1. Introduction
Timely and comprehensive childhood immunization is crucial in eliminating vaccine-preventable diseases, which significantly increase the mortality and morbidity rates among children under five (Domek et al., 2016; Mekonnen et al., 2019, 2020). Despite the importance of complete and timely immunization to cultivate a healthy new generation, the World Health Organization (2020) reported that Malaysian newborns have not been fully immunized against vaccine-preventable diseases. The incomplete immunization of infants has been attributed to parental forgetfulness about vaccination milestones and the absence of continuous and effective communication between parents and healthcare organizations (Jong et al., 2021; Mekonnen et al., 2019). Parental forgetfulness may be due to long breaks between immunization appointments and the overwhelming demands of work and household responsibilities. Moreover, inefficient communication may stem from the time-consuming and resource-intensive nature of paper-based vaccination systems, which are commonly used by Malaysian healthcare institutions (Jong et al., 2021). These systems require staff to manually schedule appointments and remind parents, which is unproductive.
We propose Virtual Health Connect (VHC), a text messaging vaccination reminder and recall system, to replace the current inefficient paper-based systems in Malaysia’s healthcare sector that might lead to improving the completion and timeliness of immunizations among children. The system consists of two main components: a web-based application and a Short Message Service (SMS) application.
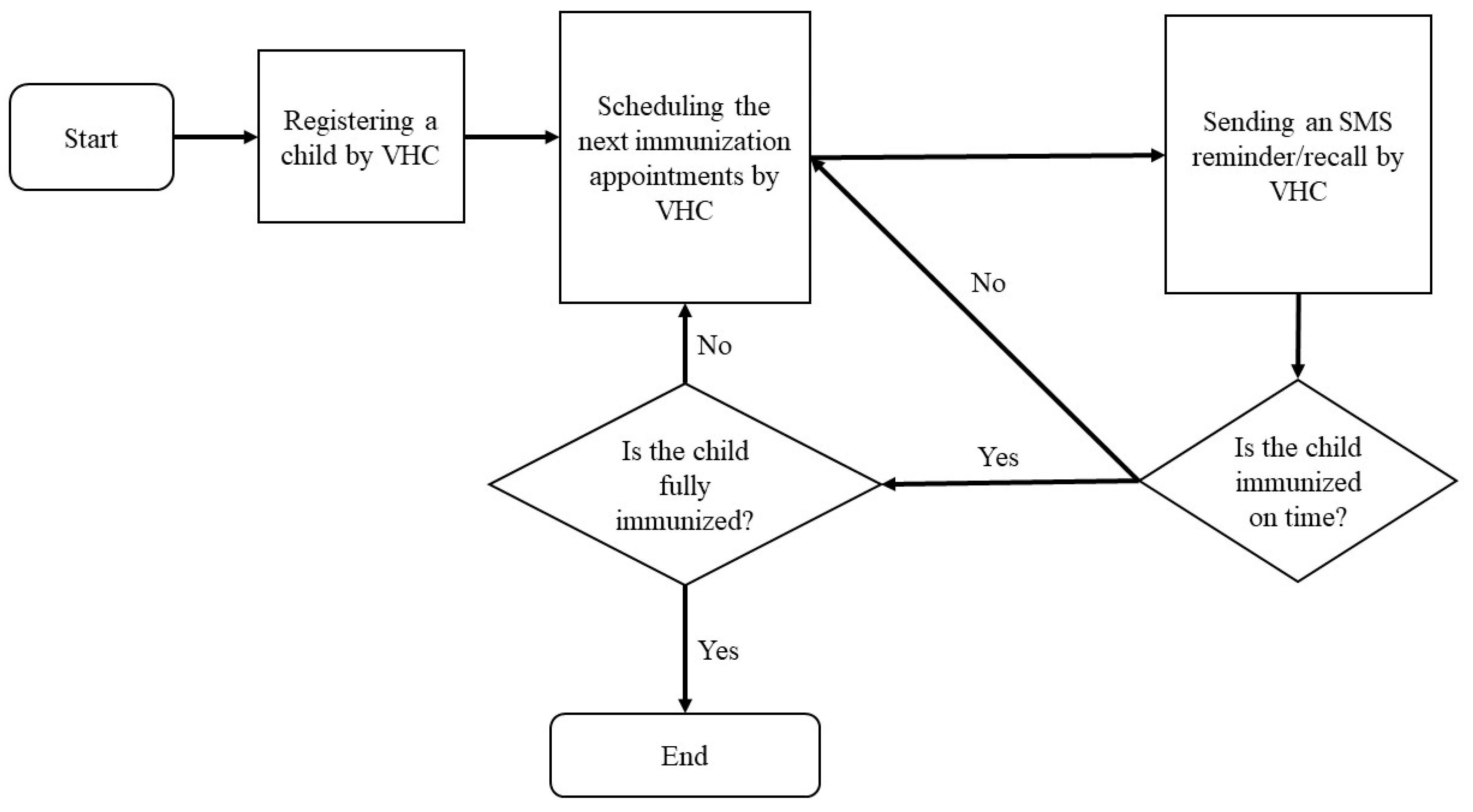
Figure 1 illustrates how the VHC manages vaccination schedules. When parents bring their children to healthcare organizations for the first vaccination, nurses register their information using the web-based application. The system then schedules the upcoming immunization appointments and sends SMS reminders in English and Bahasa Malaysia to parents’ cellphones two days before each appointment. If the child receives the vaccination on time, the system automatically schedules the next appointment and sends a reminder. Otherwise, the system reschedules the overdue vaccination and recalls the parents two days before the new date. This process continues until the child is fully immunized.
The proposed system relies on SMS to remind and recall parents about immunization appointments of their infants. This service has shown a remarkable capacity for illness management (Domek et al., 2016) and increasing attendance for health services (MacDonald et al., 2022; Mekonnen et al., 2019) in developing countries since the majority of families are those with lower socio-economic status that commonly use low-cost cellphones with text only plans. The use of SMS reminders has effectively increased vaccination coverage for various immunization programs worldwide (Domek et al., 2016; Jong et al., 2021; Harvey et al., 2015; Henrikson et al., 2018; MacDonald et. al, 2022; Wakadha et al., 2013).
A review of the literature shows that several studies, including those by Ehlman et al. (2021), Ekhaguere et al. (2019), Kagucia et al. (2021), MacDonald et al. (2022), and Mekonnen et al. (2021), have predominantly used randomized controlled trials to examine the effectiveness of SMS reminders and recalls in improving childhood vaccination coverage. However, there has been limited research on the acceptance of SMS reminders and recalls in the healthcare sector. For example, in a previous study by Karkonasasi et al. (2019), a conceptual model based on the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) was proposed to determine the factors influencing the intention to use such a system among Malaysian health centers, but the model was not tested.
Moreover, Tagbo et al. (2020) examined the acceptability of reminder and recall in vaccination services and the challenges to their implementation among service providers in Nigeria. Hostetter et al. (2013) also generally studied the provider preferences and concerns regarding text message reminder and recall for early childhood vaccinations in the USA. However, these studies primarily used descriptive statistics to examine the acceptability of SMS reminders and recalls in the healthcare sector, which lack statistical power and cannot examine the causal relationships between predictors and acceptance.
