1. Introduction
The development of edible films and coatings from polymers of renewable origin represents a promising strategy to tackle the unceasing usage of fossil sources for producing packaging materials, thus eventually avoiding unpleasant consequences at the environmental level [
1,
2,
3]. In this scenario, gelatin has been extensively regarded as a potential replacement for synthetic polymers due to its intrinsic features, namely biodegradability, biocompatibility, and good shielding ability against the penetration of gases, oils, and volatile compounds, as well as of UV light [
4,
5]. In addition, gelatin is recognized for its excellent film-forming characteristics and adhesiveness [
6,
7,
8]. Fish gelatin, in particular, has represented a valid choice to meet the requirements set by Kosher and Halal dietary laws [
9]. However, it has been pointed out that both moisture sensitivity and poor mechanical properties restrict the use of gelatin as food packaging material only to products with low/medium water activity [
10,
11].
In an attempt to improve the functional properties of gelatin-based films, researchers proposed a combination with other compounds able to compensate for the inherent drawbacks of gelatin. In this regard, it was shown that the incorporation of essential oils (EOs) in gelatin films had a positive effect on the water vapor barrier properties [2,12‒16], besides having well-known antimicrobial activity. For example, it has recently been proposed the use of CEO for the generation of active packaging films and coatings for fungal growth control on postharvest fruits [
17]. Similarly, cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) can be successfully used in combination with fish gelatin to yield nanocomposite structures with superior mechanical characteristics [18‒23].
Within the field of biopolymer films and coatings, cellulose from bacterial sources has raised a great deal of attention compared to its plant-based counterpart in the last few years due to two main reasons: first, bacterial cellulose (BC) shows a comparatively greater purity owing to the absence of lignin, hemicelluloses, organic compounds, and pectin [
24]; second, the higher degree of crystallinity found in BC than in plant cellulose straightforwardly facilitates its hydrolysis to nanocrystals (BCNCs) via a top-down technique, thus boosting processing yields [
18,
25].
In a previous study [
26], the effect of pH (3.5, and 5) on the properties of nanoemulsions from fish gelatin-bacterial cellulose nanocrystals containing cinnamon essential oil (CEO-GelA/BCNCs) was investigated, so as to serve the purpose of acting as natural controlled-release systems in the food sector (e.g., active packaging). To this end, specific parameters such as size, ζ-potential, morphology, and encapsulation efficiency of the achieved nanoemulsions were carefully assessed. It was concluded that the addition of gelatin within the tested formulations granted a full coverage of CEO nanodroplets, already surrounded by a web of BCNCs, which then translated into a greater emulsion stability throughout the investigated storage window (30 days at 42°C). A more recent study explored the functionality of CEO-GelA/BCNCs films, arising from nanoemulsions at pH 5, in terms of optical behavior, surface wettability, gas/vapor screening effect, and mechanical properties [
22]. Surprisingly, no effects on film transparency and haze were disclosed when applying CEO of increasing concentration during the main preparation step. On top of this, the barrier properties displayed by the obtained films seemed to shift the target towards the shelf-life extension of fresh products, both in the forms of coating or as the inner layer of the packaging system (i.e., the coating in direct contact with the food). Notwithstanding these interesting results, no information was retrieved as far as the effect of lower pH on film functionality is concerned, with the latter being of utmost importance to possibly widen the range of targeted applications in the food packaging sector.
Therefore, inspired by such a premise, this study was conceived to perform a deep characterization of cinnamon-based films made of gelatin and cellulose nanocrystals obtained using a previously optimized method [
22,
26], starting from emulsions at pH 3.5. To this purpose, several analyses were executed so as to put under the spotlight the optical (transmittance and haze), wetting, solubility, and mechanical properties of the final films, whereas FT-IR spectroscopy enabled collecting information on the degree of interactions established at the intra-/intermolecular level among single nanoemulsion components.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw materials and chemicals
In this work, we used type A gelatin (200 Bloom) extracted from fish skin as obtained (GelA, Kosher, and Halal certified) from Weishardt (Graulhet, France). As an active compound, cinnamon (
Cinnamomum zeylanicum) essential oil (CEO) extracted from bark was used. According to the supplier (Plant Therapy Essential Oils Corporate, Twin Falls, USA), its composition determined by GC-MS is as follows: E-cinnamaldehyde: 70.6%; E-cinnamyl acetate: 5.3%; β-caryophyllene: 5.1%; linalool: 4.2%; eugenol: 3.7%; 1,8-cineole + β-phellandrene: 1.2%. For the BC production,
Komagataeibacter sucrofermentans DSM 15973 (Leibniz Institute DSMZ-German Collection of Microorganisms and Cell Cultures, Braunschweig, Germany) was used in a static fermentation setup, according to the procedure described elsewhere [
27]. Sulfuric acid (99% v/v), ethanol (96% v/v), and dialysis tubing cellulose membrane (12 kDa, average flat width 43 mm) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich-Merck (Milano, Italy).
