Introduction
SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)-induced respiratory failure is the leading cause of COVID-19 mortality. [
1] Fibrin accumulation within the alveolar spaces appears to be a major pathophysiological driver of severe lung disease. Increased tissue factor expression and suppression of fibrinolysis due to a rise in plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) activity, within the alveolar space and systemically, may contribute to the pathophysiologic changes. [
2,
3]
Clot dissolution with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rt-PA) and other fibrinolytic drugs is widely used for thrombotic cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events and the strategy studied in pulmonary thrombotic diseases. [
4] In pre-clinical acute lung injury models, increased clearance of fibrin from the alveolar space, improved oxygenation, reduced lung inflammation, and improved survival was reported [
5,
6], these effects were replicated in varying degrees in clinical studies ranging from case reports in COVID-19-induced respiratory failure to small clinical trials in patients with and without COVID-19. [
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12]
Several therapeutic advances to treat patients hospitalized with COVID-19-induced respiratory failure have emerged with a primary focus on the reduction of the viral burden and suppression of immune dysregulation and inflammation. [
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18] However, COVID-19-induced respiratory failure mortality remains high at 25–60%, [
19] which emphasizes the urgent need for additional therapeutic modalities to facilitate a multipronged attack.
This proof-of-concept pilot study aimed to test the safety of nebulized rt-PA and investigate clinical efficacy in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 respiratory failure that required respiratory support.
Materials and Methods
Study design and participants
The study was titled ‘A Pilot, Open Label, Phase II Clinical Trial of Nebulized Recombinant Tissue-Plasminogen Activator (rt-PA)’ (clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT04356833) and was approved by the National Research Ethics Committee (REC) and Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency. Health Research Authority (HRL) approval was granted on 17th April 2020 (REC reference: 20/SC/0187). Procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use Good Clinical Practice (ICH GCP) guidelines and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975.
Written informed consent was obtained from conscious patients. When a patient could not give written informed consent due to intubation and sedation, the study was discussed with the patient’s next of kin, and consent was obtained from an independent professional representative, typically another consultant in intensive care not involved in the direct care of the patient or involved in the study. Patients consented at the first opportunity after regaining consciousness and consent could be withdrawn at any time. Supplementary Methods contains the informed consent procedure.
Recruitment for Cohort one (C1) occurred from 23rd April to 30th July 2020, during the first COVID-19 surge. Sequential recruitment to the standard of care (SOC) arm alone was challenging and a protocol amendment allowed for the recruitment of matched historical controls (MHC) retrospectively for comparison with C1 on 15th October 2020. Recruitment for Cohort two (C2) occurred between 21st January and 19th February 2021 and all patients were assigned to receive rt-PA with SOC. It is to be noted that SOC itself continued to rapidly evolve through the pandemic with the incorporation of new therapies becoming part of SOC, and our comparison between groups reflects SOC of the time in all study groups (C1, MHC and C2).
Further recruitment details are provided in the Supplementary Methods. After enrolment or the first dose of nebulized rt-PA, patients were followed until the end of the study (EOS). EOS was day 28 or earlier in the event of death or discharge. Day one for MHC was when patients met the inclusion criteria.
Inclusion criteria in the treatment arm for both cohorts included COVID-19 diagnosis (confirmed by
polymerase chain reaction [PCR] or radiologically [C1, n=0; C2, n/N=3/26]); ≥16 years of age; and severe acute COVID-19 respiratory failure determined by a PaO
2/FiO
2 [P/F] ratio of <300 mmHg [
20]) that required respiratory support (including invasive mechanical ventilation). For consistency and allowing for a relatively small recruitment number to be expected (given the competition with many other studies) and perceived much poorer outcomes from IMV, the respiratory support was stratified into two groups only, the invasive mechanical ventilation via an endotracheal tube (IMV) and non-invasive respiratory support (NIRS) for all other forms of respiratory support such as non-invasive ventilation (NIV), continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), high flow nasal oxygen (HFNO) or conventional oxygen therapy (venturi and non-breathing masks).
In IMV patients, P/F ratio was calculated with the arterial partial pressure of oxygen (PaO
2, P) and fraction of inspired oxygen therapy (FiO
2, F) (Table S1) [
21]. In NIRS patients, arterial blood gas analysis was often not performed, and PaO
2 was imputed by non-linear calculation from oxygen saturation on pulse oximetry (SpO
2), with FiO
2 calculated from tables based on oxygen flow and device used (Table S2).
The main exclusion criteria for both cohorts were pregnancy, known allergies to rt-PA or excipients of rt-PA, patients not being actively treated or not considered suitable by the investigator, and fibrinogen levels of ≤2.0 g/L or <1.5 g/L in C1 and C2 at screening, respectively. The use of concomitant anticoagulation or antiplatelet therapy was permitted. The Supplementary Methods provide additional exclusion criteria for C1.
Study drug and dosing
Alteplase, rt-PA (Actilyse®, Boehringer Ingelheim) was reconstituted with 5 mL sterile water (2 mg/mL) and administered using an Aerogen® nebulizer. Supplementary Methods provide details of rt-PA administration.
