1. Introduction
Milk is a wholesome food and represents an important constituent of the human diet (especially for infants, schoolchildren and the elderly) as it contains nutrients that are essential for growth, bone development, immune function and other important physiological functions [
1,
2]. Milk is considered the most diverse natural food product in composition. In addition to being a good source of protein, fat and carbohydrate, milk is an ideal source of macro and microelements such as calcium (Ca), potassium (K), phosphorous (P), magnesium (Mg), zinc (Zn), iron (Fe), copper (Cu), manganese (Mn) and selenium (Se). However, milk also can contain toxic elements, the most important of which is lead (Pb), which is known to have deleterious effects on the developing nervous system of children [
2,
3]. Milk can also be contaminated by other toxic metals such as cadmium (Cd), mercury (Hg), arsenic (As) and nickel (Ni) and even by high concentrations of essential elements (such as Co, Cr, Cu, Fe and Zn) [
4,
5].
The composition of milk is greatly influenced by the nutritional status of the cow, as well as the stage of lactation, management, productive stage, genetics and breed [
6]. Moreover, the essential trace element profile of milk, particularly toxic element residues, are largely affected by the environment where the cows are raised [
3,
5,
7]. Heavy metals mainly enter cow’s milk through cattle feed and drinking water (as well as via the atmosphere). The feed and water can, in turn, be contaminated through the soil via sewage sludge used as fertilizer, artificial fertilizers, metals used in fungicidal agents and other agricultural chemicals, and also via wastewater from various industries. The risk of milk becoming contaminated is particularly high in areas affected by anthropogenic pollution, such as smelting or mining areas and highly industrialized regions, allowing the transfer of metal contamination to the atmosphere, soil, water, animal feed, animals and their products, and finally to humans [
2,
3,
5,
8,
9,
10]. In the case of Pb, milk can become contaminated when cows graze and drink water at roadsides. In addition, factors related to the manufacturing practices (particularly hygiene during milking) and possible contamination from the equipment during processing [
4,
5] can also increase the concentration of this toxic element in milk. In recent years, contamination of milk by toxic elements (particularly Pb) has been indicated to be one of the most serious aspects of environmental pollution for human health, because milk is widely consumed, especially by children [
3]. Numerous studies have therefore been conducted in order to monitor the presence of toxic elements in milk and related products (see
Table 2 for a review), particularly in developing countries where information from national monitoring programmes is scarce and legislation aimed at environmental protection is sometimes less restrictive than in other more developed countries.
The concentrations of metals in milk sometimes exceed the maximum limits recommended. According to the European Commission [
11] and Codex Alimentarius Commission the maximum limit for Pb is 0.020 mg/l, but the Brazilian legislation (Decree nº. 55871/65) [
12] establishes a higher limit, of 0.05 mg/l. Previous studies carried out in different states of Brazil indicated that Pb concentrations in milk exceeded the maximum limits [
13,
14,
15]. However, at present there are no data on the concentrations of toxic and trace elements in cow’s milk produced in the semi-arid region of Pernambuco. Study of the transfer of Pb to the rock-soil-plant-milk systems is essential in view of the high natural levels of Pb in the rock and soil in this region [
16,
17,
18]. The dairy basin in the state of Pernambuco plays an important role in the local economy and in supplying milk, since it is an important producing area, where milk is treated industrially and is also sold at fairs and local markets [
17]. The rearing system in most of the properties in the region is extensive or semi-intensive, and some of the Pb ingested by cows via consumption of contaminated forage could be transferred to the milk [
16,
17,
18].
The main objective of the present study was to provide information about the levels of toxic (Cd and Pb) and essential (Cu, Fe and Zn) elements in cow’s milk produced in the State of Pernambuco and to determine the main factors influencing the concentrations of these elements (e.g. proximity to road, presence of effluents, and the milking method) to evaluate whether the consumption of cow’s milk produced in the region can be considered a public health risk.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
The milk samples analyzed in this study (n =142) were produced by cows raised in extensive and semi-intensive dairy farm systems in the mesoregion of Agreste de Pernambuco (Garanhuns microregion). The samples were collected between September and December 2018. The distance between each farm and local, state and/or federal roads was determined. The proximity of the farms to major roads was considered close when the distance was less than 3 km and distant otherwise. Regarding effluents, the influence of hydrographic features (large and small rivers, as well as springs and other sources such as wells and dams) on the farms and access to these sources by the cows was taken into account. The milking method was classified as manual (performed manually by a responsible worker) or automatic (carried out by means of milking machinery). Raw milk samples (15 ml each) were obtained from cows in the early lactation stage (11 to 100 days postpartum). The first 3 jets of milk were discarded and the next 15 ml was collected. Samples were stored at 4 °C in 15 ml sterile plastic containers with a lid (Falcon®) and sent to the Clinical Pathology Laboratory of the Garanhuns Cattle Clinic (UFRPE), where they were then stored at -20 °C until analysis.
Figure 1.
Municipality of Garanhuns and milk production in the Pernambuco dairy basin.
Figure 1.
Municipality of Garanhuns and milk production in the Pernambuco dairy basin.
2.2. Reagents and Standard Solutions
All solutions were prepared using ultrapure water of resistance 18 MΩ cm 1 produced by a Milli-Q purification system (Millipore Corp., Bedford, MA). Stock standard solutions of the elements (1000 mg/L) were of ultrapure grade (ICP Multi element standard solution IV certiPUR). Nitric acid (69%) was obtained from Merck (Poole, UK).
2.3. Sample Analysis
Samples were subjected to acid digestion before analysis. The microwave-assisted digestion procedure was carried out at the Research Support Center (CENAPESQ) of the Federal Rural University of Pernambuco (UFRPE). Briefly, each sample of raw bovine milk (5 ml) was placed in a glass flask with 10 ml of HNO3 and digested in a microwave oven (model MarsXpress-CEM Technology Inside) for 28 minutes (step 1: 110 °C for 8 min, step 2: 170 °C during 10 min, and step 3: 170 °C for 10 min.) Digested samples were filtered through pyramid-folded filter paper (weight 80g m 2, filtration rate 20-25 seconds) into a new sterile Falcon® container.
The concentrations of Cd, Pb, Cu, Fe and Zn were determined by atomic emission spectrometry with inductively coupled plasma (ICP-OES) (Optima 7000 DV) in the Soil Chemistry Laboratory (DEPA) (UFRPE). All samples were analyzed in duplicate, and the concentrations were expressed in mg/L.
An analytical quality control programme was applied throughout the study. Blank samples were run alongside the test samples and the values thus obtained were subtracted from the sample readings. The limits of detection (LOD) in the acid digest were calculated as three times the standard deviation of the reagent blanks: 0.012 (Cd), 0.036 (Pb), 0.14 (Cu), 0.85 (Fe) and 0.93 (Zn) µg/L. The elemental concentrations of all samples analyzed were above the respective LODs. To check the accuracy of the analytical method, multi-element standard solutions were used for calibration and run with the samples. The precision of the method was expressed as the analytical recovery, which in all cases was within an acceptable range (90 to 110%), with a relative standard deviation (RSD) <10%.
2.4. Statistical and Chemometric Analysis
An X142x5 matrix was used to analyze the data, with the rows corresponding to the 142 milk samples and the columns to the contents of the 5 toxic and essential metals determined by ICP-OES. Other information regarding the factors evaluated (proximity to main roads, presence of effluents and milking system) were also included as qualitative variables in the data matrix. The data distribution was checked using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test; as the data were not normally distributed, they were log-transformed before analysis and presented as geometric means. A general linear model (GLM) was used to evaluate the effect of the proximity of the farm to main roads (0: no; 1: yes); the presence of effluents (0: no; 1: yes); and milking method (0: automatic, 1: manual) and their interactions on the toxic and essential trace element concentrations in milk. The statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS for Windows v.24 (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA) and test results were considered statistically significant at P<0.05.
In addition, two unsupervised chemometric techniques, principal component analysis (PCA) and hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) were used to reveal the latent structures residing in the data set and to evaluate the relationship between samples and variables. PCA was used to display the information contained in the data in a reduced dimension with minimum loss of data variance, and HCA (an unsupervised display chemometric technique, often used to complement PCA) was used to establish clusters of samples (and variables) based on the distance measures between them in the 5-multidimensional space [
19]. All chemometric techniques were carried out using Statgraphics Centurion XVI v.16.1.15 (Statistical Graphics Corporation, Rockville, MD, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Toxic and Essential Trace Element Concentrations in Milk
The toxic and essential trace element concentrations determined in the milk samples are presented in
Table 1. The concentrations of these elements determined in other studies around the world are shown in
Table 2 for comparative purposes.
