Submitted:
26 June 2023
Posted:
27 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Medicinal plants and their cultivable endophyte resources
2.1. Culturable endophytic bacteria diversity in medicinal plants
2.2. Culturable endophytic fungal diversity in medicinal plants
2.3. Culturable endophytic actinomycetes diversity in medicinal plants
| Host plant | Tissue | Endophytic actinomycetes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dioscorea opposita | Streptomyces sp. | [43] | |
| Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. | Roots, leaf | Nocardia sp. | [45,46] |
| Thymus roseus | Root, stem, leaf | Nocardiopsis sp., Micrococcus sp., Kocuria sp., and etc. | [47] |
| Viola odorata | Root | Streptomyces sp. | [48] |
| Xanthium sibiricum | Leaf, seed | Streptomyces sp. | [49] |
| Kandelia candel | Root | Nocardioides sp. | [51] |
| Mentha haplocalyx | Bark | Nakamurella sp. | [52] |
| Acacia mangium | Root | Fodinicola sp. | [53] |
3. Beneficial effects of Endophytes from medicinal plants on the host
3.1. Promoting the growth of medicinal plants
3.2. Enhance the stress resistance of medicinal plants
3.3. Promoting the accumulation of secondary metabolites in medicinal plants
3.4. Helping the host resist pathogens
4. Medicinal components produced by endophytes in medicinal plants
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aye, M.M.; Aung, H.T.; Sein, M.M.; Armijos, C. A Review on the Phytochemistry, Medicinal Properties and Pharmacological Activities of 15 Selected Myanmar Medicinal Plants. Molecules 2019, 24, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, P.; Shen, T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Xiao, W. Challenges and opportunities for improving the druggability of natural product: Why need drug delivery system? Biomed Pharmacother 2023, 164, 114955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Wang, Y.L.; Yan, K.; Deng, Q.Q.; Li, F.Z.; Liang, X.J.; Hua, Q. Nanostructures in Chinese herbal medicines (CHMs) for potential therapy. Nanoscale Horiz 2023. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, A.; Noman, M.; Bano, U.; Akhtar, J.; Shaikh, Y.; Yar, M.S. Global uses of traditional herbs for hepatic diseases and other pharmacological actions: A comprehensive review. Polim Med 2023. [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, C.; Bai, D.; Chen, N.; Hu, J.; Zhang, J. Perspectives of international multi-center clinical trials on traditional Chinese herbal medicine. Front Pharmacol 2023, 14, 1195364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, S.; Kumar, P.; Dahiya, P.; Maheshwari, R.; Dang, A.S.; Suneja, P. Endophytism: A Multidimensional Approach to Plant-Prokaryotic Microbe Interaction. Front Microbiol 2022, 13, 861235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, M.; Gupta, S.; Dhar, M.K.; Kaul, S. Endophytic Fungi-Mediated Biocatalysis and Biotransformations Paving the Way Toward Green Chemistry. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2021, 9, 664705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouda, S.; Das, G.; Sen, S.K.; Shin, H.S.; Patra, J.K. Endophytes: A Treasure House of Bioactive Compounds of Medicinal Importance. Front Microbiol 2016, 7, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalini, M.S.; Prakash, H.S. Diversity and bioprospecting of actinomycete endophytes from the medicinal plants. Lett Appl Microbiol 2017, 64, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tshikhudo, P.P.; Ntushelo, K.; Mudau, F.N. Sustainable Applications of Endophytic Bacteria and Their Physiological/Biochemical Roles on Medicinal and Herbal Plants: Review. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, A.H.; Attia, M.S.; Kandil, E.K.; Fawzi, M.M.; Abdelrahman, A.S.; Khader, M.S.; Khodaira, M.A.; Emam, A.E.; Goma, M.A.; Abdelaziz, A.M. Bioactive compounds and biomedical applications of endophytic fungi: A recent review. Microb Cell Fact 2023, 22, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.H.; Si, J.P.; Wu, L.S. Metabolites of medicine food homology-derived endophytic fungi and their activities. Curr Res Food Sci 2022, 5, 1882–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, A.; Pandey, P.; Tripathi, S.N.; Kalra, A. Perspectives and potential applications of endophytic microorganisms in cultivation of medicinal and aromatic plants. Front Plant Sci 2022, 13, 985429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stierle, A.; Strobel, G.; Stierle, D. Taxol and taxane production by Taxomyces andreanae, an endophytic fungus of Pacific yew. Science 1993, 260, 214–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Zhang, Q.L.; Hua, J.W.; Cheng, W.L.; Qin, L.P. The traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz.: A review. J Ethnopharmacol 2018, 226, 143–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wang, S.; Wu, J.; He, B.; Zhu, B.; Qin, L. Influence of tissue and geographic locality on culturable endophytic bacteria of Atractylodes macrocephala. Microbiology (Reading) 2021, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, M.; Cui, H.; Li, J.; Wang, M. Transcriptomic Landscape of Medicinal Dendrobium Reveals Genes Associated With the Biosynthesis of Bioactive Components. Front Plant Sci 2020, 11, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Lin, Y.; Farag, M.A.; Li, Z.; Shao, P. Dendrobium as a new natural source of bioactive for the prevention and treatment of digestive tract diseases: A comprehensive review with future perspectives. Phytomedicine 2023, 114, 154784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.S.; Liu, J.M.; Sun, J.; Sun, Y.F.; Liu, J.N.; Jia, N.; Fan, B.; Dai, X.F. Diversity of culture-independent bacteria and antimicrobial activity of culturable endophytic bacteria isolated from different Dendrobium stems. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 10389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Zhao, L. The Mulberry (Morus alba L.) Fruit-A Review of Characteristic Components and Health Benefits. J Agric Food Chem 2017, 65, 10383–10394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.-W.; Park, M.; Lee, H.-J. Mulberry (Morus alba L.) Leaf Extract and 1-Deoxynojirimycin Improve Skeletal Muscle Insulin Resistance via the Activation of IRS-1/PI3K/Akt Pathway in db/db Mice. Life 2022, 12, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.; Gao, Y.; Xue, J.; Yang, Y.; Yin, J.; Wu, T.; Zhang, M. Phytochemicals, Pharmacological Effects and Molecular Mechanisms of Mulberry. Foods 2022, 11, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Wang, F.; Zhang, M.; Ou, T.; Wang, R.; Strobel, G.; Xiang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Xie, J. Diversity of cultivable endophytic bacteria in mulberry and their potential for antimicrobial and plant growth-promoting activities. Microbiol Res 2019, 229, 126328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shurigin, V.; Alaylar, B.; Davranov, K.; Wirth, S.; Bellingrath-Kimura, S.D.; Egamberdieva, D. Diversity and biological activity of culturable endophytic bacteria associated with marigold (Calendula officinalis L.). AIMS Microbiol 2021, 7, 336–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazarika, S.N.; Saikia, K.; Borah, A.; Thakur, D. Prospecting Endophytic Bacteria Endowed With Plant Growth Promoting Potential Isolated From Camellia sinensis. Front Microbiol 2021, 12, 738058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarte, M.E.; Gismondi, M.I.; Llorente, B.E.; Larraburu, E.E. Isolation of endophytic bacteria from the medicinal, forestal and ornamental tree Handroanthus impetiginosus. Environ Technol 2022, 43, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, A.; Das, R.; Mazumdar, R.; Thakur, D. Culturable endophytic bacteria of Camellia species endowed with plant growth promoting characteristics. J Appl Microbiol 2019, 127, 825–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, A.A.; Ramalho, M.O.; Moreau, C.S.; Campos, A.E.C.; Harakava, R.; Bueno, O.C. Exploring the diversity and potential interactions of bacterial and fungal endophytes associated with different cultivars of olive (Olea europaea) in Brazil. Microbiol Res 2022, 263, 127128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolytaite, A.; Vaitiekunaite, D.; Antanyniene, R.; Baniulis, D.; Frercks, B. Monilinia fructigena Suppressing and Plant Growth Promoting Endophytic Pseudomonas spp. Bacteria Isolated from Plum. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbe, A.A.; Gupta, S.; Stirk, W.A.; Finnie, J.F.; Van Staden, J. Growth-Promoting Characteristics of Fungal and Bacterial Endophytes Isolated from a Drought-Tolerant Mint Species Endostemon obtusifolius (E. Mey. ex Benth.) N. E. Br. Plants (Basel) 2023, 12, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlangu, S.G.; Tai, S.L. Morphological and molecular characterization of bacterial endophytes from Centella asiatica leaves. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 2022, 20, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priyanto, J.A.; Prastya, M.E.; Astuti, R.I.; Kristiana, R. The Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activities of the Endophytic Bacteria Associated with Archidendron pauciflorum against Multidrug-Resistant Strains. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 2023. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punia, A.; Joshi, R.; Kumar, R. Identification and quantification of eight alkaloids in Aconitum heterophyllum using UHPLC-DAD-QTOF-IMS: A valuable tool for quality control. Phytochem Anal 2022, 33, 1121–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafeez, S.; Yaqoob, S.; Magray, A.R.; Kamili, A.N.; Ganai, B.A. Molecular characterization of fungal endophyte diversity isolated from Aconitum heterophyllum: A critically endangered medicinal plant of Kashmir Himalaya. Int Microbiol 2023. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matraszek-Gawron, R.; Chwil, M.; Terlecki, K.; Skoczylas, M.M. Current Knowledge of the Antidepressant Activity of Chemical Compounds from Crocus sativus L. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2022, 16, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, Z.; Arshad, M.S.; Ali, A.; Aziz, A.; Khalid, W.; Afzal, M.F.; Bangar, S.P.; Addi, M.; Hano, C.; Lorenzo, J.M. Potential Role of Phytochemical Extract from Saffron in Development of Functional Foods and Protection of Brain-Related Disorders. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022, 2022, 6480590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Qin, L.; Zhu, B. Diversity of Culturable Endophytic Fungi in Crocus sativus and Their Correlation with Crocin Content. Curr Microbiol 2023, 80, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.K.; Yang, J.S.; Huang, Y.F.; Liu, J.S.; Tsai, C.W.; Bau, D.T.; Chang, W.S. Culture Separation, Identification and Unique Anti-pathogenic Fungi Capacity of Endophytic Fungi from Gucheng Salvia Miltiorrhiza. In Vivo 2021, 35, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarsaiya, S.; Jain, A.; Jia, Q.; Fan, X.; Shu, F.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Shi, J.; Chen, J. Molecular Identification of Endophytic Fungi and Their Pathogenicity Evaluation Against Dendrobium nobile and Dendrobium officinale. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Leng, F.; Li, S.; Zhu, N.; Chen, K.; Wang, Y. Culturable endophytic fungi community structure isolated from Codonopsis pilosula roots and effect of season and geographic location on their structures. BMC Microbiol 2023, 23, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Rustamova, N.; Ning, H.; Paerhati, P.; Lu, C.; Yili, A. Diversity and Biological Activities of Endophytic Fungi from the Flowers of the Medicinal Plant Vernonia anthelmintica. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Tao, S.; Hou, G.; Zhao, F.; Tan, S.; Meng, Q. Dioscorea spp.: Bioactive Compounds and Potential for the Treatment of Inflammatory and Metabolic Diseases. Molecules 2023, 28, 2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Zhou, Y.; Li, C.; Wu, W.; Xu, Y.; Xia, W.; Huang, D.; Huang, X. Identification and genomic analyses of a novel endophytic actinobacterium Streptomyces endophytica sp. nov. with potential for biocontrol of yam anthracnose. Front Microbiol 2023, 14, 1139456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Lyu, Q.; Zheng, W.; Yang, Q.; Cao, G. Traditional application and modern pharmacological research of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. Chin Med 2021, 16, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, P.; Chen, Y.; Zou, F.; Zhou, J.; Zou, W.; Gao, J. Nocardiopsis eucommiae sp. nov., a novel endophytic actinomycete isolated from leaves of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2022, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, P.; Li, K.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, F.; He, J.; Zou, W.; Gao, J. Nocardiopsis changdeensis sp. nov., an endophytic actinomycete isolated from the roots of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 2023, 76, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, Z.; Ma, J.; Egamberdieva, D.; Abdelshafy Mohamad, O.A.; Abaydulla, G.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.J.; Li, L. Diversity and Antimicrobial Potential of Cultivable Endophytic Actinobacteria Associated With the Medicinal Plant Thymus roseus. Front Microbiol 2020, 11, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salwan, R.; Rana, A.; Saini, R.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, M.; Sharma, V. Diversity analysis of endophytes with antimicrobial and antioxidant potential from Viola odorata: An endemic plant species of the Himalayas. Braz J Microbiol 2023. [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, K.; Tang, X.; Gao, J. Streptomyces xanthii sp. nov. and Streptomyces roseirectus sp. nov. isolated from a Chinese medicinal plant. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2021, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vurukonda, S.S.K.P.; Giovanardi, D.; Stefani, E. Plant Growth Promoting and Biocontrol Activity of Streptomyces spp. as Endophytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2018, 19, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.S.; Chen, F.; Chen, X.H.; Zheng, Z.Q.; Ma, X.; Tuo, L. Nocardioides mangrovi sp. nov., a novel endophytic actinobacterium isolated from root of Kandelia candel. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2022, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.R.; Chen, M.S.; Yang, C.; An, M.B.; Li, H.Y.; Shi, H.C.; Tuo, L. Nakamurella flava sp. nov., a novel endophytic actinobacterium isolated from Mentha haplocalyx Briq. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2020, 70, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, H.T.T.; Suwannapan, W.; Koomsiri, W.; Inahashi, Y.; Take, A.; Matsumoto, A.; Thamchaipenet, A. Fodinicola acaciae sp. nov., an Endophytic Actinomycete Isolated from the Roots of Acacia mangium Willd. and Its Genome Analysis. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Gao, J.; Munir, I.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Moe, T.S.; Xue, J.; Zhang, X. Characterization of Endophytic Fungi, Acremonium sp., from Lilium davidii and Analysis of Its Antifungal and Plant Growth-Promoting Effects. Biomed Res Int 2021, 2021, 9930210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, L.; Wang, Q.; Wu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, M.; Ye, K.; Dai, W.; Huang, J. Biocontrol and plant growth promotion potential of endophytic Bacillus subtilis JY-7-2L on Aconitum carmichaelii Debx. Front Microbiol 2022, 13, 1059549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Qiuhong, L.; Fuqiang, Y.; Shuhui, Z.; Suohui, T.; Linyuan, F. Plant growth-promoting activities of bacterial endophytes isolated from the medicinal plant Pairs polyphylla var. yunnanensis. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 2021, 38, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, P.; Chaturvedi, P.; Sharma, C.; Bhatnagar, P. Improved seed germination and plant growth mediated by compounds synthesized by endophytic Aspergillus niger (isolate 29) isolated from Albizia lebbeck (L.) Benth. 3 Biotech 2022, 12, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purushotham, N.; Jones, E.; Monk, J.; Ridgway, H. Community Structure of Endophytic Actinobacteria in a New Zealand Native Medicinal Plant Pseudowintera colorata (Horopito) and Their Influence on Plant Growth. Microb Ecol 2018, 76, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, E.; Mishra, J.; Arora, N.K. Multifaceted Interactions Between Endophytes and Plant: Developments and Prospects. Frontiers in Microbiology 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Chen, L.; Xin, H.L.; Zheng, C.J.; Rahman, K.; Han, T.; Qin, L.P. A Friendly Relationship between Endophytic Fungi and Medicinal Plants: A Systematic Review. Frontiers in Microbiology 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mili, C. Bioprospecting of endophytes associated with Solanum species: A mini review. Arch Microbiol 2023, 205, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Lang, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X. Plant-beneficial Streptomyces dioscori SF1 potential biocontrol and plant growth promotion in saline soil within the arid and semi-arid areas. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2023, 30, 70194–70212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonmahome, P.; Namwongsa, J.; Vorasoot, N.; Jogloy, S.; Riddech, N.; Boonlue, S.; Mongkolthanaruk, W. Single and co-inoculum of endophytic bacteria promote growth and yield of Jerusalem artichoke through upregulation of plant genes under drought stress. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0286625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wu, H.; Pu, Q.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Z.; Hu, X.; Li, O. Complete genome of Sphingomonas paucimobilis ZJSH1, an endophytic bacterium from Dendrobium officinale with stress resistance and growth promotion potential. Arch Microbiol 2023, 205, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ren, Y.; He, C.; Yao, J.; Wei, M.; He, X. Complementary Effects of Dark Septate Endophytes and Trichoderma Strains on Growth and Active Ingredient Accumulation of Astragalus mongholicus under Drought Stress. J Fungi (Basel) 2022, 8, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Hou, W.P.; Christensen, M.J.; Li, X.Z.; Xia, C.; Li, C.J.; Nan, Z.B. Role of Epichloe Endophytes in Improving Host Grass Resistance Ability and Soil Properties. J Agr Food Chem 2020, 68, 6944–6955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Chen, W.H.; Liu, S.Y.; Wu, J.J.; Zhu, Y.T.; Qin, L.P.; Zhu, B. Beneficial Relationships Between Endophytic Bacteria and Medicinal Plants. Frontiers in Plant Science 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godara, H.; Ramakrishna, W. Endophytes as nature's gift to plants to combat abiotic stresses. Letters in Applied Microbiology 2023, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, J.; Qi, Y.; Chu, S.; Ma, Y.; Xu, L.; Lv, S.; Zhang, H.; Yang, D.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Endophytic fungus Cladosporium tenuissimum DF11, an efficient inducer of tanshinone biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza roots. Phytochemistry 2022, 194, 113021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Jin, X.; Yang, M.; Xue, S.; Luo, L.; Cao, X.; Zhang, C.; Qiao, S.