Submitted:
28 June 2023
Posted:
29 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1. Pathogenesis of Fibrosis
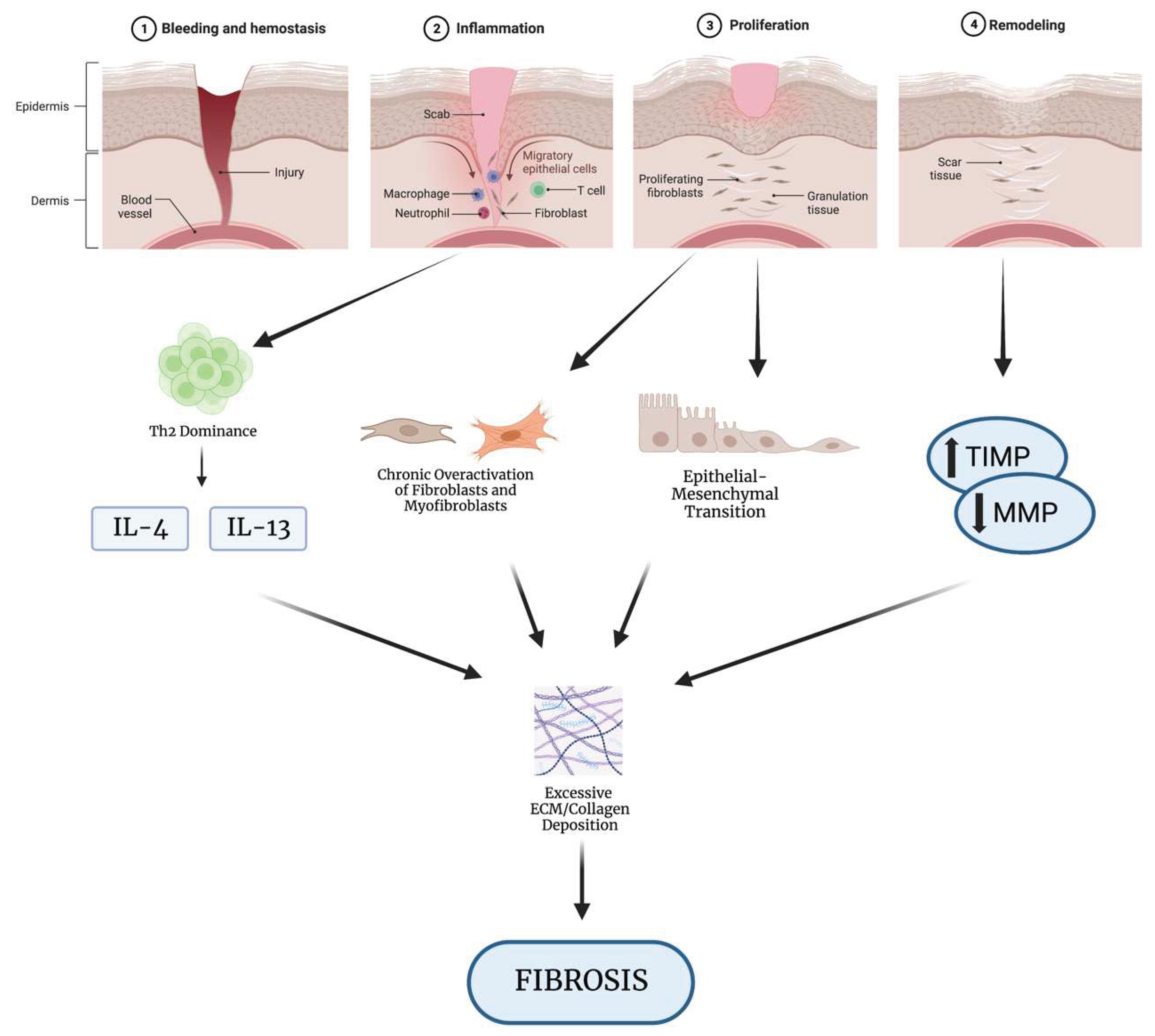
1.1. Overview of Wound Healing
1.2. How Dysregulation of Wound Healing Leads to Fibrosis
2. Organ-Specific Fibrosis
2.1. Pulmonary Fibrosis
2.2. Hepatic Fibrosis
2.3. Cardiac Fibrosis
3. Existing Fibrosis Treatments
3.1. Antifibrotic Agents
3.2. Antifibrotic Drugs: Nintedanib and Pirfenidone
4. Novel Anti-fibrotic Therapies
4.1. Antifibrotic Role of BMP7
4.3. Relaxin
4.4. Reprogramming as a Treatment for Fibrosis
5. Future Direction and Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thannickal VJ, Zhou Y, Gaggar A, Duncan SR (2014) Fibrosis: ultimate and proximate causes. Journal of Clinical Investigation 124:4673–4677. [CrossRef]
- Wynn T (2008) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of fibrosis. J Pathol 214:199–210. [CrossRef]
- Henderson NC, Rieder F, Wynn TA (2020) Fibrosis: from mechanisms to medicines. Nature 587:555–566. [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee A, Epperly Mw, Fisher R, Hou W, Shields D, Wang H, Greenberger Js, Ortiz La (2021) Silica Induced Lung Fibrosis Is Associated With Senescence, Fgr, and Recruitment of Bone Marrow Monocyte/Macrophages. In Vivo (Brooklyn) 35:3053–3066. [CrossRef]
- Weiskirchen R, Weiskirchen S, Tacke F (2019) Organ and tissue fibrosis: Molecular signals, cellular mechanisms and translational implications. Mol Aspects Med 65:2–15. [CrossRef]
- Wynn TA, Ramalingam TR (2012) Mechanisms of fibrosis: therapeutic translation for fibrotic disease. Nat Med 18:1028–40. [CrossRef]
- Jun J-I, Lau LF (2018) Resolution of organ fibrosis. J Clin Invest 128:97–107. [CrossRef]
- Eckes B, Eming SA (2017) Tissue fibrosis: a pathomechanistically unresolved challenge and scary clinical problem. Exp Dermatol 26:135–136. [CrossRef]
- Shinde A, V. , Humeres C, Frangogiannis NG (2017) The role of α-smooth muscle actin in fibroblast-mediated matrix contraction and remodeling. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease 1863:298–309. [CrossRef]
- Wynn TA (2007) Common and unique mechanisms regulate fibrosis in various fibroproliferative diseases. Journal of Clinical Investigation 117:524–529. [CrossRef]
- Broughton G, Janis JE, Attinger CE (2006) The Basic Science of Wound Healing. Plast Reconstr Surg 117:12S-34S. [CrossRef]
- Heng MCY (2011) Wound healing in adult skin: aiming for perfect regeneration. Int J Dermatol 50:1058–1066. [CrossRef]
- Laurens N, Koolwijk P, De Maat Mpm (2006) Fibrin structure and wound healing. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis 4:932–939. [CrossRef]
- Yun S-H, Sim E-H, Goh R-Y, Park J-I, Han J-Y (2016) Platelet Activation: The Mechanisms and Potential Biomarkers. Biomed Res Int 2016:1–5. [CrossRef]