2.2. Emulsion and film preparation
BCNCs aqueous suspension and Pickering emulsions were prepared according to methods reported in a previous work [
26]. In particular, Pickering emulsions were obtained using different amounts of CEO (4.5 – 72 μL) added to 2.25 g of BCNCs suspension (pH 3.5) and applying a first emulsification using a UP200St ultrasonicator (Hielscher, Teltow, Germany) at 40 W for 5 min. Afterward, the BCNCs/CEO emulsion was mixed with a fish gelatin aqueous solution (10% w/w) to finally obtain CEO-GelA/BCNCs emulsions with BCNCs and gelatin concentrations of 0.06 % and 3 % (w/w), respectively. Eventually, six samples coded as T1G (0.03 % v/w CEO), T2G (0.06 % v/w CEO), T3G (0.12 % v/w CEO), T4G (0.24 % v/w CEO), T5G (0.36 % v/w CEO), and T6G (0.48 % v/w CEO) were obtained and systematically analyzed.
The preparation of the films took place by spreading 6.5 g of each emulsion (T1G – T6G) into Petri dishes (10 cm diameter), which were then stored at 23 ± 1 ºC and 50 ± 5 % RH for 48 h. The films were then peeled off from the Petri dishes and left to rest in a desiccator at 23 ± 1 ºC and 0% RH for one week to allow complete removal of water. For comparative purposes, control films were generated from CEO-free systems, namely GelA/BCNCs nanoemulsions.
2.3. Film characterization
2.3.1. Film thickness
Films thickness (δ, in μm) was measured by a digital micrometer with a precision of 1 μm (Mitutoyo, QuantuMike, Data output IP65, Serial No. 293-180, Mitutoyo Corp, Japan), at 10 different random locations both from the center and the edges of the film.
2.3.2. Optical properties
The total luminous transmittance (TT, in %) and haze (H, in %) of tested films were spectrophotometrically measured using a Lambda 650 high-performance spectrophotometer mounting a 150 mm diameter integrating sphere (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA) according to ASTM D1003 standard method [
28]. Accordingly, the sample has been placed at the entrance port of the sphere so that both diffused and specular transmitted light can be trapped.
2.3.3. Wetting properties
The wettability properties of the films’ surface were assessed by measuring the water contact angle (
θ, in °) and using an optical contact angle apparatus (OCA 15 Plus - Data Physics Instruments GmbH, Filderstadt, Germany) supported by a video measuring system with a CCD camera and digitizing adapter. Rectangular strips (5 cm
2) were mounted on a sample holder with parallel clamping jaws that allowed to flatten the surface of the films. Then, a small droplet (2.0 ± 0.5 µL) of Milli-Q water was dispensed (T = 23 ± 1 ºC, RH = 50 ± 5 %) according to the sessile drop procedure [
29]. The software SCA 20 (Data Physics Instruments GmbH, Filderstadt, Germany) was used for data acquisition and elaboration.
2.3.4. Mechanical Properties
Tensile strength (TS, in MPa), elongation at break (EAB, in %), and elastic modulus (E, in MPa) of film strips (6 cm in length, 2 cm in width) were determined using an Instron Universal Testing Machine (STM-20, Norwood, USA), and following the ASTM D882 standard [
30]. The initial separation between clamps fixing the sample and the cross-head speed was equal to 5 cm and 1.0 mm/s, respectively. For each sample, TS and EAB were calculated as shown in Equations (1) and (2), whereas E was calculated by a software-driven procedure relying on the “secant” method [
31].
where F
MAX (in N) is the maximum load, A is the cross-sectional area (in mm
2) of the samples, ∆L (in mm) is the elongation (i.e., the difference between the initial and final length of the specimen) of the film before rupture, and L
0 (in mm) is the initial length of the film.
2.3.5. Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) measurement
FT-IR analysis was carried out through an FT-IR Spectrum100 instrument (Perkin Elmer Inc., Waltham, MA), coupled with an Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR) accessory. All spectra were collected at a resolution of 4 cm−1 over a broad wavenumber range (800 – 4000 cm-1), each spectrum resulting from an average of 16 scans. Before each test, a background scan was launched to remove any spectral signal originating from carbon dioxide and moisture.
2.3.6. Water solubility (WS)
WS of films was evaluated using the method of Yao et al. [
32], with slight modifications. First, film specimens (2 × 2 cm
2) were immersed in beakers containing 10 mL distilled water and kept under gentle stirring (50 rpm) at 25°C for 24 h. The samples were then filtered using filter paper (Whatman No. 1), which was then placed in a drying oven (mod. UN 30, Memmert GmbH, Schwabach, Germany) at 105°C for 24 h until achieving a constant mass. The solubility in water of films was determined gravimetrically using an analytical balance (mod. ME204, Mettler Toledo, Novate Milanese, Italy) and calculated as follows (Equation (3)):
where W
i is the initial weight of film plus filter (in g), and W
j is the weight of dried sample residue plus filter (in g).
2.4. Statistical analysis
All the analyses were repeated at least three times unless otherwise specified. The mean values and standard deviations (SD) of the experimental data were calculated. Statistically significant differences among the averages were evaluated using a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey’s test (p ≤ 0.05) using the Minitab 18 statistical software (Coventry, UK).