The mean Cd and Pb concentrations determined in the present study were 0.007 and 0.043 mg/L respectively. The mean Cd concentrations were low and similar to those reported in other studies in unpolluted areas (generally below 0.010 mg/L) and much lower than those reported in previous studies in Brazil [
14,
20] and in polluted areas of developing countries in Asia, Africa and South America (see
Table 2). However, the concentrations of Pb are higher than reported in other recent studies conducted in relatively unpolluted areas from Europe or North America (see
Table 2), but lower than reported in previous studies in Brazil [
13,
14,
15,
20,
21]. The Pb concentrations determined in the present study are similar to those determined in some polluted regions of Iran [
8] and Peru [
22], but much lower than reported in other polluted areas in Asia or Africa (see
Table 2).
Considering the applicable legislation, the Pb content of 29.6% of the samples (42/142) was above the limit permitted under Brazilian law (Decree n. 55871/65), which is 0.05 mg/L [
12], and that of 97% of the samples (138/142) exceeded the limit established in the European Union [
11] and Codex Alimentarius Commission and the WHO, i.e. 0.020 mg/L. By contrast, the Cd content of all samples was lower than 0.02 mg/L, the limit established by Brazilian law [
12].
Previous studies conducted in Brasilia [
23], Paraná [
14] and Sao Luis [
15] also reported Pb concentrations higher than the maximum limit. The Pb and Cd contents of milk depend on the proximity of polluted areas, crowded roads, level of industrialization (see
Table 2) and also are influenced by the control and legislation limits [
3]. The concentrations determined in Western and Central Europe, USA and Canada are below levels considered to represent a risk, unlike in Brazil, Mexico, Peru, some parts of Asia or Africa and polluted areas of Eastern Europe [
3,
24]. Recent studies have reported Pb and Cd concentrations in milk higher than respectively 60 and 12 mg/kg, in some parts of India [
3], Pb concentrations in milk exceeding 13 mg/kg in Indonesia [
25].
Considering the trace elements, the mean concentrations of Cu (0.020 mg/L), Fe (0.055 mg/L) and Zn (0.621 mg/L) were generally lower than reported in other studies (see
Table 2) and can be considered within the deficient range for cow milk according to Puls [
26] (deficient ranges are Cu: 0.010-0.020; Fe: <0.2 and Zn: <0.5 mg/L; adequate ranges are Cu: 0.05-0.6; Fe: 0.2-0.63 and Zn: 2.3-4 mg/L). These results indicate that milk produced in this region is not a good source of trace elements for the local population. The mean levels of Cu and Fe in raw cow’s milk samples across the world ranged from 0.0136-36 mg/L and from 0.33-16.4 mg/L, respectively [
3]. The presence of heavy metals such as Pb and Cd is associated with changes in the trace mineral profile of milk and negatively affects the nutritional quality of the product, e.g. reducing the Fe content [
2]. Trace element deficiencies in livestock are prevalent in different regions of Brazil [
27], especially in several semi-arid climate areas. During the dry season, the pastures are generally overgrazed, leading to mineral deficiencies in the herds [
16].
Table 2.
Toxic and essential trace element concentrations (in mg/L) in cow’s milk determined in previous studies. Values are arithmetic meansm expressed in mg/kg or mg/l wet weight.
Table 2.
Toxic and essential trace element concentrations (in mg/L) in cow’s milk determined in previous studies. Values are arithmetic meansm expressed in mg/kg or mg/l wet weight.
| Country |
Region |
Cd |
Pb |
Cu |
Fe |
Zn |
Reference |
| Algeria |
Guelma area. Polluted area |
0.03 |
0.94 |
0.14 |
0.76 |
4.02 |
[28] |
| Algeria |
Polluted area |
0.030 |
|
0.239 |
1.43 |
5.98 |
[29] |
| Argentina |
Rural areas Southeast of Córdoba |
|
0.0023 |
0.0380 |
0.855 |
1.800 |
[30] |
| Bangladesh |
Dairy Farms |
0.024 |
0.015 |
0.064 |
0.333 |
|
[31] |
| Small household |
0.047 |
0.012 |
0.127 |
0.631 |
|
| Brazil |
Paraná state. Pasteurized |
0.018 |
0.281 |
|
|
|
[14] |
| Paraná state. In Natura |
0.031 |
0.181 |
|
|
|
| Brazil |
State of Goiás (supermarkets) |
0.05 |
0.24 |
0.49 |
0.96 |
3.73 |
[20] |
| Brazil |
Industrial area |
0.002 |
ND |
0.063 |
|
3.87 |
[32] |
| Non-industrial area |
0.003 |
0.003 |
0.068 |
|
3.15 |
| Brazil |
Vale of Paraíba region |
|
0.23 |
1.73 |
1.05 |
4.59 |
[13] |
| China |
Industrial |
0.00015 |
0.00286 |
|
|
|
[33] |
| Unpolluted |
0.00013 |
0.00232 |
|
|
|
| China |
Samples from Shandong and Shaanxi cities |
0.00007 |
0.0014 |
0.0324 |
0.352 |
3.234 |
[34] |
| China |
Ten main milk producing areas in China |
0.00005 |
0.00175 |
|
|
|
[35] |
| Croatia |
Four unpolluted areas |
ND |
ND-0.0071 |
0.06 0.07 |
0.26-0.30 |
3.7-4.8 |
[36] |
| Egypt |
Beni-Suef governorate |
0.051 |
0.214 |
0.0953 |
8.994 |
6.29 |
[37] |
| England |
Southern England. Conventional farmland |
|
|
0.0606 |
2.03 |
5.00 |
[38] |
| Southern England. Organic farmland |
|
|
0.0524 |
0.66 |
4.51 |
| Ethiopia |
Kosoye Amba-Rass, Tana-Abo and Nara-Awdarda, North Gondar, Amhara Regional State |
0.29 |
0.15 |
1.12 |
|
3.02 |
[39] |
| Hungary |
Highway-area |
0.005 |
0.025 |
0.336 |
0.797 |
1.494 |
[40] |
| Non-polluted |
ND |
0.012 |
0.137 |
0.788 |
2.241 |
| India |
Mining areas |
|
0.09-0.13 |
0.31-0.51 |
8.8-11.4 |
1.22-1.04 |
[41] |
| India |
Ladakh, a trans-Himalayan high altitude region |
0.007-0.009 |
0.005-0.006 |
0.23-0.30 |
3.55-4.91 |
1.99-3.76 |
[42] |
| India |
Industrial areas |
0.02-0.07 |
0.05-0.20 |
0.07-0.35 |
|
1.22-20.94 |
[43] |
| India |
Industrial area |
0.096 |
0.480 |
0.090 |
3.97 |
6.09 |
[2] |
| Non-industrial area |
0.033 |
0.250 |
0.101 |
5.10 |
3.95 |
| Indonesia |
City area, Padang |
ND |
13.6-20.6 |
1.17-2.17 |
|
28.8-53.1 |
[25] |
| Iran |
Farms close to petroleum industries |
0.0047 |
0.047 |
|
|
|
