Submitted:
28 June 2023
Posted:
28 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Immune Response to CCHF Infection
3. Animal Models for CCHF
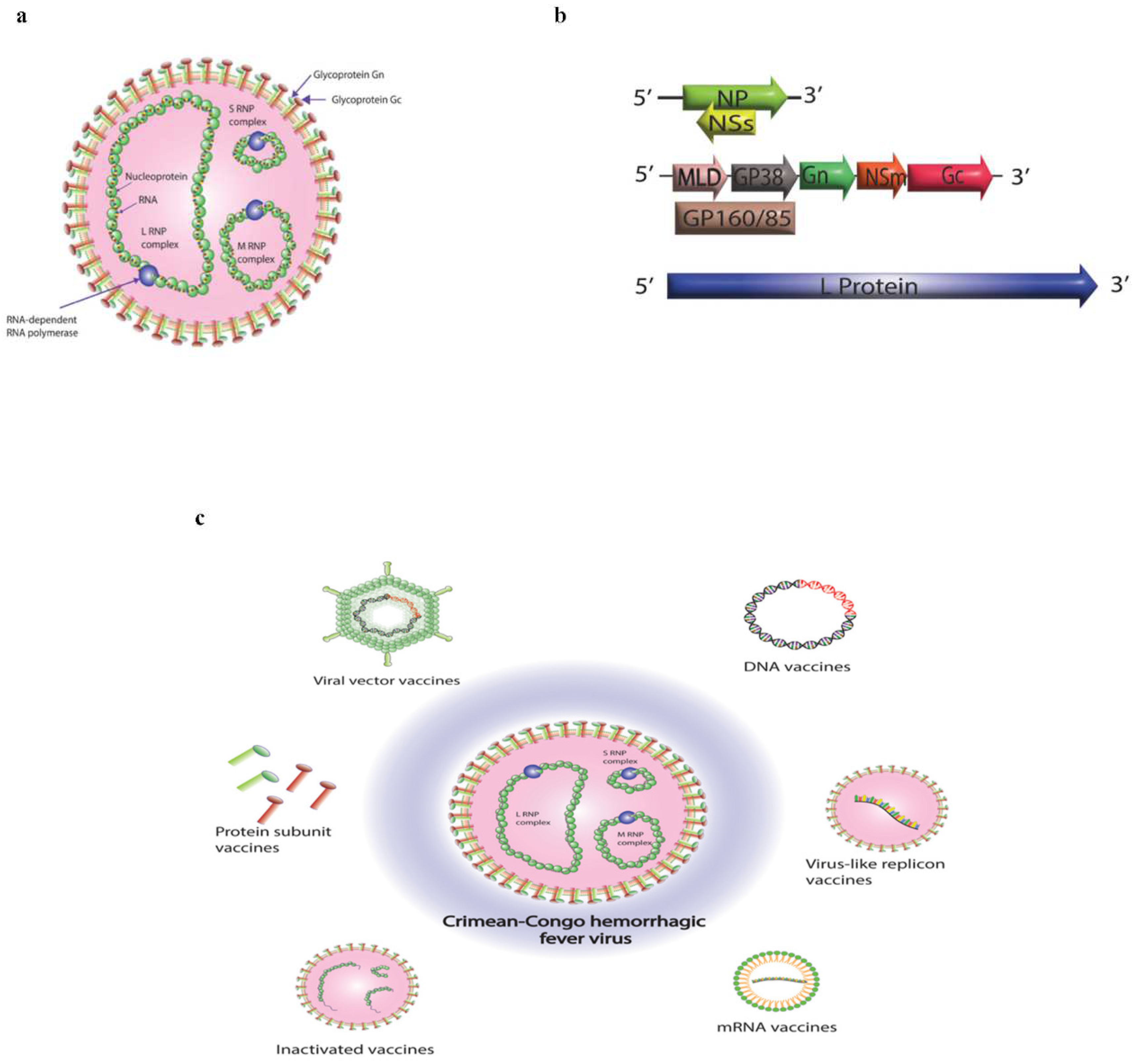
4. Vaccine Targets of CCHF
4.1. The nucleoprotein (NP)
4.2. The Glycoproteins (GPC)
5. Platforms for CCHF vaccine candidates
5.1. Inactivated Vaccines
5.2. Subunit Vaccines
5.3. DNA Vaccines
5.4. Virus Like Replicon Vaccines
5.5. mRNA Vaccines
5.6. Viral Vector Vaccines
| Vaccine design platforms | Strain name and types of antigen | Animal Models |
Doses and vaccination strategies | Spesific antibody response | Neutralizing antibody response | T cell immune response | CCHFV challenge |
Survival rate% | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inactivated vaccines | Whole CCHFV from mouse-brain | NE | Several thousand people took repeated vaccination | NE | Yes | NE | NE | NE | [142] |
| Bulgarian V42/81 strain; CCHFV whole antigen from mouse brain | NE | One group received a single dose, while the second group received four doses. | Yes | Yes | Yes | NE | NE | [143,144] | |
| Turkey-Kelkit06 strain; CCHFV whole antigen from cell culture (Vero-E6) | IFNAR-/- mice and BALB/c mice with transiently immune suppressed by mAb-5A3 | IFNAR-/- mice: Administered (IP), at doses 5 μg, 20 μg and 40 μg of inactivated vaccine, on days 0, 21 and 42. BALB/c mice: Administered (IP), at doses 5 μg, 10 μg and 20 μg of inactivated vaccine, on days 0, 14 and 27. |
Yes | Yes | Yes | Turkey-Kelkit06 strain; 1000FFU (IFNAR-/-) and 100FFU (Balb/C) |
80% protected (IFNAR-/-), 100% protected (Balb/C) | [121,145,146] | |
| Subunit vaccines | IbAr10200 strain; CCHFV Gn and Gc ectodomain | STAT1 knockout mice | Administered (IP), at doses 1.4 μg, 7.5 μg and 15 μg of Gn and Gc, on days 0 and 21 |
NE | Yes | NE | IbAr10200 strain; 100PFU | Not protected | [147] |
| IbAr10200 strain; extracellular region of Gn (eGn), extracellular region of Gc with truncation of C terminal (eGc), neutralizing antibody region of Gc (NAB) | BALB/c mice | Administered (SC), at doses1 μg, 5 μg and 20 μg of surface display protein of G-GP with eGn, eGc, at weeks 0, 3, 6 and 9 |
Yes | Yes | Yes | NE | NE | [148] | |
| Chinese Xinjiang strain HANM18; Gn and NP from CCHFV expressed in baculovirus expression system as rvAc-Gn, rvAc-NP and rvAc-Gn-NP | BALB/c mice | 107 PFU, on days 0, 14 and 28 |
Yes | NE | Yes | NE | NE | [149] | |
| CCHFV Iranian strain; Gn and Gc expressed in transgenic tobacco leaves | BALB/c mice | Feeding (leaves), at dose 10 μg of Gc/Gn, at weeks 0, 1, 2 and 3 Feeding (roots), at dose 10 μg of Gc/Gn, at weeks 0, 1, 2, 3 |
Yes | NE | NE | NE | NE | [151] | |
| DNA vaccines | IbAr10200 strain; GPC | BALB/c mice | Administered (gene gun), at dose 2.5 μg of the vaccine from each CCHFV+ RVFV + HTNV+ TBEV as total 10 μg, alone or combined, at weeks 0, 4 and 8 |
NE | Yes | NE | NE | NE | [154] |
| IbAr10200 strain; Ubiquitin linked version of Gn, Gc and NP | IFNAR-/- mice | Administered (ID), at dose 15 μg of the vaccine three times with 4 weeks interval between 1st and 2nd dose and three weeks interval between 2nd and 3rd dose | Yes | Yes | Yes | IbAr10200 strain; 400FFU | 100% protected | [116] | |
| IbAr10200 strain; GPC | IFNAR-/- mice and C57BL/6 mice with transiently immune suppressed by mAb-5A3 |
Administered (IM), at dose 25 μg of GPC, at weeks 0, 3 and 6 |
Yes | Yes | NE | IbAr10200 strain; 100PFU | Protective efficacy 71,4% for IFNAR-/- mice and 60% for transiently immune suppressed mice | [155] | |
| IbAr 10200 strain; GPC from | C57BL/6 mice with transiently immune suppressed by mAb-5A3 | Administered (IM), at dose 50 μg of GPC, at weeks 0, 3 and 6 |
Yes | NE | Yes | IbAr10200 and Afg09-2990 strains; 100PFU |
100% protected against IbAr10200, 80% protected against Afg09-2990 |
[156] | |
| Ank-2 strain; NP with CD24 |
BALB/c for immunological responses and IFNAR-/- mice for challenge studies | Administered (IM), at dose 50 μg of pV-N13 and 40 μg of pV-N13 with 10 μg of CD24, on days 0 and 14 |
Yes | NE | Yes | Ank-2 strain; 1000 TCID50 |
100% protected | [157] | |
| IbAr10200 strain; NP, N terminal Gn and C terminal Gc fused with LAMP1 to generate three candidate vaccines | Human MHC (HLA-A11/DR1) | Administered (IM), at dose 70 μg pVAX-LAMP1-NP, 70 μg pVAX-LAMP1-Gn, 70 μg pVAX-LAMP1-Gc, at weeks 0, 3 and 6 |
Yes | Yes | Yes | IbAr10200 strain; 100 TCID50 CCHFV tecVLPS |
Instead of measuring survival percentages, NanoLuc activities measured, NP had the lowest levels of NanoLuc activities in their liver, spleen, and kidney | [158] | |
| Hoti strain; Ubiquitin fused with GPC and NP |
Cynomolgus macaque | Administered (IM), at dose1 mg of pNP + 1 mg of pGPC, on days 0, 21 and 42 |
Yes | Poor neutralization acitivity | Yes | Hoti strain; 1X105 TCID50 |
Survival percentage was not assessed due to the non-uniform lethality of CCHFV in this animal model | [159] | |
| Viral like replicon particles (VRP) vaccines | IbAr10200 strain; S and L segment, Oman 98 strain; M segment |
IFNAR-/- mice | Administered (SC), at dose 105 TCID50 or 103 TCID50 of VRPs, single vaccination |
Yes | NE | NE | IbAr1020 strain; 100 TCID50 |
Low dose showed 77% protection and high dose showed 100% protection | [160] |
| IbAr10200 strain; S and L segment, Oman 98 strain; M segment |
IFNAR-/- mice | Administered (SC), at dose 1 × 105 TCID50 VRPs, single vaccination |
Yes | NE | NE | Oman 97 strain and CCHFV-Turkey strain; 100 TCID50 |
100% protected | [161] | |
| IbAr10200 strain; S and L segment, Oman 98 strain; M segment |
IFNAR-/- mice | Administered (SC), at dose 1 × 105 TCID50 VRPs, single vaccination |
NE | NE | NE | CCHFV-Turkey strain; 100 TCID50 |
After 14,7, and 3days following vaccination; 100% protected |
[162] | |
| Hoti strain; Gn and Gc |
BALB/c mice | Administered (SC), at dose 106 particles, at weeks 0, 2 and 5 |
Yes | Yes | NE | NE | NE | [164] | |
| SPU 187/90 strain; NP | NIH-III Heterozygous mice strain | Administered (IM), at dose 100 μg Sindbis replicon (expressing NP), on days 0, 21 and 42 Administered (IM), at dose 100 μg of Sindbis replicon (expressing NP) + 50 μg Poly (I:C), on days 0, 21 and 42 |
Yes | NE | Yes | NE | NE | [166] | |
| Hoti strain; NP and GPC |
C57BL/6 mice with transiently immune suppressed by mAb-5A3 | Administered (IM), at dose 2.5 μg of NP, 2.5 μ GPC and 5 μg of NP+GPC, on days 0 and 28 |
Yes | Poor neutralization activity | Yes | UG3010; 100TCID50 | 100% protected for NP and NP+GPC, 40% protected for GPC |
[167] | |
| mRNA vaccines | Ank-2 strain; NP |
C57BL/6 mice for immunogenicity and IFNAR-/- mice for challenge studies |
Administered (IM), at dose 25 μg of NP, at weeks 0 and 2 |
Yes | No | Yes | Ank-2 strain; 100LD50 |
Double dose immunized group showed 100% protection | [170] |
| IbAr10200 strain; NP, Gn and Gc | IFNAR-/- mice | Administered (ID), at doses 10 μg of NP, 10 μg of Gn, 10 μg of Gc and 20 μg of NP+ Gn+ Gc, at weeks 0 and 3 |
Yes | Yes | Yes | IbAr10200 strain; 400FFU |
100% protected | [171] | |
| Viral vector-based vaccines | IbAr10200 strain; GPC expressed in modified vaccinia virus Ankara | IFNAR-/- mice | Administered (IM), at dose 107 PFU, at weeks 0 and 2 |
Yes | NE | Yes | IbAr10200 strain; 200TCID50 |
100% protected | [174] |
| IbAr10200 strain; NP expressed in modified vaccinia virus Ankara | IFNAR-/- mice | Administered (IM), at dose 107 PFU, at weeks 0 and 2 |
Yes | NE% | Yes | IbAr10200 strain; 200TCID50 | Not protected | [175] | |
| IbAr10200 strain; NP expressed in Adenovirus type 5 | IFNAR-/- mice | Administered (IM), 1.25x107 PFU for first dose at day 0, Administered (IN), 1x108 PFU for second dose at day 28 |
