Submitted:
16 June 2023
Posted:
19 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
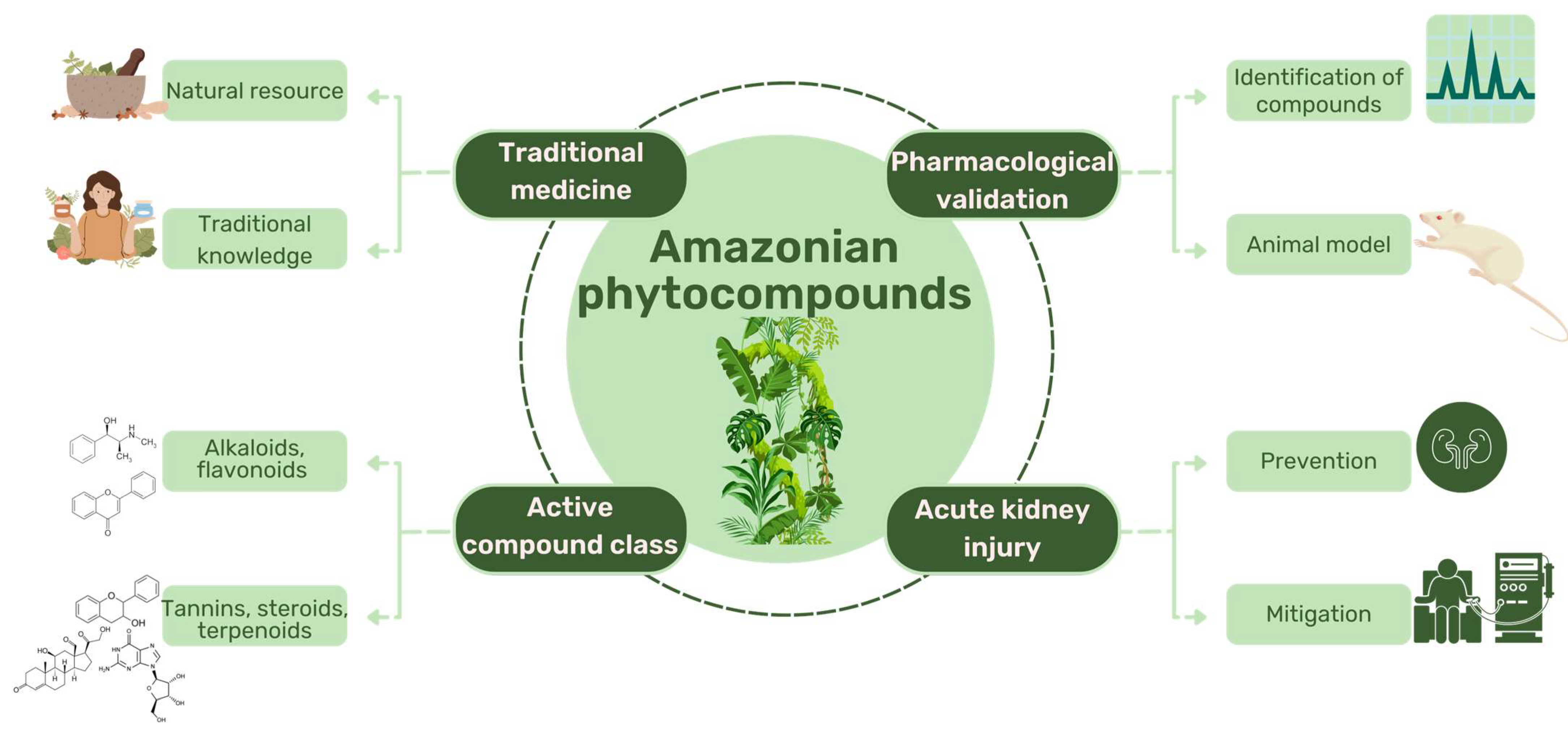
2. Secondary Metabolites and Nephroprotective Potential in Amazonian Plant Species
2.1. Classes of Compounds Present in Amazonian Plant Species
2.1.1. Alkaloids
2.1.2. Flavonoids
2.1.3. Tannins
2.1.4. Steroids
2.1.5. Terpenoids
2.2. Nefroprotective Potential of Amazonian Plant Species
2.2.1. Banisteriopsis caapi (Spruce ex Griseb.) Morton
2.2.2. Peganum harmala L.
2.2.3. Passiflora edulis Sims
2.2.4. Annona muricata L.
2.2.5. Uncaria tomentosa (Willd.) DC.
2.2.6. Hymenaea courbaril L.
2.2.7. Echinodorus macrophyllus (Kunth) Micheli
2.2.8. Acmella oleracea (L.) R. K. Jansen
2.2.9. Rosmarinus officinalis L.
2.3. Nefroprotective Potential of Compounds from Amazonian Plant Species
3. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koga, R. de C.R.; Teixeira dos Santos, A.V.T. de L.; Rodrigues Sarquis, R. do S.F.; Carvalho, J.C.T. Bauhinia Guianensis Aubl., a Plant from Amazon Biome with Promising Biologically Active Properties: A Systematic Review. Pharmacogn Rev 2021, 15, 76–81. [CrossRef]
- Sales, P.F.; Koga, R. de C.R.; de Souza, A.A.; do Nascimento, A.L.; Pinheiro, F.C.; Alberto, A.K.M.; da Costa, M.J.; Carvalho, J.C.T. Pharmacological Potential and Mechanisms of Action Involved in Oil Species from the Brazilian Amazon: The Case of Abelmoschus Esculentus L. Moench, Euterpe Oleracea Martius and Bixa Orellana Linné. Pharmacogn Rev 2023, 24–42. [CrossRef]
- Méril-Mamert, V.; Ponce-Mora, A.; Sylvestre, M.; Lawrence, G.; Bejarano, E.; Cebrián-Torrejón, G. Antidiabetic Potential of Plants from the Caribbean Basin. Plants 2022, 11, 1360. [CrossRef]
- Rates, S.M.K. Plants as Source of Drugs. Toxicon 2001, 39, 603–613. [CrossRef]
- Heitor, R. da S.; Daniele, da C. de A.; Ariadna, L.P.; Hady, K.; Jesus, R.R.A.; José, C.T.C. Euterpe Oleracea Mart. (Aai): An Old Known Plant with a New Perspective. Afr J Pharm Pharmacol 2016, 10, 995–1006. [CrossRef]
- Carvalho J Fitoterápicos Anti-Inflamatórios; 2nd ed.; Pharmabooks: São Paulo, 2017; ISBN 139788589731805.
- Carvalho, J.C.T.; Perazzo, F.F.; Machado, L.; Bereau, D. Biologic Activity and Biotechnological Development of Natural Products. Biomed Res Int 2013, 2013, 1–4. [CrossRef]
- Isgut, M.; Rao, M.; Yang, C.; Subrahmanyam, V.; Rida, P.C.G.; Aneja, R. Application of Combination High-Throughput Phenotypic Screening and Target Identification Methods for the Discovery of Natural Product-Based Combination Drugs. Med Res Rev 2018, 38, 504–524. [CrossRef]
- Najmi, A.; Javed, S.A.; al Bratty, M.; Alhazmi, H.A. Modern Approaches in the Discovery and Development of Plant-Based Natural Products and Their Analogues as Potential Therapeutic Agents. Molecules 2022, 27, 349. [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.G.; Lee, H.K.; Cho, K.B.; Park, S. il A Review of Natural Products for Prevention of Acute Kidney Injury. Medicina (B Aires) 2021, 57, 1266. [CrossRef]
- Neyra, J.A.; Chawla, L.S. Acute Kidney Disease to Chronic Kidney Disease. Crit Care Clin 2021, 37, 453–474. [CrossRef]
- Kellum, J.A.; Romagnani, P.; Ashuntantang, G.; Ronco, C.; Zarbock, A.; Anders, H.-J. Acute Kidney Injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2021, 7, 52. [CrossRef]
- Macedo, E.; Bouchard, J.; Soroko, S.H.; Chertow, G.M.; Himmelfarb, J.; Ikizker, T.A.; Paganini, E.P.; Mehta, R.L. Fluid Accumulation, Recognition and Staging of Acute Kidney Injury in Critically-Ill Patients. Crit Care 2010, 14, R82. [CrossRef]
- Lewington, A.J.P.; Cerdá, J.; Mehta, R.L. Raising Awareness of Acute Kidney Injury: A Global Perspective of a Silent Killer. Kidney Int 2013, 84, 457–467. [CrossRef]
- Makris, K.; Spanou, L. Acute Kidney Injury: Definition, Pathophysiology and Clinical Phenotypes. Clin Biochem Rev 2016, 37, 85–98.