- Wang P-H, Huang B-S, Horng H-C, Yeh C-C, Chen Y-J (2018) Wound healing. Journal of the Chinese Medical Association 81:94–101. [CrossRef]
- Parks WC, Wilson CL, López-Boado YS (2004) Matrix metalloproteinases as modulators of inflammation and innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 4:617–29. [CrossRef]
- Kim SY, Nair MG (2019) Macrophages in wound healing: activation and plasticity. Immunol Cell Biol 97:258–267. [CrossRef]
- Gantwerker EA, Hom DB (2011) Skin: Histology and Physiology of Wound Healing. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am 19:441–453. [CrossRef]
- Li J, Tan J, Martino MM, Lui KO (2018) Regulatory T-Cells: Potential Regulator of Tissue Repair and Regeneration. Front Immunol 9:. [CrossRef]
- Short WD, Wang X, Keswani SG (2022) The Role of T Lymphocytes in Cutaneous Scarring. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle) 11:121–131. [CrossRef]
- Wynn TA (2004) Fibrotic disease and the TH1/TH2 paradigm. Nat Rev Immunol 4:583–594. [CrossRef]
- Reinke JM, Sorg H (2012) Wound Repair and Regeneration. European Surgical Research 49:35–43. [CrossRef]
- Hinz B (2007) Formation and Function of the Myofibroblast during Tissue Repair. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 127:526–537. [CrossRef]
- Barker TH (2011) The role of ECM proteins and protein fragments in guiding cell behavior in regenerative medicine. Biomaterials 32:4211–4214. [CrossRef]
- Kalluri R, Weinberg RA (2009) The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Journal of Clinical Investigation 119:1420–1428. [CrossRef]
- Diller RB, Tabor AJ (2022) The Role of the Extracellular Matrix (ECM) in Wound Healing: A Review. Biomimetics 7:87. [CrossRef]
- Tonnesen MG, Feng X, Clark RAF (2000) Angiogenesis in Wound Healing. Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings 5:40–46. [CrossRef]
- Rousselle P, Braye F, Dayan G (2019) Re-epithelialization of adult skin wounds: Cellular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 146:344–365. [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez AC de O, Costa TF, Andrade Z de A, Medrado ARAP (2016) Wound healing - A literature review. An Bras Dermatol 91:614–620. [CrossRef]
- Caley MP, Martins VLC, O’Toole EA (2015) Metalloproteinases and Wound Healing. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle) 4:225–234. [CrossRef]
- Kandhwal M, Behl T, Singh S, Sharma N, Arora S, Bhatia S, Al-Harrasi A, Sachdeva M, Bungau S (2022) Role of matrix metalloproteinase in wound healing. Am J Transl Res 14:4391–4405.
- DiPietro LA, Polverini PJ (1993) Role of the macrophage in the positive and negative regulation of wound neovascularization.