Yes | NE | NE | IbAr10200 strain; 1000LD50 | 78% protected | [177] | |
| Ank-2 strain; NP expressed in Bovine Herpesvirus Type 4 (BoHV-4) |
BALB/c mice for serological assay and IFNAR-/- mice for challenge studies | Administered (IP), at dose 100 TCID50, at weeks 0 and 2 |
Yes | No | Yes | Ank-2 strain 100LD50 | 100% protected | [178] | |
| IbAr10200 strain; GPC expressed in ChAdOx2 (Chimpanzee Adenovirus) | BALB/c mice for immunogenicity and IFNAR-/- mice for challenge studies | Administered (IM), at dose 5X107 infectious unit (IU), on days 0 and 14 |
Yes | Yes | Yes | IbAr10200 strain; 200FFU |
100% protected | [179] | |
| IbAr10200 strain; GPC was expressed in Vesicular Stomatitis Virus expression system | STAT1 knock out mice | Administered (IP), at dose 107 PFU on days 0 and 21 |
Yes | Yes | NE | Turkey2004 strain; 50PFU |
100% protected | [180] |
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CCHFV | Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus |
| S | small |
| M | medium |
| L | large |
| RdRp | RNA-dependent RNA polymerase |
| NP | nucleoprotein |
| GPC | glycoprotein precursor |
| OTU | ovarian tumor |
| IFN | interferon |
| ISGs | interferon-stimulated genes |
| IFNAR-/- | IFN1 deficient mice |
| mAb | monoclonal antibody |
| TLR | toll-like receptor |
| PRRs | pattern recognition receptors |
| PAMPs | pathogen-associated molecular patterns |
| DIC | disseminated intravascular coagulation |
| Nabs | neutralizing antibodies |
| bsAbs | bispecific antibodies |
| Stat1−/− | signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 |
| IV | intravenous |
| SC | subcutaneous |
| NSM | nonstructural M protein |
| MLD | mucin-like domain |
| Al(OH)3 | aluminum hydroxide |
| IS | immune-suppressed |
| S2 | drosophila schneider 2 |
| GEM-PA | enhancer matrix-protein anchor |
| LAMP1 | lysosome-associated membrane protein 1 |
| VRP | Virus like replicon |
| VEEV | Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus |
| WNV | West Nile virus |
| LNP | lipid nanoparticle |
| AdHu5 | adenovirus type 5 |
| ChAdOx2 | chimpanzee adenovirus |
| rVSV | recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus |
| BoHV-4 | bovine herpesvirus type 4 |
| ORF | open reading frame |
References
- Abudurexiti, A.; Adkins, S.; Alioto, D.; Alkhovsky, S.V.; Avšič-Županc, T.; Ballinger, M.J.; Bente, D. A.; Beer, M.; Bergeron, É.; Blair, C.D.; et al. Taxonomy of the order Bunyavirales: update 2019. Arch of Virol 1949–1965 2019, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrison, A.R.; Alkhovsky Альхoвский Сергей Владимирoвич, S.V.; Avšič-Županc, T.; Bente, D. A.; Bergeron, É.; Burt, F.; Di Paola, N.; Ergünay, K.; Hewson, R.; Kuhn, J.H.; et al. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Nairoviridae. J Gen Virol 2020, 101, 798–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, S.D.; Surtees, R.; Walter, C.T.; Ariza, A.; Bergeron, É.; Nichol, S.T.; Hiscox, J.A.; Edwards, T.A.; Barr, J.N. Structure, function, and evolution of the Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus nucleocapsid protein. J Virol 2012, 86, 10914–10923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, W.; Ji, W.; Deng, M.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, H.; Yang, C.; Deng, F.; Wang, H.; Hu, Z.; et al. Crimean–Congo hemorrhagic fever virus nucleoprotein reveals endonuclease activity in bunyaviruses. P Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012, 109, 5046–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, A.J.; Vincent, M.J.; Nichol, S.T. ; Characterization of the glycoproteins of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus. J Virol 2002, 76, 7263–7275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, A.J.; Vincent, M.J.; Erickson, B.R.; Nichol, S.T. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus glycoprotein precursor is cleaved by furin-like and SKI-1 proteases to generate a novel 38-kilodalton glycoprotein. J Virol 2006, 80, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honig, J.E.; Osborne, J.C.; Nichol, S.T. Crimean–Congo hemorrhagic fever virus genome L RNA segment and encoded protein. Virology 2004, 321, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholte, F.E.M.; Zivcec, M.; Dzimianski, J.V.; Deaton, M.K.; Spengler, J.R.; Welch, S.R.; Nichol, S.T.; Pegan, S.D.; Spiropoulou, C.F.; Bergeron, É. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus suppresses innate immune responses via a ubiquitin and ISG15 specific protease. Cell reports 2017, 20, 2396–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perng, Y.C.; Lenschow, D.J. ISG15 in antiviral immunity and beyond. Nat Rev Microbiol 2018, 16, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumakov, M. P. 30 Years of investigation of Crimean hemorrhagic fever (Russian). Труды Института пoлиoмиелита и вирусных энцефалитoв Академии медицинских наук CCCР 1974, 22, 5–18. [Google Scholar]
- Butenko, A.M.; Chumakov, M.P.; Rubin, V.N. Isolation and investigation of Astrakhan strain (‘‘Drozdov’’) of Crimean hemorrhagic fever virus and data on serodiagnosis of this infection. Mater. 15 Nauchn. Sess. Inst. Polio Virus Entsefalitov (Moscow) 3, 88–90. Whitehouse C.A. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever. Antiviral Research 2004, 145–160. [Google Scholar]
- Chumakov, M.P.; Butenko, A.M.; Shalunova, N.V.; Mart'ianova, L.I.; Smirnova, S.E.; Bashkirtsev, I.N.; Zavodova, T. I.; Rubin, S.G.; Tkachenko, E.A.; Karmysheva, V.I.a. Novye dannye o viruse-vozbuditele krymskoĭ gemorragicheskoĭ likhoradki [New data on the viral agent of Crimean hemorrhagic fever]. Voprosy virusologii 1968, 13, 377. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simpson, D.I.; Knight, E.M.; Courtois, G.; Williams, M.C.; Weinbren, M.P.; Kibukamusoke, J.W. Congo virus: a hitherto undescribed occurring In Africa. I. Human isolations—clinical notes. East Afr Med J 1967, 44, 86–92. [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse, C.A. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever. Antiviral Res 2004, 64, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorou, R.; Pierroutsakos, I.N.; Maltezou, H.C. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever. Curr Opin Infect Dis 2007, 20, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargili, A.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Spengler, J.R.; Lukashev, A.; Nuttall, P.A.; Bente, D.A. The role of ticks in the maintenance and transmission of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus: a review of published field and laboratory studies. Antiviral Res 2017, 144, 93–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ergönül, Ö. Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever. Lancet Infect Dis 2006, 6, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourya, D.T.; Yadav, P.D.; Shete, A.; Majumdar, T.D.; Kanani, A.; Kapadia, D.; Chandra, V.; Kachhiapatel, A.J.; Joshi, P.T.; Upadhyay, K.J.; et al. Serosurvey of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus in domestic animals, Gujarat, India, 2013. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 2014, 14, 690–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, A.J.; Swanepoel, R.; Cornel, A.J.; Mathee, O. Experimental studies on the replication and transmission of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus in some African tick species. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1989, 40, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, S.W.; Linthicum, K.J.; Moulton, J.R. Transmission of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus in two species of Hyalomma ticks from infected adults to cofeeding immature forms. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1993, 48, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, T.M.; Linthicum, K.J.; Bailey, C.L.; Watts, D.M.; Moulton, J.R. Experimental transmission of Crimean- Congo haemorrhagic fever virus by Hyalomma truncatum Koch. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1989, 40, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okorie, T.G. Comparative studies on the vector capacity of the different stages of Amblyomma variegatum Fabricius and Hyalomma rufipes Koch for Congo virus, after intracoelomic inoculation. Veterinary Parasitology 1991, 38, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Azazy, O.M.; Scrimgeour, E.M. Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus infection in the western province of Saudi Arabia. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1997, 91, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanepoel, R.; Shepherd, A.J.; Leman, P.A.; Shepherd, S.P.; McGillivray, G.M.; Erasmus, M.J.; Searle, L.A.; Gill, D.E. Epidemiologic and clinical features of Crimean- Congo hemorrhagic fever in southern Africa. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1987, 36, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, Y.C.; Kong, L.X.; Lee, L.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Li, F.; Cai, B.J.; Gao, S.Y. Characteristics of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus (Xinjiang strain) in China. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1985, 34, 1179–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Gear, J.H.; Thomson, P.D.; Hopp, M.; Andronikou, S.; Cohn, R.J.; Ledger, J.; Berkowitz, F.E. Congo-Crimean haemorrhagic fever in South Africa. Report of a fatal case in the Transvaal. S Afr Med J 1982, 62, 576–580. [Google Scholar]
- Saluzzo, J.F.; Aubry, P.; McCormick, J.; Digoutte, J.P. Haemorrhagic fever caused by Crimean Congo haemorrhagic fever virus in Mauritania. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1985, 79, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunster, L.; Dunster, M.; Ofula, V.; Beti, D.; Kazooba-Voskamp, F.; Burt, F.; Swanepoel, R.; DeCock, K.M. First documentation of human Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever, Kenya. Emerg Infect Dis 2002, 8, 1005–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantawi, H.H.; Al-Moslih, M.I.; Al-Janabi, N.Y.; Al-Bana, A.S.; Mahmud, M.I.; Jurji, F.; Yonan, M.S.; Al-Ani, F.; Al-Tikriti, S.K. Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus in Iraq: isolation, identification and electron microscopy. Acta Virol 1980, 24, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, T.F.; Nitschko, H.; Jäger, G.; Nsanze, H.; Longson, M.; Pugh, R.N.; Abraham, A.K. Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever in Oman. Lancet 1995, 346, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Azazy, O.M.; Scrimgeour, E.M. Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus infection in the western province of Saudi Arabia. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1997, 91, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinikar, S.; Ghiasi, S.M.; Naddaf, S.; Piazak, N.; Moradi, M.; Razavi, M.R.; Afzali, N.; Haeri, A.; Mostafavizadeh, K.; Ataei, B.; et al. A serological survey in suspected human patients of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever in Iran by determination of IgM-specific ELISA method during 2000–2004. Arch Iranian Med 2005, 8, 52–55. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, M.L.; Ayazi, E.; Mohareb, E.; Yingst, S.; Zayed, A.; Rossi, C.A.; Schoepp, R.J.; Mofleh, J.; Fiekert, K.; Akhbarian, Z.; et al. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever, Afghanistan, 2009. Emerg Infect Dis 2011, 17, 1940–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burney, M.I.; Ghafoor, A.; Saleen, M.; Webb, P.A.; Casals, J. Nosocomial outbreak of viral hemorrhagic fever caused by Crimean hemorrhagic fever-Congo virus in Pakistan, January 1976. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1980, 29, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.C.; Mehta, M.; Mourya, D.T.; Gandhi, S. Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever in India. Lancet 2011, 378, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.D.; Patil, D.Y.; Shete, A.M.; Kokate, P.; Goyal, P.; Jadhav, S.; Sinha, S.; Zawar, D.; Sharma, S. K.; Kapil, A.; et al. Nosocomial infection of CCHF among healthcare workers in Rajasthan, India. BMC Infect Dis 2016, 16, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negredo, A.; de la Calle-Prieto, F.; Palencia-Herrejón, E.; Mora-Rillo, M.; Astray-Mochales, J.; Sánchez-Seco, M. P.; Bermejo Lopez, E.; Menárguez, J.; Fernández-Cruz, A.; Sánchez-Artola, B.; et al. Autochthonous Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever in Spain. N Engl J Med 2017, 377, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, A.; Bino, S.; Llagami, A.; Brahimaj, B.; Papadimitriou, E.; Pavlidou, V.; Velo, E.; Cahani, G.; Hajdini, M.; Pilaca, A.; et al. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever in Albania, 2001. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2002, 21, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papa, A.; Christova, I.; Papadimitriou, E.; Antoniadis, A. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever in Bulgaria. EmergInfect Dis 2004, 10, 1465–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drosten, C.; Minnak, D.; Emmerich, P.; Schmitz, H.; Reinicke, T. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever in Kosovo. J Clin Microbiol 2002, 40, 1122–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceianu, C.S.; Panculescu-Gatej, R.I.; Coudrier, D.; Bouloy, M. First serologic evidence for the circulation of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus in Romania. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 2012, 12, 718–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karti, S.S.; Odabasi, Z.; Korten, V.; Yilmaz, M.; Sonmez, M.; Caylan, R.; Akdogan, E.; Eren, N.; Koksal, I.; Ovali, E.; et al. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever in Turkey. Emerg Infect Dis 2004, 10, 1379–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonbak, S.; Aktas, M.; Altay, K.; Azkur, A.K.; Kalkan, A.; Bolat, Y.; Dumanli, N.; Ozdarendeli, A. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus: genetic analysis and tick survey in Turkey. J Clin Microbiol 2006, 44, 4120–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, G.R.; Buzgan, T.; Irmak, H.; Safran, A.; Uzun, R.; Cevik, M.A.; Torunoglu, M.A. The epidemiology of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever in Turkey 2002-2007. Int J Infect Dis 2009, 13, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midilli, K.; Gargili, A.; Ergonul, O.; Elevli, M.; Ergin, S.; Turan, N.; Sengöz, G.; Ozturk, R.; Bakar, M. The first clinical case due to AP92 like strain of Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever virus and a field survey. BMC Infect Dis 2009, 9, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canakoglu, N.; Berber, E.; Ertek, M.; Yoruk, M.D.; Tonbak, S.; Bolat, Y.; Aktas, M.; Kalkan,A. ; Ozdarendeli, A. Pseudo-Plaque Reduction Neutralization Test (PPRNT) for the Measurement of Neutralizing Antibodies to Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus. Virol J 2013, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control: Crimean-Congo Haemorrhagic Fever. In: ECDC. Annual epidemiological report for 2019. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/crimean-congo-haemorrhagic-fever-annual-epidemiological-report-2019 (accessed on 3 February 2021).
