1. Introduction
When planning dental-supported prosthesis, several steps are involved to ensure a successful outcome. Among them, an accurate and precise preparation of the prosthetic margin or finishing line, which is the interface between the prepared tooth and the dental prosthesis, is crucial to ensure longevity and satisfactory aesthetic results to the final restoration. The finishing line can be positioned either supragingival or subgingival, depending on various factors such as aesthetics, accessibility, and periodontal condition. The margin should be well-defined, properly finished and polished, to facilitate impression taking and manufacturing of a fixed prosthesis with a seamless transition between the natural tooth and the prosthetic material. A precise margin, exhibiting a smooth and continuous contour, is crucial to ensure accurate adaptation and seating of the prosthesis, minimizing gaps or discrepancies that could compromise restoration integrity. Diamond or carbide finishing burs, diamond stones of descending grit and rubber points mounted on rotary handpieces such as turbine and high-speed electric handpiece are commonly used to finalize preparation margin.
The introduction in dentistry of ultrasonic-driven devices specifically designed for osseous surgery opened broader possibilities in the treatment of hard tissues, including tooth structure [
1]. Piezoelectric devices for bone surgery have a wide range of applications in various fields of oral and maxillofacial surgery, such as impacted teeth removal, maxillary sinus floor elevation, ridge splitting, implant site preparation, crown lengthening and orthodontic corticotomies [
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7]. The active tip of piezoelectric handpieces, vibrating at ultrasonic frequencies (typically in the range of 25-30 kHz), allows for precise and controlled action on mineralized tissues while sparing surrounding soft tissue [
8]. This selectivity is due to the difference in physical properties and vibrational characteristics between hard and soft tissues. Hard tissues have a higher density and stiffness and ultrasonic vibrations produce linear elastic micro-fractures [
9]. The ultrasonic blade sets up stress conditions in the hard tissues such that cracks propagate ahead in a controlled mode. Soft tissues are more flexible and may vibrate without rupture at the same frequency as the tip of the instrument. Nevertheless, damage may occur when soft tissue is tightly entrapped or bound to the bone and, subsequently, cannot freely vibrate [
10]. This selective cutting capability may be useful also in prosthodontics during finishing of subgingival prosthetic margins, diminishing the risk of damaging adjacent soft tissue and possibly enhancing the gingival response to the preparation procedures [
11].
Previous studies comparing rotary and ultrasonic instruments in this specific application are present in literature, with the aim to determine which approach produced the smoothest surface [
12,
13,
14,
15,
16]. However, standardization of active tip grit was not performed in these investigations. The use of burs and ultrasonic inserts of different granulometry may significantly impact on surface roughness, making difficult to discern the role of the tip movement (rotation vs. vibration) on the final result.
Hence, the aim of the present study is to compare the influence of the type of movement generated by different handpieces (turbine, high-speed electric handpiece and piezoelectric device) on surface roughness of enamel and dentin when using diamond-coated working tips of the same granulometry.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample preparation
The present in vitro study was conducted on fifteen first molars without tooth decay, fillings or other issues, extracted from 45-60 years old patients and stored in saline solution at room temperature. The use of extracted teeth for the present study was authorized by the Ethical Committee of Friuli Venezia Giulia (C.E.U.R. Friuli-Venezia Giulia, Italy – n◦ 194/2019). Before beginning the experimental phase, the samples were rinsed with fresh saline solution and incorporated in a gypsum matrix. The occlusal portion was removed using a diamond-coated water wheel and then refined with a 120-130 μm grit bur (405LC, Intensiv, Collina d’Oro, Switzerland) in order to obtain a flat and homogeneous surface with adequate exposure of the dentin core, avoiding pulp involvment. Each tooth surface was then divided into three portions and every portion was finished with one of the three tested instruments: turbine (Synea Vision TK98L, W&H, Burmoos, Austria), high-speed electric handpiece (Synea Vision WK99LT, W&H, Burmoos, Austria) and piezoelectric handpiece (Piezosurgery Touch, Mectron, Carasco, Italy) (
Figure 1-1b). The piezoelectric unit was set at “Perio” power. A diamond-coated bur (FG862M/016C, Sweden & Martina, Padova, Italy) and a diamond-coated tip (TF12D60, Mectron, Carasco, Italy) were used with the different devices by the same experienced operator (CS) with 4x magnification loupes. Tooth preparation was conducted with the samples placed on a compression load cell to verify that load applied to the handpieces never exceeded 150 g [
17,
18]. The working part of rotary burs and piezoelectric tips presented the same granulometry (60 μm). The instruments were changed every five sample preparations, as suggested in literature [
19]. Burs and tips were used with the longitudinal axis parallel to the occlusal surface and moved with homogenous and monodirectional movement for 30 seconds.
