Submitted:
17 June 2023
Posted:
19 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Pathophysiology related to spike protein
3. Autophagy mechanism
3.2. Regulation of Autophagy
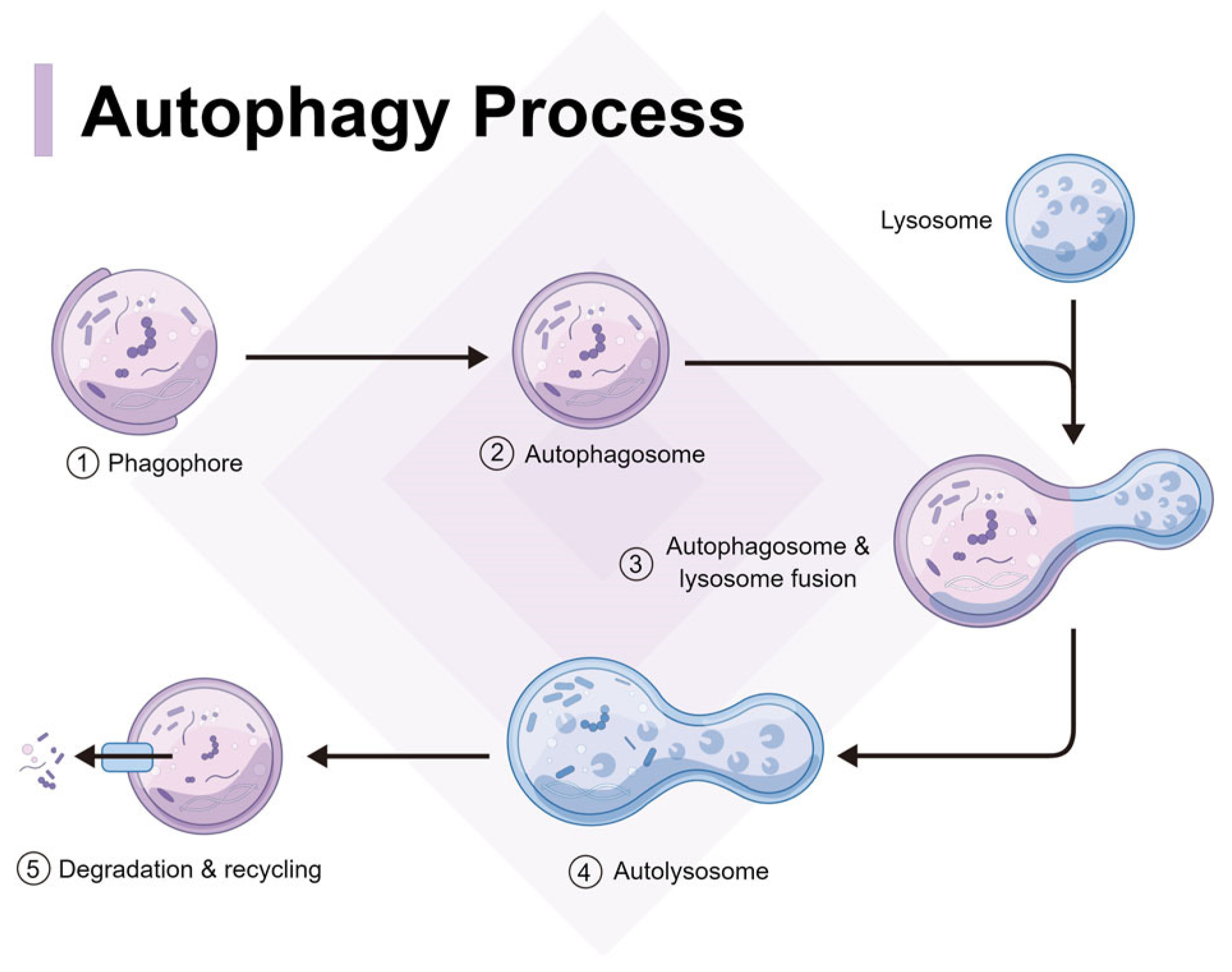
4. Autophagy of spike protein and aggregates
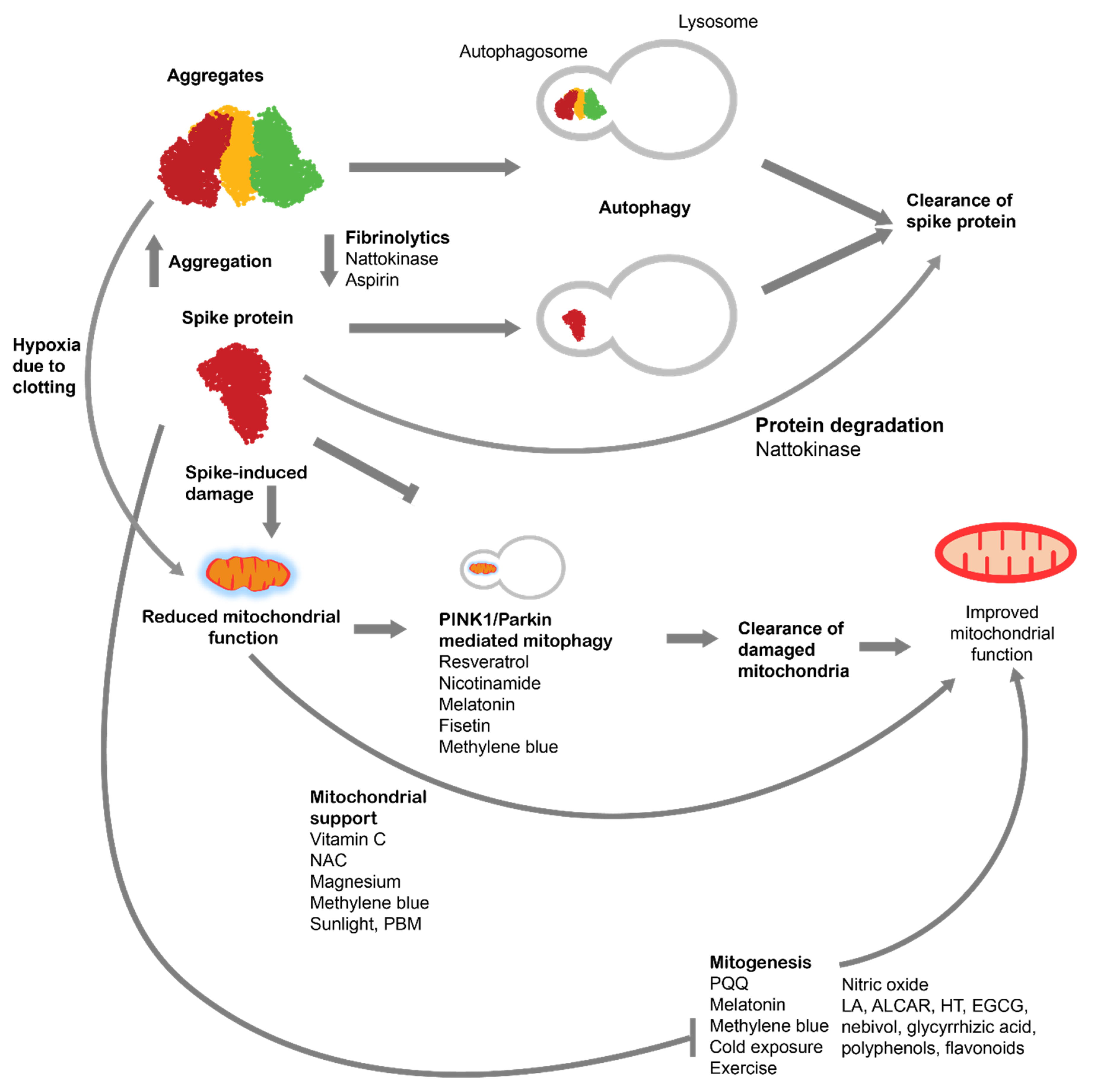
4. Autophagy for treatment of spike protein-induced pathologies
4.1. Fasting and autophagy
4.2. Compounds for increasing autophagy
4.2.1. Spermidine
4.2.2. Caffeine
4.2.3. Resveratrol
4.2.4. Curcumin
4.2.5. Other compounds
5. Improving mitochondrial function
5.1. Mitophagy
5.2. Mitochondrial biogenesis
5.2.1. PQQ
5.2.2. Cold exposure
5.2.3. Endurance exercise
5.2.4. Nitric Oxide
5.2.5. Melatonin
5.2.6. Others
5.3. Improving Mitochondrial Function
5.3.1. Vitamin C
5.3.2. N-acetyl cysteine
5.3.3. Magnesium
5.3.4. Methylene Blue
5.3.5. Light therapy
5.3.6. Others
6. Conclusion
Abbreviations
| ACE2 | angiotensin converting enzyme 2 |
| ALCAR | Acetyl-L-Carnitine |
| BMR | basal metabolic rate |
| CR | caloric restriction |
| CMA | chaperone-mediated autophagy |
| EGCG | Epigallocatechin gallate |
| GH | growth hormone |
| GSH | hepatic glutathione |
| IF | Intermittent fasting |
| LA | Lipoic acid |
| mTOR | mammalian target of rapamycin |
| MB | methylene blue |
| NAC | N-acetyl cysteine |
| NIR | Near-infrared radiation |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| PBM | photobiomodulation |
| RBD | Receptor binding domain |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| S1 | spike protein S1 subunit |
| TRE | Time -restricted eating |
| PGC-1α | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α |
| PQQ | pyrroloquinoline quinone |
References
- Venegas-Borsellino C, Sonikpreet, Martindale RG. From Religion to Secularism: the Benefits of Fasting. Curr Nutr Rep [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2023 May 18];7:131–138. Available from: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13668-018-0233-2. [CrossRef]
- Fazel M. Medical implications of controlled fasting. J R Soc Med [Internet]. 1998 [cited 2023 May 18];91:260–263. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1296701/. [CrossRef]
- Sanchetee P, Sanchetee P, Garg MK. Effect of Jain Fasting on Anthropometric, Clinical and Biochemical Parameters. Indian J Endocrinol Metab [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2023 May 18];24:187–190. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7333753/.
