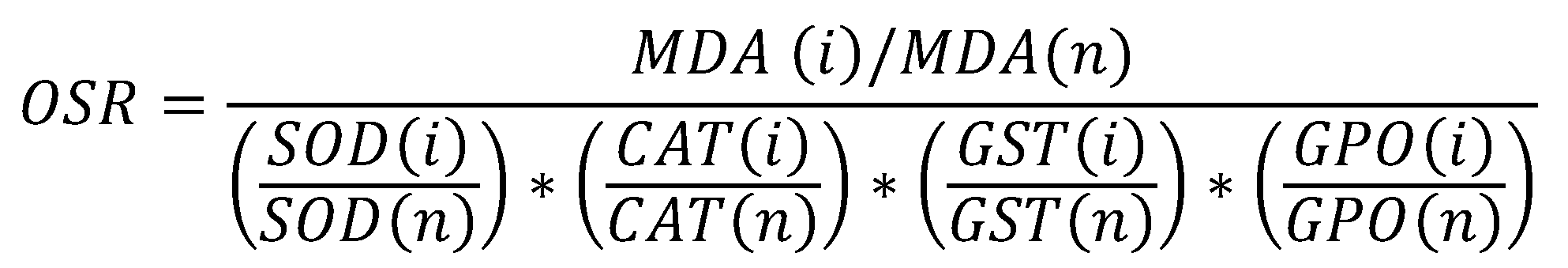Introduction
Among all cancers, gastric cancer is the third most common. Despite numerous studies, in recent years its prognosis has not improved significantly, and the number of patients who died from this cancer in 2018, according to world epidemiological data, was about 783,000 [
1,
2,
3]. Gastric cancer, like many other types of cancer, has a background of chronic inflammation caused by infection (
H. pylori) or exposure to environmental factors [
4,
5].
As precancerous conditions progress, free radical activity increases and the risk of various cancers increases too. Oxidative stress is a source of damage to cell membranes, DNA destruction, followed by metaplasia of epithelial cells of the gastric mucosa into adenocarcinoma [
6]. Some scientists come to the conclusion that damage to cell membranes and other structures inside the cell by free oxygen radicals underlies many pathological processes that lead to various diseases. Depending on which structures are damaged - the hereditary substance (DNA) or the outer membrane - either an oncological disease develops or other disorders are observed. Reactive oxygen species damage the structure of DNA, proteins and various membrane structures of cells.
The main function of neutrophilic granulocytes is phagocytosis, which allows the elimination of a foreign antigen. The final stage of phagocytosis is associated with the production of reactive oxygen species in the respiratory burst. The greater the number of reactive oxygen species, the more complete the phagocytosis and the higher the functional activity of neutrophilic granulocytes are observed. Therefore, the study of the chemiluminescent activity of neutrophilic granulocytes indirectly reflects their functional activity. In addition, there is evidence that neutrophilic granulocytes have a protumor effect in malignant tumor progression in the form of neoangiogenesis activation, tumor cell invasion, and induction of T-cell immunosuppression [
7,
8,
9]. On the other hand, neutrophils are effector antitumor cells, and the cytotoxic effect of neutrophil granules promotes tumor destruction [
10,
11]. However, the involvement of the nonspecific link of immunity and the role of neutrophils in carcinogenesis are assessed ambiguously [
12,
13,
14].
Given the relationship between the indicators of the chemiluminescent activity of neutrophilic granulocytes and the lipid peroxidation-antioxidant defense system, we assume that neutrophilic granulocytes contribute to the development of oxidative stress in gastric cancer due to the release of a large amount of reactive oxygen species in the respiratory burst. The greater the functional activity of neutrophilic granulocytes, the more reactive oxygen species are formed, which shift the balance towards prooxidants.
The purpose of this study: to study the processes of lipid peroxidation and the activity of antioxidant defense enzymes depending on the chemiluminescent activity of neutrophilic granulocytes in patients with gastric cancer associated with H. pylori infection, depending on the stage. We plan to study whether the intensity of neutrophil chemiluminescence (the amount of ROS) affects the severity of oxidative stress in gastric cancer.
Materials and Methods
- 1.
