Submitted:
15 June 2023
Posted:
19 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract

Keywords:
Introduction
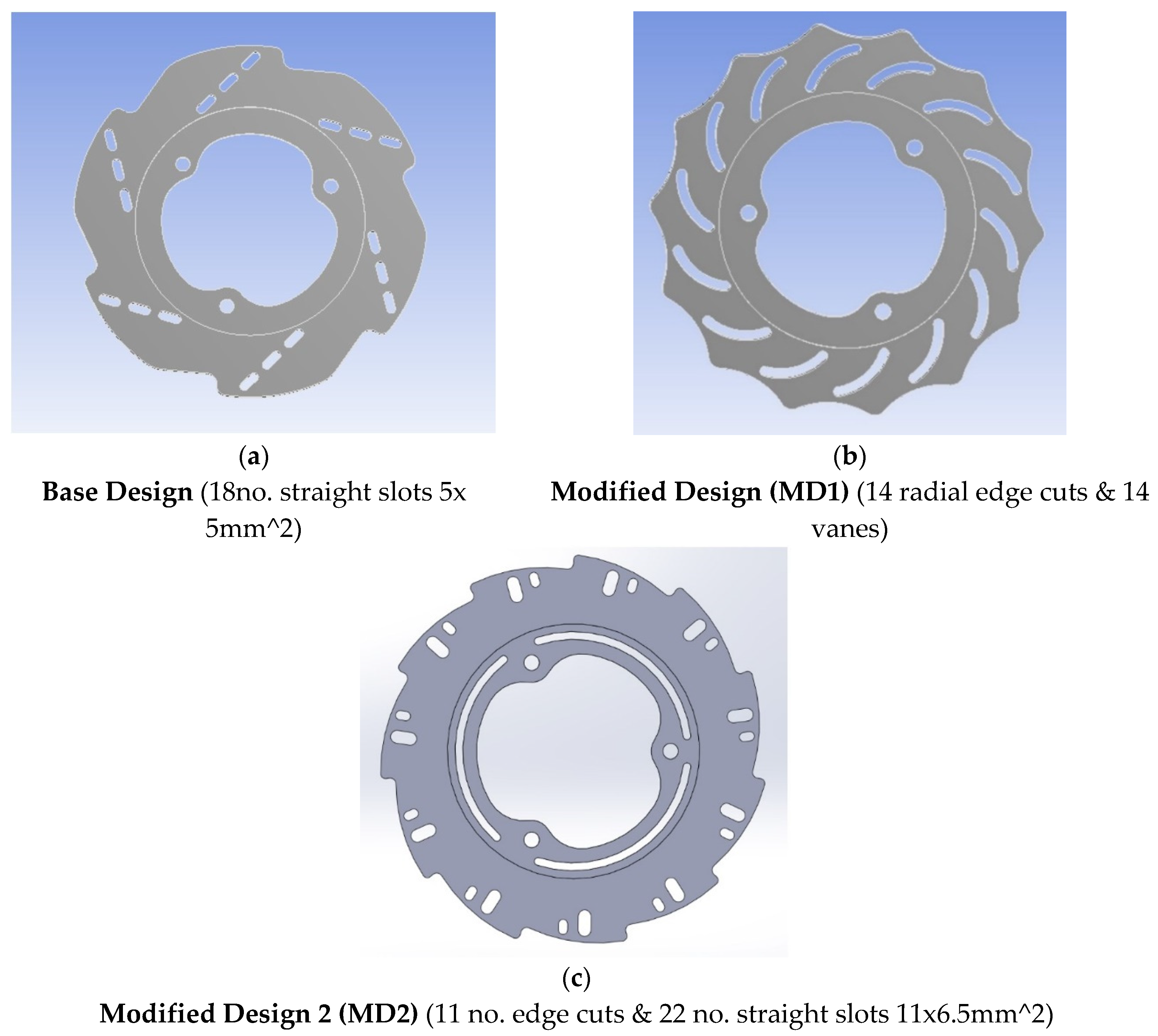
Model of disk brake rotor
Finite element modelling