3. Results & Discussion
3.1. Thickness measurement
The mean values of edible films’ thickness are displayed in
Table 1. The thickness of the films increased monotonically with the concentration of CEO until reaching a maximum value (~ 37 μm) for the T4G sample, after which a decrease for the formulations T5G and T6G was observed. An opposite trend was previously reported, inasmuch as no significant differences (p > 0.05) in terms of thickness between control film and CEO-based GelA/BCNCs films were highlighted [
22]. At the same time, the results of this study are supported by previous works, whereby the low chemical affinity between gelatin and CEO could have reduced the intermolecular interactions; at the same time, CEO has been demonstrated to act as a plasticizer [
26], thus leading to a less dense network with a high free volume, which can be deemed as the cause of thickness increments [
14]. Similar results were obtained by Jamróz et al. [
33] in a work on the thickening effect of Lavender essential oil when embedded in a film-forming starch/furcellaran/gelatin matrix, and by Kilinic et al. [
34], who showed that adding
Origanum onites L. essential oil into gelatin resulted in a significant increase of films’ thickness.
3.2. Optical properties
The behavior of CEO-GelA/BCNCs films hit with visible light is here expressed in terms of TT and H values (
Table 1). In line with previous findings [
22], no statistical differences (p > 0.05) were revealed among the samples in terms of total transmittance, which indicates that increasing CEO concentration did not lead to any significant change in the total transmitted light. In addition, haze analysis revealed that with increasing CEO loading in the film formulations, the ‘see-through’ capability of the films did not change significantly from the formulation T1G to T4G. However, a significant, though limited, increase in haze was instead observed for the highest CEO concentrations (0.36 % v/w and 0.48 % v/w) (
Table 1). This could be due to the increased scattering of the incident light due to the CEO droplets in the films [
22]. These results are in agreement with the findings of Tongnuanchan et al. [
2] and Yao et al. [
24], who reported a joint behavior for the fish skin gelatin films incorporated with citrus essential oil and gelatin-chitosan films supplemented with D-limonene, respectively.
However, according to the acceptability threshold of 3% in the haze to grant adequate display of the packaged food [
35], it can be said that all the films had acceptable optical properties for potential applications as a food packaging material. This can be even deduced from a visual inspection of the films (
Figure 1).
3.3. Wetting properties
Table 1 shows the mean water contact angles formed on the surface of gelatin-cellulose nanocrystals films containing different CEO concentrations.
θ has been widely adopted as a diagnostic parameter to discriminate between materials with a hydrophobic (
θ > 65°) or hydrophilic (
θ < 65°) surface features [
36,
37]. At the same time, in the design and development of engineered surfaces,
θ can be advantageously used to monitor any significant change in the surface properties of a given material ensuing from physicochemical treatments. In this work, we expected that the addition of CEO could have somehow led to an increase in the hydrophobic behavior of the CEO-based GelA/BCNCs films. Compared to the control films, the addition of CEO to GelA/BCNCs systems induced a significant (p < 0.05) increase in the
θ values, which is ascribable to the intrinsic hydrophobic nature of the essential oil. However, there was not a significant difference among CEO-loaded films, suggesting that CEO concentration cannot be considered a limiting factor in the hydrophobic behavior of the film surfaces within the investigated range (0.03 % v/w ‒ 0.48 % v/w). Interestingly, similar values of
θ when adding CEO to GelA/BCNCs systems produced at pH = 5 were detected [
22]. Overall, these results are in full agreement with previous findings demonstrating that the incorporation of oregano, mint, and D-limonene essential oils in gelatin/chitosan-based formulations increased the surface hydrophobicity of films thereof [
12,
13,
32].
3.4. Mechanical properties
As far as the mechanical properties are concerned, it is clearly seen (
Table 2) that GelA/BCNCs films exhibited higher TS and E compared to CEO-incorporated films, which instead have a higher elongation at rupture. From a practical point of view, these data indicate that pristine gelatin/cellulose nanocrystal films are stiffer and more brittle than the same films added with CEO, whereas the latter are more stretchable as demonstrated by the higher EAB. The impairment of TS and E, as well as the increase in EAB, pertaining to tested films upon CEO addition linearly correlated (averaged R
2 = 0.987) with the increase in thickness for T1G-T4G samples observed in
Table 1. The overall behavior of the films tested in this work is well-known in the literature and has been previously reported by other authors. In particular, the addition of CEO (as other plasticizing molecules) increased the free volume of the polymer network, presumably hindering not only gelatin-gelatin intermolecular interactions but also gelatin-BCNCs bonds (e.g., hydrogen bonding), which is reflected in the decrease of both TS and E [38‒40]. For the same reason, CEO improved film extensibility, due to its plasticizing effect that enhanced the mobility of gelatin molecules [
5,
40]. Similarly, Wu et al. [
38] observed that CEO nanoliposomes added to fish gelatin curbed the brittleness of generated films, at the expense of lower TS values. Analogous conclusions were drawn by Nunes et al. [
41] when incorporating lemon essential oils and green tea extracts in gelatin films. Interestingly, differences (though comparable) values of TS, EAB, and E are reported in the literature for films produced from either fish or bovine/porcine/chicken-based gelatins [2,5,12,42‒47]. This difference mainly depends on the variation in the aminoacidic content, which is known to mostly affect the gelatin strength. At the same time, a certain degree of variation has been reported for fish gelatin. In this other case, the temperature of the water where the fish lives explains the different values found in the literature [
40,
48,
49]. For instance, gelatin derived from cold-water fish has lower amino acid content compared to that extracted from warm-water fish [
50].
