1. Introduction
Heavy metals (HM) are naturally occurring elements. However, during past few decades’ anthropogenic activities, industrial and agricultural practices involving the use of chemical pesticides, fertilizers, and sludge, as well as manure composts, metallurgy, and electroplating, have led to their greater accumulation in the soil, which has long-lasting effects on the ecosystem. Some heavy metals (Cu, Zn, Mn, Ni, Co and Fe) act as micronutrients and are necessary for plants and animals in small amounts but if their concentration exceeds certain threshold value, then they can turn out to be eco toxic due to their bioaccumulation in food chain. Other heavy metals such as Cd, Cr, Pb, As, Se, U, Au, Hg are highly toxic even at low concentrations (Gupta etal.2016, S. Dutta etal 2018, Janczak-Pieniazek 2023). This poses a serious threat since heavy metals are non-biodegradable, hazardous, and persistent, which causes them to accumulate in the soil (Zafar-ul-Hye etal 2020) and may trigger physiological and biochemical responses in plants (Kisa, D etal. 2016) and result in oxidative damage to plants (K.S Anjitha etal. 2021). Additionally, the consumption of plant products from crops cultivated in heavy metal-contaminated areas could potentially have a detrimental effect on human health (Mansour etal.2014). Phytoremediation, which offers 'green' cleanup for contaminated areas, is crucial in order to tackle this environmental issue because other existing methods, such as excavation, heat treatment, electro remediation, chemical precipitation, metal leaching, soil washing, or replacement, are all rather pricy and intrusive (Kebert etal.2022).
Heavy metals have been shown to influence a number of cellular organelles in biological systems, including the cell membrane, mitochondria, lysosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, nuclei, and many enzymes involved in metabolism, detoxification, and damage repair. Exposure to metal ions can cause injury to the cell membrane, and damage to the photosynthetic pigments, these ions may interact with nuclear proteins and DNA in cells, leading to DNA damage and conformational changes that may trigger apoptosis, cancer, or modification of the cell cycle (Tchounwou etal. 2012, Emamverdian etal. 2015). As plants are sessile in nature, they recognize these toxic metals stress signals and activate various defense responses to enable functional flexibility under the stressful constraints without disturbing cellular and developmental physiological processes (Yang et al. 2018, Arnold etal.2019). Increased levels of harmful chemicals in plant tissues set off a chain reaction that results in the overproduction of reactive oxygen species. Enzymatic and non-enzymatic systems have both been created by plants to scavenge Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) (Das K etal. 2014, Siqueira MC etal. 2021, Alsherif etal. 2022). Antioxidants are one of them, the term "antioxidant" refers to a class of substances that remove, neutralize, and scavenge ROS in order to protect the cell from harm brought on by exposure of antioxidants, manipulating the biosynthesis and accumulation of plants’ secondary metabolites. In this way, these antioxidants bring about structural and functional stabilization through signaling processes and pathways against HM stress (Anjitha etal. 2021).
The secondary molecules are occasionally produced in living plant cells and do not significantly contribute to the primary lives of the plants that produce them. Besides, their production is at minimal levels that are compatible with a plant species' growth physiology (Ncube & Staden 2015). Enhanced production of secondary metabolites is an adaptive vibrant detoxification mechanism evolved in plant life to reduce the injurious effects triggered by toxic metals (Edreva etal.2008,Tasiu Isah, 2019).Of these secondary metabolites, flavonoids(K. Izbiańska et al.2014) and phenolics (Kısa D etal.2016,Ghori etal 2019) are considered as stressful responses that help plants to live on metal contaminated soil.
Flavonoids act as promising abiotic stress markers. Flavonoids perform a protective role under stressful circumstances by neutralizing radical changes before they cause adverse effects in the cell. As a part of plantenvironment communication, they are among the most vital secondary metabolites produced in almost every plant parts. Flavonoids increase plants' tolerance to abiotic stress at physiological and biochemical levels by increasing antioxidant capacity, controlling cellular redox, activating stress-responsive transcription factors (TFs), regulating osmoregulation, and participating in the stress response signaling network as a signaling molecule (Shomali etal.2022).
Phenolic compounds have manifold roles regarding plant defense responses to heavy metal stress by mitigating the toxic effects of HM. In order to estimate the range of tolerance to stress factors that occur in plants, researchers can use the concentration of phenols in plant tissues as an excellent indicator. Increased phenolic compound production in heavy metal-stressed plants helps shield them from oxidative stress (Sharma etal, 2019).
Hydrocotyle umbellata L. (the invasive perennial herb) belongs to the family of Araliaceae (Hamdy etal.2018). Due to its many filiform roots, stoloniferous reproduction, and quick growth in marshy areas as well as marginal lands, its phytoremediation potential against different heavy metals (Bokhari etal 2022, Taufikurahman et al 2019 & Rashid M. etal 2020) has been studied.
However, total phenolic content (TPC) and total flavonoids content (TFC) under the influence of Cu, Cd & As either alone or in combination has been scarcely evaluated in Hydrocotyle umbellata L. Therefore, the aim of present study is to evaluate TPC and TFC in Hydrocotyle umbellata L. against the stress of Cu, Cd and As, individually as well as in combination, in different parts of the plant to examine their role in Phytoremediation of these HM. Moreover, CART model had been employed for first time in such studies.
2. Results
In order to compare the levels of metals in various plant sections across five different treatments, a two-way ANOVA was used in this study. The numerical outcomes of this analysis are shown in tables below. Basic descriptive data, such as the count, total, mean, and variance, are provided for each plant part and treatment in the
Table 1,
Table 2,
Table 3,
Table 4,
Table 5,
Table 6,
Table 7,
Table 8 and
Table 9. Plant component and treatment were examined as potential drivers of variance.
2.1. Total Phenolic content (TPC)
TPC for Cd, Cu and As, alone and in combination, at 760 nm showed the following results.
The two-way ANOVA for Cd exposure revealed no significant interactions between plant part and treatments, on TPC proving that the effect of treatments of Cd concentration was independent of the plant part and TPC was consistent. The study revealed that neither the treatments nor the plant parts had any discernible effects on the concentration of TPC (F (4, 18) = 0.491, p=0.74) or F (2, 18) = 1.549, p=0.27, respectively). These findings imply that no treatment significantly affected the Cd concentration, and that the TPC was stable throughout the various plant components as shown in
Table 1. There were no significant effects of plant part or treatment concentration on TPC at 760nm when metal is Cd.
The descriptive data for plant parts and treatments concentration for Cu metal in
H. umbellata L. are enlisted in
Table 2. Two-way ANOVA for Cu exposure revealed that there was a significant effect of plant parts on TPC when exposed to Cu stress (p= 0.009606). However, there was no significant effect of concentration of treatment on TPC when exposed to Cu (p value= 0.475848), implying that different plant parts may accumulate Cu to different extent but treatment concentration employed in recent studies had no impact on TPC.
Data describing the count, concentration treatments, plant parts and total and variance for As toxicity in recent studies are provided in
Table 3. Two-way ANOVA results showed that there was a significant effect of plant part on TPC when exposed to As toxicity (p= 0.037). But there was no significant effect of treatment concentration on TPC when exposed to As (p= 0.430971). With a computed F-value of 5.077166 and a p-value of 0.037708, the results demonstrated that plant component was a substantial source of variation in TPC and that there were considerable variations in As levels throughout the root, stem, and leaf. With a calculated F-value of 1.07065 and a p-value of (0.4309) >0.05, concentration was not discovered to be a significant source of variance. These results collectively imply that different plant sections may accumulate As to varying degrees, but that the particular treatment employed in this investigation had no appreciable impact on As concentrations. These findings may be relevant for ecological and agricultural applications as well as for understanding how As is absorbed and distributed in plants.
