1. Introduction
Since the emergence of SARS-CoV-2 in late 2019, new variants of concern (VOCs) have emerged, leading to a prolonged combat against COVID-19. Among them are the variants Alpha, Beta, Gamma and Delta, originated from the UK, South Africa, Brazil and India, respectively. The spread of a new VOC has great implications to public health, since genetic changes may increase virus transmissibility and disease severity. Furthermore, it may reduce effectiveness of vaccines or lead to diagnostic failures [1, 2]. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the SARS-CoV-2 RNA may cause false negative results in the diagnosis of the virus using genetic methods, originally developed for the wild-type strain (Wuhan reference strain) [
3]. RT-PCR, the gold standard method for SARS-CoV-2 detection, may miss variant virus identification when the mutations interfere with primer binding [4, 5]. Vogel et al. aimed to reduce false negative results by multiplexed RT-PCR, developing a set of dedicated primers for variants sharing common mutations [
6]. Mass spectrometry (MS) methods for SARS-CoV-2 identification, based on unique peptides markers, were reported since the beginning of the pandemic [7-11]. In previous studies, we demonstrated a rapid SARS-CoV-2 identification assay, using mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). The assay is based on the identification of six SARS-CoV-2 specific peptides, four of them are derived from the spike protein (SFIEDLLFNK, FLPFQQFGR, FQILLALHR and HTPINLVR), and the other two are derived from nucleocapsid protein (GFYAEGSR and AYNVTQAFGR) [
10]. An improvement of the assay’s sensitivity up to 1x10
3 PFU/ml is achieved by pre-concentration and purification step using immunomagnetic beads coated with SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, combined with a sensitive MRM-based LC-MS/MS analytical method for the target markers [
11].
Along with the emergence of VOCs and the accumulating knowledge of mutations occurring during the spread of the virus, sequence conservation of the selected peptide markers among different variants become a fundamental requirement for SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis assay. Therefore, inter-strains conservation was one of the main criteria for marker selection in our previous study [
10]. However, apart from preventing false negative results in the diagnosis process, and considering variant infectivity and breakthrough infection, identification of the specific variant is of great importance. To date, genetic sequencing is the gold standard method to discriminate between variants. Yet, it is time consuming (days) and relatively expensive [12, 13]. Recently, researchers have begun to evaluate the efficacy of MS-based proteomics approaches for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Mann et al. pioneered MALDI-FT-ICR MS, a peptide mass fingerprinting method, to detect the Alpha, Beta, Gamma and Delta variants. As a peptide mass fingerprinting approach, MS/MS spectra were not acquired, and the method required isolation of the S-protein. They successfully measured the masses of mutated peptides and constructed a phylogenetic tree to track variant evolution [
3]. Maus et al. highlighted the importance of including variants of concern in assay design and detected variant peptides from the N and ORF1ab proteins [
14]. Starr et al. investigated the mutational space of SARS-CoV-2, and assays have been performed to measure the effect of spike protein mutations on binding to the ACE-2 receptor [
15]. Suddnapas et al. studied the potential for LC-MS/MS identification of Beta, Gamma, Delta and Omicron variants based on synthetic peptides that mimic the unique tryptic peptides theoretically obtained from tryptic digestion of variants. This study evaluates the analytical method sensitivity for synthetic theoretical variant peptides, however this approach was not examined using the SARS-CoV-2 variants in real clinical specimens. Variant detection is not only dependent on the prototypic peptides’ properties but also on the efficiency of variant tryptic digestion process and the highly complex background matrix of clinical specimen [
16]. Considering the current and probable future state of the growing repertoire of SARS-CoV-2 protein mutations, a method combining universal detection of SARS-CoV-2 together with specific identification for SARS-CoV-2 variants, would be valuable.