- Pamunuwa, G.; Karunaratne, D.N.; Waisundara, V.Y. Antidiabetic Properties, Bioactive Constituents, and Other Therapeutic Effects of Scoparia Dulcis. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2016, 2016, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Stöckigt, J. Trends for Diverse Production Strategies of Plant Medicinal Alkaloids. Nat Prod Rep 2010, 27, 1469. [CrossRef]
- Zenk, M.H.; Juenger, M. Evolution and Current Status of the Phytochemistry of Nitrogenous Compounds. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 2757–2772. [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, B. Roles of Alkaloids from Medicinal Plants in the Management of Diabetes Mellitus. J Chem 2021, 2021, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Putra, I.M.W.A.; Fakhrudin, N.; Nurrochmad, A.; Wahyuono, S. A Review of Medicinal Plants with Renoprotective Activity in Diabetic Nephropathy Animal Models. Life 2023, 13, 560. [CrossRef]
- Gangasani, J.K.; Pemmaraju, D.B.; Murthy, U.S.N.; Rengan, A.K.; Naidu, V.G.M. Chemistry of Herbal Biomolecules. In Herbal Biomolecules in Healthcare Applications; Elsevier, 2022; pp. 63–79.
- Sawant, M.; Isaac, J.C.; Narayanan, S. Analgesic Studies on Total Alkaloids and Alcohol Extracts of Eclipta Alba (Linn.) Hassk. Phytotherapy Research 2004, 18, 111–113. [CrossRef]
- Morales-García, J.A.; de la Fuente Revenga, M.; Alonso-Gil, S.; Rodríguez-Franco, M.I.; Feilding, A.; Perez-Castillo, A.; Riba, J. The Alkaloids of Banisteriopsis Caapi, the Plant Source of the Amazonian Hallucinogen Ayahuasca, Stimulate Adult Neurogenesis in Vitro. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 5309. [CrossRef]
- Batista, L.L.; Nascimento, L.C. do; Guimarães, G.F.; Matias Pereira, A.C.; Koga, R. de C.R.; Teixeira dos Santos, A.V.T. de L.; Fernandes, C.P.; Teixeira, T.A.; Hu, Y.; Hu, X.; et al. A Review of Medicinal Plants Traditionally Used to Treat Male Sexual Dysfunctions – the Overlooked Potential of Acmella Oleracea (L.) R.K. Jansen. Pharmacogn Rev 2021, 15, 01–11. [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, H.; Yarani, R.; Pociot, F.; Popović-Djordjević, J. Anti-Diabetic Potential of Plant Alkaloids: Revisiting Current Findings and Future Perspectives. Pharmacol Res 2020, 155, 104723. [CrossRef]
- Salahshoor, M.; Roshankhah, S.; Motavalian, V.; Jalili, C. Effect of Harmine on Nicotine-Induced Kidney Dysfunction in Male Mice. Int J Prev Med 2019, 10, 97. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Boonen, J.; Chauhan, N.S.; Thakur, M.; de Spiegeleer, B.; Dixit, V.K. Spilanthes Acmella Ethanolic Flower Extract: LC–MS Alkylamide Profiling and Its Effects on Sexual Behavior in Male Rats. Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 1161–1169. [CrossRef]
- Beecher, G.R. Overview of Dietary Flavonoids: Nomenclature, Occurrence and Intake. J Nutr 2003, 133, S3248–S3254. [CrossRef]
- Banjarnahor, S.D.S.; Artanti, N. Antioxidant Properties of Flavonoids. Medical Journal of Indonesia 2015, 23, 239–244. [CrossRef]
- Van Acker, S.A.B.E.; Van Den Berg, D.; Tromp, M.N.J.L.; Griffioen, D.H.; Van Bennekom, W.P.; Van Der Vijgh, W.J.F.; Bast, A. Structural Aspects of Antioxidant Activity of Flavonoids. Free Radic Biol Med 1996, 20, 331–342. [CrossRef]
- Vinayagam, R.; Xu, B. Antidiabetic Properties of Dietary Flavonoids: A Cellular Mechanism Review. Nutr Metab (Lond) 2015, 12, 60. [CrossRef]
- Rufino, A.T.; Costa, V.M.; Carvalho, F.; Fernandes, E. Flavonoids as Antiobesity Agents: A Review. Med Res Rev 2021, 41, 556–585. [CrossRef]
- Unnikrishnan, M.K.; Veerapur, V.; Nayak, Y.; Mudgal, P.P.; Mathew, G. Antidiabetic, Antihyperlipidemic and Antioxidant Effects of the Flavonoids. In Polyphenols in Human Health and Disease; Elsevier, 2014; pp. 143–161.
- Maleki, S.J.; Crespo, J.F.; Cabanillas, B. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Flavonoids. Food Chem 2019, 299, 125124. [CrossRef]
- Di Carlo, G.; Mascolo, N.; Izzo, A.A.; Capasso, F. Flavonoids: Old and New Aspects of a Class of Natural Therapeutic Drugs. Life Sci 1999, 65, 337–353. [CrossRef]
- Al Aboody, M.S.; Mickymaray, S. Anti-Fungal Efficacy and Mechanisms of Flavonoids. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 45. [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Liu, T.; Chen, K.; Xia, Y.; Dai, W.; Xu, S.; Xu, L.; Wang, F.; Wu, L.; Li, J.; et al. Isorhamnetin: A Hepatoprotective Flavonoid Inhibits Apoptosis and Autophagy via P38/PPAR-α Pathway in Mice. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2018, 103, 800–811. [CrossRef]
- Vauzour, D.; Vafeiadou, K.; Rodriguez-Mateos, A.; Rendeiro, C.; Spencer, J.P.E. The Neuroprotective Potential of Flavonoids: A Multiplicity of Effects. Genes Nutr 2008, 3, 115–126. [CrossRef]
- Al-Khayri, J.M.; Sahana, G.R.; Nagella, P.; Joseph, B. V.; Alessa, F.M.; Al-Mssallem, M.Q. Flavonoids as Potential Anti-Inflammatory Molecules: A Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 2901. [CrossRef]
- Vargas, F.; Romecín, P.; García-Guillén, A.I.; Wangesteen, R.; Vargas-Tendero, P.; Paredes, M.D.; Atucha, N.M.; García-Estañ, J. Flavonoids in Kidney Health and Disease. Front Physiol 2018, 9. [CrossRef]
- Silva, W.T.; Santos, J.G. dos; Watanabe, M.; Vattimo, M. de F.F. Efeito Renoprotetor Dos Flavonoides Do Vinho Na Nefrotoxicidade Do Imunossupressor Tacrolimus. Acta Paulista de Enfermagem 2011, 24, 388–392. [CrossRef]
- Galati, G.; O’Brien, P.J. Potential Toxicity of Flavonoids and Other Dietary Phenolics: Significance for Their Chemopreventive and Anticancer Properties. Free Radic Biol Med 2004, 37, 287–303. [CrossRef]
- Orhan, D.D.; Özçelik, B.; Özgen, S.; Ergun, F. Antibacterial, Antifungal, and Antiviral Activities of Some Flavonoids. Microbiol Res 2010, 165, 496–504. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Banu, G.S.; Pappa, P.V.; Sundararajan, M.; Pandian, M.R. Hepatoprotective Activity of Trianthema Portulacastrum L. against Paracetamol and Thioacetamide Intoxication in Albino Rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2004, 92, 37–40. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Murugesan, A.G. Hypolipidaemic Activity of Helicteres Isora L. Bark Extracts in Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2008, 116, 161–166. [CrossRef]
- Barbehenn, R. V.; Peter Constabel, C. Tannins in Plant–Herbivore Interactions. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 1551–1565. [CrossRef]
- White, T. Tannins—Their Occurrence and Significance. J Sci Food Agric 1957, 8, 377–385. [CrossRef]
- Bacelo, H.A.M.; Santos, S.C.R.; Botelho, C.M.S. Tannin-Based Biosorbents for Environmental Applications – A Review. Chemical Engineering Journal 2016, 303, 575–587. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, Y. Tannins from Canarium Album with Potent Antioxidant Activity. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 2008, 9, 407–415. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-B.; Ding, Y.-S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.-B.; Cui, B.-S.; Bai, J.-Y.; Lin, M.-B.; Hou, Q.; Zhang, P.-C.; Li, S. Anti-Inflammatory Hydrolyzable Tannins from Myricaria Bracteata. J Nat Prod 2015, 78, 1015–1025. [CrossRef]
- Tamokou, J.D.D.; Mbaveng, A.T.; Kuete, V. Antimicrobial Activities of African Medicinal Spices and Vegetables. In Medicinal Spices and Vegetables from Africa; Elsevier, 2017; pp. 207–237.
