Submitted:
15 June 2023
Posted:
16 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
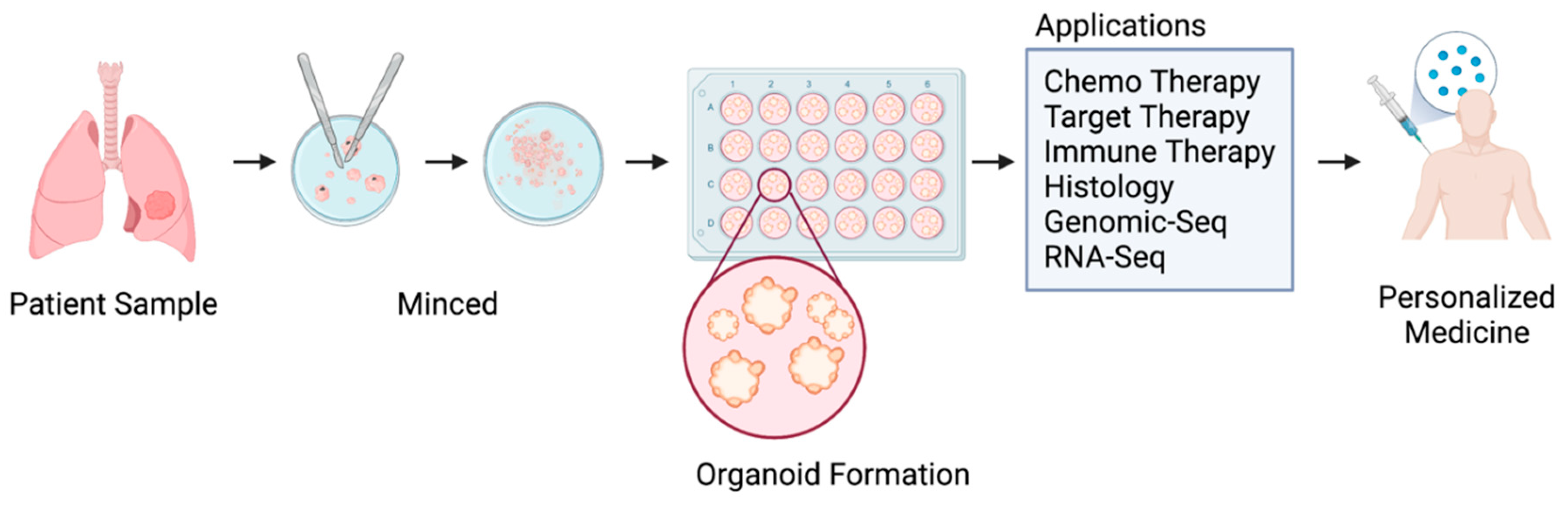
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Organoid technology for high-throughput drug screening
3.2. PDOs in Preclinical Studies
3.3. PDOs in clinical studies - an enhanced model for personalized drug screening
3.4. Mechanistic studies involving PDOs
4. Conclusions and future directions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pikor, L.A.; Ramnarine, V.R.; Lam, S.; Lam, W.L. Genetic alterations defining NSCLC subtypes and their therapeutic implications. Lung Cancer 2013, 82, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudin, C.M.; Brambilla, E.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Sage, J. Small-cell lung cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2021, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byers, L.A.; Rudin, C.M. Small cell lung cancer: where do we go from here? Cancer 2015, 121, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, F.R.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Mulshine, J.L.; Kwon, R.; Curran, W.J., Jr.; Wu, Y.L.; Paz-Ares, L. Lung cancer: current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet 2017, 389, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Rodriguez-Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csoszi, T.; Fulop, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus Chemotherapy for PD-L1-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N Engl J Med 2016, 375, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Z.F.; Ma, P.C. Emerging insights of tumor heterogeneity and drug resistance mechanisms in lung cancer targeted therapy. J Hematol Oncol 2019, 12, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Zhao, Y.; Arkenau, H.T.; Lao, T.; Chu, L.; Xu, Q. Signal pathways and precision therapy of small-cell lung cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2022, 7, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Jin, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. Signaling pathways and targeted therapies in lung squamous cell carcinoma: mechanisms and clinical trials. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2022, 7, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotow, J.; Bivona, T.G. Understanding and targeting resistance mechanisms in NSCLC. Nat Rev Cancer 2017, 17, 637–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altorki, N.K.; Markowitz, G.J.; Gao, D.; Port, J.L.; Saxena, A.; Stiles, B.; McGraw, T.; Mittal, V. The lung microenvironment: an important regulator of tumour growth and metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer 2019, 19, 9–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiam-Galvez, K.J.; Allen, B.M.; Spitzer, M.H. Systemic immunity in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2021, 21, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, W.H.; McAteer, J.A.; Smith, J.R.; Braunschweiger, W.R. Type II alveolar pneumonocytes in vitro. Int Rev Cytol Suppl 1979, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Iich, E.; Lee, J.H. Organogenesis of adult lung in a dish: Differentiation, disease and therapy. Dev Biol 2016, 420, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleijs, M.; van de Wetering, M.; Clevers, H.; Drost, J. Xenograft and organoid model systems in cancer research. Embo J 2019, 38, e101654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Mun, H.; Sung, C.O.; Cho, E.J.; Jeon, H.J.; Chun, S.M.; Jung, D.J.; Shin, T.H.; Jeong, G.S.; Kim, D.K.; et al. Patient-derived lung cancer organoids as in vitro cancer models for therapeutic screening. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, N.; Hoshi, H.; Higa, A.; Hiyama, G.; Tamura, H.; Ogawa, M.; Takagi, K.; Goda, K.; Okabe, N.; Muto, S.; et al. An In Vitro System for Evaluating Molecular Targeted Drugs Using Lung Patient-Derived Tumor Organoids. Cells 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiMasi, J.A.; Reichert, J.M.; Feldman, L.; Malins, A. Clinical approval success rates for investigational cancer drugs. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2013, 94, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, K.M.; Riedlinger, G.M.; Rosenfeld, J.; Ganesan, S.; Pine, S.R. Patient-Derived Xenograft Models of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Their Potential Utility in Personalized Medicine. Front Oncol 2017, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bredenoord, A.L.; Clevers, H.; Knoblich, J.A. Human tissues in a dish: The research and ethical implications of organoid technology. Science 2017, 355, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clevers, H.C. Organoids: Avatars for Personalized Medicine. Keio J Med 2019, 68, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iakobachvili, N.; Peters, P.J. Humans in a Dish: The Potential of Organoids in Modeling Immunity and Infectious Diseases. Front Microbiol 2017, 8, 2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.L.; Yu, X.; James, I.O.; Zhang, H.Y.; Yang, J.; Radulescu, A.; Zhou, Y.; Besner, G.E. Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor protects intestinal stem cells from injury in a rat model of necrotizing enterocolitis. Lab Invest 2012, 92, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Vries, R.G.; Snippert, H.J.; van de Wetering, M.; Barker, N.; Stange, D.E.; van Es, J.H.; Abo, A.; Kujala, P.; Peters, P.J.; et al. Single Lgr5 stem cells build crypt-villus structures in vitro without a mesenchymal niche. Nature 2009, 459, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancaster, M.A.; Knoblich, J.A. Generation of cerebral organoids from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Protoc 2014, 9, 2329–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.; Manfrin, A.; Lutolf, M.P. Progress and potential in organoid research. Nat Rev Genet 2018, 19, 671–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasco, S.; Kedaigle, A.J.; Simmons, S.K.; Nash, A.; Rocha, M.; Quadrato, G.; Paulsen, B.; Nguyen, L.; Adiconis, X.; Regev, A.; et al. Individual brain organoids reproducibly form cell diversity of the human cerebral cortex. Nature 2019, 570, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-E.; Shin, N.; Kook, M.G.; Kong, D.; Kim, N.G.; Choi, S.W.; Kang, K.-S. Human iNSC-derived brain organoid model of lysosomal storage disorder in Niemann-Pick disease type C. Cell death & disease 2020, 11, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Vela, I.; Sboner, A.; Iaquinta, P.J.; Karthaus, W.R.; Gopalan, A.; Dowling, C.; Wanjala, J.N.; Undvall, E.A.; Arora, V.K.; et al. Organoid cultures derived from patients with advanced prostate cancer. Cell 2014, 159, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clevers, H. Modeling Development and Disease with Organoids. Cell 2016, 165, 1586–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drost, J.; Clevers, H. Organoids in cancer research. Nat Rev Cancer 2018, 18, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachs, N.; de Ligt, J.; Kopper, O.; Gogola, E.; Bounova, G.; Weeber, F.; Balgobind, A.V.; Wind, K.; Gracanin, A.; Begthel, H.; et al. A Living Biobank of Breast Cancer Organoids Captures Disease Heterogeneity. Cell 2018, 172, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driehuis, E.; Kretzschmar, K.; Clevers, H. Establishment of patient-derived cancer organoids for drug-screening applications. Nature protocols 2020, 15, 3380–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.H.; Ma, S. Organoids as research models for hepatocellular carcinoma. Experimental cell research 2022, 411, 112987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiao, A.; Dias, S.; Soares, A.F.; Pereira, C.L.; Oliveira, C.; Sarmento, B. Advances in the use of 3D colorectal cancer models for novel drug discovery. Expert opinion on drug discovery 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doffo, J.; Bamopoulos, S.A.; Kose, H.; Orben, F.; Zang, C.; Pons, M.; den Dekker, A.T.; Brouwer, R.W.W.; Baluapuri, A.; Habringer, S.; et al. NOXA expression drives synthetic lethality to RUNX1 inhibition in pancreatic cancer. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2022, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, J.R.; Onaitis, M.W.; Rawlins, E.L.; Lu, Y.; Clark, C.P.; Xue, Y.; Randell, S.H.; Hogan, B.L. Basal cells as stem cells of the mouse trachea and human airway epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009, 106, 12771–12775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hild, M.; Jaffe, A.B. Production of 3-D Airway Organoids From Primary Human Airway Basal Cells and Their Use in High-Throughput Screening. Curr Protoc Stem Cell Biol 2016, 37, IE 9 1–IE 9 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadkarni, R.R.; Abed, S.; Draper, J.S. Organoids as a model system for studying human lung development and disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2016, 473, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.W.; Huang, S.X.; de Carvalho, A.; Ho, S.H.; Islam, M.N.; Volpi, S.; Notarangelo, L.D.; Ciancanelli, M.; Casanova, J.L.; Bhattacharya, J.; et al. A three-dimensional model of human lung development and disease from pluripotent stem cells. Nat Cell Biol 2017, 19, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Duan, X.; Yang, L.; Nilsson-Payant, B.E.; Wang, P.; Duan, F.; Tang, X.; Yaron, T.M.; Zhang, T.; Uhl, S.; et al. Identification of SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors using lung and colonic organoids. Nature 2021, 589, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadur Lakshminarasimha Murthy, P.; Sontake, V.; Tata, A.; Kobayashi, Y.; Macadlo, L.; Okuda, K.; Conchola, A.S.; Nakano, S.; Gregory, S.; Miller, L.A.; et al. Human distal lung maps and lineage hierarchies reveal a bipotent progenitor. Nature 2022, 604, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, J. Patient-Derived Organoids Predict Cancer Treatment Response. Jama 2018, 319, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevers, H.; Bender, E. Q&A: Hans Clevers. Banking on organoids. Nature 2015, 521, S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeber, F.; van de Wetering, M.; Hoogstraat, M.; Dijkstra, K.K.; Krijgsman, O.; Kuilman, T.; Gadellaa-van Hooijdonk, C.G.; van der Velden, D.L.; Peeper, D.S.; Cuppen, E.P.; et al. Preserved genetic diversity in organoids cultured from biopsies of human colorectal cancer metastases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2015, 112, 13308–13311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachs, N.; Papaspyropoulos, A.; Zomer-van Ommen, D.D.; Heo, I.; Bottinger, L.; Klay, D.; Weeber, F.; Huelsz-Prince, G.; Iakobachvili, N.; Amatngalim, G.D.; et al. Long-term expanding human airway organoids for disease modeling. Embo J 2019, 38, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verissimo, C.S.; Overmeer, R.M.; Ponsioen, B.; Drost, J.; Mertens, S.; Verlaan-Klink, I.; Gerwen, B.V.; van der Ven, M.; Wetering, M.V.; Egan, D.A.; et al. Targeting mutant RAS in patient-derived colorectal cancer organoids by combinatorial drug screening. Elife 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauli, C.; Hopkins, B.D.; Prandi, D.; Shaw, R.; Fedrizzi, T.; Sboner, A.; Sailer, V.; Augello, M.; Puca, L.; Rosati, R.; et al. Personalized In Vitro and In Vivo Cancer Models to Guide Precision Medicine. Cancer Discov 2017, 7, 462–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Qin, Z.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Q.; Yang, S.; Rivard, C.; Gao, G.; Ng, T.L.; Tu, M.M.; et al. HER2 exon 20 insertions in non-small-cell lung cancer are sensitive to the irreversible pan-HER receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor pyrotinib. Ann Oncol 2019, 30, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.H.; Chu, X.P.; Zhang, J.T.; Nie, Q.; Tang, W.F.; Su, J.; Yan, H.H.; Zheng, H.P.; Chen, Z.X.; Chen, X.; et al. Genomic characteristics and drug screening among organoids derived from non-small cell lung cancer patients. Thorac Cancer 2020, 11, 2279–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Karthaus, W.R.; Lee, Y.S.; Gao, V.R.; Wu, C.; Russo, J.W.; Liu, M.; Mota, J.M.; Abida, W.; Linton, E.; et al. Tumor Microenvironment-Derived NRG1 Promotes Antiandrogen Resistance in Prostate Cancer. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 279–296 e279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Gao, Y.; Liang, B.W.; Cao, X.Q.; Sun, Z.J.; Yu, J.H.; Liu, Z.D.; Han, Y. Patient-derived organoids of non-small cells lung cancer and their application for drug screening. Neoplasma 2020, 67, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Qian, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, L.; Yu, L.; Liu, X.; Wu, G.; Wang, Y.; Luo, W.; Fang, F.; et al. Human Lung Adenocarcinoma-Derived Organoid Models for Drug Screening. iScience 2020, 23, 101411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, H.; Higa, A.; Hoshi, H.; Hiyama, G.; Takahashi, N.; Ryufuku, M.; Morisawa, G.; Yanagisawa, Y.; Ito, E.; Imai, J.I.; et al. Evaluation of anticancer agents using patient-derived tumor organoids characteristically similar to source tissues. Oncol Rep 2018, 40, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Mun, H.; Sung, C.O.; Cho, E.J.; Jeon, H.J.; Chun, S.M.; Jung, D.J.; Shin, T.H.; Jeong, G.S.; Kim, D.K.; et al. Patient-derived lung cancer organoids as in vitro cancer models for therapeutic screening. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-Y.; Kim, S.-M.; Lim, S.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, S.-J.; Yang, S.-D.; Yun, M.R.; Kim, C.G.; Gu, S.R.; Park, C.; et al. Modeling Clinical Responses to Targeted Therapies by Patient-Derived Organoids of Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2021, 27, 4397–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomerenke, A. Organotypic Models of Lung Cancer. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2018, 09, 09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.J.; Shin, T.H.; Kim, M.; Sung, C.O.; Jang, S.J.; Jeong, G.S. A one-stop microfluidic-based lung cancer organoid culture platform for testing drug sensitivity. Lab chip 2019, 19, 2854–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gmeiner, W.H.; Miller, L.D.; Chou, J.W.; Dominijanni, A.; Mutkus, L.; Marini, F.; Ruiz, J.; Dotson, T.; Thomas, K.W.; Parks, G.; et al. Dysregulated Pyrimidine Biosynthesis Contributes to 5-FU Resistance in SCLC Patient-Derived Organoids but Response to a Novel Polymeric Fluoropyrimidine, CF10. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, T.; Lin, S.; Ji, M.; Xue, N.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; et al. A novel orally active microtubule destabilizing agent S-40 targets the colchicine-binding site and shows potent antitumor activity. Cancer Letters 2020, 495, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kim, S.M.; Lim, S.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, S.J.; Yang, S.D.; Yun, M.R.; Kim, C.G.; Gu, S.R.; Park, C.; et al. Modeling Clinical Responses to Targeted Therapies by Patient-Derived Organoids of Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2021, 27, 4397–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verduin, M.; Hoeben, A.; De Ruysscher, D.; Vooijs, M. Patient-Derived Cancer Organoids as Predictors of Treatment Response. Frontiers in oncology 2021, 11, 641980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraon, P.; Snider, J.; Schormann, W.; Rai, A.; Radulovich, N.; Sánchez-Osuna, M.; Coulombe-Huntington, J.; Huard, C.; Mohammed, M.; Lima-Fernandes, E.; et al. Chemical Genetics Screen Identifies COPB2 Tool Compounds That Alters ER Stress Response and Induces RTK Dysregulation in Lung Cancer Cells. J Mol Biol 2021, 433, 167294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Sui, X.; Song, F.; Li, Y.; Li, K.; Chen, Z.; Yang, F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Lung cancer organoids analyzed on microwell arrays predict drug responses of patients within a week. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gainor, J.F.; Curigliano, G.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, D.H.; Besse, B.; Baik, C.S.; Doebele, R.C.; Cassier, P.A.; Lopes, G.; Tan, D.S.W.; et al. Pralsetinib for RET fusion-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (ARROW): a multi-cohort, open-label, phase 1/2 study. Lancet Oncol 2021, 22, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigematsu, H.; Takahashi, T.; Nomura, M.; Majmudar, K.; Suzuki, M.; Lee, H.; Wistuba, II; Fong, K. M.; Toyooka, S.; Shimizu, N.; et al. Somatic mutations of the HER2 kinase domain in lung adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res 2005, 65, 1642–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Greve, J.; Teugels, E.; Geers, C.; Decoster, L.; Galdermans, D.; De Mey, J.; Everaert, H.; Umelo, I.; In't Veld, P.; Schallier, D. Clinical activity of afatinib (BIBW 2992) in patients with lung adenocarcinoma with mutations in the kinase domain of HER2/neu. Lung Cancer 2012, 76, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kris, M.G.; Camidge, D.R.; Giaccone, G.; Hida, T.; Li, B.T.; O'Connell, J.; Taylor, I.; Zhang, H.; Arcila, M.E.; Goldberg, Z.; et al. Targeting HER2 aberrations as actionable drivers in lung cancers: phase II trial of the pan-HER tyrosine kinase inhibitor dacomitinib in patients with HER2-mutant or amplified tumors. Ann Oncol 2015, 26, 1421–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazieres, J.; Barlesi, F.; Filleron, T.; Besse, B.; Monnet, I.; Beau-Faller, M.; Peters, S.; Dansin, E.; Fruh, M.; Pless, M.; et al. Lung cancer patients with HER2 mutations treated with chemotherapy and HER2-targeted drugs: results from the European EUHER2 cohort. Ann Oncol 2016, 27, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyman, D.M.