Numerical data for TPC for treatments, plant parts, sum and variance is described in
Table 4 for combined metals (Cu, Cd and As). The root, stem, and leaf were all present in five counts and their corresponding sums and averages of TPC values were observed in the two-way ANOVA for combined metals. Each of the five treatment groups had three counts of TPC observations, with their sums, averages, and variances shown in
Table 4.
ANOVA results for investigating the effects of plant portion on TPC exhibited the following characteristics: Sum of Squares (SS) = 0.169057, two degrees of freedom, Mean Sum of Squares (MS) = 0.084528, F = 2.548455, p = 0.139215, and F critical = 4.45897. Similarly, the treatments had an MS of 0.121897 and an SS of 0.487587, both with four degrees of freedom. Overall, but not significantly, the types of plant parts and employed treatments had an impact on the TPC. Treatment concentration had a significant effect on TPC with p value of 0.055381 when exposed to combined metals (As, Cu &Cd).
From above results it is shown that when the plant material is a leaf or stem and the metal is As, the average TPC at 760 nm is 0.91, When the plant part is a stem and the metal is Cu, the value is 0.64; when it is a stem and the metal is Cd or combined, the value is 0.83; when it is a root and the metal is Cu, the value is 0.41; when it is a root and the metal is combined, the value is 0.71; when it is a leaf, the value is 0.68; and when it is a leaf and the metal is Cd or Cu, the value is 1.02. Average TPC under different metals decreases in following order: As > Cd > Cu > combined metals.
Cd, Cu, and As are the three metals that were investigated. Each metal was found in equal amounts in the plant's root, stem, and leaf, among which each had a count of 5. TPC's sum, average, and variance for each metal-part combination are shown in
Table 5 along with their corresponding totals.
Based to our ANOVA findings, the TPC was significantly influenced by both the metal type and the plant component. The F-values for the metal type and plant component were 9.022 and 13.50465, respectively, while the mean square values were 0.624 for the metal type and 0.934 for the plant component. There was a statistically significant difference in averages across various metal types and plant sections, as shown by the P-values for both variables being less than 0.05(7.61E-05, 2.22E-05). With a P-value of 0.341, the interaction term was not statistically significant. This shows that the plant component is not a factor in the effect of metal type on the response variable. Overall, these findings highlight the significance of taking plant part and metal type into account when analyzing the response variable.
The results indicated that both the plant component and the type of metal employed had a sizable impact on the outcomes. Significant results were also obtained from the two components' interaction. This implies that the results were more significantly influenced by the combination of metal type and plant component than by either condition alone. These findings can be useful in understanding how various metals affect various plant sections and interact with one another.
The results showed a considerable impact of metal type according to plant parts, with significant variation in each metal-part combination's sum and average as well as its individual totals. Additionally, there was a substantial difference in the sum and average of TPC for each metal and component combination, as well as their individual totals, indicating a considerable impact of the plant part on the outcomes.
The combination of the two factors—metal type and plant part—had a greater influence on the outcomes than each element alone, according to the interaction between the two factors, which was also statistically significant. According to the relatively low variance for each metal-part combination, the findings were uniform across all plant components and metal kinds.
3.2. Total Flavonoids Content (TFC)
TFC measurements at 510 nm for metals Cd, Cu and As were carried out singly and in combination to see their impact on TFC and showed the following results. The data description for TFC under Cd metal in
Hydrocotyle umbellata L. are enlisted in
Table 6. The study's findings shown for Cd are such that the average count, total, and variance of the root, stem, and leaf samples did not differ significantly from one another. With respect to the root, stem, and leaf samples, the average counts were, respectively, 0.647, 0.581, and 0.663, with variance values of 0.269, 0.285, and 0.296. The five treatments did, however, show substantial variances from one another. With an average value of 1.187 and a variance value of 0.003, Treatment 4 had the highest sum value, and Treatment 5 had the lowest sum value of 0.383.
We can infer from the Two-Way ANOVA results that the Plant Part factor had no discernible impact on the samples when exposed to Cd, because the F-value was 0.062 and the P-value was 0.939, both of which are higher than the significance level of 0.05. Similar for the Treatment factor, TFC was not significantly affected by it, when exposed to Cd because the F-value was 3.557 and the P-value was 0.059, both of which are more than the significance level of 0.05.
The data description including plant part, treatment concentration, total count, average and variance for Cu exposure for TFC at 510 nm are described in
Table 7. With an F-value of 0.509 and a P-value of 0.731, the results of the Two-Way ANOVA demonstrated that the Treatments factor had no discernible influence on the samples. Interestingly, the Plant Part factor had an F-value of 0.968 and a P-value of 0.420, indicating that it had no discernible impact on the samples. Overall, the results indicate that the samples were unaffected by Cu exposure, and there were no significant changes noted in TFC between the Plant Parts when exposed to Cu toxicity.
There were no appreciable variations among the plant parts, according to the findings of the As exposure assay. With variance values of 0.244, 0.224, and 0.012, respectively, the average values for the Root, Stem, and Leaf samples were 0.397, 0.332, and 0.216, respectively as shown in
Table 8. The TFC values for different treatments did, however, differ significantly from one another. The maximum sum value for Treatment 4 was 1.954, with average values of 0.651 and 0.251, and the lowest sum value for Treatment 3 was 0.377, with average values of 0.126 and 0.007. The results of the two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) revealed that the Treatments factor had no discernible impact on the TFC, with an F-value of 1.116 and a P-value of 0.41. Similarly, the Plant Part factor also showed a non-significant effect on the TFC, with an F-value of 0.273 and a P-value of 0.768. Overall, the findings suggest that As exposure had a non-significant effect on the Plant Parts, and there were no significant differences among the treatments.
The results for the combined metals exposure showed that there were no significant differences among the Plant Parts. The average values for Root, Stem, and Leaf samples were 0.104, 0.181, and 0.266, respectively, with variance values of 0.008, 0.007, and 0.079, respectively as shown in
Table 9. However, there were significant differences observed due to the treatments. Treatment 3 had the highest sum value of 1.342, with an average value of 0.447333 and a variance value of 0.074, while Treatment 5 had the lowest sum value of 0.216, with an average value of 0.072 and a variance value of 0.001. This was further proven by Two-Way ANOVA, with an F-value of 5.148 and a P-value of 0.024, these findings demonstrated that the Treatments factor significantly affected the TFC. The Plant Part factor had an F-value of 2.453 and a P-value of 0.148 but had no statistically significant impact on the TFC.