- Okuda, T. Systematics and Health Effects of Chemically Distinct Tannins in Medicinal Plants. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 2012–2031. [CrossRef]
- Ajebli, M.; Eddouks, M. The Promising Role of Plant Tannins as Bioactive Antidiabetic Agents. Curr Med Chem 2019, 26, 4852–4884. [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Luo, C.; He, Y.; Huang, H.; Ran, F.; Liao, W.; Tan, P.; Fan, S.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, D.; et al. Hepatoprotective Effects of Different Extracts From Triphala Against CCl4-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice. Front Pharmacol 2021, 12. [CrossRef]
- Smeriglio, A.; Barreca, D.; Bellocco, E.; Trombetta, D. Proanthocyanidins and Hydrolysable Tannins: Occurrence, Dietary Intake and Pharmacological Effects. Br J Pharmacol 2017, 174, 1244–1262. [CrossRef]
- Oladele, J.O.; Oladele, O.T.; Ademiluyi, A.O.; Oyeleke, O.M.; Awosanya, O.O.; Oyewole, O.I. Chaya (Jatropha Tanjorensis) Leafs Protect against Sodium Benzoate Mediated Renal Dysfunction and Hepatic Damage in Rats. Clinical Phytoscience 2020, 6, 13. [CrossRef]
- Kolekar, S.M.; Jain, B.U.; Kondawarkar, M.S. A Review on Steroids and Terpenoids (Stereochemistry, Structural Elucidation, Isolation of Steroids and Terpenoids). Research Journal of Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms and Technology 2019, 11, 126. [CrossRef]
- Moreau, R.A.; Nyström, L.; Whitaker, B.D.; Winkler-Moser, J.K.; Baer, D.J.; Gebauer, S.K.; Hicks, K.B. Phytosterols and Their Derivatives: Structural Diversity, Distribution, Metabolism, Analysis, and Health-Promoting Uses. Prog Lipid Res 2018, 70, 35–61. [CrossRef]
- Asami, T. Brassinosteroid Biosynthesis Inhibitors. Trends Plant Sci 1999, 4, 348–353. [CrossRef]
- Jovanović-Šanta, S.S.; Petri, E.T.; Klisurić, O.R.; Szécsi, M.; Kovačević, R.; Petrović, J.A. Antihormonal Potential of Selected D-Homo and D-Seco Estratriene Derivatives. Steroids 2015, 97, 45–53. [CrossRef]
- Singh A R; Bajaj V K; Shekhawat P S; Singh K Screening of Potential Male Contraceptive Drugs from Natural Resources: An Overview. Int J Pharm Sci Res 2013, 4, 1654–1668.
- Thao, N.P.; Luyen, B.T.T.; Kim, E.J.; Kang, J. Il; Kang, H.K.; Cuong, N.X.; Nam, N.H.; Kiem, P. Van; Minh, C. Van; Kim, Y.H. Steroidal Constituents from the Edible Sea Urchin Diadema Savignyi Michelin Induce Apoptosis in Human Cancer Cells. J Med Food 2015, 18, 45–53. [CrossRef]
- Rattanasopa, C.; Phungphong, S.; Wattanapermpool, J.; Bupha-Intr, T. Significant Role of Estrogen in Maintaining Cardiac Mitochondrial Functions. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2015, 147, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Sultan, A. Steroids: A Diverse Class of Secondary Metabolites. Med Chem (Los Angeles) 2015, 5. [CrossRef]
- Aav, R.; Kanger, T.; Pehk, T.; Lopp, M. Unexpected Reactivity of Ethyl 2-(Diethylphosphono)Propionate Toward 2,2-Disubstituted-1,3-Cyclopentanediones. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat Elem 2005, 180, 1739–1748. [CrossRef]
- Espirito Santo, B.L.S. do; Santana, L.F.; Kato Junior, W.H.; de Araújo, F. de O.; Bogo, D.; Freitas, K. de C.; Guimarães, R. de C.A.; Hiane, P.A.; Pott, A.; Filiú, W.F. de O.; et al. Medicinal Potential of Garcinia Species and Their Compounds. Molecules 2020, 25, 4513. [CrossRef]
- Mahipal, P.; Pawar, R.S. Nephroprotective Effect of Murraya Koenigii on Cyclophosphamide Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats. Asian Pac J Trop Med 2017, 10, 808–812. [CrossRef]
- Dennis, J.; Witting, P. Protective Role for Antioxidants in Acute Kidney Disease. Nutrients 2017, 9, 718. [CrossRef]
- Ashour, M.; Wink, M.; Gershenzon, J. Biochemistry of Terpenoids: Monoterpenes, Sesquiterpenes and Diterpenes. In Biochemistry of Plant Secondary Metabolism; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK; pp. 258–303.
- Croteau R; Kutchan T M; Lewis N G Natural Products (Secondary Metabolites). In Biochemistry And molecular Biology of Plants; BUCHANAN B B, GRUISSEM W, JONES R L, Eds.; American Society of Plant Physiologists: Rockville, 2000; Vol. 24, pp. 1250–1319.
- Ludwiczuk, A.; Skalicka-Woźniak, K.; Georgiev, M.I. Terpenoids. In Pharmacognosy; Elsevier, 2017; pp. 233–266.
- Jahangeer, M.; Fatima, R.; Ashiq, M.; Basharat, A.; Qamar, S.A.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Therapeutic and Biomedical Potentialities of Terpenoids – A Review. J Pure Appl Microbiol 2021, 15, 471–483. [CrossRef]
- Vattimo, M. de F.F.; Silva, N.O. da Uncária Tomentosa e a Lesão Renal Aguda Isquêmica Em Ratos. Revista da Escola de Enfermagem da USP 2011, 45, 194–198. [CrossRef]
- Morton C V. Tropicos.Org. Missouri Botanical Garden.
- Schwarz, M.J.; Houghton, P.J.; Rose, S.; Jenner, P.; Lees, A.D. Activities of Extract and Constituents of Banisteriopsis Caapi Relevant to Parkinsonism. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2003, 75, 627–633. [CrossRef]
- Pic-Taylor, A.; da Motta, L.G.; de Morais, J.A.; Junior, W.M.; Santos, A. de F.A.; Campos, L.A.; Mortari, M.R.; von Zuben, M.V.; Caldas, E.D. Behavioural and Neurotoxic Effects of Ayahuasca Infusion (Banisteriopsis Caapi and Psychotria Viridis) in Female Wistar Rat. Behavioural Processes 2015, 118, 102–110. [CrossRef]
- Samoylenko, V.; Rahman, Md.M.; Tekwani, B.L.; Tripathi, L.M.; Wang, Y.-H.; Khan, S.I.; Khan, I.A.; Miller, L.S.; Joshi, V.C.; Muhammad, I. Banisteriopsis Caapi, a Unique Combination of MAO Inhibitory and Antioxidative Constituents for the Activities Relevant to Neurodegenerative Disorders and Parkinson’s Disease. J Ethnopharmacol 2010, 127, 357–367. [CrossRef]
- Santos, B.W.L.; Moreira, D.C.; Borges, T.K. dos S.; Caldas, E.D. Components of Banisteriopsis Caapi, a Plant Used in the Preparation of the Psychoactive Ayahuasca, Induce Anti-Inflammatory Effects in Microglial Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 2500. [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, A.; Jalili, C.; Salahshoor, M.; Javanmardy, S.; Ravankhah, S.; Akhshi, N. Harmine Mitigates Cisplatin-Induced Renal Injury in Male Mice through Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Apoptosis Effects. Res Pharm Sci 2022, 17, 417. [CrossRef]
- Araújo Galdino, O.; de Souza Gomes, I.; Ferreira de Almeida Júnior, R.; Conceição Ferreira de Carvalho, M.I.; Abreu, B.J.; Abbott Galvão Ururahy, M.; Cabral, B.; Zucolotto Langassner, S.M.; Costa de Souza, K.S.; Augusto de Rezende, A. The Nephroprotective Action of Passiflora Edulis in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 17546. [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Bai, M.; Li, H.; Li, L. Anxiolytic and Sedative Activities of Passiflora Edulis f. Flavicarpa. J Ethnopharmacol 2010, 128, 148–153. [CrossRef]
- Sena, L.M.; Zucolotto, S.M.; Reginatto, F.H.; Schenkel, E.P.; De Lima, T.C.M. Neuropharmacological Activity of the Pericarp of Passiflora Edulis Flavicarpa Degener: Putative Involvement of C -Glycosylflavonoids. Exp Biol Med 2009, 234, 967–975. [CrossRef]
- Doungue, H.T.; Kengne, A.P.N.; Kuate, D. Neuroprotective Effect and Antioxidant Activity of Passiflora Edulis Fruit Flavonoid Fraction, Aqueous Extract, and Juice in Aluminum Chloride-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease Rats. Nutrire 2018, 43, 23. [CrossRef]
- Taïwe, G.S.; Kuete, V. Passiflora Edulis. In Medicinal Spices and Vegetables from Africa; Elsevier, 2017; pp. 513–526.