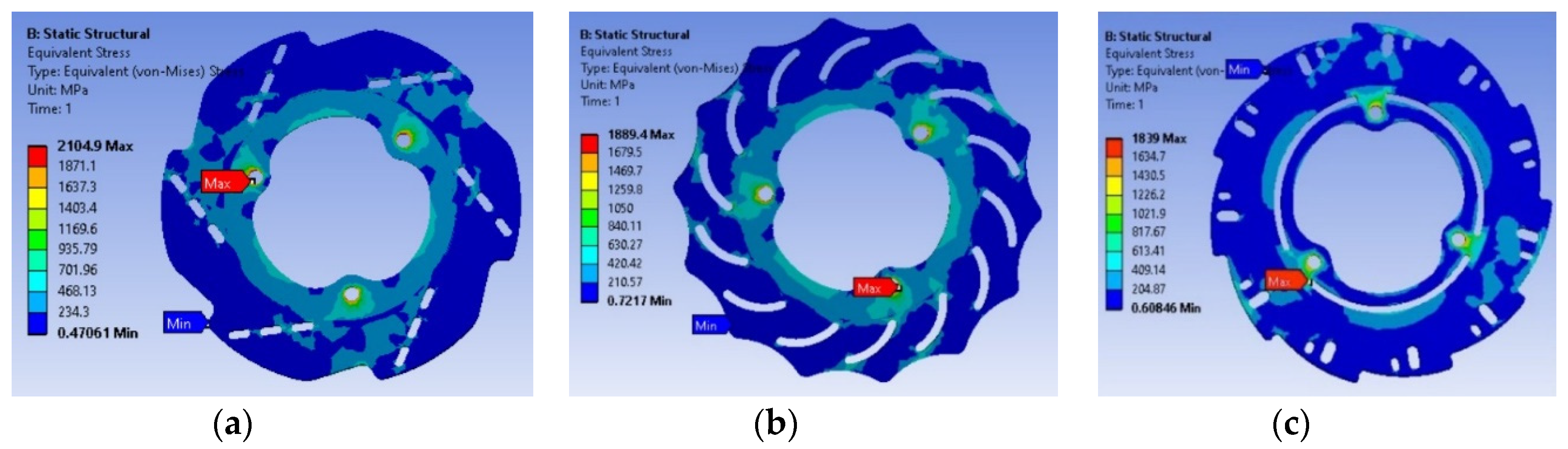
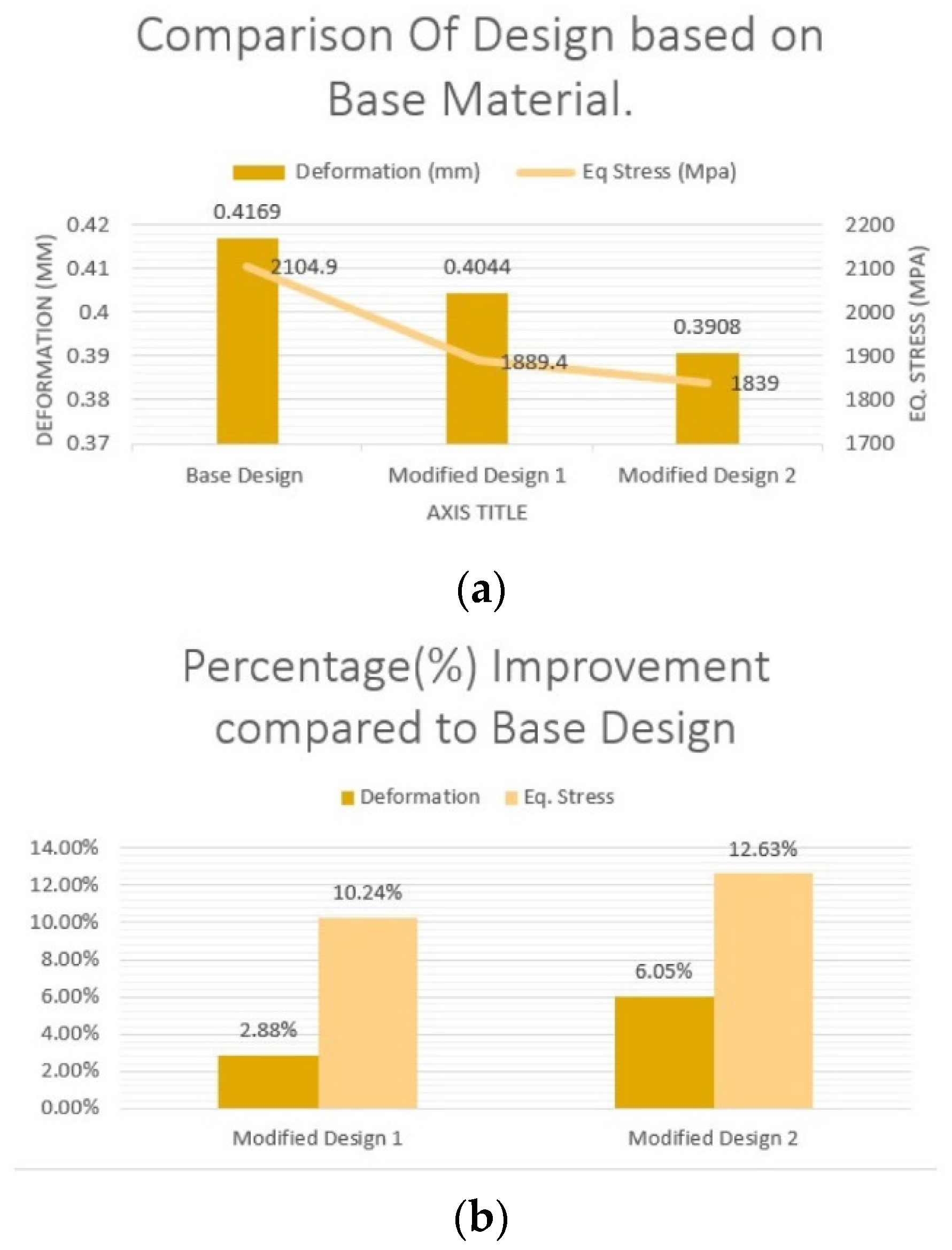