Finally, it must be noted that the superior mechanical properties of CEO-GelA/BCNCs films produced at pH = 5 [
22] compared to films prepared at pH = 3.5 (this work) can be explained considering the pH effect on the strength of fish gelatin-based films, as thoroughly described in the work of Etxabide et al. [
51]. More specifically, at a pH = 3.5 pH the net positive charge is much higher than at pH = 5, which would then promote a more intense electrostatic repulsion at the intermolecular level.
3.5. FTIR measurements
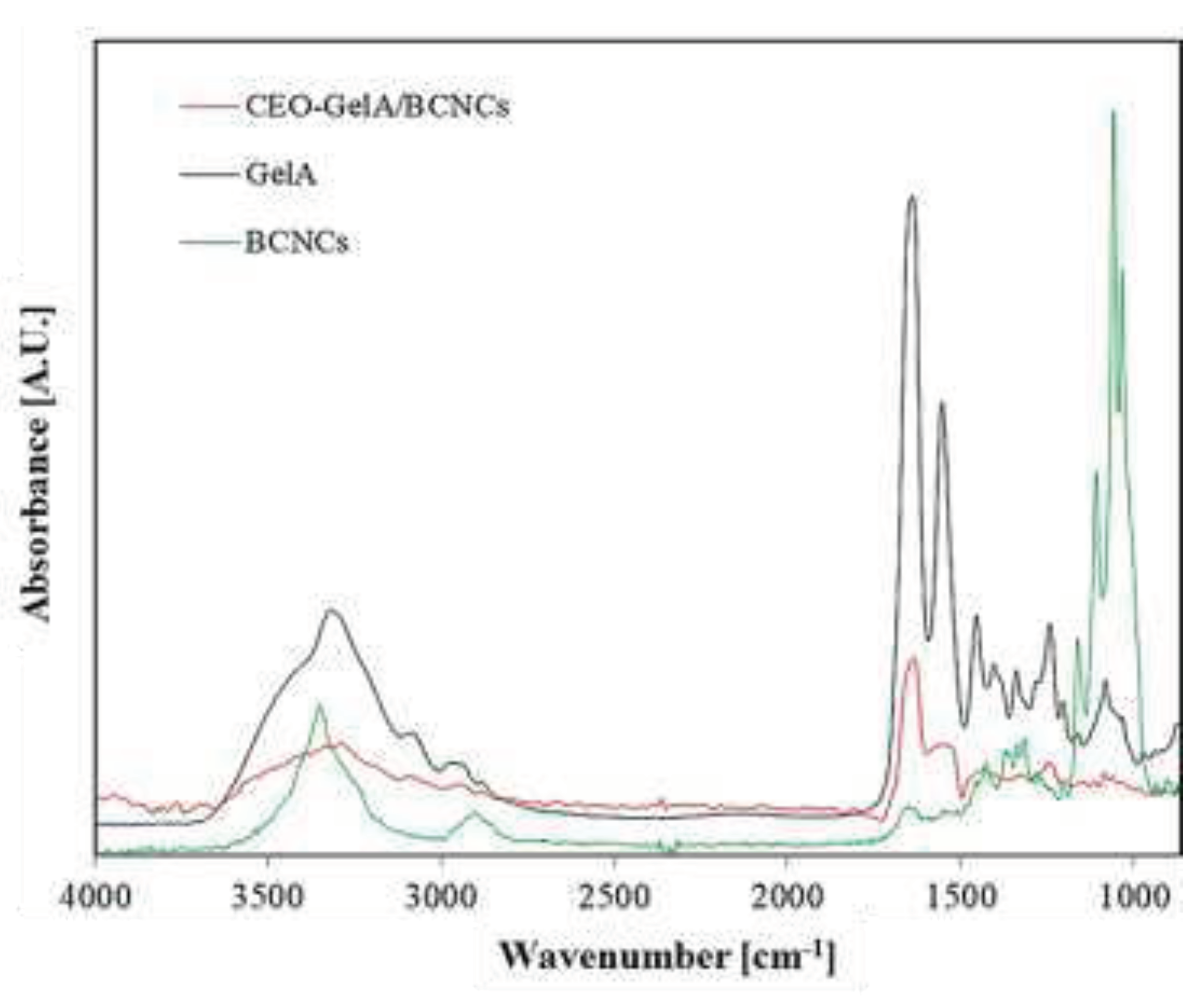
The FTIR spectra of neat fish gelatin, BCNCs, and CEO-based films thereof provided important insights into the occurrence of intermolecular interactions among the individual components (
Figure 2). At a first glance, the CEO-GelA/BCNCs spectrum reveals the characteristic fingerprint of the CEO dominated by several peaks within the 1800 – 600 cm
-1 range. According to Jeyaratnama et al. [
52], the peak at 1566 cm
-1 corresponds to the C=C skeletal vibration of the aromatic ring of CEO, whereas the peak at 1434 cm
-1 is assigned to the vibrational absorption of C–OH moieties. The peak at 1324 cm
-1 is attributed to –CH
2 swing in alkanes and =C–H in-plane bending absorption of the aromatic ring, with the symmetric expansion of C–O–C of aromatic acid ester and vibrational stretching of C–OH groups of phenolic components being assigned to the absorbance at 1244 cm
-1. In addition, the peak at 746 cm
-1 involves the vibrational absorption of =C-H in the benzene ring and, ultimately, the peak at 692 cm
-1 is attributed to the alkenes' vibration absorption. The clear observation of the above peaks suggests that CEO was properly embedded in the main polymer phase, that is, GelA/BCNCs emulsion, upon film preparation.