- Cohen K. Native American medicine. Altern Ther Health Med. 1998;4:45–57.
- Sanz-Biset J, Cañigueral S. Plant use in the medicinal practices known as “strict diets” in Chazuta valley (Peruvian Amazon). Journal of Ethnopharmacology [Internet]. 2011 [cited 2023 May 18];137:271–288. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378874111003576. [CrossRef]
- Krakoff LR. Fasting and ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. Blood Pressure Monitoring [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2023 May 18];22:258. Available from: https://journals.lww.com/bpmonitoring/fulltext/2017/10000/Fasting_and_ambulatory_blood_pressure_monitoring.7.aspx?casa_token=MOrFZgoYpSYAAAAA:I3XPuv1eoTQ4qCJ6MGQI4R5TvGs8jwe1b5oq8bv_THHWEH3fj13SEPj9Y5rwA6w49IlwN9bfK85Xet-Q-g9Z4Z4.
- Hoffman VJ. Eating and Fasting for God in Sufi Tradition. Journal of the American Academy of Religion [Internet]. 1995 [cited 2023 May 18];63:465–484. Available from: https://www.jstor.org/stable/1465088.
- Patterson RE, Laughlin GA, Sears DD, et al. INTERMITTENT FASTING AND HUMAN METABOLIC HEALTH. J Acad Nutr Diet [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2023 May 18];115:1203–1212. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4516560/. [CrossRef]
- Visioli F, Mucignat-Caretta C, Anile F, et al. Traditional and Medical Applications of Fasting. Nutrients [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 May 18];14:433. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/14/3/433. [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad S, Gaikwad P, Saxena V. Principles of Fasting in Ayurveda. International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology. 2017;6:787–792.
- Wang C, Ming L, Jia L, et al. Long-Term Extreme Fasting Following a Traditional Chinese “Bigu” Regimen: A Preliminary Retrospective and Prospective Cohort Study [Internet]. Rochester, NY; 2019 [cited 2023 May 18]. Available from: https://papers.ssrn.com/abstract=3474499.
- Ganesh Iyyer S, Mooventhan A, Nandakumar B. Effectiveness of Liquid Fasting with Yoga and Naturopathy Treatments in Reducing Metabolic and Cardiovascular Risks in Obesity. Adv Mind Body Med. 2021;35:24–28.
- Chockalingam A, Kumar S, Ferrer MS, et al. Siddha fasting in obese acute decompensated heart failure may improve hospital outcomes through empowerment and natural ketosis. EXPLORE [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 May 18];18:714–718. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1550830721002500. [CrossRef]
- Ljungqvist O, Søreide E. Preoperative fasting. British Journal of Surgery [Internet]. 2003 [cited 2023 May 18];90:400–406. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.4066. [CrossRef]
- Temkin O. The falling sickness: a history of epilepsy from the Greeks to the beginnings of modern neurology. JHU Press; 1994.
- Hubert V, Weiss S, Rees AJ, et al. Modulating Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy and Its Clinical Applications in Cancer. Cells. 2022;11:2562. [CrossRef]
- Galan-Acosta L, Xia H, Yuan J, et al. Activation of chaperone-mediated autophagy as a potential anticancer therapy. Autophagy [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2023 May 21];11:2370–2371. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2015.1106666. [CrossRef]
- Kaushik S, Cuervo AM. The coming of age of chaperone-mediated autophagy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2023 May 21];19:365–381. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41580-018-0001-6. [CrossRef]
- Swank Z, Senussi Y, Manickas-Hill Z, et al. Persistent Circulating Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Spike Is Associated With Post-acute Coronavirus Disease 2019 Sequelae. Clinical Infectious Diseases [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2023 May 24];76:e487–e490. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciac722. [CrossRef]
- Theoharides TC. Could SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Be Responsible for Long-COVID Syndrome? Mol Neurobiol. 2022;59:1850–1861.
- Attinà A, Leggeri C, Paroni R, et al. Fasting: How to Guide. Nutrients [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 May 24];13:1570. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/13/5/1570.
- Kepp O, Chen G, Carmona-Gutierrez D, et al. A discovery platform for the identification of caloric restriction mimetics with broad health-improving effects. Autophagy [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2023 May 24];16:188–189. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2019.1688984. [CrossRef]
- Patikorn C, Roubal K, Veettil SK, et al. Intermittent Fasting and Obesity-Related Health Outcomes: An Umbrella Review of Meta-analyses of Randomized Clinical Trials. JAMA Network Open [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 May 24];4:e2139558. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.39558. [CrossRef]
- Liang S, Bao C, Yang Z, et al. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces IL-18-mediated cardiopulmonary inflammation via reduced mitophagy. Sig Transduct Target Ther [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2023 May 19];8:1–15. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41392-023-01368-w.
- Clough E, Inigo J, Chandra D, et al. Mitochondrial Dynamics in SARS-COV2 Spike Protein Treated Human Microglia: Implications for Neuro-COVID. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2021;16:770–784. [CrossRef]
- Sun X, Yu J, Wong SH, et al. SARS-CoV-2 targets the lysosome to mediate airway inflammatory cell death. Autophagy. 2022;18:2246–2248.
- Nguyen V, Zhang Y, Gao C, et al. The Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Impairs Lipid Metabolism and Increases Susceptibility to Lipotoxicity: Implication for a Role of Nrf2. Cells [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 May 19];11:1916. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4409/11/12/1916.
- Li F, Li J, Wang P-H, et al. SARS-CoV-2 spike promotes inflammation and apoptosis through autophagy by ROS-suppressed PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 May 19];1867:166260. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925443921001939.
- Davidovich P, Kearney CJ, Martin SJ. Inflammatory outcomes of apoptosis, necrosis and necroptosis. Biol Chem. 2014;395:1163–1171. [CrossRef]
- Kim ES, Jeon M-T, Kim K-S, et al. Spike Proteins of SARS-CoV-2 Induce Pathological Changes in Molecular Delivery and Metabolic Function in the Brain Endothelial Cells. Viruses [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 May 8];13:2021. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8538996/.
- Huynh TV, Rethi L, Lee T-W, et al. Spike Protein Impairs Mitochondrial Function in Human Cardiomyocytes: Mechanisms Underlying Cardiac Injury in COVID-19. Cells [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2023 May 8];12:877. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10046940/.
- Pickrell AM, Youle RJ. The roles of PINK1, parkin, and mitochondrial fidelity in Parkinson’s disease. Neuron. 2015;85:257–273.
- Tanaka K. The PINK1–Parkin axis: An Overview. Neuroscience Research [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2023 May 8];159:9–15. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168010219305711.
- Jin SM, Lazarou M, Wang C, et al. Mitochondrial membrane potential regulates PINK1 import and proteolytic destabilization by PARL. Journal of Cell Biology [Internet]. 2010 [cited 2023 May 8];191:933–942. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201008084. [CrossRef]
- Li X, Hou P, Ma W, et al. SARS-CoV-2 ORF10 suppresses the antiviral innate immune response by degrading MAVS through mitophagy. Cell Mol Immunol [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 May 19];19:67–78. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41423-021-00807-4.
- Couzin-Frankel J. The mystery of the pandemic’s ‘happy hypoxia.’ Science [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2023 May 19];368:455–456. Available from: https://www.science.org/doi/full/10.1126/science.368.6490.455. [CrossRef]
- Pujhari S, Paul S, Ahluwalia J, et al. Clotting disorder in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Reviews in Medical Virology [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 May 19];31:e2177. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/rmv.2177. [CrossRef]
- Adzigbli L, Sokolov EP, Wimmers K, et al. Effects of hypoxia and reoxygenation on mitochondrial functions and transcriptional profiles of isolated brain and muscle porcine cells. Sci Rep [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 May 19];12:19881. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-24386-0. [CrossRef]
- Solaini G, Baracca A, Lenaz G, et al. Hypoxia and mitochondrial oxidative metabolism. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics [Internet]. 2010 [cited 2023 May 19];1797:1171–1177. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0005272810000575.
- Halma MTJ, Rose J, Lawrie T. The Novelty of mRNA Viral Vaccines and Potential Harms: A Scoping Review. J [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2023 Apr 20];6:220–235. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2571-8800/6/2/17. [CrossRef]
- Khan S, Shafiei MS, Longoria C, et al. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces inflammation via TLR2-dependent activation of the NF-κB pathway. Elife. 2021;10:e68563.
- Hsu AC-Y, Wang G, Reid AT, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein promotes hyper-inflammatory response that can be ameliorated by Spike-antagonistic peptide and FDA-approved ER stress and MAP kinase inhibitors in vitro [Internet]. bioRxiv; 2020 [cited 2022 Dec 30]. p. 2020.09.30.317818. Available from: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.09.30.317818v1.
- Forsyth CB, Zhang L, Bhushan A, et al. The SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Protein Promotes MAPK and NF-kB Activation in Human Lung Cells and Inflammatory Cytokine Production in Human Lung and Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Microorganisms. 2022;10:1996.
- Lei Y, Zhang J, Schiavon CR, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Impairs Endothelial Function via Downregulation of ACE 2. Circulation Research [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2022 Dec 7];128:1323–1326. Available from: https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318902. [CrossRef]
- Choi J-Y, Park JH, Jo C, et al. SARS-CoV-2 spike S1 subunit protein-mediated increase of beta-secretase 1 (BACE1) impairs human brain vessel cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022;626:66–71.