Therefore, we aim to extend the limited research on the acceptance of SMS immunization reminder and recall systems in the healthcare sector by proposing a research model based on the extended TAM. The proposed model examines the factors affecting nurses’ attitude and intention to use the system. Our proposed model is novel in that it includes new predictors of attitude, namely, perceived compatibility and perceived privacy and security issues. We focused on nurses’ perspectives on the VHC because they are the primary frontline staff in healthcare institutions who are responsible for managing vaccination records (Lulin et al., 2020a, 2020b). By examining their viewpoints, we can gain insight into the factors that influence or hinder their acceptance of VHC.
We conduct a survey among nurses in Malaysian government hospitals and clinics. We analyzed the survey data using partial least squares-structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) to determine the significant factors influencing their attitude and intention to use VHC. In addition, we use artificial neural network (ANN) to determine the most significant predictors of nurses’ attitude and intention with higher accuracy. As a result, we can offer valuable insights to healthcare decision-makers, helping them to make informed decisions that advance health services.
In the following sections, we will present our proposed research model and develop our hypotheses. We will then describe our research methodology, including survey design, sampling and data collection procedures, data examination, and demographic profile. We will also check the collected data for non-response bias, and common method bias in the research methodology section. Our results section will cover the assessment of the measurement model and the structural model. We will also apply a multi-analytical approach using PLS-SEM and ANNs in the results section. We will then discuss our findings and mention our practical and theoretical contributions. Finally, we will address research limitations and future directions before concluding the paper.
2. The Proposed Research Model
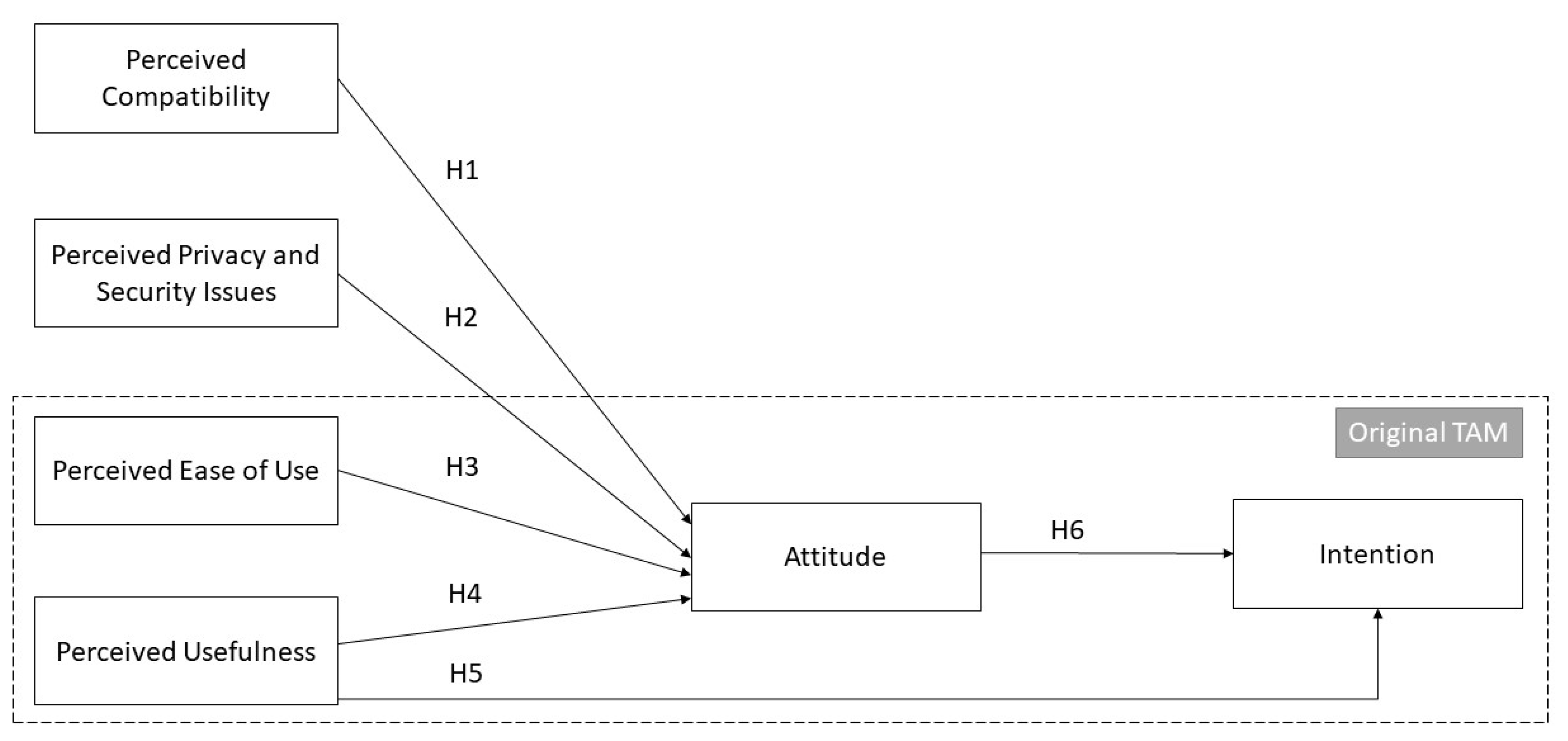
According to the TAM proposed by Davis (1989), a user’s attitude toward behavior and subjective criteria determine their behavioral intention towards technology, which in turn impacts their behavior. While perceived ease of use and perceived usefulness are two main factors affecting user’s Information Technology (IT) acceptance, the external variables of the TAM have not been clearly defined (Feng et al., 2021; Hsiao & Chen, 2016; Lee et al., 2012). Therefore, we attempt to address the limitation of TAM by proposing new predictors of attitude, namely, perceived compatibility and perceived privacy and security issues. We also include the original predictors of TAM namely perceived ease of use and perceived usefulness, as they are commonly supported by the literature as discussed in the following. Studying the new predictors, along with the original predictors of the TAM, can provide a deeper understanding of the acceptance mechanism of VHC by the nurses. The proposed research model is illustrated in
Figure 2, and the hypotheses are discussed as follows.
3. Hypotheses Development
The compatibility of VHC is conceptualized as the extent the system is perceived to be compatible with the current values and prior experiences of nurses, and their requirements in the workplace in administrating the childhood vaccinations (Rogers, 1995). Nurses’ attitude toward using VHC is also conceptualized as their positive or negative feelings about working with the system (Davis et al., 1989). Kuo et al. (2013) reported that the compatibility of mobile EMR systems with nurses’ work practices enhanced their willingness to use these systems. In contrast, a lack of integration of an electronic health system into healthcare practices may lead to its failure because the users hesitate to utilize it to complete their daily work routines (Gagnon et al., 2016).
To streamline the management of childhood vaccination, VHC replaces the paper-based forms that nurses presently use with the equivalent electronic forms. Additionally, the system is easy to install, maintain and operate on electronic devices in the workplace. Consequently, we propose that when nurses assume that VHC is compatible with their work settings, they feel optimistic about using it:
H1. Perceived compatibility of VHC with the workplace will have a significant and positive effect on nurses’ attitude toward using the system.