Subjects
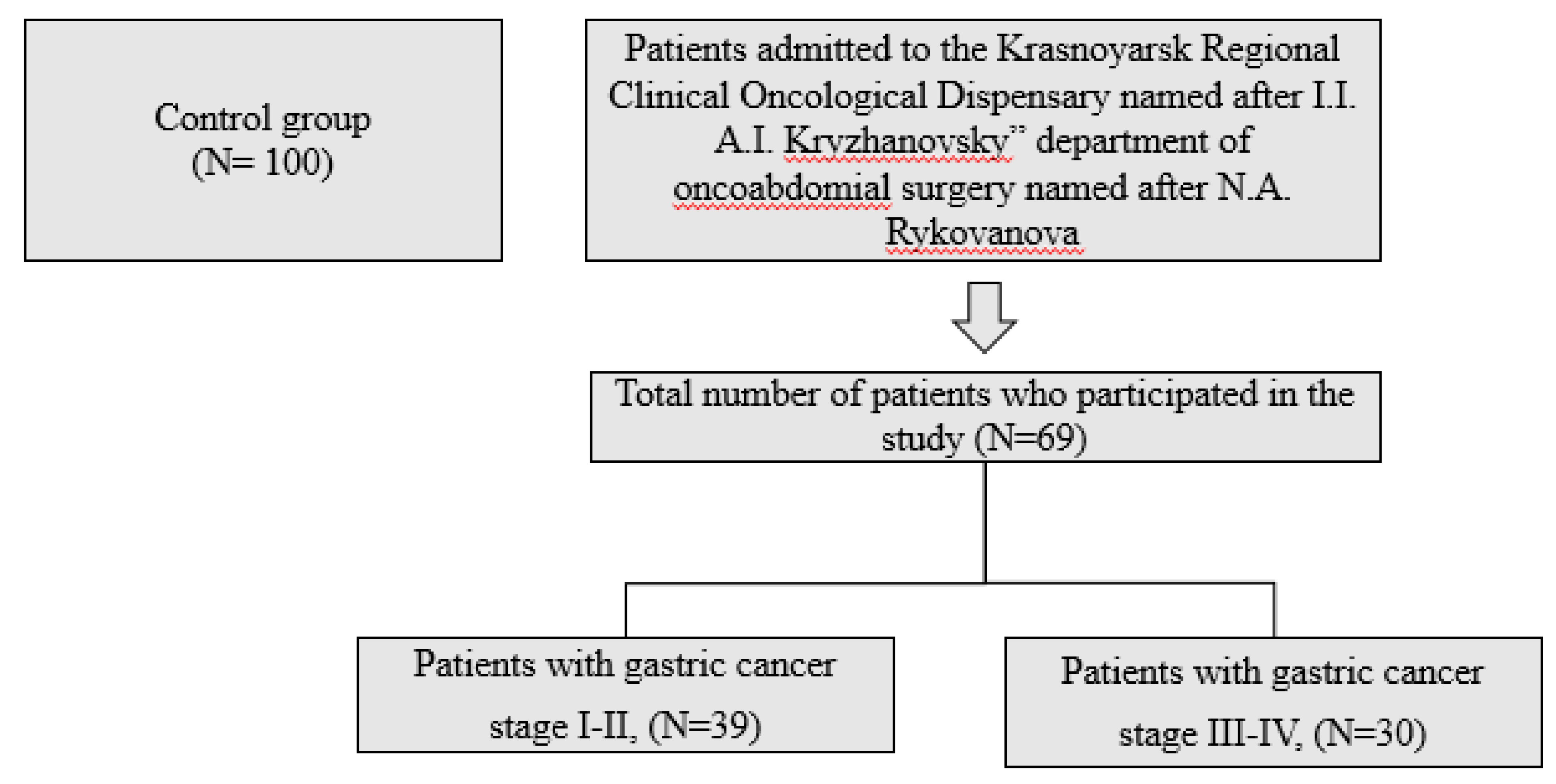
The study included 39 patients with stage I-II gastric cancer and 30 patients with stage III-IV gastric cancer (from 45 to 59 years, mean age 53 ± 5.7). Clinical examination of patients with gastric cancer was carried out in the Krasnoyarsk Regional Clinical Oncological Dispensary named after V.I. A.I. Kryzhanovsky” department of oncoabdomial surgery named after N.A. Rykovanov (
Figure 1). The diagnosis was made on the basis of clinical, anamnestic, laboratory and instrumental data by an oncologist. Inclusion of patients in the study, taking of biological material was carried out upon admission of patients to the hospital before the start of therapy. The material of the study was venous blood, which was taken from the patient in the morning from 8 to 9 o’clock, on an empty gastric, from the cubital vein, into Vacutainer tubes with separating gel and double clotting activator (silica) and with sodium heparin solution (5 U/ml).