[8] |
| Iran |
Arak city |
0.00395 |
0.0125 |
|
|
|
[44] |
| Iran |
Industrial regions of Iran |
0.00111 |
0.0140 |
0.427 |
|
0.571 |
[45] |
| Iran |
Lorestan province |
0.10 |
2.72 |
0.14 |
|
3.07 |
[46] |
| Italy |
Industrial area |
ND |
0.02 |
0.07-0.08 |
14.5-16.8 |
2.21-2.86 |
[47] |
| Italy |
Calabria |
0.0002 |
0.001 |
0.003 |
|
2.02 |
[1] |
| Kazakhstan |
Almaty region. Unpolluted |
0.0027 |
0.0045 |
|
|
|
[48] |
| Korea |
Supermarkets |
0.00238 |
0.00335 |
0.3834 |
|
4.754 |
[49] |
| Kosovo |
Rural areas |
0.001 |
0.0017 |
0.018 |
0.426 |
3.151 |
[50] |
| Mexico |
Areas irrigated with wastewater |
|
0.03 |
0.01 |
|
0.71 |
[9] |
| Mexico |
Puebla, industrial wastewater |
0.002 |
0.024 |
0.030 |
|
|
[51] |
| Moscow |
Moscow region |
0.004-0.011 |
0.075-0.110 |
0.11-0.21 |
0.55-0.82 |
1.21-141 |
[52] |
| Pakistan |
Sargodha. Near traffic road |
0.04–0.3 |
0.3–0.8 |
|
|
|
[53] |
| Peru |
Near metallurgical complex |
0.020 |
0.058 |
|
|
|
[22] |
| Peru |
Mining-metallurgical industries |
0.018 |
0.577 |
|
|
|
[10] |
| Poland |
Lubuskie Province Organic farms |
0.0035-0.0040 |
0.037-0.041 |
0.038-0.045 |
0.198-0.258 |
3.02-3.28 |
[54] |
| Poland |
Low-level industrialization |
<0.004 |
0.012 |
0.360 |
|
4.83 |
[55] |
| High-level industrialization |
<0.004 |
0.234 |
1.33 |
|
15.84 |
| Romania |
Intermediate-level industrial |
0.0039 |
0.120 |
2.4 |
|
4.8 |
[56] |
| Intensive industrial |
0.007 |
0.577 |
0.837 |
|
4.8 |
| Small cattle farms |
0.007 |
0.024 |
0.265 |
|
3.18 |
| Romania |
No industry |
0.006 |
0.066 |
0.30 |
|
2.5 |
[57] |
| Serbia |
Novi Sad (Vojvodina) market |
0.00349 |
0.0754 |
0.118 |
|
|
[58] |
| Spain |
Organic farms |
0.000135 |
0.000653 |
0.041 |
0.425 |
3.326 |
[59] |
| Conventional farms |
0.000098 |
0.000516 |
0.051 |
0.395 |
3.639 |
| Conventional (supermarket) |
0.000087 |
0.000267 |
0.069 |
0.351 |
3.933 |
| Spain |
Unpolluted region. Organic |
ND |
0.000519 |
0.039 |
0.271 |
2.851 |
[7] |
| Unpolluted region. Conventional |
ND |
0.000389 |
0.048 |
0.301 |
3.368 |
| Spain |
Farms near mining and industrial area and highway traffic |
<0.002 |
0.004 |
|
|
|
[60] |
| Sri Lanka |
Four agro-climatic zones |
0.001–0.002 |
0.005–0.02 |
0.02–0.12 |
0.49–3.15 |
1.49-2.93 |
[61] |
| Turkey |
Local markets in the city of Edirne |
|
|
0.138 |
3.1 |
3.4 |
[62] |
| Turkey |
Iğdır City |
0.0001-0.004 |
0.050 |
0.08-1.80 |
|
2.21-32.5 |
[63] |
| Turkey |
Close to highways |
0.39 |
1.85 |
0.62 |
4.2 |
1.85 |
[64] |
| Zambia |
Farms near mining area |
|
0.002 |
|
|
|
[65] |
3.2. Effects of Proximity to Main Roads, Presence of Effluents and Milking Method on Toxic and Trace Element Concentrations in Milk
A general linear model was applied to the data in order to evaluate the effect of factors that potentially influence the toxic and trace element concentrations in milk samples (proximity of the farm to major roads, presence of effluents in the vicinity of farm and the milking method) The results are presented in
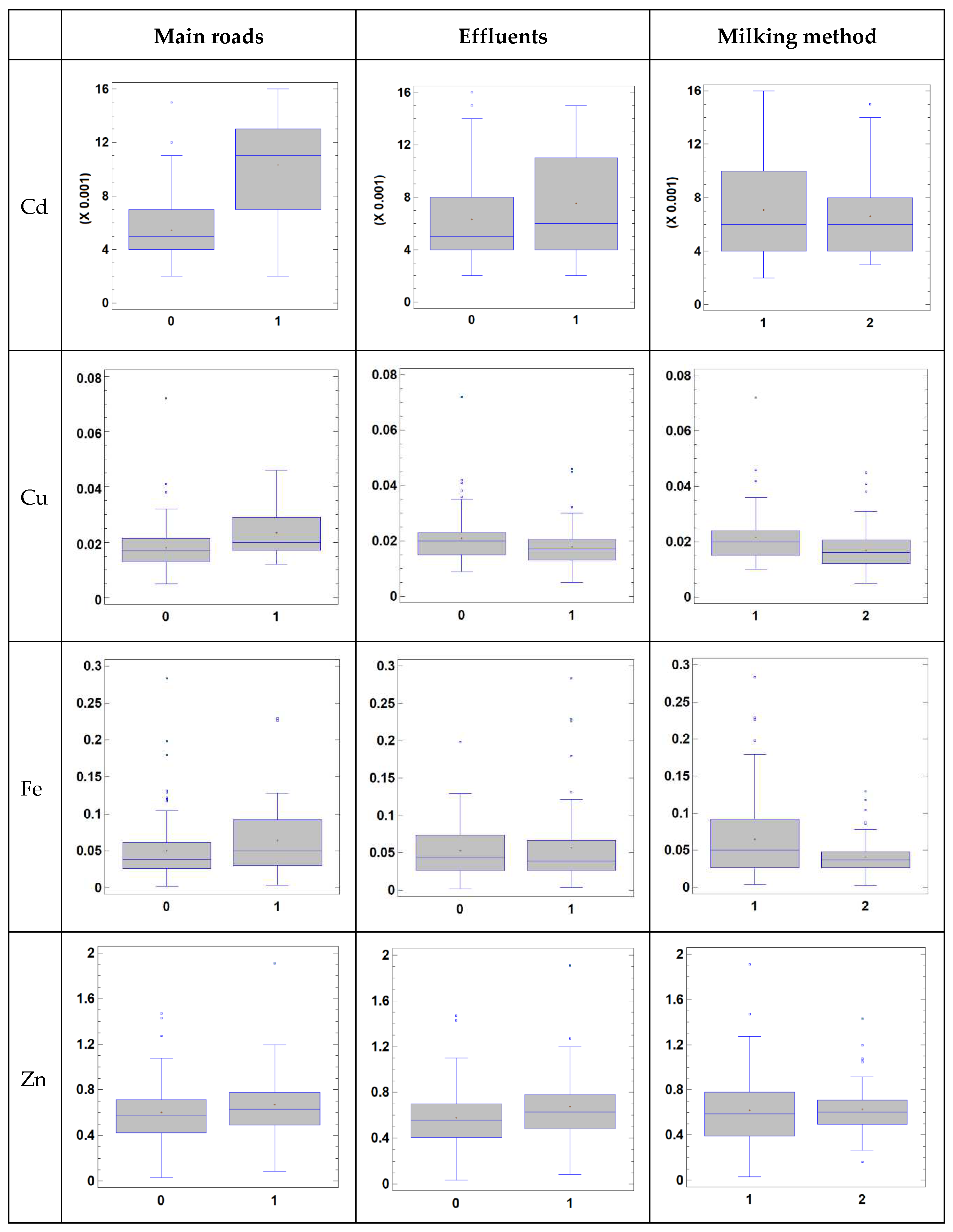
Table 3, and it can be seen proximity to major roads (R) had a significant influence on the concentrations of Pb, Cd, and Cu in the milk samples. The presence of effluents in the vicinity of farm (E) only influenced the Cu concentration, while the milking method (M) did not influence the metallic profile of the samples.
The proximity of the farm to major roads was the most important factor in the analysis, exerting a significant effect on the Pb, Cd and Cu concentrations in milk, which were 90, 94 and 32 % higher in the milk samples from farms close to major roads than in milk samples from farms distant from major roads (
Figure 1). The influence of the proximity to major roads on toxic element accumulation in milk, blood, water, soils, forage and other food products is well known [
40,
53,
66]. Kodrik et al. [
40] reported significantly higher levels of Cd (0.005 vs. ND mg/L), Pb (0.025 vs. 0.012 mg/L) and Cu (0.336 vs. 0.137 mg/L) in cow’s milk originating from traffic-intensive areas in Hungary, whereas Fe concentrations (0.797 vs. 0.788 mg/L) were similar to those in milk produced in unpolluted green areas and the Zn concentrations were lower in the former than in the latter (1.494 vs. 2.241 mg/L). Tahir et al. [
53]reported high levels of Cd (0.04-0.3 mg/L) and Pb (0.3-0.8 mg/L) in cow’s milk in Pakistan, which were attributed to Cd- and Pb-contaminated feed, air pollution and drinking water contaminated by dust from areas close to roads. Similar results were reported by Bigucu et al. [
64] in areas of Turkey close to major roads. The levels of contamination in the milk were also higher in these studies than in the present study.
Figure 1.
Box and whiskers plot showing the effect of proximity of farms to main roads, the presence of effluents and milking method on toxic and trace element concentrations in milk (in mg/L).
Figure 1.
Box and whiskers plot showing the effect of proximity of farms to main roads, the presence of effluents and milking method on toxic and trace element concentrations in milk (in mg/L).
Leaded petrol has caused more exposure to Pb than any other source worldwide, contaminating air, dust, soil, drinking water and food crops, and it has caused harmfully high human blood Pb levels around the world, especially in children [
67]Lead persists in the environment and can bioaccumulate in bodies, with long-term effects after the initial source of Pb has disappeared [
67]. Some decades after Pb was banned in petrol, residues of this metal in milk have largely decreased, but emissions of toxic metals associated with motor vehicles are still considered among the most important sources of heavy metals in the environment, and high concentrations of heavy metals are found in soils near roads/highways [
68]. Monitoring heavy metal concentrations in roadside environments therefore remains of great importance.