The perceived privacy and security issues of VHC refer to the extent to which nurses believe that using the system could compromise the privacy and security of children’s and parents’ personal information (Egea & Gonzále, 2011). These concerns may arise due to the potential for unauthorized access to sensitive information, which could result in legal issues for health centers and a loss of trust among parents who share their information with these centers (Alanazi et al., 2020; Jimma & Enyew, 2022). These concerns also demonstrated an adverse influence on willingness to implement electronic medical records (EMRs) around the world as mentioned by Jimma and Enyew (2022). Therefore, we propose that when nurses perceive the privacy and security issues of VHC, their attitude toward using the system is influenced adversely:
H2. Perceived privacy and security issues of VHC for the personal information of parents and their children will have a significant and adverse effect on nurses’ attitude toward using the system.
The perceived usefulness and the perceived ease of use of VHC refer to the degrees to which nurses believe that using the system would improve their job routine and would be effortless in administrating the childhood vaccinations, respectively. Moreover, the intention to use the system is conceptualized as the degree of nurses’ intention to use VHC (Davis et al., 1989). The previous studies on electronic health records (EHRs) (Gagnon et al., 2014, 2016; Vitari & Ologeanu-Tadde, 2018), EMRs (Akwaowo et al., 2022; Tsai et al., 2019), and mobile EMRs (Kuo et al., 2013) supported the significant relationship between the perceived usefulness and intention. However, Gagnon et al. ’s (2014) integrated and psychosocial models did not support this relationship. In addition, the studies on EMRs (Tsai et al., 2019) and EHRs (Alanazi et al., 2020) concluded that the perceived usefulness and the perceived ease of use significantly influenced attitude toward using the systems.
We assume that nurses would find VHC useful and easy to use in their workspace since it enables them to efficiently and smoothly administer the immunization by using an automated SMS feature to remind and recall parents through cellphones. Moreover, they assume the system to be useful and easy to use due to its ready-to-apply vaccination plans and visual reporting tools. Therefore, we hypothesize that the perceived ease of use determines their attitude while the perceived usefulness determines their attitude and intention:
H3. Perceived ease of use of VHC in the workplace will have a significant and positive effect on nurses’ attitude toward using the system.
H4. Perceived usefulness of VHC in the workplace will have a significant and positive effect on nurses’ attitude toward using the system.
H5. Perceived usefulness of VHC in the workplace will have a significant and positive effect on nurses’ intention to use the system.
The significant effect of attitude on intention has been supported by earlier studies on hospital information technologies (Lulin et al., 2020a, 2020b), EMRs (Tsai et al., 2019), and mobile EMRs (Kim et al., 2016). Considering the compatibility of VHC with the current work settings and its practical features that simplify immunization administration, nurses may feel positive working with the system, which subsequently leads to their higher intention to use it in the workplace. Therefore, we hypothesize that:
H6. Nurses’ attitude toward using VHC will have a significant and positive effect on their intention to use the system.
4. Research Methodology
In the following, we will investigate the design of the survey. We will then explain the sampling and data collection procedures. Next, we will discuss the data examination procedure and present the demographic profile of the respondents. Finally, we will examine the data for the presence of non-response bias and common method bias (CMB).
4.1. Survey Design
In the introduction of the survey, we briefly explained the advantages of VHC for simplifying and accelerating the vaccination administration by healthcare institutions. We also informed them that the objective of the survey was to determine the factors influencing the acceptance of VHC. We also added some snapshots of the system as shown in Appendix A, Figure A1 to provide the respondents with a clear picture of the system when completing the survey. We then asked several questions to understand the demographic profile of the respondents. Next, we used a five-point Likert scale ranging from “strongly disagree” to “strongly agree” to measure the measurement constructs using closed-ended questions. We adapted the measurement items from those studies shown in Appendix B, Table B1.
Two experts thoroughly examined the survey for content validity. We then refined the survey based on their feedback to avoid ambiguity and further clarified the instruments. This involved changing the wording and structure of the questions to ensure that the questions were clear and easily understood by the participants. We also conducted a pilot study among 31 respondents selected using convenience sampling to examine the reliability of measurement items. We then improved the questions and layout of the survey as some respondents found it vague. In terms of the reliability of measurement items, there were no major issues based on Nunnally (1978). We did not consider the data from the pilot study for the primary data analysis and did not invite those who participated in the pilot study to take part in the main survey.
4.2. Sampling and Data Collection Procedures
We determined the sample size before collecting data using power analyses considering the background of the model and the data characteristics (Marcoulides & Chin, 2013). The smallest sample size based on Cohen (1992) is 113, considering 5% as the significance level for the statistical power of 80% and R2 values of at least 0.1. We applied simple random sampling to give each item of the population the same opportunity to participate in the study. Considering the response rate of 25% of the pilot study, we distributed the self-administrated questionnaires by post among 452 government hospitals and clinics in the Northern region of Malaysia with a valid address in the list of hospitals and clinics published by the Ministry of Health, Malaysia. We requested the nurses to complete the survey because their viewpoints about VHC would be critical to its effective acceptance, considering that they would be the main frontline staff in healthcare institutions (Lulin et al., 2020a, 2020b) in managing vaccination records using VHC.
4.3. Data Examination
After receiving 128 out of 452 questionnaires, we carefully examined the data for missing values and straight-lining response patterns. We removed seven cases due to the following reasons: two cases had more than 15% missing data, three respondents did not answer most items related to attitude and intention constructs, and two cases showed straight-lining response patterns. We also developed box plots using IBM SPSS Statistics 28 and found no outliers, using 3.0 as the inter-quartile range rule multipliers. Additionally, our analysis showed no major issues with data distribution as the absolute values of skewness and kurtosis for each item were close to 1.
4.4. Demographic Profile
Based on the demographic profile presented in
Table 1, the majority of the informants were young adults between the ages of 18-44 years old (76%), with the highest representation being those between the ages of 25-34 years old (33.1%). Additionally, the majority of the participants were female (67.8%). In terms of education, the informants with a diploma or secondary school education were the most represented (77.7%), while those with a master’s degree were the least represented (9.1%). Moreover, when it comes to working experience, the majority of those surveyed had 3 to 5 years of experience (43.8%). Finally, most participants had not previously accepted a text messaging vaccination reminder and recall system in the workplace (75.2%).
4.5. Non-Response Bias
Non-response bias occurs when the responses of survey participants differ significantly from those who do not respond. This can limit the accuracy of the survey analysis (Compton et al., 2019). To detect the presence of non-response bias in our collected data, we compared the responses of the first and last 50 participants, who were considered as early and late respondents, respectively. This is because the late respondents may have a similar response pattern to those who did not participate in the survey (Johnson & Wislar, 2012). We used an independent sample t-test to analyze the mean differences of all constructs for these two groups. Our results showed that the mean differences were not statistically significant. Therefore, we concluded that non-response bias was not present in our data.
4.6. Common Method Bias
Common Method Bias (CMB) is a type of bias that arises from the measurement method rather than the constructs being measured (Campbell & Fiske, 1959; Podsakoff et al., 2003). It can lead to incorrect conclusions about the relationships between constructs by either inflating or deflating the findings (Doty & Glick, 1998). Therefore, it is important to check for CMB in survey studies that use self-administered questionnaires, especially when both predictor and criterion constructs are measured using items answered by the same respondents (Podsakoff et al., 2003).
We used the procedural remedies and statistical control proposed by Podsakoff et al. (2003), Podsakoff et al. (2012), and Williams et al. (2010) to check for CMB. In procedural remedies, we ensured the respondents that their responses would be strictly confidential, and that there would be no desired or correct answer. Moreover, we placed a time lag between the measurement items by inserting the demographic questions.