The initial dosing regimen in C1 was 10 mg every 6 hours for 72 hours. Recruitment was staggered to ensure patient safety and details are provided in the Supplementary Methods. Dosing was amended after observing significant desaturation in patient three, 36 hours after the last dose of the initial three-day block of rt-PA was administered. An urgent safety measure was implemented to allow re-treatment of this patient with a second three-day block of rt-PA. This resulted in a protocol amendment to allow dosing to take place for a minimum of five days, and a maximum of 14 days. The rationale was underpinned by the fact that clot burden has an impact on the duration of lysis, and importantly, the final enzyme responsible for clot lysis is plasmin generated from plasminogen when activated by rt-tPA. This resulted in a move from a fixed treatment regimen to an endpoint-driven treatment regimen; treatment was discontinued if blood fibrinogen levels fell to <1.5 g/L (potential toxicity due to systemic absorption) or patients no longer required oxygen (resolution of the interalveolar clot burden). Treatment could be restarted within five days from the last dose of treatment if there was a recurrence of COVID-19-induced respiratory symptoms or a worsening of P/F ratio considered related to treatment discontinuation.
Details of the C2 treatment regimen
C2 on IMV received 20 mg rt-PA every eight hours (60 mg daily) for a maximum of 14 treatment days. For patients receiving NIRS, a loading dose of 20 mg every eight hours was administered for the first two days (60 mg daily) followed by 20 mg every 12 hours (twice daily; 40 mg total) for a total of 14 days. Patients on IMV were given a higher dose to account for wastage in the circuit. If patients deteriorated and required IMV, they were allowed to receive a higher treatment dose. Treatment was discontinued if blood fibrinogen levels fell to <1.0 g/L or if the patient maintained normal SpO2 on room air for 48 hours.
Study endpoints
Primary endpoints to assess safety included the incidence and severity of major bleeding events related to rt-PA, a decrease in fibrinogen levels to ≤1.5 g/L or <1.0 g/L during the treatment period and 48 hours after the last dose of treatment for C1 and C2 respectively, and the number and nature of serious adverse events (SAEs) related to rt-PA. The fibrinogen levels were lower in C2, as there was no evidence of systemic absorption in C1 and the levels in C2 are thresholds associated with a potentially increased risk of bleeding tendency. All bleeding events were categorized as adverse events (AE) of special interest and evaluated for severity (mild, moderate, and severe) and casualty; the International Society of Haemostasis and Thrombosis (ISTH) Scientific and Standardisation Committee definition of major bleeding events in patients on anti-hemostatic medications was used to grade severity (Table S3). [
22] A bleeding event was evaluated for relatedness if it occurred within 30 hours of the last rt-PA dose.
The secondary endpoint of efficacy was determined as the change in P/F ratio from baseline (BL) which was assessed daily during treatment, at treatment cessation, and three- and five-days post-treatment cessation. Other secondary endpoints included changes in clinical status assessed by a 7-point World Health Organisation (WHO) ordinal scale until EOS (Table S4), the outcome (discharge, in-patient or death) at EOS, changes in lung compliance (defined as tidal volume/peak inspiratory pressure from BL and absolute values), Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) during treatment and through five days after the end of treatment, number of oxygen, ventilator and intensive free care days at EOS, and the number of new oxygen or ventilation requirements before EOS.
Biomarkers of fibrinolysis
Blood samples were taken for exploratory assessment of potential biomarkers including, but not restricted to, plasminogen, alpha-2 antiplasmin (α2AP), tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA), PAI-1, and a range of inflammatory cytokines and coagulation proteins. All other monitoring was done as per routine SOC.
Statistical analysis
Since the study was conducted early in the pandemic, the planned recruitment numbers were based on feasibility and planned recruitment rate instead of statistical considerations. An Independent Data Monitoring Committee was established to provide oversight on the conduct of the study, particularly in relation to the causality of bleeding events, and dose escalation strategy and provide recommendations on the continuation of the study.
Descriptive statistics were used to describe all AEs including bleeding events of special interest. In C1, the efficacy analysis was a comparison of P/F ratios between the rt-PA group and MHC at the EOS, adjusting for the BL P/F ratio, using a linear regression model. A sensitivity analysis was performed, fitting a similar model that controlled for the length of follow-up, as well as the BL P/F ratio. In a further sensitivity analysis, a mixed effects linear regression model was used to compare groups over time and account for the clustering of ratios within patients using a random effect. The model incorporated all P/F ratio measurements over time, with treatment allocation, time, and BL P/F ratio as fixed effects, together with a random slope for time and a random effect at the patient level.
Analysis of C1 and C2 was undertaken separately. C2 analysis was limited to descriptive statistics. Continuous variables are summarized using a number of observations, mean, standard deviation (SD), median, interquartile range (IQR), and minimum and maximum values. Categorical data were summarized using a number of observations and percentages. Further exploratory and post hoc analyses were conducted, and details of all statistical analyses are provided in Supplementary Methods.
Results
In total, 27 patients enrolled in cohort 1 (Figure S2a); nine patients received nebulized rt-PA with SOC and 18 patients were recruited as MHC receiving SOC only. In the rt-PA group, six (66.6%) patients received IMV, and three (33.3%) patients received NIRS, none of whom progressed to IMV. Patient characteristics of C1 are shown in
Table 1.
