1. Introduction
Climate change is a global phenomenon generally caused by the nature and accelerated by anthropogenic activities. Climate change can be seen through rising air temperature and fluctuating precipitation both in both in time and magnitude or intensity [
1]. In case of islands and coastal environment, climate change can also be seen in sea level rise, oceanic acidification, frequency of storm surges, tsunamis, and seawater intrusion [
2,
3,
4]. As per Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) (2014), coastal ecosystem and its communities are vulnerable to climate change at significant level. Vulnerability is usually expressed in form of exposure, sensitivity, absorption and adaptation to the stressor [
4], and can be assessed using qualitative or quantitative means.
A study of impact of climate change on the environment of Andaman and Nicobar was designed to understand the dynamics of forest cover and thermal profile of the region. The islands’ system prospers various terrestrial, coastal, and oceanic ecosystems like mangroves, coral reefs, and seagrass beds with large organism diversity [
5,
6,
7,
8]. Andaman and Nicobar Islands, also known as ‘Emerald’ and ‘Kalapani’ are situated in the Bay of Bengal [
9,
10]. The islands cover only 0.25% of the country's landmass and about 86% of the area is under fragile tropical rain forests with a great diversity of flora and fauna. It has a unique assemblage of endemic species and a great diversity of soils, geology, climate, geography, and topography [
11]. The region is frequently exposed to tectonic activities, earthquakes and volcanic eruptions (Curray et al., 1979). The disastrous tsunami waves of 26th December 2004, flooded the coast, dropping the sea level and wave crest, inundating the land islands. It took many days to recede water completely. This catastrophic event adversely affected the human life, terrestrial, coastal, and marine biodiversity. Coastal aquifers became vulnerable to saltwater intrusion, precisely after the December 2004 earthquake [
13,
14]. Earlier also, there was a land subsidence reported in middle Andaman in 1986 [
15]. Current paper focus on the study of role of climate change on vegetation, urban built-up and waterbodies in relation to temperature. Satellite remote sensing and GIS was used to estimate the qualitative and quantitative change in vegetation, waterbodies and settlement in the area using Landsat data. Support Vector Machine classification was used to classify the study area from 1990 to 2019. Further, the vegetation index, water index, and Built-up index was used for further analysis of land use and land cover classes. The importance and correlation of indexes with respect to their classes is explained below.
- 1.1.
Vegetation index- The Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) has been widely used for vegetation mapping in the last few decades. The chlorophyll region has strong absorption for the red band and a high reflection for near-infra-red region. NDVI is derived from red and near infra-red reflection using the formula NDVI = (NIR-Red)/(NIR+Red). NDVI and vegetation productivity are strongly related. Here, the red light is absorbed by chlorophyll content of vegetation and; near-infrared (NIR) light is scattered by mesophyll content of Plants [
16]. The relation of fraction of absorbed photosynthetic active radiation (fAPAR) and NDVI is well documented both empirically and theoretically [
17,
18]. Therefore, NDVI is widely used for spatial and temporal mapping of vegetation distribution [
19], vegetation biomass (Reed et al., 1994), vegetation quality (based on greenness) for herbivores [
20] and land degradation in the various ecosystem [
21,
22]. It is also been used to differentiate savannah, non-forest, dense forest, evergreen forest-seasonal forests, tree- shrubs, and agricultural fields. However, the interference of soil reflectance on NDVI in sparsely distributed vegetated areas [
23] and, However, the interference of soil reflectance on NDVI in sparsely distributed vegetated areas and, the saturation in NIR band in densely vegetated regions, lowers the sensitivity of the NDVI [
23]. Despite that NDVI is very helpful to study environmental influence on plants species.
- 1.2.
Water index- Normalized difference water index (NDWI) has been primarily used to delineate water bodies while eliminating the soil and vegetation features simultaneously. It can also be used to measure the water quality through turbidity in water [
24]. NDWI is also proposed to study vegetation liquid water detection from space. It is defined as ((p (0.86 µm) - p (1.24µm))/ ((p (0.86 µm) + p (1.24 µm)), where p represents the reflectance units in respective band. Both channels have high reflectance for vegetation canopies. The absorption of liquid water is negligible for 0.86 µm but weak absorption is present near 1.24 µm. Also, canopy scattering increases water absorption [
25].
- 1.3.
Built-up index- The development of a built-up index such as the Normalized Difference Built-up Index (NDBI) is used for automatic extraction of the built-up area from the rest of the class. This index is based on the higher spectral response of built-ups in the mid-infra-red region than in the near-infrared region. Additionally, this index is further used to study built-up density, growth of urban centers, dynamics of sprawl, and also for future prediction with the help of other indices [
27,
28,
29]. Rapid urbanization has brought many negative environmental impacts to the world such as less precipitation or irregular precipitation, higher temperature, and more dryness [
30].
2. Study area
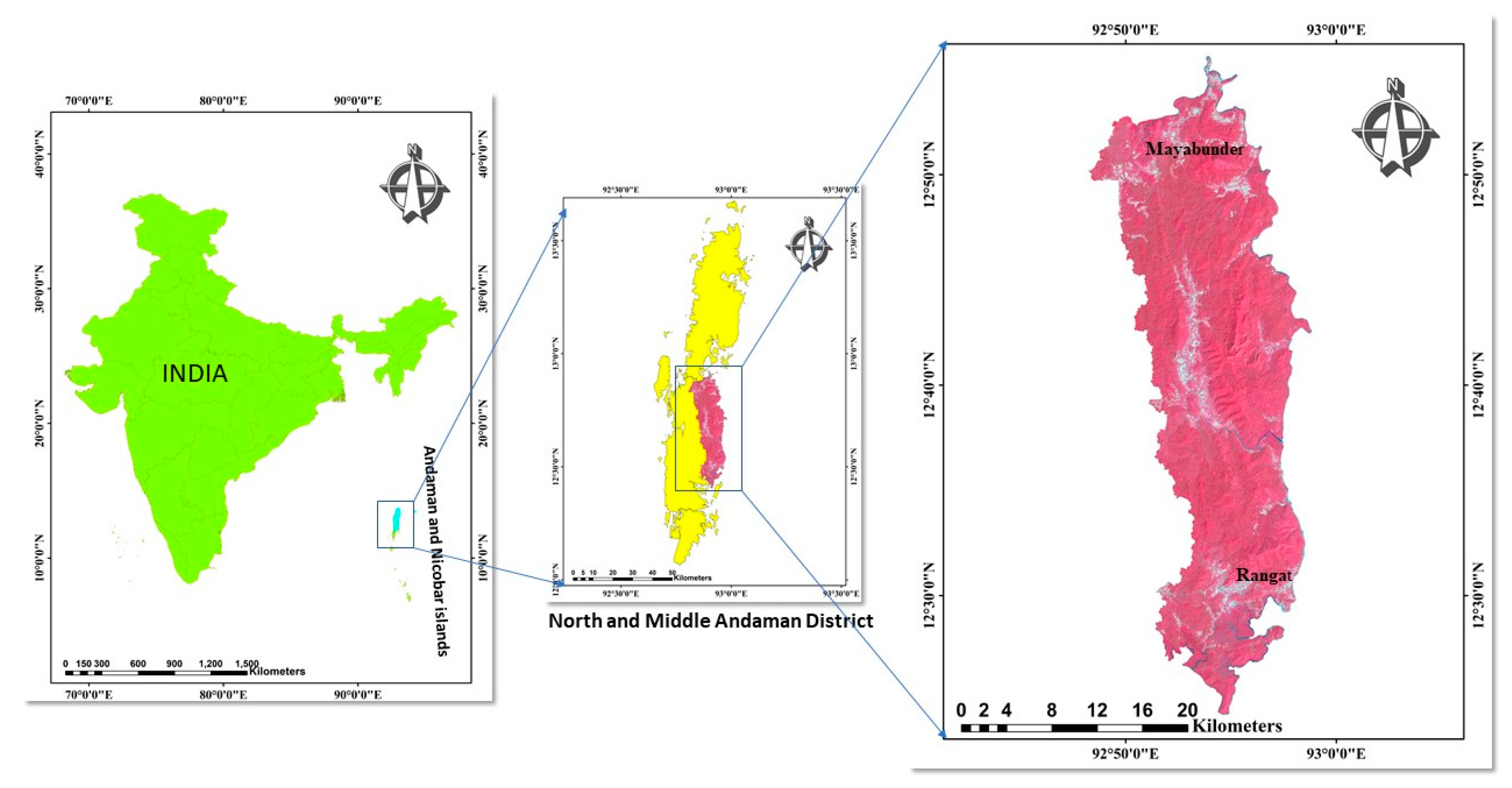
The study area covers the eastern portion of middle Andaman consisting of Mayabunder and Rangat (
Figure 1). It has an area of 556.21 km
2 in which more than 80 percent of the region comes under forest region. The region is the fragment of the old Gondwana landmass, a southward extension of Arakan Yoma tectonic units from Cape Negrais to Achin head of Sumatra. The topography of islands is low range hills and narrow valleys in an undulating terrain from steep slopes to coastal plains. The land can be subdivided into high to low dissected hills and valleys, moderate dissected upper plateau, offshore islands, and young coastal plains. The huge hill ranges are covered by dense forests. The coastal margin covers saline marshes to salt-affected patches with some undulating uplands [
14]. The springs and perennial streams associated with igneous rocks or limestone are the only sources of fresh water supply. Panchavati hills having highly fractured igneous or limestones rocks is the main source of spring. Study area falls under agro-climatic zone XV. The island has a mean annual rainfall of 3180 mm. It experienced the highest rainfall in 1961 of 4300 mm and the lowest in 1979 (1550mm). The climate of the region is coastal tropical to subtropical with humidity of 79% - 89% with temperatures ranging from 27°C to 33°C in summer and 21°C to 25°C in the winter season [
31].
3. Materials and Methods
Publicly available satellite data of Landsat series with less than 10 % cloud was downloaded (EarthExplorer (usgs.gov)) on a temporal scale of 5 years (07-02-2019, 12-02-2015, 07-02-2010, 12-02-2005, 07-02-2000, 18-01-1990) from 3:30 pm to 4:30 pm. The support vector machine was used to classify data that uses a set of support vectors based on labeled training samples on ArcGIS 10.8 platform. Accuracy assessment was done with google earth pro software and field observation. The indices for each class were calculated using ERDAS 2014 software using the following formula:
NDVI = (NIR - Red)/ (NIR + Red)
NDWI = (Green - NIR)/ (Green + NIR)
NDBI = (SWIR – NIR) / (SWIR + NIR)
Where NIR stands for Near infrared, SWIR stands for shortwave infrared; red and green are red and green bands respectively.