Here, we present a MS-based methodology for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 in clinical specimens that enables universal detection, independent of genetic mutations, alongside with variant-specific identification. The universal detection of all SARS-CoV-2 variants is based on markers common to all variants, while the identification of the specific variant relies on variant-specific markers. Determining a specific set of markers for a given variant combines a multistep procedure starting with a search for in-silico derived variant tryptic peptides originating from viral proteins, followed by tryptic digest of a cell-cultured SARS-CoV-2 variant and HR-LC-MS/MS analysis of variant unique peptides. This methodology can be further implemented for future SARS-CoV-2 variants or other emerging pathogens.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
All solvents and chemicals used in LC-MS/MS analysis were of LC-MS grade. Acetonitrile (Cat. Number 120410100), water (Cat. Number 232141B1) and formic acid (99% purity, Cat Number 691413) were purchased from Bio Lab. Ammonium bicarbonate (NH4HCO3, Cat Number A6141-500G) and Octyl-β-D-glucopyranoside (OG, Cat Number O8001-1G) were acquired from Sigma-Aldrich. Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4, Cat. Number 02-023-1A) and sequencing grade modified trypsin (Cat. Number V5111) were purchased from Biological Industries.
2.2. Cell lines and viruses
African green monkey kidney clone E6 cells (Vero E6, ATCC® CRL-1586™) were grown in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) containing 10% Fetal bovine serum (FBS), MEM nonessential amino acids (NEAA), 2 mM L-Glutamine, 100 Units/mL penicillin, 0.1 mg/mL streptomycin, 12.5 Units/mL Nystatin (P/S/N) (Biological Industries, Israel). Calu3 cells (ATCC HTB-55) were grown in RPMI supplemented with 10% FBS, NEAA, 2 mM L-glutamine, P/S/N, and 1% Na-pyruvate. Cells were cultured at 37°C, in a 5% CO2 in 95% humidity.
SARS-CoV-2 wild-type strain (GISAID accession EPI_ISL_406862) was propagated (four passages) in Vero E6 cells. SARS-CoV-2 variants were provided by the Central Virology Lab of the Israel Ministry of Health [
17]. Alpha (B.1.1.7, GISAID accession EPI_ISL_4169857) was passaged once in Vero E6, followed by two passages in Calu3 cells. Beta (B.1.351, GISAID accession EPI_ISL_4169885), Gamma (P.1, GISAID accession EPI_ISL_4169886), and Delta (B.1.617.2, GISAID accession EPI_ISL_4169986) variants were propagated in Vero E6 cells. All virus handling and work were conducted in a BSL3 facility in accordance with the biosafety guidelines of the Israel Institute for Biological Research (IIBR). All virus stocks were tittered on Vero E6 cells as previously described [
10].
2.3. Tryptic digestion
Tryptic digestion was conducted as previously described [10, 11]. In brief, a total volume of 100 µL samples (SARS-CoV-2 buffer spiked viruses) were heated for denaturation (95°C, 10 minutes) in the presence of 0.2% Octyl β Glucopyranoside (OG). After 2 minutes cooling, 2 µL of sequencing grade modified trypsin (0.5 μg/µL) were added (final concentration 1 μg/100 µL) to the sample tubes, followed by 2 hours incubation at 50°C with continuous rotating (600 RPM). The tryptic digestion was stopped by adding 10 µL of 10% formic acid (final concentration 1%), followed by 2 minutes centrifugation (14,000 rpm). The resulting supernatants were transferred to LC-MS analysis vials.
2.4. High-resolution LC–MS/MS (Orbitrap)
LC-MS analysis was performed on an Agilent 1290 HPLC (Agilent Technologies, Palo Alto, CA, USA) coupled to Q-exactive plus Orbitrap MS/MS instrument (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) equipped with a heated electrospray ionization source operated in positive mode. This high-resolution MS system enables the identification of SARS-CoV-2 proteins derived from genetic variants tryptic peptides according to their accurate mass and sequence determination using Full MS DIA acquisition mode. Chromatographic separations were performed on a 1.7 µm UPLC C18 column (150 x 2.1mm, 1.7 µm) kept at 40℃., based on charged surface hybrid (CSH) technology, applying water/acetonitrile acidic (1% formic acid) gradient and 10-minute cycle time. Mobile phases were 1% formic acid in H2O (A) and 1% formic acid in ACN:H2O (4:1 v/v, B). The gradient profile was 100% A held for 0.3 min, linearly decreased to 75% A over 4 min, held for 0.5 min, then decreased to 0% A over 2.5 min, held for 1 min, then increased to 100% A over 0.1 min and held for another 1.9 min, for a total run time of 10 min. The flow rate was 0.4 mL/min and the injection volume was 10 µL. The operating parameters were as follows: electrospray voltage, 1.25 kV; sheath gas flow rate, 45 (arbitrary units); auxiliary gas, 10 (arbitrary units); sweep gas, 2 (arbitrary units); auxiliary gas heater temperature, 400°C; S-lens RF level, 55 and capillary temperature, 275°C. The MS spectra were acquired with 140,000 mass resolution (at 200 m/z) from m/z 250-2000, Automatic gain control (AGC) target of 3x106, and maximum injection time (IT) of 100ms. The MS/MS spectra were acquired using tryptic peptides inclusion list, 35,000 mass resolution (at 200 m/z), an isolation window of 1 m/z and AGC target of 2x105. The collision gas was nitrogen, and the collision energy was set at 20V.