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; Won, H.; Rodon, J.; Saura, C.; Shapiro, G.I.; Juric, D.; Quinn, D.I.; Moreno, V.; Doger, B.; et al. HER kinase inhibition in patients with HER2- and HER3-mutant cancers. Nature 2018, 554, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Ying, S.; Xu, S.; Huang, J.; Wu, D.; Lv, D.; Bei, T.; Liu, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of pyrotinib in advanced lung adenocarcinoma with HER2 mutations: a multicenter, single-arm, phase II trial. BMC Med 2022, 20, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacini, L.; Jenks, A.D.; Lima, N.C.; Huang, P.H. Targeting the Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor (FGFR) Family in Lung Cancer. Cells 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krook, M.A.; Reeser, J.W.; Ernst, G.; Barker, H.; Wilberding, M.; Li, G.; Chen, H.Z.; Roychowdhury, S. Fibroblast growth factor receptors in cancer: genetic alterations, diagnostics, therapeutic targets and mechanisms of resistance. Br J Cancer 2021, 124, 880–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R.; Radulovich, N.; Ng, C.; Liu, N.; Notsuda, H.; Cabanero, M.; Martins-Filho, S.N.; Raghavan, V.; Li, Q.; Mer, A.S.; et al. Organoid Cultures as Preclinical Models of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2020, 26, 1162–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchinetti, F.; Hollebecque, A.; Bahleda, R.; Loriot, Y.; Olaussen, K.A.; Massard, C.; Friboulet, L. Facts and New Hopes on Selective FGFR Inhibitors in Solid Tumors. Clin Cancer Res 2020, 26, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyse, S.; Huang, P.H. Targeting EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2019, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Jeong, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Pyo, K.H.; Park, C.W.; Heo, S.G.; Yun, M.R.; Lim, S.; et al. Antitumor Activity of Amivantamab (JNJ-61186372), an EGFR-cMet Bispecific Antibody, in Diverse Models of EGFR Exon 20 Insertion-Driven NSCLC. Cancer Discovery 2020, 15, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banda, M.; McKim, K.L.; Myers, M.B.; Inoue, M.; Parsons, B.L. Outgrowth of erlotinib-resistant subpopulations recapitulated in patient-derived lung tumor spheroids and organoids. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0238862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Li, L.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, C.; Qin, Y.; Liu, H.; Ren-Heidenreich, L.; Shi, B.; Ren, H.; Chu, X.; et al. Coexistence of EGFR with KRAS, or BRAF, or PIK3CA somatic mutations in lung cancer: a comprehensive mutation profiling from 5125 Chinese cohorts. Br J Cancer 2014, 110, 2812–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taverna, J.A.; Hung, C.N.; DeArmond, D.T.; Chen, M.; Lin, C.L.; Osmulski, P.A.; Gaczynska, M.E.; Wang, C.M.; Lucio, N.D.; Chou, C.W.; et al. Single-Cell Proteomic Profiling Identifies Combined AXL and JAK1 Inhibition as a Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Lung Cancer. Cancer Res 2020, 80, 1551–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dost, A.F.M.; Moye, A.L.; Vedaie, M.; Tran, L.M.; Fung, E.; Heinze, D.; Villacorta-Martin, C.; Huang, J.; Hekman, R.; Kwan, J.H.; et al. Organoids Model Transcriptional Hallmarks of Oncogenic KRAS Activation in Lung Epithelial Progenitor Cells. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 27, 663–678.e668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachogiannis, G.; Hedayat, S.; Vatsiou, A.; Jamin, Y.; Fernandez-Mateos, J.; Khan, K.; Lampis, A.; Eason, K.; Huntingford, I.; Burke, R.; et al. Patient-derived organoids model treatment response of metastatic gastrointestinal cancers. Science 2018, 359, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yu, L.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Huang, W. Patient-derived organoid (PDO) platforms to facilitate clinical decision making. Journal of translational medicine 2021, 19, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putker, M.; Millen, R.; Overmeer, R.; Driehuis, E.; Zandvliet, M.M.J.M.; Clevers, H.; Boj, S.F.; Li, Q.-X. Medium-Throughput Drug- and Radiotherapy Screening Assay using Patient-Derived Organoids. Journal of visualized experiments : JoVE. [CrossRef]