Seven bleeding events occurred in four of the nine patients during rt-PA treatment (
Table 2 and S6). These events were reported as AE of special interest and categorized as five mild and two moderate; all resolved completely. All bleeds and AEs were deemed unrelated to rt-PA. The MHC group were not reviewed for bleeding events. In addition, there were no measured decreases in plasma fibrinogen levels (<1.5 g/L) during the treatment period and 48 hours after the last dose of rt-PA.
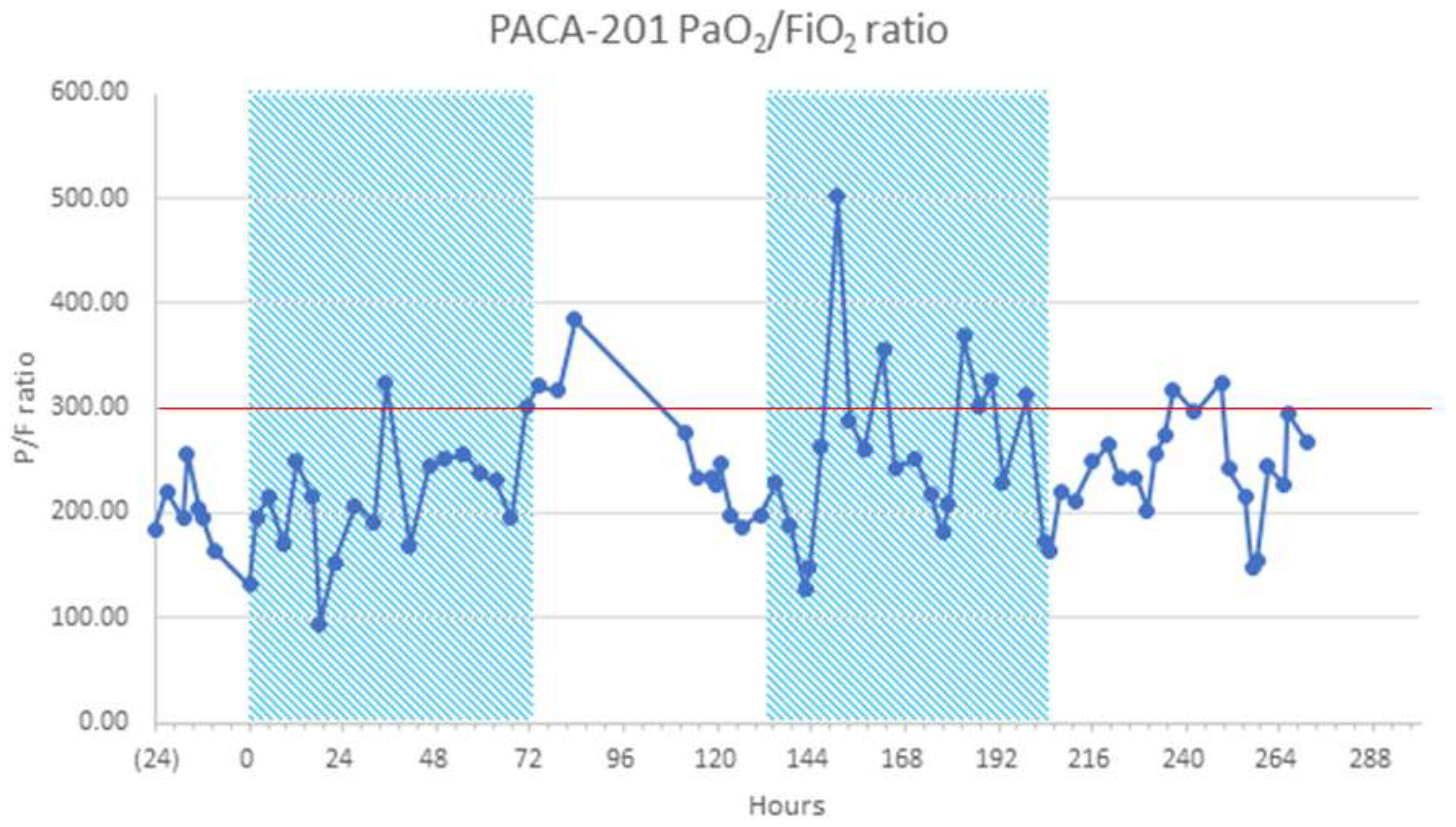
The P/F ratio improved during the 28-day study period in the rt-PA and MHC groups (
Table 3). One patient that improved to a P/F ratio >400 on oxygen supplementation by nasal cannula deteriorated 24 to 36 hours after the 12
th and final dose of rt-PA (
Figure 1). This patient was not a candidate for IMV because of previous bronchiectasis; instead, they were treated twice with rt-PA. This observation prompted a change in the dosing schedule for the remaining three patients in C1.
A sensitivity analysis using a linear mixed effects model, showed a higher mean P/F ratio in the rt-PA group compared to the MHC group, with an estimated mean difference of 50.6 (95% confidence interval [CI], 6.7–94.4).
Among the rt-PA group, at the EOS, three (33.3%) patients were discharged before Day 28, five (55.6%) remained as in-patients, and one patient (11.1%) had died. In the MHC group, six (33.3%) patients had been discharged before Day 28, two (11.1%) were in-patients, and ten (55.6%) had died. Patients in the rt-PA group (n=9) received treatment for a mean (SD) duration of 6.7 (4.6) days (
Table 4 and S5).