The control group was formed from 100 practically healthy middle-aged blood donors (48.7±3.9 years) without gastroenterological complaints and gastroenterological anamnesis, without changes in the gastric mucosa. The study did not include patients with HIV infection, hepatitis, tuberculosis, gastric ulcer, and concomitant acute and chronic diseases in the acute phase. The study did not include patients who refused to participate in the research study.
The study was conducted with the permission of the Biomedical Ethics Committee at the Federal Research Center «Krasnoyarsk Science Center» of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, as well as with the permission of the Ethics Committee of the Krasnoyarsk Regional Clinical Oncological Dispensary named after I.I. A.I. Kryzhanovsky” (protocol No.2 of 10.02.2020). In the work with the examined patients, the ethical principles laid down by the Helsinki Declaration of the World Medical Association were observed. All participants signed an informed consent form to participate in the study.
- 2.
Endoscopic examination, histologic examination, H. pylori test, and gastric juice sampling
The study included patients with gastric cancer with verified Helicobacter pylori infection, which was proved by histological, urease and culture methods. All biopsies were examined by an experienced pathologist. To avoid contamination, the endoscope was washed and disinfected by immersion in a detergent solution. Specific antibodies (IgG) to Helicobacter pylori were detected by enzyme immunoassay (BIOHIT HealthCare, Helsinki, Finland). Antibody titers of 30 EIU or more were considered positive, less than 30 EIU were considered negative for H. pylori. In all patients included in the study, infection of the gastric mucosa with Helicobacter pylori was confirmed by histological examination with a modified Giemsa stain, a positive urease test (CLOtest; Delta West, Bentley, Western Australia), a positive culture test for Helicobacter pylori, and specific serum antibodies to Helicobacter pylori.
- 3.
Determination of the chemiluminescent activity of neutrophilic granulocytes
As a method for studying the activity of neutrophilic granulocytes (NG), we used chemiluminescent analysis of spontaneous and induced production of ROS by NG. Assessment of spontaneous and induced chemiluminescence was carried out for 90 minutes on a BLM-3607 biochemiluminescent analyzer (SKTB Nauka, Russia). The results were recorded and the analyzer was controlled via a personal computer. The following characteristics were determined: the time for the curve to reach the maximum intensity of chemiluminescence (Tmax is the time of activation of neutrophils), the maximum value of the intensity of chemiluminescence (Imax is the maximum amount of ROS produced by neutrophils per unit time), the area of the chemiluminescence curve (S is the total amount of ROS produced by neutrophils). Luminol was used as a chemiluminescence enhancer. Opsonized zymosan served as the respiratory burst inducer. The enhancement of chemiluminescence induced by opsonized zymosan was evaluated by the ratio of the area of induced (Sind) to the area of spontaneous (Ssp) chemiluminescence and was designated by the activation index.
“Lipid peroxidation - antioxidant protection” system
The following parameters of the pro-oxidant-antioxidant system (MDA, SOD, CAT, GST, GPO, CP) have been studied in the blood serum of the studied patients. To determine lipid peroxidation and the antioxidant system, a spectrophotometric method was used on a Thermo SCIENTIFIC GENESYS 10vis instrument (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA).
Measurement of malondialdehyde content (MDA)
MDA is a secondary product of lipid peroxidation. The principle of the method is based on the interaction with 2-thiobarbituric acid (TBA) to form a chromogen with an absorption maximum in the red part of the visible spectrum with a wavelength of 532 nm. The measurement of the MDA content is carried out taking into account the molar extinction coefficient of the formed chromogen, equal to 1.56 10
5M-1 cm
−1, and is expressed in µmol/l:
Measurement of superoxide dismutase (SOD) content
The enzyme superoxide dismutase inhibits the autoxidation reaction of adrenaline in an alkaline environment. The intensity of the adrenaline autoxidation reaction is estimated by an increase in absorption at a wavelength of 347 nm, due to the accumulation of oxidation products and the formation of adrenochrome with an absorption maximum at a wavelength of 480 nm.
Measurement of catalase content
The determination of catalase activity is based on the formation of a yellow-colored complex of hydrogen peroxide with ammonium molybdate that was not destroyed during the catalase reaction. Catalase activity is calculated by the formula:
Measurement of glutathione-S-transferase content
The content of the glutathione-S-transferase enzyme is determined by the rate of formation of glutathione-S-conjugates during the interaction of reduced glutathione with 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (CDNB). The increase in the content of conjugates during the reaction is recorded spectrophotometrically at a wavelength of 340 nm (maximum absorption of glutathione-S-CDNB).
