Submitted:
16 June 2023
Posted:
16 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Clinical assessment
2.3. MRI acquisition
2.4. Gray matter volume and Curve index measurements
2.5. Statistical analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics, clinical characteristics, and gait characteristics
3.2. Association between gait characteristics and mild cognitive impairment
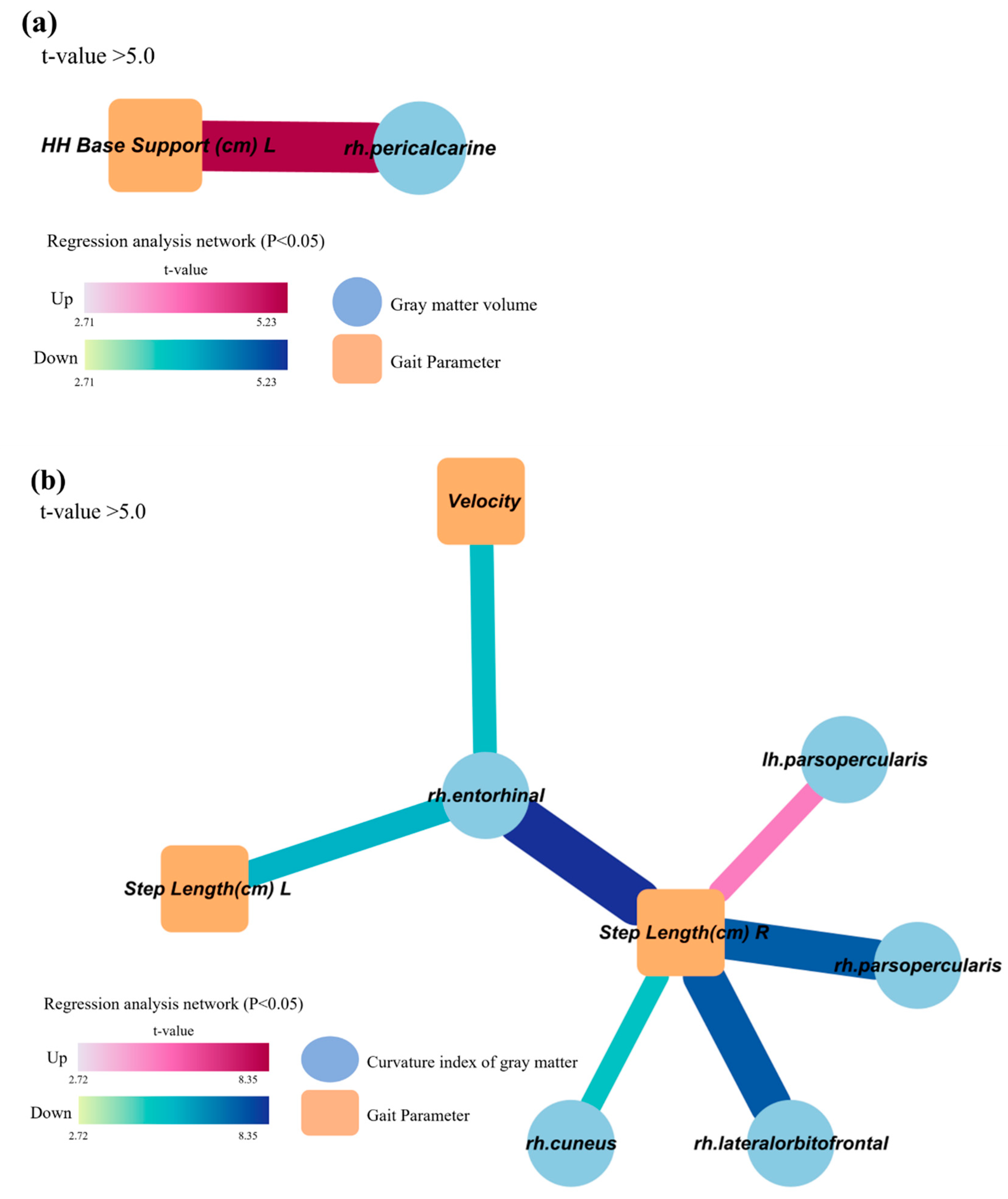
3.3. Decreased and distorted gray matter areas associated with gait characteristics related to cognitive dysfunction
4. Discussion
Funding
Data Availability
References
- Petersen, R.C. Mild cognitive impairment as a diagnostic entity. J Intern Med 2004, 256, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, R.C.; Doody, R.; Kurz, A.; Mohs, R.C.; Morris, J.C.; Rabins, P.V.; Ritchie, K.; Rossor, M.; Thal, L.; Winblad, B. Current concepts in mild cognitive impairment. Arch Neurol 2001, 58, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahureksa, L.; Najafi, B.; Saleh, A.; Sabbagh, M.; Coon, D.; Mohler, M.J.; Schwenk, M. The Impact of Mild Cognitive Impairment on Gait and Balance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Studies Using Instrumented Assessment. Gerontology 2017, 63, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verghese, J.; LeValley, A.; Hall, C.B.; Katz, M.J.; Ambrose, A.F.; Lipton, R.B. Epidemiology of gait disorders in community-residing older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc 2006, 54, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amboni, M.; Barone, P.; Hausdorff, J.M. Cognitive contributions to gait and falls: evidence and implications. Mov Disord 2013, 28, 1520–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimbeni, A.; Caruso, S.; Salatino, A.; Carenza, M.; Rigano, M.; Raviolo, A.; Ricci, R. Dual task-related gait changes in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Funct Neurol 2015, 30, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Yogev-Seligmann, G.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Giladi, N. The role of executive function and attention in gait. Mov Disord 2008, 23, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorov, A.; Beichel, R.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Finet, J.; Fillion-Robin, J.C.; Pujol, S.; Bauer, C.; Jennings, D.; Fennessy, F.; Sonka, M.; et al. 3D Slicer as an image computing platform for the Quantitative Imaging Network. Magn Reson Imaging 2012, 30, 1323–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, A.M.; Fischl, B.; Sereno, M.I. Cortical surface-based analysis. I. Segmentation and surface reconstruction. Neuroimage 1999, 9, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verghese, J.; Robbins, M.; Holtzer, R.; Zimmerman, M.; Wang, C.; Xue, X.; Lipton, R.B. Gait dysfunction in mild cognitive impairment syndromes. J Am Geriatr Soc 2008, 56, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluger, A.; Gianutsos, J.G.; Golomb, J.; Ferris, S.H.; George, A.E.; Franssen, E.; Reisberg, B. Patterns of motor impairement in normal aging, mild cognitive decline, and early Alzheimer's disease. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci 1997, 52B, P28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisoni, G.B.; Galluzzi, S.; Bresciani, L.; Zanetti, O.; Geroldi, C. Mild cognitive impairment with subcortical vascular features: clinical characteristics and outcome. J Neurol 2002, 249, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, P.A.; Wilson, R.S.; Aggarwal, N.T.; Arvanitakis, Z.; Kelly, J.; Bienias, J.L.; Bennett, D.A. Parkinsonian signs in subjects with mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 2005, 65, 1901–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, E.D.; Schupf, N.; Manly, J.; Marder, K.; Tang, M.X.; Mayeux, R. Association between mild parkinsonian signs and mild cognitive impairment in a community. Neurology 2005, 64, 1157–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGough, E.L.; Kelly, V.E.; Logsdon, R.G.; McCurry, S.M.; Cochrane, B.B.; Engel, J.M.; Teri, L. Associations between physical performance and executive function in older adults with mild cognitive impairment: gait speed and the timed "up & go" test. Phys Ther 2011, 91, 1198–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, N.L.; Rosano, C.; Boudreau, R.M.; Simonsick, E.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Sutton-Tyrrell, K.; Hardy, S.E.; Atkinson, H.H.; Yaffe, K.; Satterfield, S.; et al. Executive function, memory, and gait speed decline in well-functioning older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2010, 65, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Steen, B.; Matousek, M.; Andreasson, L.A.; Larsson, L.; Palsson, S.; Sundh, V.; Skoog, I. A population-based study on brain atrophy and motor performance in elderly women. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2001, 56, M633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, G.F.; Whitney, S.L.; Blatt, P.J.; Morris, L.O.; Vance, J.M. Temporal and spatial characteristics of gait during performance of the Dynamic Gait Index in people with and people without balance or vestibular disorders. Phys Ther 2008, 88, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfern, M.S.; Jennings, J.R.; Mendelson, D.; Nebes, R.D. Perceptual inhibition is associated with sensory integration in standing postural control among older adults. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci 2009, 64, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrochon, A.; Kemoun, G.; Dugue, B.; Berthoz, A. Cognitive Impairment Assessment through Visuospatial Memory Can Be Performed with a Modified Walking Corsi Test Using the 'Magic Carpet'. Dement Geriatr Cogn Dis Extra 2014, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangen, G.G.; Engedal, K.; Bergland, A.; Moger, T.A.; Mengshoel, A.M. Relationships between balance and cognition in patients with subjective cognitive impairment, mild cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer disease. Phys Ther 2014, 94, 1123–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allali, G.; Assal, F.; Kressig, R.W.; Dubost, V.; Herrmann, F.R.; Beauchet, O. Impact of impaired executive function on gait stability. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 2008, 26, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamacher, D.; Liebl, D.; Hodl, C.; Hessler, V.; Kniewasser, C.K.; Thonnessen, T.; Zech, A. Gait Stability and Its Influencing Factors in Older Adults. Front Physiol 2018, 9, 1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanshahi, M. Willed action and its impairments. Cogn Neuropsychol 1998, 15, 483–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheridan, P.L.; Solomont, J.; Kowall, N.; Hausdorff, J.M. Influence of executive function on locomotor function: divided attention increases gait variability in Alzheimer's disease. J Am Geriatr Soc 2003, 51, 1633–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppen, E.M.; Grond, J.V.; Hafkemeijer, A.; Barkey Wolf, J.J.H.; Roos, R.A.C. Structural and functional changes of the visual cortex in early Huntington's disease. Hum Brain Mapp 2018, 39, 4776–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollaert, R.E.; Poe, K.; Hubbard, E.A.; Motl, R.W.; Pilutti, L.A.; Johnson, C.L.; Sutton, B.P. Associations of functional connectivity and walking performance in multiple sclerosis. Neuropsychologia 2018, 117, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onder, H.; Buyuk, F. Gait Dyspraxia due to Right Occipital Infarct. J Mov Disord 2019, 12, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witter, M.P.; Doan, T.P.; Jacobsen, B.; Nilssen, E.S.; Ohara, S. Architecture of the Entorhinal Cortex A Review of Entorhinal Anatomy in Rodents with Some Comparative Notes. Front Syst Neurosci 2017, 11, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Braak, E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol 1991, 82, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, R.; Bartha, R.; Montero-Odasso, M. Entorhinal Cortex Volume Is Associated With Dual-Task Gait Cost Among Older Adults With MCI: Results From the Gait and Brain Study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2019, 74, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, A.L.; Verghese, J.; Metti, A.L.; Boudreau, R.M.; Aizenstein, H.J.; Kritchevsky, S.; Harris, T.; Yaffe, K.; Satterfield, S.; Studenski, S.; et al. Slowing gait and risk for cognitive impairment: The hippocampus as a shared neural substrate. Neurology 2017, 89, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Chastan, N.; Bair, W.N.; Resnick, S.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Studenski, S.A. The brain map of gait variability in aging, cognitive impairment and dementia-A systematic review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2017, 74, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryden, D.W.; Roesch, M.R. Executive control signals in orbitofrontal cortex during response inhibition. J Neurosci 2015, 35, 3903–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, A.; Friedman, N.P.; Emerson, M.J.; Witzki, A.H.; Howerter, A.; Wager, T.D. The unity and diversity of executive functions and their