26 patients were enrolled on the second cohort, and all received rt-PA (Figure S2b). At the time of screening, 12 (46.2%) were receiving IMV and 14 (53.9%) were receiving NIRS, of the latter, four required IMV for variable periods. Additional patient characteristics for C2 are shown in
Table 1.
Among the 26 patients, there were 25 bleeding events (
Table 2 and S6); 17 were in the IMV group, and eight were in the NIRS group. These events were reported as AE of special interest and categorized as 18 mild, five moderate, and two severe. Of these, four bleeding events in three patients were considered possibly related to rt-PA treatment, with one being categorized as a severe AE and the other three as mild (
Table 2). No patients experienced fibrinogen levels below 1.0 g/L at any time during the study. One patient had a fibrinogen value of 1.0 g/L two and three days after the initiation of rt-PA treatment which prompted holding a dose of rt-PA.
In the IMV group, the mean (SD) P/F ratio was 120 (28) the day before the first dose of rt-PA, and a small increase was seen for most patients by their last day of treatment, with a mean increase from BL (SD) of 48 (126) (
Table 2 and Figure S4). In patients receiving NIRS, the mean (SD) P/F ratio was 126 (42) the day before the first dose of rt-PA, and an increase was seen for most patients by their last day of treatment, with a mean change (SD) of 114 (92).