The characteristic peak of gelatin at 3316 cm-1 (amide A) is associated with the N-H stretching coupled with hydrogen bonding, while the peak centered at 3089 cm-1 (amide B) is assigned to the C-H stretching vibrations. In the amide I/III region (1650 – 1200 cm-1), the peak at 1638 cm-1 is related to the gelatin coil structure and is due to the C=O stretching vibration/hydrogen bonding coupled with COO‒ groups. The peaks at 1554 cm-1 and 1242 cm-1 are caused by bending and in-plane vibration of C-N/N-H groups of bound amides, respectively [14,53‒59].
Concerning the BCNCs spectrum (
Figure 2), the peak located at around 3350 cm
-1 (ʋ(OH) stretching vibrations) indicates that hydroxyl groups in BCNCs contributed to the formation of different types of inter- and intramolecular hydrogen bonds [
60,
61], whereas the peaks at 1316, 1162, and 1110 cm
-1 are prerogative of the crystalline cellulose (ɷs(CH
2) bending vibration), asymmetrical stretching of C-O-C glycosidic bonds, and stretching vibration of C‒O, respectively [
62]. At last, the small peaks at 1058 and 1035 cm
-1 are due to C-O stretching vibrations of aliphatic primary and secondary alcohol of cellulose [
63].
The addition of CEO within the GelA/BCNCs formulation caused both subtle shifts in wavenumbers as well as broadening/narrowing of the characteristic peaks of the main polymers. This is a clear evidence of the interactions that occurred between the characteristic groups of BCNCs and gelatin, thus indicating good molecular compatibility [
23] and possible conformational changes ensuing from these interactions [64‒66].
3.6. WS measurements
Water solubility values of GelA/BCNCs films, added or not with CEO, are summarized in
Table 1. The addition of the CEO remarkably led to a decrease in WS compared to the GelA/BCNCs formulation. In addition, the WS evolution was in an inverse relationship with the concentration of CEO, with a minimum value reached with the T6G sample (0.48 % v/w CEO). This effect has to be ascribed to the increased hydrophobicity of films upon CEO addition, which eventually yielded a lower water solubility. To date, different authors have investigated the influence of essential oils on the solubility of biopolymeric films in aqueous media. Nunes et al. [
41] reported that adding lemon nanoemulsion and green tea extract into gelatin films caused an increase in the water solubility, which was attributed to the establishment of interactions between the hydrophobic groups of oil and tea extract with those distributed along the gelatin chains. Gomez-Estaca et al. [
67] and Kavoosi et al. [
68] demonstrated that gelatin susceptibility to water solubilization dramatically improved upon clove essential oil and thyme nanoemulsion addition, respectively. Conversely, in full agreement with our results, Jamróz et al. [
33] and Kilinic et al. [
34] highlighted a great decrease in film water solubility after Lavender and
Origanum onites L. essential oils addition to gelatin films.
4. Conclusions
This work shed light on the functional (e.g., optical, surface, and mechanical) and structural properties of CEO-GelA/BCNCs edible films obtained from nanoemulsions prepared at low pH levels. In particular, despite the thickness increase following the CEO incorporation, no impairment of the total transmittance of the films was recorded, whereas a significant increase in haze was observed solely for the highest CEO concentration. In addition, the CEO allowed increasing the overall hydrophobic character of the films, which was reflected in a high repellency of the surface towards water and in a low degree of solubility in water. Finally, the addition of the essential oil allowed to reduce the inherent brittleness of Gel-A/BCNCs films, thus making them more suitable for potential food packaging applications. Pending future assessment of the CEO release profile associated with designed films, the outcome of this work suggests their potential utilization as films and coatings for those applications where it is of utmost importance to slow down the water loss process while keeping mechanical integrity and an adequate display of the product (e.g., fruits/vegetables, but also meat and seafood products).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.S.R., A.G., and S.F.; methodology, M.S.R., A.G., and S.F.; formal analysis, M.S.R., M.T., and S.F.; investigation, M.S.R., A.G., D.C., and S.F.; data curation, M.S.R., and S.F.; writing – original draft preparation, M.S.R.; writing – review & editing, A.G., M.T., D.C., and S.F.; visualization, M.S.R., D.C., and S.F.; supervision, A.G., and S.F.; project administration, A.G., and S.F.; funding acquisition, A.G., and S.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
A.G.: M.R.S., and M.T. are grateful to the Ministry of Science, Research and Technology of Iran and the University of Mohaghegh Ardabili, for financial support of this project. D.C. and S.F. wish to acknowledge the project “One Health Action Hub: University Task Force for the resilience of territorial ecosystems” supported by Università degli Studi di Milano –PSR 2021 -GSA -Linea 6.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Avena-Bustillos, R.; Chiou, B.S.; Olsen, C.; Bechtel, P.; Olson, D.; McHugh, T. Gelation, oxygen permeability, and mechanical properties of mammalian and fish gelatin films. Journal of food science 2011, 76, E519–E524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongnuanchan, P.; Benjakul, S.; Prodpran, T. Properties and antioxidant activity of fish skin gelatin film incorporated with citrus essential oils. Food chemistry 2012, 134, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echegaray, M.; Mondragon, G.; Loli, M.; González, A.; Peña-Rodriguez, C.; Arbelaiz, A. Physicochemical and mechanical properties of gelatin reinforced with nanocellulose and montmorillonite. Journal of Renewable Materials 2016, 4, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanmani, P.; Rhim, J.