The enzyme content is determined using the millimolar extinction coefficient for GS-CDNB at a wavelength of 340 nm, equal to 9.6 mM-1 cm
−1, and determined in micromoles of formed glutathione-S-conjugates per minute per 1 g Hb:
Measurement of glutathione peroxidase content
Glutathione peroxidase (GPO) catalyzes the reaction between glutathione (GSH) and tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TBH):
Enzyme activity is assessed by the change in the GSH content in samples before and after incubation with a model substrate in the course of a color reaction with dithionitro(bis)benzoic acid (DTNBA). Measure the extinction of the experimental and control samples on a spectrophotometer at a wavelength of 412 nm. Zeroed in distilled water.
Activity is calculated by the formula
Measurement of ceruloplasmin (CP) content in blood serum (Revin method)
The method is based on the oxidation of n-phenylenediamine with the participation of ceruloplasmin. According to the optical density of the resulting products, the activity of ceruloplasmin is judged.
Measurement of the coefficient of oxidative stress (COS)
An individual ratio of prooxidants to antioxidants was determined for each patient with gastric cancer included in the study (
Figure 2)
In the formula, i are the values of the indicators of the studied patient, and n are the values of the indicators of the control group (proper values), while COS normally tends to 1, with an increase in COS more than 1, a shift in the balance towards prooxidants and the development of oxidative stress are detected.
- 4.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis of the obtained results was performed using the Statistica v.12.0 program (StftSoft Inc., USA). To assess differences in groups, nonparametric Kruskal-Wallis tests (for three or more comparison groups) and Mann-Whitney (for pairwise comparison) were used. Comparison of groups on a qualitative binary trait was carried out using a two-sided Fisher’s exact test. Data are presented as Median (Me) and interquartile range (Q25-Q75). To determine the correlations, the Spearman method was used, since at least one of the distributions of the analyzed quantitative characteristics is not normal. When the value of the correlation coefficient |r|≥0.75, the relationship between the signs was assessed as strong, at a coefficient of 0.25<|r|<0.75 - the dependence of the average strength, at |r|≤0.25 - a weak degree of correlation. When comparing the signs characterizing the frequency, Fisher’s exact test was used.
Results
- 1.
Baseline patient characteristics
The mean age of 169 examined patients and the comparison group was 54.3 years (±9.4). The gastric cancer group included sixty-nine patients and were randomized after three were excluded due to refusal to sign informed consent. Patients with gastric cancer were divided according to the stages of the disease - patients with stage I-II gastric cancer and patients with stage III-IV gastric cancer. The control and study groups were similar in terms of baseline demographic data (
Table 1).
- 2.
Correlation relationships between indicators of chemiluminescent activity of neutrophilic granulocytes and the system “lipid peroxidation - antioxidant defence”
When studying the correlation relationships between the indicators of the chemiluminescent activity of neutrophilic granulocytes and lipid peroxidation - antioxidant defence, we found unidirectional relationships in all the studied groups, which made it possible to assume a direct relationship between the functional activity of neutrophils and manifestations of oxidative stress.
In patients with gastric cancer at stages I-II of the disease, 5 strong correlations were found: Imax spon. – SOD, Imax spon. – GST, Imax spon. – GPO, Imax spon. – CP, Imax induced. – MDA; 7 average correlation relationships: Imax spon. – MDA, Imax spon. – CAT, Imax induced. – SOD, Imax induced. – CAT, Imax induced. – GST, Imax induced. – GPO, Imax induced. – CP (
Table 2).
When analyzing correlations in patients with stage III-IV gastric cancer, it was revealed: 4 strong correlations: Imax spon. – CAT, Imax spon. – GPO, Imax spon. – CP, Imax induced. – SOD; 8 average correlation relationships: Imax spon. – MDA, Imax spon. – SOD, Imax spon. – GST, Imax induced. – MDA, Imax induced. – CAT, Imax induced. – GST, Imax induced. – GPO, Imax induced. – CP (
Table 3).
- 3.
Distribution of groups of patients with gastric cancer depending on the activity of neutrophilic granulocytes
After the found correlation relationships between the indicators of chemiluminescent activity of neutrophilic granulocytes and the system lipid peroxidation - antioxidant defence, we assumed that the greater the functional activity of neutrophilic granulocytes, the more reactive oxygen species are formed, which shift the balance towards prooxidants. At the next stage of the study, we ranked all patients with gastric cancer associated with
H. pylori infection, according to the activity of neutrophilic granulocytes (
Table 4).