The land surface temperature was extracted from Landsat thermal data using the split-window algorithm and mono window algorithm for Landsat 8 and Landsat (4-5) respectively [
32,
33]. The correlation and other calculation of data was computed using MS-EXCEL with XLSTAT extension.
4. Result
4.1. LULC classification:
Support vector machine classification was done from 1990 to 2019. The classification was done in forest cover, urban built-up, and water bodies. The Forest region was further classified into the Evergreen Forests (Moist evergreen), Deciduous Forest (semi-evergreen), and forest with the blurred pixel (moist deciduous forest or open forest). The naming of the forest region was done based on the relative appearance of the forest under a false-color composite. The total area of the region is about 556.21 km
2 of which 85 percent of the region is under forest cover as shown in
Figure 2.
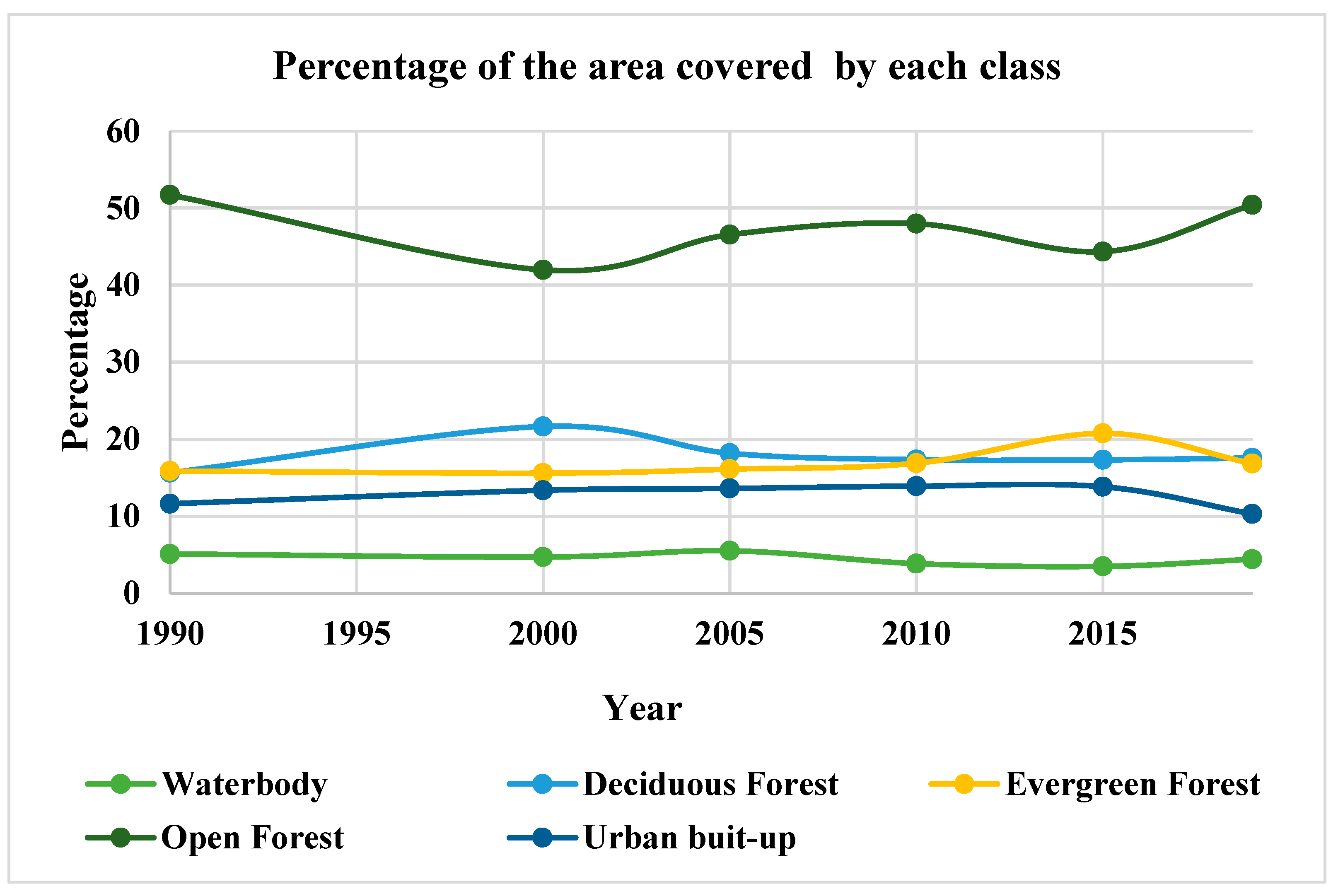
Most of the region is covered by forest in which Open Forest pixel shares 50 percent of total area. Deciduous Forest, and Evergreen Forest shares around 20 percent each. The region has only 5 percent of waterbodies. The forest region is shown in different shades of green, the water in blue, and the urban area in brown color. The temporal change in land use and land cover is identified using a classification matrix. The year-wise percentage of each class is shown using the graph (
Figure 3). Open Forest shows highest fluctuation and least fluctuation is being observed in both waterbodies and urban built-up. With respect to land use-landcover change, waterbody shows a fluctuation found highest in 1990 and lowest in 2015 but no significant change in overall water cover in the region. Similarly, Evergreen Forest and Open Forest do show fluctuation from year 2015 to 2019. The “Deciduous Forest” slightly increases in 2000, then remain constant after a small decrease in area. On the other hand, there is an increasing trend in a built-up area, that slightly decreased in 2019.
4.2. LULC change detection:
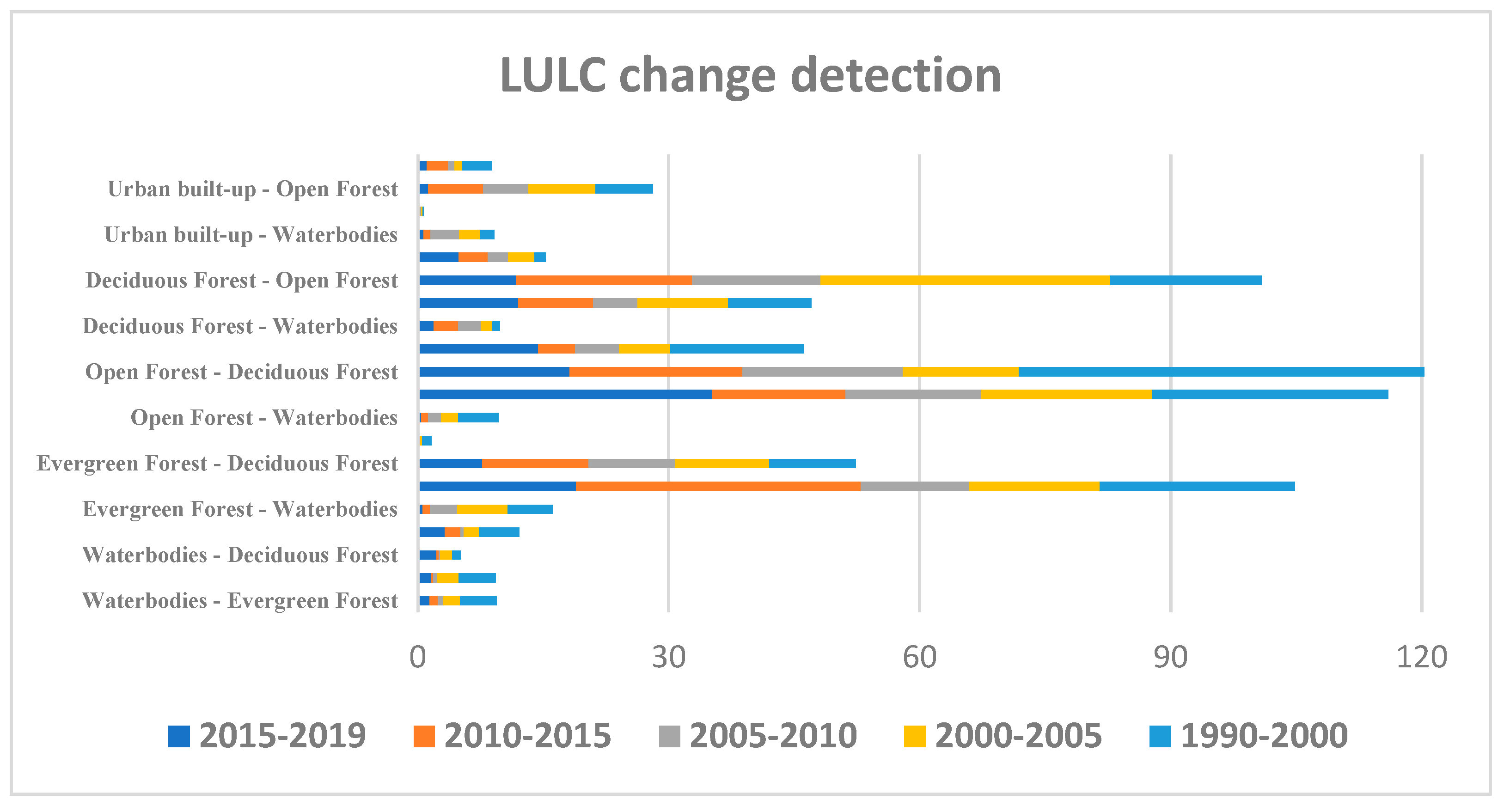
In LULC change graph (
Figure 4), the bar shows the change in LULC from 1990-2000, 2000-2005, 2005-2010, 2010-2015 and 2015-2019. The graph shows that significant conversion has occurred in forests cover. The conversion of Open Forest into Evergreen Forest is maximum in 2015-2019 (35 km
2) and least conversion happened between 2005 to 2015 (16 km
2). The conversion of Evergreen Forest into Open Forest is 34 km
2 in 2010-2015 and minimum in 2005-2010 (13 km
2). Open Forest is converted into Deciduous Forest maximum in 1990-2000 (51 km
2). The conversion of forest region into urban built-up happened maximum in 2015-2019 and 1990-2000 that is around 19 km
2. The urban area is mainly formed after clearing the forest classified in Open Forest. A smaller part of waterbodies is also converted into urban built-up. Some part of the study area is also submerged into waterbodies. The submergence is 3.55 km
2 ,47 km
2, 10.92 km
2, 12.00 km
2 and 12.73 km
2 for 2015-2019, 2010-2015, 2005-2010, 2000-2005, and 1990-2000 respectively into waterbodies in 2015-2019, 2010-2015, 2005-2010, 2000-2005, and 1990-2000 is 3.55 km
2, 5.47 km
2, 10.92 km
2, 12.00 km
2, 12.73 km
2 respectively. The inter-conversion of forest class or change in forest abundance, submergence of land into water may be explained either change in characteristics of forest region due to climate change or any other catastrophic event or extension of one forest region into another.