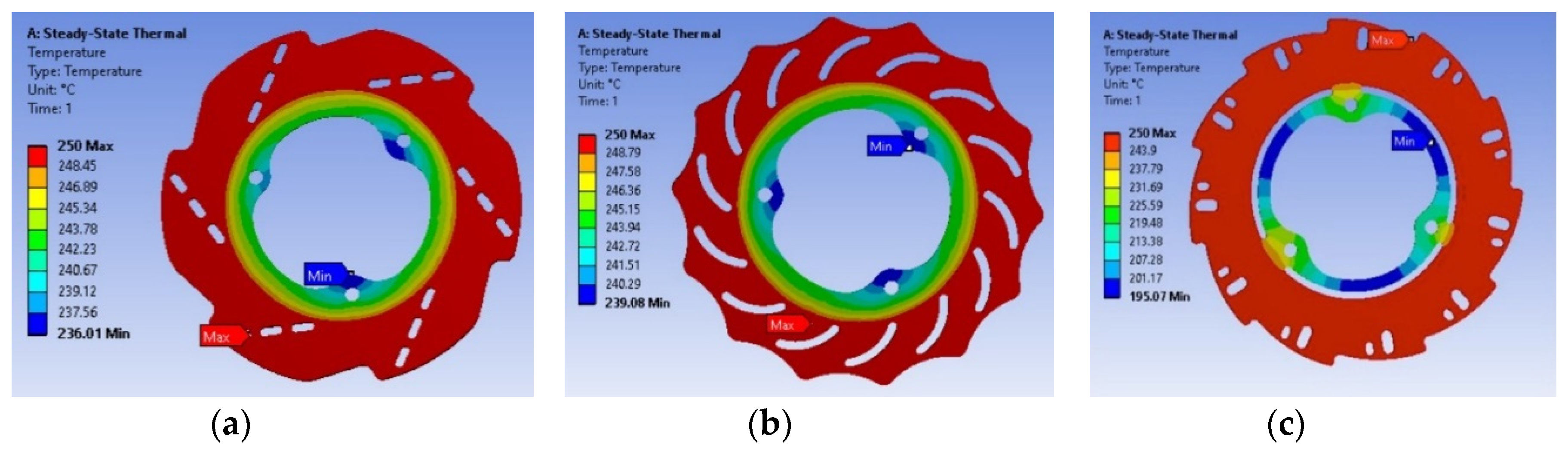
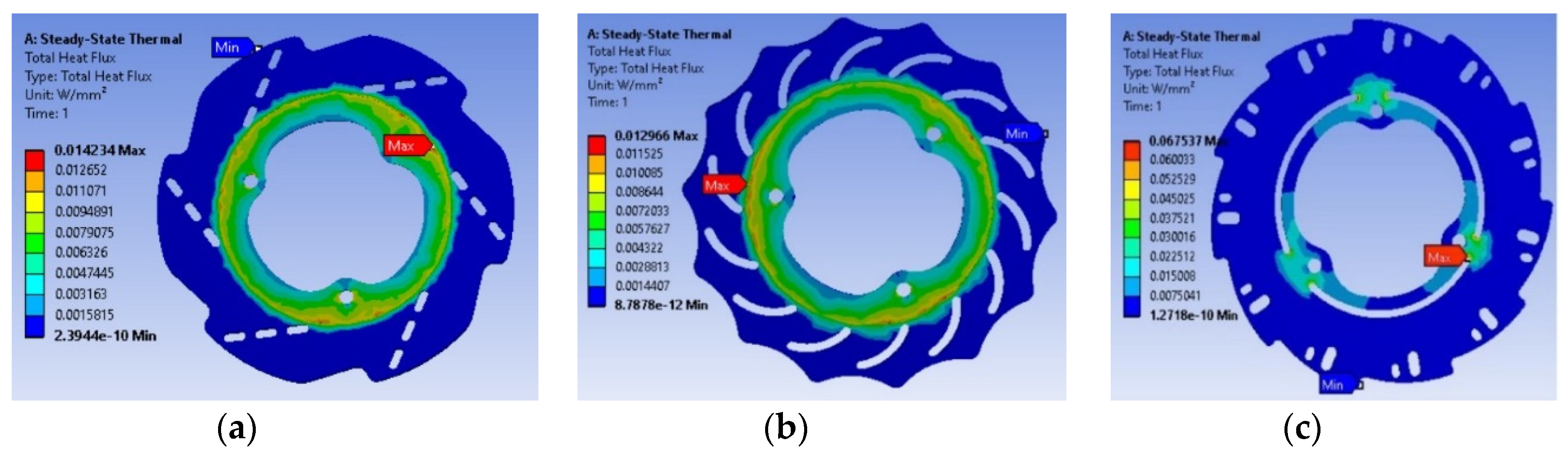
Results and Analysis
- (a).