The presence of effluents was also found to be a significant factor regarding the Cu of the milk, although samples from farms affected by effluents had lower Cu concentrations (23%) than samples from farms not affected by effluents. No significant interactions between the presence of effluents and proximity to roads were found, and milk samples from farms close to and distant from main roads had lower Cu contents when they were close to sources of effluents. Concentrations of Cu in milk are known to be influenced by the environment, industrialization and anthropogenic activities. A large part of the Pernambuco hydrographic basin receives industrial effluents, and the water cannot be used to supply the city, as it contains toxic elements, and the rivers in these areas are contaminated and affected by anthropogenic activities. As in the present study, Ogundiran et al. [
69]reported that the Cu content was significantly higher in milk from cows reared in an industrialized area than in milk from cows reared in unpolluted areas. These findings suggest that other factors/trace elements present in the effluents may interact negatively with the Cu metabolism in cows, leading to a significant reduction in the Cu concentration in the milk. For example, complex non-competitive negative interactions between Cu, sulphur and molybdenum and competitive interactions with Cd and Zn for the metallothionein binding sites are known to occur in ruminants [
6]Other interactions between Cu and Cd [
70,
71] and Cu and Pb [
72] have also been described in cattle. Increased levels of Cd and Pb interfere with the metabolism of the essential trace elements, in particular with metabolism of Cu, with calves at risk of Cu deficiency [
71]Such interactions are sometimes difficult to interpret as they depend on the chemical form and relative concentrations of the elements in the environment and can involve more than two elements [
2,
72].
3.3. Chemometric Analysis: PCA and HCA
Chemometric analysis can be used for detailed examination of large sets of data, enabling visualization of complex interactions between samples, variables and among samples and variables. Latent structures and relationships residing in the data matrix are commonly studied by means of two display chemometric techniques: PCA and HCA.
PCA was used for the primary evaluation of the 5-dimension data set. PCA transforms the autoscaled data matrix
X142x5 into a product of two matrices: the score matrix S145xPC, which includes information about the samples, and the loadings matrix LPCxPC, which includes information related to the variables. When the number of principal components (PC) selected is smaller than the number of original variables, PCA produces visualization of the data matrix in a reduced dimension, simplifies the original problem and enables examination of the relationships between samples and between variables through score and loadings plots, respectively [
19].
In the present study, PCA was applied to the original autoscaled data matrix, and the first two PCs were considered sufficient to represent all data. The first two principal components explained 75.38% of the total variance; the remaining PCs yielded eigenvalues <1, indicating poor information content (
Table 4).
This enabled evaluation of the whole data set by using a 2D-score (or loading) plot, where the samples (or variables) are represented in the space defined by the first two principal components. Examination of the sample scores in this plot produced some interesting results. A natural separation of the samples into two groups according to the proximity of the farms to major roads was detected (
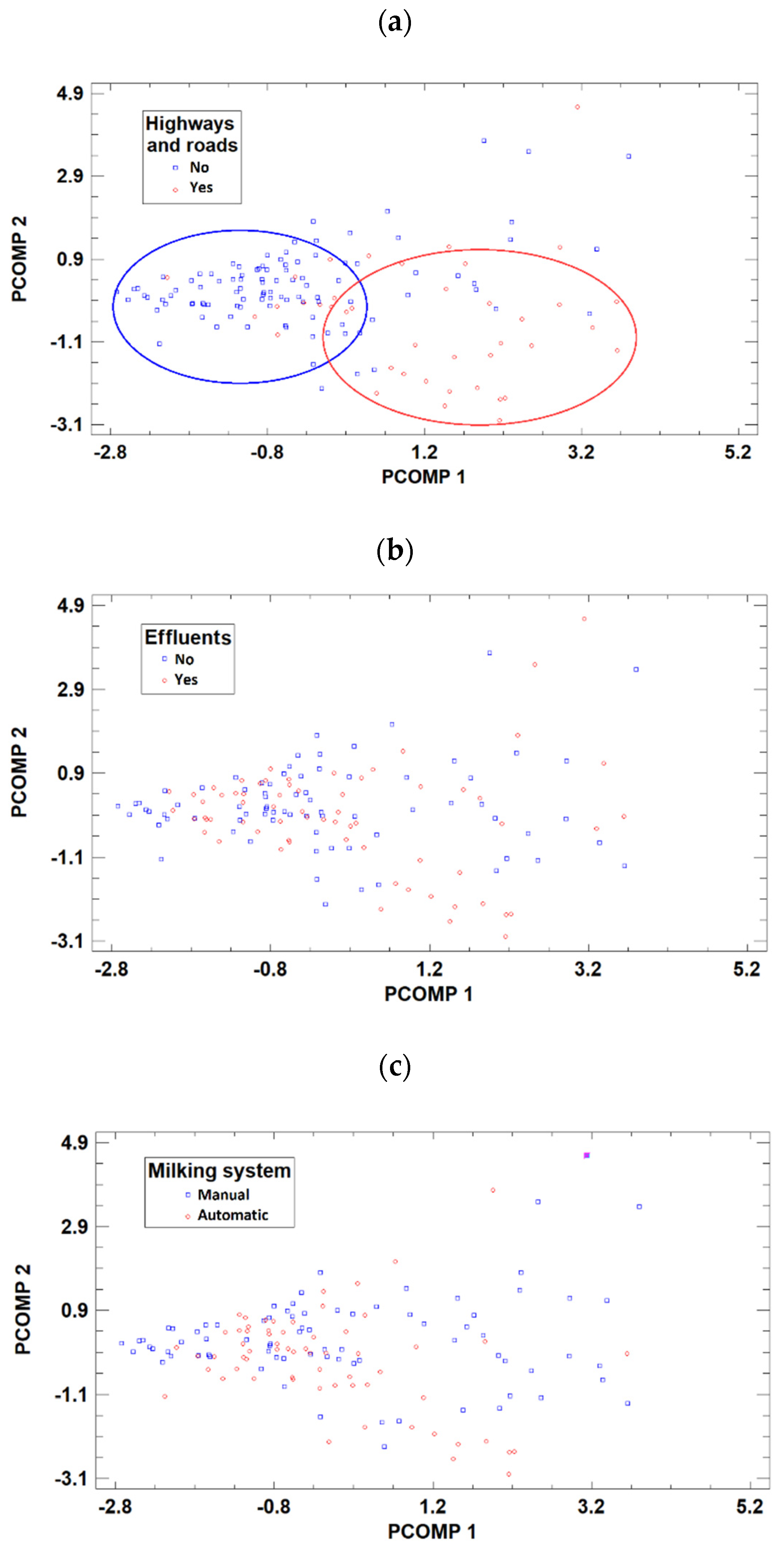
Figure 2a), implying an evident influence of the traffic emissions in the metal content of the milk. Despite this “natural” separation, there was also some degree of overlap between the two categories in the 5-multidimensional space of the variables, as seen in the score-plot.
Figure 2.
2D-score plot of the samples obtained by PCA according to (a), the proximity the farms to major roads, (b) the presence of effluents and (c) the milking method.
Figure 2.
2D-score plot of the samples obtained by PCA according to (a), the proximity the farms to major roads, (b) the presence of effluents and (c) the milking method.