The results of the Two-Way ANOVA for the effects of metal type and plant part on TFC showed that there were significant differences between the metal types and the plant parts. The average TFC values for Cd exposure for the Root, Stem, and Leaf samples were, respectively, 0.647, 0.581, and 0.663, with variance values of, 0.269, 0.285, and 0.296. The average TFC values for Cu exposure for the Root, Stem, and Leaf samples were 0.119, 0.593, and 0.47, respectively, with variance values of 0.005, 0.361 and 0.251, respectively. The average TFC values with exposure to As for the Root, Stem, and Leaf samples were 0.397, 0.332, and 0.216, with variance values of 0.244, 0.223, and 0.012, respectively. The average TFC values for Combined metal exposure for the Root, Stem, and Leaf samples were, respectively, 0.104, 0.181, and 0.266, with a variance value of 0.097 as shown in
Table 10. The metal type had a substantial impact on TFC, according to the Two-Way ANOVA results. The F-value for the metal type factor was 3.101 with a P-value of 0.035, while the F-value for the plant part was 0.293 with a P-value of 0.747. The interaction impact between metal type and plant part has an F-value of 0.533815 and a P-value of 0.779. Overall, the results indicate that the TFC is significantly influenced by the type of metal but the plant part as well as their interaction did not significantly influence TFC.
3.3. CART Models
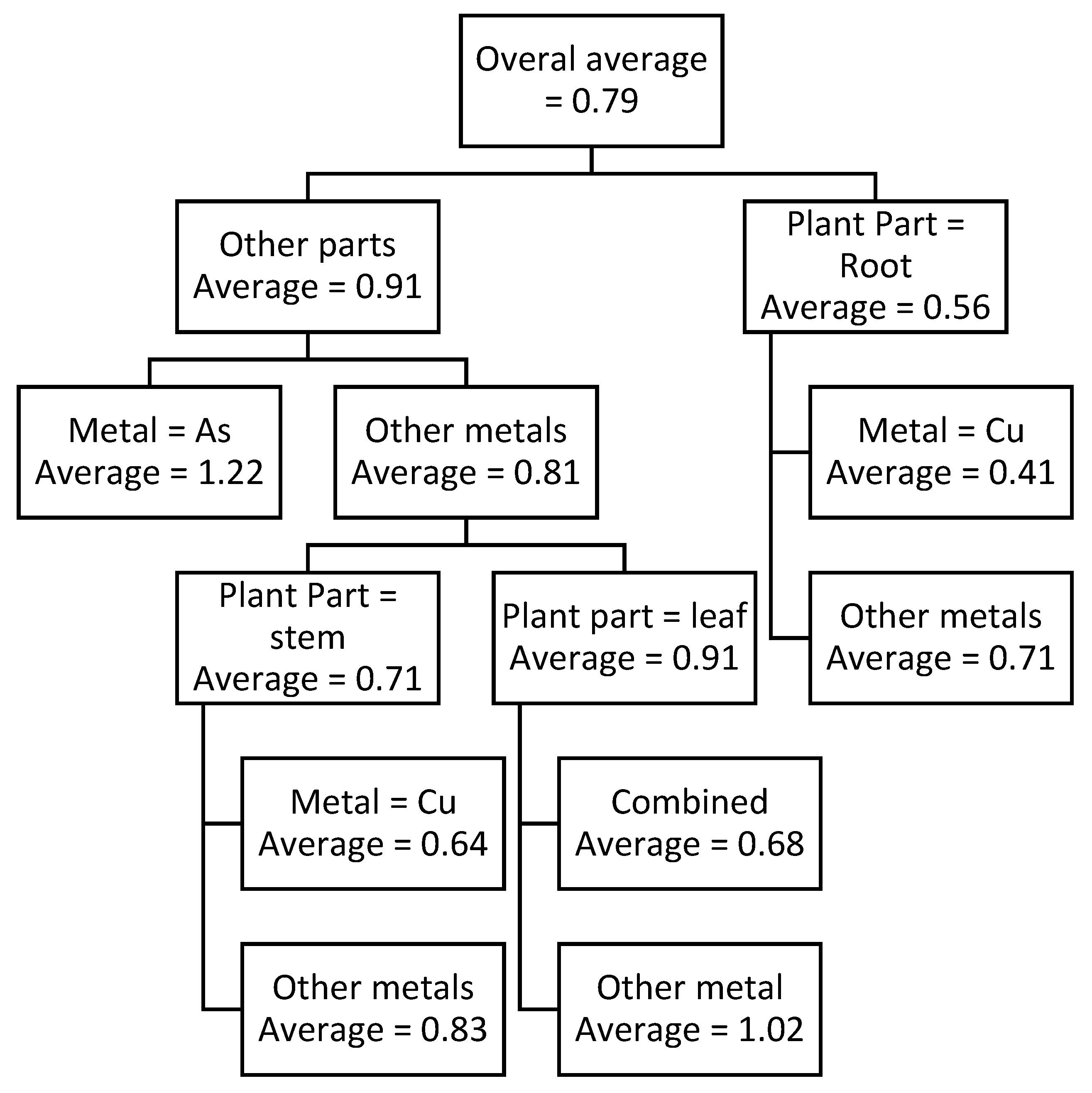
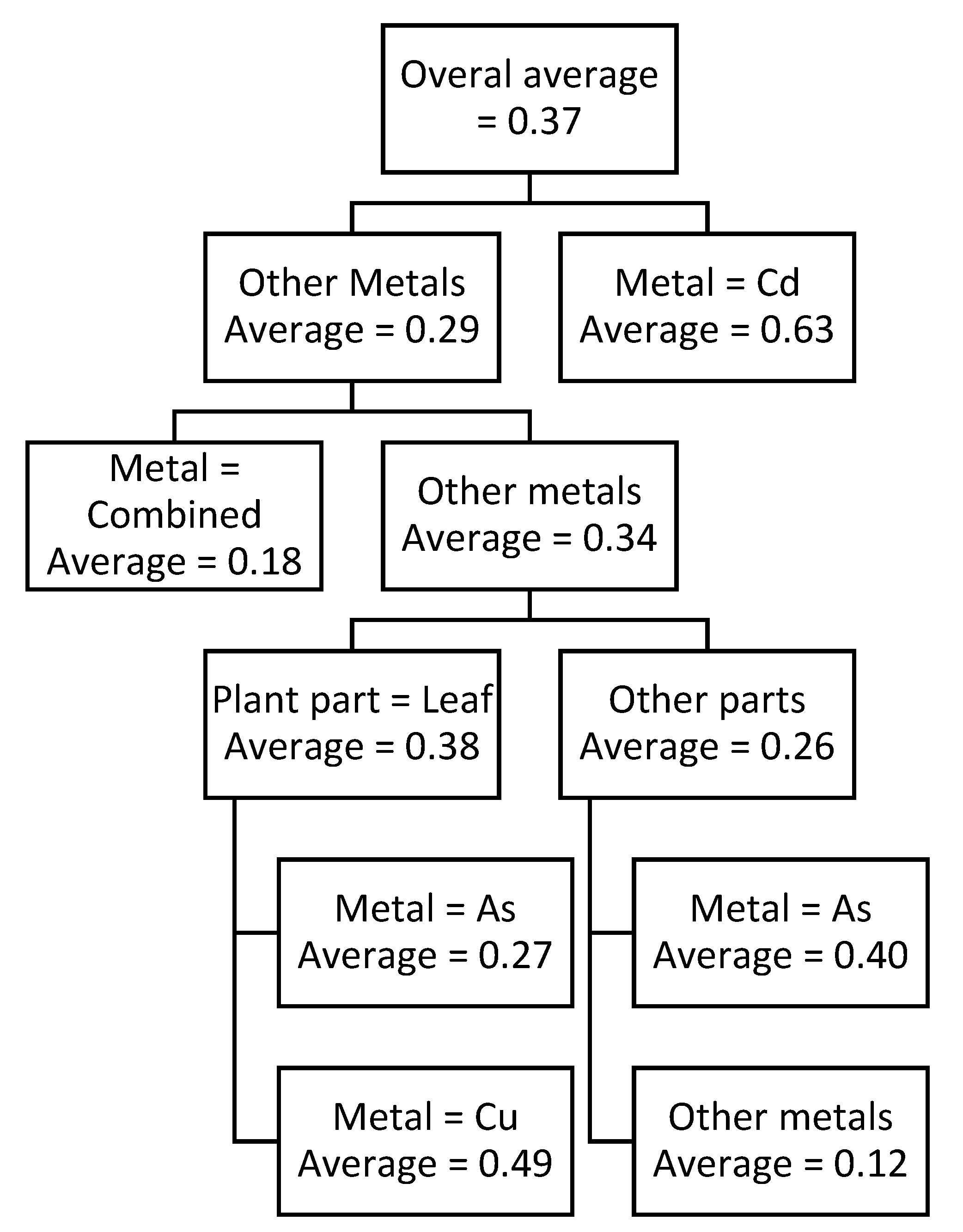
Two prediction models were developed in this study, using CART approach. One of them was for predicting TPC and the other for predicting TFC which are shown in
Figure 2 and
Figure 3, respectively. CART models, due to their branching structure, can efficiently clarify the interrelationships of variables and their impact on the output variable (TPC or TFC, in this case). CART models shown in the
Figure 2 and
Figure 3 show the condition for each node and the average TPC or TFC values for that condition. For example, the top node shows the overall average of the data for both cases. Whereas for the CART for predicting TPC (
Figure 2), the node on the extreme left-hand side in the third level shows the average TPC content of 1.12 when As is used as the metal regardless of any other factor. For the convenience of the reader,
Table 11 and
Table 12 show the statements which were extracted from CART models and the average TPC and TFC content at that condition.