2.2. Roughness analysis
The quantitative analysis of the surface roughness of the different surfaces was carried out using an optical profilometer (Talysurf CLI 1000, Taylor Hobson, Leicester, UK). Before proceeding with the analysis, the samples were observed under an optical microscope to carry out the measurements perpendicularly to the main orientation of the grooves. Equal portions of enamel and dentin were analyzed for each sample: each area was analyzed 5 times using an inductive transducer with medium range setting (range of use: 494 μm-8.4 nm) with an acquisition speed set at 50 μm/s. The following roughness parameters were collected: mean roughness (Ra), skewness (Rsk) and kurtosis (Rku), in order to evaluate the symmetry of the profile relative the midline (Rsk) and the sharpness of peaks and valleys (Rku).
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) analysis
Qualitative analysis was performed by scanning electron microscope SEM (Quanta 250, FEI, Hillsboro, OR, USA) operating in environmental conditions. Surface details of the different dental samples, burs and ultrasonic inserts were acquired before and after use at different magnification (200x-800x for tooth samples and 30x-100x for burs and inserts).
2.4. Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed with SPSS v.24 software (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). Data distribution was analyzed with Shapiro-Wilk test. Due to non-normal distribution, non-parametric tests were performed. Kruskal-Wallis test was used to compare roughness produced by the different handpieces within the same substrate and Mann-Whitney test was used for one-to-one comparison between the different handpieces according to the different substrates. Statistical significance was set at p<0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Roughness analysis