In statistical control, we applied Harman’s single factor test to check for CMB. After entering all measurement items, we performed an exploratory factor analysis with an orthogonal rotation of Varimax and principal component analysis. The largest variance explained by a single factor was 28.75%. Moreover, we detected six factors that explained 66.38% of the variance, considering the Eigenvalue greater than one criterion. Therefore, CMB was not present in our data because a single factor did not explain the highest variance(Podsakoff et al., 2003).
5. Results
We examine the measurement model using SmartPLS 4 software (Ringle et al., 2022) and evaluate the direct effects in the structural model. Next, we identify the most important factors influencing attitude by using its significant predictors as input neurons for artificial neural networks built with SPSS 26.
5.1. Measurement Model
We used PLS-SEM for data analysis because it does not require a large or normally distributed sample (Hair et al., 2021, 2019). We assessed the reflective measurement model’s convergent and discriminant validity using confirmatory factor analysis. Convergent validity was evaluated through factor loading, composite reliability (CR), and average variance extracted (AVE) (Chang, 2020).
For factor loading, we dropped one item from each of the perceived privacy and security issues and intention constructs because of outer loadings below 0.7. Although one item of the perceived ease of use construct obtained outer loadings below 0.7, we maintained the item because the construct’ CR was decreased after the removal of the item. All constructs had CR values ranging from 0.822 to 0.901, exceeding the recommended threshold of 0.7. Therefore, all constructs were reliable in terms of internal consistency. Moreover, all constructs had AVE values ranging from 0.536 to 0.714, exceeding the recommended threshold of 0.5. Therefore, convergent validity was established for the measurement model.
We examined discriminant validity using Heterotrait–Monotrait Ratio (HTMT). We dropped one item of the perceived privacy and security issues construct due to the high correlations with the intention construct’s items. Then, the confidence interval excluded the value 1 for all pairs of constructs. Therefore, discriminant validity was established.
Table 2 lists the findings of the measurement model assessment.
5.2. Structural Model
Before analyzing the direct effects of our PLS path model, we checked for collinearity issues among the constructs by evaluating the inner variance inflation factor (VIF) values of all pairs of endogenous and exogenous constructs. The VIF values ranged from 1.048 to 1.279, indicating no collinearity issues. We then proceeded to examine the regression results using bootstrapping with 5000 samples to assess the significance of path coefficients (Hair et al., 2021). We used a one-tailed test to determine whether the influence of each exogenous construct on its corresponding endogenous construct was positive or negative (Kock, 2015).
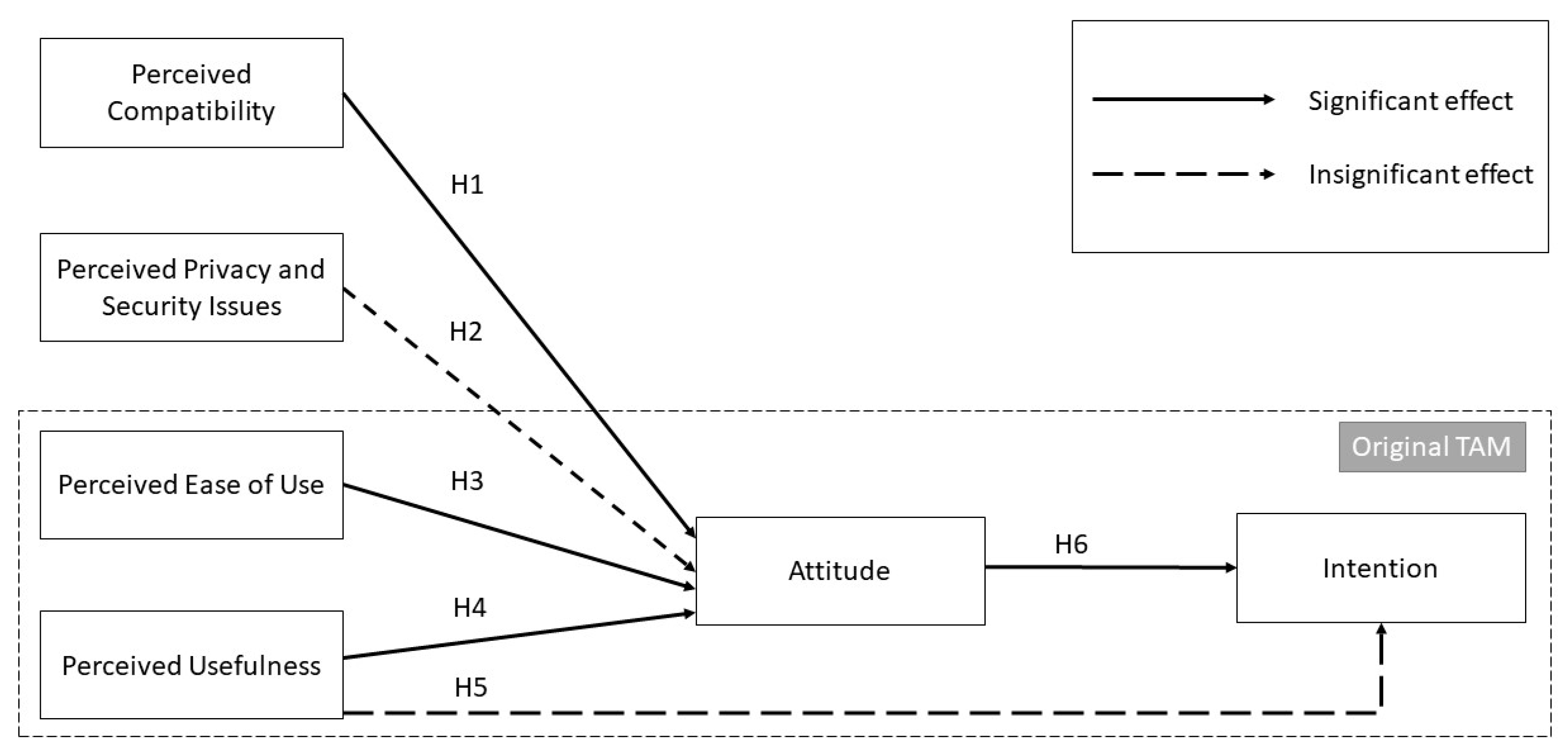
Table 3 presents the results of our hypothesis testing for the direct effects. Our findings showed that hypotheses H1, H3, H4, and H6 were significantly supported as their confidence intervals did not include zero. However, hypotheses H2 and H5 were not supported due to their T-values. According to Hair et al. (2021), the model’s predictive powers of attitude and intention were weak, considering the R
2 values of 0.386 and 0.250 for the respective constructs.
5.3. Multi-Analytical Approach of PLS-SEM and Artificial Neural Network
Artificial neural networks can achieve high prediction accuracy, but they are not suitable for hypothesis testing because of their complex operation. On the other hand, conventional linear statistical techniques, for instance, PLS-SEM, only examine linear relationships, resulting in the over-simplification of complex decision-making processes in organizations (Li et al., 2015). Consequently, we integrated PLS-SEM and ANN to build a multi-analytical approach to accurately determine the most significant predictors of attitude and intention.