- Landén NX, Li D, Ståhle M (2016) Transition from inflammation to proliferation: a critical step during wound healing. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 73:3861–3885. [CrossRef]
- Xue M, Jackson CJ (2015) Extracellular Matrix Reorganization During Wound Healing and Its Impact on Abnormal Scarring. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle) 4:119–136. [CrossRef]
- El Ayadi A, Jay JW, Prasai A (2020) Current Approaches Targeting the Wound Healing Phases to Attenuate Fibrosis and Scarring. Int J Mol Sci 21:. [CrossRef]
- Jones RE, Foster DS, Hu MS, Longaker MT (2019) Wound healing and fibrosis: current stem cell therapies. Transfusion (Paris) 59:884–892. [CrossRef]
- Koh TJ, DiPietro LA (2011) Inflammation and wound healing: the role of the macrophage. Expert Rev Mol Med 13:e23. [CrossRef]
- Yussof SJMohd, Omar E, Pai DR, Sood S (2012) Cellular events and biomarkers of wound healing. Indian Journal of Plastic Surgery 45:220–228. [CrossRef]
- Diegelmann RF (2004) Wound healing: an overview of acute, fibrotic and delayed healing. Frontiers in Bioscience 9:283. [CrossRef]
- Gause WC, Wynn TA, Allen JE (2013) Type 2 immunity and wound healing: evolutionary refinement of adaptive immunity by helminths. Nat Rev Immunol 13:607–614. [CrossRef]
- Gieseck RL, Wilson MS, Wynn TA (2018) Type 2 immunity in tissue repair and fibrosis. Nat Rev Immunol 18:62–76. [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann KF, Cheever AW, Wynn TA (2000) IL-10 and the Dangers of Immune Polarization: Excessive Type 1 and Type 2 Cytokine Responses Induce Distinct Forms of Lethal Immunopathology in Murine Schistosomiasis. The Journal of Immunology 164:6406–6416. [CrossRef]
- Kendall RT, Feghali-Bostwick CA (2014) Fibroblasts in fibrosis: novel roles and mediators. Front Pharmacol 5:. [CrossRef]
- Gomes RN, Manuel F, Nascimento DS (2021) The bright side of fibroblasts: molecular signature and regenerative cues in major organs. NPJ Regen Med 6:43. [CrossRef]
- Desmouliere A, Darby IA, Laverdet B, Bonté F (2014) Fibroblasts and myofibroblasts in wound healing. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 301. [CrossRef]
- Klingberg F, Hinz B, White ES (2013) The myofibroblast matrix: implications for tissue repair and fibrosis. J Pathol 229:298–309. [CrossRef]
- Giannandrea M, Parks WC (2014) Diverse functions of matrix metalloproteinases during fibrosis. Dis Model Mech 7:193–203. [CrossRef]
- Rohani MG, Parks WC (2015) Matrix remodeling by MMPs during wound repair. Matrix Biology 44–46:113–121. [CrossRef]
- Arpino V, Brock M, Gill SE (2015) The role of TIMPs in regulation of extracellular matrix proteolysis. Matrix Biology 44–46:247–254. [CrossRef]
- Chuliá-Peris L, Carreres-Rey C, Gabasa M, Alcaraz J, Carretero J, Pereda J (2022) Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors in Pulmonary Fibrosis: EMMPRIN/CD147 Comes into Play. Int J Mol Sci 23:6894. [CrossRef]
- Liu L, Sun Q, Davis F, Mao J, Zhao H, Ma D (2022) Epithelial–mesenchymal transition in organ fibrosis development: current understanding and treatment strategies. Burns Trauma 10:. [CrossRef]
- Grande MT, López-Novoa JM (2009) Fibroblast activation and myofibroblast generation in obstructive nephropathy. Nat Rev Nephrol 5:319–328. [CrossRef]
- Rout-Pitt N, Farrow N, Parsons D, Donnelley M (2018) Epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT): a universal process in lung diseases with implications for cystic fibrosis pathophysiology. Respir Res 19:136. [CrossRef]
- Di Gregorio J, Robuffo I, Spalletta S, Giambuzzi G, De Iuliis V, Toniato E, Martinotti S, Conti P, Flati V (2020) The Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition as a Possible Therapeutic Target in Fibrotic Disorders. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:. [CrossRef]
- Savin IA, Zenkova MA, Sen’kova A V. (2022) Pulmonary Fibrosis as a Result of Acute Lung Inflammation: Molecular Mechanisms, Relevant In Vivo Models, Prognostic and Therapeutic Approaches. Int J Mol Sci 23:14959. [CrossRef]
- Noble PW, Barkauskas CE, Jiang D (2012) Pulmonary fibrosis: patterns and perpetrators. Journal of Clinical Investigation 122:2756–2762. [CrossRef]
- Vij R, Strek ME (2013) Diagnosis and Treatment of Connective Tissue Disease-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. Chest 143:814–824. [CrossRef]
- Harari S, Caminati A (2010) IPF: new insight on pathogenesis and treatment. Allergy 65:537–553. [CrossRef]
- Antoniou KM, Margaritopoulos GA, Tomassetti S, Bonella F, Costabel U, Poletti V (2014) Interstitial lung disease. European Respiratory Review 23:40–54. [CrossRef]
- Kreuter M, Müller-Ladner U, Costabel U, Jonigk D, Heußel CP (2021) The Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Fibrosis. Dtsch Arztebl Int. [CrossRef]
- Shao T, Shi X, Yang S, Zhang W, Li X, Shu J, Alqalyoobi S, Zeki AA, Leung PS, Shuai Z (2021) Interstitial Lung Disease in Connective Tissue Disease: A Common Lesion With Heterogeneous Mechanisms and Treatment Considerations. Front Immunol 12:. [CrossRef]
- Wilson MS, Wynn TA (2009) Pulmonary fibrosis: pathogenesis, etiology and regulation. Mucosal Immunol 2:103–121. [CrossRef]
- Selman M, King TE, Pardo A (2001) Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Prevailing and Evolving Hypotheses about Its Pathogenesis and Implications for Therapy. Ann Intern Med 134:136. [CrossRef]
- Gifford AH, Matsuoka M, Ghoda LY, Homer RJ, Enelow RI (2012) Chronic inflammation and lung fibrosis: pleotropic syndromes but limited distinct phenotypes. Mucosal Immunol 5:480–484. [CrossRef]
- Bringardner BD, Baran CP, Eubank TD, Marsh ClayB (2008) The Role of Inflammation in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Antioxid Redox Signal 10:287–302. [CrossRef]
- Bataller R, Brenner DA (2005) Liver fibrosis. Journal of Clinical Investigation 115:209–218. [CrossRef]
- Han H, Desert R, Das S, Song Z, Athavale D, Ge X, Nieto N (2020) Danger signals in liver injury and restoration of homeostasis. J Hepatol 73:933–951. [CrossRef]