2.5. Bioinformatic analysis
The list of mutations in the Alpha, Beta, Gamma and Delta variants with regard to the SARS-CoV-2 reference sequence (Wuhan, accession # NC_045512.2) was generated from variant-call analysis of the in-house whole genome sequencing conducted in the past and submitted to the GISAID depository (GISAID identifiers as follows: Alpha variant: EPI_ISL_416985, Beta variant: EPI_ISL_41669885, Gamma variant: EPI_ISL_4169886, Delta variant: EPI_ISL_4169986). The mutations detected were all in accordance with the documented list of mutations available at the time of the research (Alpha strain [
18], Beta strain [
19], Gamma strain [
20], Delta strain-
www.outbreak.info.com). The list of mutations in each of the four variants, as mapped from the in-house genomic sequencing, is provided in Table S1. Prediction of potential trypsin cleavage sites was conducted with PeptideCutter (
www.web.expasy.org/peptide_cutter). The generated peptides were subjected to sequence similarity searches against the nr (non-redundant,
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) database using Blast [
21]. The algorithm parameters were adjusted to short sequences, and self-hits were eliminated.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Methodology for SARS-CoV-2 variants specific diagnosis
Recently we have published an assay for COVID-19 diagnosis, based on identification of six unique and specific peptide markers, derived from the SARS-CoV-2 spike and nucleocapsid proteins [10, 11]. The sequence conservation of these markers, among different known strains of SARS-CoV-2 was of major concern, considering the accumulating knowledge of mutations occurring during the spread of the virus. Therefore, a main parameter in the selection of these markers, was their universality (identical sequence in >99.8% of known strains). However, for discriminative identification of SARS-CoV-2 VOCs, the identification of unique variant markers is required. Nucleotide polymorphisms resulting in genetic variant peptides is characterized by specific amino acids substitutions, which determine variants marker unique sequences. Our new methodology for developing a variant-specific diagnosis method is schematically shown in
Figure 1. Defining a specific set of markers for a given variant combines a multistep procedure starting with in-silico identification of trypsin-digested peptides originating from viral proteins, followed by tryptic digest of a cell-cultured SARS-CoV-2 variant and HR-LC-MS/MS analysis for peptides identification and variant markers panel determination. The final method is an expanding analytical method for identification of SARS-CoV-2 variants, which is based on a fixed panel of markers common to all variants and on a flexible set of variant-specific markers which is updated for newly discovered variants. Given a known variant, the universal markers shared by all variant strains and those specific to that variant will be identified in the specimen. For a new emerging variant strain, only the markers common to all variants will be detected in the sample. Knowing the sequence of a new variant and using our methodology for developing MS-based diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 variants, will enable adding a set of variant-specific markers to the expanding analytical method.