The second step of chemometric analysis consisted of using HCA. This unsupervised chemometric procedure searches for groups of samples (or variables) in the multidimensional space. It is based in an algorithm that arranges similar samples (or variables) into groups called clusters. The similarity between objects is calculated on the basis of the distance that separates them, considering that near samples in the 5-dimensional space of the variables will be very similar to each other. In the present case, the similarity was measured as the squared Euclidean distance, and the Ward method was used as agglomerative algorithm procedure to identify clusters [
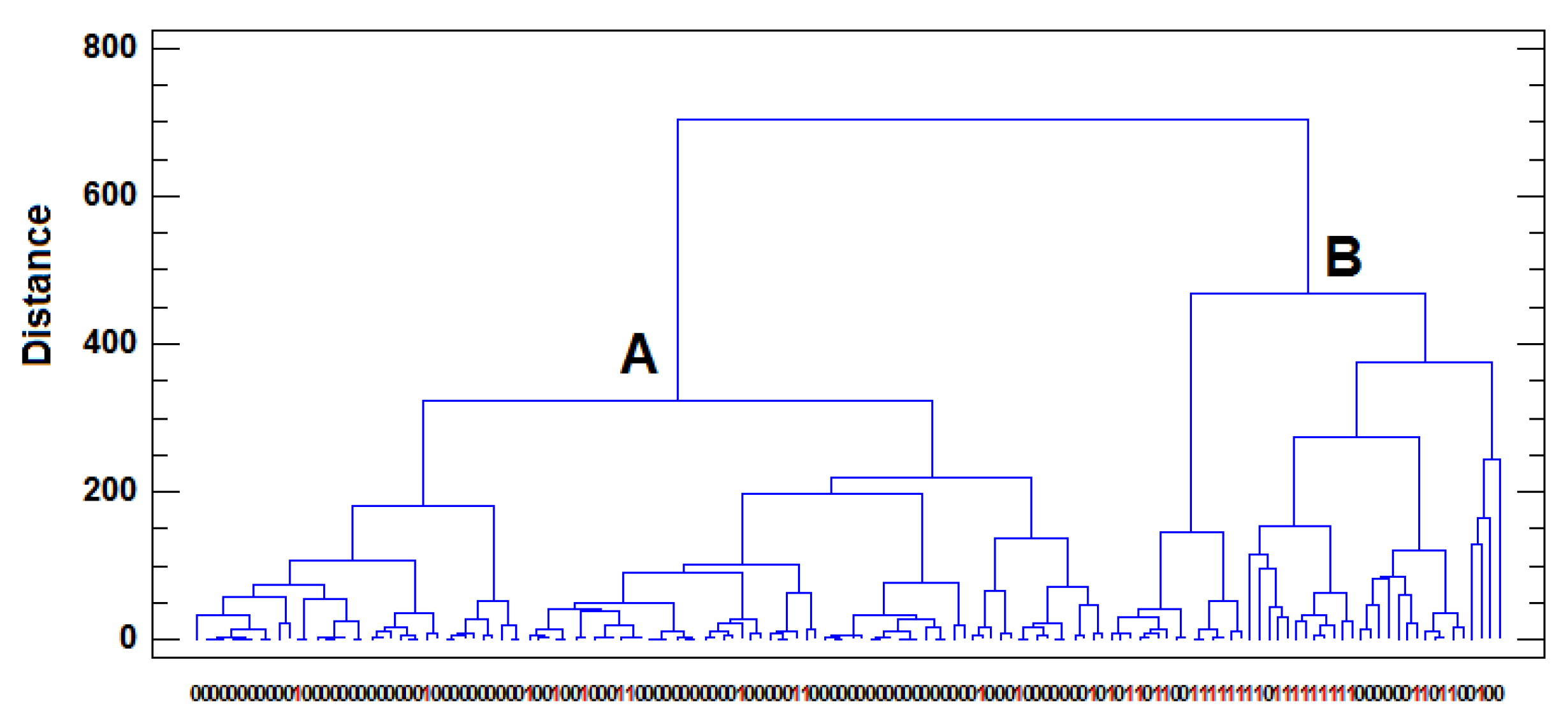
73]. The dendrogram of the milk samples obtained when HCA was applied to the complete data set in the autoscaled
X142x5 matrix can be seen in
Figure 4. Examination of the dendrogram revealed the presence of two clusters of milk samples in the 5-dimensional space defined by the metal variables. The first cluster (A) is composed of samples from farms distant from major roads, while the second (B) mainly includes samples from farms close to major roads. The presence of samples near roads in cluster A and the appearance of samples far from roads in cluster B demonstrate some degree of overlap between clusters previously indicated by PCA.
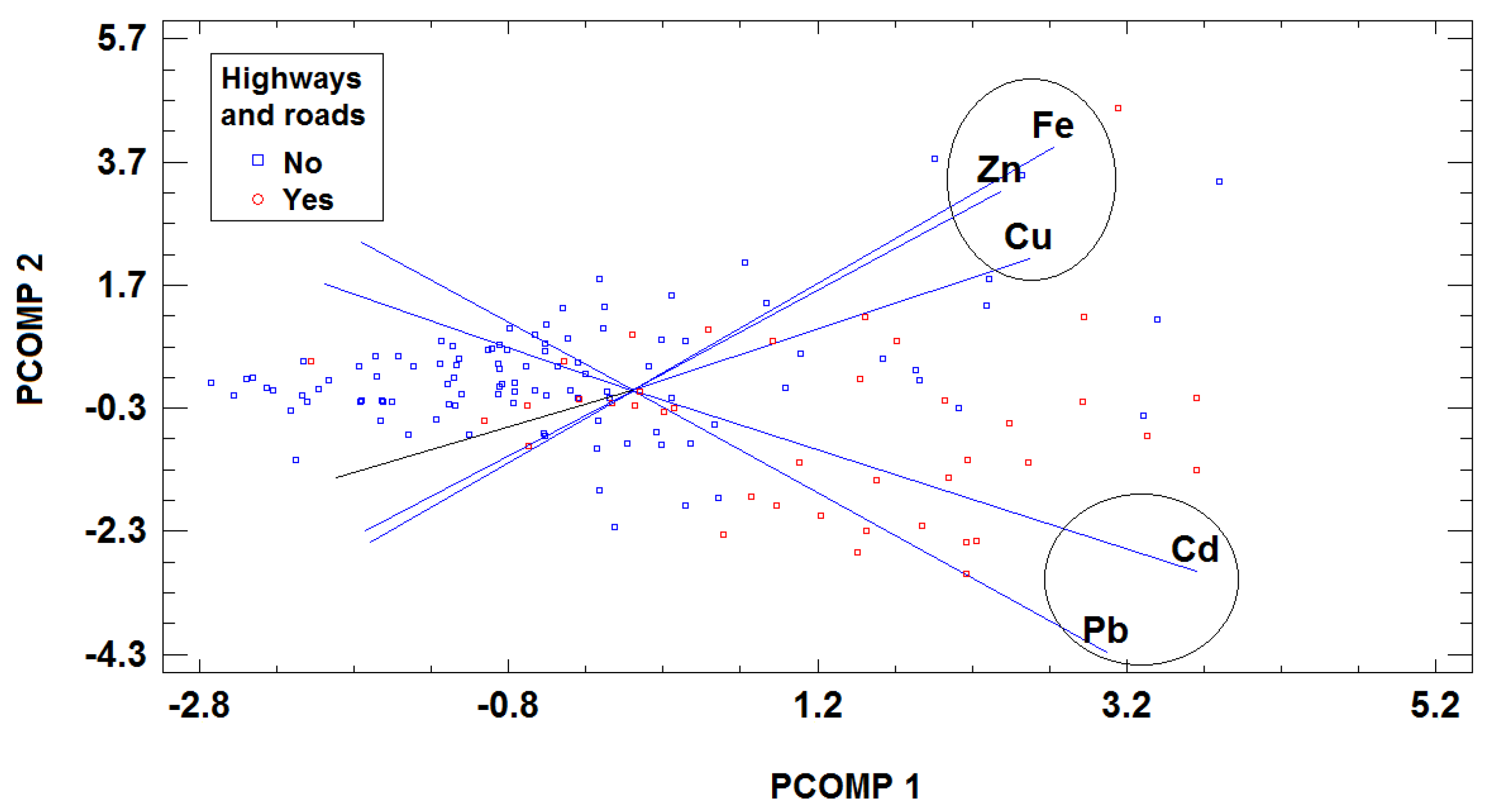
Figure 3.
Biplot of the whole data set obtained by PCA. Samples are coded according to the proximity of major roads.
Figure 3.
Biplot of the whole data set obtained by PCA. Samples are coded according to the proximity of major roads.
This separation in two clear groups does not occur for either the milking type or the effluent factors, thus confirming the conclusion reached in the PCA that the most significant factor affecting the metal content of the samples is the traffic in the proximity of livestock farms. Moreover, the group of milk samples from farms far from major roads were more similar to each other than the group of milk samples from farms close to major roads were (
Figure 4). This was an expected result as the distance of the farms from major roads was variable. It has been reported that levels of heavy metal contamination (Pb and Cd are the most widely studied) in both soils and forage decreases to background levels with increasing distance on both sides of major roads [
53,
67]. Cattle and other animals that are grazed close to roads have been shown to have higher blood Pb levels than animals housed indoors [
2,
74], and the significant correlation between blood and milk Pb levels increases the potential human exposure[
2,
74]. One of the most important causes of high Pb content in milk from rural, relatively unpolluted areas may be the proximity to major roads or transhumance along roads and/or motorways [
64,
75].
Figure 4.
Dendrogram of the samples according to the proximity of major roads obtained by HCA (Squared Euclidean distance and Ward agglomerative method).
Figure 4.
Dendrogram of the samples according to the proximity of major roads obtained by HCA (Squared Euclidean distance and Ward agglomerative method).