The CART model for predicting TPC shows that the highest TPC is observed when leaf is exposed to Cd or Cu which is 1.02. Whereas the lowest TPC is observed root is exposed to Cu which is 0.41, which is shown in
Table 11. The CART model for predicting TFC shows that the highest TFC value is observed for Cd irrespective of plant part, this value is 0.63. On the other hand, lowest TFC value is observed when plant root or stem is exposed to Cu. These values are shown in
Table 12. Based on above findings, it can be concluded that Cu normally produces a lower reaction in terms of TPC and TFC in the plant while Cd produced a higher reaction in the plant for its stabilization.
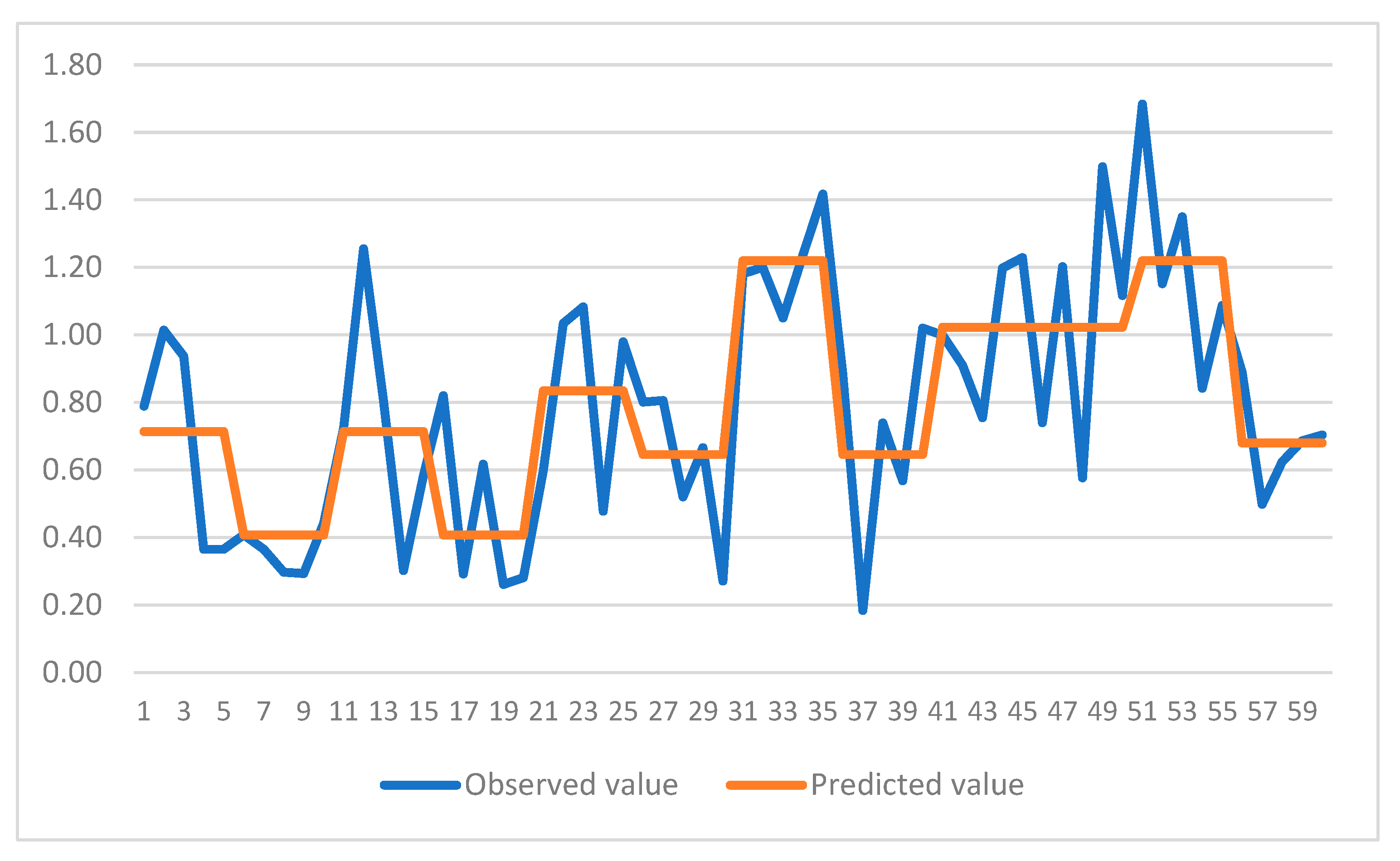
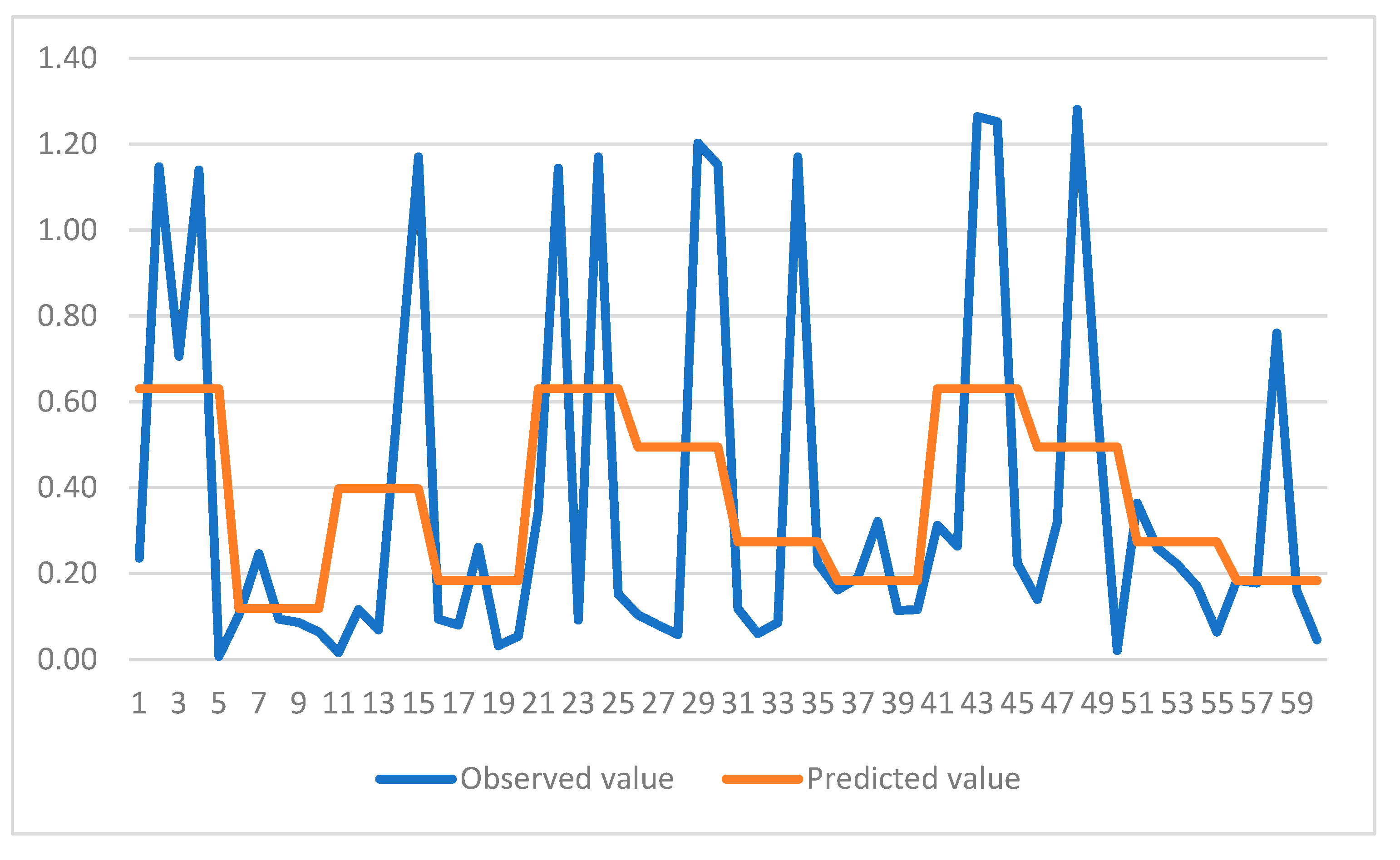
Figure 4 and
Figure 5 show comparison of predicted and observed values for the CART models. It can be observed that models have been able to capture the trend of variation for both cases. Hence, use of CART models is highly recommended for future studies in this area. Furthermore, it can be observed that the trends revealed through multiple ANOVA tests are more conveniently and efficiently incorporated in the CART models for each case. This would be another reason for employing these models in similar studies comprising of experimental data.
3. Discussion
HMs have toxic effects on plants, and these effects vary depending on the type of metal, the concentration of metal, plant part and the plant's tolerance towards that metal. Production of certain phytochemicals is one of the defense mechanisms against the stress caused by metal. ROS are generated as a result of HM exposure, and results in the production of phenolic and flavonoids in plants. Phenolic molecules distinguish themselves in plants by serving a variety of purposes, showcasing their antioxidant potential under varied stress circumstances (Vidal etal, 2020). Abiotic stress can cause a drop or rise in phenolic compounds in plants (Król et al., 2014). Production of secondary metabolites in plants differ with the type of metal used.
A key factor determining how plants react and how it affects secondary metabolism is the concentration of heavy metals. In the current study, the concentration of single metal had no significant effect on TPC and TFC but in case of combined metals, stress in TFC and TPC decreases with increasing metal stress. At lower concentrations the production of TPC and TFC were higher but when metal concentration increased, a decline in the production of total phenolics and total flavonoids was noticed. The formation of secondary metabolites is linked to heavy metal stress in plants. However, an excess of metals, especially heavy metals, can be harmful to plants; as a result, plant cells have systems in place to prevent their toxic accumulation (Eghbaliferiz and Iranshahi, 2016). Moreover, as reported by González-Mendoza etal.2018 that