- Chan, W.-J.J.; McLachlan, A.J.; Hanrahan, J.R.; Harnett, J.E. The Safety and Tolerability of Annona Muricata Leaf Extract: A Systematic Review. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 2019, 72, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Gyesi, J.N.; Opoku, R.; Borquaye, L.S. Chemical Composition, Total Phenolic Content, and Antioxidant Activities of the Essential Oils of the Leaves and Fruit Pulp of Annona Muricata L. (Soursop) from Ghana. Biochem Res Int 2019, 2019, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Adewole, S.; Caxton-Martins, E. Morphological Changes and Hypoglycemic Effects of Annona Muricata Linn. (Annonaceae) Leaf Aqueous Extract on Pancreatic β-Cells of Streptozotocin-Treated Diabetic Rats. African Journal of Biomedical Research 2009, 9. [CrossRef]
- Pilarski, R.; Zieliński, H.; Ciesiołka, D.; Gulewicz, K. Antioxidant Activity of Ethanolic and Aqueous Extracts of Uncaria Tomentosa (Willd.) DC. J Ethnopharmacol 2006, 104, 18–23. [CrossRef]
- Batiha, G.E.-S.; Magdy Beshbishy, A.; Wasef, L.; Elewa, Y.H.A.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Taha, A.E.; Al-Sagheer, A.A.; Devkota, H.P.; Tufarelli, V. Uncaria Tomentosa (Willd. Ex Schult.) DC.: A Review on Chemical Constituents and Biological Activities. Applied Sciences 2020, 10, 2668. [CrossRef]
- Khoo, S.F.; Oehlschlager, A.C.; Ourisson, G. Structure and Stereochemistry of the Diterpenes of Hymenaea Courbaril (Caesalpinioideae) Seed Pod Resin. Tetrahedron 1973, 29, 3379–3388. [CrossRef]
- SPERA, K.D.; FIGUEIREDO, P.A.; SANTOS, P.C.E.; BARBOSA, F.C.; ALVES, C.P.; DOKKEDAL, A.L.; SALDANHA, L.L.; SILVA, L.P.; FIGUEIREDO, C.R.; FERREIRA, P.C.; et al. Genotoxicity, Anti-Melanoma and Antioxidant Activities of Hymenaea Courbaril L. Seed Extract. An Acad Bras Cienc 2019, 91. [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.M.; Miranda, R.R.S.; Ferraz, V.P.; Pereira, M.T.; de Siqueira, E.P.; Alcântara, A.F.C. Changes in the Essential Oil Composition of Leaves of Echinodorus Macrophyllus Exposed to γ-Radiation. Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia 2013, 23, 600–607. [CrossRef]
- Gasparotto, F.; Lívero, F.; Palozi, R.; Ames, M.; Nunes, B.; Donadel, G.; Ribeiro, R.; Lourenço, E.; Kassuya, C.; Junior, A. Heart-Protective Effects of Echinodorus Grandiflorus in Rabbits That Are Fed a High-Cholesterol Diet. Planta Med 2018, 84, 1271–1279. [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, D.C.; Martins, B.P.M.P.; Medeiros, D.L.; Santos, S. V.; Gayer, C.R.; Velozo, L.S.; Coelho, M.G. Antinociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of the Hexanic Extract of" Echinodorus Macrophyllus"(Kunth) Micheli in Mice. Brazilian Journal of Health and Biomedical Sciences 2019, 18, 25–32.
- Spinozzi, E.; Ferrati, M.; Baldassarri, C.; Cappellacci, L.; Marmugi, M.; Caselli, A.; Benelli, G.; Maggi, F.; Petrelli, R. A Review of the Chemistry and Biological Activities of Acmella Oleracea (“Jambù”, Asteraceae), with a View to the Development of Bioinsecticides and Acaricides. Plants 2022, 11, 2721. [CrossRef]
- Abeysiri, G.R.P.I.; Dharmadasa, R.M.; Abeysinghe, D.C.; Samarasinghe, K. Screening of Phytochemical, Physico-Chemical and Bioactivity of Different Parts of Acmella Oleraceae Murr. (Asteraceae), a Natural Remedy for Toothache. Ind Crops Prod 2013, 50, 852–856. [CrossRef]
- Prachayasittikul, S.; Suphapong, S.; Worachartcheewan, A.; Lawung, R.; Ruchirawat, S.; Prachayasittikul, V. Bioactive Metabolites from Spilanthes Acmella Murr. Molecules 2009, 14, 850–867. [CrossRef]
- Batista, L.L.; Koga, R. de C.R.; Teixeira, A.V.T. de L.; Teixeira, T.A.; de Melo, E.L.; Carvalho, J.C.T. Clinical Safety of a Pharmaceutical Formulation Containing an Extract of Acmella Oleracea (L.) in Patients With Premature Ejaculation: A Pilot Study. Am J Mens Health 2023, 17, 155798832311678. [CrossRef]
- Souza, G.; Dias Ribeiro da Silva, I.; Duarte Viana, M.; Costa de Melo, N.; Sánchez-Ortiz, B.; Maia Rebelo de Oliveira, M.; Ramos Barbosa, W.; Maciel Ferreira, I.; Tavares Carvalho, J. Acute Toxicity of the Hydroethanolic Extract of the Flowers of Acmella Oleracea L. in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio): Behavioral and Histopathological Studies. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 173. [CrossRef]
- Borges, R.S.; Ortiz, B.L.S.; Pereira, A.C.M.; Keita, H.; Carvalho, J.C.T. Rosmarinus Officinalis Essential Oil: A Review of Its Phytochemistry, Anti-Inflammatory Activity, and Mechanisms of Action Involved. J Ethnopharmacol 2019, 229, 29–45. [CrossRef]
- Uritu, C.M.; Mihai, C.T.; Stanciu, G.-D.; Dodi, G.; Alexa-Stratulat, T.; Luca, A.; Leon-Constantin, M.-M.; Stefanescu, R.; Bild, V.; Melnic, S.; et al. Medicinal Plants of the Family Lamiaceae in Pain Therapy: A Review. Pain Res Manag 2018, 2018, 1–44. [CrossRef]
- Linnaeus C V. Tropicos.Org. Missouri Botanical Garden.