- Bhargavan B, Kanmogne GD. SARS-CoV-2 Spike Proteins and Cell-Cell Communication Inhibits TFPI and Induces Thrombogenic Factors in Human Lung Microvascular Endothelial Cells and Neutrophils: Implications for COVID-19 Coagulopathy Pathogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:10436.
- Buzhdygan TP, DeOre BJ, Baldwin-Leclair A, et al. The SARS-CoV-2 spike protein alters barrier function in 2D static and 3D microfluidic in-vitro models of the human blood-brain barrier. Neurobiol Dis. 2020;146:105131.
- Nyström S, Hammarström P. Amyloidogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. J Am Chem Soc. 2022;144:8945–8950.
- Petrlova J, Samsudin F, Bond PJ, et al. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein aggregation is triggered by bacterial lipopolysaccharide. FEBS Letters [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 May 21];596:2566–2575. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/1873-3468.14490. [CrossRef]
- Gill JR, Tashjian R, Duncanson E. Autopsy Histopathologic Cardiac Findings in 2 Adolescents Following the Second COVID-19 Vaccine Dose. Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2022 Oct 1];146:925–929. Available from: https://doi.org/10.5858/arpa.2021-0435-SA. [CrossRef]
- Schwab C, Domke LM, Hartmann L, et al. Autopsy-based histopathological characterization of myocarditis after anti-SARS-CoV-2-vaccination. Clin Res Cardiol. 2023;112:431–440.
- Choi S, Lee S, Seo J-W, et al. Myocarditis-induced Sudden Death after BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination in Korea: Case Report Focusing on Histopathological Findings. J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36:e286.
- Mörz M. A Case Report: Multifocal Necrotizing Encephalitis and Myocarditis after BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccination against COVID-19. Vaccines [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2022 Oct 6];10:1651. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2076-393X/10/10/1651. [CrossRef]
- Tsukada M, Ohsumi Y. Isolation and characterization of autophagy-defective mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Letters [Internet]. 1993 [cited 2023 May 8];333:169–174. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1016/0014-5793%2893%2980398-E. [CrossRef]
- Suzuki SW, Onodera J, Ohsumi Y. Starvation Induced Cell Death in Autophagy-Defective Yeast Mutants Is Caused by Mitochondria Dysfunction. Chandra D, editor. PLoS ONE [Internet]. 2011 [cited 2023 May 8];6:e17412. Available from: https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0017412. [CrossRef]
- Shang C, Liu Z, Zhu Y, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Causes Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Mitophagy Impairment. Front Microbiol. 2021;12:780768.
- Yang X, Zhang R, Nakahira K, et al. Mitochondrial DNA Mutation, Diseases, and Nutrient-Regulated Mitophagy. Annu Rev Nutr. 2019;39:201–226.
- Chourasia AH, Boland ML, Macleod KF. Mitophagy and cancer. Cancer & Metabolism [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2023 May 8];3:4. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40170-015-0130-8. [CrossRef]
- Park H, Kang J-H, Lee S. Autophagy in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Hunter for Aggregates. International Journal of Molecular Sciences [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2023 May 8];21:3369. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/9/3369. [CrossRef]
- Su L, Zhang J, Gomez H, et al. Mitochondria ROS and mitophagy in acute kidney injury. Autophagy [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2023 May 8];19:401–414. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2022.2084862. [CrossRef]
- Cheng Y, Luo R, Wang K, et al. Kidney disease is associated with in-hospital death of patients with COVID-19. Kidney International [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2023 May 8];97:829–838. Available from: https://www.kidney-international.org/article/S0085-2538(20)30255-6/fulltext. [CrossRef]
- Bruchfeld A. The COVID-19 pandemic: consequences for nephrology. Nat Rev Nephrol [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 May 8];17:81–82. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41581-020-00381-4. [CrossRef]
- Vargas JNS, Hamasaki M, Kawabata T, et al. The mechanisms and roles of selective autophagy in mammals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2023 May 8];24:167–185. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41580-022-00542-2. [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto H, Zhang S, Mizushima N. Autophagy genes in biology and disease. Nat Rev Genet [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2023 May 21];24:382–400. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41576-022-00562-w. [CrossRef]
- Lei Y, Klionsky DJ. Transcriptional regulation of autophagy and its implications in human disease. Cell Death Differ [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2023 May 21];1–14. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41418-023-01162-9. [CrossRef]
- Kriegenburg F, Ellgaard L, Hartmann-Petersen R. Molecular chaperones in targeting misfolded proteins for ubiquitin-dependent degradation. The FEBS Journal [Internet]. 2012 [cited 2023 May 21];279:532–542. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08456.x. [CrossRef]
- Hartl FU, Bracher A, Hayer-Hartl M. Molecular chaperones in protein folding and proteostasis. Nature [Internet]. 2011 [cited 2023 May 21];475:324–332. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/nature10317.
- Arndt V, Rogon C, Höhfeld J. To be, or not to be — molecular chaperones in protein degradation. Cell Mol Life Sci [Internet]. 2007 [cited 2023 May 21];64:2525. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-7188-6. [CrossRef]
- Dice JF. Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy. Autophagy [Internet]. 2007 [cited 2023 May 21];3:295–299. Available from: https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.4144. [CrossRef]
- Lescat L, Véron V, Mourot B, et al. Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy in the Light of Evolution: Insight from Fish. Molecular Biology and Evolution [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2023 May 21];37:2887–2899. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msaa127. [CrossRef]
- Liao Z, Wang B, Liu W, et al. Dysfunction of chaperone-mediated autophagy in human diseases. Mol Cell Biochem [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 May 21];476:1439–1454. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-04006-z. [CrossRef]
- Finn PF, Dice JF. Ketone Bodies Stimulate Chaperone-mediatedAutophagy *. Journal of Biological Chemistry [Internet]. 2005 [cited 2023 May 21];280:25864–25870. Available from: https://www.jbc.org/article/S0021-9258(20)61402-8/abstract.
- Cuervo AM, Knecht E, Terlecky SR, et al. Activation of a selective pathway of lysosomal proteolysis in rat liver by prolonged starvation. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology [Internet]. 1995 [cited 2023 May 21];269:C1200–C1208. Available from: https://journals.physiology.org/doi/abs/10.1152/ajpcell.1995.269.5.C1200. [CrossRef]
- Schneider JL, Suh Y, Cuervo AM. Deficient Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy in Liver Leads to Metabolic Dysregulation. Cell Metabolism [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2023 May 21];20:417–432. Available from: https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/abstract/S1550-4131(14)00274-5. [CrossRef]
- Hurley JH, Young LN. Mechanisms of Autophagy Initiation. Annual Review of Biochemistry [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2023 May 21];86:225–244. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-061516-044820. [CrossRef]
- Montella-Manuel S, Pujol-Carrion N, Mechoud MA, et al. Bulk autophagy induction and life extension is achieved when iron is the only limited nutrient in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem J. 2021;478:811–837. [CrossRef]
- Bento CF, Renna M, Ghislat G, et al. Mammalian Autophagy: How Does It Work? Annu Rev Biochem [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2023 May 21];85:685–713. Available from: https://www.annualreviews.org/doi/10.1146/annurev-biochem-060815-014556. [CrossRef]
- Cheng X, Chen Q, Sun P. Natural phytochemicals that affect autophagy in the treatment of oral diseases and infections: A review. Frontiers in Pharmacology [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 May 22];13. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2022.970596. [CrossRef]
- Halma MTJ, Plothe C, Marik P, et al. Strategies for the Management of Spike Protein-Related Pathology. Microorganisms [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2023 May 22];11:1308. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2076-2607/11/5/1308. [CrossRef]
- Tanikawa T, Kiba Y, Yu J, et al. Degradative Effect of Nattokinase on Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2. Molecules [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2022 Sep 30];27:5405. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9458005/.
- Oba M, Rongduo W, Saito A, et al. Natto extract, a Japanese fermented soybean food, directly inhibits viral infections including SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2022 Sep 30];570:21–25. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0006291X21010718.
- Grune T, Jung T, Merker K, et al. Decreased proteolysis caused by protein aggregates, inclusion bodies, plaques, lipofuscin, ceroid, and ‘aggresomes’ during oxidative stress, aging, and disease. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology [Internet]. 2004 [cited 2023 May 22];36:2519–2530. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1357272504001670.
- Fujita M, Nomura K, Hong K, et al. Purification and Characterization of a Strong Fibrinolytic Enzyme (Nattokinase) in the Vegetable Cheese Natto, a Popular Soybean Fermented Food in Japan. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications [Internet]. 1993 [cited 2023 Mar 13];197:1340–1347. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0006291X83726240. [CrossRef]
- Sumi H, Hamada H, Tsushima H, et al. A novel fibrinolytic enzyme (nattokinase) in the vegetable cheese Natto; a typical and popular soybean food in the Japanese diet. Experientia [Internet]. 1987 [cited 2023 Apr 8];43:1110–1111. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01956052. [CrossRef]
- Chen H, McGowan EM, Ren N, et al. Nattokinase: A Promising Alternative in Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases. Biomark�Insights [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2023 Mar 13];13:1177271918785130. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1177/1177271918785130. [CrossRef]
- Jang J-Y, Kim T-S, Cai J, et al. Nattokinase improves blood flow by inhibiting platelet aggregation and thrombus formation. Lab Anim Res [Internet]. 2013 [cited 2023 Apr 8];29:221–225. Available from: https://synapse.koreamed.org/articles/1053773. [CrossRef]
- Pais E, Alexy T, Holsworth J, et al. Effects of nattokinase, a pro-fibrinolytic enzyme, on red blood cell aggregation and whole blood viscosity. Clinical Hemorheology and Microcirculation [Internet]. 2006 [cited 2023 Apr 8];35:139–142. Available from: https://content.iospress.com/articles/clinical-hemorheology-and-microcirculation/ch914.