The EOS outcomes (28d) for patients on IMV and NIRS, respectively, were as follows: 33.3% and 14.3% remained as inpatients, 25% and 64.3% had been discharged, and 41.7% and 21.4% died. The total mean (SD) treatment duration for C1 (n=26) was 9.1 (4.6) days. Patients receiving IMV (n=12) and NIRS (n=14) received rt-PA for a mean (SD) of 10.5 (4.2) and 7.9 (4.6) days, respectively (
Table 4 and Table S5).
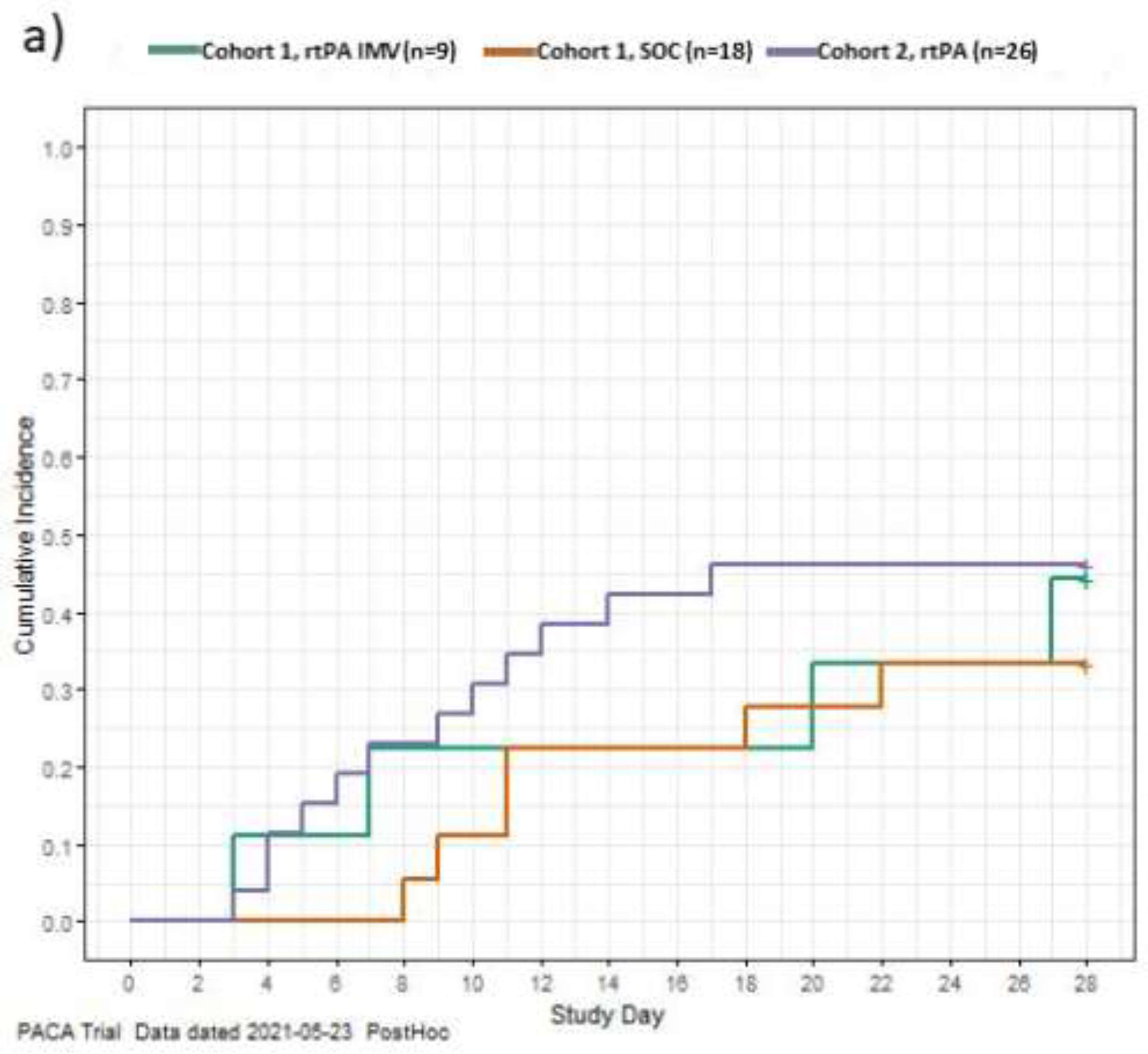
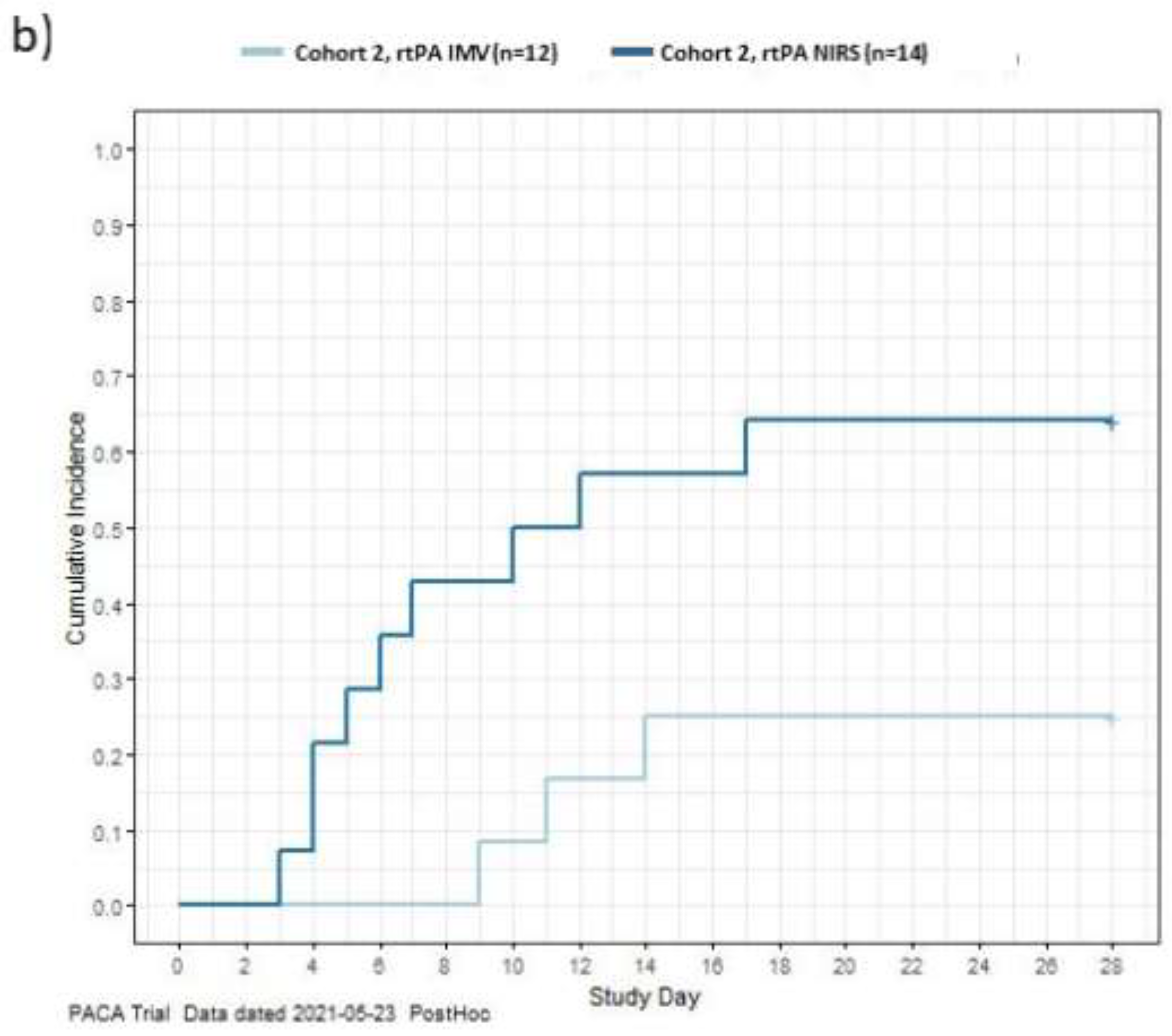
7-point World Health Organization (WHO) scale
To explore the treatment effect, a post hoc exploration was conducted of the data to describe the time to recovery from COVID-19 for each patient in the study using the WHO’s minimal common outcome measure set for COVID-19, recovery was defined as achieving an absolute WHO ordinal score of 1 or 2, or discharge [
23]. Data for patients who did not recover or died were censored on Day 28. The exploration of the data aligns with published literature. [
17] The cumulative incidences of recovery during the 28-day study period are shown in
Figure 2. In C1, patients receiving rt-PA had a more rapid recovery compared to MHC patients. In C2, NIRS patients recovered more rapidly than IMV patients. This is likely due to patients on NIRS receiving lower initial WHO scores so less recovery was required to achieve a score of 1 or 2 compared to patients on IMV who received higher initial WHO scores (Table S4;
Figure 2).