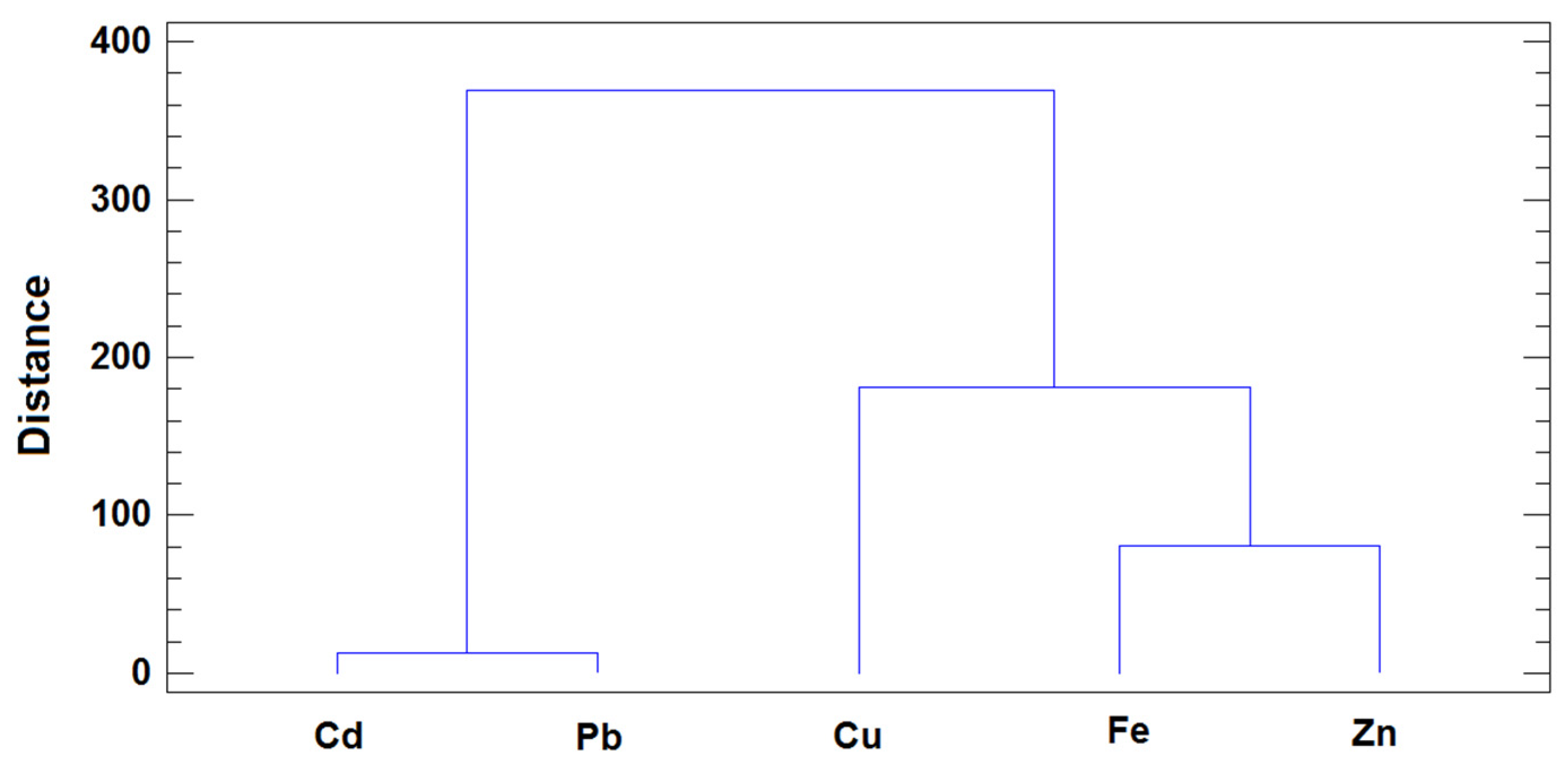
Additionally, HCA was used to evaluate associations between variables, and in this case two clusters of variables were also detected (
Figure 5): the first included toxic metals Cd and Pb and the second comprised the essential trace elements. The variable arrangement may be directly linked to the differences in these metals according to the presence or absence of any major roads in the proximity of the farm where the milk samples were collected. In the plots, the metals are ordered from left to right on the basis of their capacity to distinguish between samples near and far from main roads. The variables in the first cluster (Cd and Pb) showed clearly different levels for samples on the basis of the road factor (with higher levels in milk from farms near main roads). Some differences in Cu concentrations were also observed for both classes, but with lower discriminatory capacity, while Fe and Zn showed similar or equal ranges. These results are consistent with those obtained by PCA and when the GLM was considered for testing the effect of the road factor in the metal content of milk samples.
Taking into account the high concentrations of Pb in almost 30% of the milk samples analyzed, as well as the low content of other essential mineral elements, the consumption of milk from this region may represent a health risk to the population. More extensive studies that include larger sample sizes and different metals, and that determine Pb levels in the rock and soil should be conducted to clarify the risk associated with consumption of milk in the study region.
4. Conclusions
The study findings indicate that raw cow’s milk from the Pernambuco State contains high levels of Pb, but low levels of the essential elements Cu, Fe and Zn. A high percentage of samples exceeded the maximum limit for Pb established in the current Brazilian legislation. This finding was attributed to the proximity of the farms to the major roads and was confirmed by using multivariate chemometric techniques (PCA and HCA). Both unsupervised chemometric approaches demonstrated the main influence of proximity to transportation infrastructures on the metal content of milk. On the other hand, neither the impact of the presence of effluents in the vicinity of the farm or the milking method had an important effect on the metal profile of the product. Thus, according to metal levels detected, consumption of cow’s milk produced in this region can be considered risk to public health due to the high levels of Pb and the low levels of essential minerals such as Cu, Zn and Fe in some samples.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.F.d.O.F., M.L.-A., G.V.M., P.C.S., C.L.M., N.d.A.C. and M.M.; methodology, E.F.d.O.F., M.L.-A., G.V.M., P.C.S. and M.M.; software, M.L.-A., C.H.-L. and M.M.; validation, E.F.d.O.F., M.L.-A., P.C.S. and M.M.; formal analysis, E.F.d.O.F., M.L.-A., P.C.S., C.H.-L. and M.M.; investigation, E.F.d.O.F., G.V.M., P.C.S., C.L.M. and N.d.A.C.; resources, M.L.-A., G.V.M., P.C.S., C.L.M., N.d.A.C. and M.M.; data curation, M.L.-A., C.H.-L. and M.M.; writing—original draft preparation, E.F.d.O.F., M.L.-A., G.V.M., P.C.S., C.H.L. and M.M.; writing—review and editing, E.F.d.O.F., M.L.-A., C.H.L. and M.M.; supervision, M.L.-A., P.C.S. and M.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available in the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest regarding publication of the results.
References
- Licata, P.; Trombetta, D.; Cristani, M.; Giofrè, F.; Martino, D.; Calò, M.; Naccari, F. Levels of “Toxic” and “Essential” Metals in Samples of Bovine Milk from Various Dairy Farms in Calabria, Italy. Environ Int 2004, 30, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, R.C.; Swarup, D.; Kumar, P.; Nandi, D.; Naresh, R.; Ali, S.L. Milk Trace Elements in Lactating Cows Environmentally Exposed to Higher Level of Lead and Cadmium around Different Industrial Units. Science of The Total Environment 2008, 404, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudebbouz, A.; Boudalia, S.; Bousbia, A.; Habila, S.; Boussadia, M.I.; Gueroui, Y. Heavy Metals Levels in Raw Cow Milk and Health Risk Assessment across the Globe: A Systematic Review. Science of The Total Environment 2021, 751, 141830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Enb, M.A. Donia, N.S. Abd Rabou, A.A.K. Abou-Arab, M.H. El-Senaity, Chemical Composition of Raw Milk and Heavy Metals Behavior during Processing of Milk Products. Global Vet. 2009, 3, 268–275. [Google Scholar]
- Pšenková, M.; Toman, R.; Tančin, V. Concentrations of Toxic Metals and Essential Elements in Raw Cow Milk from Areas with Potentially Undisturbed and Highly Disturbed Environment in Slovakia. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2020, 27, 26763–26772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suttle, N.F. Mineral Nutrition of Livestock, Four ed.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2010; ISBN 9781845934729. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Bermúdez, R.; López-Alonso, M.; Miranda, M.; Fouz, R.; Orjales, I.; Herrero-Latorre, C. Chemometric Authentication of the Organic Status of Milk on the Basis of Trace Element Content. Food Chem 2018, 240, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norouzirad, R.; González-Montaña, J.-R.; Martínez-Pastor, F.; Hosseini, H.; Shahrouzian, A.; Khabazkhoob, M.; Ali Malayeri, F.; Moallem Bandani, H.; Paknejad, M.; Foroughi-nia, B.; et al. Lead and Cadmium Levels in Raw Bovine Milk and Dietary Risk Assessment in Areas near Petroleum Extraction Industries. Science of The Total Environment 2018, 635, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, N.P.C. –; Sánchez, F.C.–; Sato, M.P.–; Guillermo, E.S.–; Cervantes, E.R.– Health Risk Due to Chronic Heavy Metal Consumption via Cow’s Milk Produced in Puebla, Mexico, in Irrigated Wastewater Areas. Food Additives \& Contaminants: Part B 2019, 12, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Bedriñana, J.; Chirinos-Peinado, D.; Ríos-Ríos, E.; Machuca-Campuzano, M.; Gómez-Ventura, E. Dietary Risk of Milk Contaminated with Lead and Cadmium in Areas near Mining-Metallurgical Industries in the Central Andes of Peru. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 2021, 220, 112382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Commision Regulation (EU) No 1881/2006 Commission Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 Setting Maximum Levels for Certain Contaminants in Foodstuffs; 2006; Vol. 173;
- ANVISA Decree Number 55.871/65. <http://anvisa.gov.br> 2016, 1–23.