A total of 69 patients with gastric cancer associated with Helicobacter pylori were examined. In patients with stage I-II gastric cancer, the following was found: 10 patients (26% of those examined) showed normal activity of neutrophilic granulocytes (corresponded to the values of the control group); 8 patients (21% of those examined) had increased chemiluminescent (CL) activity of neutrophils; 21 patients (54% of those examined) had reduced activity of neutrophilic granulocytes (p<0.05).
When examining patients at III-IV stages of the disease, it was found: 10 patients (33% of those examined) with normal activity. neutrophilic granulocytes; 13 patients (44% of those examined) with increased neutrophil activity (p<0.05); 7 patients (23% examined) with reduced activity of neutrophilic granulocytes. Thus, in the early stages of gastric cancer associated with H. pylori infection, patients are dominated by reduced CL activity of neutrophils, and in the later stages, increased activity.
- 4.
Chemiluminescence of neutrophilic granulocytes in patients with gastric cancer at different stages of the disease
At the next stage, we studied the chemiluminescence of neutrophilic granulocytes in patients with stage I-II gastric cancer with low neutrophil activity and stage III-IV gastric cancer with high activity of neutrophilic granulocytes.
It was found that the median values of spontaneous luminescence intensity in patients with stage III-IV gastric cancer increased by 1.5 times compared with the control group and the group of patients with stage I-II gastric cancer (p
1-3=0.03; p
2-3 =0.02) (
Table 5). When considering the spontaneous area under the curve, an increase in this indicator was found in patients with gastric cancer of both I-II and III-IV stages compared with the control group (p
1-2<0.001, p
1-3<0.001), in patients with gastric cancer III -IV stage there was an increase in the spontaneous area under the curve compared with patients with gastric cancer at stages I-II (p
2-3<0.001). In patients with stage III-IV gastric cancer, an increase in the induced intensity of chemiluminescence of neutrophilic granulocytes was revealed compared with the control group and the group of patients with stage I-II gastric cancer (p
1-3=0.04; p
2-3=0.01). When studying the induced area under the curve in patients with gastric cancer stages I-II and III-IV, this indicator increased relative to the control group (p
1-2<0.001, p
1-3<0.001), in addition, in patients at stages III-IV of the disease, increase in the induced area under the curve compared with patients with gastric cancer at stages I-II (p
2-3<0.001).
- 5.
Indicators of the system “lipid peroxidation - antioxidant protection” (LPO-AOP) in gastric cancer, depending on the stage of the disease
We measured the parameters of the LPO-AOP system in patients with gastric cancer at different stages of the disease. At the same time, in subsequent experiments, data were taken from patients with stage I-II gastric cancer with low activity of neutrophilic granulocytes - 21 patients, and in the group with stage III-IV gastric cancer, patients were taken in whom the activity of neutrophilic granulocytes was increased - 13 people. The content of the LPO product (malonic dialdehyde) and the content of the main enzymes of the antioxidant defense system were studied (superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione-S-transferase, glutathione peroxidase, ceruloplasmin).
Was found an increase in the median MDA in patients with stage I-II gastric cancer and stage III-IV gastric cancer relative to the control group (MDA: p
1-2=0.001; p
1-3=0.001;) (
Table 6).
Further, the state of the AOP system in the groups of patients was assessed. It was found that the median values of superoxide dismutase, catalase activity, glutathione-S-transferase and glutathione peroxidase and ceruloplasmin in plasma increased in all groups of patients compared with the control group (SOD: p1-2=0.03; p1-3=0.002, CAT: p1-2=0.03, p1-3=0.03, GST: p1-2=0.04, p1-3=0.046, GPO: p1-2=0.01, p1-3=0.023, CP: p1-2<0.001; p1-3<0.001). In addition, in patients with stage III-IV gastric cancer, there was a significant increase in the level of ceruloplasmin compared with patients with gastric cancer in stages I-II of the disease (CP: p2-3<0.001).
The coefficient of oxidative stress reflects the balance of the processes of lipid peroxidation from the antioxidant system and normally tends to 1. When calculating the coefficient of oxidative stress in patients suffering from gastric cancer, it was found that the COS at stages I-II of the disease was 2.8, and at stages III-IV it increased up to 3,9.