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Sun, W.; Cheng, Q. Improving Health Benefits with Considering Traditional and Modern Health Benefits of Peganum Harmala. Clinical Phytoscience 2021, 7, 18. [CrossRef]
- Niroumand, M.C.; Farzaei, M.H.; Amin, G. Medicinal Properties of Peganum Harmala L. in Traditional Iranian Medicine and Modern Phytotherapy: A Review. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2015, 35, 104–109. [CrossRef]
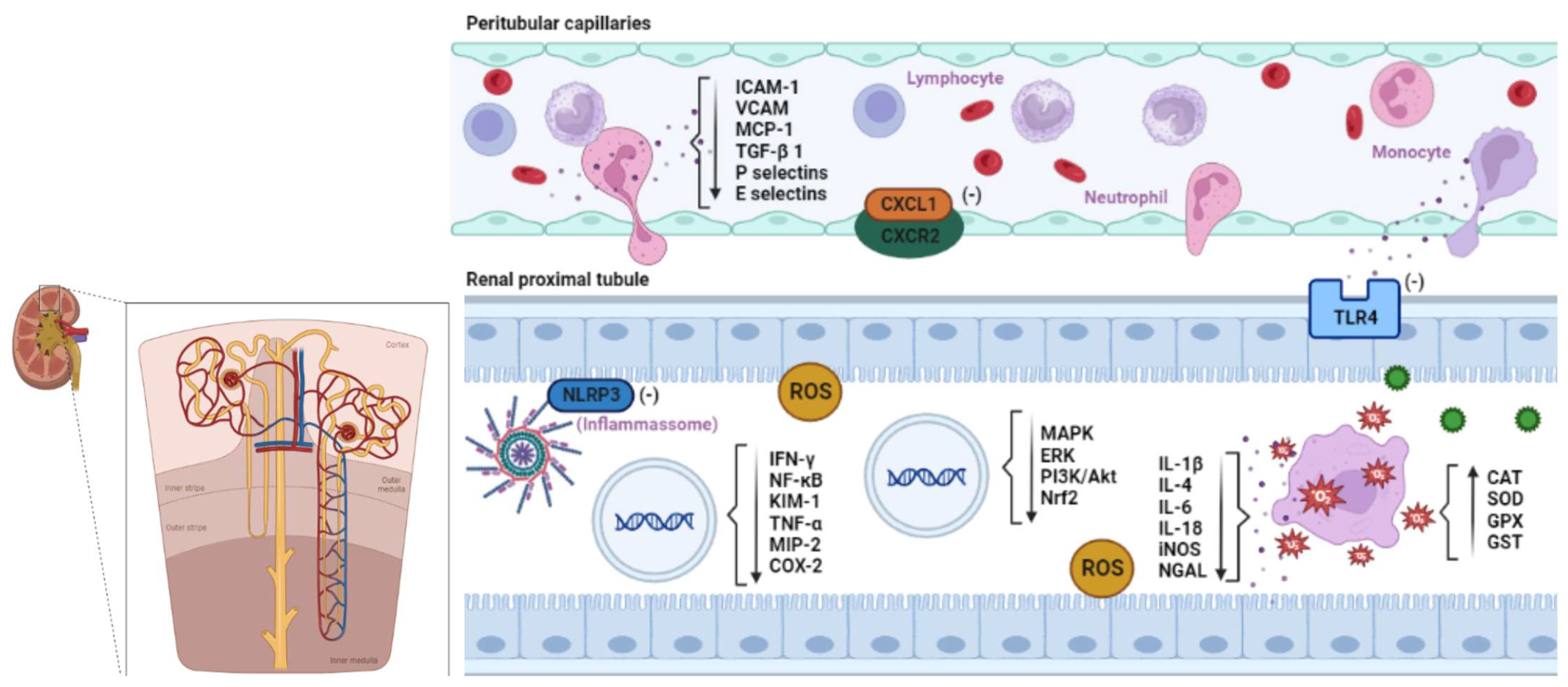
- Niu, X.; Yao, Q.; Li, W.; Zang, L.; Li, W.; Zhao, J.; Liu, F.; Zhi, W. Harmine Mitigates LPS-Induced Acute Kidney Injury through Inhibition of the TLR4-NF-ΚB/NLRP3 Inflammasome Signalling Pathway in Mice. Eur J Pharmacol 2019, 849, 160–169. [CrossRef]
- Sims J Tropicos.Org. Missouri Botanical Garden. .
- De Melo, N.F.; Cervi, A.C.; Guerra, M. Karyology and Cytotaxonomy of the Genus Passiflora L. (Passifloraceae). Plant Systematics and Evolution 2001, 226, 69–84. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-J.; Zhou, T.; Wang, F.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.-J.; Zheng, J.; Xu, D.-P.; Li, H.-B. The Effects of Syzygium Samarangense, Passiflora Edulis and Solanum Muricatum on Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury. Int J Mol Sci 2016, 17, 1616. [CrossRef]
- Salles, B.C.C.; Leme, K.C.; da Silva, M.A.; da Rocha, C.Q.; Tangerina, M.M.P.; Vilegas, W.; Figueiredo, S.A.; Duarte, S.M. da S.; Rodrigues, M.R.; de Araújo Paula, F.B. Protective Effect of Flavonoids from Passiflora Edulis Sims on Diabetic Complications in Rats. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 2021, 73, 1361–1368. [CrossRef]
- Linnaeus C V. Tropicos.Org. Missouri Botanical Garden.
- Leboeuf, M.; Cavé, A.; Bhaumik, P.K.; Mukherjee, B.; Mukherjee, R. The Phytochemistry of the Annonaceae. Phytochemistry 1980, 21, 2783–2813. [CrossRef]
- Moghadamtousi, S.; Fadaeinasab, M.; Nikzad, S.; Mohan, G.; Ali, H.; Kadir, H. Annona Muricata (Annonaceae): A Review of Its Traditional Uses, Isolated Acetogenins and Biological Activities. Int J Mol Sci 2015, 16, 15625–15658. [CrossRef]
- Adedapo, A.A.; Oni, O.A.; Falayi, O.O.; Ogunmiluyi, I.O.; Ogunpolu, B.S.; Omobowale, T.O.; Oyagbemi, A.A.; Oguntibeju, O.O.; Yakubu, M.A. Annona Muricata Mitigates Glycerol-Induced Nephrotoxicities in Male Albino Rats through Signaling Pathways of Angiotensin Conversion Enzyme, Kidney Injury Molecule-1, and Antioxidant Properties. Sci Afr 2022, 16, e01225. [CrossRef]
- Bremekamp C E B. Tropicos.Org. Missouri Botanical Garden.
- Conserva, L.; Ferreira, J. Borreria and Spermacoce Species (Rubiaceae): A Review of Their Ethnomedicinal Properties, Chemical Constituents, and Biological Activities. Pharmacogn Rev 2012, 6, 46. [CrossRef]
- Kala, S.C. Medicinal Attributes of Family Rubiaceae. International Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Science 2015, 5, 179–181.
- Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 5–29. [CrossRef]
- Valente, L.M.M.; Bizarri, C.H.B.; Liechocki, S.; Barboza, R.S.; Paixão, D. da; Almeida, M.B.S.; Benevides, P.J.C.; Magalhães, A.; Siani, A.C. Kaempferitrin from Uncaria Guianensis (Rubiaceae) and Its Potential as a Chemical Marker for the Species. J Braz Chem Soc 2009, 20, 1041–1045. [CrossRef]
- Pilarski, R.; Zieliński, H.; Ciesiołka, D.; Gulewicz, K. Antioxidant Activity of Ethanolic and Aqueous Extracts of Uncaria Tomentosa (Willd.) DC. J Ethnopharmacol 2006, 104, 18–23. [CrossRef]
- Machado, D.I.; de Oliveira Silva, E.; Ventura, S.; Vattimo, M. de F.F. The Effect of Curcumin on Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Diabetic Rats. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2798. [CrossRef]
- Mostacedo C B; Uslar Y Plantas Silvestres Con Frutos y Semillas Comestibles Del Departamento de Santa Cruz, Bolivia: Un Inventario Preliminar. Revista de la Sociedad Boliviana de Botánica 1999, 2, 203–226.
- Sales, G.W.P.; Batista, A.H.M.; Rocha, L.Q.; Nogueira, N.A.P. Efeito Antimicrobiano e Modulador Do Óleo Essencial Extraído Da Casca de Frutos Da Hymenaea Courbaril L. Revista de Ciências Farmacêuticas Básica e Aplicada 2014, 35, 709–715.
- Tiago, P.V.; Larocca, D.; Silva, I.V. da; Carpejani, A.A.; Tiago, A.V.; Dardengo, J. de F.E.; Rossi, A.A.B. Caracterização Morfoanatômica, Fitoquímica e Histoquímica de Hymenaea Courbaril (Leguminosae), Ocorrente Na Amazônia Meridional. Rodriguésia 2020, 71. [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.M.; Paula, S.R.P. de; Ferreira, F.R. de L.; Nogueira, A.C. Morphological Characterization of Fruit, Seed and Seedling and Germination of Hymenaea Courbaril L. (Fabaceae) ('Jatobá’). Journal of Seed Science 2016, 38, 204–211. [CrossRef]
- Gorchov, D.L.; Palmeirim, J.M.; Ascorra, C.F. Dispersal of Seeds of Hymenaea Courbaril (Fabaceae) in a Logged Rain Forest in the Peruvian Amazonian. Acta Amazon 2004, 34, 251–259. [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.G. dos; Sivieri, K.; Miglioli da Mata, B.P.; Salgaço, M.K.; Silva do Sacramento, L.V. Jatobá ( Hymenaea Courbaril L.). In Handbook of Phytonutrients in Indigenous Fruits and Vegetables; CABI: GB, 2022; pp. 266–280.