- Soares, V.A.; Kus, M.M.M.; Peixoto, A.L.C.; Carrocci, J.S.; Salazar, R.F.S.; Izário Filho, H.J. Determination of Nutritional and Toxic Elements in Pasteurized Bovine Milk from Vale Do Paraiba Region (Brazil). Food Control 2010, 21, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.C.S.; Lindino, C.A.; Gonçalves Junior, A.C.; Gomes, G.D. Determinação de Cd, Cr e Pb No Leite e Na Alimentação Bovina Do Brasil. Rev Inst Adolfo Lutz 2013, 72, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro Sant’Ana, M.A.; de Carvalho, T.C.; da Silva, I.F. Concentration of Heavy Metals in UHT Dairy Milk Available in the Markets of São Luís, Brazil, and Potential Health Risk to Children. Food Chem 2021, 346, 128961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, C.M.; Amaral, R.S.; Tabosa, J.N.; Santos Júnior, J.A.; Menezes, R.S.C.; Farias, E.E.G.; Bezerra, J.D.; Silvestre, R.G.; Oliveira, G.F. Pb-210 in Rock and Soils of the Semi-Arid Agreste Region of Pernambuco, Brazil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 2009, 82, 647–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, C.M.; Amaral, R.S.; Tabosa, J.N.; Júnior, J.A.S.; Menezes, R.S.C.; Ribeiro, F.C.A. Estimation of Dose Due to Ingestion of 210Pb in Milk from Dairy Cattle in the Semi-Arid Region of Pernambuco, Brazil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 2010, 85, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, C.M.; Amaral, R.S.; Ribeiro, F.C.A.; Tabosa, J.N.; Júnior, J.A.S.; Menezes, R.S.C. Lead Poisoning Risk for Dairy Cows in the Semi-Arid Region of Pernambuco, Brazil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 2011, 86, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.D. Chemometrics: A Textbook. D. L. Massart. B. G. M. Vandeginste, S. N. Deming, Y. Michotte, and L. Kaufman, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1988. ISBN 0-444-42660-4. Price Dfl 175.00. J Chemom 1988, 2, 298–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, J.; Mesquita, A.; Gonçalves, R. DETERMINAÇÃO DE METAIS PESADOS EM LEITE INTEGRAL BOVINO PASTEURIZADO NO ESTADO DE GOIÁS DETERMINING HEAVY METALS IN PASTEURIZED WHOLE BOVINE MILK IN STATE OF GOIÁS. Ciência Animal Brasileira 2008, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Bragato, N.; Borges, N.C.; Fioravanti, M.C.S. B-Mode and Doppler Ultrasound of Chronic Kidney Disease in Dogs and Cats. Vet Res Commun 2017, 41, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirinos-Peinado, D.M.; Castro-Bedriñana, J.I. Lead and Cadmium Blood Levels and Transfer to Milk in Cattle Reared in a Mining Area. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, C.S.P. De; Arruda, A.F.; Cunha, L.R. Da; SouzaDe, J.R.; Braga, J.W.B.; Dórea, J.G. Toxic Metals (Pb and Cd) and Their Respective Antagonists (Ca and Zn) in Infant Formulas and Milk Marketed in Brasilia, Brazil. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2010, 7, 4062–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwierzchowski, G.; Ametaj, B.N. Mineral Elements in the Raw Milk of Several Dairy Farms in the Province of Alberta. Foods 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketut Budaraga, I.; Salihat, R.A. Heavy Metals Analysis (Cd, Pb, Zn, Cu, Cr) and Calcium in Padang and Padang Panjang Fresh Cow’s Milk. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 2022, 1038, 012076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puls, R. Mineral Levels in Animal Health, Second Ed. ed; Clearbrook: Sherpa International, British Columbia, Canada, 1994; ISBN 096934290X. [Google Scholar]
- Bomjardim, H.A.; Oliveira, C.M.C.; Silveira, J.A.S.; Silva, N.S.; Duarte, M.D.; Faial, K.C.F.; Brito, M.F.; Barbosa, J.D. Deficiências Minerais Em Vacas Em Lactação Da Bacia Leiteira Do Município de Rondon Do Pará, Estado Do Pará. Pesquisa Veterinária Brasileira 2015, 35, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudebbouz, A.; Boudalia, S.; Bousbia, A.; Gueroui, Y.; Boussadia, M.I.; Chelaghmia, M.L.; Zebsa, R.; Affoune, A.M.; Symeon, G.K. Determination of Heavy Metal Levels and Health Risk Assessment of Raw Cow Milk in Guelma Region, Algeria. Biol Trace Elem Res 2023, 201, 1704–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bousbia, A.; Boudalia, S.; Gueroui, Y.; Ghebache, R.; Amrouchi, M.; Belase, B.; Meguelati, S.; Belkheir, B.; Benidir, M.; Chelaghmia, M.L. HEAVY METALS CONCENTRATIONS IN RAW COW MILK PRODUCED IN THE DIFFERENT LIVESTOCK FARMING TYPES IN GUELMA PROVINCE (ALGERIA): CONTAMINATION AND RISK ASSESSMENT OF CONSUMPTION. J Anim Plant Sci 2019, 29, 386–395. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Carrera, A.L.; Arellano, F.E.; Fernández-Cirelli, A. Concentration of Trace Elements in Raw Milk from Cows in the Southeast of Córdoba Province, Argentina. Dairy Sci Technol 2016, 96, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhib, M.I.; Chowdhury, M.A.Z.; Easha, N.J.; Rahman, M.M.; Shammi, M.; Fardous, Z.; Bari, M.L.; Uddin, M.K.; Kurasaki, M.; Alam, M.K. Investigation of Heavy Metal Contents in Cow Milk Samples from Area of Dhaka, Bangladesh. Int J Food Contam 2016, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, M.V. de; Vianna, M.W. de S.; Zandim, B.M.; Fernandes, R.B.A.; Fontes, M.P.F. Metais Pesados Em Amostras Biológicas de Bovinos. Ciência Rural 2009, 39, 1774–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Liu, H.; Qu, X.; Zhou, X.; Gao, Y.; Yang, H.; Zheng, N.; Wang, J. Heavy Metals in Raw Milk and Dietary Exposure Assessment in the Vicinity of Leather-Processing Plants. Biol Trace Elem Res 2021, 199, 3303–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Qu, X.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Zheng, N. Analysis of 22 Elements in Milk, Feed, and Water of Dairy Cow, Goat, and Buffalo from Different Regions of China. Biol Trace Elem Res 2017, 176, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zheng, N.; Su, C.; Wang, J.; Soyeurt, H. Relationships between Pb, As, Cr, and Cd in Individual Cows’ Milk and Milk Composition and Heavy Metal Contents in Water, Silage, and Soil. Environmental Pollution 2019, 255, 113322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilandžić, N.; Čalopek, B.; Sedak, M.; Đokić, M.; Gajger, I.T.; Murati, T.; Kmetič, I. Essential and Potentially Toxic Elements in Raw Milk from Different Geographical Regions of Croatia and Their Health Risk Assessment in the Adult Population. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis 2021, 104, 104152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshref, A.M.S.; Moselhy, W.A.; Hassan, N.E.-H.Y. Heavy Metals and Trace Elements Levels in Milk and Milk Products. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization 2014, 8, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, N.; Faludi, G.; Beauclercq, S.; Pitt, J.; Desnica, N.; Pétursdóttir, Á.; Newton, E.E.; Angelidis, A.; Givens, I.; Juniper, D.; et al. Macromineral and Trace Element Concentrations and Their Seasonal Variation in Milk from Organic and Conventional Dairy Herds. Food Chem 2021, 359, 129865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akele, M.L.; Abebe, D.Z.; Alemu, A.K.; Assefa, A.G.; Madhusudhan, A.; de Oliveira, R.R. Analysis of Trace Metal Concentrations in Raw Cow’s Milk from Three Dairy Farms in North Gondar, Ethiopia: Chemometric Approach. Environ Monit Assess 2017, 189, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodrik, L.; Wagner, L.; Imre, K.; Polyak, K.F.; Besenyei, F.; Husveth, F. The Effect of Highway Traffic on Heavy Metal Content of Cow Milk and Cheese. Hungarian Journal of Industry and Chemistry 2011, 39, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.; Singh, A.K. Human Health Risk Assessment Due to Metals in Cow’s Milk from Singhbhum Copper and Iron Mining Areas, India. J Food Sci Technol 2020, 57, 1415–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, A.; Bharti, V.K.; Kalia, S.; Kumar, B.; Chaurasia, O.P. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals Through Cow Milk Consumption in Trans-Himalayan High-Altitude Region. Biol Trace Elem Res 2021, 199, 4572–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasotha, A.; Dabadé, D.S.; Singh, V.P.; Sivakumar, T. Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Milk from Cows Reared around Industrial Areas in India. Environ Geochem Health 2021, 43, 1799–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Akbaridastjerdi, H.; Jafari, H.; Farahi, A.; Shahabi, A.; Javdani, H.; Teimoory, H.; Yahyaei, M.; Malekirad, A.A. Assessment of Dairy Products Consumed on the Arakmarket as Determined by Heavy Metal Residues. Health N Hav 2014, 6, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, Y.; Ahmadi, F.; Fakhari, F. Voltammetric Determination of Pb, Cd, Zn, Cu and Se in Milk and Dairy Products Collected from Iran: An Emphasis on Permissible Limits and Risk Assessment of Exposure to Heavy Metals. Food Chem 2016, 192, 1060–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tizhoosh, M.; Tizhoosh, H. The Concentration of Zinc, Lead, Cadmium and Copper in Raw Milk Production in Industrial Farms in Khorramabad, Iran. Int Proc Chem Biol Environ Eng 2016, 93, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Monteverde, V.; Camilleri, G.; Arfuso, F.; Pennisi, M.; Perillo, L.; Patitò, G.; Gioia, G.; Castronovo, C.; Piccione, G. Heavy Metal Levels in Milk and Serum of Dairy Cows from Different Farms Located near an Industrial Area. Animals 2022, 12, 2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarsembayeva, N.; Abdigaliyeva, T.; Utepova, Z.; Biltebay, A.; Zhumagulova, S. Heavy Metal Levels in Milk and Fermented Milk Products Produced in the Almaty Region, Kazakhstan. Vet World 2020, 13, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.; Jeong, I.S.; Hwang, I.M.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, S.H.; Nho, E.Y.; Choi, J.Y.; Park, K.S.; Kim, K.S. Analysis of Minor and Trace Elements in Milk and Yogurts by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS). Food Chem 2014, 147, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragusha, B.; Aliu, H.; Dizman, S. Concentrations of Metal Residues in Domestically Produced and Imported Milk in Kosovo. S Afr J Anim Sci 2022, 51, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numa Pompilio, C.-G.; Francisco, C.-S.; de María-Torres Marco Tulio, F.; Sergio Samuel, S.-M.; Fernanda Elisa, G.-J. Heavy Metals in Blood, Milk and Cow’s Urine Reared in Irrigated Areas with Wastewater. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safonov, V. Assessment of Heavy Metals in Milk Produced by Black-and-White Holstein Cows from Moscow. Current Research in Nutrition and Food Science 2020, 8, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.; Iqbal, M.; Abbas, M.; Tahir, M.A.; Nazir, A.; Iqbal, D.N.; Kanwal, Q.; Hassan, F.; Younas, U. Comparative Study of Heavy Metals Distribution in Soil, Forage, Blood and Milk. Acta Ecologica Sinica 2017, 37, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilarczyk, R.; Wójcik, J.; Czerniak, P.; Sablik, P.; Pilarczyk, B.; Tomza-Marciniak, A. Concentrations of Toxic Heavy Metals and Trace Elements in Raw Milk of Simmental and Holstein-Friesian Cows from Organic Farm. Environ Monit Assess 2013, 185, 8383–8392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujka, M.; Pankiewicz, U.; Kowalski, R.; Mazurek, A.; Slepecka, K.; Góral, M. Determination of the Content of Pb, Cd, Cu, Zn in Dairy Products from Various Regions of Poland. Open Chem 2019, 17, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miclean, M.; Cadar, O.; Levei, L.; Roman; Ozunu, A. Metal (Pb, Cu, Cd, and Zn) Transfer along Food Chain and Health Risk Assessment through Raw Milk Consumption from Free-Range Cows. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2019, 16, 4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Năstăsescu, V.; Mititelu, M.; Goumenou, M.; Docea, A.O.; Renieri, E.; Udeanu, D.I.; Oprea, E.; Arsene, A.L.; Dinu-Pîrvu, C.E.; Ghica, M. Heavy Metal and Pesticide Levels in Dairy Products: Evaluation of Human Health Risk. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2020, 146, 111844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suturović, Z.; Kravić, S.; Milanović, S.; Đurović, A.; Brezo, T. Determination of Heavy Metals in Milk and Fermented Milk Products by Potentiometric Stripping Analysis with Constant Inverse Current in the Analytical Step. Food Chem 2014, 155, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey-Crespo, F.; Miranda, M.; López-Alonso, M. Essential Trace and Toxic Element Concentrations in Organic and Conventional Milk in NW Spain. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2013, 55, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Montaña, J.R.; Senís, E.; Gutiérrez, A.; Prieto, F. Cadmium and Lead in Bovine Milk in the Mining Area of the Caudal River (Spain). Environ Monit Assess 2012, 184, 4029–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diyabalanage, S.; Kalpage, M.D.; Mohotti, D.G.; Dissanayake, C.K.K.; Fernando, R.; Frew, R.D.; Chandrajith, R. Comprehensive Assessment of Essential and Potentially Toxic Trace Elements in Bovine Milk and Their Feeds in Different Agro-Climatic Zones of Sri Lanka. Biol Trace Elem Res 2021, 199, 1377–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakircioglu, D.; Topraksever, N.; Yurtsever, S.; Kizildere, M.; Kurtulus, Y.B. Investigation of Macro, Micro and Toxic Element Concentrations of Milk and Fermented Milks Products by Using an Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometer, to Improve Food Safety in Turkey. Microchemical Journal 2018, 136, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyuncu, M.; Alwazeer, D. Determination of Trace Elements, Heavy Metals, and Antimony in Polyethylene Terephthalate–Bottled Local Raw Cow Milk of Iğdır Region in Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 2019, 191, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigucu, E.; Kaptan, B.; Palabiyik, I.; Oksuz, O. The Effect of Environmental Factors on Heavy Metal and Mineral Compositions of Raw Milk and Water Samples. Journal of Tekirdag Agricultural Faculty 2016, 13, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Zyambo, G.; Yabe, J.; Muzandu, K.; Mkandawire, E.; Choongo, K.; Kataba, A.; Chawinga, K.; Liazambi, A.; Nakayama, S.; Nakata, H.; et al. Human Health Risk Assessment from Lead Exposure through Consumption of Raw Cow Milk from Free-Range Cattle Reared in the Vicinity of a Lead–Zinc Mine in Kabwe. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19, 4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caggiano, R.; Sabia, S.; D’Emilio, M.; Macchiato, M.; Anastasio, A.; Ragosta, M.; Paino, S. Metal Levels in Fodder, Milk, Dairy Products, and Tissues Sampled in Ovine Farms of Southern Italy. Environ Res 2005, 99, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, R.; Zilli Vieira, C.L.; Rosenbaum, M.H.; Bischoff, K.; Mordarski, D.C.; Brown, M.J. The Urban Lead (Pb) Burden in Humans, Animals and the Natural Environment. Environ Res 2021, 193, 110377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bou Kheir, R.; Shomar, B.; Greve, M.B.; Greve, M.H. On the Quantitative Relationships between Environmental Parameters and Heavy Metals Pollution in Mediterranean Soils Using GIS Regression-Trees: The Case Study of Lebanon. J Geochem Explor 2014, 147, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogundiran, M.B.; Ogundele, D.T.; Afolayan, P.G.; Osibanjo, O. Heavy Metals Levels in Forage Grasses, Leachate and Lactating Cows Reared around Lead Slag Dumpsites in Nigeria. Int J Environ Res 2012, 6, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Alonso, M.; Benedito, JL.; Miranda, M.; Castillo, C.; Hernández, J.; Shore, RF. Interactions between Toxic and Essential Trace Metals in Cattle from a Region with Low Levels of Pollution. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 2002, 42, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, M.; López-Alonso, M.; Castillo, C.; Hernández, J.; Benedito, J.L. Effects of Moderate Pollution on Toxic and Trace Metal Levels in Calves from a Polluted Area of Northern Spain. Environ Int 2005, 31, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.L.; Montaña, F.P.; Miranda, M.; Castillo, C.; Hernández, J.; Benedito, J.L. Interactions between Toxic (As, Cd, Hg and Pb) and Nutritional Essential (Ca, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Mo, Ni, Se, Zn) Elements in the Tissues of Cattle from NW Spain. BioMetals 2004, 17, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massart, D.L.; Kaufman, L. Hierarchical Clustering Methods. In The interpretation of analytical chemical data by the use of cluster analysis; John Wiley & Sons Inc: New York, USA, 1983; pp. 75–99. [Google Scholar]
- Swarup, D.; Patra, R.C.; Naresh, R.; Kumar, P.; Shekhar, P. Blood Lead Levels in Lactating Cows Reared around Polluted Localities; Transfer of Lead into Milk. Science of The Total Environment 2005, 347, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derakhshesh, S.M.; Rahimi, E. Determination of Lead Residue in Raw Cow Milk from Different Regions of Iran by Flameless Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. American-Eurasian Journal of Toxicological Sciences 2012, 4, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).