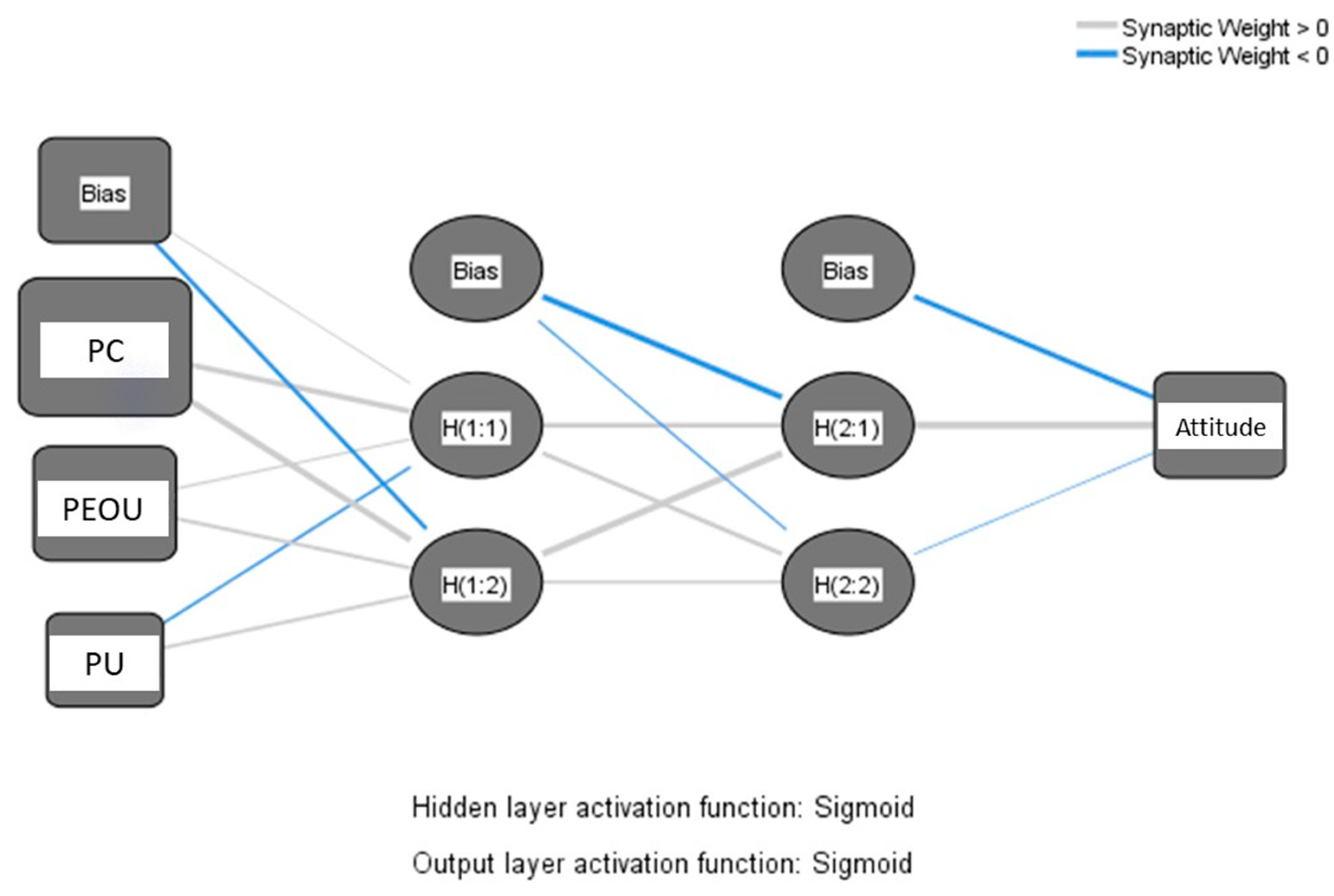
We developed our model using the feed-forward-back-propagation algorithm, where the significant predictors of the PLS path model (perceived compatibility, perceived ease of use, and perceived usefulness) were considered the input neurons. Moreover, attitude was considered the dependent variable. Ten-fold cross-validation was considered to avoid over-fitting, using 90% of the data for network training and the remaining for testing (Li et al., 2015). The Root Mean Square of Errors (RMSEs) of training and testing for all ten ANN models were calculated to measure the models’ predictive accuracy. We examined the prediction accuracy of the models with Sigmoid as the activation function of all layers and two hidden layers because the models achieved a higher prediction accuracy in these settings.
Figure 3 shows the ninth ANN model that achieved the lowest RMSE for testing. The influence of the input neuron on the output is determined by the color and width of the synaptic weight between them. The weight appears in blue when the influence is negative and in grey when it is positive.
Table 4 illustrates the RMSEs of the ten models. They achieved precise prediction accuracy since their average RMSEs were small (0.126 for training and testing). The RMSEs are in line with previous studies (Liébana-Cabanillas et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2023). We conducted a sensitivity analysis to rank the predictors by determining their relative importance. Considering the normalized variable importance values in
Table 5, the most significant predictor of attitude was perceived compatibility (100%), followed by perceived ease of use (66.73%), and perceived usefulness (36.10%). Since our findings showed that only attitude significantly influenced intention, we did not apply the multi-analytical approach for the intention construct.
6. Discussion
The original TAM’s external variables have not been studied adequately in examining user IT acceptance. Consequently, this model may not completely capture the complexity of real-world IT adoption and use. Therefore, we have proposed the extended TAM including two new predictors of attitude: perceived compatibility and perceived privacy and security issues to study the acceptance of VHC among nurses. In our examination of the new factors, we found that nurses’ attitude towards using VHC was affected only by perceived compatibility, which is consistent with the findings of Kuo et al. (2013). This finding is due to replacing paper-based forms currently completed by staff with computerized forms in VHC that simplify and speed up childhood immunization management. The system can also be installed and operated on standard electronic devices in the workplace effortlessly.
However, we could not determine any adverse or significant relationship between perceived privacy and security issues and attitude, contradicting the findings of Jimma and Enyew (2022). In VHC, we minimize recording any sensitive records in the database, for instance, credit card information and confidential data about parents and children’s chronic diseases to avoid causing any possible inconvenience to them in case of data leakage. Moreover, applying the latest encryption techniques to secure the stored data and requesting nurses to bypass the two-factor authentication to login into the system could probably inhibit any unauthorized access.
Evaluating the predominant factors of TAM model namely perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use demonstrated that they significantly raised nurses’ attitude toward using VHC. These findings are supported by Alanazi et al. (2020) and Tsai et al. (2019). VHC simplifies the management of vaccination records for nurses by utilizing predefined and customizable immunization plans, allowing efficient and effortless childhood vaccination. Additionally, the system automatically sends SMS reminders to parents prior to vaccination appointments and recalls them if they miss an appointment. Furthermore, VHC provides visual reporting tools that allow nurses to monitor upcoming and overdue immunization appointments on a weekly, monthly, and annual basis, streamlining the process of monitoring vaccination coverage.
However, despite the significant relationship between perceived usefulness and attitude, this factor did not impact nurses’ intention to use VHC significantly, supported by Gagnon et al. (2014). The use of text messaging vaccination reminder and recall systems, such as VHC, is not widely explored in Malaysia’s healthcare sector, which primarily relies on paper-based systems to manage vaccinations. This observation is consistent with the results of our survey, demonstrating that a majority of the respondents had not previously used such systems in their workplace. Consequently, their perceived usefulness of the system may not significantly raise their intention, possibly due to a lack of expertise in utilizing the system. This insignificant finding may also be attributed to the extensive data entry required by nurses when using VHC for childhood immunization management.