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; et al. Primary and secondary metabolites produced in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots by an endophytic fungal elicitor from Mucor fragilis. Plant Physiol Biochem 2021, 160, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoudi Khorasani, F.; Ganjeali, A.; Asili, J.; Cheniany, M. Beneficial effects of endophytic fungi inoculation on tanshinones and phenolic compounds of Salvia abrotanoides. Iran J Basic Med Sci 2023, 26, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.T.; Luo, S.Q.; Yang, Z.N.; Wang, Y.S.; Ding, Q.; Wang, K.F.; Yang, S.X.; Wang, Y. Endophytic fungi stimulate the concentration of medicinal secondary metabolites in houttuynia cordata thunb. Plant Signal Behav 2021, 16, 1929731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.G.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Chen, L.; Ming, Q.L.; Sheng, K.X.; Chen, X.; Rahman, K.; Feng, K.M.; Su, J.; Han, T. An endophytic fungus Schizophyllum commune isolated from Panax ginseng enhances hairy roots growth and ginsenoside biosynthesis. Can J Microbiol 2023. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palanichamy, P.; Krishnamoorthy, G.; Kannan, S.; Marudhamuthu, M. Bioactive potential of secondary metabolites derived from medicinal plant endophytes. Egyptian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences 2019, 5, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santra, H.K.; Banerjee, D. Antifungal activity of volatile and non-volatile metabolites of endophytes of Chloranthus elatior Sw. Front Plant Sci 2023, 14, 1156323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, T.; Bashir, A.; Farooq, S.; Riyaz-Ul-Hassan, S. Burkholderia gladioli E39CS3, an endophyte of Crocus sativus Linn., induces host resistance against corm-rot caused by Fusarium oxysporum. J Appl Microbiol 2022, 132, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, U.; Pal, T.; Yadav, N.; Singh, V.K.; Tripathi, V.; Choudhary, K.K.; Shukla, A.K.; Sunita, K.; Kumar, A.; Bontempi, E.; et al. Current Scenario and Future Prospects of Endophytic Microbes: Promising Candidates for Abiotic and Biotic Stress Management for Agricultural and Environmental Sustainability. Microb Ecol 2023. [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, S.; Robertson, L.P.; Kosgahakumbura, L.; Fernando, C.; Goransson, U.; Wang, H.; Hettiarachchi, C.; Gunasekera, S. Antibacterial eremophilane sesquiterpenoids from Xylaria feejeensis, an endophytic fungi of the medicinal plant Geophila repens. Fitoterapia 2023, 167, 105496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Liu, G.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, N. Screening saikosaponin d (SSd)-producing endophytic fungi from Bupleurum scorzonerifolium Willd. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 2022, 38, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, J.P.; Liu, S.F.; Yin, C.Y.; Tang, D.Y.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, L.X. 7-Methoxy-13-dehydroxypaxilline: New indole diterpenoid from an endophytic fungus Penicillium sp. Nb 19. Nb 19. Nat Prod Res 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, F.; Tian, Y. Antimicrobial Potential of Endophytic Fungi From Artemisia argyi and Bioactive Metabolites From Diaporthe sp. AC1. AC1. Front Microbiol 2022, 13, 908836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santra, H.K.; Maity, S.; Banerjee, D. Production of Bioactive Compounds with Broad Spectrum Bactericidal Action, Bio-Film Inhibition and Antilarval Potential by the Secondary Metabolites of the Endophytic Fungus Cochliobolus sp. APS1 Isolated from the Indian Medicinal Herb Andrographis paniculata. Molecules 2022, 27, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yehia, R.S. Multi-Function of a New Bioactive Secondary Metabolite Derived from Endophytic Fungus Colletotrichum acutatum of Angelica sinensis. J Microbiol Biotechnol 2023, 33, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.; Song, L.; Fu, W.; Liu, L. Anti-Alzheimer's Natural Products Derived from Plant Endophytic Fungi. Molecules 2023, 28, 2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.M.; Mahmoud, B.K.; Millan-Aguinaga, N.; Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Fouad, M.A. The endophytic Fusarium strains: A treasure trove of natural products. RSC Adv 2023, 13, 1339–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.C.; Wang, L.; Pan, Y.P.; Zheng, X.X.; Liang, X.N.; Sheng, L.L.; Zhang, D.