Assessment of fibrinolysis biomarkers
The activity of plasminogen, α2AP, PAI-1 antigen (Ag), t-PA Ag, and t-PA/PAI complex during rt-PA treatment is presented in the Supplemental Results Figure S5). There were no significant changes or obvious patterns induced by rt-PA treatment.
Discussion
This proof-of-concept study is the first clinical trial investigating the use of nebulized rt-PA in patients with COVID-19-induced respiratory failure. Previous reports were limited to a case report on COVID respiratory failure and a small trial in a non-COVID population. Alteplase demonstrated a favourable safety profile and was associated with an improvement in the P/F ratio among patients with a range of respiratory dysfunction severity. Importantly, the study established a dosing regimen of nebulized rt-PA that was feasible and safe and resulted in a favourable clinical response.
For EOS clinical outcomes, in C1, only one patient (11.0%) receiving rt-PA died during the 28-day study period compared to ten (55.6%) in the MHC group. In C2, five (41.7%) and three (21.4%) patients receiving IMV and NIRS, respectively, died during the study period. While these findings and an improvement in P/F ratio were found in the C1 cohort compared to MHC, given the small sample size, they should be viewed as hypothesis-generating and proof-of-concept to support the rationale for a larger, randomized trial.
Alteplase requires plasminogen for its mechanism of action, and therefore significant bleeding is unlikely due to the low availability of plasminogen. Indeed, the administration of nebulized rt-PA did not appear to induce an increase in systemic markers of fibrinolysis. No patients experienced pulmonary hemorrhage or had clinically significant decreases in systemic fibrinogen, only a few bleeding events were attributable to rt-PA and no SAEs of special interest were attributable to rt-PA. In all patients with significant bleeding considered related to rt-PA, concurrent therapeutic anticoagulation with low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) was in use, which might have contributed to the risk of bleeding. Furthermore, the safety of nebulized rt-PA has been demonstrated in patients with plastic bronchitis, with a range of doses and durations that did not result in bleeding complications. [
24] The use of clinical response for early termination of treatment and an upper limit for treatment duration improves the safety profile. Moreover, our post-hoc, exploratory analyses of key fibrinolysis pathway inhibitors revealed that rt-PA treatment did not result in increased systemic fibrinolysis, suggesting minimal absorption, potentially contributing to the favourable safety profile.
Given that this study was conducted in unprecedented times during the COVID-19 pandemic, there are several limitations to this study that may have been prevented if the study was conducted in less unpredictable circumstances. The nature of the study population meant that a change in a patient’s condition could result in an alteration in ventilation type post-enrolment. Although all patients had a P/F ratio of <300 at enrolment, P/F ratio for NIRS and IMV was calculated by different methods: for those receiving NIRS, P/F ratio was determined by converting SpO
2 and oxygen flow rate and using imputed values [
21,
25], whereas P/F ratio was readily available for those receiving IMV. Further, the NIRS group was heterogeneous to the device used to improve oxygen concentration. The use of MHC for comparison in C1 is a limitation as patients who consented to participate in trials may differ, with the potential for selection bias; this has been reviewed extensively. [
26] Furthermore, the retrospective nature of the matching makes the efficacy comparison between the two groups exploratory, and one of the major aims of this study was to generate adequate data for a sample size calculation for a future study. Additionally, there were differences in the patients enrolled in the C1 and C2 cohorts, with a higher number of bacterial co-infections in C2 patients, most of whom received steroids and interleukin-6 inhibitors. Both cohorts received the SOC at the time of the study which was rapidly evolving, as demonstrated by the differences in concomitant treatments (
Table 4). Moreover, the duration of illness before enrolment was shorter in C2 which could have impacted the duration of respiratory support. Reactive protocol amendments were required to incorporate learnings associated with the novel administration route.
Direct administration of drugs into the airways is challenging, particularly in breathless patients despite the perceived advantages. Dosing of inhaled drugs needs to account for the loss in the ventilation circuit, ambient aerosolization and varying disease severity, and conventional drugs tend to have wide therapeutic windows. Protein-based therapeutics typically have narrow therapeutic windows and importantly tend to be expensive. Whilst the delivery of rt-PA with an Aerogen nebulizer has been investigated extensively [
27], delivery in NIRS patients was challenging. Furthermore, the assessment of bleeding was complicated by concurrent anticoagulant therapy, whilst this was not a confounder for assessing efficacy, it is an important contributor to the determination of the safety of rt-PA. Indeed, the challenges of the assessment of efficacy and bleeding secondary to anticoagulation in COVID-19 have been extensively reviewed [
28,
29].
Despite these limitations, this study serves as a proof-of-concept that nebulized rt-PA delivery to the airways is safe, even in patients receiving therapeutic anticoagulation with LMWH. However, the magnitude of clinical impact in relation to the duration of oxygen support, duration of ventilation and need for invasive ventilation needs further assessment.
Conclusions
In this proof-of-concept study, nebulized rt-PA demonstrated favourable safety with no excess bleeding in patients hospitalized with COVID-19-induced respiratory failure. The results should be utilized as a first step towards more extended research in the field and will provide valuable scientific knowledge and direction to optimize the design of future studies.