high concentration of HMs causes a drop in the accumulation of phenolic compounds, affected by the plant’s inability to synthesize new phenolic compounds and flavonoids. Janczak-Pieniazek et al., 2023 worked on different varieties of winter wheat with various concentrations of Pb and Cu and found that higher concentrations led to a fall in flavonoid levels. But in another study, increase in production of TPC was reported by increasing treatment concentration in leaves and roots of Kandelia obovate by application of Cd and Zn (Chen etal.2018).
Production of secondary metabolites is also linked to the plant part after HM accumulation. In the current study, it has also been found that production of secondary metabolites also vary in different parts of H. umbellata L. Highest phenolic and flavonoid contents were found in leaves followed by stem and least value was found in roots after application of Cd, Cu, As and combined metals stress. When exposed to Cd or Cu, leaves show the highest TPC, which is 1.02. and the lowest TPC found for a root exposed to copper, which is 0.41. According to the current study, Cd has the highest TFC value, which is 0.63, among all plant parts. On the other hand, when plant roots or stems are exposed to Cu, the lowest TFC value is seen. Cu typically creates a lower reaction in the plant in terms of TPC and TFC, however Cd provided a stronger reaction for the plant's stabilization. Similar results were reported previously by Makuch-Pietraś etal.2023, in which phenolic and flavonoid contents were highest in leaves than other parts when antioxidant activities in relation to the transport of heavy metals (Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb, Ni and Cr) from the soil to different parts of Betula pendula were studied. Similarly, an increase in TPC was observed in leaves of corn when exposed to Cd, Cu & Pb (Kisa D. etal.2016). Higher levels of phenolics and flavonoids were noticed in leaves of Prosopis glandulosa as compared to control plants under Cd and Cu toxicity (Mendoza G. D etal.2019). Higher content of total phenolic and flavonoids was also detected in N. biserrata collected from contaminated sites as compared to control plants (Manan F. A etal.2015). Whereas some studies showed decline in total phenolic compounds under heavy metal stress. Kisa D.et. al. 2019 reported a reduction in TPC in leaves of tomato under Cu, Cd and Pb stress and also that decrease can be related to treatment doses. Whereas enhanced TPC and TFCs were reported in Gynura procumbens under Cd and Cu stress individually, but under combined stress a reduction was observed in them. Moreover, lower levels of heavy metals encouraged the production of secondary metabolites (Ibrahim M.H 2017). In another study, the exposure to Cu considerably boosted the synthesis of phenolic compounds in roots and shoots of Imperata. Cylindrical. (Vidal C. etal 2020).