-W. Physical, mechanical and antimicrobial properties of gelatin based active nanocomposite films containing AgNPs and nanoclay. Food Hydrocolloids 2014, 35, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongnuanchan, P.; Benjakul, S.; Prodpran, T.; Pisuchpen, S.; Osako, K. Mechanical, thermal and heat sealing properties of fish skin gelatin film containing palm oil and basil essential oil with different surfactants. Food Hydrocolloids 2016, 56, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martucci, J.F.; Ruseckaite, R.A. Biodegradation of three-layer laminate films based on gelatin under indoor soil conditions. Polymer Degradation and Stability 2009, 94, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, C.; Guo, J.; Li, X.; Lin, W.; Li, D. Preparation and properties of dialdehyde carboxymethyl cellulose crosslinked gelatin edible films. Food hydrocolloids 2012, 27, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, C.; Mondragon, G.; Algar, I.; Mondragon, I.; Martucci, J.; Ruseckaite, R. Gelatin films: renewable resource for food packaging. Gelatin: production, applications and health implications. Nova Science Publishers, NY 2013, 1-15.
- Regenstein, J.; Chaudry, M. Kosher and halal issues pertaining to edible films and coatings. Protein-based films and coatings.(Ed. Aristippos Gennadios). CRC Press. NewYork 2002, 601-620.
- Pérez-Gago, M.B.; Krochta, J. Protein-based films and coatings. Edible coatings and films to improve food quality 2012, 13–77. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, S.F.; Rezaei, M.; Zandi, M.; Ghavi, F.F. Preparation and functional properties of fish gelatin–chitosan blend edible films. Food chemistry 2013, 136, 1490–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.F.; Rezaei, M.; Zandi, M.; Farahmandghavi, F. Development of bioactive fish gelatin/chitosan nanoparticles composite films with antimicrobial properties. Food chemistry 2016, 194, 1266–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scartazzini, L.; Tosati, J.; Cortez, D.; Rossi, M.; Flôres, S.; Hubinger, M.; Di Luccio, M.; Monteiro, A. Gelatin edible coatings with mint essential oil (Mentha arvensis): Film characterization and antifungal properties. Journal of Food Science and Technology 2019, 56, 4045–4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Sun, X.; Guo, X.; Ge, S.; Zhang, Q. Physicochemical properties, antimicrobial activity and oil release of fish gelatin films incorporated with cinnamon essential oil. Aquaculture and Fisheries 2017, 2, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, M.J.; Nasiraie, L.R.; Zomorrodi, S.; Jafarian, S. Development and characterization of novel active opopanax gum and gelatin bio-nanocomposite film containing zinc oxide nanoparticles and peppermint essential oil. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization 2023, 17, 1953–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, F.A.M.; Khoshkalampour, A.; Moghadam, F.A.M.; PourvatanDoust, S.; Naeijian, F.; Ghorbani, M. Preparation and physicochemical evaluation of casein/basil seed gum film integrated with guar gum/gelatin based nanogel containing lemon peel essential oil for active food packaging application. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2023, 224, 786–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadat Razavi, M.; Golmohammadi, A.; Nematollahzadeh, A.; Ghanbari, A.; Davari, M.; Carullo, D.; Farris, S. Production of Innovative essential oil-based emulsion coatings for fungal growth control on postharvest fruits. Foods 2022, 11, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.; Hatna, S. High performance edible nanocomposite films containing bacterial cellulose nanocrystals. Carbohydrate Polymers 2012, 87, 2031–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehnad, D.; Emam-Djomeh, Z.; Mirzaei, H.; Jafari, S.-M.; Dadashi, S. Optimization of physical and mechanical properties for chitosan–nanocellulose biocomposites. Carbohydrate Polymers 2014, 105, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, S.; Dufresne, A.; Md. Tahir, P.; Karimi, A.; Abdulkhani, A. Biodegradable starch-based composites: effect of micro and nanoreinforcements on composite properties. Journal of Materials Science 2014, 49, 4513–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondragon, G.; Peña-Rodriguez, C.; González, A.; Eceiza, A.; Arbelaiz, A. Bionanocomposites based on gelatin matrix and nanocellulose. European Polymer Journal 2015, 62, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, M.S.; Golmohammadi, A.; Nematollahzadeh, A.; Rovera, C.; Farris, S. Cinnamon essential oil encapsulated into a fish gelatin-bacterial cellulose nanocrystals complex and active films thereof. Food Biophysics 2022, 17, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taokaew, S.; Seetabhawang, S.; Siripong, P.; Phisalaphong, M. Biosynthesis and characterization of nanocellulose-gelatin films. Materials 2013, 6, 782–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; Pei, Q.; Wang, H. Macrofibers with high mechanical performance based on aligned bacterial cellulose nanofibers. ACS applied materials & interfaces 2017, 9, 20330–20339. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, K.-W.; Lin, H.-Y. Quality characteristics of chinese-style meatball containing bacterial cellulose (Nata). Journal of food science 2004, 69, SNQ107–SNQ111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, M.S.; Golmohammadi, A.; Nematollahzadeh, A.; Fiori, F.; Rovera, C.; Farris, S. Preparation of cinnamon essential oil emulsion by bacterial cellulose nanocrystals and fish gelatin. Food Hydrocolloids 2020, 109, 106111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovera, C. , Ghaani, M., Santo, N., Trabattoni, S., Olsson, R. T., Romano, D., Farris, S. Enzymatic hydrolysis in the green production of bacterial cellulose nanocrystals. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 2018, 6, 7725–7734. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM. Standard Test Method for Haze and Luminous Transmittance of Transparent Plastics. Designation D 1003-00. American Society for Testing and Materials. Philadelphia, PA.