Nurses’ attitude toward using VHC also had a significant and positive effect on their intention, supported by Kim et al. (2016), Lulin et al. (2020a, 2020b), and Tsai et al. (2019). When nurses gain positive feelings about using VHC due to its compatibility with the current work practices, and its simplicity and helpfulness in the workplace, they would intend to use it in their healthcare institutions. Moreover, they do not express any significant concerns regarding the safety of children’s and parents’ personal information, as the system is highly secure and minimizes the collection of sensitive data.
Given that the attitude predictors, namely perceived compatibility, perceived ease of use and perceived usefulness were found to be significant, an artificial neural network was utilized to determine which predictors had a greater impact on attitude. Based on the ANN models, perceived compatibility was the most significant factor of attitude, followed by perceived ease of use and perceived usefulness. When VHC is perceived to be compatible, it is easier for nurses to integrate it into their daily work routines, leading to a more positive attitude toward its use. Then, when the system is perceived as easy to use, nurses tend to embrace and use it regularly, raising their attitude toward using the system. Next, nurses are more likely to recognize the value and benefits of VHC when perceive it as useful, leading to a positive perception of the system.
Figure 4 demonstrates the significant and insignificant effects of the final research model.
7. Contributions
Our study offers the following practical and theoretical contributions.
7.1. Practical Contributions
Our findings show that a text messaging vaccination reminder and recall system like VHC should simplify the immunization administration to be highly accepted by nurses in the workplace. Therefore, considering innovative features like Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and speech recognition in the system to facilitate tedious data entry tasks, could raise their positive perspectives toward the system. In addition to using SMS as the primary communication channel, incorporating automated phone calls can be beneficial for parents with impaired vision. This additional feature can improve accessibility and ensure that all parents receive important immunization reminders. Furthermore, utilizing email-based reminders can enable nurses to provide more comprehensive educational information to parents, emphasizing the significance of immunization and addressing any potential concerns or questions they may have.
Moreover, the system’s process and design should represent nurses’ current work style precisely to be compatible with healthcare organizations. Consequently, software developers are encouraged to entirely comprehend the existing paper-based systems by interviewing the board of directors and nurses and assessing vaccination record forms to effectively implement them in the system. They are also encouraged to develop several prototypes, perform usability tests, and seek board of directors’ and nurses’ feedback to develop a compatible system that addresses the requirements of healthcare institutions. Meanwhile, the board of directors and nurses need to allocate sufficient time for software developers to explain their current vaccination procedures and requirements.
In addition, software developers should make sure that VHC is useful, so that nurses feel positive about it. This means that the system should be designed in a way that makes it easy for nurses to find the information they need to complete their tasks efficiently. The system should also provide nurses with the tools they need to deliver high-quality care for registered infants. Finally, the board of directors and software developers should organize training workshops for nurses to help them learn how to use VHC efficiently.
The results of the multi-analytical approach using PLS-SEM and ANN also showed that VHC developers should focus on making the system compatible, easy to use and useful in the workplace, accordingly. Therefore, they can improve the attitude of nurses toward VHC.
7.2. Theoretical Contribution
This study contributes to the narrow literature about the acceptance of VHC and text messaging vaccination reminder and recall systems among healthcare institutions. Since the external predictors of the original TAM have not been clearly studied, we proposed new predictors of attitude, namely, perceived compatibility and perceived privacy and security issues. Among those, we found that perceived compatibility led to the positive perspectives of nurses about the system, adding to the present predictors of attitude in the TAM. Our findings also showed that the predominant factors of the TAM, namely, perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use significantly increased nurses’ attitudes toward using VHC. Their attitude toward using VHC also led to the determination to use the system. Finally, applying a multi-analytical approach of PLS-SEM and ANN helped us determine the most significant factors of nurses’ attitudes with higher accuracy. We found that perceived compatibility was the most significant factor influencing nurses’ attitudes towards using VHC, followed by perceived ease of use and perceived usefulness.
8. Research Limitations and Future Directions
We examined the acceptance of VHC among Malaysia’s government hospitals and clinics. Future studies should be conducted in the private sector to assess the acceptance in this setting, which may have different needs and priorities than the public sector. Moreover, the research model was only evaluated by collecting nurses’ responses. Considering other medical personnel with a high possibility of using VHC, for instance, physicians might generalize the results. Furthermore, the data were merely collected using self-administrated questionnaires, which might cause ambiguity for the respondents and encourage them to answer the measurement items in a socially desirable manner. Therefore, applying mixed research methods, including surveys and interviews, could be considered to overcome these issues. Finally, trial studies should be conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of VHC in improving the completion and timeliness of immunizations among infants.
9. Conclusion
Despite the potential benefits of text messaging vaccination reminder and recall systems in simplifying and accelerating childhood immunization administration, their use has not been widely explored in Malaysia’s healthcare sector. Therefore, we proposed VHC and conducted a survey study to examine the factors that influence nurses’ attitudes and intentions to use the system within the healthcare sector. Considering the external variables of TAM have not been clearly determined, we proposed new predictors of attitude, namely, perceived compatibility, and perceived privacy and security issues to address the limitations of TAM. By including these additional predictors, we aimed to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the factors that influence technology acceptance. Our findings demonstrate that among the new predictors, only perceived compatibility could raise the nurses’ attitude, demonstrating that the compatibility of VHC with the nurses’ current work setting had a vital role in building their positive perspective on the system. Furthermore, we have noticed that the nurses would be optimistic to use VHC if they perceived it as useful and easy to use in their workplace. Their attitudes toward using VHC also played a determining role in their intention to use the system. The findings of the multi-analytical approach of PLS-SEM and ANN also showed that perceived compatibility was the most significant factor influencing nurses’ attitudes, followed by perceived ease of use and perceived usefulness. These insights may help healthcare decision-makers by making informed decisions that advance health services. Our findings may have significant implications for managerial and software development practices within the healthcare industry, particularly in regard to the successful development, implementation, and acceptance of VHC and similar systems, which may ultimately lead to raising childhood vaccination coverage and protecting infants against preventable diseases. Moreover, it could further contribute to the current narrow literature about the acceptance factors of these systems and mitigate the limitation of TAM by providing further knowledge about predictors driving positive attitudes toward the systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.K.; Funding Acquisition, K.K., C.Y. and M.V.; Methodology, K.K.; Supervision, C.Y.; Writing – Original Draft Preparation, K.K., C.Y., M.V. and S.A.M.; Writing – Review & Editing, K.K., C.Y., M.V. and S.A.M.; Visualization, K.K.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Human Research Ethics Committee from Universiti Sains Malaysia (FWA Reg. NO: 00007718; IRB Reg. NO: 00004494, Date: 10th July 2013).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. They were also informed that engaging in the survey was voluntary, and the collected data would remain confidential and only be used for academic purposes.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset can be provided by the authors.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the respected editors and reviewers for their helpful comments and suggestions that significantly helped improve our research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
References
- Akwaowo, C. D., Sabi, H. M., Ekpenyong, N., Isiguzo, C. M., Andem, N. F., Maduka, O., Dan, E., Umoh, E., Ekpin, V., & Uzoka, F. M. (2022). Adoption of electronic medical records in developing countries—A multi-state study of the Nigerian healthcare system. Frontiers in Digital Health 4, 239. [CrossRef]
- Al Alawi, S. , Al Dhaheri, A., Al Baloushi, D., Al Dhaheri, M., & Prinsloo, E. A. (2014). Physician user satisfaction with an electronic medical records system in primary healthcare centres in Al Ain: A qualitative study. BMJ Open, 4(11), e005569. [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, B. , Butler-Henderson, K., & Alanazi, M. (2020). Perceptions of healthcare professionals about the adoption and use of EHR in Gulf Cooperation Council countries: A systematic review. BMJ Health & Care Informatics, 27(1). [CrossRef]
- Alhuwail, D. (2020). Understanding health information management practices in public hospitals in Kuwait. Health Information Management Journal, 49(2-3), 127-136. [CrossRef]
- Arpaci, I. (2019). A hybrid modeling approach for predicting the educational use of mobile cloud computing services in higher education. Computers in Human Behavior, 90, 181–187. [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.W. (2020). What drives organizations to switch to cloud ERP systems? The impacts of enablers and inhibitors. Journal of Enterprise Information Management, 33, 3, 600–626. [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. (1992). A power primer. Psychological Bulletin, 112, 1, 155–159. [CrossRef]
- Compton, J. , Glass, N., & Fowler, T. (2019). Evidence of Selection Bias and Non-Response Bias in Patient Satisfaction Surveys. The Iowa Orthopaedic Journal, 39, 1, 195.