4.3. Spatial description of unchanged region of LULC
The LULC class pixel (shown in their respective color) (
Figure 5) from 2015-2019, 2010-2015, 2005-2010, 2000-2005, and 1990-2000 did not show any change with time. The interconnected lineaments provide a good subsurface hydrology that constantly supported preservation of forest ecosystem. The abundance of Open Forest was observed in the upper middle and lower part of the study area while, the unchanged patches of Deciduous Forest were observed maximum in Mayabunder, and some clustered patches in the north and southern part of the region. Evergreen Forests were found to be in scattered patches throughout the area. Urban built-up was found to be clustered in the middle, northern and southern parts of the study area. Open forest region shows higher groundwater recharge capacity and unconverted open forest depicts the stable hydrological condition of the area. The changed part of forest cover (shown in black color) can be seen nearer to urban built-up specifically near Rangat in the Middle Andaman that found drastic change in forest cover during the years.
4.4. The accuracy assessment of the classifications shown in Table 1.
4.5. Vegetation and Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI)
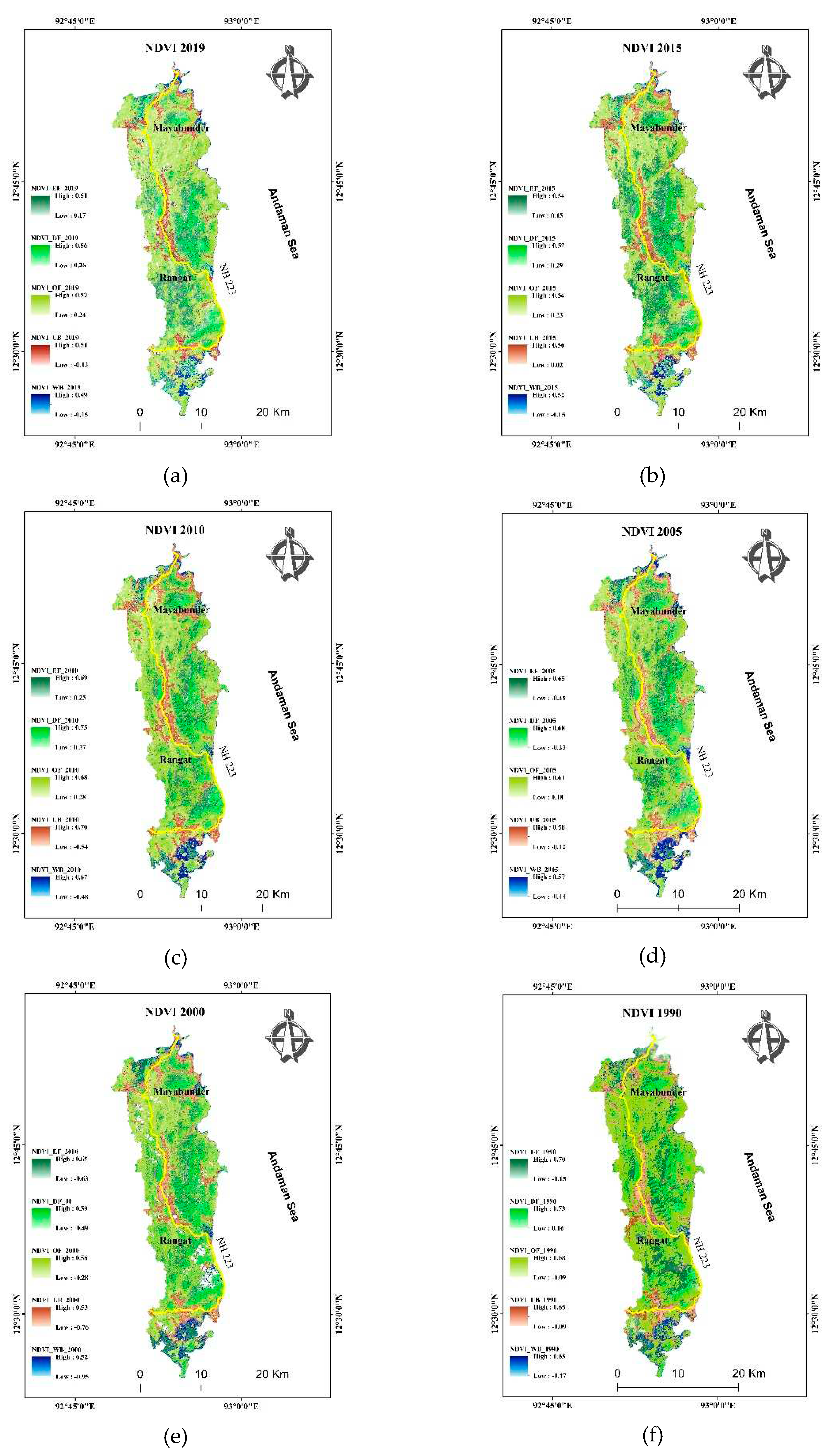
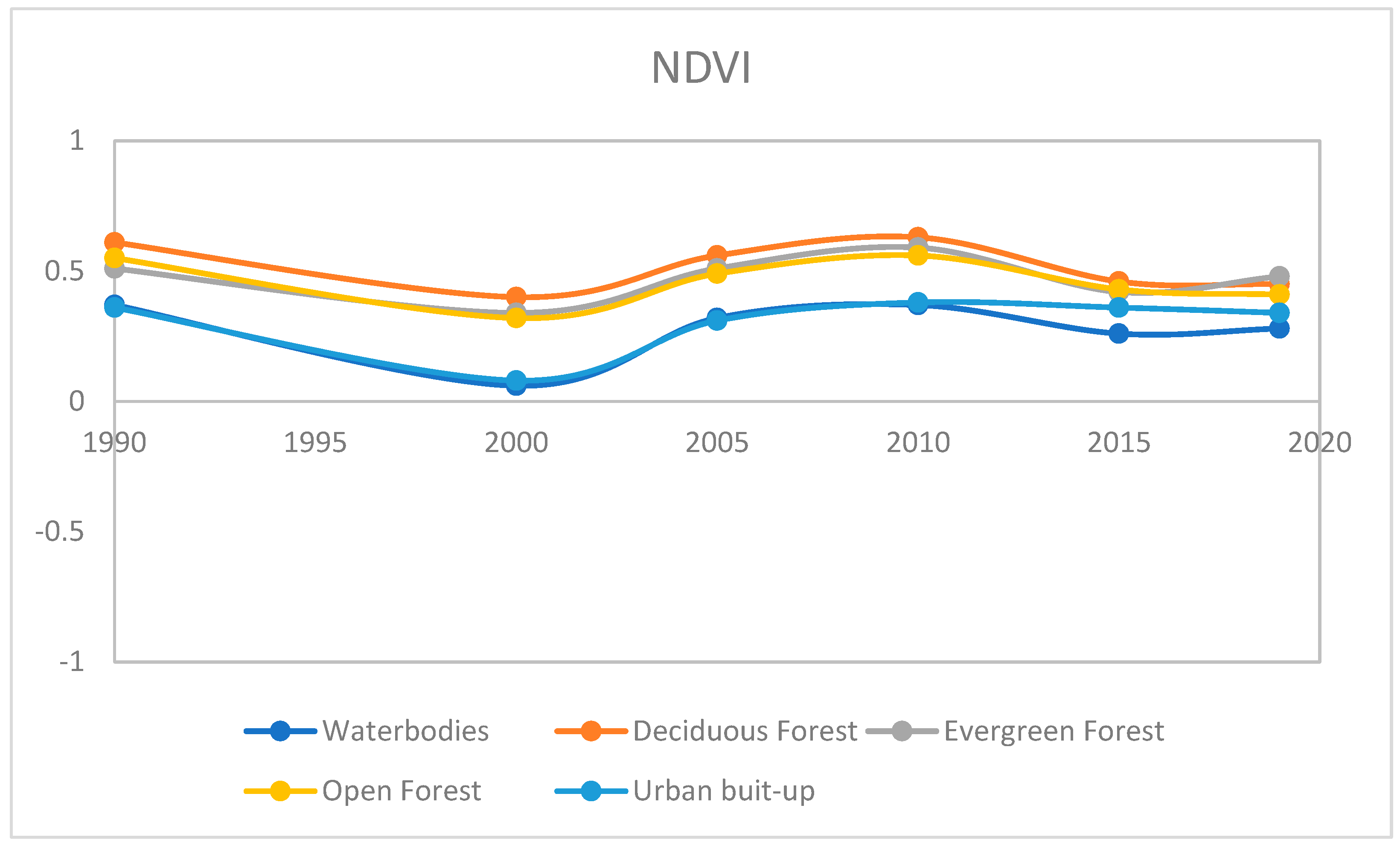
The time-series NDVI (
Figure 6) and a smoothened curve of the mean value was plotted for time series analysis of the study area (
Figure 7). NDVI of the classified class was calculated to interpret the vegetation characteristics of each class. The Deciduous Forest showed a higher NDVI value than the Evergreen Forest which was found to be further higher than Open Forest. The yearly trend of all the classes that decreased in 1990-2000, increased in 2000-2005-2010 and remain constant after a small decrease in their value. The higher value of NDVI indicates the characteristics of vegetation as well as the health of the vegetation type [
19,
20]. As the vegetation of the area is already classified then NDVI may depicts the health of vegetation over the years. The health or abundance of the vegetation decreased from 1990 to 2000 and further increased from 2000 to 2010 and decreased in 2010 and 2019. The fluctuation of the trend may be due to various natural hazards such as earthquakes, tsunamis, groundwater fluctuation, and seawater intrusion. The vegetation in Andaman is sensitive to minute changes in the surrounding which serves as an indicator of the dynamic climate variations.
