaccine (nucleoside modified) – COMIRNATY | Pfizer/BioNTech: Comirnaty – COVID19 Vaccine Tracker |
| CanSino | Ad5-nCoV-S [Recombinant] | Non-Replicating Viral Vector | 10 | 14 | 19 May 2022 | 18 to 59 years of age | 12 months Storage temperature: 2°C to 8°C | CanSino Biologics Inc. | CONVIDECIA | WHO - Prequalification of Medical Products (IVDs, Medicines, Vaccines and Immunization Devices, Vector Control) | CanSino: Convidecia – COVID19 Vaccine Tracker |
| Janssen | Ad26.COV2-S [recombinant] | Non-Replicating Viral Vector | 113 | 26 | 12 March 2021 | 18 years and older | 24 months Storage temperature: -25°C to -15°C | Janssen–Cilag International NV | COVID-19 Vaccine (Ad26.COV2-S [recombinant]) | Janssen (Johnson & Johnson): Jcovden – COVID19 Vaccine Tracker |
| Oxford/AstraZeneca | ChAdOx1-S ([recombinant] | Non-Replicating Viral Vector | 149 | 73 | 15 February 2021 | 18 years and older | 6 months Storage temperature: 2°C to 8°C | AstraZeneca/SK Bioscience Co. Ltd | WHO Recommendation AstraZeneca/SKBio - COVID-19 Vaccine (ChAdOx1-S [recombinant]) | Oxford/AstraZeneca: Vaxzevria – COVID19 Vaccine Tracker |
| Covishield | ChAdOx1-S ([recombinant] | Non-Replicating Viral Vector | 49 | 6 | 15 February 2021 | 18 years and older | 9 months Storage temperature: 2°C to 8°C | Serum Institute of India Pvt. Ltd | COVISHIELD | WHO - Prequalification of Medical Products (IVDs, Medicines, Vaccines and Immunization Devices, Vector Control) | Serum Institute of India: Covishield (Oxford/ AstraZeneca formulation) – COVID19 Vaccine Tracker |
| Covaxin | Whole Virion Inactivated Corona Virus vaccine | Inactivated | 14 | 16 | 03 November 2021 | 18 years and older | 9 months Storage temperature: 2°C to 8°C | Bharat Biotech International Ltd. | COVAXIN | WHO - Prequalification of Medical Products (IVDs, Medicines, Vaccines and Immunization Devices, Vector Control) | Bharat Biotech: Covaxin – COVID19 Vaccine Tracker |
| SinoPharm | COVID-19 Vaccine (Vero Cell), Inactivated | Inactivated | 93 | 39 | 07 May 2021 | 18 years and older | 24 months Storage temperature: 2°C to 8° C | Beijing Institute of Biological Products Co., Ltd. (BIBP) | COVID-19 Vaccine (Vero Cell), Inactivated | Sinopharm (Beijing): Covilo – COVID19 Vaccine Tracker |
| Sinovac | COVID-19 Vaccine (Vero Cell), Inactivated | Inactivated | 56 | 42 | 01 June 2021 | 3 to 59 years of age | 24 months Storage temperature: 2°C to 8° C | Sinovac Life Sciences Co., Ltd. | CoronaVac | WHO - Prequalification of Medical Products (IVDs, Medicines, Vaccines and Immunization Devices, Vector Control) | Sinovac: CoronaVac – COVID19 Vaccine Tracker |
| Vaccine | Approved countries | Trials | Links |
| Anhui Zhifei Longcom: Zifivax | 4 | 21 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/27/ |
| Bagheiat-allah University of Medical Sciences: Noora vaccine | 1 | 3 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/129/ |
| Bharat Biotech: Covaxin | 14 | 16 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/9/ |
| Bharat Biotech: iNCOVACC | 1 | 4 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/87/ |
| Biological E Limited: Corbevax | 2 | 7 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/54/ |
| CanSino: Convidecia | 10 | 14 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/2/ |
| CanSino: Convidecia Air | 2 | 5 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/162/ |
| Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology:Abdala | 6 | 5 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/67/ |
| Chumakov center: KoviVac | 3 | 5 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/100/ |
| Gamaleya: Gam-COVID-Vac | 1 | 2 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/191/ |
| Gamaleya : Sputnik light | 26 | 7 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/126/ |
| Gamaleya : Sputnik V | 74 | 25 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/12/ |
| Gennova Biopharmaceuticals Ltd: Gemcovac-16 | 1 | 2 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/200/ |
| Health institutes of Turkey: Turkovac | 1 | 8 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/77/ |
| Instituto Finlay de Vacunas Cuba : Soberana 02 | 4 | 2 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/52/ |
| Instituto Finlay de Vacunas Cuba : Soberana Plus | 2 | 5 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/119/ |
| Janssen (Johnson & Johnson) | 113 | 26 | https://covid19.trackvaccines. /vaccines/1/ |
| Livzon Mabpharm Inc: V-01 | 1 | 7 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/108/ |