- Zhang C-Y, Yuan W-G, He P, Lei J-H, Wang C-X (2016) Liver fibrosis and hepatic stellate cells: Etiology, pathological hallmarks and therapeutic targets. World J Gastroenterol 22:10512. [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann C, Djerir NEH, Danckaert A, Fernandes J, Roux P, Charrueau C, Lachagès A-M, Charlotte F, Brocheriou I, Clément K, Aron-Wisnewsky J, Foufelle F, Ratziu V, Hainque B, Bonnefont-Rousselot D, Bigey P, Escriou V (2020) Hepatic stellate cell hypertrophy is associated with metabolic liver fibrosis. Sci Rep 10:3850. [CrossRef]
- Seki E, Schwabe RF (2015) Hepatic inflammation and fibrosis: Functional links and key pathways. Hepatology 61:1066–1079. [CrossRef]
- Tanwar S, Rhodes F, Srivastava A, Trembling PM, Rosenberg WM (2020) Inflammation and fibrosis in chronic liver diseases including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatitis C. World J Gastroenterol 26:109–133. [CrossRef]
- Ismail M, Pinzani M (2009) Reversal of liver fibrosis. Saudi Journal of Gastroenterology 15:72. [CrossRef]
- Tan Z, Sun H, Xue T, Gan C, Liu H, Xie Y, Yao Y, Ye T (2021) Liver Fibrosis: Therapeutic Targets and Advances in Drug Therapy. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:. [CrossRef]
- Frangogiannis NG (2021) Cardiac fibrosis. Cardiovasc Res 117:1450–1488. [CrossRef]
- Jiang W, Xiong Y, Li X, Yang Y (2021) Cardiac Fibrosis: Cellular Effectors, Molecular Pathways, and Exosomal Roles. Front Cardiovasc Med 8:. [CrossRef]
- Talman V, Ruskoaho H (2016) Cardiac fibrosis in myocardial infarction—from repair and remodeling to regeneration. Cell Tissue Res 365:563–581. [CrossRef]
- Gao X-M, White DA, Dart AM, Du X-J (2012) Post-infarct cardiac rupture: Recent insights on pathogenesis and therapeutic interventions. Pharmacol Ther 134:156–179. [CrossRef]
- van den Borne SWM, Diez J, Blankesteijn WM, Verjans J, Hofstra L, Narula J (2010) Myocardial remodeling after infarction: the role of myofibroblasts. Nat Rev Cardiol 7:30–37. [CrossRef]
- Shinde A V., Frangogiannis NG (2014) Fibroblasts in myocardial infarction: A role in inflammation and repair. J Mol Cell Cardiol 70:74–82. [CrossRef]
- Berk BC, Fujiwara K, Lehoux S (2007) ECM remodeling in hypertensive heart disease. Journal of Clinical Investigation 117:568–575. [CrossRef]
- Schimmel K, Ichimura K, Reddy S, Haddad F, Spiekerkoetter E (2022) Cardiac Fibrosis in the Pressure Overloaded Left and Right Ventricle as a Therapeutic Target. Front Cardiovasc Med 9:. [CrossRef]
- SCHIAU C, LEUCUȚA D-C, DUDEA SM, MANOLE S (2021) Myocardial Fibrosis as a Predictor of Ventricular Arrhythmias in Patients With Non-ischemic Cardiomyopathy. In Vivo (Brooklyn) 35:1677–1685. [CrossRef]
- Xie T, Wang Y, Deng N, Huang G, Taghavifar F, Geng Y, Liu N, Kulur V, Yao C, Chen P, Liu Z, Stripp B, Tang J, Liang J, Noble PW, Jiang D (2018) Single-Cell Deconvolution of Fibroblast Heterogeneity in Mouse Pulmonary Fibrosis. Cell Rep 22:3625–3640. [CrossRef]
- Dobie R, Wilson-Kanamori JR, Henderson BEP, Smith JR, Matchett KP, Portman JR, Wallenborg K, Picelli S, Zagorska A, Pendem S V, Hudson TE, Wu MM, Budas GR, Breckenridge DG, Harrison EM, Mole DJ, Wigmore SJ, Ramachandran P, Ponting CP, Teichmann SA, Marioni JC, Henderson NC (2019) Single-Cell Transcriptomics Uncovers Zonation of Function in the Mesenchyme during Liver Fibrosis. Cell Rep 29:1832-1847.e8. [CrossRef]
- Peyser R, MacDonnell S, Gao Y, Cheng L, Kim Y, Kaplan T, Ruan Q, Wei Y, Ni M, Adler C, Zhang W, Devalaraja-Narashimha K, Grindley J, Halasz G, Morton L (2019) Defining the Activated Fibroblast Population in Lung Fibrosis Using Single-Cell Sequencing. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 61:74–85. [CrossRef]
- Ortiz La, Lasky J, Gozal E, Ruiz V, Lungarella G, Cavarra E, Brody Ar, Friedman M, Pardo A, Selman M (2001) Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Deficiency Alters Matrix Metalloproteinase 13/Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase 1 Expression in Murine Silicosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 163:244–252. [CrossRef]
- Fang L, Murphy AJ, Dart AM (2017) A Clinical Perspective of Anti-Fibrotic Therapies for Cardiovascular Disease. Front Pharmacol 8:186. [CrossRef]
- Dolivo DM, Reed CR, Gargiulo KA, Rodrigues AE, Galiano RD, Mustoe TA, Hong SJ (2023) Anti-fibrotic effects of statin drugs: A review of evidence and mechanisms. Biochem Pharmacol 214:115644. [CrossRef]
- Kim JW, Barrett K, Loke Y, Wilson AM (2021) The effect of statin therapy on disease-related outcomes in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Respir Med Res 80:100792. [CrossRef]
- Fernández Fabrellas E, Peris Sánchez R, Sabater Abad C, Juan Samper G (2018) Prognosis and Follow-Up of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Medical Sciences 6:51. [CrossRef]
- Finnerty JP, Ponnuswamy A, Dutta P, Abdelaziz A, Kamil H (2021) Efficacy of antifibrotic drugs, nintedanib and pirfenidone, in treatment of progressive pulmonary fibrosis in both idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and non-IPF: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pulm Med 21:411. [CrossRef]
- Hostettler KE, Zhong J, Papakonstantinou E, Karakiulakis G, Tamm M, Seidel P, Sun Q, Mandal J, Lardinois D, Lambers C, Roth M (2014) Anti-fibrotic effects of nintedanib in lung fibroblasts derived from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Res 15:157. [CrossRef]
- Epstein Shochet G, Wollin L, Shitrit D (2018) Fibroblast-matrix interplay: Nintedanib and pirfenidone modulate the effect of IPF fibroblast-conditioned matrix on normal fibroblast phenotype. Respirology 23:756–763. [CrossRef]
- Huh J-Y, Lee JH, Song JW (2021) Efficacy and safety of combined use of pirfenidone and nintedanib in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias PA468. [CrossRef]
- Pirfenidone vs. Nintedanib for Fibrotic Lung Disease After Coronavirus Disease-19 Pneumonia (PINCER). https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04856111. Accessed 14 Jun 2023.