contributions to complex "Frontal Lobe" tasks: a latent variable analysis. Cogn Psychol 2000, 41, 49–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, M.G.; Chiang, J.; Pogoda, J.M.; Gomez, M.; Thomas, K.; Marion, S.D.; Miller, K.J.; Siddarth, P.; Yi, X.; Zhou, F.; et al. Executive function changes before memory in preclinical Alzheimer's pathology: a prospective, cross-sectional, case control study. PLoS One 2013, 8, e79378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennberg, A.M.V.; Savica, R.; Hagen, C.E.; Roberts, R.O.; Knopman, D.S.; Hollman, J.H.; Vemuri, P.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Petersen, R.C.; Mielke, M.M. Cerebral Amyloid Deposition Is Associated with Gait Parameters in the Mayo Clinic Study of Aging. J Am Geriatr Soc 2017, 65, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacoboni, M.; Dapretto, M. The mirror neuron system and the consequences of its dysfunction. Nat Rev Neurosci 2006, 7, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total (n=80) |
Early MCI (n=53) |
Late MCI (n=27) |
p value | |
| Mean age | 74.6±5.74 | 74.6±5.33 | 74.6±6.58 | 0.95 |
| Gender, female (%) | 58 (72.5) | 43 (81.1) | 15 (55.6) | 0.020 |
| Year of education | 6.88±3.980 | 5.94±4.069 | 8.72±3.114 | 0.003 |
| Number of comorbidities | 3.7±1.70 | 3.9±1.61 | 3.1±1.77 | 0.047 |
| Depression scale | 4.9±4.09 | 4.9±4.24 | 5.1±3.83 | 0.833 |
| Anxiety scale | 6.8±6.52 | 7.1±6.87 | 6.3±5.86 | 0.600 |
| QOL scale | 34.4±8.67 | 33.3±8.39 | 36.5±9.00 | 0.124 |
| Stress scale | 1.57±0.664 | 1.62±0.716 | 1.49±0.551 | 0.423 |
| Height | 156.1±8.11 | 155.4±7.98 | 157.7±8.30 | 0.232 |
| Weight | 61.0±10.92 | 61.9±11.47 | 59.3±9.72 | 0.324 |
| BMI, mean (SD) | 25.0±3.70 | 25.6±3.84 | 23.8±3.17 | 0.045 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 87.8±10.12 | 87.6±10.39 | 88.1±9.75 | 0.825 |
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 128.6±18.27 | 130.0±18.44 | 126.0±17.97 | 0.349 |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 77.0±9.82 | 77.4±9.41 | 76.1±10.73 | 0.606 |
| Fasting glucose (mg/dL) | 108.8±26.28 | 111.3±28.44 | 104.0±21.08 | 0.240 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL | 162.4±32.54 | 34.0±4.67 | 30.1±5.79 | 0.913 |
| Total (n=80) |
Early MCI (n=53) |
Late MCI (n=27) |
p value | |
| Gait velocity | 93.6±20.16 | 93.9±21.48 | 90.9±17.35 | 0.404 |
| Cadence | 107.1±11.52 | 106.4±12.02 | 108.3±10.58 | 0.498 |
| Step time (sec) | ||||
| Left | 0.6±0.07 | 0.6±0.07 | 0.6±0.06 | 0.575 |
| Right | 0.6±0.07 | 0.6±0.07 | 0.6±0.05 | 0.348 |
| Step length (cm) | ||||
| Left | 51.8±8.52 | 52.9±8.60 | 49.7±8.09 | 0.111 |
| Right | 52.3±8.27 | 53.0±8.15 | 50.9±8.47 | 0.268 |
| Cycle time (sec) | ||||
| Left | 1.1±0.13 | 1.1±0.15 | 1.1±0.11 | 0.418 |
| Right | 1.1±0.13 | 1.1±0.15 | 1.1±0.11 | 0.468 |
| H-H base support (cm) | ||||
| Left | 9.0±3.12 | 8.5±3.14 | 10.1±2.82 | 0.027 |
| Right | 8.8±2.99 | 8.1±2.78 | 10.2±2.95 | 0.002 |
| Swing % of cycle | ||||
| Left | 36.8±2.28 | 36.9±2.23 | 36.7±2.42 | 0.776 |
| Right | 36.6±2.45 | 36.9±2.70 | 35.9±1.75 | 0.085 |