Author Contributions
Each author has made a substantial contribution to the conception OR design of the work; OR the acquisition, analysis, OR interpretation of data; OR the creation of new software used in the work; OR has drafted the work or substantially revised it; AND has approved the submitted version; AND has agreed both to be personally accountable for the author’s contributions and to ensure that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work, even ones in which the author was not personally involved, are appropriately investigated, resolved, and the resolution documented in the literature.
Funding
Royal Free Charity Trust Fund 35 provided funding for the study. The study drug was provided by Boehringer Ingelheim (BI). BI had no role in the design, analysis, or interpretation of the results. They were given the opportunity however to review the manuscript for medical and scientific accuracy since it relates to BI substances and intellectual property considerations.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
This study was approved by the national research ethics committee and Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency and performed in accordance with good clinical practice. Adult consent to participate.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable
Availability of Data and Materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files. Anonymous, individual participant data that underline the results reported in this article will be made available to others, along with the study protocol, statistical analysis plans and information sheets at publication, with no end date. The data will be made available on application to the corresponding author, with permissions from Chief Investigator and study sponsor (p.chowdary@ucl.ac.uk; a.j.evans@ucl.ac.uk). Applications for data sharing will need to explain what the data will be used for. If the application is approved by the authors, the data will be shared. Data request proposals should be directed to the CI, p.chowdary@ucl.ac.uk. To gain access, data requestors will need to sign a data-sharing agreement. The following abstract has previously been Published: A pilot, open-label, phase II clinical trial of nebulized recombinant tissue-plasminogen activator in patients with COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome: the PACA trial. Presented at the British Society for Haemostasis and Thrombosis conference. Aberdeen, United Kingdom. 2022. Abstract OC-15.
Competing Interests
PC has served on advisory boards for Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, CSL Behring, Chugai, Freeline, NovoNordisk, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, Spark, Sobi and Takeda; and has received research funding from Bayer, CSL Behring, Freeline, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, SOBI and Takeda. HP is a founder and director of LUNAC Therapeutics, which is currently developing a novel anticoagulant. KAS reports research funding from the US Food and Drug Administration (R01 FD005393) that provides support for a clinical trial of inhaled t-PA in children with acute plastic bronchitis and the US National Institutes of Health (R35 GM136312); she also serves as a paid consultant for FHI Clinical. SS has served on an advisory board for Ambu A/S. AB is the founder of Amore Health Ltd and receives an honorarium from Daiichi Sankyo, Pfizer, BMS, Bayer, Novartis, Roche, Napp, Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly, Astra Zeneca, Novartis, and Amgen for lecturing and scientific advice. All other authors have no relevant disclosures.
Acknowledgements
PC takes responsibility for the content of the manuscript, including the data analysis, and manuscript preparation. PC, BA, KG, JF, RA, NM, and HP conceived this study. PC, BA, MW, KS, ML, SB, EW and KG commented on the paper, oversaw the analysis and edited the final manuscript. PC, BA, MW, EW and KG led the writing of the paper, with editorial support from Eleanor Broadberry from Meridian HealthComms, in compliance with good publishing practice (GPP3) guidelines. MW, EW, and FR accessed and verified the underlying data and were responsible for data cleaning and analysis. All authors contributed to drafting the paper and revised the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors gave final approval of the version to be published. All authors had full access to summary data reported in this study. We would like to extend our sincerest gratitude to all the colleagues and hospital staff who worked tirelessly throughout the pandemic and without whom, this work would not have been possible. Firstly, we would like to thank our colleagues in the intensive care unit (ICU), in particular the matrons, Sean Carroll and Sinead Hanton, and research nurses, Filipe Helder and Amitaa Maharajh for their support, and bedside nurses who bore the responsibility of drug administration. We would also like to extend our thanks to ICU consultants who acted as professional legal consultees on behalf of critical care patients. Equally, we would like to thank colleagues within the respiratory team. Their expertise was instrumental to our role in treating patients on 8N and 8E wards. A special mention to lead Nurse Mary Emerson; we were grateful for her knowledge, support and for facilitating the training for the nebulizer and drug administration on the wards. We would like to thank Aarti Nandani and all the staff in the Royal Free clinical trials pharmacy for their immense support throughout the whole pandemic, especially considering their ever-increasing workload at the time. Thanks also to the HSL coagulation laboratory, the Trust R&D department and all the staff working to cover during a very challenging time. We are also very grateful to the Royal Free charity for funding the study. Finally, we would like to thank all the clinical nurses, physiotherapists, research data managers and healthcare professionals within the Haemophilia department (and wider hospital) for all their many efforts in supporting this study. This trial was overseen by an independent data monitoring committee, chaired by Professor Najib Rahman, Director of the Oxford Respiratory Trials Unit, University of Oxford and comprises the following committee members; Professor Mike Makris, Dr Jonathan Silversides, and Professor Henry Watson.
References
- Ruan Q, Yang K, Wang W, Jiang L, Song J. Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China. Intensive Care Med 2020, 46, 846–848. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idell S, James KK, Coalson JJ. Fibrinolytic activity in bronchoalveolar lavage of baboons with diffuse alveolar damage: trends in two forms of lung injury. Critical care medicine 1992, 20, 1431–1440. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whyte CS, Morrow GB, Mitchell JL, Chowdary P, Mutch NJ. Fibrinolytic abnormalities in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and versatility of thrombolytic drugs to treat COVID-19. Journal of thrombosis and haemostasis : JTH 2020, 18, 1548–1555. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagstaff AJ, Gillis JC, Goa KL. Alteplase. Drugs 1995, 50, 289–316.