- Estrada-Pena, A.; Palomar, A.M.; Santibanez, P. Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus in Ticks, Southwestern Europe, 2010. Emerg Infect Dis 2012, 18, 179–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spengler, J.R.; Bergeron, E.; Spiropoulou, C.F. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever and expansion from endemic regions. Curr Opin Virol 2019, 34, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Geographic distribution of Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever. Available online: https://www.who.int/ emergencies/diseases/crimean-congo-haemorrhagic-fever/Global_ CCHFRisk_2017.jpg?ua=1 (accessed on 4 November 2019).
- Hoogstraal, H. The epidemiology of tick-borne Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever in Asia, Europe, and Africa. J Med Entomol 1979, 15, 307–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameson, L.J.; Morgan, P.J.; Medlock, J.M.; Watola, G.; Vaux, A.G.C. Importation of Hyalomma marginatum, vector of CrimeanCongo haemorrhagic fever virus, into the United Kingdom by migratory birds. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 2012, 3, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomar, A.M.; Portillo, A.; Santiba ́ n ̃ ez, P. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus in ticks from migratory birds, Morocco. Emerg Infect Dis 2013, 19, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capek, M.; Literak, I.; Kocianova, E.; Sychra, O.; Najer, T.; Trnka, A.; Kverek, P. Ticks of the Hyalomma marginatum complex transported by migratory birds into Central Europe. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 2014, 5, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrada-Peña, A.; Venzal, J.M. Climate niches of tick species in the Mediterranean region: modeling of occurrence data, distributional constraints, and impact of climate change. J Med Entomol 2007, 44, 1130–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatansever, Z. ; Uzun, R.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Ergonul, O. etc. In Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever: A Global Perspective, 1st ed.; Ergonul, O., Whitehouse, C.A., Eds.; Dordrecht, Netherlands, 2007; p. 328. ISBN 978-1-4020-6105-9. [Google Scholar]
- Estrada-Peña, A.; Sánchez, N.; Estrada-Sánchez, A. An assessment of the distribution and spread of the tick Hyalomma marginatum in the western Palearctic under different climate scenarios. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 2012, 12, 758–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrada-Peña, A.; Jameson, L.; Medlock, J.; Vatansever, Z.; Tishkova, F. Unraveling the ecological complexities of tickassociated Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus transmission: a gap analysis for the western Palearctic. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 2012, 12, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, J.; Usman, M.; Nadeem, A.; Sethi, S.A.; Salman, M. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever: a first case from Abbottabad, Pakistan. Int J Infect Dis 2009, 13, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameson, L.J.; Medlock, J.M. Results of HPA tick surveillance in Great Britain. Vet Rec 2009, 165, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spengler, J.R.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Garrison, A.R.; Schmaljohn, C.; Spiropoulou, C.F.; Bergeron, E.; Bente, D. A chronological review of experimental infection studies on the role of wild animals and livestock in maintenance and transmission of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus. Antiviral Res 2016, 135, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallhi, T.H.; Khan, Y.H.; Sarriff. A.; Khan, A.H. Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus and Eid-Ul- Adha festival in Pakistan. Lancet Infect Dis 2016, 16, 1332–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisholm, K.; Dueger, E.; Fahmy, N.T.; Samaha, H.A.T.; Zayed, A.; Abdel-Dayem, M.; Villinski, J.T. Crimean-congo hemorrhagic fever virus in ticks from imported livestock, Egypt. Emerg Infect Dis 2012, 18, 181–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehouse, C.A. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever. Antivir Res 2004, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ergonul, O. Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever. Lancet lnfect Dis 2006, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çevik, M.A.; Erbay, A.; Bodur, H.; Gülderen, E.; Baştuğ, A.; Kubar, A. Clinical and laboratory features of CrimeanCongo hemorrhagic fever: predictors of fatality. Int J Infect Dis 2008, 12, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürbüz, Y.; Sencan, I.; Oztürk, B.; Tütüncü, E. A case of nosocomial transmission of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever from patient to patient. Int J Infect Dis 2009, 13, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, H.; Sheybani, F.; Bojdi, A.; Khosravi, N.; Mostafavi, I. Fatal nosocomial spread of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever with very short incubation period. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2013, 88, 469–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildirmak, T.; Tulek, N.; Bulut, C. Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever: transmission to visitors and healthcare workers. Infection 2016, 44, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblebicioglu, H.; Sunbul, M.; Guner, R.; Bodur, H.; Bulut, C.; Duygu, F. Healthcare-associated Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever in Turkey, 2002–2014: a multicentre retrospective cross-sectional study. Clin Microbiol Infect 2016, 22, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehand, M.S.; Al-Shorbaji, F.; Millett, P.; Murgue, B. The WHO R&D Blueprint: 2018 review of emerging infectious diseases requiring urgent research and development efforts. Antivir Res 2018, 159, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bente, D. A. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever: history, epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical syndrome and genetic diversity. Antivir. Res 2013, 100, 159–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, S.E.; Hawman, D.W.; Sorvillo, T.E; O'Neal, T.J.; Bird, B.H.; Rodriguez, L.L; Bergeron, É.; Nichol, S.T.; Montgomery, J.M.; Spiropoulou, C.F.; et al. Immunobiology of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever. Antiviral Res 2022, 199, 105244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawman, D.W; Feldmann, H. Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus. Nat Rev Microbiol 2023, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, I.; Lundkvist, A.; Haller, O.; Mirazimi, A. 2006. Type I interferon inhibits Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus in human target cells. J Med Virol 2006, 78, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawman, D.W.; Meade-White, K.; Haddock, E.; Habib, R.; Scott, D.; Thomas, T.; Rosenke, R.; Feldmann, H. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever mouse model recapitulating human convalescence. J Virol 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawman, David. W.; Meade-White, K.; Leventhal, S.; Carmody, A.; Haddock, E.; Hasenkrug, K.; Feldmann, H. T- cells and interferon gamma are necessary for survival following Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus infection in mice. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bente, D.A.; Alimonti, J.B.; Shieh, W.-J.; Camus, G.; Stro ̈her, U.; Zaki, S.; Jones, S.M. Pathogenesis and immune response of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus in a STAT-1 knockout mouse model. J Virol 2010, 84, 11089–11100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereczky, S.; Lindegren, G.; Karlberg, H. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus infection is lethal for adult type I interferon receptor- knockout mice. J Gen Virol 2010, 91, 1473–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindquist, M.E.; Zeng, X.; Altamura, L.A.; Daye, S.P.; Delp, K.L.; Blancett, C.; Coffin, K.M.; Koehler, J.W.; Coyne, S.; Shoemaker, C.J.; et al. Exploring Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus-induced hepatic injury using antibody-mediated type I interferon blockade in mice. J Virol 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, S.; Engin, A.; Ozbilüm, N.; Bakır, M. Toll-like receptor 7 Gln11Leu, c.4- 151A/G, and +1817G/Tpolymorphisms in Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever. J Med Virol 2015, 87, 1090–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engin, A.; Arslan, S.; O ̈zbilüm, N.; Bakir, M. Is there any relationship between Toll-like receptor 3 c.1377C/Tand -7C/A polymorphisms and susceptibility to Crimean Congo hemorrhagic fever? J Med. Virol 2016, 88, 1690–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, F.; Mirazimi, A. Interferon and cytokine responses to Crimean Congo hemorrhagic fever virus; an emerging and neglected viral zonoosis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2008, 19, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habjan, M.; Andersson, I.; Klingström, J.; Schümann, M.; Martin, A.; Zimmermann, P.; Wagner, V.; Pichlmair, A.; Schneider, U.; Mühlberger, E.; et al. Processing of genome 51 termini as a strategy of negative-strand RNA viruses to avoid RIG-I-dependent interferon induction. PLoS One 2008, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spengler, J.R.; Patel, J.R.; Chakrabarti, A.K.; Zivcec, M.; García-Sastre, A.; Spiropoulou, C.F.; Bergeron, E. RIG-I mediates an antiviral response to Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus. J Virol 2015, 89, 10119–10229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zivcec, M.; Metcalfe, M.G.; Albariño, C.G.; Guerrero, L.W.; Pegan, S.D.; Spiropoulou, C.F.; Bergeron, É. Assessment of inhibitors of pathogenic Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus strains using virus-like particles. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2015, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, H.; McFadden, G. 1999. Apoptosis: an innate immune response to virus infection. Trends Microbiol 1999, 7, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, G. Host defense, viruses and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 2001, 8, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlberg, H.; Tan, Y.; J. & Mirazimi, A. Crimean–Congo haemorrhagic fever replication interplays with regulation mechanisms of apoptosis. J Gen Virol 2015, 96, 538–546. [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R; Paranhos-Baccalà, G; Vernet, G.; Peyrefitte, C. N. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus-infected hepatocytes induce ER-stress and apoptosis crosstalk. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 29712. [CrossRef]
- Barnwal, B.; Karlberg, H.; Mirazimi, A.; Tan, Y.J. The Non-structural Protein of Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus Disrupts the Mitochondrial Membrane Potential and Induces Apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2016, 291, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wu, M. Pattern recognition receptors in health and diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2021, 6, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol 2010, 11, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogensen, T.H. Pathogen recognition and inflammatory signaling in innate immune defenses. Clin Microbiol Rev 2009, 22, 240–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, K.; Dixit, V.M. Signaling in innate immunity and inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2012, 4, a006049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly-Andersen, A.M.; Douagi, I.; Kraus, A.A.; Mirazimi, A. Crimean Congo hemorrhagic fever virus infects human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Virology 2009, 390, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ergönül, Ö.; Şeref, C.; Eren, Ş.; Çelikbaş, A.; Baykam, N.; Dokuzoğuz, B.; Gönen, M.; Can, F. Cytokine response in crimean-congo hemorrhagic fever virus infection. J Med Virol 2017, 89, 1707–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saksida, A.; Duh, D.; Wraber, B.; Dedushaj, I.; Ahmeti, S.; Avsic-Zupanc, T. Interacting roles of immune mechanisms and viral load in the pathogenesis of crimean-congo hemorrhagic fever. Clin Vaccine Immunol 2010, 17, 1086–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, A.; Bino, S.; Velo, E.; Harxhi, A.; Kota, M.; Antoniadis, A. Cytokine levels in Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever. J Clin Virol 2006, 36, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papa, A.; Tsergouli, K.; Çağlayık, D.Y.; Bino, S.; Como, N.; Uyar, Y.; Korukluoglu, G. Cytokines as biomarkers of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever. J Med Virol 2016, 88, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ergönül, O. Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever. Lancet Infect Dis 2006, 6, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altay, F.A.; Elaldi, N.; Şentürk, G.Ç.; Altin, N.; Gözel, M.G.; Albayrak, Y.; Şencan, İ. Serum sTREM-1 level is quite higher in Crimean Congo Hemorrhagic Fever, a viral infection. J Med Virol 2016, 88, 1473–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidinejad, M.A.; Esmaeili Gouvarchin Ghaleh, H.; Farzanehpour, M.; Bolandian, M.; Dorostkar, R. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever from the immunopathogenesis, clinical, diagnostic, and therapeutic perspective: A scoping review. Asian Pac J Trop Med 2021, 14, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, A.J.; Swanepoel, R.; Leman, P.A. Antibody response in Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever. Rev Infect Dis 1989, 11, S801–S806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burt, F.J.; Leman, P.A.; Abbott, J.C.; Swanepoel, R. Serodiagnosis of Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever. Epidemiol Infect 1994, 113, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ergunay, K.; Kocak Tufan, Z.; Bulut, C.; Kinikli, S.; Demiroz, A.P.; Ozkul, A. Antibody responses and viral load in patients with Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever: a comprehensive analysis during the early stages of the infection. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2014, 79, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, S.; Elaldi, N.; Kubar, A.; Gursoy, N.; Yilmaz, M.; Karakus, G.; Gunes, T.; Polat, Z.; Gozel, M.G.; Engin, A.; Dokmetas, I.; Bakir, M.; Yilmaz, N.; Sencan, M. Sequential determination of serum viral titers, virus-specific IgG antibodies, and TNF-α, IL-6, IL-10, and IFN-γ levels in patients with Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever. BMC Infect Dis 2014, 14, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duh, D.; Saksida, A.; Petrovec, M.; Ahmeti, S.; Dedushaj, I.; Panning, M.; Drosten, C.; Avsic-Zupanc, T. Viral load as predictor of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever outcome. Emerg Infect Dis 2007, 13, 1769–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolotti-Ciarlet, A.; Smith, J.; Strecker, K.; Paragas, J.; Altamura, L.A.; McFalls, J.M.; Frias-Stäheli, N.; García-Sastre, A.; Schmaljohn, C.S.; Doms, R.W. Cellular localization and antigenic characterization of crimean-congo hemorrhagic fever virus glycoproteins. J Virol 2005, 79, 6152–6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivcec, M.; Guerrero, L.I.W.; Albariño, C.G.; Bergeron, É.; Nichol, S.T.; Spiropoulou, C.F. Identification of broadly neutralizing monoclonal antibodies against Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus. Antiviral Res 2017, 146, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, J.W.; Shoemaker, C.J.; Lindquist, M.E.; Zeng, X.; Daye, S.P.; Williams, J.A.; Liu, J.; Coffin, K.M.; Olschner, S.; Flusin, O.; Altamura, L.A.; Kuehl, K.A.; Fitzpatrick, C.J.; Schmaljohn, C.S.; Garrison, A.R. GP38-targeting monoclonal antibodies protect adult mice against lethal Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus infection. Sci Adv 2019, 5, eaaw9535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Moyer, C.L.; Abelson, D.M.; Deer, D.J.; ElOmari, K.; Duman, R.; Lobel, L.; Lutwama, J.J.; Dye, J.M.; Wagner, A.; Chandran, K.; Cross, R.W.; Geisbert, T.W.; Zeitlin, L.; Bornholdt, Z.A.; McLellan, J.S. Structure and Characterization of Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus GP38. J Virol 2020, 94, e02005–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fels, J.M.; Maurer, D.P.; Herbert, A.S.; Wirchnianski, A.S.; Vergnolle, O.; Cross, R.W.; Abelson, D.M.; Moyer, C.L.; Mishra, A.K.; Aguilan, J.T.; et al. Protective neutralizing antibodies from human survivors of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever. Cell 2021, 184, 3486–3501.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanoglu, I.; Guner, R.; Carhan, A.; Kocak Tufan, Z.; Yagci-Caglayik, D.; Guven, T.; Yilmaz, G.R.; Tasyaran, M.A. Crucial parameter of the outcome in Crimean Congo hemorrhagic fever: Viral load. J Clin Virol 2016, 75, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawman, D.W.; Meade-White, K.; Leventhal, S.; Feldmann, F.; Okumura, A.; Smith, B.; Scott, D.; Feldmann, H. Immunocompetent mouse model for Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus. eLife 2021, 10, e63906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinkula, J.; Devignot, S.; Åkerström, S.; Karlberg, H.; Wattrang, E.; Bereczky, S.; MousaviJazi, M.; Risinger, C.; Lindegren, G.; Vernersson, C.; et al. Immunization with DNA Plasmids Coding for Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus Capsid and Envelope Proteins and/or Virus-Like Particles Induces Protection and Survival in Challenged Mice. J Virol 2017, 91, e02076–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goedhals, D.; Paweska, J.T.; Burt, F.J. Long-lived CD8+ T cell responses following Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus infection. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2017, 11, e0006149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, S.E. A comparative study of the Crimean hemorrhagic fever-Congo group of viruses. Arch Virol 1979, 62, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teijaro, J.R.; Ng, C.; Lee, A.M.; Sullivan, B.M.; Sheehan, K.C.; Welch, M.; Schreiber, R.D.; de la Torre, J.C.; Oldstone, M.B. Persistent LCMV infection is controlled by blockade of type I interferon signaling. Science 2013, 340, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.R.; Hollidge, B.; Daye, S.; Zeng, X.; Blancett, C.; Kuszpit, K.; Bocan, T.; Koehler, J.W.; Coyne, S.; Minogue, T.; et al. Neuropathogenesis of Zika Virus in a Highly Susceptible Immunocompetent Mouse Model after Antibody Blockade of Type I Interferon. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2017, 11, e0005296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, S.T.I.; Yetiskin, H.; Kalkan, A.; Ozdarendeli, A. Evaluation of the cell culture based and the mouse brain derived inactivated vaccines against Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus in transiently immune-suppressed (IS) mouse model. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2020, 14, e0008834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, J.W.; Zeng, X.; Cline, C.R.; Smith, J.M.; Daye, S.P.; Carey, B.D.; Blancett, C.D.; Shoemaker, C.J.; Liu, J.; Fitzpatrick, C.J.; et al. The host inflammatory response contributes to disease severity in Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus infected mice. PLoS Pathog 2022, 18, e1010485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spengler, J.R.; KellyKeating, M.; McElroy, A.K.; Zivcec, M.; ColemanMcCray, J.D.; Harmon, J.R.; Bollweg, B.C.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Bergeron, É.; Keck, J.G.; et al. Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever in Humanized Mice Reveals Glial Cells as Primary Targets of Neurological Infection. J Infect Dis 2017, 216, 1386–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bility, M.T.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Luan, Y.; Li, F.; Chi, L.; Zhang, L.; Tu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Fu, Y.; et al. Hepatitis B virus infection and immunopathogenesis in a humanized mouse model: induction of human-specific liver fibrosis and M2-like macrophages. PLoS Pathog 2014, 10, e1004032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lüdtke, A.; Oestereich, L.; Ruibal, P.; Wurr, S.; Pallasch, E.; Bockholt, S.; Ip, W.H.; Rieger, T.; Gómez-Medina, S.; Stocking, C.; et al. Ebola virus disease in mice with transplanted human hematopoietic stem cells. J Virol 2015, 89, 4700–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinikar, S.; Ghiasi, S.M.; Moradi, M.; Goya, M.M.; Shirzadi, M.R.; Zeinali, M.; Meshkat, M.; Bouloy, M. Geographical distribution and surveillance of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever in Iran. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 2010, 10, 705–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagci-Caglayik, D.; Korukluoglu, G.; Uyar, Y. Seroprevalence and risk factors of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever in selected seven provinces in Turkey. J Med Virol 2014, 86, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsalve-Arteaga, L.; Alonso-Sardón, M.; Muñoz Bellido, J.L.; Vicente Santiago, M.B.; Vieira Lista, M.C.; López Abán, J.; Muro, A.; Belhassen-García, M. Seroprevalence of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever in humans in the World Health Organization European region: A systematic review. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2020, 14, e0008094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butenko, A.M.; Chumakov, M.P.; Smirnova, S.E.; Vasilenko, S.M.; Zavodova, T.I.; Tkachenko, E.A.; et al. Isolation of Crimean hemorrhagic fever virus from blood of patients and corpse material (from 1968–1969 investigation data) in Orstov, Astrakhan Oblast, and Bulgaria. Mater 3 Oblast Nauchn Prakt Konf (Rostovno-Donu, May 1970); 1970. p. 6–25. [Russian, translated NAMRU-3 T522]. 19 May.