- Delgado, C.; Mendez-Callejas, G.; Celis, C. Caryophyllene Oxide, the Active Compound Isolated from Leaves of Hymenaea Courbaril L. (Fabaceae) with Antiproliferative and Apoptotic Effects on PC-3 Androgen-Independent Prostate Cancer Cell Line. Molecules 2021, 26, 6142. [CrossRef]
- Campelo, D.S.; Campelo, T.P.T.; Ferraz, A.B.F. Avaliação Das Características Químicas e Biológicas Da Garrafada de Carobinha; Digital Editora: Canoas, 2021;
- Gindri-Sinhorin, V. Avaliação Antioxidante Do Extrato Da Semente de Hymenaea Courbaril l. (Jatobá) Em Camundongos Tratados Com Acetaminofeno. Revista Cubana de Plantas Medicinales 2020, 25.
- Lisboa, E.M. de J.; Albiero, L.R.; Melchiors, N.; Borges, W.S. de P.; Lima, V. da S.; Rodrigues, F.D.; Sinhorin, V.D.G.; Castoldi, L. Evaluation of the Antitumor and Antioxidant Effects of Jatobá (Hymenaea Courbaril) Extracts / Avaliação Do Efeito Antitumoral e Antioxidante de Extratos Do Jatobá (Hymenaea Courbaril). Brazilian Journal of Development 2021, 7, 116001–116018. [CrossRef]
- Micheli M Tropicos.Org. Missouri Botanical Garden.
- Portella, V.G.; Cosenza, G.P.; Diniz, L.R.L.; Pacheco, L.F.; Cassali, G.D.; Caliari, M.V.; Brandão, M. das G.L.; Vieira, M.A.R. Nephroprotective Effect of Echinodorus Macrophyllus Micheli on Gentamicin-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats. Nephron Extra 2012, 2, 177–183. [CrossRef]
- Dutra, R.C.; Tavares, C.Z.; Ferraz, S.O.; Sousa, O. V.; Pimenta, D.S. Investigação Das Atividades Analgésica e Antiinflamatória Do Extrato Metanólico Dos Rizomas de Echinodorus Grandiflorus. Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia 2006, 16, 469–474. [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.M.; Provance, D.W.; Kaplan, M.A.C.; Figueiredo, M.R. Echinodorus Grandiflorus : Ethnobotanical, Phytochemical and Pharmacological Overview of a Medicinal Plant Used in Brazil. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2017, 109, 1032–1047. [CrossRef]
- Garcia, E. de F.; de Oliveira, M.A.; Godin, A.M.; Ferreira, W.C.; Bastos, L.F.S.; Coelho, M. de M.; Braga, F.C. Antiedematogenic Activity and Phytochemical Composition of Preparations from Echinodorus Grandiflorus Leaves. Phytomedicine 2010, 18, 80–86. [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, E.L. do; Watanabe, M.; Fonseca, C.D. da; Schlottfeldt, F. dos S.; Vattimo, M. de F.F. Renoprotective Effect of the Echinodorus Macrophyllus in Induced Renal Injury. Acta Paulista de Enfermagem 2014, 27, 12–17. [CrossRef]
- Jansen R K. Tropicos.Org. Missouri Botanical Garden.
- Kostić, A.Ž.; Janaćković, P.; Kolašinac, S.M.; Dajić Stevanović, Z.P. Balkans’ Asteraceae Species as a Source of Biologically Active Compounds for the Pharmaceutical and Food Industry. Chem Biodivers 2020, 17. [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, P.R.; Anholeto, L.; Ferreira Rodrigues, R.; Arnosti, A.; Bechara, G.; de Carvalho Castro, K.; Camargo-Mathias, M. Cytotoxic Effects of Extract of Acmella Oleracea in the Ovaries and Midgut of Rhipicephalus Sanguineus Latreille, 1806 (Acari: Ixodidae) Female Ticks. J Microsc Ultrastruct 2019, 7, 28. [CrossRef]
- S. Borges, L. da; A.R. Vieir, M.; O.M. Marqu, M.; Vianello, F.; P.P. Lima, G. Influence of Organic and Mineral Soil Fertilization on Essential Oil of Spilanthes Oleracea Cv. Jambuarana. American Journal of Plant Physiology 2012, 7, 135–142. [CrossRef]
- da Silva Borges, L.; de Souza Vieira, M.C.; Vianello, F.; Goto, R.; Lima, G.P.P. Antioxidant Compounds of Organically and Conventionally Fertilized Jambu ( Acmella Oleracea ). Biological Agriculture & Horticulture 2016, 32, 149–158. [CrossRef]
- Ratnasooriya, W.D.; Pieris, K.P.P.; Samaratunga, U.; Jayakody, J.R.A.C. Diuretic Activity of Spilanthes Acmella Flowers in Rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2004, 91, 317–320. [CrossRef]
- Yadav R; Kharya M D; Yadav N; Savadi R Diuretic Activity of <i>Spilanthes Acmella<i> Murr. Leaves Extract in Rats. International Journal Of Research in Pharmacy and Chemistry 2011, 1, 57–61.
- Gerbino, A.; Schena, G.; Milano, S.; Milella, L.; Barbosa, A.F.; Armentano, F.; Procino, G.; Svelto, M.; Carmosino, M. Spilanthol from Acmella Oleracea Lowers the Intracellular Levels of CAMP Impairing NKCC2 Phosphorylation and Water Channel AQP2 Membrane Expression in Mouse Kidney. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0156021. [CrossRef]
- Zappi, D.C.; Filardi, F.L.R.; Leitman, P.; Souza, V.C.; Walter, B.M.T.; Pirani, J.R.; Morim, M.P.; Queiroz, L.P.; Cavalcanti, T.B.; Mansano, V.F.; et al. Growing Knowledge: An Overview of Seed Plant Diversity in Brazil. Rodriguésia 2015, 66, 1085–1113. [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, L.; Duque, S.; Sanchez, I.; Quiñones, D.; Rodriguez, F.; Garcia-Abujeta, J.L. Allergic Contact Dermatitis from Rosemary ( Rosmarinus Officinalis L.). Contact Dermatitis 1997, 37, 248–249. [CrossRef]
- Emami, F.; Ali-Beig, H.; Farahbakhs, S.; Mojabi, N.; Rastegar-M, B.; Arbabian, S.; Kazemi, M.; Tekieh, E.; Golmanesh, L.; Ranjbaran, M.; et al. Hydroalcoholic Extract of Rosemary (Rosmarinus Officinalis L.) and Its Constituent Carnosol Inhibit Formalin-Induced Pain and Inflammation in Mice. Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences 2013, 16, 309–316. [CrossRef]
- Sotelo-Félix, J.I.; Martinez-Fong, D.; Muriel, P.; Santillán, R.L.; Castillo, D.; Yahuaca, P. Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Rosmarinus Officinalis (Lamiaceae) in the Alleviation of Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Acute Hepatotoxicity in the Rat. J Ethnopharmacol 2002, 81, 145–154. [CrossRef]
- Almela, L.; Sánchez-Muñoz, B.; Fernández-López, J.A.; Roca, M.J.; Rabe, V. Liquid Chromatograpic–Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Phenolics and Free Radical Scavenging Activity of Rosemary Extract from Different Raw Material. J Chromatogr A 2006, 1120, 221–229. [CrossRef]