Ra and Rsk were significantly different between enamel and dentin only after the use of turbine (p=0.004 and p=0.007, respectively). No significant differences for all roughness parameters (Ra, Rsk and Rku) were demonstrated between enamel and dentin when using high-speed electric handpiece or piezoelectric device. Complete results are reported in
Table 1.
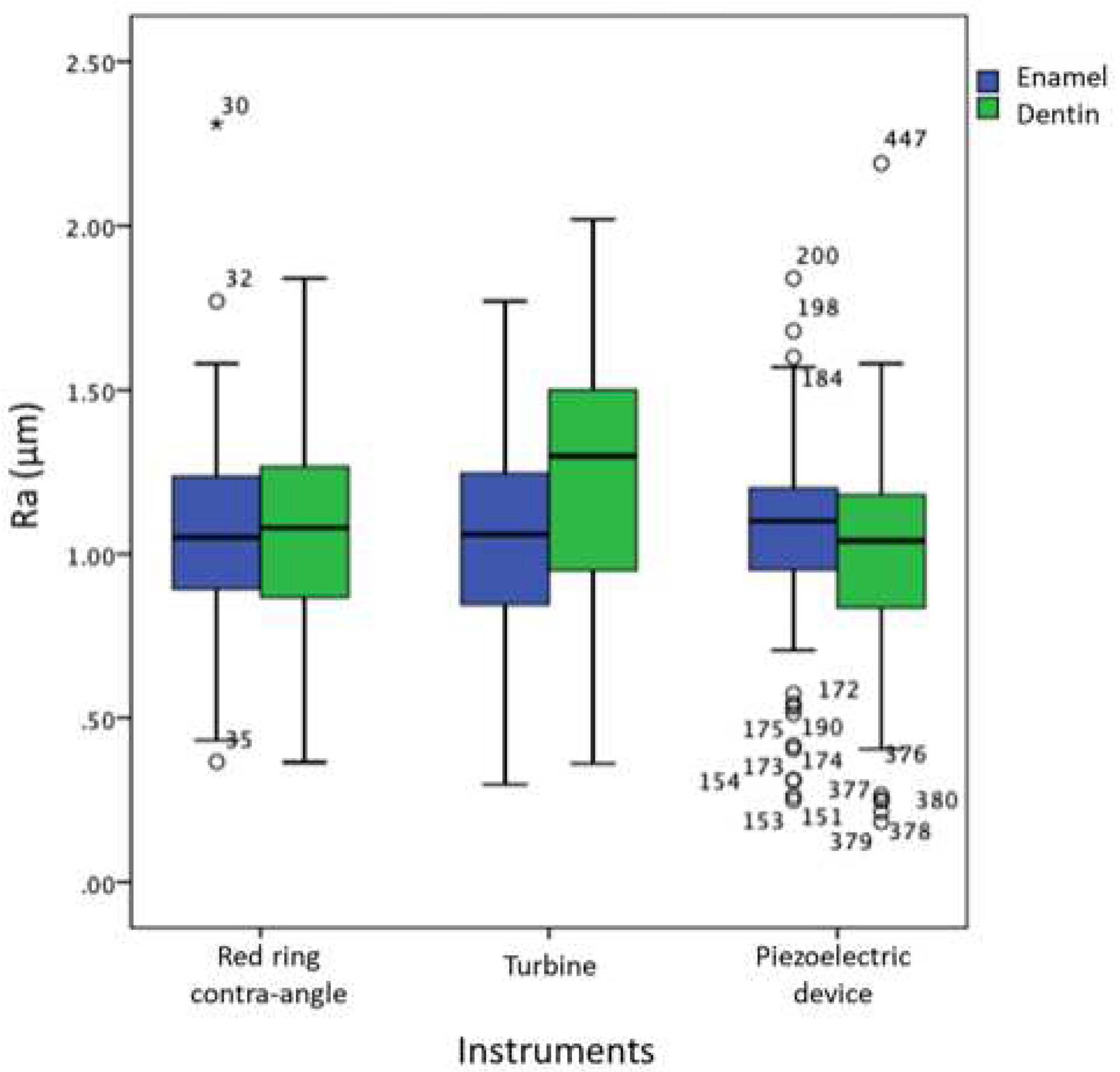
In detail, Ra measured on enamel showed no significant differences between the three devices (turbine-piezoelectric handpiece p=0.562; turbine-high-speed electric handpiece p=0.738; piezoelectric handpiece high-speed electric handpiece p= 0.806) (
Figure 2).
Turbine used on dentin produced a significantly higher Ra both when compared to piezoelectric handpiece (p=0.001) and when compared to high-speed electric handpiece (p=0.012). No significant Ra differences were demonstrated on dentin between high-speed electric handpiece and piezoelectric handpiece (p=0.411).
Rsk resulted significantly higher on enamel when using the turbine in comparison with the high-speed electric handpiece (p=0.048) or the piezoelectric handpiece (p=0.005). Rsk was significantly higher also on dentin when using the turbine in comparison with both other handpieces (p=0.000), whilst no significant differences were recorded on both substrates when comparing piezoelectric handpiece and high-speed electric handpiece (enamel: p=0.410; dentin: p=0.813). All the comparisons made for Rku parameter in both substrates did not show significant differences between the various handpieces. Complete results are listed in