The correlation between levels of TPC and TFC with the type of metal used is also established in the present study. Overall, in recent studies the average TFC decreases in the order: Cd > Cu > As > Combined metals. Average TPC under different metals decreases in following order As > Cd> Cu > combined metals. The highest average was observed for As in the leaf, while the lowest average was observed for Cu in the root. These findings can be useful in understanding the impact of different metals on different parts of the plant, as well as how they interact with one another. This information can be used to inform future research and potentially guide strategies for managing metal pollution in the environment.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Collection of Plant Material
Plant material of Hydrocotyle umbellata L. was collected from a marshy area of Jinnah Abad in District Abbottabad, Pakistan and then propagated through rhizome cuttings. As soon as the rhizome developed fresh meristematic buds, the plants were dug out, properly cleaned with distilled water and then transplanted to pots containing Hoagland (Hoagland &Arnon1950) solution. After attaining a consistent size, plants from each pot having uniform fresh weight (0.50±10 g) were carefully chosen. We used Randomized Block Design (RBD). The control group was set without giving any metal treatment, but the experimental group were treated with various metal concentrations. After every three days, nutrient solution was constantly examined and add-on to stable transpiration loss.
4.2. Metal Treatments
Metal treatments were given on the base of the literature survey. Different aqueous solutions of selected metals with the maximum and minimum concentration, ranging from g L-1, mgL-1, to µg L-1, were prepared. For HM stress, a solution of Copper sulphate (CuSO4.5H2O) was prepared at the following 5 different molar concentrations i.e. 5, 10, 15, 20, 25 mg/L. For Cadmium a solution of Cadmium chloride (CdCl2. H2O) was synthesized by using 200,400,600,800 and 1000µg/L. For Arsenic toxicity a solution of Arsenic trioxide was prepared (As2O3) for following 5 different concentrations: 0.5, 0.75, 1.0, 1.25 and 1.5mg/L. And for combined metals stress the above concentrations were combined for each treatment of As, Cd and Cu..On 10th day of metal treatment, plants were harvested and separated into roots, stolon and leaves.Plant parts were bathed with distilled water to get rid of any adsorbent particles and air-dried on blotting paper.
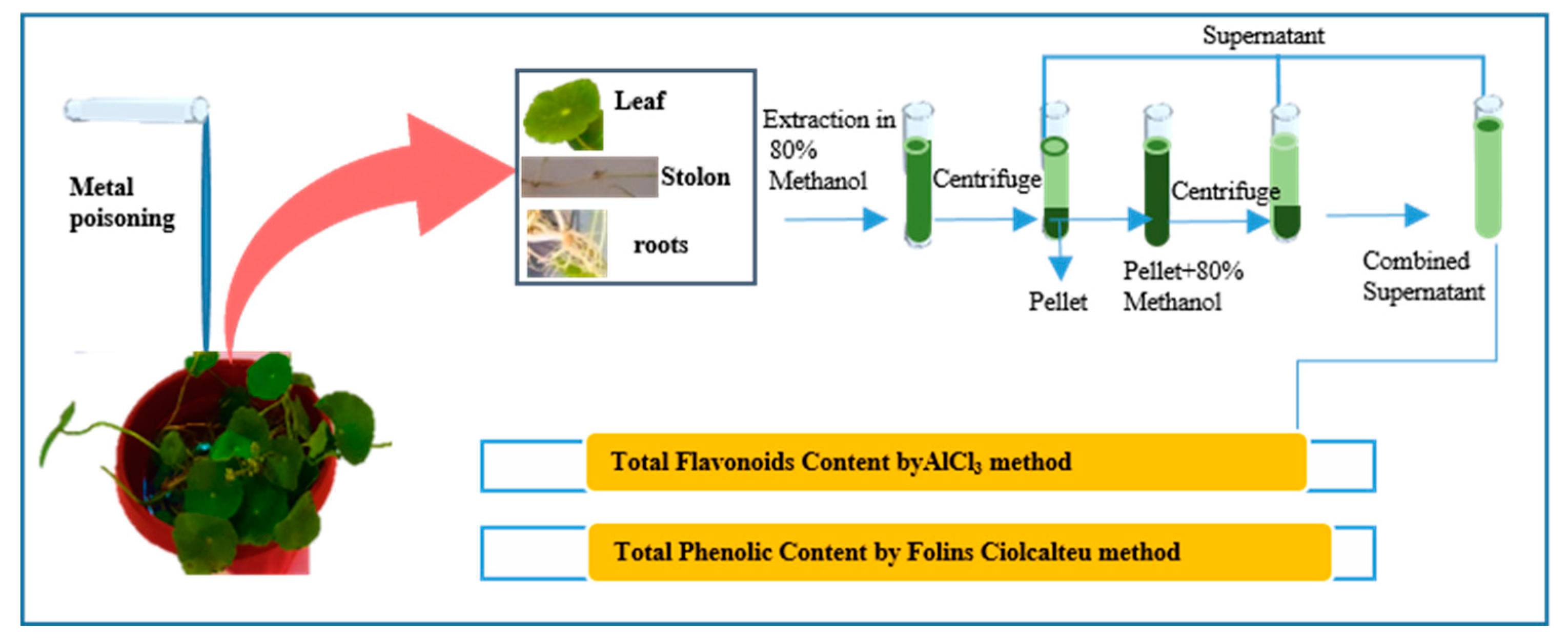
4.3. Methanol Extract Preparation for Total Phenolic, Flavonoid content
By following the protocol of Martinez-Villaluenga etal 2009, 80% aqueous methanol (1g/10ml) extracts were prepared from fresh samples of roots, stem and leaves of
H. umbellata L. and placed at shaker incubator at 37℃ for 2 hours. Then the mixture was centrifuged at 6000 rpm for 15 minutes. Fresh supernatants were collected in a sterile container; this procedure was repeated thrice. The solid residue was re-extracted three times in methanol (1/10w/v) and supernatants were pooled for determination of TPC and TFC as shown in
Figure 1.
4.4. Determination of Total Phenolic and Flavonoids Content
The Folin and Ciocalteu reagent was used to calculate the total phenolics in the extracts, by adopting the procedure reported by Chandra et al. (2014). Using a spectrophotometer, measurements of the sample and the standard were taken at 760 nm in comparison to the reagent blank. Folin-Ciocalteu's phenol reagent (1:1) and water (0.6 mL) were combined with the test sample (0.2 mL). After 5 minutes, the mixture was added 1 mL of saturated sodium carbonate solution (8% w/v in water), and the volume was then increased to 3 mL with distilled water. After centrifuging the reaction for 30 minutes in the dark, the absorbance of blue color in various samples was measured at 760 nm. On the basis of a gallic acid standard curve, the phenolic content was estimated as gallic acid equivalents GAE/g of plant material.
4.5. Determination of Total Flavonoids Content
The sample's total flavonoid content was determined using the Aluminum chloride colorimetric method (Chandra et al., 2014). Quercetin was utilized to create the standard calibration curve for the measurement of total flavonoid concentration. The standard quercetin solutions were made by serially diluting quercetin with methanol (5-200 g/mL) after the stock quercetin solution was made by dissolving 5.0 mg of quercetin in 1.0 mL of methanol. Standard quercetin extracts or solutions in a volume of 0.6 mL were separately combined with 0.6 mL of 2% Aluminum chloride. The mixture was then left at room temperature for 60 minutes. The absorbance of the reaction mixtures was measured using a spectrophotometer against a blank at 510nm. The total flavonoid content of the test was determined using the calibration plot, and the result was expressed as mg quercetin equivalent (QE)/g of plant material.