| Medicago: Covifenz | 1 | 6 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/26/ |
| Medigen: MVC-COV1901 | 4 | 15 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/24/ |
| Moderna: Spikevax | 88 | 70 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/22/ |
| Moderna: Spikevax Bivalent Original/Omicron BA.1 | 38 | 5 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/210/ |
| Moderna: Spikevax Bivalent Original/Omicron BA.4/BA.5 | 33 | 2 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/224/ |
| National Vaccine and Serum institute: Recombinant SARS-Cov-2 Vaccine(CHO cell) | 1 | 3 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/114/ |
| Novavax: Nuvaxovid | 40 | 22 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/25/ |
| Organization of Defensive innovation and research: FAKHRAVAC (MIVAC) | 1 | 3 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/97/ |
| Oxford/AstraZeneca: Vaxzevria | 149 | 73 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/4/ |
| Pfizer/BioNtech: Comirnaty | 149 | 100 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/6/ |
| Pfizer/BioNtech: Comirnaty Bivalent Original /Omicron BA.1 | 35 | 3 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/223/ |
| Pfizer/BioNtech: Comirnaty Bivalent Original /Omicron BA.4/BA.5 | 33 | 4 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/225/ |
| PT Bio Farma : IndoVac | 1 | 4 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/187/ |
| Razi Vaccine and Serum Research Institute : Razi Cov Pars | 1 | 5 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/82/ |
| Research Institute for Biological Safety Problems (RIBSP): QazVac | 2 | 3 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/30/ |
| Sanofi/GSK: VidPrevtyn Beta | 30 | 3 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/165/ |
| Serum Institute of India: Covishield(Oxford/AstraZeneca formulation) | 49 | 6 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/48/ |
| Serum Institute of India: Covovax ( Novavax formulation) | 6 | 7 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/123/ |
| Shenzhen Kangtai Biological Products Co: KCONVAC | 2 | 7 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/47/ |
| Shifa Pharmed Industrial Co: COVIran Barekat | 1 | 6 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/83/ |
| Sinopharm (Beijing) Covilo | 93 | 39 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/5/ |
| Sinopharm (Wuhan) : Inactivated (Vero cells) | 2 | 9 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/16/ |
| Sinovac : CoronaVac | 56 | 42 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/7/ |
| SK Bioscience Co Ltd : SKYCovione | 1 | 7 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/81/ |
| Takeda: TAK-019 (Novavax formulation) | 1 | 3 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/80/ |
| Takeda : TAK -919 (Moderna formulation) | 1 | 2 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/79/ |
| Valneva: VLA2001 | 33 | 9 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/69/ |
| Vaxine/CinnaGen Co: SpikoGen | 1 | 8 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/8/ |
| Vector State Research center of Virology and biotechnology: Aurora -Cov | 1 | 2 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/169/ |
| Vector State Research center of Virology and biotechnology: EpiVacCorona | 4 | 4 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/32/ |
| WalVax: AWcorna | 1 | 4 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/23/ |
| Zydus Cadila: ZyCov-D | 1 | 6 | https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/29/ |
| System | Long-COVID Complications |
|---|---|
| Neuropsychiatric (371–375) | Chronic Fatigue syndrome Headache Myelitis Neuropathies Paresthesia Parkinsonism Cogwheel rigidity Optic neuritis Anosmia Ageusia Encephalitis Epilepsy Bell’s palsy Myoclonus Transient Ischemic Attack Stroke Depression Anxiety |
|
Pulmonary (151,376–379) |
Pulmonary fibrosis Pulmonary thromboembolism Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Pulmonary embolism Pneumothorax |
| Cardiovascular (12,13) | Dysrhythmias Atrial Fibrillation/flutter Ventricular arrhythmias Sinus tachycardia/bradycardia Inflammatory heart disease Pericarditis/myocarditis Coronary artery disease Cardiomyopathy (ischemic/nonischemic) |
| Endocrine (14) |
Fulminant type diabetes/autoimmune diabetes/ new-onset transient hyperglycemia |
| Rheumatology (380–382) | Polyarthritis Osteoporosis Osteonecrosis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