- Kurosawa Y, Nirengi S, Homma T, et al. A single-dose of oral nattokinase potentiates thrombolysis and anti-coagulation profiles. Sci Rep. 2015;5:11601. [CrossRef]
- Hsu R-L, Lee K-T, Wang J-H, et al. Amyloid-Degrading Ability of Nattokinase from Bacillus subtilis Natto. J Agric Food Chem [Internet]. 2009 [cited 2023 Mar 13];57:503–508. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1021/jf803072r. [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa Y, Chatake T, Chiba-Kamoshida K, et al. Purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction experiment of nattokinase from Bacillus subtilis natto. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2010;66:1670–1673. [CrossRef]
- Frallicciardi J, Gabba M, Poolman B. Determining small-molecule permeation through lipid membranes. Nat Protoc [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 May 22];17:2620–2646. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-022-00734-2. [CrossRef]
- Jamshed H, Beyl RA, Della Manna DL, et al. Early Time-Restricted Feeding Improves 24-Hour Glucose Levels and Affects Markers of the Circadian Clock, Aging, and Autophagy in Humans. Nutrients [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2023 May 9];11:1234. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/11/6/1234.
- Alirezaei M, Kemball CC, Flynn CT, et al. Short-term fasting induces profound neuronal autophagy. Autophagy [Internet]. 2010 [cited 2023 May 9];6:702–710. Available from: https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.6.6.12376. [CrossRef]
- Godar RJ, Ma X, Liu H, et al. Repetitive stimulation of autophagy-lysosome machinery by intermittent fasting preconditions the myocardium to ischemia-reperfusion injury. Autophagy [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2023 May 9];11:1537–1560. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2015.1063768. [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Lopez N, Tarabra E, Toledo M, et al. System-wide Benefits of Intermeal Fasting by Autophagy. Cell Metabolism [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2023 May 9];26:856-871.e5. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1550413117306083. [CrossRef]
- Fernandes SA, Demetriades C. The Multifaceted Role of Nutrient Sensing and mTORC1 Signaling in Physiology and Aging. Frontiers in Aging [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 May 22];2. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fragi.2021.707372. [CrossRef]
- Kim J, Guan K-L. mTOR as a central hub of nutrient signalling and cell growth. Nat Cell Biol [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2023 May 22];21:63–71. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41556-018-0205-1. [CrossRef]
- Yu L, McPhee CK, Zheng L, et al. Termination of autophagy and reformation of lysosomes regulated by mTOR. Nature. 2010;465:942–946. [CrossRef]
- Regmi P, Heilbronn LK. Time-Restricted Eating: Benefits, Mechanisms, and Challenges in Translation. iScience [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2023 May 22];23:101161. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2589004220303461.
- Longo VD, Mattson MP. Fasting: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Applications. Cell Metab [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2022 Oct 4];19:181–192. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3946160/. [CrossRef]
- Mattson MP, Longo VD, Harvie M. Impact of intermittent fasting on health and disease processes. Ageing Research Reviews [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2023 May 22];39:46–58. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1568163716302513. [CrossRef]
- Anton SD, Moehl K, Donahoo WT, et al. Flipping the Metabolic Switch: Understanding and Applying the Health Benefits of Fasting. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2018;26:254–268. [CrossRef]
- Patterson RE, Sears DD. Metabolic Effects of Intermittent Fasting. Annual Review of Nutrition [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2023 May 22];37:371–393. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-nutr-071816-064634. [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury EA, Richardson JD, Tsintzas K, et al. Effect of extended morning fasting upon ad libitum lunch intake and associated metabolic and hormonal responses in obese adults. Int J Obes [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2023 May 22];40:305–311. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/ijo2015154. [CrossRef]
- Fuhrman J, Sarter B, Glaser D, et al. Changing perceptions of hunger on a high nutrient density diet. Nutr J [Internet]. 2010 [cited 2023 May 22];9:51. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-9-51. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira CLP, Boulé NG, Berg A, et al. Consumption of a High-Protein Meal Replacement Leads to Higher Fat Oxidation, Suppression of Hunger, and Improved Metabolic Profile After an Exercise Session. Nutrients [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 May 22];13:155. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/13/1/155. [CrossRef]
- Zauner C, Schneeweiss B, Kranz A, et al. Resting energy expenditure in short-term starvation is increased as a result of an increase in serum norepinephrine. The American journal of clinical nutrition. 2000;71:1511–1515. [CrossRef]
- Catenacci VA, Pan Z, Ostendorf D, et al. A randomized pilot study comparing zero-calorie alternate-day fasting to daily caloric restriction in adults with obesity. Obesity. 2016;24:1874–1883. [CrossRef]
- Thissen J-P, Ketelslegers J-M, Underwood LE. Nutritional regulation of the insulin-like growth factors. Endocrine reviews. 1994;15:80–101. [CrossRef]
- Ho KY, Veldhuis JD, Johnson ML, et al. Fasting enhances growth hormone secretion and amplifies the complex rhythms of growth hormone secretion in man. The Journal of clinical investigation. 1988;81:968–975. [CrossRef]
- Harvie MN, Pegington M, Mattson MP, et al. The effects of intermittent or continuous energy restriction on weight loss and metabolic disease risk markers: a randomized trial in young overweight women. International journal of obesity. 2011;35:714–727. [CrossRef]
- Harvie M, Wright C, Pegington M, et al. The effect of intermittent energy and carbohydrate restriction v. daily energy restriction on weight loss and metabolic disease risk markers in overweight women. British Journal of Nutrition. 2013;110:1534–1547. [CrossRef]
- He Z, Xu H, Li C, et al. Intermittent fasting and immunomodulatory effects: A systematic review. Frontiers in Nutrition [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2023 May 22];10. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2023.1048230. [CrossRef]
- Lettieri-Barbato D, Cannata SM, Casagrande V, et al. Time-controlled fasting prevents aging-like mitochondrial changes induced by persistent dietary fat overload in skeletal muscle. PLOS ONE [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2023 May 22];13:e0195912. Available from: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0195912. [CrossRef]
- Singh R, Mohapatra L, Tripathi AS. Targeting mitochondrial biogenesis: a potential approach for preventing and controlling diabetes. Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 May 20];7:212. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43094-021-00360-x. [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Morales P, León-Contreras JC, Granados-Pineda J, et al. Protection against renal ischemia and reperfusion injury by short-term time-restricted feeding involves the mitochondrial unfolded protein response. Free Radical Biology and Medicine [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2023 May 22];154:75–83. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0891584920305657.
- Real-Hohn A, Navegantes C, Ramos K, et al. The synergism of high-intensity intermittent exercise and every-other-day intermittent fasting regimen on energy metabolism adaptations includes hexokinase activity and mitochondrial efficiency. PLOS ONE [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2023 May 22];13:e0202784. Available from: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0202784. [CrossRef]
- Cheng C-W, Adams GB, Perin L, et al. Prolonged Fasting Reduces IGF-1/PKA to Promote Hematopoietic-Stem-Cell-Based Regeneration and Reverse Immunosuppression. Cell Stem Cell [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2023 May 22];14:810–823. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1934590914001519.
- Sutton EF, Beyl R, Early KS, et al. Early Time-Restricted Feeding Improves Insulin Sensitivity, Blood Pressure, and Oxidative Stress Even without Weight Loss in Men with Prediabetes. Cell Metabolism [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2023 May 22];27:1212-1221.e3. Available from: https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/abstract/S1550-4131(18)30253-5. [CrossRef]
- Rajpal A, Ismail-Beigi F. Intermittent fasting and ‘metabolic switch’: Effects on metabolic syndrome, prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2023 May 22];22:1496–1510. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/dom.14080. [CrossRef]
- Guo Y, Luo S, Ye Y, et al. Intermittent Fasting Improves Cardiometabolic Risk Factors and Alters Gut Microbiota in Metabolic Syndrome Patients. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 May 22];106:64–79. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgaa644. [CrossRef]
- Furmli S, Elmasry R, Ramos M, et al. Therapeutic use of intermittent fasting for people with type 2 diabetes as an alternative to insulin. Case Reports [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2023 May 22];2018:bcr. Available from: https://casereports.bmj.com/content/2018/bcr-2017-221854. [CrossRef]
- Albosta M, Bakke J. Intermittent fasting: is there a role in the treatment of diabetes? A review of the literature and guide for primary care physicians. Clinical Diabetes and Endocrinology [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 May 22];7:3. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40842-020-00116-1. [CrossRef]
- Mattson MP, Wan R. Beneficial effects of intermittent fasting and caloric restriction on the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular systems. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry [Internet]. 2005 [cited 2023 May 22];16:129–137. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S095528630400261X. [CrossRef]
- Martin B, Mattson MP, Maudsley S. Caloric restriction and intermittent fasting: Two potential diets for successful brain aging. Ageing Research Reviews [Internet]. 2006 [cited 2023 May 22];5:332–353. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1568163706000523. [CrossRef]
- Clifton KK, Ma CX, Fontana L, et al. Intermittent fasting in the prevention and treatment of cancer. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 May 22];71:527–546. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.3322/caac.21694. [CrossRef]
- Pietrocola F, Lachkar S, Enot DP, et al. Spermidine induces autophagy by inhibiting the acetyltransferase EP300. Cell Death and Differentiation [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2023 May 9];22:509. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4326581/. [CrossRef]
- Ali MA, Poortvliet E, Strömberg R, et al. Polyamines in foods: development of a food database. Food & Nutrition Research [Internet]. 2011 [cited 2023 May 9]; Available from: https://foodandnutritionresearch.net/index.php/fnr/article/view/595.
- Madeo F, Hofer SJ, Pendl T, et al. Nutritional Aspects of Spermidine. Annual Review of Nutrition [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2023 May 9];40:135–159. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-nutr-120419-015419. [CrossRef]
- Soda K, Kano Y, Sakuragi M, et al. Long-term oral polyamine intake increases blood polyamine concentrations. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2009;55:361–366.