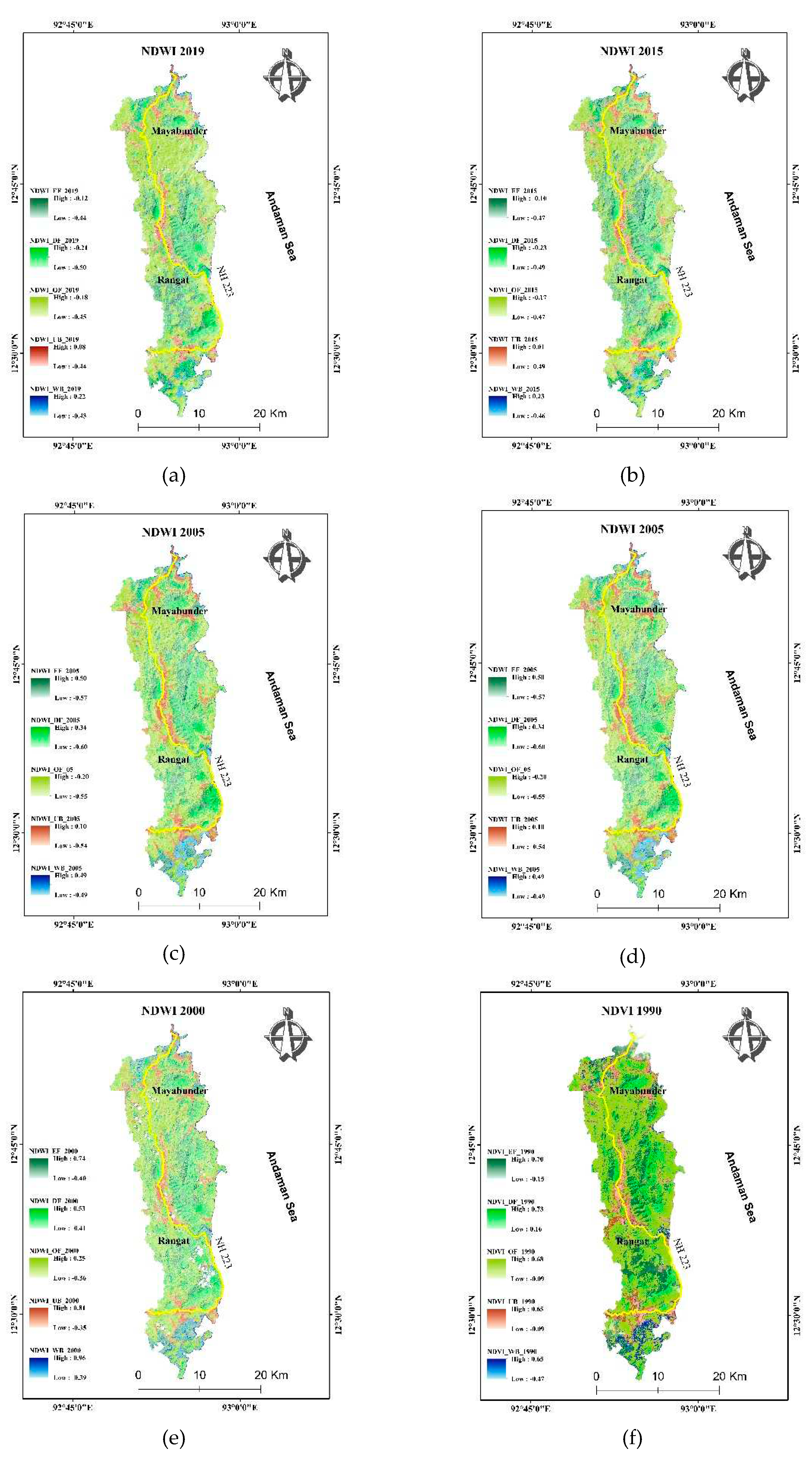
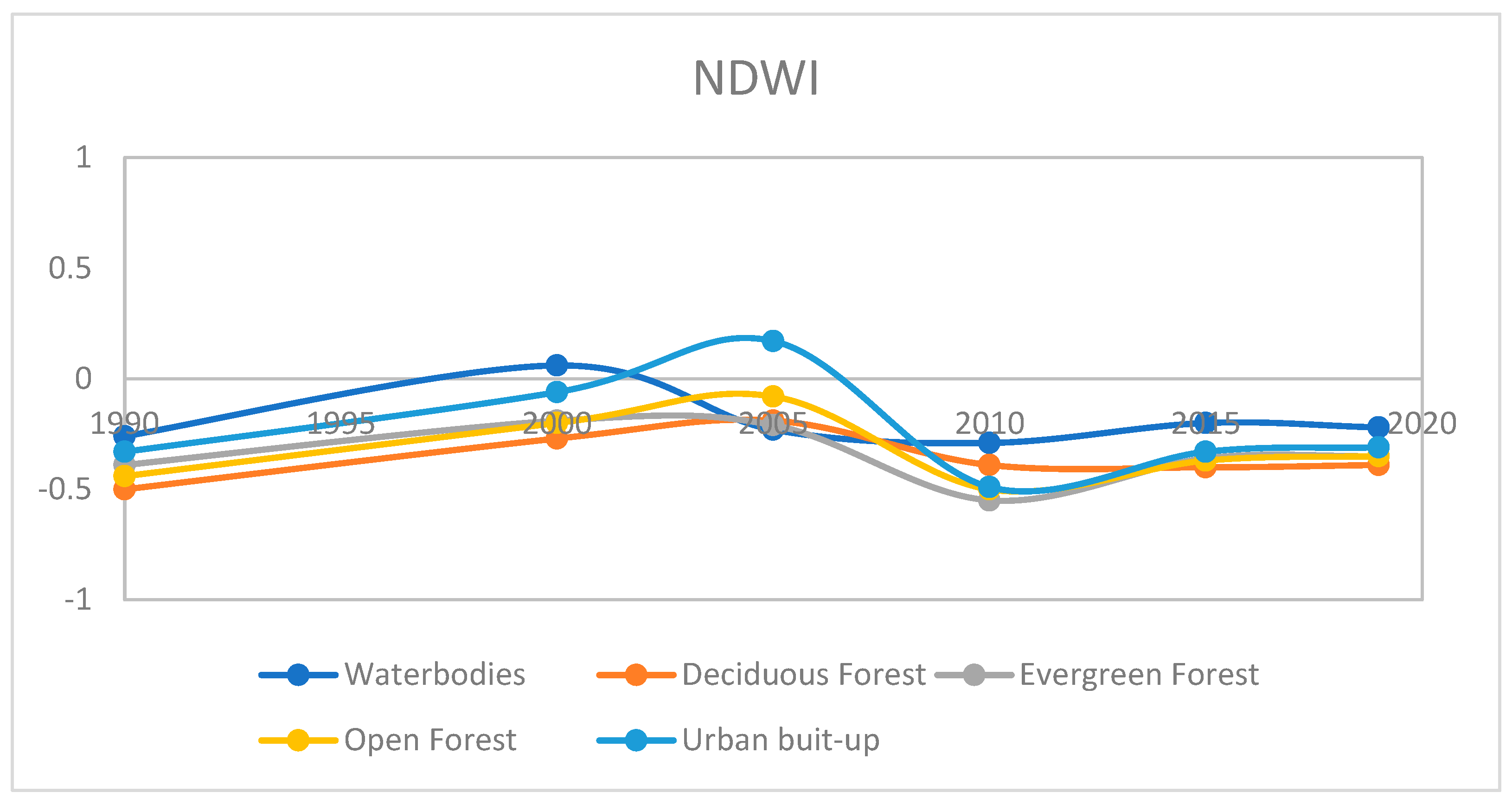
4.6. Waterbodies and Normalized difference water index (NDWI)
NDWI is very effective for mapping water bodies and evapotranspiration of vegetation (
Figure 8). It is widely used for estimating the vegetation water content at the canopy level. NDWI is sensitive to detecting the water content in internal leaf structure. It was widely used for the assessment of the water quality of the water body, draught monitoring, and vegetation water stress. It is also used for surface water detection and quality estimation of the water such as pollutants, salts, algae, and dust particles from land surfaces. NDWI works on the phenomenon of absorbance of water in higher wavelength region and scattering of infrared or reflection blue light into the atmosphere. The higher value of NDWI depicts the concentration of solute particles in water [
24]. The concentration of other particles increased from 1990 to 2000, then decreased from 2000 to 2010 then remains constant at a little higher value (
Figure 8). Lower water quality can be further interpreted based on the higher value of NDVI (
Figure 7) (organic component or turbidity), and the dominance of inorganic particles as there is a higher value of NDBI (
Figure 11). The higher value of NDWI in 2005 is possibly due to the 2004 tsunami. The abundance of nutrients, sunlight, and water may lead to eutrophication from 2005-2010 as there is a decrease in the value of NDBI and an increase in the value of NDVI simultaneously.