- Marzieh Zohrabi The Study of 24 h Post Treatment Effects of the Aqueous Extract of Rosmarinus Officinalis after Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion in Rat. Journal of Physiology and Pathophysiology 2012, 3. [CrossRef]
- El-Demerdash, F.M.; El-Sayed, R.A.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. Rosmarinus Officinalis Essential Oil Modulates Renal Toxicity and Oxidative Stress Induced by Potassium Dichromate in Rats. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology 2021, 67, 126791. [CrossRef]
- Orban, J.-C.; Quintard, H.; Cassuto, E.; Jambou, P.; Samat-Long, C.; Ichai, C. Effect of N-Acetylcysteine Pretreatment of Deceased Organ Donors on Renal Allograft Function. Transplantation 2015, 99, 746–753. [CrossRef]
- Méril-Mamert, V.; Ponce-Mora, A.; Sylvestre, M.; Lawrence, G.; Bejarano, E.; Cebrián-Torrejón, G. Antidiabetic Potential of Plants from the Caribbean Basin. Plants 2022, 11, 1360. [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.-K.; Sung, S.-A.; Cho, W.-Y.; Go, K.-J.; Kim, H.-K. Macrophages Contribute to the Initiation of Ischaemic Acute Renal Failure in Rats. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2006, 21, 1231–1239. [CrossRef]
- Ricardo, S.D.; van Goor, H.; Eddy, A.A. Macrophage Diversity in Renal Injury and Repair. Journal of Clinical Investigation 2008, 118, 3522–3530. [CrossRef]
- Bonventre, J. V.; Zuk, A. Ischemic Acute Renal Failure: An Inflammatory Disease? Kidney Int 2004, 66, 480–485. [CrossRef]
- Jablonska, J.; Wu, C.-F.; Andzinski, L.; Leschner, S.; Weiss, S. CXCR2-Mediated Tumor-Associated Neutrophil Recruitment Is Regulated by IFN-β. Int J Cancer 2014, 134, 1346–1358. [CrossRef]
- Glennon-Alty, L.; Hackett, A.P.; Chapman, E.A.; Wright, H.L. Neutrophils and Redox Stress in the Pathogenesis of Autoimmune Disease. Free Radic Biol Med 2018, 125, 25–35. [CrossRef]
- Issa, R.; Xie, S.; Lee, K.-Y.; Stanbridge, R.D.; Bhavsar, P.; Sukkar, M.B.; Chung, K.F. GRO-α Regulation in Airway Smooth Muscle by IL-1β and TNF-α: Role of NF-ΚB and MAP Kinases. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 2006, 291, L66–L74. [CrossRef]
- Korbecki, J.; Kupnicka, P.; Chlubek, M.; Gorący, J.; Gutowska, I.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I. CXCR2 Receptor: Regulation of Expression, Signal Transduction, and Involvement in Cancer. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 2168. [CrossRef]
- Gay, N.J.; Symmons, M.F.; Gangloff, M.; Bryant, C.E. Assembly and Localization of Toll-like Receptor Signalling Complexes. Nat Rev Immunol 2014, 14, 546–558. [CrossRef]
- Sollinger, D.; Eißler, R.; Lorenz, S.; Strand, S.; Chmielewski, S.; Aoqui, C.; Schmaderer, C.; Bluyssen, H.; Zicha, J.; Witzke, O.; et al. Damage-Associated Molecular Pattern Activated Toll-like Receptor 4 Signalling Modulates Blood Pressure in l-NAME-Induced Hypertension. Cardiovasc Res 2014, 101, 464–472. [CrossRef]
- Bomfim, G.F.; Santos, R.A. Dos; Oliveira, M.A.; Giachini, F.R.; Akamine, E.H.; Tostes, R.C.; Fortes, Z.B.; Webb, R.C.; Carvalho, M.H.C. Toll-like Receptor 4 Contributes to Blood Pressure Regulation and Vascular Contraction in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Clin Sci 2012, 122, 535–543. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-M.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-G.; Kim, S.-Y.; Seo, J.-W.; Choi, Y.-W.; Kim, D.-J.; Jeong, K.-H.; Lee, T.-W.; Ihm, C.-G.; et al. Hyperuricemia-Induced NLRP3 Activation of Macrophages Contributes to the Progression of Diabetic Nephropathy. American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology 2015, 308, F993–F1003. [CrossRef]
- Anders, H.-J.; Schaefer, L. Beyond Tissue Injury—Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns, Toll-Like Receptors, and Inflammasomes Also Drive Regeneration and Fibrosis. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2014, 25, 1387–1400. [CrossRef]
- Bauernfeind, F.G.; Horvath, G.; Stutz, A.; Alnemri, E.S.; MacDonald, K.; Speert, D.; Fernandes-Alnemri, T.; Wu, J.; Monks, B.G.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; et al. Cutting Edge: NF-ΚB Activating Pattern Recognition and Cytokine Receptors License NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation by Regulating NLRP3 Expression. The Journal of Immunology 2009, 183, 787–791. [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.P.; Tadagavadi, R.K.; Ramesh, G.; Reeves, W.B. Mechanisms of Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity. Toxins (Basel) 2010, 2, 2490–2518. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ramesh, G.; Norbury, C.C.; Reeves, W.B. Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity Is Mediated by Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Produced by Renal Parenchymal Cells. Kidney Int 2007, 72, 37–44. [CrossRef]
- Peres, L.A.B.; Cunha Júnior, A.D. da Acute Nephrotoxicity of Cisplatin: Molecular Mechanisms. Jornal Brasileiro de Nefrologia 2013, 35, 332–340. [CrossRef]
- Han, W.K.; Bailly, V.; Abichandani, R.; Thadhani, R.; Bonventre, J. V. Kidney Injury Molecule-1 (KIM-1): A Novel Biomarker for Human Renal Proximal Tubule Injury. Kidney Int 2002, 62, 237–244. [CrossRef]
- Regueira, T.; Andresen, M.; Mercado, M.; Downey, P. Fisiopatología de La Insuficiencia Renal Aguda Durante La Sepsis. Med Intensiva 2011, 35, 424–432.
- Bastos, V.P.D.; Gomes, A.S.; Lima, F.J.B.; Brito, T.S.; Soares, P.M.G.; Pinho, J.P.M.; Silva, C.S.; Santos, A.A.; Souza, M.H.L.P.; Magalhães, P.J.C. Inhaled 1,8-Cineole Reduces Inflammatory Parameters in Airways of Ovalbumin-Challenged Guinea Pigs. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 2011, 108, 34–39. [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, N.A.G.; Carvalho Rodrigues, M.A.; Martins, N.M.; dos Santos, A.C. Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity and Targets of Nephroprotection: An Update. Arch Toxicol 2012, 86, 1233–1250. [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, G.; Reeves, W.B. P38 MAP Kinase Inhibition Ameliorates Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity in Mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2005, 289, F166-74. [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Munir, S.; Badshah, S.L.; Khan, N.; Ghani, L.; Poulson, B.G.; Emwas, A.-H.; Jaremko, M. Important Flavonoids and Their Role as a Therapeutic Agent. Molecules 2020, 25, 5243. [CrossRef]