- Crameri, K. A. , Maher, L., Van Dam, P., & Prior, S. (2022). Personal electronic healthcare records: What influences consumers to engage with their clinical data online? A literature review. Health Information Management Journal, 51, 1, 3–12. [CrossRef]
- Davis, F. D. (1989). Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Quarterly, 13, 3, 319–340.
- Davis, F. D. , Bagozzi, R. P., & Warshaw, P. R. (1989). User acceptance of computer technology: A comparison of two theoretical models. Management Science, 35, 8, 982–1003.
- Domek, G. J. , Contreras-Roldan, I. L., O’Leary, S. T., Bull, S., Furniss, A., Kempe, A., & Asturias, E. J. (2016). SMS text message reminders to improve infant vaccination coverage in Guatemala: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Vaccine, 34, 21, 2437–2443. [CrossRef]
- Doty, D. H. , & Glick, W. H. (1998). Common methods bias: Does common methods variance really bias results? Organizational Research Methods, 1, 4, 374–406. [CrossRef]
- Egea, J. M. O. , & González, M. V. R. (2011). Explaining physicians’ acceptance of EHCR systems: An extension of TAM with trust and risk factors. Computers in Human Behavior, 27(1), 319-332. [CrossRef]
- Ehlman, D. C. , Magoola, J., Tanifum, P., Wallace, A. S., Behumbiize, P., Mayanja, R., Luzze, H., Yukich, J., Daniels, D., Mugenyi, K., Baryarama, F., Ayebazibwe, N., & Conklin, L. (2021). Evaluating a Mobile Phone-Delivered Text Message Reminder Intervention to Reduce Infant Vaccination Dropout in Arua, Uganda: Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR research protocols, 10(2), e17262. [CrossRef]
- Ekhaguere, O. A. , Oluwafemi, R. O., Badejoko, B., Oyeneyin, L. O., Butali, A., Lowenthal, E. D., & Steenhoff, A. P. (2019). Automated phone call and text reminders for childhood immunisations (PRIMM): a randomised controlled trial in Nigeria. BMJ global health, 4(2), e001232. [CrossRef]
- Faul, F. , Erdfelder, E., Buchner, A., & Lang, A. G. (2009). Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behavior Research Methods, 41, 1149-1160. [CrossRef]
- Feng, G. C. , Su, X., Lin, Z., He, Y., Luo, N., & Zhang, Y. (2021). Determinants of Technology Acceptance: Two Model-Based Meta-Analytic Reviews. Journalism and Mass Communication Quarterly 98(1), 83–104. [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, M. P. , Talla, P. K., Simonyan, D., Godin, G., Labrecque, M., Ouimet, M., & Rousseau, M. (2014). Electronic health record acceptance by physicians: Testing an integrated theoretical model. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, , 48, 17-27. [CrossRef]
- Guo, U. , Chen, L., & Mehta, P. H. (2017). Electronic health record innovations: Helping physicians–one less click at a time. Health Information Management Journal, 46(3), 140-144.
- Hair, J. F. , Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2021). A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) (3rd ed.). SAGE Publications, Inc.
- Hair, J. F. , Risher, J. J., Sarstedt, M., & Ringle, C. M. (2019). When to use and how to report the results of PLS-SEM. European Business Review 31(1), 2–24. [CrossRef]
- Harvey, H. , Reissland, N., & Mason, J. (2015). Parental reminder, recall and educational interventions to improve early childhood immunisation uptake: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Vaccine 33(25), 2862-2880. [CrossRef]
- Henrikson, N. B. , Zhu, W., Baba, L., Nguyen, M., Berthoud, H., Gundersen, G., & Hofstetter, A. M. (2018). Outreach and reminders to improve human papillomavirus vaccination in an integrated primary care system. Clinical Pediatrics. 57(13), 1523–1531. [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, J. L. , & Chen, R. F. (2016). Critical factors influencing physicians’ intention to use computerized clinical practice guidelines: An integrative model of activity theory and the technology acceptance model. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making, 16(3), 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Ilie, V. , Van Slyke, C., Parikh, M. A., & Courtney, J. F. (2009). Paper versus electronic medical records: The effects of access on physicians’ decisions to use complex information technologies. Decision Sciences 40(2), 213-241. [CrossRef]
- Jimma, B. L. , & Enyew, D. B. (2022). Barriers to the acceptance of electronic medical records from the perspective of physicians and nurses: A scoping review. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked 31, 100991. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T. P. , & Wislar, J. S. (2012). Response Rates and Nonresponse Errors in Surveys. JAMA 307(17), 1805–1806. [CrossRef]
- Jong, K. M. , Sikora, C. A., & MacDonald, S. E. (2021). Childhood immunization appointment reminders and recalls: strengths, weaknesses and opportunities to increase vaccine coverage. Public Health 194, 170–175. [CrossRef]
- Kagucia, E. W. , Ochieng, B., Were, J., Hayford, K., Obor, D., O’Brien, K. L., & Gibson, D. G. (2021). Impact of mobile phone delivered reminders and unconditional incentives on measles-containing vaccine timeliness and coverage: a randomised controlled trial in western KenyaBMJ Global Health, 6(1), e003357. [CrossRef]
- Karkonasasi, K. , Yu-N, C., Mousavi, S. A., & Baharudin, A. S. (2020). Malaysian Health Centers’ Intention to Use an SMS-Based Vaccination Reminder and Management System: A Conceptual Model. In Emerging Trends in Intelligent Computing and Informatics: Data Science, Intelligent Information Systems and Smart Computing 4 (pp. 960-969). Springer International Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. , Lee, K. H., Hwang, H., & Yoo, S. (2016). Analysis of the factors influencing healthcare professionals’ adoption of mobile electronic medical record (EMR) using the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology (UTAUT) in a tertiary hospital. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making 16(1), 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Kock, N. (2015). One-Tailed or Two-Tailed P Values in PLS-SEM? International Journal of E-Collaboration 11(2), 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Kuo, K. M. , Liu, C. F., & Ma, C. C. (2013). An investigation of the effect of nurses’ technology readiness on the acceptance of mobile electronic medical record systems. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making 13(1), 88. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H. W. , Ramayah, T., & Zakaria, N. (2012). External factors in hospital information system (HIS) adoption model: A case on Malaysia. Journal of Medical Systems 36(4), 2129-2140. [CrossRef]
- Leong, L. Y. , Hew, T. S., Tan, G. W. H., & Ooi, K. B. (2013). Predicting the determinants of the NFC-enabled mobile credit card acceptance: A neural networks approach. Expert Systems with Applications, 40(14), 5604-5620. [CrossRef]