- Rovera, C.; Türe, H.; Hedenqvist, M.S.; Farris, S. Water vapor barrier properties of wheat gluten/silica hybrid coatings on paperboard for food packaging applications. Food Packaging and Shelf Life 2020, 26, 100561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM. Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Thin Plastic Sheeting. Designation D 882-18. American Society for Testing and Materials. Philadelphia, PA.
- Cozzolino, C.A.; Campanella, G.; Türe, H.; Olsson, R.T.; Farris, S. Microfibrillated cellulose and borax as mechanical, O2-barrier, and surface-modulating agents of pullulan biocomposite coatings on BOPP. Carbohydrate polymers 2016, 143, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Ding, D.; Shao, H.; Peng, Q.; Huang, Y. Antibacterial activity and physical properties of fish gelatin-chitosan edible films supplemented with D-Limonene. International Journal of Polymer Science 2017, 2017, 1837171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamróz, E.; Konieczna-Molenda, A.; Para, A. Ternary potato starch-furcellaran-gelatin film–a new generation of biodegradable foils. Polimery 2017, 62, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilinc, D.; Ocak, B.; Özdestan-Ocak, Ö. Preparation, characterization and antioxidant properties of gelatin films incorporated with Origanum onites L. essential oil. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization 2021, 15, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unalan, I.U.; Wan, C.; Figiel, Ł.; Olsson, R.T.; Trabattoni, S.; Farris, S. Exceptional oxygen barrier performance of pullulan nanocomposites with ultra-low loading of graphene oxide. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 275703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.-F.; Huang, Z.; Yuan, X.-Y.; Wang, X.-Y.; Li, M. Structure and properties of carboxymethyl cellulose/soy protein isolate blend edible films crosslinked by Maillard reactions. Carbohydrate polymers 2010, 79, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogler, E.A. Structure and reactivity of water at biomaterial surfaces. Advances in colloid and interface science 1998, 74, 69–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, H.; Ge, S.; Wang, S.; Qin, Z.; Chen, L.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Q. The preparation, characterization, antimicrobial stability and in vitro release evaluation of fish gelatin films incorporated with cinnamon essential oil nanoliposomes. Food Hydrocolloids 2015, 43, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.; Valdés, A.; Beltran, A.; Garrigós, M.C. Gelatin-based films and coatings for food packaging applications. Coatings 2016, 6, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, N.S.; Sarbon, N.M. Physical and mechanical characteristics of gelatin-based films as a potential food packaging material: a review. Membranes 2022, 12, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, J.C.; Melo, P.T.S.; Lorevice, M.V.; Aouada, F.A.; de Moura, M.R. Effect of green tea extract on gelatin-based films incorporated with lemon essential oil. Journal of Food Science and Technology 2021, 58, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpi, N.; Hardianti, E. Preparation and characterization of biodegradable film based on skin and bone fish gelatin. In Proceedings of IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; p. 012050.
- Atmaka, W.; Yudhistira, B.; Putro, M. Characteristic study of chitosan addition in Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) bone based gelatin film. In Proceedings of IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; p. 012028.
- Jiang, M.; Liu, S.; Du, X.; Wang, Y. Physical properties and internal microstructures of films made from catfish skin gelatin and triacetin mixtures. Food hydrocolloids 2010, 24, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jridi, M.; Abdelhedi, O.; Salem, A.; Kechaou, H.; Nasri, M.; Menchari, Y. Physicochemical, antioxidant and antibacterial properties of fish gelatin-based edible films enriched with orange peel pectin: Wrapping application. Food Hydrocolloids 2020, 103, 105688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Yang, H.-J.; Song, K.B. Characterization of a starfish gelatin film containing vanillin and its application in the packaging of crab stick. Food Science and Biotechnology 2016, 25, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suderman, N.; Isa, M.; Sarbon, N. Characterization on the mechanical and physical properties of chicken skin gelatin films in comparison to mammalian gelatin films. Proceedings of IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; p. 012033.