- Hofstra JJ, Cornet AD, Declerck PJ, et al. Nebulized fibrinolytic agents improve pulmonary fibrinolysis but not inflammation in rat models of direct and indirect acute lung injury. PloS one 2013, 8, e55262. [CrossRef]
- Camprubí-Rimblas M, Tantinyà N, Bringué J, Guillamat-Prats R, Artigas A. Anticoagulant therapy in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Ann Transl Med 2018, 6, 36. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelaal Ahmed Mahmoud A, Mahmoud HE, Mahran MA, Khaled M. Streptokinase Versus Unfractionated Heparin Nebulization in Patients With Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS): A Randomized Controlled Trial With Observational Controls. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 2020, 34, 436–443. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardaway RM, Harke H, Tyroch AH, Williams CH, Vazquez Y, Krause GF. Treatment of severe acute respiratory distress syndrome: a final report on a phase I study. Am Surg 2001, 67, 377–382. [CrossRef]
- Barrett CD, Moore HB, Moore EE, et al. Fibrinolytic therapy for refractory COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome: Scientific rationale and review. Res Pract Thromb Haemost 2020, 4, 524–531. [CrossRef]
- Gram J, Münster AM, Dilling-Hansen B, Al Lavassani H, Lahoz AX, Jespersen J. Inhalation/intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator and inhaled heparin in a patient with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Fibrinolysis and Proteolysis 1999, 13, 209–212. [CrossRef]
- Barrett CD, Moore HB, Moore EE, et al. Study of Alteplase for Respiratory Failure in SARS-CoV-2 COVID-19: A Vanguard Multicenter, Rapidly Adaptive, Pragmatic, Randomized Controlled Trial. Chest 2021.
- Barrett CD, Oren-Grinberg A, Chao E, et al. Rescue therapy for severe COVID-19-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome with tissue plasminogen activator: A case series. The journal of trauma and acute care surgery 2020, 89, 453–457. [CrossRef]
- Kalil AC, Patterson TF, Mehta AK, et al. Baricitinib plus Remdesivir for Hospitalized Adults with Covid-19. N Engl J Med 2021, 384, 795–807. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertaina M, Nunez-Gil IJ, Franchin L, et al. Non-invasive ventilation for SARS-CoV-2 acute respiratory failure: a subanalysis from the HOPE COVID-19 registry. Emerg Med J 2021, 38, 359–365. [CrossRef]
- 15. Lawler PR, Goligher EC, Berger JS, et al. Therapeutic Anticoagulation with Heparin in Noncritically Ill Patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med 2021, 385, 790–802. [CrossRef]
- Horby P, Lim WS, Emberson JR, et al. Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med 2021, 384, 693–704. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beigel JH, Tomashek KM, Dodd LE, et al. Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19 - Final Report. N Engl J Med 2020, 383, 1813–1826. [CrossRef]
- Gupta A, Gonzalez-Rojas Y, Juarez E, et al. Early Treatment for Covid-19 with SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody Sotrovimab. N Engl J Med 2021, 385, 1941–1950. [CrossRef]
- Aranda-Valderrama P, Kaynar AM. The basic science and molecular mechanisms of lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. International anesthesiology clinics 2018, 56, 1–25. [CrossRef]
- Ranieri VM, Rubenfeld GD, Thompson BT, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin Definition. Jama 2012, 307, 2526–2533.
- Brown SM, Duggal A, Hou PC, et al. Nonlinear Imputation of PaO2/FIO2 From SpO2/FIO2 Among Mechanically Ventilated Patients in the ICU: A Prospective, Observational Study. Crit Care Med 2017, 45, 1317–1324. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulman S, Kearon C. Definition of major bleeding in clinical investigations of anti hemostatic medicinal products in non-surgical patients. Journal of thrombosis and haemostasis : JTH 2005, 3, 692–694. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A minimal common outcome measure set for COVID-19 clinical research. Lancet Infect Dis 2020, 20, e192–e197. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colaneri M, Quarti A, Pozzi M, Gasparini S, Carloni I, de Benedictis FM. Management of plastic bronchitis with nebulized tissue plasminogen activator: another brick in the wall. Ital J Pediatr 2014, 40, 18. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown SM GC, Moss M, Rice TW, Schoenfeld D, Hou PC, et al. . Nonlinear Imputation of PaO2/FIO2 From SpO2/FIO2 Among Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Chest 2016, 150, 307–313. [CrossRef]
- Arabi YM, Cook DJ, Zhou Q, et al. Characteristics and Outcomes of Eligible Nonenrolled Patients in a Mechanical Ventilation Trial of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine 2015, 192, 1306–1313. [CrossRef]
- Dunn JS, Nayar R, Campos J, et al. Feasibility of tissue plasminogen activator formulated for pulmonary delivery. Pharm Res 2005, 22, 1700–1707. [CrossRef]
- Connors JM, Moll M, Levy JH. Interpreting recent clinical studies for COVID-19: A continual process with more new data. Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med 2021, 101016.
- Chowdary, P. COVID-19 coagulopathy - what should we treat? Exp Physiol 2022, 107, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).