- Fagbami, A.H.; Tomori, O.; Fabiyi, A.; Isoun, T.T. Experimantal Congo virus (Ib -AN 7620) infection in primates. Virologie. 1975, 26, 33–7. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Sastre, A. Diversity, replication, pathogenicity and cell biology of Crimean Congo hemorrhagic fever virus. Mount Sinai School of Medicine New York, 2010.
- Haddock, E.; Feldmann, F.; Hawman, D.W.; Zivcec, M.; Hanley, P.W.; Saturday, G.; Scott, D.P.; Thomas, T.; Korva, M.; Avšič-Županc, T.; Safronetz, D.; Feldmann, H. A cynomolgus macaque model for Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever. Nat Microbiol 2018, 3, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, R.W.; Prasad, A.N.; Borisevich, V.; Geisbert, J.B.; Agans, K.N.; Deer, D.J.; Fenton, K.A.; Geisbert, T.W. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus strains Hoti and Afghanistan cause viremia and mild clinical disease in cynomolgus monkeys. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2020, 14, e0008637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.R.; Shoemaker, C.J.; Zeng, X.; Garrison, A.R.; Golden, J.W.; Schellhase, C.W.; Pratt, W.; Rossi, F.; Fitzpatrick, C.J.; Shamblin, J.; et al. Persistent Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus infection in the testes and within granulomas of non-human primates with latent tuberculosis. PLoS Pathog 2019, 15, e1008050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmaljohn, C.S.; Nichol, S.T. Bunyaviridae. In Fields virology, 5th ed.; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Griffin, D.E., Lamb, R.A., Martin, M.A., Roizman, B., Straus, S.E., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, 2007; Volume 1, pp. 1741–1789. ISBN 0781760607/9780781760607. [Google Scholar]
- Karaaslan, E.; Çetin, N.S.; Kalkan-Yazıcı, M.; Hasanoğlu, S.; Karakeçili, F.; Özdarendeli, A.; Kalkan, A.; Kılıç, A.O.; Doymaz, M.Z. Immune responses in multiple hosts to Nucleocapsid Protein (NP) of Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus (CCHFV). PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2021, 15, e0009973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyde, V.M.; Khristova, M.L.; Rollin, P.E.; Ksiazek, T.G.; Nichol, S.T. Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus Genomics and Global Diversity. J Virol 2006, 80, 8834–8842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalkan-Yazıcı, M.; Karaaslan, E.; Çetin, N.S.; Hasanoğlu, S.; Güney, F.; Zeybek, U.; Doymaz, M.Z. Cross-Reactive anti-Nucleocapsid Protein Immunity against Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus and Hazara Virus in Multiple Species. J Virol 2021, 95, e02156–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altamura, L.A.; Bertolotti-Ciarlet, A.; Teigler, J.; Paragas, J.; Schmaljohn, C.S.; Doms, R.W. Identification of a novel C-terminal cleavage of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus PreGN that leads to generation of an NSM protein. J Virol 2007, 81, 6632–6642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrison, A.R.; Radoshitzky, S.R.; Kota, K.P.; Pegoraro, G.; Ruthel, G.; Kuhn, J.H.; Altamura, L.A.; Kwilas, S.A.; Bavari, S.; Haucke, V.; Schmaljohn, C.S. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus utilizes a clathrin and early endosome-dependent entry pathway. Virology 2013, 444, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, N.; Enguehard, M.; Denolly, S.; Levy, C.; Neveu, G.; Lerolle, S.; Devignot, S.; Weber, F.; Bergeron, E.; Legros, V.; Cosset, F.L. The interplays between Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus (CCHFV) M segment-encoded accessory proteins and structural proteins promote virus assembly and infectivity. PLoS Pathog 2020, 16, e1008850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkachenko, Y.A.; Butenko, A.M.; Butenko, S.A.; Zavodova, T.I.; Chumakov, M.P. Prophylactic characteristics of a protective Crimean hemorrhagic fever vaccine. In: Chumakov, M.P.(Ed.), Crimean Hemorrhagic Fever-Materials of the 3rd Scientific-practical Conference in Rostov-na-Donu Region, Rostav-na-Donu, USSR [Russian], 1970; pp. 136–138.
- Christova, I.; Kovacheva, T.; Georgieva, D. , Ivanova, S.; Argirov, D. Vaccine against Congo- Crimean haemorhagic fever virus—Bulgarian input in fighting the disease. Probl Infect Parasit Dis 2010, 37, 7–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi-Jazi, M.; Karlberg, H.; Papa, A.; Christova, I.; Mirazimi, A. Healthy individuals’ immune response to the Bulgarian Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus vaccine. Vaccine 2012, 30, 6225–6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canakoglu, N.; Berber, E.; Tonbak, S.; Ertek, M.; Sozdutmaz, I.; Aktas, M.; Kalkan, A.; Ozdarendeli, A. Immunization of knock-out a/b interferon receptor mice against high lethal dose of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus with a cell culture based vaccine. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2015, 9, e0003579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berber, E.; Canakoglu, N.; Tonbak, S.; Ozdarendeli, A. Development of a protective inactivated vaccine against Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever infection. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortekaas, J.; Vloet, R.P.; McAuley, A.J.; Shen, X.; Bosch, B.J.; de Vries, L.; Moormann, R.J. , Bente, D.A. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus subunit vaccines induce high levels of neutralizing antibodies but no protection in STAT1 knockout mice. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 2015, 15, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, S.; Shi, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, N.; Bi, J.; Jiao, C.; Li, E.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Jin, H.; Huang, P.; Yan, F.; Yang, S.; Xia, X. GEM-PA-Based Subunit Vaccines of Crimean Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Induces Systemic Immune Responses in Mice. Viruses 2022, 14, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, P.; Jiang, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y. Evaluation of the immunogenicity of vaccine candidates developed using a baculovirus surface display system for Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus in mice. Front Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1107874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stander, J.; Mbewana, S.; Meyers, A.E. Plant-Derived Human Vaccines: Recent Developments. BioDrugs 2022, 36, 573–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghiasi, S.M.; Salmanian, A.H.; Chinikar, S.; Zakeri, S. Mice orally immunized with a transgenic plant expressing the glycoprotein of Crimean- Congo hemorrhagic fever virus. Clin Vaccine Immunol 2011, 18, 2031–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, H.L.; Pertmer, T.M. DNA vaccines for viral infections: basic studies and applications. Adv Virus Res 2000, 55, 1–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Xia, F.; Chen, H.; Cui, B.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, P.; Chen, J.; Luo, M. A Guide to Nucleic Acid Vaccines in the Prevention and Treatment of Infectious Diseases and Cancers: From Basic Principles to Current Applications. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021, 9, 633776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spik, K.; Shurtleff, A.; McElroy, A.K.; Guttieri, M.C.; Hooper, J.W.; SchmalJohn, C. Immunogenicity of combination DNA vaccines for Rift Valley fever virus, tick-borne encephalitis virus, Hantaan virus, and Crimean Congo hemorrhagic fever virus. Vaccine 2006, 24, 4657–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, A.R.; Shoemaker, C.J.; Golden, J.W.; Fitzpatrick, C.J.; Suschak, J.J.; Richards, M.J.; Badger, C.V.; Six, C.M.; Martin, J.D.; Hannaman, D.; et al. A DNA vaccine for Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever protects against disease and death in two lethal mouse models. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2017, 11, e0005908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suschak, J.J.; Golden, J.W.; Fitzpatrick, C.J.; Shoemaker, C.J.; Badger, C.V.; Schmaljohn, C.S.; Garrison, A.R. A CCHFV DNA vaccine protects against heterologous challenge and establishes GP38 as immunorelevant in mice. NPJ vaccines 2021, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aligholipour Farzani, T.; Hanifehnezhad, A.; Földes, K.; Ergünay, K.; Yilmaz, E.; Hashim Mohamed Ali, H.; Ozkul, A. Co-delivery effect of CD24 on the Immunogenicity and Lethal Challenge Protection of a DNA Vector Expressing Nucleocapsid Protein of Crimean Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus. Viruses 2019, 11, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.L.; Zhang, L.Q.; Liu, X.Q.; Ye, W.; Zhao, Y.X.; Zhang, L.; Qiang, Z.X.; Zhang, L.X.; Lei, Y.F.; Jiang, D.B.; Cheng, L.F.; Zhang, F.L. Construction and evaluation of DNA vaccine encoding Crimean Congo hemorrhagic fever virus nucleocapsid protein, glycoprotein N- terminal and C-terminal fused with LAMP1. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2023, 13, 1121163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawman, D.W.; Ahlén, G.; Appelberg, K.S.; Meade-White, K.; Hanley, P.W.; Scott, D.; Monteil, V.; Devignot, S.; Okumura, A.; Weber, F.; Feldmann, H.; Sällberg, M.; Mirazimi, A. A DNA-based vaccine protects against Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus disease in a cynomolgus macaque model. Nat Microbiol 2021, 6, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholte, F.E.M.; Spengler, J.R.; Welch, S.R.; Harmon, J.R.; Coleman-McCray, J.D.; Freitas, B.T.; Kainulainen, M.H.; Pegan, S.D.; Nichol, S.T.; Bergeron, É.; Spiropoulou, C.F. Single-dose replicon particle vaccine provides complete protection against Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus in mice. Emerg Microbes lnfect 2019, 8, 575–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spengler, J.R.; Welch, S.R.; Scholte, F.E.M.; Coleman-McCray, J.D.; Harmon, J.R.; Nichol, S.T.; Bergeron, É.; Spiropoulou, C.F. Heterologous protection against Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever in mice after a single dose of replicon particle vaccine. Antiviral Res 2019, 170, 104573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spengler, J.R.; Welch, S.R.; Scholte, F.E.M.; Rodriguez, S.E.; Harmon, J.R.; Coleman-McCray, J.D.; Nichol, S.T.; Montgomery, J.M.; Bergeron, É.; Spiropoulou, C.F. Viral replicon particles protect IFNAR-/- mice against lethal Crimean- Congo hemorrhagic fever virus challenge three days after vaccination. Antiviral Res 2021, 191, 105090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kümmerer, B.M. Establishment and Application of Flavivirus Replicons. Adv Exp Med Biol 2018, 1062, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.T.; Höglund, U.; Larsson, O.; Appelberg, S.; Mirazimi, A.; Johansson, M.; Melik, W. Enhanced Seroconversion to West Nile Virus Proteins in Mice by West Nile Kunjin Replicon Virus-like Particles Expressing Glycoproteins from Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus. Pathogens 2022, 11, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorchakov, R.; Volkova, E.; Yun, N.; Petrakova, O.; Linde, N.S.; Paessler, S.; Frolova, E.; Frolov, I. Comparative analysis of the alphavirus-based vectors expressing Rift Valley fever virus glycoproteins. Virology 2007, 366, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipih, T.; Heise, M.; Burt, F.J. Immunogenicity of a DNA-Based Sindbis Replicon Expressing Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus Nucleoprotein. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leventhal, S.S.; Meade-White, K.; Rao, D.; Haddock, E.; Leung, J.; Scott, D.; Archer, J.; Randall, S.; Erasmus, J.H.; Feldmann, H.; Hawman, D.W. Replicating RNA vaccination elicits an unexpected immune response that efficiently protects mice against lethal Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus challenge. eBioMedicine 2022, 82, 104188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, N.; Weissman, D.; Whitehead, K.A. mRNA vaccines for infectious diseases: principles, delivery and clinical translation. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2021, 20, 817–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gote, V.; Bolla, P.K.; Kommineni, N.; Butreddy, A.; Nukala, P.K.; Palakurthi, S.S.; Khan, W.A. A Comprehensive Review of mRNA Vaccines. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aligholipour Farzani, T.; Földes, K.; Ergunay, K.; Gurdal, H.; Bastug, A.; Ozkul, A. Immunological Analysis of a CCHFV mRNA Vaccine Candidate in Mouse Models. Vaccines 2019, 7, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appelberg, S.; John, L.; Pardi, N.; Végvári, Á.; Bereczky, S.; Ahlén, G.; Monteil, V.; Abdurahman, S. ; Mikaeloff, F.; Beattie, M.; Tam, Y.; Sällberg, M.; Neogi, U.; Weissman, D.; Mirazimi, A. Nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccines protect IFNAR−/− mice against Crimean Congo hemorrhagic fever virus infection. J Virol 2021, 96, e01568–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, N.; O'Connor, D.; Lambe, T.; Pollard, A.J. Viral vector vaccines. Curr Opin Immunol 2022, 77, 102210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liang, B.; Wang, W.; Li, L.; Feng, N.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, T.; Yan, F.; Yang, S.; Xia, X. Viral vectored vaccines: design, development, preventive and therapeutic applications in human diseases. Sig Transduct Target Ther 2023, 8, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttigieg, K.R.; Dowall, S.D.; Findlay-Wilson, S.; Miloszewska, A.; Rayner, E.; Hewson, R.; Carroll, M.W. A novel vaccine against Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever protects 100% of animals against lethal challenge in a mouse model. PLoS One 2014, 9, e91516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowall, S.D.; Buttigieg, K.R.; Findlay-Wilson, S.J.; Rayner, E.; Pearson, G.; Miloszewska, A.; Graham, V.A.; Carroll, M.W.; Hewson, R.A. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever (CCHF) viral vaccine expressing nucleoprotein is immunogenic but fails to confer protection against lethal disease. Hum Vaccines Immunother 2016, 12, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivcec, M.; Safronetz, D.; Scott, D.P.; Robertson, S.; Feldmann, H. Nucleocapsid protein-based vaccine provides protection in mice against lethal Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus challenge. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2018, 12, e0006628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aligholipour Farzani, T.; Földes, K.; Hanifehnezhad, A.; Yener Ilce, B.; Bilge Dagalp, S.; Amirzadeh Khiabani, N.; Ergünay, K.; Alkan, F.; Karaoglu, T.; Bodur, H.; Ozkul, A. Bovine herpesvirus type 4 (BoHV-4) vector delivering nucleocapsid protein of Crimean-congo hemorrhagic fever virus induces comparable protective immunity against lethal challenge in IFNα/β/γR−/− mice models. Viruses 2019, 11, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, J.E.; Gilbride, C.; Dowall, S.; Morris, S.; Ulaszewska, M.; Spencer, A.J.; Rayner, E.; Graham, V.A.; Kennedy, E.; Thomas, K.; Hewson, R.; Gilbert, S.C.; Belij-Rammerstorfer, S.; Lambe, T. Adenoviral vectored vaccination protects against Crimean-Congo Haemorrhagic Fever disease in a lethal challenge model. eBioMedicine 2023, 90, 104523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, S.E.; Cross, R.W.; Fenton, K.A.; Bente, D.A.; Mire, C.E.; Geisbert, T.W. Vesicular Stomatitis Virus-Based Vaccine Protects Mice against Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 7755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowall, S.D.; Graham, V.A.; Rayner, E.; Hunter, L.; Watson, R.; Taylor, I.; Rule, A.; Carroll, M.W.; Hewson, R. Protective effects of a Modified Vaccinia Ankara-based vaccine candidate against Crimean-Congo Haemorrhagic Fever virus require both cellular and humoral responses. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0156637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