3.2. In-silico mapping of potential variant-specific markers
Aiming to evaluate peptides that may provide a diagnostic tool for variant identification using MS, we first conducted an in-silico tryptic digestion analysis of the viral proteins containing mutations with respect to the Wuhan reference strain (Table S1). This analysis was conducted for four representative VOCs- Alpha, Beta, Gamma and Delta. Each peptide generated by the in silico tryptic digest and containing a mutation with respect to its orthologous sequence in the Wuhan reference sequence, was considered as a potential candidate. Only peptides longer than 5 amino acids were considered, to minimalized cross with unrelated, not SARS-CoV-2 proteins, a cross which may lead to false positive results. To avoid adsorption to the chromatographic system, which may cause poor reproducibility and carry over between injections, we focused on peptides that were shorter than 24 amino acids. The in-silico analysis resulted in a total of 37 potential peptide markers (6, 6, 13 and 12 for the Alpha, Beta, Gamma and Delta variants, respectively) (Table S2), of which almost half derived from the highly abundant spike protein. To further assess their specificity with respect to other human pathogens, the peptides were subjected to a sequence similarity search against the comprehensive NCBI non-redundant (nr) database, revealing 28 unique peptides, and 9 additional peptides which share an ortholog with a non-relevant human clinical organism (Table S2).
3.3. Identification of unique markers in cell-cultured VOCs using HR-LC-MS/MS analysis
To evaluate the actual ability to identify the predicted variant-specific markers and their formation in real life samples, we cultured the four variants (Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Delta) in Vero E6 cells. A rapid, simple, and efficient tryptic digestion process was performed, similar to the procedure described in our previous studies [10, 11]. Samples containing 106 PFU/mL of each cell-cultured SARS-CoV-2 variant were preheated (95 °C, 10 min) to inactivate the virus and denature viral proteins, which improved subsequent digestion efficiency. The samples were then trypsin-digested (in triplicates, 120 min 50 ºC) followed by analysis using LC-coupled to a high-resolution MS/MS.
The analytical method described recently [10, 11] was used for the identification of SARS-CoV-2 variants peptides markers. First, the existence of the six universal markers, which are characterized by their universality, was proven to be common to all SARS-CoV-2 variants. To characterize a unique set of markers for each variant (Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Delta), the potential markers were searched according to the m/z of multiple charged ions which were calculated for the in-silico predicted tryptic peptides (Table S2). For each variant, at least two unique markers, derived mainly from S and N viral proteins, were identified using LC-MS/MS analysis, according to accurate mass and fragmentation pattern, which indicate on amino acid sequences (Table 1). These markers appeared in all replicates for each variant. The characteristic markers of each variant were not found in any of the other variants, ascertaining their uniqueness to the variant strain.