4.6. Linking TPC and TFC to Remediation
In the context of phytoremediation, there is a strong correlation between the level of total phenolics, flavonoids, and HMs in plants. Because of their strong antioxidant qualities and capacity to absorb and detoxify the metals, plants with higher total phenolic and flavonoid content are better able to remove heavy metals from polluted soil.
In general, efficient phytoremediation solutions require an understanding of the underlying mechanisms governing the interaction between heavy metal stress and phytochemical synthesis. Plants are a significant tool for phytoremediation because of the interaction between HMs, TPC, and TFC, which has an important effect on how well they can remove toxins from the environment. Conversely, the plants having high TFC and TPC can be used for phytoremediation of HMs which, on absorbing metal from surrounding, will drop its level of TPC and TFC.
4.7. Statistical Analyses
Two types of analysis were used in this study, Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) and Classification and Regression Trees (CART). The first one is a statistical technique used for comparisons while the latter is used for developing prediction models.
ANOVA is used for making statistical comparisons about different effects of one or more variables which are acting simultaneously on the collected samples. The use of this technique can determine which variables have significant effects and what is their estimate (Scheffe, 1999). In this technique, difference between means of several types of samples is checked for its statistical significance, in relation to variance within the group of same variables (Larson, 2008). ANOVA can be one-way, two-way or multivariable depending on the number of effects to be investigated. In the present study, two-way ANOVA was used to determine the effects of plant part, treatment type and metal type on TPC and TFC. This analysis is based on Fisher (F) statistic, which is calculated as the ratio of variance within the group to the overall variance. In this study, F-statistic of the ANOVA tests is compared with standard F-value and the significance level is set at 5% which is commonly found for statistical tests (Sawyer, 2009).
CART models use a tree-building algorithm using if-then split conditions. At each node of the tree, the best split of data is determined by using Gini (G) index (Razi and Athapilly, 2005). G-index depends upon the nature of the variable (continuous, discrete, etc.). In the end, the model selects the variable having the lowest index value. The process is repeated for each node until further splitting of the data is no longer possible (Daniya et al., 2020).
5. Conclusions
The present study is the first report on heavy metal levels, preliminary screening of phenolic and flavonoid contents in Hydrocotyle umbellata L. after exposure to As, Cd and Cu metals alone and in combination. Experimental results were analyzed using descriptive statistics, ANOVA tests and CART models. Following conclusions were drawn from the experimental data and analysis.
The concentration of single metal has no significant effect on TPC and TFC but in case of combined metals stress TFC and TPC decreases with increasing metal stress. At lower concentrations, the production of TPC and TFC were higher but when metals concentration increase, there is a decline in the production of total phenolics and flavonoids. Average TFC decreases in the order: Cd > Cu > As > Combined metals. Average TPC under different metals decreases in following order: As > Cd> Cu > combined metals. It has also been found that production of secondary metabolites also vary in different parts of H.umbellata L. Highest Phenolics and flavonoids were found in leaves followed by stem and least value was found in leaves after application of Cd, Cu, As and combined metals stress. The results of the CART model also support these findings. In addition, these models were able to provide a graphical summary of all the results obtained from the previous analysis along with the multi-level interaction of different metal types and plat parts. Hence, their use is highly recommended for future studies.
It was concluded that the plant produces significant levels of TPC and TFC for combating HMs stress. Therefore, it can be successfully implied in phytoremediation of areas contaminated with Cu, Cd, and As alone or their combination.
Author Contributions
For research articles with several authors, a short paragraph specifying their individual contributions must be provided. The following statements should be used “Conceptualization, Q.M. and G.M.S.G.; methodology, Q.M.; S.S.; S.H.S.; software, U.G.; validation, X.X., Y.Y. and Z.Z.; formal analysis, S.S.; investigation, S.S.H.; resources, Q.M.; data curation, G.D.A.; writing—original draft preparation, S. H.S.; writing—review and editing, Q.M.; G.M.S.G.; visualization, A.F.A.; supervision, Q.M.; project administration, K.F.A.; funding acquisition, A.F.A.; G.D.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors would like to extend their sincere appreciation to the Researchers Supporting Project Number (RSPD2023R561), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to extend their sincere appreciation to the Researchers Supporting Project Number (RSPD2023R561), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gupta, A.; Joia, J.; Sood, A.; Sood, R.; Sidhu, Y.; Kaur, G. Microbes as Potential Tool for Remediation of Heavy Metals: A Review. J. Microb. Biochem. Technol. 2016, 8, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Mitra, M.; Agarwal, P.; Mahapatra, K.; De, S.; Sett, U.; Roy, S. Oxidative and genotoxic damages in plants in response to heavy metal stress and maintenance of genome stability. Plant Signal. Behav. 2018, 13, e1460048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jańczak-Pieniążek, M.; Cichoński, J.; Michalik, P.; Chrzanowski, G. Effect of Heavy Metal Stress on Phenolic Compounds Accumulation in Winter Wheat Plants. Molecules 2023, 28, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar-Ul-Hye, M.; Naeem, M.; Danish, S.; Fahad, S.; Datta, R.; Abbas, M.; Rahi, A.A.; Brtnicky, M.; Holátko, J.; Tarar, Z.H.; et al. Alleviation of Cadmium Adverse Effects by Improving Nutrients Uptake in Bitter Gourd through Cadmium Tolerant Rhizobacteria. Environments 2020, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kısa, D.; Elmastaş, M.; Öztürk, L.; Kayır. Responses of the phenolic compounds of Zea mays under heavy metal stress. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2016, 59, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K.S. Anjitha, P.P. Sameena, Jos T. Puthur Functional aspects of plant secondary metabolites in metal stress tolerance and their importance in pharmacology Plant Stress Volume 2, December 2021. 20 December.
- Mansour, S.A. Heavy metals of special concern to human health and environment. In Practical Food Safety: Contemporary Issues and Future Directions; JohnWiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 213–233. [Google Scholar]
- Kebert, M.; Kostić, S.; Vuksanović, V.; Markić, A.G.; Kiprovski, B.; Zorić, M.; Orlović, S. Metal- and Organ-Specific Response to Heavy Metal-Induced Stress Mediated by Antioxidant Enzymes’ Activities, Polyamines, and Plant Hormones Levels in Populus deltoides. Plants 2022, 11, 3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. Mol. Clin. Environ. Toxicol. 2012, 101, 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamverdian, A.; Ding, Y.; Mokhberdoran, F.; Xie, Y. Heavy Metal Stress and Some Mechanisms of Plant Defense Response. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wen, K.-S.; Ruan, X.; Zhao, Y.-X.; Wei, F.; Wang, Q. Response of Plant Secondary Metabolites to Environmental Factors. Molecules 2018, 23, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, P.A.; Kruuk, L.E.B.; Nicotra, A.B. How to analyse plant phenotypic plasticity in response to a changing climate. New Phytol. 2019, 222, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Roychoudhury, A. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and response of antioxidants as ROS-scavengers during environmental stress in plants. Front. Environ. Sci. 2014, 2, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, M.C.; Kanashiro, S.; Domingos, M.; Rinaldi, M.C.S.; Tavares, A.R. Physiological and biochemical changes in tree seedlings growing in urban forest soil contaminated with copper in São Paulo, Brazil. Plant Soil 2021, 464, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsherif, E.A.; Al-Shaikh, T.M.; AbdElgawad, H. Heavy Metal Effects on Biodiversity and Stress Responses of Plants Inhabiting Contaminated Soil in Khulais, Saudi Arabia. Biology 2022, 11, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ncube, B.; Van Staden, J. Tilting Plant Metabolism for Improved Metabolite Biosynthesis and Enhanced Human Benefit. Molecules 2015, 20, 12698–12731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edreva A, Velikova V, Tsonev T, et al. Stress-protective role of secondary metabolites: diversity of functions and mechanisms. Gen Appl Plant Physiol. 2008, 34, 67–78 CAS Google Scholar. [Google Scholar]
- Tasiu Isah Stress and defense responses in plant secondary metabolites production Biological Research volume 52, Article number: 39 (2019).