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Q. Research advances on endophytic fungi and their bioactive metabolites. Bioproc Biosyst Eng 2023, 46, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzimande, B.; Makhwitine, J.P.; Mkhwanazi, N.P.; Ndlovu, S.I. Developments in Exploring Fungal Secondary Metabolites as Antiviral Compounds and Advances in HIV-1 Inhibitor Screening Assays. Viruses 2023, 15, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Zheng, M.; Xi, X.; Cao, H.; Cui, X.; Guo, H.; Han, C. Yield enhancement strategies of rare pharmaceutical metabolites from endophytes. Biotechnol Lett 2018, 40, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mursyidah, A.K.; Hafizzudin-Fedeli, M.; Muhammad, N.A.N.; Latiff, A.; Firdaus-Raih, M.; Wan, K.L. Dissecting the Biology of Rafflesia Species: Current Progress and Future Directions Made Possible with High-Throughput Sequencing Data. Plant Cell Physiol 2023. [CrossRef]
- Riva, V.; Mapelli, F.; Bagnasco, A.; Mengoni, A.; Borin, S. A Meta-Analysis Approach to Defining the Culturable Core of Plant Endophytic Bacterial Communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 2022, 88, e0253721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zhang, C.M.; Ju, X.Y.; Xiong, Y.W.; Xing, K.; Qin, S. Community Composition and Metabolic Potential of Endophytic Actinobacteria From Coastal Salt Marsh Plants in Jiangsu, China. Frontiers in Microbiology 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, W.J.; Miao, L.Y.; Fan, S.P.; Lv, P.W.; Lin, A.H.; Geng, H.; Song, F.J.; Zhang, P. New insights into the composition and diversity of endophytic bacteria in cultivated Huperzia serrata. Can J Microbiol 2023. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, M.; Heinrich, M.; Booker, A. Medicinal Plant Analysis: A Historical and Regional Discussion of Emergent Complex Techniques. Frontiers in Pharmacology 2020, 10, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Applequist, W.L.; Brinckmann, J.A.; Cunningham, A.B.; Hart, R.E.; Heinrich, M.; Katerere, D.R.; van Andel, T. Scientists & apos; Warning on Climate Change and Medicinal Plants. Planta Med 2020, 86, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.Q.; Ouyang, Y.; Tang, Z.Y.; Lao, C.C.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Cheng, C.S.; Zhou, H. Review on the Development and Applications of Medicinal Plant Genomes. Frontiers in Plant Science 2021, 12, 791219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilario, S.; Goncalves, M.F.M. Endophytic Diaporthe as Promising Leads for the Development of Biopesticides and Biofertilizers for a Sustainable Agriculture. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwibedi, V.; Rath, S.K.; Joshi, M.; Kaur, R.; Kaur, G.; Singh, D.; Kaur, G.; Kaur, S. Microbial endophytes: Application towards sustainable agriculture and food security. Appl Microbiol Biot 2022, 106, 5359–5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Thapa, S.; Mahawar, H.; Kumar, D.; Geat, N.; Singh, S.K. Prospecting potential of endophytes for modulation of biosynthesis of therapeutic bioactive secondary metabolites and plant growth promotion of medicinal and aromatic plants. Anton Leeuw Int J G 2022, 115, 699–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.D.; Liu, J.N.; Chen, C.; Mo, X.L.; Tan, Q.; He, Y.; Wang, Z.K.; Yin, J.; Zhou, G.Y. The Multifunctions and Future Prospects of Endophytes and Their Metabolites in Plant Disease Management. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Rai, A.K.; Dahiya, D.; Chettri, R.; Nigam, P.S. Exploring endophytes for in vitro synthesis of bioactive compounds similar to metabolites produced in vivo by host plants. AIMS Microbiol 2021, 7, 175–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Anand, U.; Lopez-Bucio, J.; Radha; Kumar, M.; Lal, M.K.; Tiwari, R.K.; Dey, A. Biostimulants and environmental stress mitigation in crops: A novel and emerging approach for agricultural sustainability under climate change. Environ Res 2023, 116357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, D.C.; de Paula, S.; Torres, A.G.; de Souza, V.H.M.; Pascholati, S.F.; Schmidt, D.; Neto, D.D. Endophytic Fungi: Biological Control and Induced Resistance to Phytopathogens and Abiotic Stresses. Pathogens 2021, 10, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, K.; Kumar, V.; Prasher, I.B.; Sethi, M.; Raj, H.; Ranjan, H.; Chand, S.; Pandey, G.K. Bioactive molecules from fungal endophytes and their applications in pharmaceutical industries: Challenges and future scope. J Basic Microb 2023. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
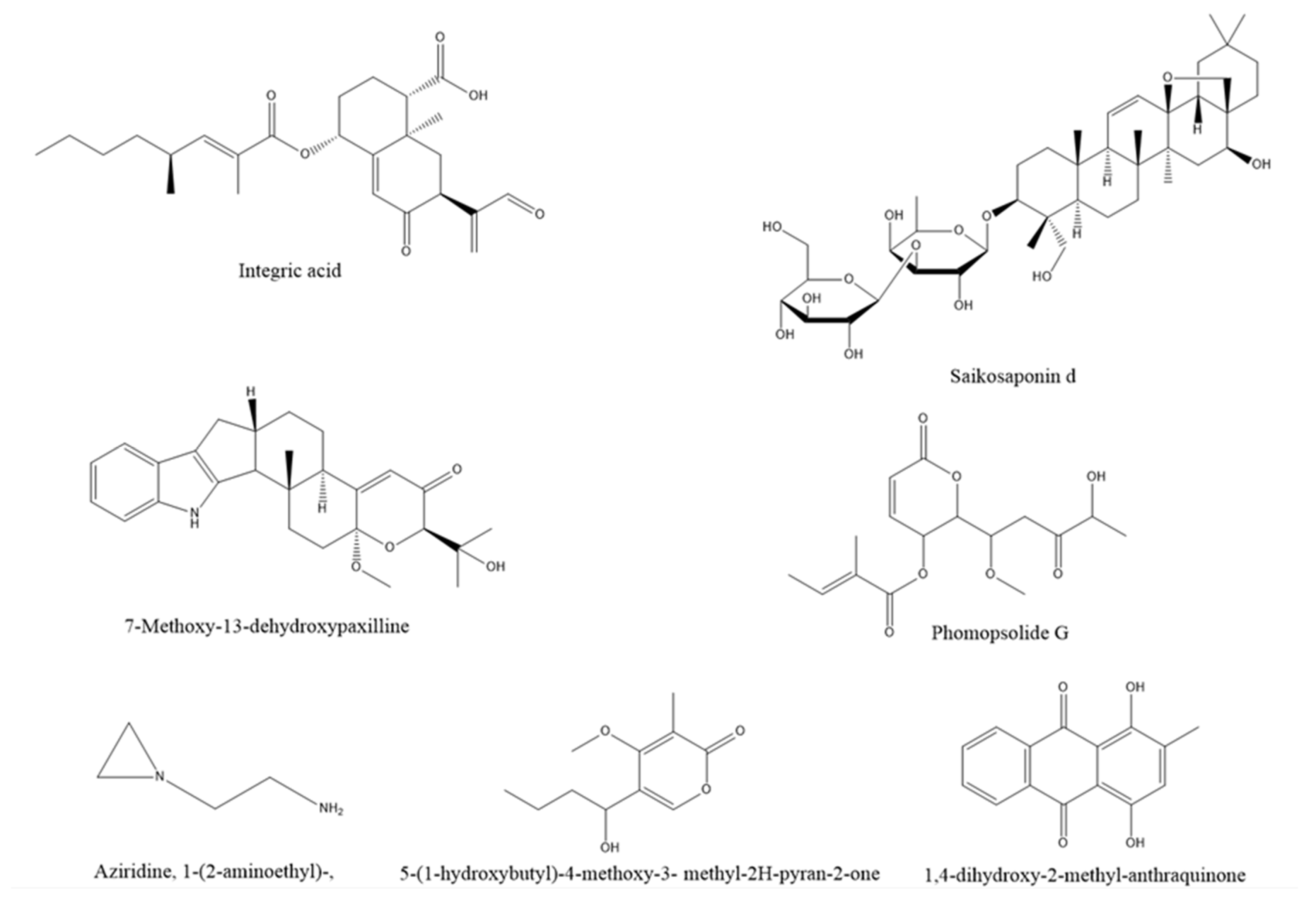
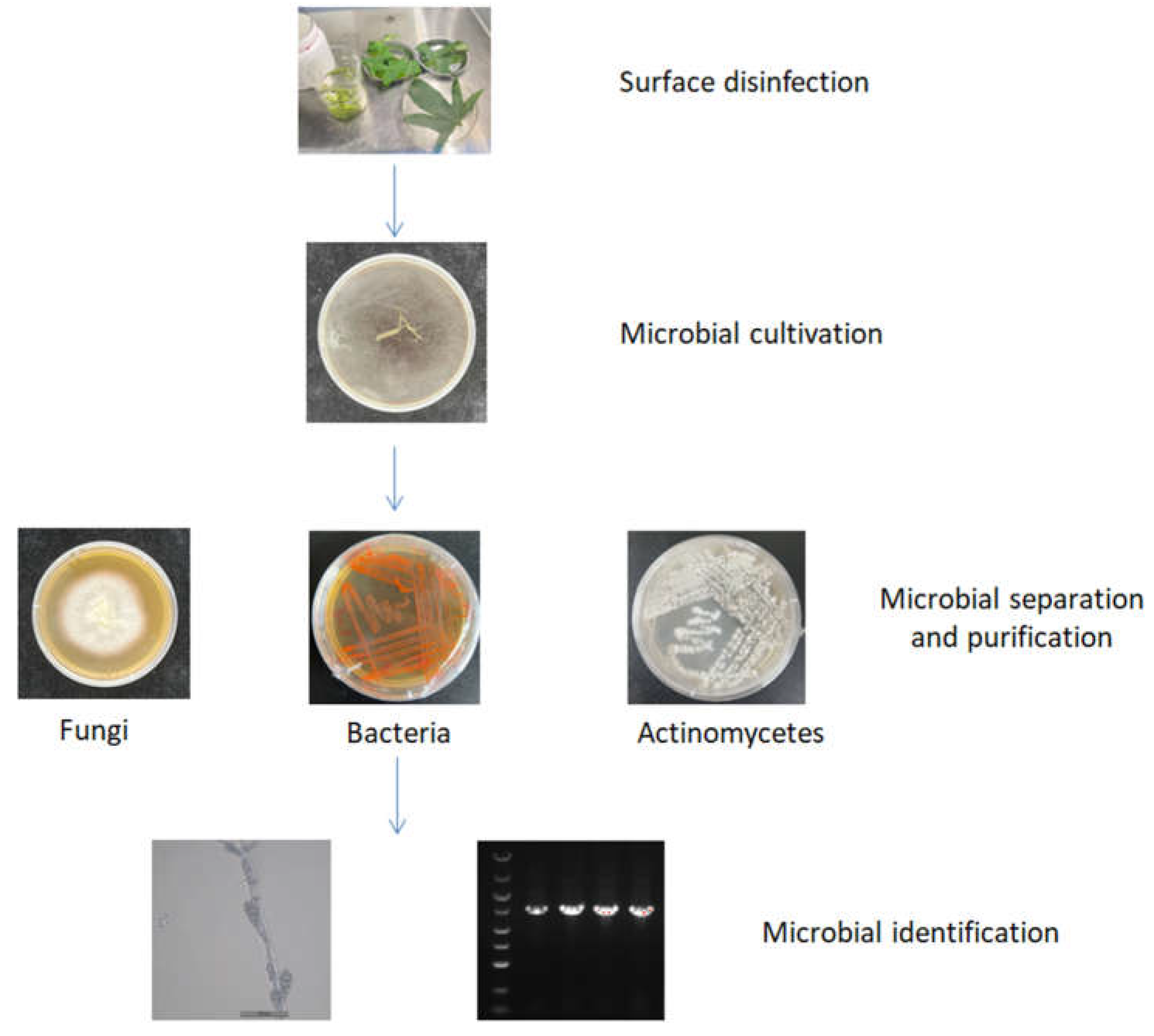
| Host plant | Tissue | Endophytic bacteria | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atractylodes macrocephala | Root, stem, leaf | Bacillus sp., Rhodococcus sp. Mycobacterium sp., Pseudomonas sp., Mycolicibacterium sp., Leucobacter sp., Enterobacter sp., Rhizobium sp., Glutamicibacter sp. and others, for a total of 58 genera. | [16] |
| Dendrobium | Stem | Bacillus sp., Enterobacter sp., Klebsiella sp., Pantoea sp., Pseudomonas sp., Curtobacterium sp., Burkholderia sp., Microbacterium sp., Lysinibacillus sp., and others, for a total of 23 genera. | [19] |
| Mulberry | Stem | Pantoea sp., Bacillus sp., Pseudomonas sp., Curtobacterium sp., Sphingomonas sp. and others, for a total of 36 genera. | [23] |
| Marigold (Calendula officinalis L.) | Root, shoot | Pantoea sp., Enterobacter sp., Pseudomonas sp., Achromobacter sp., Xanthomonas sp., Rathayibacter sp., Agrobacterium sp., Pseudoxanthomonas sp., and Beijerinckia sp.. | [24] |
| Camellia sinensis | Leaf, root | Bacillus sp., Acinetobacter sp., Stenotrophomonas sp., Brevundimonas sp., Pseudomonas sp., Ochrobactrum sp., Alcaligenes sp., and others, for a total of 16 genera. | [25] |
| Handroanthus impetiginosus | Leaf | Bacillus sp., Paenibacillus sp., Pseudomonas sp., Rhizobium sp., Rummeliibacillus sp. and Methylobacterium sp.. | [26] |
| European plum (Prunus domestica) | Shoot | Pseudomonas sp. and Agrobacterium sp. | [29] |
| Mint (Endostemon obtusifolius) | Leaf, root | Paenibacillus sp. etc. | [30] |
| Centella asiatica | Leaf | Pseudomonas sp., Novosphingobium sp., Chryseobacterium sp., Enterobacter sp., Agrobacterium sp., Pantoea sp. and Paraburkholderia sp. | [31] |
| Archidendron pauciflorum | Root, leaf, stem | Bacillus sp. etc. | [32] |
| Host plant | Tissue | Endophytic fungi | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aconitum heterophyllum | Root, stem, leaf | Arthrinium sp., Chaetomium sp., Purpureocillium sp., Alternaria sp., Penicillium sp., Aspergillus sp., Cladosporium sp., and Bjerkandera sp. | [34] |
| Crocus sativus | Corm, scape, leaf, petal, and stigma | Penicillium sp., Sistotrema sp., and Bjerkandera sp. | [37] |
| Salvia miltiorrhiza | Root | Fusarium sp., Epicoccum sp., Aspergillus sp., Arthrinium sp., Coprinellus sp., Dictyosporium sp., Colletotrichum sp., Rhizoctonia sp., Phomopsis sp. and Pithomyces sp. | [38] |
| Mint (Endostemon obtusifolius) | Root, leaf | Fusarium sp. etc. | [30] |
| Dendrobium | Leaf | Colletotrichum sp., Fusariumand sp., and Trichoderma sp. | [39] |
| Codonopsis pilosula | Root | Fusarium sp., Aspergillus sp., Alternaria sp., Penicillium sp., Plectosphaerella sp. etc. | [40] |
| Vernonia anthelmintica | Flower | Ovatospora sp., Chaetomium sp., Thielavia sp. and Aspergillus sp. | [41] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