| Stance % of cycle | ||||
| Left | 63.2±2.28 | 63.1±2.23 | 63.3±2.42 | 0.795 |
| Right | 63.4±2.46 | 63.1±2.70 | 64.1±1.74 | 0.051 |
| Double support % of cycle | ||||
| Left | 26.4±4.20 | 26.0±4.41 | 27.2±3.72 | 0.242 |
| Right | 26.6±4.41 | 26.2±4.74 | 27.2±3.67 | 0.354 |
| Step time variability (%) | ||||
| Left | 4.1±2.77 | 4.1±2.72 | 4.2±2.91 | 0.849 |
| Right | 3.7±2.56 | 3.5±2.76 | 4.1±2.10 | 0.318 |
| Step length variability (%) | ||||
| Left | 2.4±1.65 | 2.3±1.45 | 2.6±2.00 | 0.400 |
| Right | 4.8±3.45 | 4.4±3.43 | 5.5±3.45 | 0.169 |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | ||||
| OR (95% CI) | p value | OR (95% CI) | p value | OR (95% CI) | p value | |
| Gait velocity | 0.990 (0.967, 1.013) | 0.400 | 0.968 (0.940, 0.998) | 0.035 | 0.957 (0.924, 0.991) | 0.015 |
| Cadence | 1.015 (0.973, 1.057) |
0.493 | 1.008 (0.959, 1.059) |
0.763 | 1.011 (0.955, 1.069) |
0.712 |
| Step time (sec) | ||||||
| Left | 0.135 (0.000, 136.191) |
0.570 | 0.700 (0.000, 2222.031) |
0.931 | 0.896 (0.000, 8368.103) |
0.981 |
| Right | 0.025 (0.000, 53.164) |
0.347 | 0.083 (0.000, 687.854) |
0.589 | 0.069 (0.000, 2747.780) |
0.621 |
| Step length (cm) | ||||||
| Left | 0.955 (0.901, 1.011) |
0.114 | 0.878 (0.805, 0.958) |
0.003 | 0.805 (0.711, 0.912) |
0.001 |
| Right | 0.968 (0.913, 1.025) |
0.266 | 0.894 (0.822, 0.972) |
0.009 | 0.861 (0.781, 0.950) |
0.003 |
| Cycle time (sec) | ||||||
| Left | 0.213 (0.005, 8.789) |
0.415 | 0.504 (0.007, 38.928) |
0.757 | 0.567 (0.004, 83.640) |
0.824 |
| Right | 0.252 (0.006, 10.106) |
0.464 | 0.475 (0.006, 37.650) |
0.739 | 0.496 (0.003, 75.879) |
0.785 |
| H-H base support (cm) | ||||||
| Left | 1.192 (1.015, 1.400) |
0.033 | 1.167 (0.978, 1.392) |
0.087 | 1.288 (1.047, 1.584) |
0.017 |
| Right | 1.292 (1.083, 1.542) |
0.004 | 1.266 (1.040, 1.541) |
0.019 | 1.391 (1.108, 1.746) |
0.005 |
| Swing % of cycle | ||||||
| Left | 0.971 (0.792, 1.189) |
0.773 | 0.864 (0.684, 1.091) |
0.218 | 0.724 (0.541, 0.967) |
0.029 |
| Right | 0.844 (0.694, 1.027) |
0.090 | 0.716 (0.560, 0.916) |
0.008 | 0.539 (0.378, 0.768) |
0.001 |
| Stance % of cycle | ||||||
| Left | 1.028 (0.839, 1.260) |
0.792 | 1.154 (0.913, 1.458) |
0.230 | 1.377 (1.031, 1.839) |
0.030 |
| Right | 1.183 (0.973, 1.439) |
0.092 | 1.392 (1.089, 1.779) |
0.008 | 1.845 (1.298, 2.621) |
0.001 |
| Double support % of cycle | ||||||
| Left | 1.069 (0.956, 1.194) |
0.242 | 1.161 (1.014, 1.329) |
0.030 | 1.357 (1.155, 1.641) |
0.002 |
| Right | 1.051 (0.946, 1.167) |
0.352 | 1.149 (1.009, 1.308) |
0.036 | 1.354 (1.130, 1.623) |
0.001 |
| Step time variability | ||||||
| Left | 1.017 (0.860, 1.201) |
0.847 | 1.022 (0.854, 1.222) |
0.815 | 1.045 (0.844, 1.295) |
0.684 |
| Right | 1.095 (0.915, 1.311) |
0.320 | 1.147 (0.942, 1.397) |
0.173 | 1.188 (0.963, 1.465) |
0.109 |
| Step length variability | ||||||
| Left | 1.143 (0.865, 1.512) | 0.347 | 1.178 (0.863, 1.609) |
0.302 | 1.166 (0.845, 1.609) |
0.350 |
| Right | 1.098 (0.961, 1.255) | 0.170 | 1.149 (0.986, 1.339) |
0.076 | 1.215 (1.027, 1.436) |
0.023 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