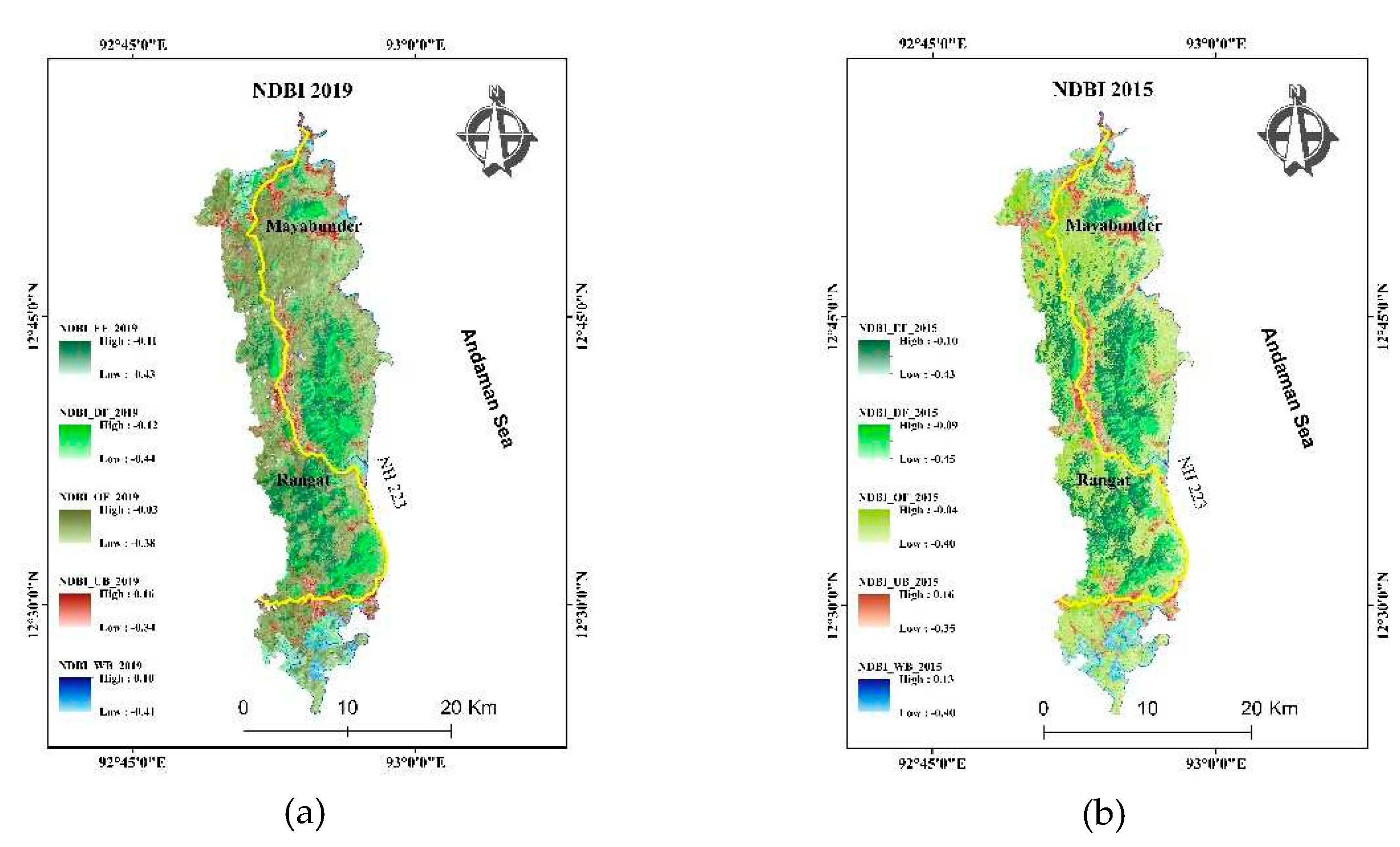
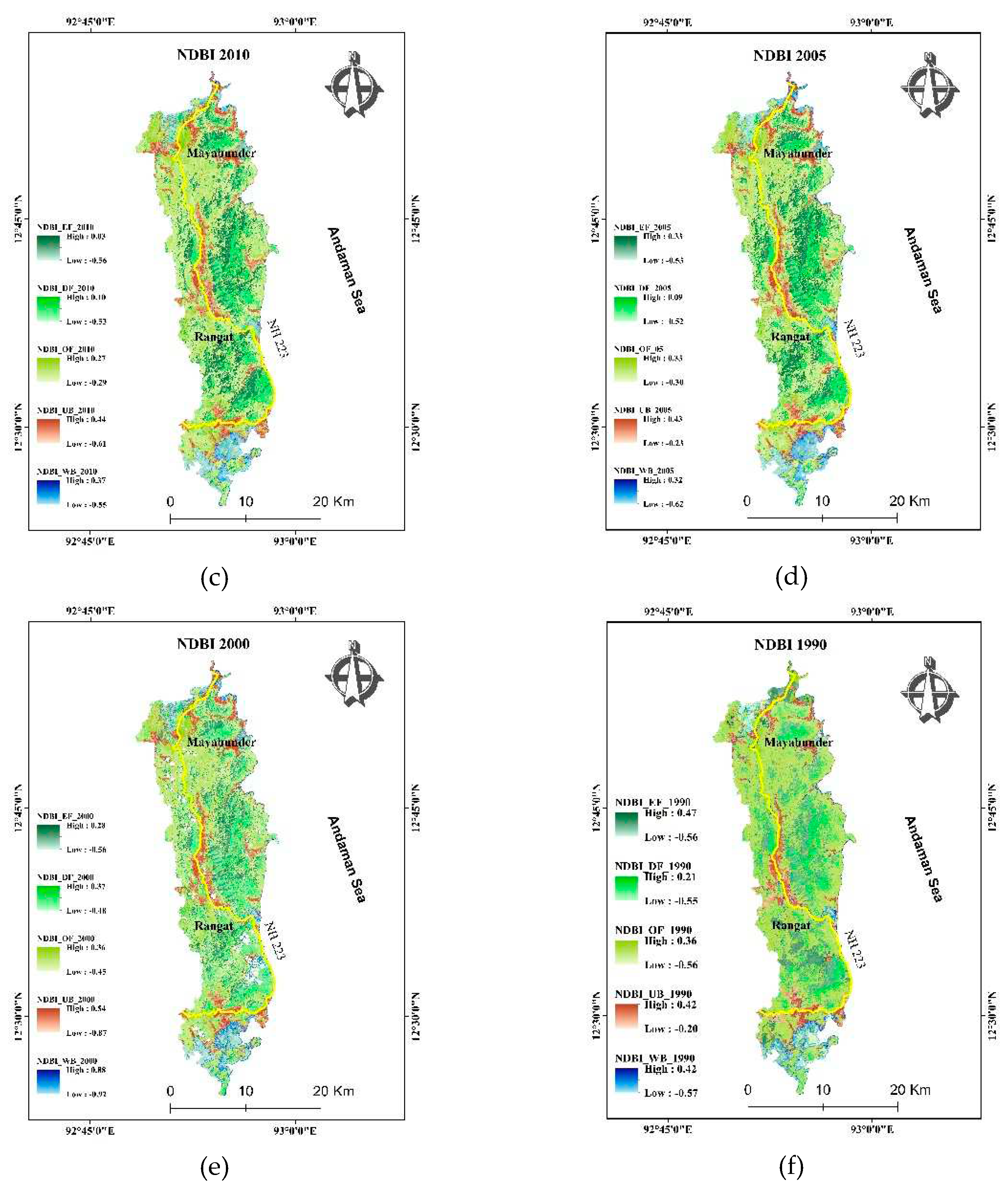
4.7. Built-up and Normalized difference built-up index (NDBI)
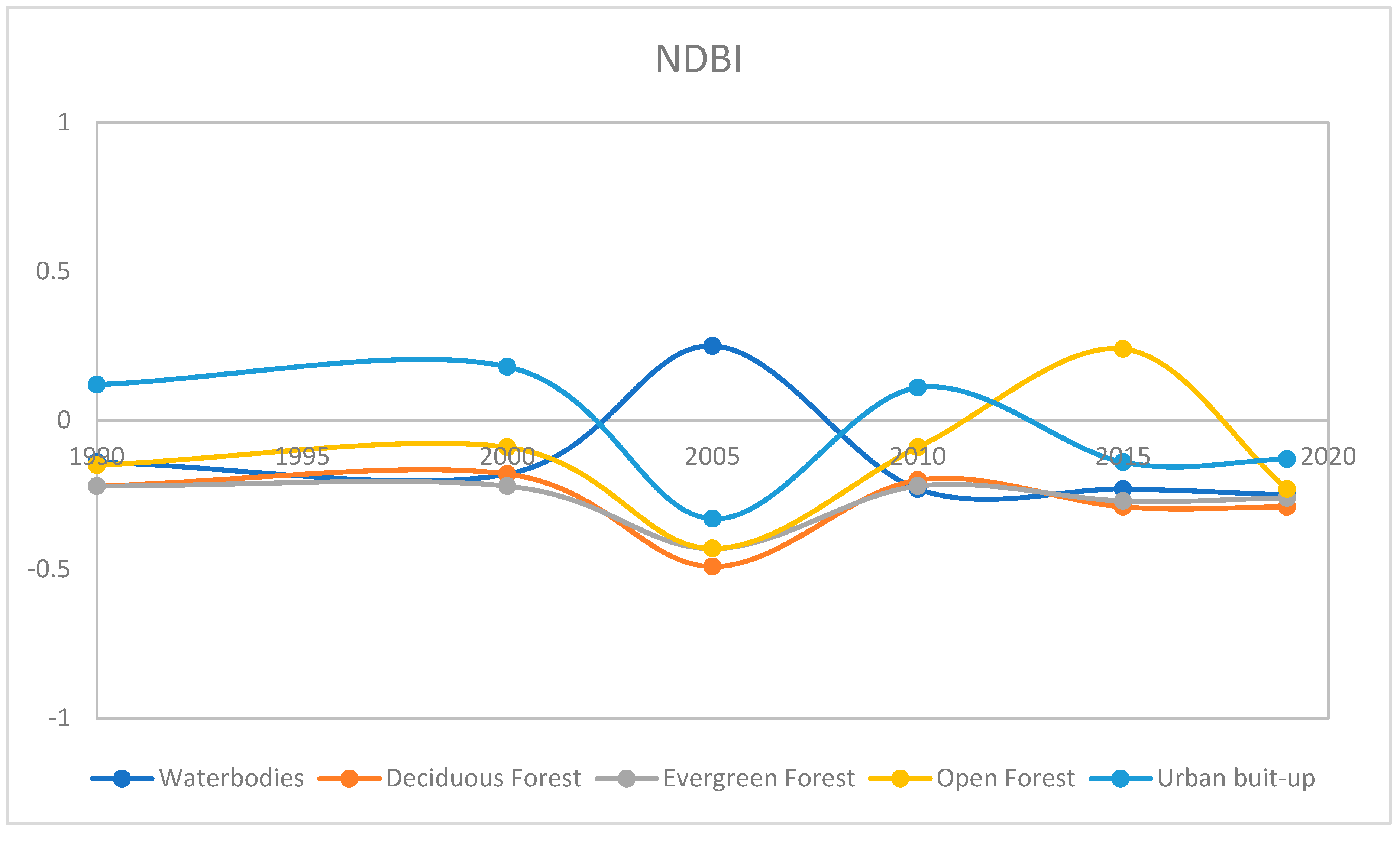
NDBI is usually used for mapping both barren land and urban built-up. NDBI was calculated for each class and compared for each year (
Figure 10). The yearly change in the value of NDBI fluctuates similar way in all the forest regions. Its values were abruptly high in waterbodies and lower in 2005 possibly due to Tsunami in 2004 (
Figure 11). The higher value of NDBI in waterbodies indicates the possibility of an increase in turbidity in water. The area also has a small proportion of built-up. It is clustered on the eastern coast of the island. Rangat and Mayabunder area are two major cities in the region. The built-up area was formed after clearing the forest land of the region. As urban built-up is already classified using SVM, the built-up index (NDBI) can be used for the estimation of built-up density [
28]. The built-up area shows a fluctuating trend with the lowest value in 2005 and slightly increasing in 2010 and decreasing from 2015 to 2019 (
Figure 11). The urban density is not increased since 2005 as lots of damage happened in the tsunami (2004), but it improved in 2010 after a lot of rehabilitation in the area. The result shows that urban density did not improve much after the year 2010.