- El-Saber Batiha G, Al-Gareeb AI, Saad HM, Al-Kuraishy HM (2022) COVID-19 and corticosteroids: a narrative review. Inflammopharmacology 30:1189–1205. [CrossRef]
- Wells AU, Flaherty KR, Brown KK, Inoue Y, Devaraj A, Richeldi L, Moua T, Crestani B, Wuyts WA, Stowasser S, Quaresma M, Goeldner R-G, Schlenker-Herceg R, Kolb M, Abe S, Aburto M, Acosta O, Andrews C, Antin-Ozerkis D, Arce G, Arias M, Avdeev S, Barczyk A, Bascom R, Bazdyrev E, Beirne P, Belloli E, Bergna MA, Bergot E, Bhatt N, Blaas S, Bondue B, Bonella F, Britt E, Buch K, Burk J, Cai H, Cantin A, Castillo Villegas DM, Cazaux A, Cerri S, Chaaban S, Chaudhuri N, Cottin V, Crestani B, Criner G, Dahlqvist C, Danoff S, Dematte D’Amico J, Dilling D, Elias P, Ettinger N, Falk J, Fernández Pérez ER, Gamez-Dubuis A, Giessel G, Gifford A, Glassberg M, Glazer C, Golden J, Gómez Carrera L, Guiot J, Hallowell R, Hayashi H, Hetzel J, Hirani N, Homik L, Hope-Gill B, Hotchkin D, Ichikado K, Ilkovich M, Inoue Y, Izumi S, Jassem E, Jones L, Jouneau S, Kaner R, Kang J, Kawamura T, Kessler R, Kim Y, Kishi K, Kitamura H, Kolb M, Kondoh Y, Kono C, Koschel D, Kreuter M, Kulkarni T, Kus J, Lebargy F, León Jiménez A, Luo Q, Mageto Y, Maher TM, Makino S, Marchand-Adam S, Marquette C, Martinez R, Martínez M, Maturana Rozas R, Miyazaki Y, Moiseev S, Molina-Molina M, Morrison L, Morrow L, Moua T, Nambiar A, Nishioka Y, Nunes H, Okamoto M, Oldham J, Otaola M, Padilla M, Park JS, Patel N, Pesci A, Piotrowski W, Pitts L, Poonyagariyagorn H, Prasse A, Quadrelli S, Randerath W, Refini R, Reynaud-Gaubert M, Riviere F, Rodríguez Portal JA, Rosas I, Rossman M, Safdar Z, Saito T, Sakamoto N, Salinas Fénero M, Sauleda J, Schmidt S, Scholand MB, Schwartz M, Shapera S, Shlobin O, Sigal B, Silva Orellana A, Skowasch D, Song JW, Stieglitz S, Stone H, Strek M, Suda T, Sugiura H, Takahashi H, Takaya H, Takeuchi T, Thavarajah K, Tolle L, Tomassetti S, Tomii K, Valenzuela C, Vancheri C, Varone F, Veeraraghavan S, Villar A, Weigt S, Wemeau L, Wuyts W, Xu Z, Yakusevich V, Yamada Y, Yamauchi H, Ziora D (2020) Nintedanib in patients with progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases—subgroup analyses by interstitial lung disease diagnosis in the INBUILD trial: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial. Lancet Respir Med 8:453–460. [CrossRef]
- Richeldi L, du Bois RM, Raghu G, Azuma A, Brown KK, Costabel U, Cottin V, Flaherty KR, Hansell DM, Inoue Y, Kim DS, Kolb M, Nicholson AG, Noble PW, Selman M, Taniguchi H, Brun M, Le Maulf F, Girard M, Stowasser S, Schlenker-Herceg R, Disse B, Collard HR (2014) Efficacy and Safety of Nintedanib in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. New England Journal of Medicine 370:2071–2082. [CrossRef]
- Behr J, Prasse A, Kreuter M, Johow J, Rabe KF, Bonella F, Bonnet R, Grohe C, Held M, Wilkens H, Hammerl P, Koschel D, Blaas S, Wirtz H, Ficker JH, Neumeister W, Schönfeld N, Claussen M, Kneidinger N, Frankenberger M, Hummler S, Kahn N, Tello S, Freise J, Welte T, Neuser P, Günther A, Behr J, Kreuter M, Johow J, Rabe KF, Bonella F, Bonnet R, Grohe C, Held M, Wilkens H, Hammerl P, Koschel D, Blaas S, Wirtz H, Ficker JH, Neumeister W, Schönfeld N, Claussen M, Kneidinger N, Frankenberger M, Hummler S, Kahn N, Tello S, Freise J, Welte T, Neuser P, Günther A, Schade-Brittinger C, Aminossadati B, Nasemann C, Yahiaoui S, Dupuy Backofen C, Hahmann M, Wittenberg M, Drakopanagiotakis F, von der Beck D, Ghofrani S, Heinemann S, Krauss E, Rethorn H, Koch A, Leuschner G, Matthes S, Neurohr C, Veit T, Milger-Kneidinger K, Herth F, Benstz J, Hummler S, Bahmer T, Biller H, Waschki B, Apel R-M, Costabel U, Börner E, Wessendorf T, Arnrich M, Ilie L, Wald A, Seyfarth H-J, Reinhardt C, Cinar A, Vogler M, Huhn SM, Richter J, Neff U, Blum TG, Vesenbeckh S, Boch C, Semper H, Wilke A, Pfeifer M, Schweda A, Krill A, Lensch C, Joa F, Schröder B, Plaßmeier A, Baron S, Froehling KP, Waschki B (2021) Pirfenidone in patients with progressive fibrotic interstitial lung diseases other than idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (RELIEF): a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2b trial. Lancet Respir Med 9:476–486. [CrossRef]
- Aluganti Narasimhulu C, Singla DK (2020) The Role of Bone Morphogenetic Protein 7 (BMP-7) in Inflammation in Heart Diseases. Cells 9:. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen TQ, Goldschmeding R (2008) Bone Morphogenetic Protein-7 and Connective Tissue Growth Factor: Novel Targets for Treatment of Renal Fibrosis? Pharm Res 25:2416–2426. [CrossRef]