- Karolina Izbiańska, Magdalena Arasimowicz-Jelonek, Joanna Deckert., Phenylpropanoid pathway metabolites promote tolerance response of lupine roots to lead stress Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 110 (2014) 61–67.
- Ghori, N.-H.; Ghori, T.; Hayat, M.Q.; Imadi, S.R.; Gul, A.; Altay, V.; Ozturk, M. Heavy metal stress and responses in plants. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 1807–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shomali, A.; Das, S.; Arif, N.; Sarraf, M.; Zahra, N.; Yadav, V.; Aliniaeifard, S.; Chauhan, D.K.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Diverse Physiological Roles of Flavonoids in Plant Environmental Stress Responses and Tolerance. Plants 2022, 11, 3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Shahzad, B.; Rehman, A.; Bhardwaj, R.; Landi, M.; Zheng, B. Response of Phenylpropanoid Pathway and the Role of Polyphenols in Plants under Abiotic Stress. Molecules 2019, 24, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, S.A.; El Hefnawy, H.M.; Azzam, S.M.; Aboutabl, E.A. Botanical and genetic characterization of Hydrocotyle umbellata L. cultivated in Egypt. Bull. Fac. Pharmacy, Cairo Univ. 2018, 56, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokhari, S.H.; Nawaz, G.; Azizullah, A.; Mahmood-Ul-Hassan, M.; Ali, Z. Heavy metals phytofiltration potential of Hydrocotyle umbellata from Nullah Lai wastewater and its environmental risk. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2022, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taufikurahman, T.; Pradisa, M.A.S.; Amalia, S.G.; Hutahaean, G.E.M. Phytoremediation of chromium (Cr) using Typha angustifolia L., Canna indica L. and Hydrocotyle umbellata L. in surface flow system of constructed wetland. IOP Conf. Series: Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 308, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahrine Rashid , Iftilkhar Ahmad , Ashique Muhammad , Mahmood Ul Hassan Phytoremediation of battery industry effluent through aquatic macrophytes International Journal of Biological Research, 8 (1) (2020) 6-16.
- Vidal, C.; Ruiz, A.; Ortiz, J.; Larama, G.; Perez, R.; Santander, C.; Ferreira, P.A.A.; Cornejo, P. Antioxidant Responses of Phenolic Compounds and Immobilization of Copper in Imperata cylindrica, a Plant with Potential Use for Bioremediation of Cu Contaminated Environments. Plants 2020, 9, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, A.; Amarowicz, R.; Weidner, S. Changes in the composition of phenolic compounds and antioxidant properties of grapevine roots and leaves (Vitis vinifera L.) under continuous of long-term drought stress. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2014, 36, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghbaliferiz, S.; Iranshahi, M. Prooxidant Activity of Polyphenols, Flavonoids, Anthocyanins and Carotenoids: Updated Review of Mechanisms and Catalyzing Metals. Phytotherapy Res. 2016, 30, 1379–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Mendoza, D.; Troncoso-Rojas, R.; Gonzalez-Soto, T.; Grimaldo-Juarez, O.; Ceceña-Duran, C.; Duran-Hernandez, D.; Gutierrez-Miceli, F. Changes in the phenylalanine ammonia lyase activity, total phenolic compounds, and flavonoids in Prosopis glandulosa treated with cadmium and copper. 2018, 90, 1465–1472. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, Q.; Lu, H.; Li, J.; Yang, D.; Liu, J.; Yan, C. Phenolic metabolism and related heavy metal tolerance mechanism in Kandelia Obovata under Cd and Zn stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 169, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makuch-Pietraś, I, Dorota Grabek-Lejko,Anna Górka &Idalia Kasprzyk Antioxidant activities in relation to the transport of heavy metals from the soil to different parts of Betula pendula (Roth.)Journal of Biological Engineering volume 17, Article number: 19 (2023).
- González-Mendoza, D.; Troncoso-Rojas, R.; Gonzalez-Soto, T.; Grimaldo-Juarez, O.; Ceceña-Duran, C.; Duran-Hernandez, D.; Gutierrez-Miceli, F. Changes in the phenylalanine ammonia lyase activity, total phenolic compounds, and flavonoids in Prosopis glandulosa treated with cadmium and copper. 2018, 90, 1465–1472. [CrossRef]
- Manan, F.A. , Mamat D.D., Samad A.A., Ong Y.S., Ooh K.F. and Chai T.T. (2015), Heavy metal accumulation and antioxidant properties of Nephrolepis biserrata growing in heavy metal-contaminated soil, Global NEST Journal, 17(3), 544-554.
- Kısa, D. , Kayır, Ö., Sağlam, N., Şahin, S., Öztürk, L. & Elmastaş, M. (2019). CHANGES OF PHENOLIC COMPOUNDS IN TOMATO ASSOCIATED WITH THE HEAVY METAL STRESS. Bartın University International Journal of Natural and Applied Sciences, 2 (1), 35-43. 4736. Available online: https://dergipark.org.tr/en/pub/jonas/issue/47366/549252.
- Ibrahim, M.H.; Kong, Y.C.; Zain, N.A.M. Effect of Cadmium and Copper Exposure on Growth, Secondary Metabolites and Antioxidant Activity in the Medicinal Plant Sambung Nyawa (Gynura procumbens (Lour.) Merr). Molecules 2017, 22, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoagland D.R, Arnon D.I, The water culture method for growing plants without soil. California Agricultural Experiment Station Circular, 1950347, 1-32.
- Cristina Martínez-Villaluenga , Henryk Zielin´ ski , Juana Frias , Mariusz K. Piskuła , Halina Kozłowska , Concepción Vidal-Valverde . Antioxidant capacity and polyphenolic content of high-protein lupin products. Food Chemistry 112 (2009) 84–88.
- Chandra, S.; Khan, S.; Avula, B.; Lata, H.; Yang, M.H.; ElSohly, M.A.; Khan, I.A. Assessment of Total Phenolic and Flavonoid Content, Antioxidant Properties, and Yield of Aeroponically and Conventionally Grown Leafy Vegetables and Fruit Crops: A Comparative Study. Evidence-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffe, H. (1999). The Analysis of Variance (Vol. 72). John Wiley & Sons.
- Larson, M. G. (2008). Analysis of Variance. Circulation, 117(1), 115-121.
- Sawyer, S.F. Analysis of Variance: The Fundamental Concepts. J. Man. Manip. Ther. 2009, 17, 27E–38E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razi, M.A.; Athappilly, K. A comparative predictive analysis of neural networks (NNs), nonlinear regression and classification and regression tree (CART) models. Expert Syst. Appl. 2005, 29, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniya, T.; Geetha, M.; Kumar, K.S. Classification and Regression Trees with Gini Index. Adv. Math. Sci. J. 2020, 9, 8237–8247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).