Table 2.
3.2. SEM analysis
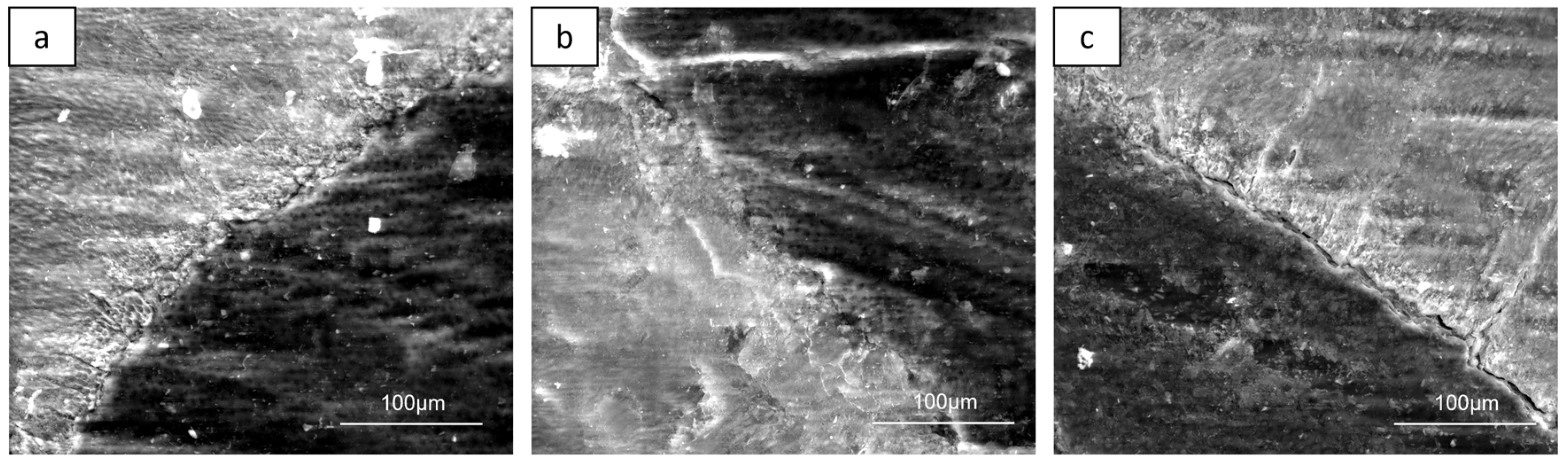
Surface qualitative analysis showed a clear parallel trend of the micro-grooves in the samples treated with turbine and high-speed electric handpiece; this characteristic is less evident in the samples prepared with piezoelectric handpiece (
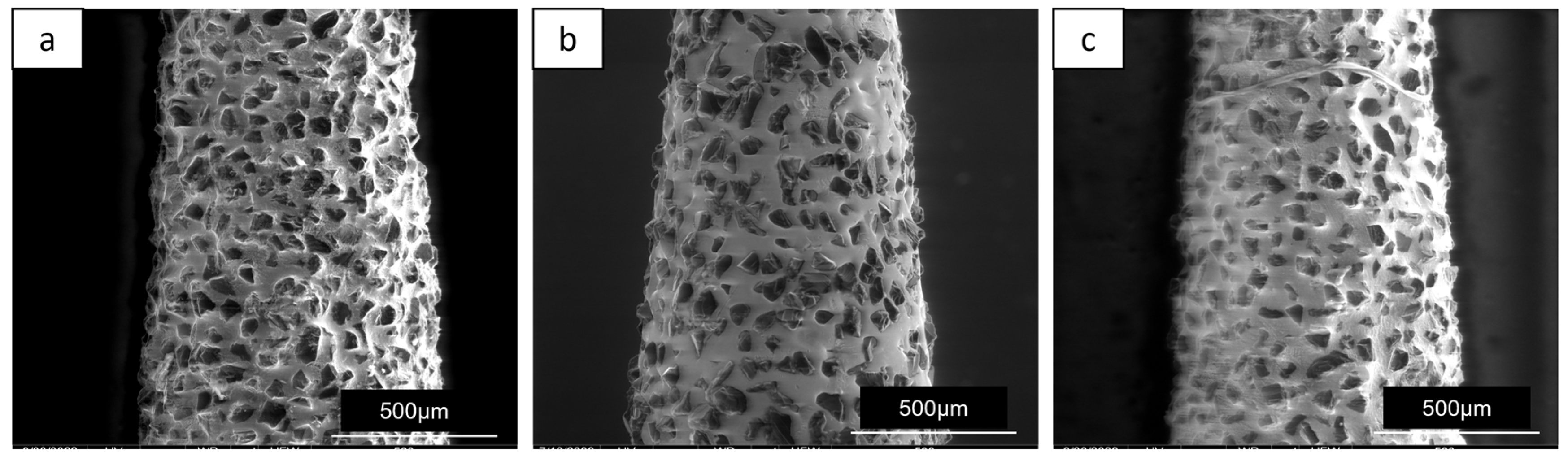
Figure 3). Piezoelectric tips appeared more worn than burs after the preparation of five samples. Burs used with high-speed electric handpiece appeared more consumed than burs used with the turbine (
Figure 4).
4. Discussion
A precise and smooth finishing line of tooth preparation facilitates the entire prosthetic workflow, from impression taking to the manufacturing of a restoration with a precise marginal fit, which could contribute to a long-term satisfactory esthetic and functional results. The present study aimed to investigate the surface roughness produced by different dental handpieces (turbine, high-speed electric contra-angle and piezoelectric handpiece) on enamel and dentin substrates when using diamond-coated working tips of the same grit size (60 μm). The analysis of surface roughness parameters, including mean roughness (Ra), skewness (Rsk), and kurtosis (Rku), along with qualitative analysis using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), provided insights into the performance and wear characteristics of the tested instruments.