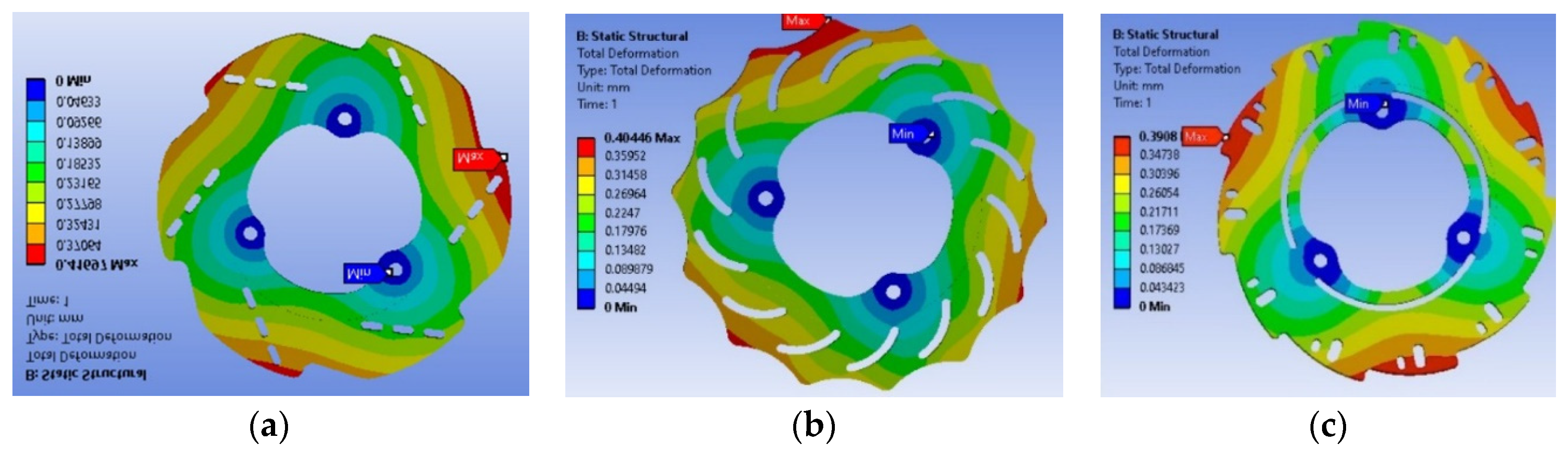
- Static structural analysis
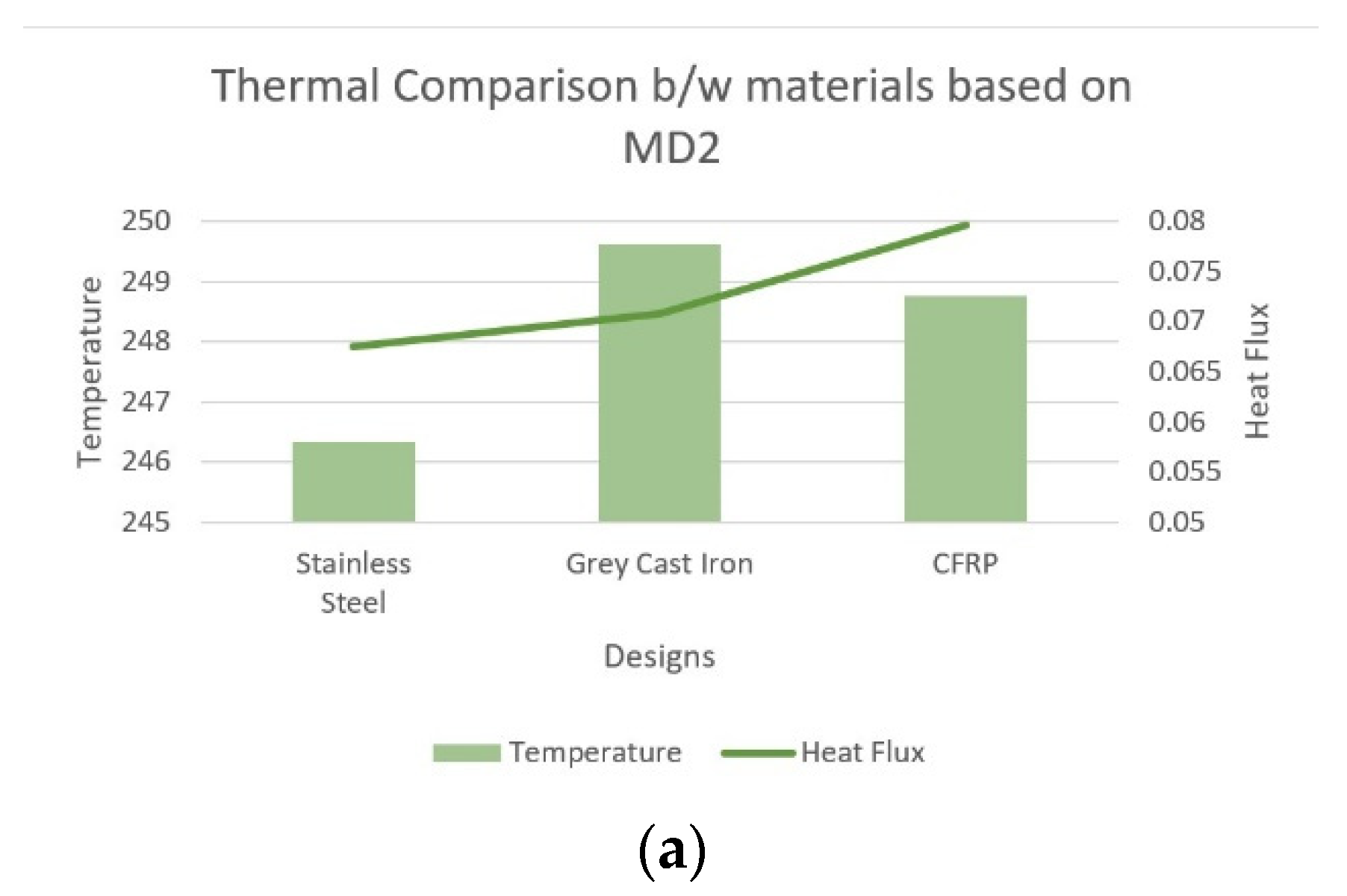
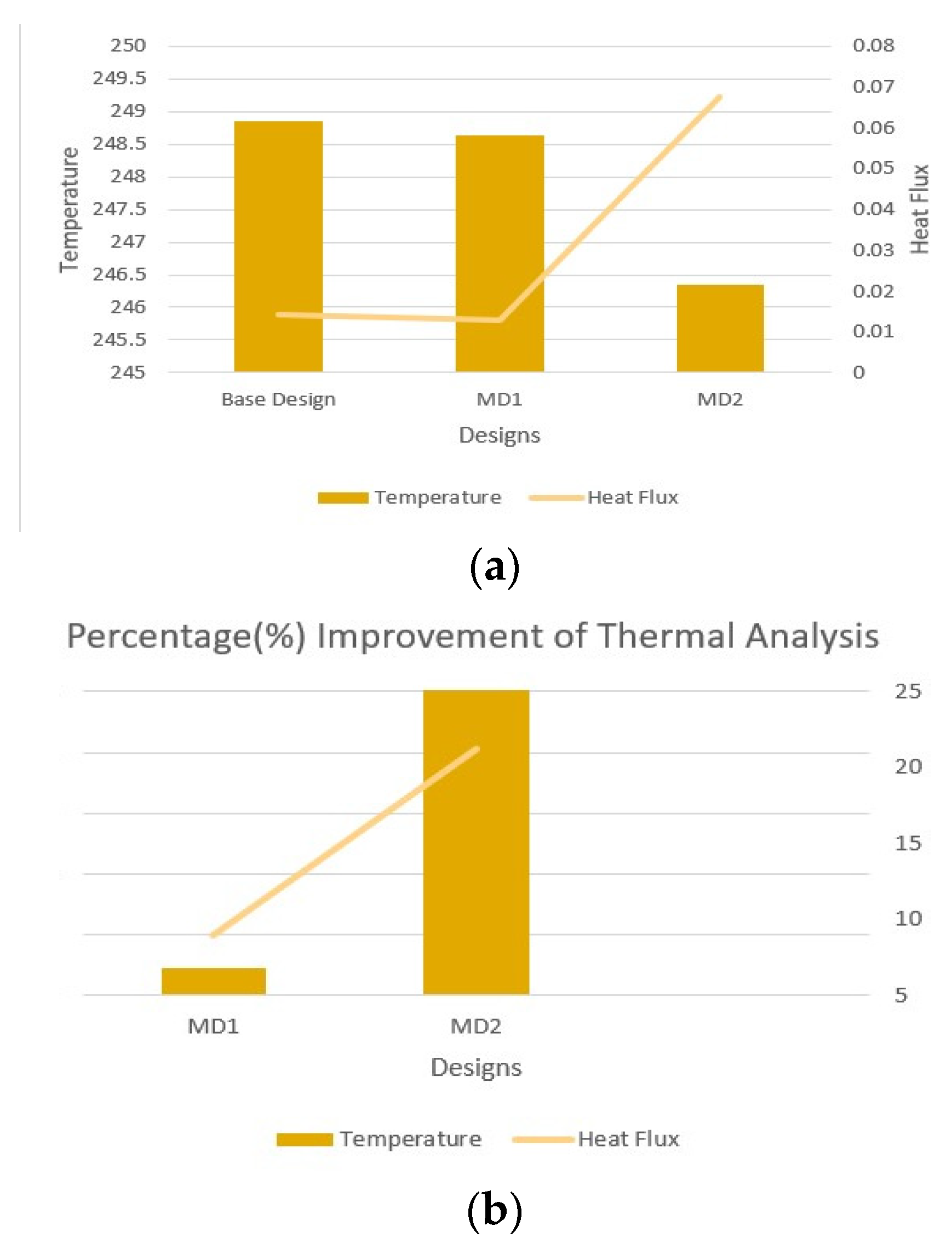
- (b). Thermal analysis
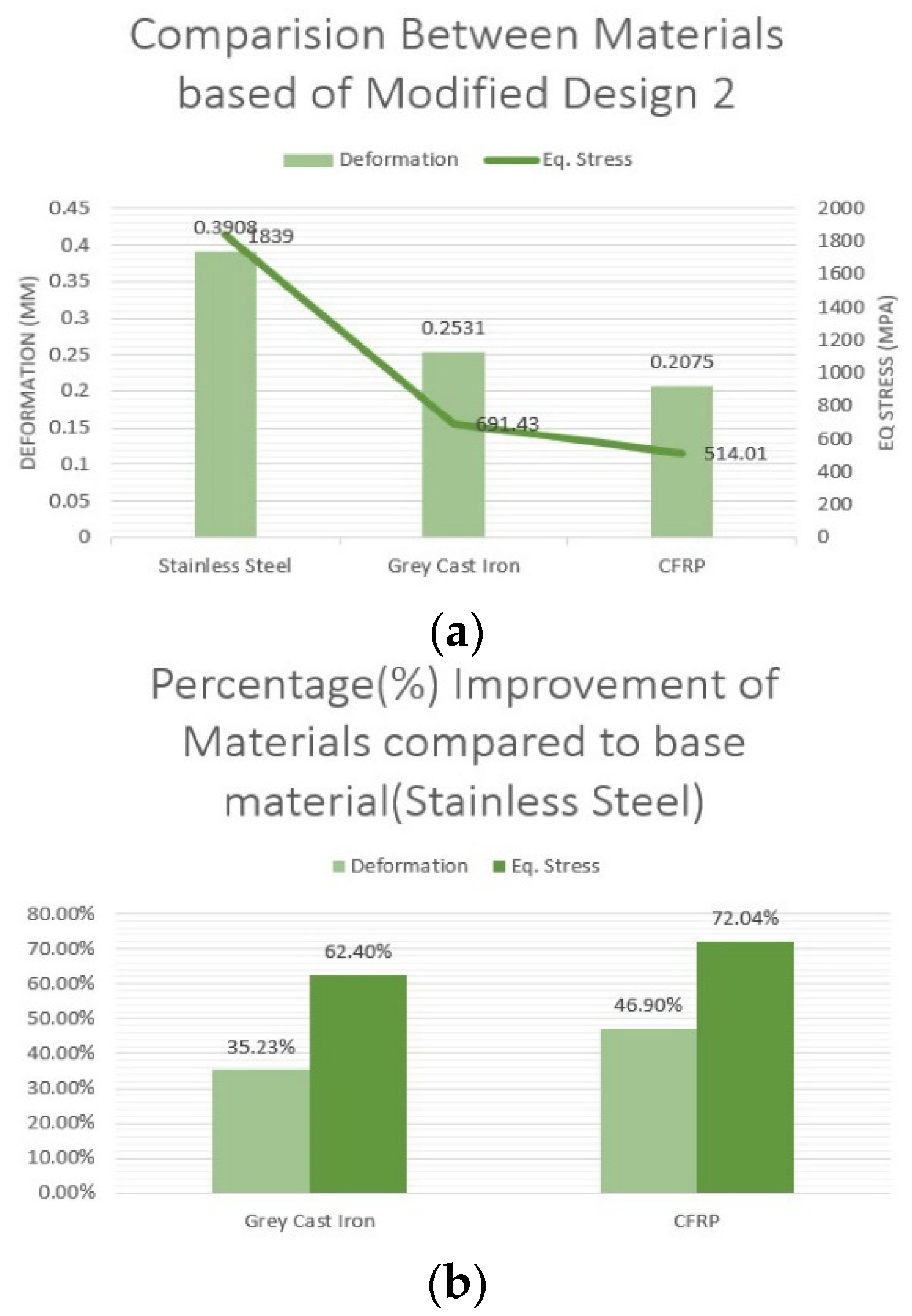
- (c). Material based analysis for MD2
Conclusion
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agbeleye, A., Esezobor, D., Balogun, S., Agunsoye, J., Solis, J., and Neville, A. (2020). “Tribological properties of aluminium-clay composites for brake disc rotor applications.” Journal of King Saud University-Science, 32(1), 21–28. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F., Sethi, M., Tripathi, R., et al. (2021). “Thermo-mechanical analysis of disk brake using finite element analysis.” Materials Today: Proceedings, 47, 4316–4321. [CrossRef]