- Dzobo, K. Taking a Full Snapshot of Cancer Biology: Deciphering the Tumor Microenvironment for Effective Cancer Therapy in the Oncology Clinic. Omics 2020, 24, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzocchi, A.; Devarasetty, M.; Herberg, S.; Petty, W.J.; Marini, F.; Miller, L.; Kucera, G.; Dukes, D.K.; Ruiz, J.; Skardal, A.; et al. Pleural Effusion Aspirate for use in 3D Lung Cancer Modeling and Chemotherapy Screening. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 2019, 5, 1937–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzocchi, A.; Dominijanni, A.; Soker, S. Pleural Effusion Aspirate for Use in 3D Lung Cancer Modeling and Chemotherapy Screening. Methods Mol Biol 2022, 2394, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palechor-Ceron, N.; Krawczyk, E.; Dakic, A.; Simic, V.; Yuan, H.; Blancato, J.; Wang, W.; Hubbard, F.; Zheng, Y.L.; Dan, H.; et al. Conditional Reprogramming for Patient-Derived Cancer Models and Next-Generation Living Biobanks. Cells 2019, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, K.K.; Monkhorst, K.; Schipper, L.J.; Hartemink, K.J.; Smit, E.F.; Kaing, S.; de Groot, R.; Wolkers, M.C.; Clevers, H.; Cuppen, E.; et al. Challenges in Establishing Pure Lung Cancer Organoids Limit Their Utility for Personalized Medicine. Cell Rep 2020, 31, 107588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Jiao, Y.; Qin, S.; Zhao, W.; Chu, Q.; Wu, K. Organoid technology in disease modelling, drug development, personalized treatment and regeneration medicine. Exp Hematol Oncol 2018, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, S.N.; Ingber, D.E. Microfluidic organs-on-chips. Nat Biotechnol 2014, 32, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.J.; Chieh, J.A.; Chen, Y.C.; Lee, K.Y.; Chan, Y.F.; Ho, S.C.; Sun, W.l.; Wang, Y.S.; Huang, W.C.; Chang, W.C.; et al. Lung Cancer On Chip for Testing Immunotherapy. In Proceedings of the 2021 21st International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems (Transducers), 20-24 June 2021; 2021; pp. 1032–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Ren, L.; Tebon, P.; Wang, C.; Zhou, X.; Qu, M.; Zhu, J.; Ling, H.; Zhang, S.; Xue, Y.; et al. Cancer-on-a-Chip for Modeling Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor and Tumor Interactions. Small 2021, 17, e2004282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassell, B.A.; Goyal, G.; Lee, E.; Sontheimer-Phelps, A.; Levy, O.; Chen, C.S.; Ingber, D.E. Human Organ Chip Models Recapitulate Orthotopic Lung Cancer Growth, Therapeutic Responses, and Tumor Dormancy In Vitro. Cell Rep 2017, 21, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingber, D.E. From tensegrity to human organs-on-chips: implications for mechanobiology and mechanotherapeutics. Biochem J 2023, 480, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Karim, M.; Hasan, M.M.; Hooper, J.; Wahab, R.; Roy, S.; Al-Hilal, T.A. Cancer-on-a-Chip: Models for Studying Metastasis. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, S.; Pinho, D.; Vila, A. Development of organoid-on-a-chip platform for preclinical drug screening. In Proceedings of the 5th World Congress on Recent Advances in Nanotechnology, RAN 2020; 2022; pp. 117-111–117-112. [Google Scholar]
- Charelli, L.E.; Ferreira, J.P.D.; Naveira-Cotta, C.P.; Balbino, T.A. Engineering mechanobiology through organoids-on-chip: A strategy to boost therapeutics. Journal of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine 2021, 15, 883–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.W.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, D.W. A Cancer Spheroid Array Chip for Selecting Effective Drug. Micromachines (Basel) 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konar, D.; Devarasetty, M.; Yildiz, D.V.; Atala, A.; Murphy, S.V. Lung-On-A-Chip Technologies for Disease Modeling and Drug Development. Biomed 2016, 7, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, S.; Palmberg, L. Air-Liquid Interface: Relevant In Vitro Models for Investigating Air Pollutant-Induced Pulmonary Toxicity. Toxicol Sci 2018, 164, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, A.; Tilley, A.E.; Shaykhiev, R.; Wang, R.; Crystal, R.G. Do airway epithelium air-liquid cultures represent the in vivo airway epithelium transcriptome? Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2011, 44, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzulo, A.A.; Starner, T.D.; Scheetz, T.E.; Traver, G.L.; Tilley, A.E.; Harvey, B.G.; Crystal, R.G.; McCray, P.B., Jr.; Zabner, J. The air-liquid interface and use of primary cell cultures are important to recapitulate the transcriptional profile of in vivo airway epithelia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2011, 300, L25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulcher, M.L.; Randell, S.H. Human nasal and tracheo-bronchial respiratory epithelial cell culture. Methods Mol Biol 2013, 945, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathis, C.; Poussin, C.; Weisensee, D.; Gebel, S.; Hengstermann, A.; Sewer, A.; Belcastro, V.; Xiang, Y.; Ansari, S.; Wagner, S.; et al. Human bronchial epithelial cells exposed in vitro to cigarette smoke at the air-liquid interface resemble bronchial epithelium from human smokers. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2013, 304, L489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, N.; Papaspyropoulos, A.; Zomer-van Ommen, D.D.; Heo, I.; Bottinger, L.; Klay, D.; Weeber, F.; Huelsz-Prince, G.; Iakobachvili, N.; Amatngalim, G.D.; et al. Long-term expanding human airway organoids for disease modeling. Embo J 2019, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa Rabago, D.; Blakely, C.M.; Haderk, F.; Bivona, T.G. Profiling Sensitivity to Targeted Therapies in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC Patient-Derived Organoids. Journal of visualized experiments : JoVE 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| # | Searches | Results |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | (((patient-derived adj3 organoid*) or patient derived) adj3 organoid*).ti,ab. | 1187 |
| 2 | exp Organoids/de [Drug Effects] | 1031 |
| 3 | (((human-derived adj3 organoid*) or human derived) adj3 organoid*).ti,ab. | 35 |
| 4 | 1 or 3 | 1218 |
| 5 | 2 and 4 | 96 |
| 6 | drug screening.mp. or exp Drug Evaluation, Preclinical/ | 297911 |
| 7 | 4 and 6 | 269 |
| 8 | 5 or 7 | 312 |
| Cancer type | Organoid Model | PDX Model (n) | Compounds Tested | Technology/ Unique culture supplement | Limitations | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adenocarcinoma | Primary lung tumor spheroids (n=14) were cultured in 3D-Matrigel culture methods | N/A | Erlotinib |
|
The number of different drug and dose combinations that can be investigated at one time is limited. | [78] |
| Adenocarcinoma (NSCLC patients with tumors stage I–III, EGFR L858R, EGFR Ex20 ins, KRAS G12C) |
1) Fresh tumor samples harvested for organoid culture. 2) Primary tumor samples and PDOs were analyzed via whole-exome sequencing and IHC. (n=7) |
N/A | 26 antineoplastic drugs tested (gefitinib, osimertinib, afatinib) | Small cohort sized used and will require further large-scale analyses to validate the findings. | [50] | |
| Small cell lung cancer – refractory (tumors stage I–III, EGFR L858R, EGFR Ex20 ins, KRAS G12C) | PDOs (n=4) were developed from human SCLC PDX samples to test if TS inhibition could be a viable strategy for SCLC treatment. | PDXs were generated from SCLC tumor biopsy samples. |
|
|
[59] | |
| 1)Adenocarcinoma 2)Squamous cell carcinoma 3)Adenosquamous carcinoma 4)Large cell carcinoma 5)Small cell lung cancer |
Surgically resected lung cancer tissues from 36 patients were embedded in Matrigel and submerged in MBM to create PDOs (n=80). |
|
|
Limitation of cancer organoid models is the lack of a cancer microenvironment. | [16] | |
| NSCLC | PDOs derived from NSCLC were cultured in vitro (n=10) | N/A |
|
[52] | ||
| Adenocarcinoma | Developed PDOs from human lung adenocarcinoma biopsy samples (n=12) | N/A |
|
Small sample size limits the power to detect molecular markers of drug response. | [53] | |
| Small cell lung cancer (n=1) | Tumor organoids were generated from primary lung cancer cells from patients with SCLC. | N/A |
|
|
Small sample sized used and will require further large-scale analyses to validate the findings. | [58] |
| Adenocarcinoma Metastatic lung cancer |
Developed PDOs from pleural effusion of patients with lung adenocarcinoma (n=2) | N/A | Cisplatin + pemetrexed; carboplatin + pemetrexed; crizotinib |
|
Small sample size. Will require further large-scale analyses to validate the findings. | [86] |
| Non-small cell lung cancer | PDO (n=1) | N/A | S-40 (oral potent tubulin destabilizing agent) | No detail description of organoid culture | Small sample size | [60] |
| 1)Squamous cell carcinoma 2)Adenosquamous carcinoma |
PDOs developed from human tumor lung cancer surgical specimens, (n=3) | N/A | 86 antineoplastic drugs tested, including molecular targeted drugs, immune checkpoint inhibitors, and cytotoxic chemotherapy |