- Soda K, Uemura T, Sanayama H, et al. Polyamine-Rich Diet Elevates Blood Spermine Levels and Inhibits Pro-Inflammatory Status: An Interventional Study. Med Sci (Basel). 2021;9:22. [CrossRef]
- Senekowitsch S, Wietkamp E, Grimm M, et al. High-Dose Spermidine Supplementation Does Not Increase Spermidine Levels in Blood Plasma and Saliva of Healthy Adults: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Pharmacokinetic and Metabolomic Study. Nutrients. 2023;15:1852. [CrossRef]
- Madeo F, Eisenberg T, Pietrocola F, et al. Spermidine in health and disease. Science [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2023 May 9];359:eaan2788. Available from: https://www.science.org/doi/full/10.1126/science.aan2788. [CrossRef]
- Wirth M, Benson G, Schwarz C, et al. The effect of spermidine on memory performance in older adults at risk for dementia: A randomized controlled trial. Cortex. 2018;109:181–188. [CrossRef]
- Schwarz C, Benson GS, Horn N, et al. Effects of Spermidine Supplementation on Cognition and Biomarkers in Older Adults With Subjective Cognitive Decline: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5:e2213875.
- Schwarz C, Stekovic S, Wirth M, et al. Safety and tolerability of spermidine supplementation in mice and older adults with subjective cognitive decline. Aging [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2023 May 9];10:19–33. Available from: https://www.aging-us.com/article/101354/text. [CrossRef]
- Ray K. Caffeine is a potent stimulator of autophagy to reduce hepatic lipid content—a coffee for NAFLD? Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol [Internet]. 2013 [cited 2023 May 9];10:563–563. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/nrgastro.2013.170.
- Pietrocola F, Malik SA, Mariño G, et al. Coffee induces autophagy in vivo. Cell Cycle [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2023 Mar 5];13:1987–1994. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4111762/.
- Ferraresi A, Titone R, Follo C, et al. The protein restriction mimetic Resveratrol is an autophagy inducer stronger than amino acid starvation in ovarian cancer cells. Molecular Carcinogenesis [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2023 Mar 5];56:2681–2691. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/mc.22711. [CrossRef]
- Josifovska N, Albert R, Nagymihály R, et al. Resveratrol as Inducer of Autophagy, Pro-Survival, and Anti-Inflammatory Stimuli in Cultured Human RPE Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:813. [CrossRef]
- Meng T, Xiao D, Muhammed A, et al. Anti-Inflammatory Action and Mechanisms of Resveratrol. Molecules [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 May 23];26:229. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/26/1/229. [CrossRef]
- Pasquereau S, Nehme Z, Haidar Ahmad S, et al. Resveratrol Inhibits HCoV-229E and SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus Replication In Vitro. Viruses. 2021;13:354. [CrossRef]
- Chen K, Zhao H, Shu L, et al. Effect of resveratrol on intestinal tight junction proteins and the gut microbiome in high-fat diet-fed insulin resistant mice. International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2023 May 23];71:965–978. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/09637486.2020.1754351. [CrossRef]
- Chatam O, Chapnik N, Froy O. Resveratrol Induces the Fasting State and Alters Circadian Metabolism in Hepatocytes. Plant Foods Hum Nutr [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 May 23];77:128–134. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11130-022-00954-7. [CrossRef]
- Park D, Jeong H, Lee MN, et al. Resveratrol induces autophagy by directly inhibiting mTOR through ATP competition. Scientific reports. 2016;6:1–11. [CrossRef]
- Hewlings SJ, Kalman DS. Curcumin: A Review of Its Effects on Human Health. Foods [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2023 May 22];6:92. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2304-8158/6/10/92. [CrossRef]
- Lee YJ, Kim N-Y, Suh Y-A, et al. Involvement of ROS in Curcumin-induced Autophagic Cell Death. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol [Internet]. 2011 [cited 2023 May 9];15:1–7. Available from: https://synapse.koreamed.org/articles/1025725. [CrossRef]
- Shakeri A, Cicero AFG, Panahi Y, et al. Curcumin: A naturally occurring autophagy modulator. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:5643–5654. [CrossRef]
- Anand P, Kunnumakkara AB, Newman RA, et al. Bioavailability of Curcumin: Problems and Promises. Mol Pharmaceutics [Internet]. 2007 [cited 2023 May 22];4:807–818. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1021/mp700113r. [CrossRef]
- Shoba G, Joy D, Joseph T, et al. Influence of piperine on the pharmacokinetics of curcumin in animals and human volunteers. Planta Med. 1998;64:353–356. [CrossRef]
- Ferrari E, Bettuzzi S, Naponelli V. The Potential of Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG) in Targeting Autophagy for Cancer Treatment: A Narrative Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 May 9];23:6075. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/23/11/6075. [CrossRef]
- Zhou J, Farah BL, Sinha RA, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG), a Green Tea Polyphenol, Stimulates Hepatic Autophagy and Lipid Clearance. PLOS ONE [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2023 May 9];9:e87161. Available from: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0087161. [CrossRef]
- Rubinsztein DC, Nixon RA. Rapamycin induces autophagic flux in neurons. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences [Internet]. 2010 [cited 2023 May 9];107:E181–E181. Available from: https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.1014633107. [CrossRef]
- Rangaraju S, Verrier JD, Madorsky I, et al. Rapamycin Activates Autophagy and Improves Myelination in Explant Cultures from Neuropathic Mice. J Neurosci [Internet]. 2010 [cited 2023 May 9];30:11388–11397. Available from: https://www.jneurosci.org/content/30/34/11388. [CrossRef]
- Sarkar S, Ravikumar B, Floto RA, et al. Rapamycin and mTOR-independent autophagy inducers ameliorate toxicity of polyglutamine-expanded huntingtin and related proteinopathies. Cell Death Differ [Internet]. 2009 [cited 2023 May 9];16:46–56. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/cdd2008110. [CrossRef]
- Sotthibundhu A, McDonagh K, von Kriegsheim A, et al. Rapamycin regulates autophagy and cell adhesion in induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7:166. [CrossRef]
- Lin S-R, Fu Y-S, Tsai M-J, et al. Natural Compounds from Herbs that can Potentially Execute as Autophagy Inducers for Cancer Therapy. Int J Mol Sci [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2023 Mar 5];18:1412. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5535904/. [CrossRef]
- Denaro CA, Haloush YI, Hsiao SY, et al. COVID-19 and neurodegeneration: The mitochondrial connection. Aging Cell. 2022;21:e13727. [CrossRef]
- Narendra D, Tanaka A, Suen D-F, et al. Parkin is recruited selectively to impaired mitochondria and promotes their autophagy. Journal of Cell Biology [Internet]. 2008 [cited 2023 May 8];183:795–803. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200809125. [CrossRef]
- Yamano K, Youle RJ. PINK1 is degraded through the N-end rule pathway. Autophagy [Internet]. 2013 [cited 2023 May 8];9:1758–1769. Available from: https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.24633. [CrossRef]
- Kazlauskaite A, Kondapalli C, Gourlay R, et al. Parkin is activated by PINK1-dependent phosphorylation of ubiquitin at Ser65. Biochemical Journal [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2023 May 8];460:127–141. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20140334. [CrossRef]
- Shiba-Fukushima K, Arano T, Matsumoto G, et al. Phosphorylation of Mitochondrial Polyubiquitin by PINK1 Promotes Parkin Mitochondrial Tethering. PLOS Genetics [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2023 May 8];10:e1004861. Available from: https://journals.plos.org/plosgenetics/article?id=10.1371/journal.pgen.1004861. [CrossRef]
- Koyano F, Okatsu K, Kosako H, et al. Ubiquitin is phosphorylated by PINK1 to activate parkin. Nature [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2023 May 8];510:162–166. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/nature13392. [CrossRef]
- Kane LA, Lazarou M, Fogel AI, et al. PINK1 phosphorylates ubiquitin to activate Parkin E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. Journal of Cell Biology [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2023 May 8];205:143–153. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201402104. [CrossRef]
- Heo J-M, Ordureau A, Paulo JA, et al. The PINK1-PARKIN Mitochondrial Ubiquitylation Pathway Drives a Program of OPTN/NDP52 Recruitment and TBK1 Activation to Promote Mitophagy. Molecular Cell [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2023 May 8];60:7–20. Available from: https://www.cell.com/molecular-cell/abstract/S1097-2765(15)00662-0. [CrossRef]
- Hu Y, Li X-C, Wang Z, et al. Tau accumulation impairs mitophagy via increasing mitochondrial membrane potential and reducing mitochondrial Parkin. Oncotarget [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2023 May 8];7:17356–17368. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4951217/. [CrossRef]
- Georgakopoulos ND, Wells G, Campanella M. The pharmacological regulation of cellular mitophagy. Nat Chem Biol [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2023 May 8];13:136–146. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/nchembio.2287. [CrossRef]
- Huang R, Xu Y, Wan W, et al. Deacetylation of nuclear LC3 drives autophagy initiation under starvation. Mol Cell. 2015;57:456–466. [CrossRef]
- Schiavi A, Maglioni S, Palikaras K, et al. Iron-Starvation-Induced Mitophagy Mediates Lifespan Extension upon Mitochondrial Stress in C. elegans. Curr Biol. 2015;25:1810–1822. [CrossRef]
- Jang S, Kang HT, Hwang ES. Nicotinamide-induced mitophagy: event mediated by high NAD+/NADH ratio and SIRT1 protein activation. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:19304–19314. [CrossRef]
- Block T, Kuo J. Rationale for Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+) Metabolome Disruption as a Pathogenic Mechanism of Post-Acute COVID-19 Syndrome. Clin Med�Insights�Pathol [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 May 8];15:2632010X221106986. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1177/2632010X221106986. [CrossRef]
- Domi E, Hoxha M, Kolovani E, et al. The Importance of Nutraceuticals in COVID-19: What’s the Role of Resveratrol? Molecules [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 May 8];27:2376. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/27/8/2376. [CrossRef]
- Wissler Gerdes EO, Vanichkachorn G, Verdoorn BP, et al. Role of senescence in the chronic health consequences of COVID-19. Translational Research [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 May 8];241:96–108. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1931524421002590. [CrossRef]