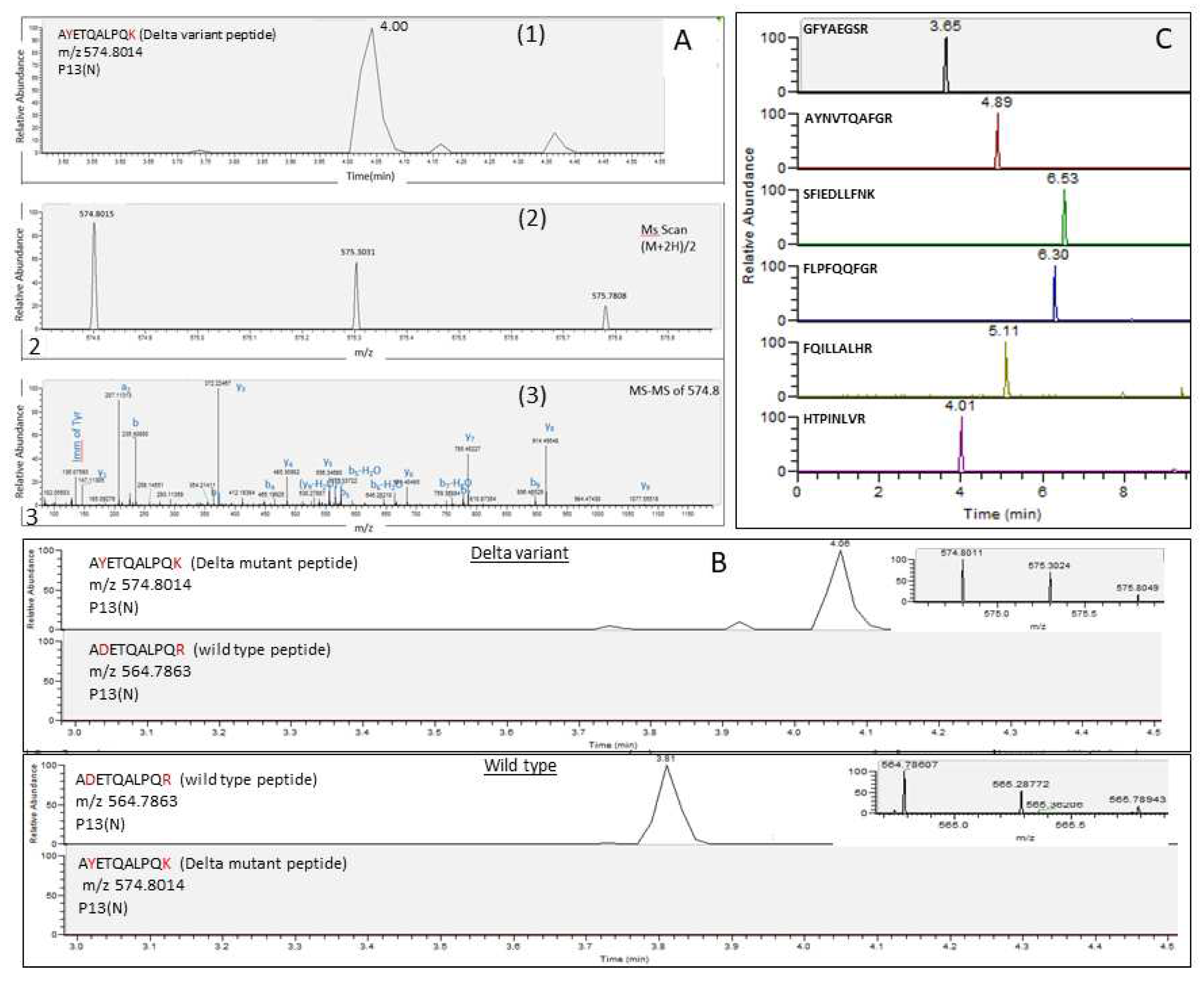
Figure 2 demonstrates the analysis of cell-cultured SARS-CoV-2 variants after tryptic digestion. A representative unique marker of the Delta variant, A
YETQALPQ
K, in which the amino acids Y and K represent mutations of D and R, respectively (A
DETQALPQ
R), was eluted at 4 min owing double charged ion (M+2H)/2, at m/z 574.8014 and typical fragmentation spectrum (
Figure 2A). This marker was not detected in wild-type Wuhan reference strain and all the other VOCs (
Figure 2B). In concordance with these findings, the corresponding wild-type peptide, A
DETQALPQ
R, was detected in all other variants but not in the Delta variant (
Figure 2B). The six SARS-CoV-2 universal markers, which were selected to be common to all variants due to their high sequence conservation, were indeed found in the Delta variant as well as in all the other analyzed variants (
Figure 2C).
3.4. Discussion and Conclusions
In the study presented here, we suggest an expanded method to monitor and specifically identify SARS-CoV-2 variants. This method combines the analysis of SARS-CoV-2 universal markers characterized by relatively high sequence conservation, therefore high likelihood to be shared by all variants, together with specific markers for each variant. This novel approach for discriminative identification, based on mass spectrometry analysis, is presented and demonstrated for four representative SARS-CoV-2 VOCs (Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Delta). This methodology is based on a multistep procedure starting with prediction of in-silico derived tryptic digested peptides originating from viral proteins, followed by actual tryptic digest of a cell-cultured SARS-CoV-2 variant and HR-LC-MS/MS analysis for variant markers panel determination. The proposed methodology necessitates preliminary knowledge of the variant sequence but may preclude the subsequent time-consuming and relatively expensive further sequencing of samples for diagnostic purposes. This procedure, compared to genetic sequencing, is rapid (few hours), easy to perform and provides an inexpensive specific diagnosis method for SARS-CoV-2 variants. The methodology demonstrated in this study, as a proof of concept, may be adjusted and implemented for the diagnosis of other SARS-CoV-2 variants or for a variety of pathogens as well.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.F, A.Z and O.S; methodology, L.F, A.Z and O.S; formal analysis, L.F; investigation, L.F, Y.Y.R and O.S; resources, Y.Y.R; software, A.Z; writing—original draft preparation, L.F, A.Z and O.S; writing—review and editing, L.F, A.Z, Y.Y.R and O.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Israel Institute for Biological Research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Otto, S.P. , et al., The origins and potential future of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern in the evolving COVID-19 pandemic. Curr Biol, 2021. 31(14): p. R918-r929.