- Zeisberg M, Yang C, Martino M, Duncan MB, Rieder F, Tanjore H, Kalluri R (2007) Fibroblasts Derive from Hepatocytes in Liver Fibrosis via Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition. Journal of Biological Chemistry 282:23337–23347. [CrossRef]
- Biyikli NK, Tugtepe H, Cakalagaoglu F, Ilki A, Alpay H (2005) Downregulation of the expression of bone morphogenetic protein 7 in experimental pyelonephritis. Pediatric Nephrology 20:1230–1236. [CrossRef]
- Murray LA, Hackett TL, Warner SM, Shaheen F, Argentieri RL, Dudas P, Farrell FX, Knight DA (2008) BMP-7 Does Not Protect against Bleomycin-Induced Lung or Skin Fibrosis. PLoS One 3:e4039. [CrossRef]
- Valcourt U, Kowanetz M, Niimi H, Heldin C-H, Moustakas A (2005) TGF-beta and the Smad signaling pathway support transcriptomic reprogramming during epithelial-mesenchymal cell transition. Mol Biol Cell 16:1987–2002. [CrossRef]
- Tacke F, Gäbele E, Bataille F, Schwabe RF, Hellerbrand C, Klebl F, Straub RH, Luedde T, Manns MP, Trautwein C, Brenner DA, Schölmerich J, Schnabl B (2007) Bone Morphogenetic Protein 7 is Elevated in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease and Exerts Fibrogenic Effects on Human Hepatic Stellate Cells. Dig Dis Sci 52:3404–3415. [CrossRef]
- Li X, An G, Wang Y, Liang D, Zhu Z, Lian X, Niu P, Guo C, Tian L (2017) Anti-fibrotic effects of bone morphogenetic protein-7-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Exp Mol Pathol 102:70–77. [CrossRef]
- Tandon A, Sharma A, Rodier JT, Klibanov AM, Rieger FG, Mohan RR (2013) BMP7 Gene Transfer via Gold Nanoparticles into Stroma Inhibits Corneal Fibrosis In Vivo. PLoS One 8:. [CrossRef]
- Midgley AC, Wei Y, Zhu D, Gao F, Yan H, Khalique A, Luo W, Jiang H, Liu X, Guo J, Zhang C, Feng G, Wang K, Bai X, Ning W, Yang C, Zhao Q, Kong D (2020) Multifunctional natural polymer nanoparticles as antifibrotic gene carriers for CKD therapy. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 31:2292–2311. [CrossRef]
- Gebert LFR, MacRae IJ (2019) Regulation of microRNA function in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 20:21–37. [CrossRef]
- Condrat CE, Thompson DC, Barbu MG, Bugnar OL, Boboc A, Cretoiu D, Suciu N, Cretoiu SM, Voinea SC (2020) miRNAs as Biomarkers in Disease: Latest Findings Regarding Their Role in Diagnosis and Prognosis. Cells 9:. [CrossRef]
- Gomez IG, MacKenna DA, Johnson BG, Kaimal V, Roach AM, Ren S, Nakagawa N, Xin C, Newitt R, Pandya S, Xia T-H, Liu X, Borza D-B, Grafals M, Shankland SJ, Himmelfarb J, Portilla D, Liu S, Chau BN, Duffield JS (2015) Anti-microRNA-21 oligonucleotides prevent Alport nephropathy progression by stimulating metabolic pathways. J Clin Invest 125:141–56. [CrossRef]
- Yang F, Li P, Li H, Shi Q, Li S, Zhao L (2015) microRNA-29b Mediates the Antifibrotic Effect of Tanshinone IIA in Postinfarct Cardiac Remodeling. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 65:456–464. [CrossRef]
- Wang J, Lee CJ, Deci MB, Jasiewicz N, Verma A, Canty JM, Nguyen J (2020) MiR-101a loaded extracellular nanovesicles as bioactive carriers for cardiac repair. Nanomedicine 27:102201. [CrossRef]
- Gallant-Behm CL, Piper J, Lynch JM, Seto AG, Hong SJ, Mustoe TA, Maari C, Pestano LA, Dalby CM, Jackson AL, Rubin P, Marshall WS (2019) A MicroRNA-29 Mimic (Remlarsen) Represses Extracellular Matrix Expression and Fibroplasia in the Skin. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 139:1073–1081. [CrossRef]
- Chioccioli M, Roy S, Newell R, Pestano L, Dickinson B, Rigby K, Herazo-Maya J, Jenkins G, Ian S, Saini G, Johnson SR, Braybrooke R, Yu G, Sauler M, Ahangari F, Ding S, DeIuliis J, Aurelien N, Montgomery RL, Kaminski N (2022) A lung targeted miR-29 mimic as a therapy for pulmonary fibrosis. EBioMedicine 85:104304. [CrossRef]
- Chahal J, Gebert LFR, Camargo C, MacRae IJ, Sagan SM (2021) miR-122–based therapies select for three distinct resistance mechanisms based on alterations in RNA structure. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 118:. [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly S (2016) MicroRNAs in fibrosis: opportunities and challenges. Arthritis Res Ther 18:11. [CrossRef]
- Zhong X, Chung ACK, Chen H-Y, Meng X-M, Lan HY (2011) Smad3-mediated upregulation of miR-21 promotes renal fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 22:1668–81. [CrossRef]