- Sarbon, N.M.; Badii, F.; Howell, N.K. Preparation and characterisation of chicken skin gelatin as an alternative to mammalian gelatin. Food hydrocolloids 2013, 30, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur Hanani, Z.; Roos, Y.; Kerry, J. Fourier transform ınfrared (FTIR) spectroscopic analysis of biodegradable gelatin films immersed in water. 11th Int Congr Eng Food 2011, 5, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ratnasari, I.; Yuwono, S.; Nusyam, H.; Widjanarko, S. Extraction and characterization of gelatin from different fresh water fishes as alternative sources of gelatin. International Food Research Journal 2013, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Etxabide, A.; Leceta, I.; Cabezudo, S.; Guerrero, P.; de la Caba, K. Sustainable fish gelatin films: From food processing waste to compost. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 2016, 4, 4626–4634. [Google Scholar]
- Jeyaratnam, N.; Nour, A.H.; Kanthasamy, R.; Nour, A.H.; Yuvaraj, A.; Akindoyo, J.O. Essential oil from Cinnamomum cassia bark through hydrodistillation and advanced microwave assisted hydrodistillation. Industrial Crops and Products 2016, 92, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanani, Z.N.; Roos, Y.H.; Kerry, J.P. Use and application of gelatin as potential biodegradable packaging materials for food products. International journal of biological macromolecules 2014, 71, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, H.; De Leo, R.; Bedin, E.; Pfeifer, F.; Siesler, H.W.; Pulvirenti, A. Comparative analysis of blend and bilayer films based on chitosan and gelatin enriched with LAE (lauroyl arginate ethyl) with antimicrobial activity for food packaging applications. Food Packaging and Shelf Life 2019, 19, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Rath, P.; Kumar, A.S.H. Chitosan from shrimp shell (Crangon crangon) and fish scales (Labeorohita): Extraction and characterization Suneeta. African Journal of Biotechnology 2016, 15, 1258–1268. [Google Scholar]
- Hoque, M.S.; Benjakul, S.; Prodpran, T. Effect of heat treatment of film-forming solution on the properties of film from cuttlefish (Sepia pharaonis) skin gelatin. Journal of Food Engineering 2010, 96, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergo, P.; Sobral, P.J.d.A. Effects of plasticizer on physical properties of pigskin gelatin films. Food Hydrocolloids 2007, 21, 1285–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamili, S.; Sadeghi, H.; Rezayat, M.; Attar, H.; Kaymaram, F. Extraction and evaluation of gelatin from yellow fin tuna (Thunnus albacares) skin and prospect as an alternative to mammalian gelatin. Iranian Journal of Fisheries Sciences 2019, 18, 903–914. [Google Scholar]
- Das, M.P.; Suguna, P.; Prasad, K.; Vijaylakshmi, J.; Renuka, M. Extraction and characterization of gelatin: a functional biopolymer. International Journal Of Pharmacy And Pharmaceutical Sciences 2017, 9, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, K.; Catchmark, J.M. The influences of added polysaccharides on the properties of bacterial crystalline nanocellulose. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 15144–15158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, N.F.; Feitosa, J.P.A.; da Gama, F.M.P.; Morais, J.P.S.; Andrade, F.K.; de Souza, M.d.S.M.; de Freitas Rosa, M. Bacterial cellulose nanocrystals produced under different hydrolysis conditions: Properties and morphological features. Carbohydrate polymers 2017, 155, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, H.L.S.; Gonçalves, C.; Cerqueira, M.Â.; do Nascimento, E.S.; Gama, M.F.; Rosa, M.F.; Borges, M.d.F.; Pastrana, L.M.; Brígida, A.I.S. Bacterial cellulose nanofiber-based films incorporating gelatin hydrolysate from tilapia skin: production, characterization and cytotoxicity assessment. Cellulose 2018, 25, 6011–6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronova, M.I.; Surov, O.V.; Guseinov, S.S.; Barannikov, V.P.; Zakharov, A.G. Thermal stability of polyvinyl alcohol/nanocrystalline cellulose composites. Carbohydrate polymers 2015, 130, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Núñez-Flores, R.; Giménez, B.; Fernández-Martín, F.; López-Caballero, M.; Montero, M.; Gómez-Guillén, M. Physical and functional characterization of active fish gelatin films incorporated with lignin. Food Hydrocolloids 2013, 30, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.M.; Men de Sá Filho, M.S.; Caceres, C.A.; Rosa, M.F.; Morais, J.P.S.; Pinto, A.M.; Azeredo, H.M. Fish gelatin films as affected by cellulose whiskers and sonication. Food Hydrocolloids 2014, 41, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazón, P.; Velazquez, G.; Ramírez, J.A.; Vázquez, M. Polysaccharide-based films and coatings for food packaging: A review. Food Hydrocolloids 2017, 68, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Estaca, J.; De Lacey, A.L.; López-Caballero, M.; Gómez-Guillén, M.; Montero, P. Biodegradable gelatin–chitosan films incorporated with essential oils as antimicrobial agents for fish preservation. Food microbiology 2010, 27, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavoosi, G.; Rahmatollahi, A.; Dadfar, S.M.M.; Purfard, A.M. Effects of essential oil on the water binding capacity, physico-mechanical properties, antioxidant and antibacterial activity of gelatin films. LWT-Food Science and Technology 2014, 57, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).