- Chakraborty, D., A. Agrawal, and S. Maiti, Rapid identification and tracking of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. The Lancet, 2021. 397(10282): p. 1346-1347.
- Mann, C., J. H. Griffin, and K.M. Downard, Detection and evolution of SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus variants of concern with mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2021. 413(29): p. 7241-7249.
- Tahamtan, A. and A. Ardebili, Real-time RT-PCR in COVID-19 detection: issues affecting the results. Expert Rev Mol Diagn, 2020. 20(5): p. 453-454.
- Tahan, S. , et al., SARS-CoV-2 E Gene Variant Alters Analytical Sensitivity Characteristics of Viral Detection Using a Commercial Reverse Transcription-PCR Assay. J Clin Microbiol, 2021. 59(7): p. e0007521.
- Vogels, C.B.F. , et al., Multiplex qPCR discriminates variants of concern to enhance global surveillance of SARS-CoV-2. PLoS Biol, 2021. 19(5): p. e3001236.
- Gouveia, D. , et al., Shortlisting SARS-CoV-2 Peptides for Targeted Studies from Experimental Data-Dependent Acquisition Tandem Mass Spectrometry Data. Proteomics, 2020. 20(14): p. e2000107.
- Gouveia, D. , et al., Proteotyping SARS-CoV-2 Virus from Nasopharyngeal Swabs: A Proof-of-Concept Focused on a 3 Min Mass Spectrometry Window. J Proteome Res, 2020. 19(11): p. 4407-4416.
- Ihling, C. , et al., Mass Spectrometric Identification of SARS-CoV-2 Proteins from Gargle Solution Samples of COVID-19 Patients. J Proteome Res, 2020. 19(11): p. 4389-4392.
- Schuster, O. , et al., Specific and Rapid SARS-CoV-2 Identification Based on LC-MS/MS Analysis. ACS Omega, 2021. 6(5): p. 3525-3534.
- Schuster, O. , et al., Coupling immuno-magnetic capture with LC-MS/MS(MRM) as a sensitive, reliable, and specific assay for SARS-CoV-2 identification from clinical samples. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2022. 414(5): p. 1949-1962.
- Frampton, D. , et al., Genomic characteristics and clinical effect of the emergent SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7 lineage in London, UK: a whole-genome sequencing and hospital-based cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis, 2021. 21(9): p. 1246-1256.
- Umair, M. , et al., Whole-genome sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 reveals the detection of G614 variant in Pakistan. PLoS One, 2021. 16(3): p. e0248371.
- Maus, A. , et al., Targeted Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Sequence Variants by Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Tryptic Peptides. J Proteome Res, 2022. 21(1): p. 142-150.
- Starr, T.N. , et al., Shifting mutational constraints in the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain during viral evolution. Science, 2022. 377(6604): p. 420-424.
- Suddhapas, K. , et al., Evaluation of Variant-Specific Peptides for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern. J Proteome Res, 2022. 21(10): p. 2443-2452.
- Lustig, Y. , et al., Neutralising capacity against Delta (B.1.617.2) and other variants of concern following Comirnaty (BNT162b2, BioNTech/Pfizer) vaccination in health care workers, Israel. Euro Surveill, 2021. 26(26).
- Rambaut, A. , Loman, N., Pybus, O., Barclay, W., Barrett, J., Carabelli, A., Connor, T., Peacock, T., Robertson, D.L., and Volz, E., Preliminary genomic characterisation of an emergent SARS-CoV-2 lineage in the UK defined by a novel set of spike mutations. Virological.org Written on behalf of COVID-19 Genomics Consortium UK, 2020.
- Tegally, H. , et al., Detection of a SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern in South Africa. Nature, 2021. 592(7854): p. 438-443.
- Faria, N.R. , et al., Genomics and epidemiology of the P.1 SARS-CoV-2 lineage in Manaus, Brazil. Science, 2021. 372(6544): p. 815-821.
- Altschul, S.F. , et al., Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol, 1990. 215(3): p. 403-10.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).