In terms of surface roughness, the present results revealed variations between different handpieces and substrates. When analyzing enamel surface, no significant differences in Ra were observed among the three devices. However, turbine generated significantly higher Ra values on dentin if compared to both piezoelectric handpiece and high-speed electric handpiece. This finding is in accordance with a previous study demonstrating that rotary cutting instruments used with electric handpieces produced the smoothest surface, whereas the same instruments used with a turbine or sonic instruments achieved similar surface roughness [
20]. The differences in surface roughness between the sonic instruments investigated in this latter study and the piezoelectric device here tested may be explained by reduced amplitude (20-60 μm) and higher frequency (25-30 kHz) of ultrasonic vibrations in comparison with sonic oscillations [
21].
The skewness parameter (Rsk) reflects the symmetry of the surface profile relative to the midline. In the present study, Rsk values were significantly higher on enamel and dentin surfaces when using the turbine compared to high-speed electric handpiece and piezoelectric handpiece. This suggests that the turbine handpiece may produce more asymmetrical surface profiles with pronounced peaks and valleys on both substrates. Conversely, the three investigated handpieces used on both substrates did not show significant differences for the kurtosis parameter (Rku), measuring the sharpness of peaks and valleys on the surface.
Summarizing, the findings of the present study demonstrated that turbine generated rougher surfaces on dentin compared to the other handpieces. Moreover, the turbine produced more asymmetrical surface profiles on both enamel and dentin. However, it should be considered that these differences in roughness (Ra) were within the range of 0.25-0.30 μm: it is still unclear if these variations, although statistically significant, will affect final clinical outcomes.
SEM analysis indicated that piezoelectric inserts, after the preparation of 5 samples, showed greater wear in comparison with burs. Additionally, the bur used with the high-speed electric handpiece exhibited more wear than the bur used with the turbine. These findings suggest that the use of piezoelectric device and high-speed electric handpiece may result in higher working tip wear compared to the turbine handpiece. This aspect, together with the initial investment for the device which can be higher due to the advanced technology involved, should be also considered by the operator in a cost/benefit analysis when selecting the most appropriate tool in the clinical practice.
The present in vitro study presents some limitations as it did not consider some relevant factors influencing the operative choices in the clinical practice, such as the ease of control of the different handpieces or the risk of injury to marginal gingiva during margin finishing. The high-speed electric handpiece works at high rotational speeds (200,000 rpm) and is associated with a constant high torque. These high-torque values provide the clinician with greater tactile feedback in comparison with turbine, allowing for more controlled operative action [
22,
23]. On their part, piezoelectric devices exploit micrometric vibrations of the working tip and the absence of rotatory movements to enhance intra-operative control in comparison with rotary instruments [
24,
25]. Furthermore, the selective cut on hard tissues of piezoelectric instruments may reduce the risk of gingival lesions when refining the preparation margin in comparison with rotary instruments [
1,
26]. All these factors, together with the outcomes investigated in the present study, should be carefully considered and balanced by the clinician when choosing the most appropriate tool to finalize tooth preparation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.S. and A.R.; methodology, C.S..; software, G.T.; validation, F.B., A.T. and G.M.; formal analysis, G.T.; investigation, A.T.; resources, G.M. and R.D.L.; data curation, F.B.; writing—original draft preparation, A.R.; writing—review and editing, C.S.; visualization, G.M.; supervision, G.T. and R.D.L.; project administration, R.D.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This in vitro study was approved by Comitato Etico Unico Regionale (CEUR) Friuli Venezia Giulia - Italy (protocol code n◦ 194/2019 approved on 06/05/2019).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Complete dataset is available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
Authors wish to thank Mectron S.p.A. and Sweden & Martina S.p.A. for donating materials used for experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Vercellotti, T. Technological characteristics and clinical indications of piezoelectric bone surgery. Minerva Stomatol. 2004, 53, 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Cicciù M, Stacchi C, Fiorillo, L. , et al. Piezoelectric bone surgery for impacted lower third molar extraction compared with conventional rotary instruments: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2021, 50, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacchi C, Troiano G, Berton F, et al. Piezoelectric bone surgery for lateral sinus floor elevation compared with conventional rotary instruments: A systematic review, meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. Int J Oral Implantol (Berl). 2020, 13, 109–121. [Google Scholar]