- Kang J-W, Hong J-M, Lee S-M. Melatonin enhances mitophagy and mitochondrial biogenesis in rats with carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis. Journal of Pineal Research [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2023 May 20];60:383–393. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/jpi.12319. [CrossRef]
- Chen C, Yang C, Wang J, et al. Melatonin ameliorates cognitive deficits through improving mitophagy in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Pineal Res. 2021;71:e12774. [CrossRef]
- Coto-Montes A, Boga JA, Rosales-Corral S, et al. Role of melatonin in the regulation of autophagy and mitophagy: A review. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology [Internet]. 2012 [cited 2023 May 20];361:12–23. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0303720712002626. [CrossRef]
- Bertholet AM, Delerue T, Millet AM, et al. Mitochondrial fusion/fission dynamics in neurodegeneration and neuronal plasticity. Neurobiology of Disease [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2023 May 20];90:3–19. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0969996115300693. [CrossRef]
- Hattori N, Saiki S, Imai Y. Regulation by mitophagy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014;53:147–150. [CrossRef]
- Jornayvaz FR, Shulman GI. Regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis. Brown GC, Murphy MP, editors. Essays in Biochemistry [Internet]. 2010 [cited 2023 May 20];47:69–84. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1042/bse0470069. [CrossRef]
- Hwang PS, Machek SB, Cardaci TD, et al. Effects of Pyrroloquinoline Quinone (PQQ) Supplementation on Aerobic Exercise Performance and Indices of Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Untrained Men. Journal of the American College of Nutrition [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2023 May 13];39:547–556. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2019.1705203. [CrossRef]
- Chung N, Park J, Lim K. The effects of exercise and cold exposure on mitochondrial biogenesis in skeletal muscle and white adipose tissue. J Exerc Nutrition Biochem. 2017;21:39–47. [CrossRef]
- Booth FW, Ruegsegger GN, Toedebusch RG, et al. Chapter Six - Endurance Exercise and the Regulation of Skeletal Muscle Metabolism. In: Bouchard C, editor. Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science [Internet]. Academic Press; 2015 [cited 2023 May 20]. p. 129–151. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1877117315001489. [CrossRef]
- Coyle EF. Physiological determinants of endurance exercise performance. Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport [Internet]. 1999 [cited 2023 May 20];2:181–189. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1440244099801728. [CrossRef]
- Cattadori G, Di Marco S, Baravelli M, et al. Exercise Training in Post-COVID-19 Patients: The Need for a Multifactorial Protocol for a Multifactorial Pathophysiology. Journal of Clinical Medicine [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 May 20];11:2228. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/11/8/2228. [CrossRef]
- Nisoli E, Clementi E, Paolucci C, et al. Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Mammals: The Role of Endogenous Nitric Oxide. Science [Internet]. 2003 [cited 2023 May 20];299:896–899. Available from: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.1079368. [CrossRef]
- Leary SC, Shoubridge EricA. Mitochondrial biogenesis: Which part of “NO” do we understand? BioEssays [Internet]. 2003 [cited 2023 May 20];25:538–541. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/bies.10298. [CrossRef]
- Shen W, Zhang X, Zhao G, et al. Nitric oxide production and NO synthase gene expression contribute to vascular regulation during exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1995;27:1125–1134. [CrossRef]
- Roberts CK, Barnard RJ, Jasman A, et al. Acute exercise increases nitric oxide synthase activity in skeletal muscle. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism [Internet]. 1999 [cited 2023 May 20];277:E390–E394. Available from: https://journals.physiology.org/doi/full/10.1152/ajpendo.1999.277.2.E390. [CrossRef]
- Hazell G, Khazova M, Cohen H, et al. Post-exposure persistence of nitric oxide upregulation in skin cells irradiated by UV-A. Sci Rep [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 May 20];12:9465. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-13399-4. [CrossRef]
- Puyaubert J, Baudouin E. New clues for a cold case: nitric oxide response to low temperature. Plant, Cell & Environment [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2023 May 20];37:2623–2630. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/pce.12329. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Vicente I, Lorenzo O. Nitric oxide regulation of temperature acclimation: a molecular genetic perspective. Journal of Experimental Botany [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 May 20];72:5789–5794. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erab049. [CrossRef]
- Zhen J, Lu H, Wang XQ, et al. Upregulation of Endothelial and Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Expression by Reactive Oxygen Species. American Journal of Hypertension [Internet]. 2008 [cited 2023 May 20];21:28–34. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/ajh.2007.14. [CrossRef]
- Kauser K, Rubanyi GM. Potential Cellular Signaling Mechanisms Mediating Upregulation of Endothelial Nitric Oxide Production by Estrogen. Journal of Vascular Research [Internet]. 2008 [cited 2023 May 20];34:229–236. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1159/000159227. [CrossRef]
- Laufs U, La Fata V, Plutzky J, et al. Upregulation of Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase by HMG CoA Reductase Inhibitors. Circulation [Internet]. 1998 [cited 2023 May 20];97:1129–1135. Available from: https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/01.CIR.97.12.1129. [CrossRef]
- Kato H, Tanaka G, Masuda S, et al. Melatonin promotes adipogenesis and mitochondrial biogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Journal of Pineal Research [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2023 May 20];59:267–275. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/jpi.12259. [CrossRef]
- Niu Y-J, Zhou W, Nie Z-W, et al. Melatonin enhances mitochondrial biogenesis and protects against rotenone-induced mitochondrial deficiency in early porcine embryos. Journal of Pineal Research [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2023 May 20];68:e12627. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/jpi.12627. [CrossRef]
- Cardinali DP, Brown GM, Pandi-Perumal SR. Possible Application of Melatonin in Long COVID. Biomolecules [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 Jan 10];12:1646. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2218-273X/12/11/1646. [CrossRef]
- Lewis Luján LM, McCarty MF, Di Nicolantonio JJ, et al. Nutraceuticals/Drugs Promoting Mitophagy and Mitochondrial Biogenesis May Combat the Mitochondrial Dysfunction Driving Progression of Dry Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Nutrients. 2022;14:1985. [CrossRef]
- Chodari L, Dilsiz Aytemir M, Vahedi P, et al. Targeting Mitochondrial Biogenesis with Polyphenol Compounds. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 May 20];2021:e4946711. Available from: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/omcl/2021/4946711/. [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Galilea M, Pérez-Matute P, Prieto-Hontoria PL, et al. α-Lipoic acid treatment increases mitochondrial biogenesis and promotes beige adipose features in subcutaneous adipocytes from overweight/obese subjects. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1851:273–281. [CrossRef]
- Shen W, Hao J, Feng Z, et al. Lipoamide or lipoic acid stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes via the endothelial NO synthase-cGMP-protein kinase G signalling pathway: Lipoamide, lipoic acid and mitochondrial biogenesis. British Journal of Pharmacology [Internet]. 2011 [cited 2023 May 20];162:1213–1224. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01134.x. [CrossRef]
- Shen W, Liu K, Tian C, et al. R-alpha-lipoic acid and acetyl-L-carnitine complementarily promote mitochondrial biogenesis in murine 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Diabetologia. 2008;51:165–174. [CrossRef]
- Nicassio L, Fracasso F, Sirago G, et al. Dietary supplementation with acetyl-l-carnitine counteracts age-related alterations of mitochondrial biogenesis, dynamics and antioxidant defenses in brain of old rats. Exp Gerontol. 2017;98:99–109. [CrossRef]
- Pesce V, Nicassio L, Fracasso F, et al. Acetyl-L-carnitine activates the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivators PGC-1α/PGC-1β-dependent signaling cascade of mitochondrial biogenesis and decreases the oxidized peroxiredoxins content in old rat liver. Rejuvenation Res. 2012;15:136–139. [CrossRef]
- Pesce V, Fracasso F, Cassano P, et al. Acetyl-L-carnitine supplementation to old rats partially reverts the age-related mitochondrial decay of soleus muscle by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1alpha-dependent mitochondrial biogenesis. Rejuvenation Res. 2010;13:148–151. [CrossRef]
- Hao J, Shen W, Yu G, et al. Hydroxytyrosol promotes mitochondrial biogenesis and mitochondrial function in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry [Internet]. 2010 [cited 2023 May 20];21:634–644. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0955286309000813. [CrossRef]
- Huang C, Chen D, Xie Q, et al. Nebivolol stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;438:211–217. [CrossRef]
- Valenti D, De Rasmo D, Signorile A, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate prevents oxidative phosphorylation deficit and promotes mitochondrial biogenesis in human cells from subjects with Down’s syndrome. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease [Internet]. 2013 [cited 2023 May 20];1832:542–552. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092544391200302X. [CrossRef]
- Lee M-S, Shin Y, Jung S, et al. Effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate on thermogenesis and mitochondrial biogenesis in brown adipose tissues of diet-induced obese mice. Food & Nutrition Research [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2023 May 20]; Available from: https://foodandnutritionresearch.net/index.php/fnr/article/view/1188. [CrossRef]
- Ha T, Kim MK, Park K, et al. Structural Modification of (−)-Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG) Shows Significant Enhancement in Mitochondrial Biogenesis. J Agric Food Chem [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2023 May 20];66:3850–3859. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b00364. [CrossRef]
- Rehman H, Krishnasamy Y, Haque K, et al. Green Tea Polyphenols Stimulate Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Improve Renal Function after Chronic Cyclosporin A Treatment in Rats. PLOS ONE [Internet]. 2013 [cited 2023 May 20];8:e65029. Available from: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0065029. [CrossRef]