Figure 10.
NDBI classification of the study area in of year (a) 2019, (b) 2015, (c) 2010, (d) 2005, (e) 2000, (e)1990.
Figure 10.
NDBI classification of the study area in of year (a) 2019, (b) 2015, (c) 2010, (d) 2005, (e) 2000, (e)1990.
Figure 11.
Average change in NDBI from 1990 to 2019 in waterbodies, Deciduous Forest, Evergreen Forest, Open Forest and Urban built-up.
Figure 11.
Average change in NDBI from 1990 to 2019 in waterbodies, Deciduous Forest, Evergreen Forest, Open Forest and Urban built-up.
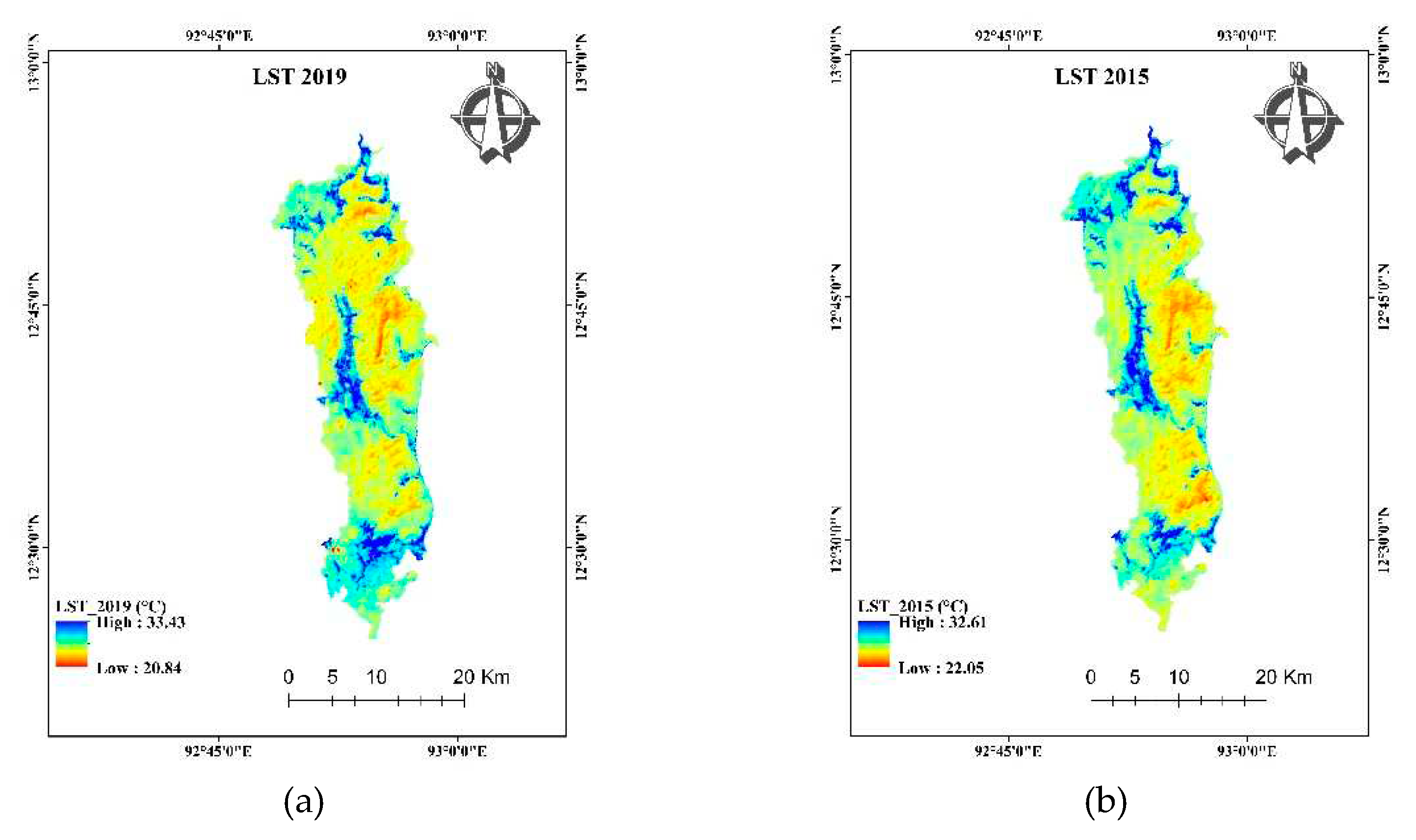
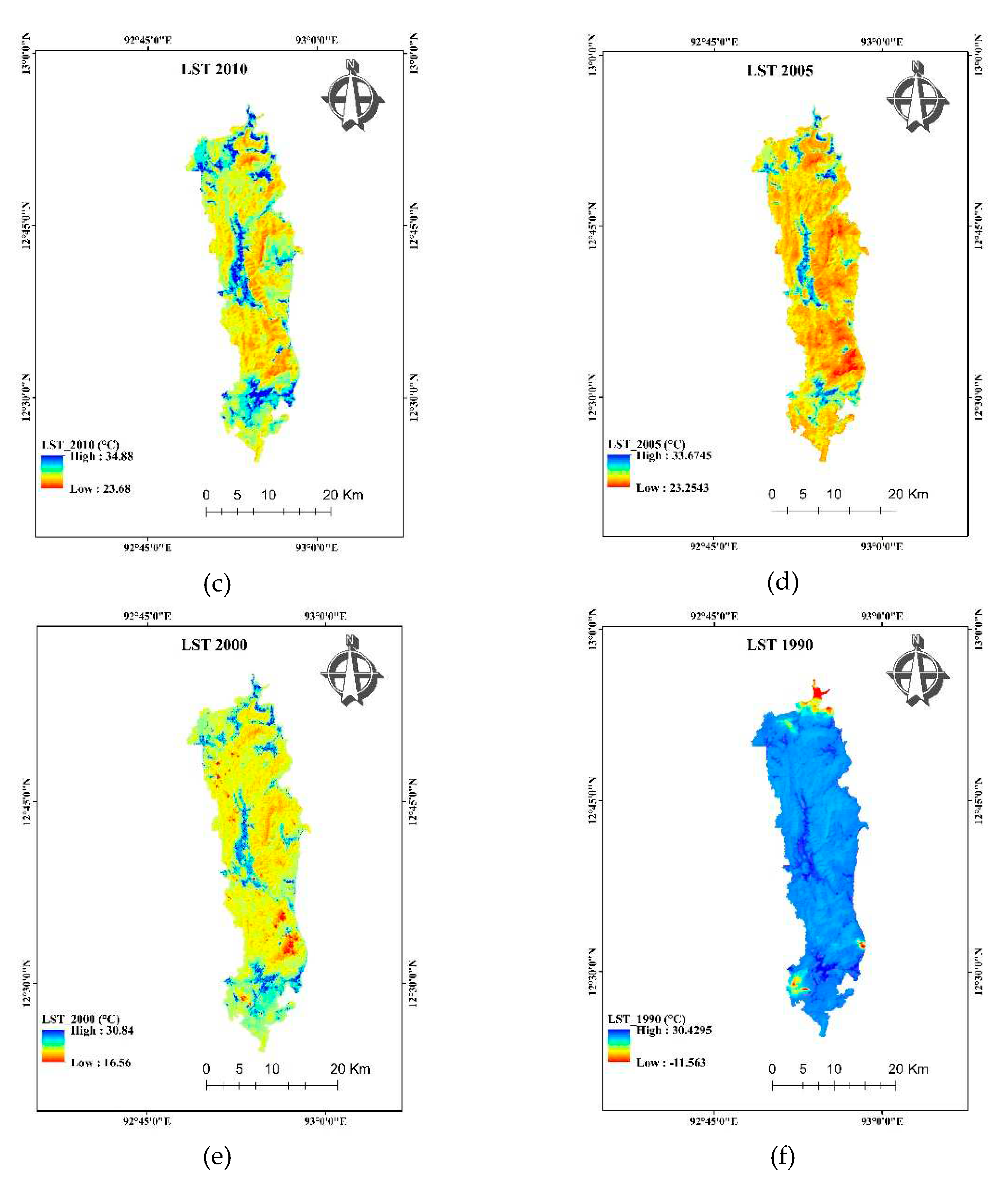
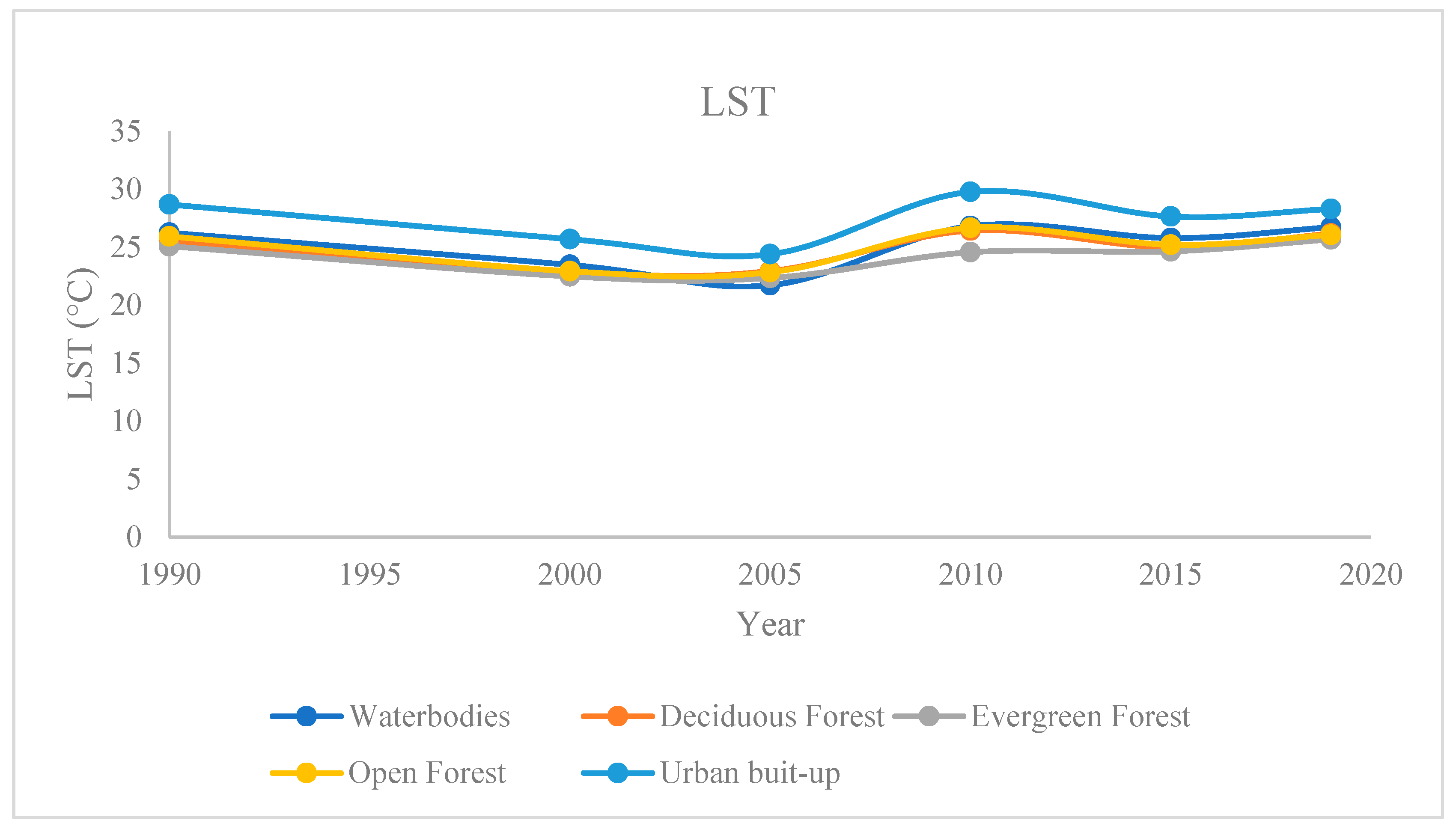
4.8. Land surface temperature (LST)
The land surface temperature of the region is shown in
Figure 12. Urban built-up contributed the highest to Land surface temperature. The constructed settlements, roads, and buildings contribute to LST in larger scale. As region is an island surrounded by sea, the average temperature does not change with the season. The temperature data of the region was calculated within a single season with a very small fluctuation in time. The contribution of land use and land cover class contribute differently to land surface temperature. The graph (
Figure 13) shows the decreasing order of contribution toward LST in urban built-up, waterbodies (except in 2005), Evergreen Forest remain lowest except in 2005. The Open Forest and Deciduous Forest shows the same contribution with some fluctuation in the year-wise trend.
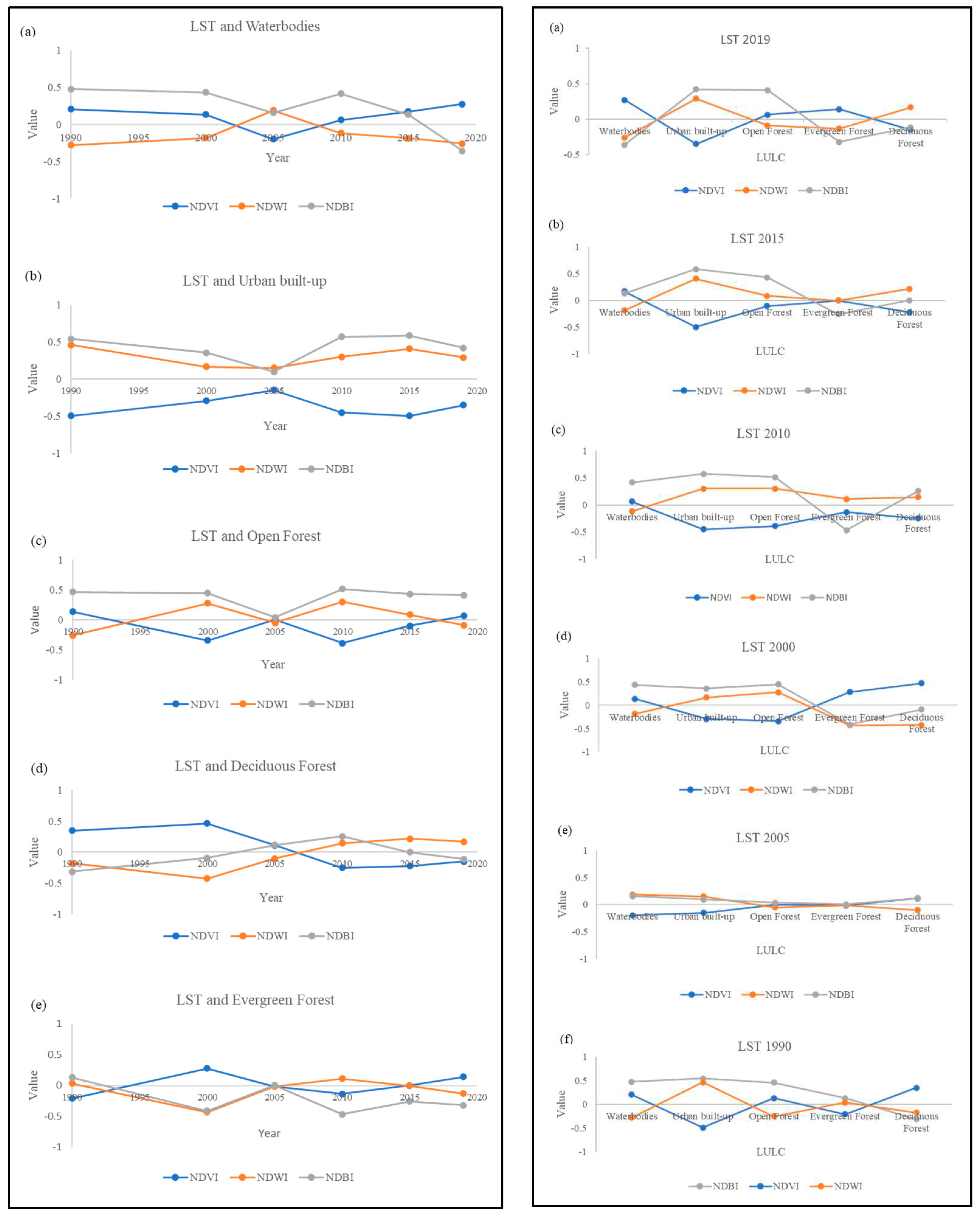
4.9. Relationship of Land Surface Temperature (LST) with water, vegetation, and urban built-up
The relationship of NDWI, NDVI, NDBI with LST in waterbodies, urban built-up, Open Forest, Deciduous Forest, Evergreen Forest was identified. The relationship was further analyzed on yearly basis. There is a fluctuation in the correlation of NDVI, NDWI and NDBI in different LULC classes. The high value of NDVI, NDWI and NDBI stands for vegetation, water bodies and bare land or built-up respectively (
Figure 14a). In correlation; values of LST-NDVI and LST-NDWI are inversely proportional to each other. NDBI showed a strong correlation with LST of urban built-up and Open Forest in all the years except 2005. NDBI of waterbodies shows a strong correlation in waterbodies in 1990, 2000, and 2010, that slightly low in 2005, 2015 and become negative in 2019 (
Figure 14b).