- Waechter J, Leite FR, Nascimento GG, Carmo Filho LC, Faot, F. The split crest technique and dental implants: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017, 46, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stacchi C, Bassi F, Troiano G, et al. Piezoelectric bone surgery for implant site preparation compared with conventional drilling techniques: A systematic review, meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. Int J Oral Implantol (Berl). 2020, 13, 141–158. [Google Scholar]
- Lavu V, Arumugam C, Venkatesan N, Sk B, Valandhan Vedha, G. A present day approach to crown lengthening - Piezosurgery. Cureus. 2019, 11, e6241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal E, Fida M, Malik DS, Irfan, S. , Gul, M. Comparison between conventional and piezocision-assisted orthodontics in relieving anterior crowding: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Orthod. 2021, 43, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stübinger S, Kuttenberger J, Filippi A, Sader R, Zeilhofer HF. Intraoral piezosurgery: preliminary results of a new technique. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005, 63, 1283–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith A, Nurse A, Graham G, Lucas, M. Ultrasonic cutting. A fracture mechanics model. Ultrasonics. 1996, 34, 197–203. [Google Scholar]
- Otake Y, Nakamura M, Henmi A, Takahashi, T. , Sasano, Y. Experimental comparison of the performance of cutting bone and soft tissue between piezosurgery and conventional rotary instruments. Sci Rep. 2018, 8, 17154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercellotti T, Nevins ML, Kim DM, et al. Osseous response following resective therapy with piezosurgery. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2005, 25, 543–549. [Google Scholar]
- Horne P, Bennani V, Chandler, N. , Purton, D. Ultrasonic margin preparation for fixed prosthodontics: a pilot study. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2012, 24, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laufer BZ, Pilo, R. , Cardash HS. Surface roughness of tooth shoulder preparations created by rotary instrumentation, hand planing, and ultrasonic oscillation. J Prosthet Dent. 1996, 75, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke I, Aquilia A, Bertassoni LE, Guazzato, M. , Klineberg, I. Surface roughness of restoration margin preparations: a comparative analysis of finishing techniques. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2015, 35, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldi D, Menini M, Colombo J, Lertora, E. , Pera, P. Evaluation of a New Ultrasonic Insert for Prosthodontic Preparation. Int J Prosthodont. 2017, 30, 496–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naumova EA, Schiml F, Arnold WH, Piwowarczyk, A. Marginal quality of ceramic inlays after three different instrumental cavity preparation methods of the proximal boxes. Clin Oral Investig. 2019, 23, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claire S, Lea SC, Walmsley AD. Characterisation of bone following ultrasonic cutting. Clin Oral Investig. 2013, 17, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funkenbusch PD, Rotella M, Chochlidakis K, Ercoli, C. Multivariate evaluation of the cutting performance of rotary instruments with electric and air-turbine handpieces. J Prosthet Dent. 2016, 116, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emir F, Ayyildiz S, Sahin, C. What is the changing frequency of diamond burs? J Adv Prosthodont. 2018, 10, 93–100. [CrossRef]
- Geminiani A, Abdel-Azim T, Ercoli C, Feng C, Meirelles L, Massironi, D. Influence of oscillating and rotary cutting instruments with electric and turbine handpieces on tooth preparation surfaces. J Prosthet Dent. 2014, 112, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 21. Stübinger S, Stricker A, Berg BI. Piezosurgery in implant dentistry. Clin Cosmet Investig Dent. 2015; 7, 115–124. [CrossRef]
- Kenyon BJ, Van Zyl, I. , Louie KG. Comparison of cavity preparation quality using an electric motor handpiece and an air turbine dental handpiece. J Am Dent Assoc. 2005, 136, 1101–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, SC. Are friends electric?: A review of the electric handpiece in clinical dental practice. Dent Update. 2013, 40, 194–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stacchi C, Berton F, Turco G, et al. Micromorphometric analysis of bone blocks harvested with eight different ultrasonic and sonic devices for osseous surgery. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2016, 44, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi F, Cicciù M, Di Lenarda, R. , et al. Piezoelectric bone surgery compared with conventional rotary instruments in oral surgery and implantology: Summary and consensus statements of the International Piezoelectric Surgery Academy Consensus Conference 2019. Int J Oral Implantol (Berl). 2020, 13, 235–239. [Google Scholar]
- Schaeren S, Jaquiéry C, Heberer M, Tolnay M, Vercellotti, T. , Martin, I. Assessment of nerve damage using a novel ultrasonic device for bone cutting. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008, 66, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).