- Rasbach KA, Schnellmann RG. Isoflavones Promote Mitochondrial Biogenesis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther [Internet]. 2008 [cited 2023 May 20];325:536–543. Available from: https://jpet.aspetjournals.org/content/325/2/536. [CrossRef]
- Henagan TM, Cefalu WT, Ribnicky DM, et al. In vivo effects of dietary quercetin and quercetin-rich red onion extract on skeletal muscle mitochondria, metabolism, and insulin sensitivity. Genes Nutr [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2023 May 20];10:2. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12263-014-0451-1. [CrossRef]
- You Y, Liang C, Han X, et al. Mulberry anthocyanins, cyanidin 3-glucoside and cyanidin 3-rutinoside, increase the quantity of mitochondria during brown adipogenesis. Journal of Functional Foods [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2023 May 20];36:348–356. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S175646461730395X. [CrossRef]
- You Y, Yuan X, Lee HJ, et al. Mulberry and mulberry wine extract increase the number of mitochondria during brown adipogenesis. Food Funct [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2023 May 20];6:401–408. Available from: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2015/fo/c4fo00719k. [CrossRef]
- Gomes JVP, Rigolon TCB, Souza MS da S, et al. Antiobesity effects of anthocyanins on mitochondrial biogenesis, inflammation, and oxidative stress: A systematic review. Nutrition [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2023 May 20];66:192–202. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0899900719300073. [CrossRef]
- Su K-Y, Yu CY, Chen Y-W, et al. Rutin, a Flavonoid and Principal Component of Saussurea Involucrata, Attenuates Physical Fatigue in a Forced Swimming Mouse Model. International Journal of Medical Sciences [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2023 May 20];11:528–537. Available from: https://www.medsci.org/v11p0528.htm. [CrossRef]
- Hamidie RDR, Yamada T, Ishizawa R, et al. Curcumin treatment enhances the effect of exercise on mitochondrial biogenesis in skeletal muscle by increasing cAMP levels. Metabolism - Clinical and Experimental [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2023 May 20];64:1334–1347. Available from: https://www.metabolismjournal.com/article/S0026-0495(15)00190-0/fulltext. [CrossRef]
- Rashedinia M, Saberzadeh J, Khosravi Bakhtiari T, et al. Glycyrrhizic Acid Ameliorates Mitochondrial Function and Biogenesis Against Aluminum Toxicity in PC12 Cells. Neurotox Res [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2023 May 20];35:584–593. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-018-9967-2. [CrossRef]
- Mogalli R, Matsukawa T, Shimomura O, et al. Cyanidin-3-glucoside enhances mitochondrial function and biogenesis in a human hepatocyte cell line. Cytotechnology [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2023 May 20];70:1519–1528. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-018-0242-4. [CrossRef]
- Kou G, Li Z, Wu C, et al. Citrus Tangeretin Improves Skeletal Muscle Mitochondrial Biogenesis via Activating the AMPK-PGC1-α Pathway In Vitro and In Vivo: A Possible Mechanism for Its Beneficial Effect on Physical Performance. J Agric Food Chem [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2023 May 20];66:11917–11925. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b04124. [CrossRef]
- Lee M-S, Kim Y. Effects of Isorhamnetin on Adipocyte Mitochondrial Biogenesis and AMPK Activation. Molecules [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2023 May 20];23:1853. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/23/8/1853. [CrossRef]
- Dusabimana T, Kim SR, Kim HJ, et al. Nobiletin ameliorates hepatic ischemia and reperfusion injury through the activation of SIRT-1/FOXO3a-mediated autophagy and mitochondrial biogenesis. Exp Mol Med [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2023 May 20];51:1–16. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/s12276-019-0245-z. [CrossRef]
- Hiramitsu M, Shimada Y, Kuroyanagi J, et al. Eriocitrin ameliorates diet-induced hepatic steatosis with activation of mitochondrial biogenesis. Sci Rep [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2023 May 20];4:3708. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/srep03708. [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi R, Yoshida T, Nii Y, et al. Sudachitin, a polymethoxylated flavone, improves glucose and lipid metabolism by increasing mitochondrial biogenesis in skeletal muscle. Nutrition & Metabolism [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2023 May 20];11:32. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-7075-11-32. [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto H, Morino K, Mengistu L, et al. Amla Enhances Mitochondrial Spare Respiratory Capacity by Increasing Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Antioxidant Systems in a Murine Skeletal Muscle Cell Line. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2023 May 20];2016:e1735841. Available from: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/omcl/2016/1735841/. [CrossRef]
- Kim H-L, Park J, Park H, et al. Platycodon grandiflorum A. De Candolle Ethanolic Extract Inhibits Adipogenic Regulators in 3T3-L1 Cells and Induces Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Primary Brown Preadipocytes. J Agric Food Chem [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2023 May 20];63:7721–7730. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b01908. [CrossRef]
- Ajaz S, McPhail MJ, Singh KK, et al. Mitochondrial metabolic manipulation by SARS-CoV-2 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with COVID-19. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 May 22];320:C57–C65. Available from: https://journals.physiology.org/doi/full/10.1152/ajpcell.00426.2020. [CrossRef]
- Abramczyk H, Brozek-Pluska B, Beton K. Decoding COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine Immunometabolism in Central Nervous System: human brain normal glial and glioma cells by Raman imaging [Internet]. bioRxiv; 2022 [cited 2023 May 22]. p. 2022.03.02.482639. Available from: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.03.02.482639v1. [CrossRef]
- Nunn AVW, Guy GW, Brysch W, et al. Understanding Long COVID; Mitochondrial Health and Adaptation—Old Pathways, New Problems. Biomedicines [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 May 22];10:3113. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9059/10/12/3113. [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Resendiz KJG, Benitez-Trinidad AB, Covantes-Rosales CE, et al. Loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) in leucocytes as post-COVID-19 sequelae. Journal of Leukocyte Biology [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 May 22];112:23–29. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/JLB.3MA0322-279RRR. [CrossRef]
- Guntur VP, Nemkov T, de Boer E, et al. Signatures of Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Impaired Fatty Acid Metabolism in Plasma of Patients with Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC). Metabolites [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 May 22];12:1026. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2218-1989/12/11/1026. [CrossRef]
- Prasada Kabekkodu S, Chakrabarty S, Jayaram P, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronaviruses contributing to mitochondrial dysfunction: Implications for post-COVID complications. Mitochondrion [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2023 May 22];69:43–56. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1567724923000053. [CrossRef]
- Mikirova N, Casciari J, Rogers A, et al. Effect of high-dose intravenous vitamin C on inflammation in cancer patients. Journal of Translational Medicine [Internet]. 2012 [cited 2023 May 22];10:189. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5876-10-189. [CrossRef]
- Kc S, Càrcamo JM, Golde DW. Vitamin C enters mitochondria via facilitative glucose transporter 1 (Gluti) and confers mitochondrial protection against oxidative injury. The FASEB Journal [Internet]. 2005 [cited 2023 Apr 8];19:1657–1667. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1096/fj.05-4107com. [CrossRef]
- Carr AC, Maggini S. Vitamin C and Immune Function. Nutrients [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2023 May 22];9:1211. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/9/11/1211. [CrossRef]
- Vineetha RC, Mathews VV, Nair RH. Chapter 28 - Ascorbic acid and the mitochondria. In: de Oliveira MR, editor. Mitochondrial Physiology and Vegetal Molecules [Internet]. Academic Press; 2021 [cited 2023 May 22]. p. 613–624. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128215623000344. [CrossRef]
- Otten AT, Bourgonje AR, Peters V, et al. Vitamin C Supplementation in Healthy Individuals Leads to Shifts of Bacterial Populations in the Gut-A Pilot Study. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021;10:1278. [CrossRef]
- Giannos P, Prokopidis K. Gut dysbiosis and long COVID-19: Feeling gutted. J Med Virol [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 May 22];94:2917–2918. Available from: https://europepmc.org/articles/PMC9088471. [CrossRef]
- Ancona G, Alagna L, Alteri C, et al. Gut and airway microbiota dysbiosis and their role in COVID-19 and long-COVID. Frontiers in Immunology [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2023 May 22];14. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1080043. [CrossRef]
- Vollbracht C, Kraft K. Feasibility of Vitamin C in the Treatment of Post Viral Fatigue with Focus on Long COVID, Based on a Systematic Review of IV Vitamin C on Fatigue. Nutrients [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 Jan 10];13:1154. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/13/4/1154. [CrossRef]
- Izzo R, Trimarco V, Mone P, et al. Combining L-Arginine with vitamin C improves long-COVID symptoms: The LINCOLN Survey. Pharmacol Res. 2022;183:106360. [CrossRef]
- Tosato M, Calvani R, Picca A, et al. Effects of l-Arginine Plus Vitamin C Supplementation on Physical Performance, Endothelial Function, and Persistent Fatigue in Adults with Long COVID: A Single-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2022;14:4984. [CrossRef]
- Rushworth GF, Megson IL. Existing and potential therapeutic uses for N-acetylcysteine: The need for conversion to intracellular glutathione for antioxidant benefits. Pharmacology & Therapeutics [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2023 Apr 8];141:150–159. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0163725813001952. [CrossRef]
- Cnubben NHP, Rietjens IMCM, Wortelboer H, et al. The interplay of glutathione-related processes in antioxidant defense. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology [Internet]. 2001 [cited 2023 May 22];10:141–152. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1382668901000771.