In the year-wise trend, the graph of NDVI and NDWI is the mirror image of each other in the correlation of LST in all the classes of the region. That means the higher the NDVI, the lower NDWI, and vice-versa.
5. Discussion
Support vector machine has given a significant accuracy despite the presence of a large number of variables in the data. Catastrophic events and climate change phenomena has changed in abundance of forest cover type and characteristics, water quality in the island region. Open Forest has showed maximum fluctuation with respect to its abundance. The relationship of LST with NDVI, NDWI, and NDBI showed the relative contribution of LULC class in rising the temperature of the region. The Land surface temperature was maximum contributed by urban built-up > Open Forest > Deciduous Forest > Evergreen Forest > water bodies. The Indices of LULC classes helped to identify the quality and variability of LULC classes in year 1990, 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, 2019 of same season showed interconversion of forest into each other as well as their characteristics. The unchanged pixel of forest cover showed the stability of subsurface hydrology that possibly linked to interconnected lineaments. It was found the NDWI and NDVI work to balance the fluctuation of change in temperature of the region. If there was a positive correlation between LST and NDVI then LST and NDWI showed a similar negative trend in that class. That further explained about forest region, higher NDVI means more healthy vegetation, and NDWI means canopy moisture; do behave like a mirror to each other in context to LST.
Author Contributions
The contribution of research article “Conceptualization, Pardeep Kumar and Saumitra Mukherjee.; methodology, Pardeep Kumar.; software, Pardeep Kumar.; validation, Saumitra Mukherjee and Pardeep Kumar.; formal analysis, Saumitra Mukherjee.; investigation, Pardeep Kumar; resources, Saumitra Mukherjee Pardeep Kumar; data curation, Pardeep Kumar; writing—Pardeep Kumar; writing—review and editing, Pardeep Kumar and Saumitra Mukherjee; visualization, Saumitra Mukherjee.; supervision, Saumitra Mukherjee. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Raw data will be available on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Keenan, R.J. Climate change impacts and adaptation in forest management: a review. Ann. For. Sci. 2015, 72, 145–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, R.J.; Wong, P.P.; Burkett, V.; Codignotto, J.; Hay, J.; McLean, R. ;... & Saito, Y. (2007). Coastal systems and low-lying areas.