Discussion
When studying the chemiluminescent activity of neutrophilic granulocytes, it was found that in patients with gastric cancer associated with
H. pylori infection, in the early stages (I-II), the majority of patients showed reduced CL activity of neutrophils, and in the late stages (III-IV) - increased. The revealed difference is probably due to the complex effect of the infectious agent and the tumor factor, while at the early stages, cells may be inhibited, and later they adapt to changes, possibly with the replacement of the function from antitumor to protumor. Neutrophils respond to mediators released by the tumor and its microenvironment, resulting in activation of either their antitumor or protumor phenotypes. This neutrophil plasticity is due to the influence of transforming growth factor β (TGF-β), β-interferon (IFN-β), IL-35, as well as the concentration of cytokines and oxygen in the tumor microenvironment [
4]. For a long time, the functional diversity of neutrophils was overlooked; however, if the activation of neutrophils causes damage to surrounding tissues, releasing reactive oxygen species and proteolytic enzymes, these cells are also critical for tissue regeneration. This is due to the fact that neutrophils are able to produce growth factors and pro-angiogenic proteins that promote revascularization. Neutrophils can induce macrophage recruitment, which in turn supports and accelerates tissue repair [
16]. Due to these opposite functions, the role of neutrophils in the development of cancer is ambiguous [
17].
N1 neutrophils are characterized by high expression of immunoactivating chemokines and cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α). TNF-α activates special receptors capable of recognizing a malignant cell and blocking its further division, as well as promoting its necrosis [
18]; intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1), which, for example, in the melanoma xenograft model promotes the aggregation and retention of T cells in the tumor niche by binding to the β2-integrin LFA-1, which leads to improved immune control and potentially limits tumor development [
19]; receptor protein Fas containing the intracellular death domain and participating in the programmed mechanism of apoptosis [
20]. The antitumor activity of N1 neutrophils is associated with the direct destruction of tumor cells through the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitric oxide or the induction of apoptosis associated with the activation of Fas/TRAIL. Other mechanisms include antibody dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and activation of T cell function [
21].
In other studies, N2 neutrophils have been shown to play a protumor role through several mechanisms. They contribute to tumor development by producing reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS), as well as stimulating tumor cell proliferation by secreting neutrophil elastase (NE), which enhances tumor invasion, metastasis progression [
22] and secretion of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9), which activates pro-TGF-β and pro-TNF-α growth factors [
23]. Neutrophils N2 act as tumor promoters and express the angiogenic chemokines CC and CXC, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and the CXCR4 receptor, which plays a key role in the penetration of tumor cells through interstitial barriers [
24]. Thus, it can be assumed that in our study, the altered CL activity of neutrophils at different stages of gastric cancer is due to their different phenotypes; in gastric cancer, N1 neutrophils are predominant in the early stages, and N2 neutrophils are predominant in the late stages.
At the molecular level, neutrophils, through the release of ROS, damage DNA, which contributes to the emergence and progression of cancer, and an increase in the mutation load. On the other hand, neutrophils contribute to the separation of tumor cells from the basement membrane, inhibiting the initial phases of carcinogenesis. The hyperoxic microenvironment limits the accumulation of neutrophils in tumors, but tumor-infiltrating neutrophils show a high antitumor potential due to increased release of ROS, which limit tumor cell proliferation and induce apoptosis [
25]. It is possible that such a multidirectional effect of ROS is associated with a different amount of ROS produced by neutrophils. On the one hand, at low levels of ROS, it promotes the survival of cancer cells, since the progression of the cell cycle, caused by growth factors and receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), requires ROS for activation [
26]. On the other hand, a high level of ROS can suppress tumor growth due to stable activation of the cell cycle inhibitor and induction of cell death [
27].
When evaluating the activity of the “lipid peroxidation - antioxidant system” in patients with gastric cancer at stages I-II and III-IV of the disease, we found unidirectional changes in the form of an increase in the amount of malondialdehyde and an increase in the activity of all AOP enzymes, which proves the role of oxidative stress in the development of the tumor process [
14,
15]. There were no statistically significant differences in LPO-AOP at different stages of gastric cancer, and there was no significant difference in the oxidative stress ratio at different chemiluminescent activity of neutrophils. This proves that different amounts of ROS produced by neutrophils are used in different cellular processes.
Conclusion
For the first time, relationships between the chemiluminescent activity of neutrophilic granulocytes and the compartments of the lipid peroxidation-antioxidant protection system in gastric cancer associated with H. pylori infection, depending on the stage, were revealed, which indicates the involvement of microphages in carcinogenesis. It was shown that, regardless of the stage of the disease, correlation relationships were unidirectional.