- Chen X, Zhang D, Wang Y, Chen K, Zhao L, Xu Y, Jiang H, Wang S (2020) Synergistic antifibrotic effects of miR-451 with miR-185 partly by co-targeting EphB2 on hepatic stellate cells. Cell Death Dis 11:402. [CrossRef]
- Jelinic M, Marshall SA, Stewart D, Unemori E, Parry LJ, Leo CH (2018) Peptide hormone relaxin: from bench to bedside. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology 314:R753–R760. [CrossRef]
- Samuel CS, Zhao C, Yang Q, Wang H, Tian H, Tregear GW, Amento EP (2005) The Relaxin Gene Knockout Mouse: A Model of Progressive Scleroderma. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 125:692–699. [CrossRef]
- Sarwar M, Du X-J, Dschietzig TB, Summers RJ (2017) The actions of relaxin on the human cardiovascular system. Br J Pharmacol 174:933–949. [CrossRef]
- Samuel CS, Unemori EN, Mookerjee I, Bathgate RAD, Layfield SL, Mak J, Tregear GW, Du X-J (2004) Relaxin Modulates Cardiac Fibroblast Proliferation, Differentiation, and Collagen Production and Reverses Cardiac Fibrosis in Vivo. Endocrinology 145:4125–4133. [CrossRef]
- Kanai AJ, Konieczko EM, Bennett RG, Samuel CS, Royce SG (2019) Relaxin and fibrosis: Emerging targets, challenges, and future directions. Mol Cell Endocrinol 487:66–74. [CrossRef]
- EVANS JA (1959) Relaxin (Releasin) Therapy in Diffuse Progressive Scleroderma. AMA Arch Derm 79:150. [CrossRef]
- Ng HH, Shen M, Samuel CS, Schlossmann J, Bennett RG (2019) Relaxin and extracellular matrix remodeling: Mechanisms and signaling pathways. Mol Cell Endocrinol 487:59–65. [CrossRef]
- Cai J, Chen X, Chen X, Chen L, Zheng G, Zhou H, Zhou X (2017) Anti-Fibrosis Effect of Relaxin and Spironolactone Combined on Isoprenaline-Induced Myocardial Fibrosis in Rats via Inhibition of Endothelial–Mesenchymal Transition. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry 41:1167–1178. [CrossRef]
- Metra M, Teerlink JR, Cotter G, Davison BA, Felker GM, Filippatos G, Greenberg BH, Pang PS, Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Adams KF, Anker SD, Arias-Mendoza A, Avendaño P, Bacal F, Böhm M, Bortman G, Cleland JGF, Cohen-Solal A, Crespo-Leiro MG, Dorobantu M, Echeverría LE, Ferrari R, Goland S, Goncalvesová E, Goudev A, Køber L, Lema-Osores J, Levy PD, McDonald K, Manga P, Merkely B, Mueller C, Pieske B, Silva-Cardoso J, Špinar J, Squire I, Stępińska J, Van Mieghem W, von Lewinski D, Wikström G, Yilmaz MB, Hagner N, Holbro T, Hua TA, Sabarwal S V., Severin T, Szecsödy P, Gimpelewicz C (2019) Effects of Serelaxin in Patients with Acute Heart Failure. New England Journal of Medicine 381:716–726. [CrossRef]
- Khanna D, Clements PJ, Furst DE, Korn JH, Ellman M, Rothfield N, Wigley FM, Moreland LW, Silver R, Kim YH, Steen VD, Firestein GS, Kavanaugh AF, Weisman M, Mayes MD, Collier D, Csuka ME, Simms R, Merkel PA, Medsger TA, Sanders ME, Maranian P, Seibold JR, Relaxin Investigators and the Scleroderma Clinical Trials Consortium (2009) Recombinant human relaxin in the treatment of systemic sclerosis with diffuse cutaneous involvement: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 60:1102–11. [CrossRef]
- Hossain MA, Kocan M, Yao ST, Royce SG, Nair VB, Siwek C, Patil NA, Harrison IP, Rosengren KJ, Selemidis S, Summers RJ, Wade JD, Bathgate RAD, Samuel CS (2016) A single-chain derivative of the relaxin hormone is a functionally selective agonist of the G protein-coupled receptor, RXFP1. Chem Sci 7:3805–3819. [CrossRef]
- Vagnozzi RJ, Kasam RK, Sargent MA, Molkentin JD (2021) Cardiac Cell Therapy Fails to Rejuvenate the Chronically Scarred Rodent Heart. Circulation 144:328–331. [CrossRef]
- Makkar RR, Kereiakes DJ, Aguirre F, Kowalchuk G, Chakravarty T, Malliaras K, Francis GS, Povsic TJ, Schatz R, Traverse JH, Pogoda JM, Smith RR, Marbán L, Ascheim DD, Ostovaneh MR, Lima JAC, DeMaria A, Marbán E, Henry TD (2020) Intracoronary ALLogeneic heart STem cells to Achieve myocardial Regeneration (ALLSTAR): a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded trial. Eur Heart J 41:3451–3458. [CrossRef]
- Liu C, Han D, Liang P, Li Y, Cao F (2021) The Current Dilemma and Breakthrough of Stem Cell Therapy in Ischemic Heart Disease. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:. [CrossRef]
- Adams E, McCloy R, Jordan A, Falconer K, Dykes IM (2021) Direct Reprogramming of Cardiac Fibroblasts to Repair the Injured Heart. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis 8:72. [CrossRef]