- Thornes, J.E. (2002). IPCC, 2001: Climate change 2001: impacts, adaptation and vulnerability, Contribution of Working Group II to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, edited by JJ McCarthy, OF Canziani, NA Leary, DJ Dokken and KS White (eds). Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, and New York, USA, 2001. No. of pages: 1032. Price: £ 34.95, ISBN 0-521-01500-6 (paperback), ISBN 0-521-80768-9 (hardback).
- Change IP, O.C. (2014). Ipcc. Climate change.
- Klein, R.J.T.; Patt, A.G. Assessing vulnerability to global environmental change: Making research useful for adaptation decision making and policy; Earthscan: London, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- McClanahan, T.R.; Cinner, J. Adapting to a changing environment: Confronting the consequences of climate change; Oxford University Press: Oxford, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, N.A.; Marshall, P.A.; Tamelander, J.; Obura, D.; Malleret-King, D.; Cinner, J.E. A framework for social adaptation to climate change: Sustaining tropical coastal communities and industries; IUCN: Gland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wongbusarakum, S.; Loper, C. Indicators to assess community-level social vulnerability to climate change: An addendum to SocMon and SEM-Pasifika regional socioeconomic monitoring guideline; CRISP and IUCN: Gland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tagore, J.K.; Soosairaj, S.; Ramana, M.V.; Sanjappa, M.; Ganeshaiah, K.N. Status assessment of the Saddlepeak Dewflower (Murdannia saddlepeakensis Ramana & Nandikar: Commelinaceae): an endemic spiderwort plant of Andaman Islands, India. J. Threat. Taxa 2016, 8, 9643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, R.V.R. Andaman and Nicobar Islands: Development and Decentralization. Mittal Publications, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hajra, P.K.; Rao, P.S.N.; Mudgal, V. (Eds.) . Flora of Andaman and Nicobar Islands; Botanical Survey of India: Calcutta, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Curray, J.R.; Moore, D.G.; Lawver, L.A.; Emmel, F.J.; Raitt, R.W.; Henry, M.; Kieckhefer, R. (1979). Tectonics of the Andaman Sea and Burma: convergent margins.
- Sankaran, R.; Andrews, H.; Vaughan, A. The ground beneath the waves: post-tsunami impact assessment of wildlife and their habitats in India; Vol II. N: Wildlife Trust of India, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bandopadhyay, P.C.; Ghosh, B.; Carter, A. Natural resources. Geological Society London Memoirs. 2017; 47, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S. Land subsidence in middle Andaman: A case study. Hydrology Journal 1986, 13, 150–156. [Google Scholar]
- Myneni, R.B.; et al. The interpretation of spectral vegetation indexes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Rem. Sens. 1995, 33, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asrar, G.; Fuchs, M.; Kanemasu, E.T.; Hatfield, J.L. Estimating Absorbed Photosynthetic Radiation and Leaf Area Index from Spectral Reflectance in Wheat 1. Agron. J. 1984, 76, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, P.; Berry, J.; Collatz, G.; Field, C.; Hall, F. Canopy reflectance, photosynthesis, and transpiration. III. A reanalysis using improved leaf models and a new canopy integration scheme.. Remote. Sens. Environ. 1992, 42, 187–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, B.C.; Brown, J.F.; Vanderzee, D.; Loveland, T.R.; Merchant, J.W.; Ohlen, D.O. Measuring phenological variability from satellite imagery. J. Veg. Sci. 1994, 5, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vourlitis, G.L.; et al. Spatial variation in regional CO2 exchange for the Kuparuk River Basin, Alaska over the summer growing season. Glob. Change Biol. 2003, 9, 930–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiam, A.K. The causes and spatial pattern of land degradation risk in southern Mauritania using multitemporal AVHRR-NDVI imagery and field data. Land Degrad. Dev. 2002, 14, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, A.M.; Cridland, S.W.; Roderick, M.L. The use of time-integrated NOAA NDVI data and rainfall to assess landscape degradation in the arid shrubland of Western Australia. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2003, 85, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.R. A soil-adjusted vegetation index (SAVI). Remote Sens. Environ. 1988, 25, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asrar, G.; et al. Estimating absorbed photosynthetic radiation and leaf area index from spectral reflectance in wheat. Agricult. J. 1984, 76, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. International journal of remote sensing 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.C. NDWI—A normalized difference water index for remote sensing of vegetation liquid water from space. Remote sensing of environment 1996, 58, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.R.; et al. Overview of radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Gao, J.; Ni, S. Use of normalized difference built-up index in automatically mapping urban areas from TM imagery. International Journal of Remote Sensing 2003, 24, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Shi, P.; Xie, D.; Zhao, Y. Improving the normalized difference built-up index to map urban built-up areas using a semiautomatic segmentation approach. Remote Sensing Letters 2010, 2010, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukristiyanti, R.; Suharyadi Jatmiko, R.H. Evaluasi Indeks Urban pada citra Landsat Multitemporal dalam ekstraksi kepadatan bangunan. Jurnal Riset Geologi dan Pertambangan 2007, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, R.K.; Seto, K.C.; Schneider, A.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Wang, W. Climate response to rapid urban growth: evidence of a human-induced precipitation deficit. Journal of Climate 2007, 20, 2299–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.C.; Ambast, S.K. (2009). Water policy for Andaman & Nicobar Islands: A scientific perspective. CARI, Port Blair, 18.
- Du, C.; Ren, H.; Qin, Q.; Meng, J.; Zhao, S. A practical split-window algorithm for estimating land surface temperature from Landsat 8 data. Remote sensing 2015, 7, 647–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chander, G.; Markham, B.L.; Helder, D.L. Summary of current radiometric calibration coefficients for Landsat MSS, TM, ETM+, and EO-1 ALI sensors. Remote sensing of environment 2009, 113, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Location map of middle Andaman.
Figure 1.
Location map of middle Andaman.
Figure 2.
SVM classification of year (a) 2019, (b) 2015, (c) 2010, (d) 2005, (e) 2000, (f) 1990.
Figure 2.
SVM classification of year (a) 2019, (b) 2015, (c) 2010, (d) 2005, (e) 2000, (f) 1990.
Figure 3.
Percentage change of area in each class of classification.
Figure 3.
Percentage change of area in each class of classification.
Figure 4.
LULC change from one class to another class in 2015-2019, 2010-2015, 2005-2010, 2000-2005, 1990-2000.
Figure 4.
LULC change from one class to another class in 2015-2019, 2010-2015, 2005-2010, 2000-2005, 1990-2000.
Figure 5.
LULC unchanged pixels from one class to another class in 2015-2019, 2010-2015, 2005-2010, 2000-2005, 1990-2000.
Figure 5.
LULC unchanged pixels from one class to another class in 2015-2019, 2010-2015, 2005-2010, 2000-2005, 1990-2000.
Figure 6.
NDVI classification of the study area in of year (a) 2019, (b) 2015, (c) 2010, (d) 2005, (e) 2000, (f) 1990.
Figure 6.
NDVI classification of the study area in of year (a) 2019, (b) 2015, (c) 2010, (d) 2005, (e) 2000, (f) 1990.
Figure 7.
Average change in NDVI from 1990 to 2019 in waterbodies, Deciduous Forest, Evergreen Forest, Open Forest, and Urban built-up.
Figure 7.
Average change in NDVI from 1990 to 2019 in waterbodies, Deciduous Forest, Evergreen Forest, Open Forest, and Urban built-up.
Figure 8.
NDWI classification of the study area in of year (a) 2019, (b) 2015, (c) 2010, (d) 2005, (e) 2000, (f) 1990.
Figure 8.
NDWI classification of the study area in of year (a) 2019, (b) 2015, (c) 2010, (d) 2005, (e) 2000, (f) 1990.
Figure 9.
Average change in NDWI from 1990 to 2019 in Waterbodies, Deciduous Forest, Evergreen Forest, Open Forest, and Urban built-up.
Figure 9.
Average change in NDWI from 1990 to 2019 in Waterbodies, Deciduous Forest, Evergreen Forest, Open Forest, and Urban built-up.
Figure 12.
LST classification of the study area in of year (a) 2019, (b) 2015, (c) 2010, (d) 2005, (e) 2000, (f) 1990.
Figure 12.
LST classification of the study area in of year (a) 2019, (b) 2015, (c) 2010, (d) 2005, (e) 2000, (f) 1990.
Figure 13.
Average change in LST from 1990 to 2019 in waterbodies, Deciduous Forest, Evergreen Forest, Open Forest and Urban built-up.
Figure 13.
Average change in LST from 1990 to 2019 in waterbodies, Deciduous Forest, Evergreen Forest, Open Forest and Urban built-up.
Figure 14.
(a) The comparison of the correlation coefficient of LST with NDVI, NDWI, NDBI, in different classes of waterbodies, urban built-up, Open Forest, Evergreen Forest and Deciduous Forest respectively, (b) The yearly comparison of the correlation coefficient of LST with Waterbodies, Urban built-up, Open Forest, Evergreen Forest, Deciduous Forest.
Figure 14.
(a) The comparison of the correlation coefficient of LST with NDVI, NDWI, NDBI, in different classes of waterbodies, urban built-up, Open Forest, Evergreen Forest and Deciduous Forest respectively, (b) The yearly comparison of the correlation coefficient of LST with Waterbodies, Urban built-up, Open Forest, Evergreen Forest, Deciduous Forest.
Table 1.
The overall accuracy and kappa coefficient of the year 2019, 2015, 2010, 2005, 2000, 1990.
Table 1.
The overall accuracy and kappa coefficient of the year 2019, 2015, 2010, 2005, 2000, 1990.
| Year |
2019 |
2015 |
2010 |
2005 |
2000 |
1990 |
| Overall Accuracy |
85.9 |
93.33 |
91.22 |
94.64 |
90.66 |
90.66 |
| Kappa coefficient |
83.32 |
92.19 |
88.71 |
93.17 |
89.06 |
89.6 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).