- Ghadimi, B., Sajedi, R., and Kowsary, F. (2013). “3d investigation of thermal stresses in a locomotive ventilated brake disc based on a conjugate thermo-fluid coupling boundary conditions.” International communications in heat and mass transfer, 49, 104–109. [CrossRef]
- Jafari, R. and Akyuz, R. (2022). “Optimization and thermal analysis of radial ventilated brake disc to enhance the cooling performance.” Case Studies in Thermal Engineering, 30, 101731. [CrossRef]
- Jian, Q., Wang, L., and Shui, Y. (2020). “Thermal analysis of ventilated brake disc based on heat transfer enhancement of heat pipe.” International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 155, 106356. [CrossRef]
- McPhee, A. D. and Johnson, D. A. (2008). “Experimental heat transfer and flow analysis of a vented brake rotor.” International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 47(4), 458–467. [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, D., Gok, M. S., and Karaoglanli, A. C. (2020). “Carbon fiber reinforced polymer (cfrp) composite materials, their characteristic properties, industrial application areas and their machinability.” Engineering Design Applications III, Springer, 235–253.
- Parab, V., Naik, K., and Dhale, A. (2014). “Structural and thermal analysis of brake disc.” International Journal of Engineering Development and Research, 2(2), 1398–1403.
- Pinca-Bretotean, C., Bhandari, R., Sharma, C., Dhakad, S. K., Cosmin, P., and Sharma, A. K. (2021). “An investigation of thermal behaviour of brake disk pad assembly with ansys.” Materials Today: Proceedings, 47, 2322–2328. [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, S., Jeevarathinam, A., Sathishkumar, K., Kumar, K. G., et al. (2022). “Temperature dissipation and thermal expansion of automotive brake disc by using different materials.” Materials Today: Proceedings, 49, 3705–3710. [CrossRef]
- T.V. Manjunath, P.M. Suresh, Structural and thermal analysis of rotor disc of disc brake, Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2 (2013) 2319–8753.
| Feature | |
| Outer Diameter | 200mm |
| Inner Diameter | 150mm |
| Thickness | 3.5mm |
| Brake pad surface (area) | 3848.22mm^2 |
| Wheel hub support | 3 |
| Material (yield strength) Stainless steel | 207MPa |
| Co-efficient of friction | 0.5 |
| Maximum pressure applied | 1MPa |
| Properties | Grey Cast Iron | CFRP |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 412.7 | 414 |
| Poisson’s Ratio | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Mass Density(kg/m^3) | 1800 | 7200 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