In patients with gastric cancer associated with H. pylori infection, regardless of stage, the proportion of neutrophilic granulocytes with normal activity does not exceed 1/3 of the total number of patients, the remaining 2/3 of patients have an altered chemiluminescent activity of neutrophilic granulocytes: in patients with gastric cancer by I -II stage of the disease, the majority revealed a reduced function of neutrophilic granulocytes, and in patients with gastric cancer stage III-IV of the disease, the majority showed increased chemiluminescent activity of neutrophilic granulocytes.
When comparing the altered chemiluminescent activity of neutrophilic granulocytes in gastric cancer, depending on the stage, an increase in Imax spon was revealed. and Imax ind. - 2 times, and the area under the curve (S spon, S ind) in the spontaneous and induced state of chemiluminescence is approximately 3 times at III-IV stages of the disease relative to stages I-II. At the same time, the time to reach the maximum of chemiluminescence at all stages of gastric cancer did not differ from the control, which indicates that cells - neutrophilic granulocytes are activated in the same way.
In all patients with gastric cancer associated with H. pylori infection, regardless of the stage of the disease, an increase in lipid peroxidation processes with activation of antioxidant defense enzymes was detected. At the same time, there are no statistically significant differences between the indicators of the system lipid peroxidation - antioxidant protection depending on the stage of gastric cancer and the chemiluminescent activity of neutrophilic granulocytes, which probably indicates that all reactive oxygen species produced by neutrophilic granulocytes in the respiratory burst are consumed locally, minimally affecting the development of oxidative stress in the blood plasma.
Author Contributions
Smirnova O.V., Sinyakov A.A. - development of the concept and design of the study, analysis and interpretation of data. Sinyakov A.A. - conducting the practical part of the study. Kasparov E.V. – validation of critical intellectual content. Smirnova O.V. - final approval of the manuscript for publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare the absence of obvious and potential conflicts of interest related to the publication of this article.
Source of financing
The authors declare no funding.
Compliance with the principles of ethics
All patients signed informed consent to participate in the study. The study was approved by the Biomedical Ethics Committee at the Federal Research Center «Krasnoyarsk Science Center» of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences (protocol No.2 of 10.02.2020).
References
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataran I, Siegel RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68: 394-424, 2018.
- Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin 63: 11-30, 2013.
- Katanoda K, Hori M, Matsuda T, Shibata A, Nishino Y, Hattori M, Soda M, Ioka A, Sobue T and Nishimoto H: An updated report on the trends in cancer incidence and mortality in Japan, 1958-2013. Jpn J Clin Oncol 45: 390-401, 2015.
- Plummer M, de Martel C, Vignat J, Ferlay J, Bray F and Franceschi S: Global burden of cancers attributable to infections in 2012: A synthetic analysis. Lancet Glob Health 4: e609-e616, 2016.
- Matsuda T, Ajiki W, Marugame T, Ioka A, Tsukuma H and Sobue T: Research group of population-based cancer registries of Japan: Population-based survival of cancer patients diagnosed between 1993 and 1999 in Japan: A chronological and international comparative study. Jpn J Clin Oncol 41: 40-51, 2011.
- Razzaghi R., Agarwal S., Kotlov N. et al. Compromised counterselection by FAS creates an aggressive subtype of germinal center lymphoma. J Exp Med. 2021. Vol. 218 (3). P. e20201173.
- Zhang Xin-Jia., Yong-Gang L., Xiao-Jun S., Xiao-Wu C., Dong Z., Da-Jian Z. The prognostic role of neutrophils to lymphocytes ratio and platelet count in gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. International Journal of Surgery. 2015. Vol. 21. P. 84–91.
- Keehoon Jung, Takahiro Heishi, Joao Incio, Dai Fukumura. Targeting CXCR4-dependent immunosuppressive Ly6Clow monocytes improves antiangiogenic therapy in colorectal cancer. PNAS. 2017. Vol. 114 (39). P. 10455–10460.
- Ustyanovska Avtenyuk, N., Choukrani G., Ammatuna E., Niki T., Cendrowicz E., Lourens H.J., Huls G., Wiersma V.R., Bremer E. Galectin-9 Triggers Neutrophil-Mediated Anticancer Immunity. Biomedicines. 2021. Vol. 10 (66). P. 10–16.
- Kraus R.F., Gruber M.A. Neutrophils-From Bone Marrow to First-Line Defense of the Innate Immune System. Front Immunol. 2021. Vol. 12 (767175). P. 1–35.