- Ieda M, Fu J-D, Delgado-Olguin P, Vedantham V, Hayashi Y, Bruneau BG, Srivastava D (2010) Direct reprogramming of fibroblasts into functional cardiomyocytes by defined factors. Cell 142:375–86. [CrossRef]
- Qian L, Huang Y, Spencer CI, Foley A, Vedantham V, Liu L, Conway SJ, Fu J, Srivastava D (2012) In vivo reprogramming of murine cardiac fibroblasts into induced cardiomyocytes. Nature 485:593–8. [CrossRef]
- Wada R, Muraoka N, Inagawa K, Yamakawa H, Miyamoto K, Sadahiro T, Umei T, Kaneda R, Suzuki T, Kamiya K, Tohyama S, Yuasa S, Kokaji K, Aeba R, Yozu R, Yamagishi H, Kitamura T, Fukuda K, Ieda M (2013) Induction of human cardiomyocyte-like cells from fibroblasts by defined factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:12667–72. [CrossRef]
- Tani H, Sadahiro T, Yamada Y, Isomi M, Yamakawa H, Fujita R, Abe Y, Akiyama T, Nakano K, Kuze Y, Seki M, Suzuki Y, Fujisawa M, Sakata-Yanagimoto M, Chiba S, Fukuda K, Ieda M (2023) Direct Reprogramming Improves Cardiac Function and Reverses Fibrosis in Chronic Myocardial Infarction. Circulation 147:223–238. [CrossRef]
- Nam Y-J, Song K, Luo X, Daniel E, Lambeth K, West K, Hill JA, DiMaio JM, Baker LA, Bassel-Duby R, Olson EN (2013) Reprogramming of human fibroblasts toward a cardiac fate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:5588–93. [CrossRef]
- Avolio E, Katare R, Thomas AC, Caporali A, Schwenke D, Carrabba M, Meloni M, Caputo M, Madeddu P (2022) Cardiac pericyte reprogramming by MEK inhibition promotes arteriologenesis and angiogenesis of the ischemic heart. Journal of Clinical Investigation 132:. [CrossRef]
- Zhang F, Ayaub EA, Wang B, Puchulu-Campanella E, Li Y, Hettiarachchi SU, Lindeman SD, Luo Q, Rout S, Srinivasarao M, Cox A, Tsoyi K, Nickerson-Nutter C, Rosas IO, Low PS (2020) Reprogramming of profibrotic macrophages for treatment of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. EMBO Mol Med 12:. [CrossRef]
- Dempsey TM, Thao V, Moriarty JP, Borah BJ, Limper AH (2022) Cost-effectiveness of the anti-fibrotics for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in the United States. BMC Pulm Med 22:18. [CrossRef]
- Rinciog C, Diamantopoulos A, Gentilini A, Bondue B, Dahlqvist C, Froidure A, Wuyts WA, Soulard S (2020) Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Nintedanib Versus Pirfenidone in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis in Belgium. Pharmacoecon Open 4:449–458. [CrossRef]
- Yamakawa H, Ieda M (2021) Cardiac regeneration by direct reprogramming in this decade and beyond. Inflamm Regen 41:20. [CrossRef]
- Craig VJ, Zhang L, Hagood JS, Owen CA (2015) Matrix Metalloproteinases as Therapeutic Targets for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 53:585–600. [CrossRef]
- Adhikari AS, Chai J, Dunn AR (2011) Mechanical Load Induces a 100-Fold Increase in the Rate of Collagen Proteolysis by MMP-1. J Am Chem Soc 133:1686–1689. [CrossRef]
| Trial Name | Intervention | Phase | Study Design | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| INBUILD (NCT02999178) |
Nintedanib: 150 mg twice daily vs placebo | III | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 663 patients with fibrosing lung disease | [97] |
| INPULSIS I (NCT01335464) |
Nintedanib: 150 mg twice daily vs placebo |
III | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 515 patients with IPF | [98] |
| INPULSIS II (NCT01335477) |
Nintedanib: 150 mg twice daily vs placebo |
III | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 551 patients with IPF | [98] |
| PINCER (NCT04856111) |
Pirfenidone (600 mg daily, escalated by 600 mg daily every 3-7 days up to targeted dose of 2400 mg daily) vs. Nintedanib (150mg twice daily) | IV | Randomized, parallel-assignment, 48 patients with COVID-19 | [95] |
| RELIEF (NCT03099187) |
Pirfenidone: 801mg three times daily vs. placebo |
IIb | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 253 patients with unclassifiable progressive fibrosing ILD | [99] |
| Fibrotic Disease | Drug/Therapy | Target | Target Expression Level | Phase | Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Renal | RG-012 | miR-21 | Down-regulation | I/II | [112] |
| Cardiac | Tanshinone IIA | miR-29b | Up-regulation | -- | [113] |
| Cardiac | miR-101a-loaded MSC extracellular nanovesicles | miR-101a | Up-regulation | -- | [114] |
| Lung | Remlarsen/MRG-201 | miR-29 | Down-regulation | II | [115] |
| Lung | MRG-229 | miR-29 | Down-regulation | -- | [116] |
| Liver | Miravirsen | miR-122 | Down-regulation | II | [117] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