- Tenório MC dos S, Graciliano NG, Moura FA, et al. N-Acetylcysteine (NAC): Impacts on Human Health. Antioxidants [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 May 22];10:967. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3921/10/6/967. [CrossRef]
- Atkuri KR, Mantovani JJ, Herzenberg LA, et al. N-Acetylcysteine—a safe antidote for cysteine/glutathione deficiency. Current Opinion in Pharmacology [Internet]. 2007 [cited 2023 May 22];7:355–359. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1471489207000896. [CrossRef]
- Aparicio-Trejo OE, Reyes-Fermín LM, Briones-Herrera A, et al. Protective effects of N-acetyl-cysteine in mitochondria bioenergetics, oxidative stress, dynamics and S-glutathionylation alterations in acute kidney damage induced by folic acid. Free Radical Biology and Medicine [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2023 May 22];130:379–396. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0891584918312449. [CrossRef]
- Kumar P, Liu C, Hsu JW, et al. Glycine and N-acetylcysteine (GlyNAC) supplementation in older adults improves glutathione deficiency, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammation, insulin resistance, endothelial dysfunction, genotoxicity, muscle strength, and cognition: Results of a pilot clinical trial. Clinical and Translational Medicine [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 May 22];11:e372. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/ctm2.372. [CrossRef]
- Barbagallo M, Veronese N, Dominguez LJ. Magnesium in Aging, Health and Diseases. Nutrients [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 May 22];13:463. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/13/2/463. [CrossRef]
- Nouri-Majd S, Ebrahimzadeh A, Mousavi SM, et al. Higher Intake of Dietary Magnesium Is Inversely Associated With COVID-19 Severity and Symptoms in Hospitalized Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study. Frontiers in Nutrition [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 May 22];9. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2022.873162. [CrossRef]
- Racay P. Effect of magnesium on calcium-induced depolarisation of mitochondrial transmembrane potential. Cell Biology International [Internet]. 2008 [cited 2023 May 22];32:136–145. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1065699507002223. [CrossRef]
- Pilchova I, Klacanova K, Tatarkova Z, et al. The Involvement of Mg2+ in Regulation of Cellular and Mitochondrial Functions. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2023 May 22];2017:e6797460. Available from: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/omcl/2017/6797460/. [CrossRef]
- Di Y, He Y-L, Zhao T, et al. Methylene Blue Reduces Acute Cerebral Ischemic Injury via the Induction of Mitophagy. Mol Med [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2023 May 23];21:420–429. Available from: https://molmed.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.2119/molmed.2015.00038. [CrossRef]
- Tucker D, Lu Y, Zhang Q. From Mitochondrial Function to Neuroprotection—an Emerging Role for Methylene Blue. Mol Neurobiol [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2023 May 23];55:5137–5153. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0712-2. [CrossRef]
- Poteet E, Winters A, Yan L-J, et al. Neuroprotective Actions of Methylene Blue and Its Derivatives. PLOS ONE [Internet]. 2012 [cited 2023 May 23];7:e48279. Available from: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0048279. [CrossRef]
- Chuang S-T, Papp H, Kuczmog A, et al. Methylene Blue Is a Nonspecific Protein–Protein Interaction Inhibitor with Potential for Repurposing as an Antiviral for COVID-19. Pharmaceuticals [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 May 23];15:621. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8247/15/5/621. [CrossRef]
- Kidd SA, Lancaster P a. L, Anderson JC, et al. Fetal Death After Exposure to Methylene Blue Dye During Mid-Trimester Amniocentesis in Twin Pregnancy. Prenatal Diagnosis [Internet]. 1996 [cited 2023 May 23];16:39–47. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/%28SICI%291097-0223%28199601%2916%3A1%3C39%3A%3AAID-PD789%3E3.0.CO%3B2-P. [CrossRef]
- Gillman, PK. Gillman PK. CNS toxicity involving methylene blue: the exemplar for understanding and predicting drug interactions that precipitate serotonin toxicity. J Psychopharmacol [Internet]. 2011 [cited 2023 May 23];25:429–436. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1177/0269881109359098. [CrossRef]
- Brasche S, Bischof W. Daily time spent indoors in German homes – Baseline data for the assessment of indoor exposure of German occupants. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health [Internet]. 2005 [cited 2023 May 23];208:247–253. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1438463905000635. [CrossRef]
- Dörre WH. Time-activity-patterns of some selected small groups as a basis for exposure estimation: a methodological study. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol. 1997;7:471–491.
- Wang S-J, Chen M-Y. The effects of sunlight exposure therapy on the improvement of depression and quality of life in post-stroke patients: A RCT study. Heliyon [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2023 May 23];6:e04379. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405844020312238. [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist PG, Epstein E, Nielsen K, et al. Avoidance of sun exposure as a risk factor for major causes of death: a competing risk analysis of the Melanoma in Southern Sweden cohort. J Intern Med. 2016;280:375–387. [CrossRef]
- Holick MF. Chapter 4 - Photobiology of Vitamin D. In: Feldman D, editor. Vitamin D (Fourth Edition) [Internet]. Academic Press; 2018 [cited 2023 May 23]. p. 45–55. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128099650000045. [CrossRef]
- Walski T, Dąbrowska K, Drohomirecka A, et al. The effect of red-to-near-infrared (R/NIR) irradiation on inflammatory processes. Int J Radiat Biol. 2019;95:1326–1336. [CrossRef]
- Begum R, Calaza K, Kam JH, et al. Near-infrared light increases ATP, extends lifespan and improves mobility in aged Drosophila melanogaster. Biology Letters [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2023 May 23];11:20150073. Available from: https://royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/full/10.1098/rsbl.2015.0073. [CrossRef]
- Hobday RA, Cason JW. The Open-Air Treatment of PANDEMIC INFLUENZA. Am J Public Health [Internet]. 2009 [cited 2023 May 23];99:S236–S242. Available from: https://ajph.aphapublications.org/doi/full/10.2105/AJPH.2008.134627. [CrossRef]
- Tsai S-R, Hamblin MR. Biological effects and medical applications of infrared radiation. J Photochem Photobiol B [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2022 Jul 7];170:197–207. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5505738/. [CrossRef]
- Shamloo S, Defensor E, Ciari P, et al. The anti-inflammatory effects of photobiomodulation are mediated by cytokines: Evidence from a mouse model of inflammation. Frontiers in Neuroscience [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2023 May 23];17. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnins.2023.1150156. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen LM-D, Malamo AG, Larkin-Kaiser KA, et al. Effect of near-infrared light exposure on mitochondrial signaling in C2C12 muscle cells. Mitochondrion. 2014;14:42–48. [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Resendiz KJG, Covantes-Rosales CE, Benítez-Trinidad AB, et al. Effect of Fucoidan on the Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (ΔΨm) of Leukocytes from Patients with Active COVID-19 and Subjects That Recovered from SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Marine Drugs [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 May 22];20:99. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/1660-3397/20/2/99. [CrossRef]
- Vásquez-Reyes S, Velázquez-Villegas LA, Vargas-Castillo A, et al. Dietary bioactive compounds as modulators of mitochondrial function. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 May 23];96:108768. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0955286321001881. [CrossRef]
- Forbes-Hernández TY, Giampieri F, Gasparrini M, et al. The effects of bioactive compounds from plant foods on mitochondrial function: A focus on apoptotic mechanisms. Food and Chemical Toxicology [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2023 May 23];68:154–182. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S027869151400146X. [CrossRef]
- Rai PK, Russell OM, Lightowlers RN, et al. Potential compounds for the treatment of mitochondrial disease. British Medical Bulletin [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2023 May 23];116:5–18. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1093/bmb/ldv046. [CrossRef]
| Spiritual Tradition | World Region | Fasting Rituals |
|---|---|---|
| Islam | Middle East, Africa, Asia, and beyond | Ramadan: Observing a month-long fast from sunrise to sunset as a religious obligation [6]. |
| Christianity | Europe, Americas, Africa, Asia, and beyond | Lent: Fasting for a period of 40 days leading up to Easter, often involving specific dietary restrictions [6]. |
| Buddhism | East Asia, Southeast Asia, South Asia | Uposatha: Observing monthly fasting days to purify the mind and reaffirm spiritual commitments [6]. |
| Hinduism | South Asia, Southeast Asia, Mauritius | Ekadashi: Fasting on the 11th day of each lunar fortnight, abstaining from grains and certain foods [6]. |
| Judaism | Middle East, Europe, Americas, Africa, Asia | Yom Kippur: Observing a 24-hour fast as a day of atonement and repentance [6]. |
| Bahá'í Faith | Global | Nineteen-Day Fast: Fasting from sunrise to sunset during the last month of the Bahá'í calendar [6]. |
| Jainism | India, East Africa | Ayambil: Observing a one-day fast by consuming only boiled water and specific foods. [3] |
| Native American | Americas | Vision Quest: Fasting and solitary retreat to seek spiritual guidance and connection with nature.Sun dance: Fasting and dancing, without water for multiple straight days [4] Plant dietas: Preparation for ceremony [5] |
| Sufism | Middle East, South Asia, North Africa, Europe | Chilla: Engaging in extended periods of fasting and meditation for spiritual growth and purification. [7] |
| Mormonism (Church of Latter Day Saints) |
North America | Fasting one day each month [6] |
| Medical Tradition | Region | Fasting Rituals |
| Ayurveda | India, South Asia | Upavasa: Observing occasional fasting as a means to cleanse the body, balance doshas, and support digestion [10]. |
| Traditional Chinese Medicine | China, East Asia | Daoist Fasting: Engaging in intermittent or prolonged fasting to restore harmony and promote vitality [11]. |
| Naturopathy | Europe, Global | Juice Fasting: Consuming only fresh fruit or vegetable juices for a specific duration to support detoxification and rejuvenation [12]. |
| Siddha Medicine | India | Ekadashi Fasting: Observing fasting on specific lunar days to eliminate toxins, promote purification, and enhance energy levels [13]. |
| Western Medicine | Global | Preoperative Fasting: Temporarily refraining from food and drink before surgical procedures to minimize the risk of complications [14]. |
| Greek Medicine | Ancient Greece, Mediterranean | Fasting was used in the treatment of epilepsy [15]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