|
Few and limited PDO examples were selected for each type drug screen. | [17] |
| 1)Lung adenocarcinoma 2)Squamous cell |
PDOs developed from 19 surgically resected lungadenocarcinomas (LUAD) and 15 lung squamous cell carcinomas (LUSC), |
|
|
[74] | ||
| Lung adenocarcinoma | Three primary lung cancer organoid models:
|
N/A |
|
Organoids culture condition previously described [74] | [63] | |
| 1) Squamous cell carcinoma 2) Adenocarcinoma 3) small cell lung cancer |
PDOs (n=21) generated from 16 adenocarcinoma and 4 squamous cell carcinoma, two small cell lung cancer organoids | On-chip drug responses of the PDX derived organoids (n=3) were consistent with the in vivo PDX results |
|
|
Well-designed pilot study would improve sensitivity and specificity of the assay. | [64] |
| Lung adenocarcinoma. | Organoids (n=84) were established from patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma. |
|
Organoids culture medium previously described [106] | This was a retrospective study which cannot provide real-time information for clinical decision making. |
[61] | |
| Lung adenocarcinoma | PDOs (n=5) were developed from fresh lung tumors obtained from treatment naïve patients. | N/A |
|
Single cell CyTOF analysis of tumor tissues | Not for high throughput screening with a higher cost | [80] |
| Adenocarcinoma HER2 mutant |
PDO (n=1) was developed from human lung tumor specimens, | Human lung tumor fragments were subcutaneously implanted in mice for generating PDX |
|
One PDO and small size of clinical trial patient cohort | [49] | |
| NSCLC | PDOs (n=2) were developed from malignant pleural effusions of patients with NSCLC with Exon20ins mutations. | Human lung tissue specimens were implanted subcutaneously in mice | Amivantamab | Organoids culture medium previously described [106] | [77] | |
| EGFR-Mutant NSCLC | Patient surgical resection or tumor biopsy specimens (n=3). | N/A | Osimertinib | Organoids culture medium previously described [106] |
|
[107] |
| Ref | Matrigel | Base medium | Bovine serum albumin | N2 | B27 | EGF (ng/mL) |
bFGF (ng/mL) |
FGF-10 (ng/mL) |
FGF-4 (ng/mL) |
Y-27632 (ROCK inhibitor) |
GlutaMax (L-glutamine alternative) |
HEPES (mM) |
R-spondin 1 (ng/mL) |
Noggin (ng/mL) |
Nicotinaminde(mM) | Prostaglandin E2 | SB202190 | N-acetylcysteine | A83-01 | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [78] | Yes | DMEM/F12 | 25% | Yes | 10 μM | Yes | Stem Pro hESC Supplement, 0.1mM 2-mercaptoethanol | |||||||||||||
| [50] | Yes | DMEM/F12 | Yes | Yes | 50 | 10 μM | ||||||||||||||
| [59] | N/A | HyStem-HP hydrogel kits | ||||||||||||||||||
| [16] | Yes | DMEM/F12 | Yes | Yes | 50 | 20 | 10 μM | |||||||||||||
| [52] | Yes | Advanced DMEM/F12 | 0.01% | Yes | Yes | 50 | 1 | 20 | 250 | 100 | 10 | 1μM | 10 μM | 1 mM | 500 nM | 2mM L-glutamine, 100 ng/ml Wnt3a, 10 nM gastrin 1 | ||||
| [53] | Yes | Advanced DMEM/F12 | Yes | Yes | 20 | 10 mM | Yes | 500 | 100 | 10 | 10 mM | 1.25 mM | 500 nM | 25 ng/mL FGF-7 | ||||||
| [58] | Yes | DMEM/F12 | Yes | Yes | 50 | 20 | 10 μM | |||||||||||||
| [86] | hydrogel cultures | RPMI 1640 | 5% fetal bovine serum | |||||||||||||||||
| [60] | No detailed description | |||||||||||||||||||
| [17] | FBIM001 medium [54] | |||||||||||||||||||
| [74] | Yes | RPMI 1640 | Yes | Yes | 50 | 100 | 100 | 10 μM | Yes | 10 | 100 | 500 nM | 250 nM CHIR 99021, 100 nM SAG | |||||||
| [63] | Yes | RPMI 1640 | Yes | Yes | 50 | 100 | 100 | 10 μM | Yes | 10 | 100 | 500 nM | 250 nM CHIR 99021, 100 nM SAG | |||||||
| [64] | Yes | DMEM/F12 | Yes | Yes | 50 | 10 μM | Yes | 10 | 5 | 3 μM | 1 mM | 5 μM | 10 μM Forskolin, 3 nM Dexamethasone | |||||||
| [61] | Yes | Advanced DMEM/F12 | Yes | 100 | 5 μM | Yes | 10 | 500 | 100 | 5 | 500 nM | 1.25 mM | 500 nM | 25 ng/mL FGF-7 | ||||||
| [80] | Yes | Advanced DMEM/F12 | Yes | Yes | 50 | 10 | 10 | 10 μM | 500 | 100 | 4 | 1μM | 5 μM | 500 nM | 20 ng/ml HGF | |||||
| [49] | Yes | Advanced DMEM/F12 | Yes | 50 | 10 | Yes | 10 | Yes* | Yes* | 10 | 10 μM | 1.25 mM | 500 nM | R-spondin and Noggin form condition medium, 1 ng/ml FGF2, Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) | ||||||
| [77] | Yes | Advanced DMEM/F12 | Yes | 100 | 5 μM | Yes | 10 | 500 | 100 | 5 | 500 nM | 1.25 mM | 500 nM | 25 ng/mL FGF-7 | ||||||
| [107] | Yes | Advanced DMEM/F12 | Yes | 100 | 5 μM | Yes | 10 | 500 | 100 | 5 | 500 nM | 1.25 mM | 500 nM | 25 ng/mL FGF-7 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