- Li, M. , Zhao, D., & Yu, Y. (2015). TOE drivers for cloud transformation: Direct or trust-mediated? Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics 27(2), 226–248. [CrossRef]
- Liébana-Cabanillas, F. , Marinković, V., & Kalinić, Z. (2017). A SEM-neural network approach for predicting antecedents of m-commerce acceptance. International Journal of Information Management 37(2), 14–24. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C. F. , & Cheng, T. J. (2015). Exploring critical factors influencing physicians’ acceptance of mobile electronic medical records based on the dual-factor model: A validation in Taiwan. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making 15(1), 4. [CrossRef]
- Lulin, Z. , Owusu-Marfo, J., Antwi, H. A., & Xu, X. (2020a). The contributing factors to nurses’ behavioral intention to use hospital information technologies in Ghana. SAGE Open Nursing 6, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Lulin, Z. , Owusu-Marfo, J., Asante Antwi, H., Antwi, M. O., & Xu, X. (2020b). Nurses’ readiness in the adoption of hospital electronic information management systems in Ghana: The application of the structural equation modeling and the UTAUT model. SAGE Open 10(2). [CrossRef]
- Luyten, J. , & Marneffe, W. (2021). Examining the acceptance of an integrated Electronic Health Records system: Insights from a repeated cross-sectional design. International Journal of Medical Informatics 150, 104450. [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, S. E. , Marfo, E., Sell, H., Assi, A., Frank-Wilson, A., Atkinson, K., Kellner, J. D., McNeil, D., Klein, K., & Svenson, L. W. (2022). Text Message Reminders to Improve Immunization Appointment Attendance in Alberta, Canada: The Childhood Immunization Reminder Project Pilot Study. JMIR MHealth and UHealth 10(11). [CrossRef]
- Marcoulides, G. A. , & Chin, W. W. (2013). You Write, but Others Read: Common Methodological Misunderstandings in PLS and Related Methods. Springer Proceedings in Mathematics and Statistics 56, 31–64.
- Mekonnen, Z. A. , Tilahun, B., Alemu, K., & Were, M. (2019). Effect of mobile phone text message reminders on improving completeness and timeliness of routine childhood vaccinations in North-West, Ethiopia: A study protocol for randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open 9(11). [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, Z. A. , Gelaye, K. A., Were, M. C., & Tilahun, B. (2020). Timely completion of vaccination and its determinants among children in northwest, Ethiopia: a multilevel analysis. BMC public health 20(1), 908. [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, Z. A. , Gelaye, K. A., Were, M., & Tilahun, B. (2021). Effect of Mobile Phone Text Message Reminders on the Completion and Timely Receipt of Routine Childhood Vaccinations: Superiority Randomized Controlled Trial in Northwest Ethiopia. JMIR mHealth and Health, 9(6), e27603. [CrossRef]
- Moore, G. C. , & Benbasat, I. (1991). Development of an instrument to measure the perceptions of adopting an information technology innovation. Information Systems Research 2(3), 192–222. [CrossRef]
- Nunnally, J. C. (1978). Psychometric Theory. McGraw-Hill.
- Oliveira, T. , Thomas, M., & Espadanal, M. (2014). Assessing the determinants of cloud computing adoption: An analysis of the manufacturing and services sectors. Information Management 51(5), 497–510. [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P. M. , MacKenzie, S. B., & Podsakoff, N. P. (2012). Sources of method bias in social science research and recommendations on how to control it. Annual Review of Psychology 63, 539–569. [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P. M. , MacKenzie, S. B., Lee, J. Y., & Podsakoff, N. P. (2003). Common Method Biases in Behavioral Research: A Critical Review of the Literature and Recommended Remedies. Journal of Applied Psychology 88(5), 879–903. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Ardura, I. , & Meseguer-Artola, A. (2016). What leads people to keep on e-learning? An empirical analysis of users’ experiences and their effects on continuance intention. Interactive Learning Environments 24(6), 1030-1053. [CrossRef]
- Rogers, E. M. (1995). Diffusion of Innovations (4th ed.). The Free Press.
- Tagbo, B. N. , Vina, O., & Stella, O. (2020). Acceptability of the Use of Reminder/Recall in Vaccination Services among Clients and Service Providers in Enugu, Nigeria. Vaccines & Vaccination Open Access 5(2). [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M. F. , Hung, S. Y., Yu, W. J., Chen, C. C., & Yen, D. C. (2019). Understanding physicians’ adoption of electronic medical records: Healthcare technology self-efficacy, service level and risk perspectives. Computer Standards & Interfaces 66, 1-11.
- Venkatesh, V. , & Bala, H. (2008). Technology acceptance model 3 and a research agenda on interventions. Decision Sciences 39(2), 273–315. [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V. , & Davis, F. D. (2000). A theoretical extension of the technology acceptance model: Four longitudinal field studies. Management Science 46(2), 186-204. [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V. , Morris, M. G., Davis, G. B., & Davis, F. D. (2003). User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS quarterly 425-478.
- Luyten, J. , & Marneffe, W. (2021). Examining the acceptance of an integrated Electronic Health Records system: Insights from a repeated cross-sectional design. International Journal of Medical Informatics 150, 104450.
- Vitari, C. , & Ologeanu-Taddei, R. (2018). The intention to use an electronic health record and its antecedents among three different categories of clinical staff. BMC Health Services Research. 18(1), 194. [CrossRef]
- Wakadha, H. , Chandir, S., Were, E. V., Rubin, A., Obor, D., Levine, O. S., Gibson, D. G., Odhiambo, F., Laserson, K. F., & Feikin, D. R. (2013). The feasibility of using mobile-phone based SMS reminders and conditional cash transfers to improve timely immunization in rural Kenya. Vaccine 31(6), 987-993. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. , Li, X., Zhu, H., & Zhao, Y. (2023). Influencing factors of livestream selling of fresh food based on a push-pull model: A two-stage approach combining structural equation modeling (SEM) and artificial neural network (ANN). Expert Systems with Applications 212, 118799. [CrossRef]
- Williams, L. J. , Hartman, N., & Cavazotte, F. (2010). Method variance and marker variables: A review and comprehensive cfa marker technique. Organizational Research Methods 13(3), 477–514. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. (2020). WHO Vaccine-Preventable Diseases: Monitoring System. 2020 Global Summary. Retrieved August 12, 2020, from https://apps.who.int/immunization_monitoring/globalsummary/countries?countrycriteria%5Bcountry%5D%5B%5D=MYS.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).