- Leyva-López, N.; Gutierrez-Grijalva, E.; Ambriz-Perez, D.; Heredia, J. Flavonoids as Cytokine Modulators: A Possible Therapy for Inflammation-Related Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2016, 17, 921. [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hu, R. Oroxylin A Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Activity on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Mouse Macrophage via Nrf2/ARE Activation. Biochemistry and Cell Biology 2014, 92, 337–348. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-L.; Dodd, G.; Thomas, S.; Zhang, X.; Wasserman, M.A.; Rovin, B.H.; Kunsch, C. Activation of Nrf2/ARE Pathway Protects Endothelial Cells from Oxidant Injury and Inhibits Inflammatory Gene Expression. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology 2006, 290, H1862–H1870. [CrossRef]
- Al-Khayri, J.M.; Sahana, G.R.; Nagella, P.; Joseph, B. V.; Alessa, F.M.; Al-Mssallem, M.Q. Flavonoids as Potential Anti-Inflammatory Molecules: A Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 2901. [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.S.; Lim, S.H.; Lee, S.R.; Choi, C.-I.; Kim, K.H. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of White Mulberry (Morus Alba L.) Fruits on Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Macrophages. Molecules 2021, 26, 920. [CrossRef]
| Species | Parts Used | Isolated or Characterized Constituents | Pharmacological activity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Banisteriopsis caapi (Spruce ex Griseb.) Morton | Stem | Harmine (1), harmaline (2) [77], tetrahydroharmine (3) and harmalinic acid (4) [78] | Analgesic [22], hallucinogen [23], anesthetic [24], antidiabetic [25], anticancerogenic [18], nephroprotective, diuretic [26] | ||
| Peganum harmala L. | Seeds | Harmol (5), harmalol (6), harmine (1) and harmaline (2) [79] | Antioxidant, nephroprotective, anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic [79] | ||
| Passiflora edulis Sims | Fruit peel, leaves, flowers, seeds | Orientin (7) and isoorientin (8) [80] | Anxiolytic, sedative, neuropathic pain [81], anticonvulsant [82], cognitive function and degenerative diseases [83], antioxidant action, antitumor action, hypoglycemic action, obesity, insomnia, nephroprotector [84] | ||
| Annona muricata L. | Leaves | Acetogenin (9) [85], δ-Cadinene (10) and α-Muurolene (11) [86] | Anticancerogenic, hepatoprotective, neurotoxic, antinociceptive, antiulcerative, chemopreventive, nephroprotective [87] | ||
| Uncaria tomentosa (Willd.) DC. | Stem | Uncarine F (12), speciophylline (13) and mitraphylline (14) [88] | Antioxidant and immunomodulator, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anticancer and diuretic [89] | ||
| Hymenaea courbaril L. | Stem and leaves | Fisetin (15), cyclosativene (16), caryophyllene (17) and α-himachalene (18) [90] | Antioxidant, antiulcerogenic, anti-inflammatory, antitumor and diuretic [91] | ||
| Echinodorus macrophyllus (Kunth) Micheli | Leaves | Linalool (19), α-caryophyllene (20), β- caryophyllene (21) [92], isovitexin (22) and isoorientin (8) [93] | Diuretic, anti-inflammatory, treatment of kidney and liver disorders [94] | ||
| Acmella oleracea (L.) R. K. Jansen | Flowers and leaves | Spilanthol (23), spermidine (24), spermine (25) and 3-acetylaleuritolic acid (26) [95,96,97] | Aphrodisiac, treatment of male sexual dysfunctions, diuretic and anti-inflammatory [98,99] | ||
| Rosmarinus officinalis L. | Leaves | Camphene (27), limonene (28), camphor (29), borneol (30), cineol (31) and linalool (19) [100] | Analgesic, anti-inflammatory, anticarcinogenic, antirheumatic, nephroprotective, spasmolytic, antihepatotoxic, atherosclerotic [101] | ||
Harmine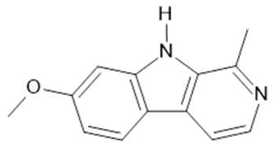 (1) |
Harmaline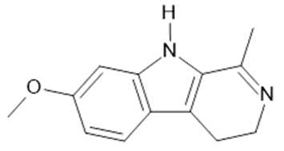 (2) |
Tetrahydroharmine 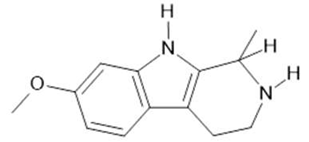 (3) |
Harmalinic acid 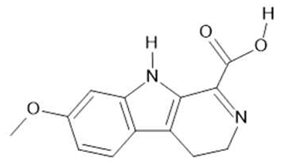 (4) |
Harmol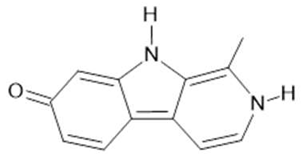 (5) |
|
Harmalol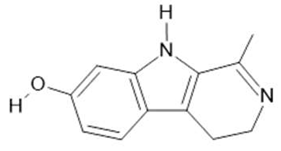 (6) |
Orientin 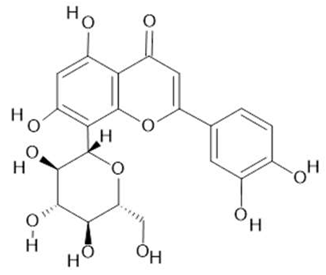 (7) |
Isoorientin 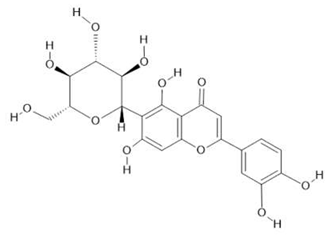 (8) |
Acetogenin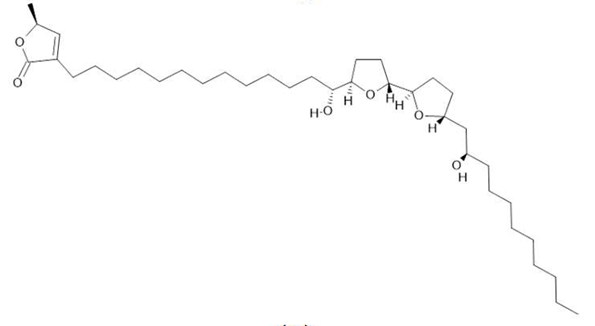 (9) |
||
δ-Cadinene 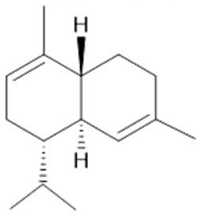 (10) |
α-Muurolene 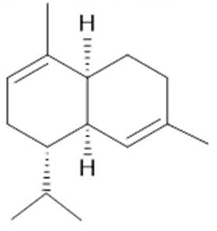 (11) |
Uncarine F 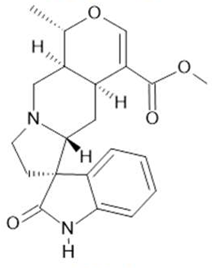 (12) |
Speciophylline 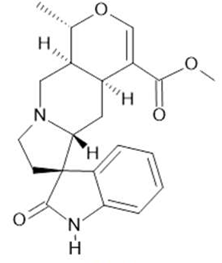 (13) |
Mitraphylline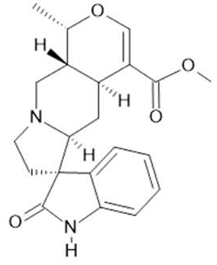 (14) |
|
Fisetin 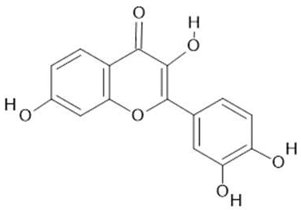 (15) |
Cyclosativene 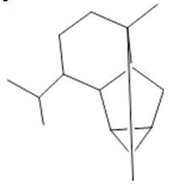 (16) |
Caryophyllene 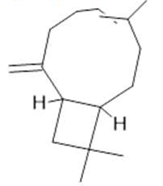 (17) |
α-himachalene 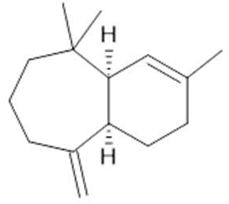 (18) |
Linalool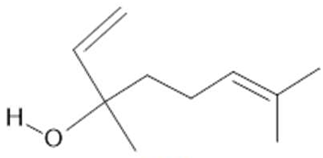 (19) |
|
α-caryophyllene 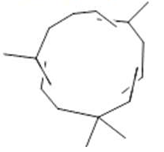 (20) |
β- caryophyllene 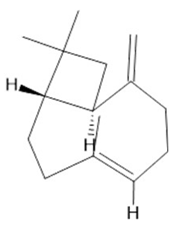 (21) |
Isovitexin 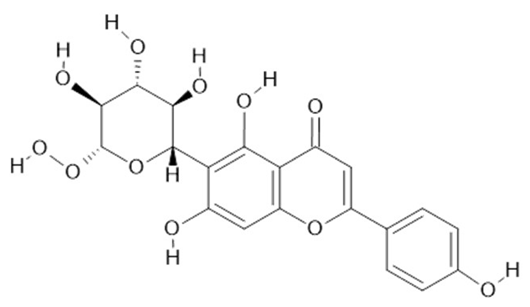 (22) |
Spilanthol 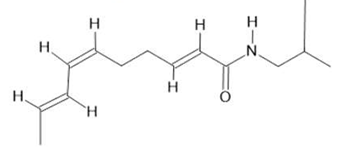 (23) |
||
Spermidine 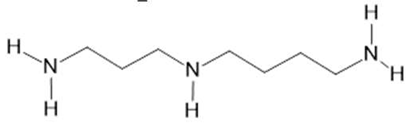 (24) |
Spermine 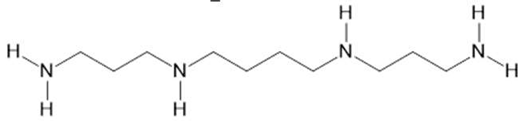 (25) |
3-acetylaleuritolic acid 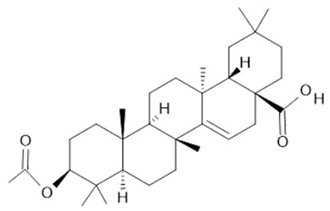 (26) |
Camphene 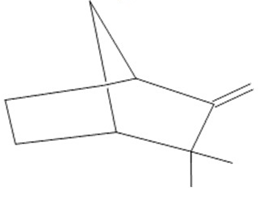 (27) |
||
Limonene 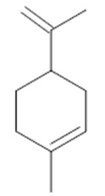 (28) |
Camphor 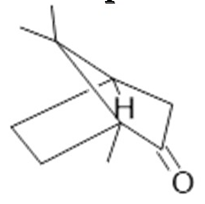 (29) |
Borneol 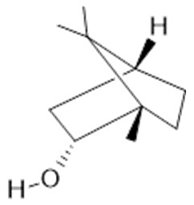 (30) |
Cineol 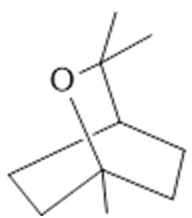 (31) |
||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