- Huang, H. Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) as a Cancer Biomarker and MMP-9 Biosensors: Recent Advances. Sensors (Basel). 2018. Vol. 18 (10). P. 3249.
- Bui, T.M., Wiesolek H.L., Sumagin R. ICAM-1: A master regulator of cellular responses in inflammation, injury resolution, and tumorigenesis. J Leukoc Biol. 2020. Vol. 108 (3). P. 787–799.
- Taya, M., Garcia-Hernandez M.L., Rangel-Moreno J., Minor B., Gibbons E., Hammes S.R. Neutrophil elastase from myeloid cells promotes TSC2-null tumor growth. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2020. Vol. 27 (4). P. 261–274.
- Dimitriou, N., Felekouras E., Karavokyros I., Alexandrou A., Pikoulis E, Griniatsos J. Neutrophils to lymphocytes ratio as a useful prognosticator for stage II colorectal cancer patients. BMC Cancer. 2018. Vol. 18 (1). P. 1202.
- Drake IM, Davies MJ, Mapstone NP, Dixon MF, Schorah CJ, White KL, Chalmers DM, Axon AT. Ascorbic acid may protect against human gastric cancer by scavenging mucosal oxygen radicals. Carcinogenesis. 1996 Mar;17(3):559-562. [CrossRef]
- Na HK, Woo JH. Helicobacter pylori Induces Hypermethylation of CpG Islands Through Upregulation of DNA Methyltransferase: Possible Involvement of Reactive Oxygen/Nitrogen Species. J Cancer Prev. 2014;19(4):259-264. [CrossRef]
- Zhuang XQ, Lin SR. Research of Helicobacter pylori infection in precancerous gastric lesions. World J Gastroentero 2000; 6: 428-429.
- Prinz C, Schoniger M, Rad R, Becker I, Keiditsch E, Wagenpfeil S, ClassenM, Rosch T, ScheppW, GerhardM. Key importance of the Helicobacter pylori adherence factor blood group antigen binding adhesin during chronic gastric inflammation. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 1903-1909.
- Zhu Y, Lin J, Li D, Du Q, Qian K, Wu Q, Zheng S. Helicobacter pylori antigen and its IgG, IgA-type specific immunocomplexes in sera from patients with Helicobacter pylori infection. ChinMed J (Engl) 2002; 115: 381-383.
- Futagami S, TakahashiH, Norose Y, KobayashiM. Systemic and local immune responses against Helicobacter pylori urease in patients with chronic gastritis: distinct IgA and IgG productive sites. Gut 1998; 43: 168-175.
- Xu H, Chaturvedi R, Cheng Y, Bussière FI, Asim M, Yao MD, et al. Spermine oxidation induced by Helicobacter pylori results in apoptosis and DNA damage: implications for gastric carcinogenesis. Cancer Res 2004; 64:8521-5; PMID:15574757. [CrossRef]
- Domellof, L. Reversal of gastric atrophy after Helicobacter pylori eradication: is it possible or not? Am J Gastroenterol 1998, 93: 1407-1408.
- Meining A, Stolte M. Close correlation of intestinal metaplasia and corpus gastritis in patients infected with Helicobacter pylori. Z Gastroenterol 2002; 40: 557-560.
- Zhu Y, Lin J, Li D, Du Q, Qian K, Wu Q, Zheng S. Helicobacter pylori antigen and its IgG, IgA-type specific immunocomplexes in sera from patients with Helicobacter pylori infection. ChinMed J (Engl) 2002; 115: 381-383.
- Figueroa G, Faundez G, Troncoso M, Navarrete P, Toledo MS. Immunoglobulin G antibody response to infection with coccoid forms of Helicobacter pylori. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 2002; 9: 1067-1071.
- Futagami S, TakahashiH, Norose Y, KobayashiM. Systemic and local immune responses against Helicobacter pylori urease in patients with chronic gastritis: distinct IgA and IgG productive sites. Gut 1998; 43: 168-175.
- Drake IM, Davies MJ, Mapstone NP, Dixon MF, Schorah CJ, White KL, Chalmers DM, Axon AT. Ascorbic acid may protect against human gastric cancer by scavenging mucosal oxygen radicals. Carcinogenesis. 1996 Mar;17(3):559-562. [CrossRef]
- Na HK, Woo JH. Helicobacter pylori Induces Hypermethylation of CpG Islands Through Upregulation of DNA Methyltransferase: Possible Involvement of Reactive Oxygen/Nitrogen Species. J Cancer Prev. 2014;19(4):259-264. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).