1. Introduction
Blockchain is a decentralized and distributed ledger that enables secure and transparent transactions without the need for intermediaries. However, there are some challenges associated with blockchain technology. One of the main limitations is its limited capacity to process a large number of transactions on the chain, which can result in slow transaction times and high transaction fees. Additionally, blockchain is susceptible to attacks from malicious actors who may attempt to manipulate the system or steal sensitive information.
To address these issues, off-blockchain payment channels have emerged as a promising solution to improve blockchain scalability. These channels allow two parties to perform continuous micropayments without the need to upload each transaction to the blockchain. This not only reduces the load on the blockchain but also improves transaction speed and reduces transaction fees. Overall, off-blockchain payment channels have the potential to enhance the efficiency and scalability of blockchain technology, making it more accessible and useful for a wider range of applications.
The security concerns surrounding micropayment via payment channels stem from the fact that there is no third-party agency overseeing the transactions, making it vulnerable to attacks by adversaries. For instance, if Alice sets up a payment channel with Bob for conducting n continual micropayments, the transactions are carried out through a hash chain. In this case, a small amount is defined as any transaction below 10 dollars, and the total transaction amount is the cumulative sum of n consecutive transactions. However, there are two potential attack scenarios that could lead to losses for either Alice or Bob:
1) During the continual transactions, either Alice or Bob may engage in fraudulent or default payments, leading to losses for the other party;
2) An external adversary may attack the intermediate link of the continuous transactions and obtain transaction messages, causing losses for either Alice or Bob.
Both of the above scenarios will cause losses to Alice or Bob.
To prevent such attacks, it is essential to establish robust security protocols and ensure that all parties involved are trustworthy and reliable. To address this issue, there are two mainstream solutions. One is the network of micropayment channels proposed by Joseph Poon et al., which uses scripting opcodes to enable secure fund transfers and enforces non-cooperation through signed multi-signature transactions on the blockchain. The other solution is a micropayment scheme based on blockchain, which uses chameleon hash functions to construct a secure hash chain for transactions. In this paper, we propose a lockable signature scheme to ensure the continuity and security of micropayments. Our proposal uses an invisible signature lock to eliminate the need for a trusted third-party agency during transaction processing, providing a secure and efficient method for parties who do not trust each other or lack a trading platform.
1.1. Our Main Contributions
We have developed a cutting-edge, high-speed, and secure micropayment system (CMS) that operates continuously using blockchain technology and payment channels.
To achieve the continuity of the transaction process, our system utilizes hash chains to connect each transaction, ensuring seamless transaction processing. Transactions are limited to amounts less than 10 dollars, and clients are supported in purchasing multiple items from vendors, with the total transaction amount being the sum of all transactions. This allows clients to purchase high-value items from vendors.
To ensure the security of our system, we have implemented a lockable signature scheme. By incorporating an invisible signature lock into each transaction, we prevent both parties from engaging in fraudulent behavior and protect against adversarial attacks. This eliminates the need for a trusted third party to be present during transactions. Our security analysis has shown that our CMS is secure and provable.
Our CMS is the first system to introduce a hidden signature lock structure into a micropayment scheme. This reduces transaction costs in off-chain payment channels. Our experimental results have demonstrated the efficiency of our system.
1.2. Organization
The remaining sections of this paper are organized as follows. Section II provides an introduction to the background knowledge relevant to this study. Section III outlines the definitions of our system model. Section IV details the construction of our CMS system. In Section V, we present an analysis of the CMS system model. Our experimental results are presented in Section VI. Section VII reviews related work in this area. Finally, we conclude the paper in Section VIII.
2. Preliminaries
In this section, we introduce certain useful preliminaries for our scheme.
2.1. Digital Signature
The Digital signature is conducive to achieve the credibility and reliability of a message. Formally, it includes the following triple of efficient algorithms based on public key cryptography:
The ken generation algorithm : It takes as input the security parameter and outputs a pair of public-private keys ;
The signing algorithm : It inputs a secret key and a message and outputs a signature .
The verification algorithm : It outputs 1 if is a valid signature on m under the public key , and outputs 0 otherwise.
Suppose there are two users, Alice and Bob, as the sender and receiver of the signature. Alice can use her private key to sign the message m to be sent, and then send the obtained signature to Bob. Bob, as the receiver, uses Alice’s public key to verify the received signature.
As we all know, the security definitions and mathematical proofs for the digital signature have been clearly and explicitly presented. When using digital signatures to construct lockable signature schemes, we must clarify the standard concepts of existential unforgeability and correctness of digital signature.
The two properties mentioned of the digital signature are as followed:
1) Existential Unforgeability: In a signature scheme, any adversary can forge the signature of a message. But the probability that the adversary forges successfully will not be greater than the negligible probability obtained by inputting the security parameters. Even if the adversary has seen the signatures of multiple messages it selects.
The situation where the adversary
has access to all signature oracles is formulated as
2)
Correctness: All secure signatures must be verifiable with a probability of unverifiability lower than the negligible probability obtained by the input security parameters. With overwhelmingly high probability, all valid signatures must verify.
2.2. Hash Function and Hash Chain
The hash function is the general term for a group of functions. All of the following characteristics are conditions that it needs to meet:
1) It can accept a string of any length as input;
2) It can generate fixed-length output values;
3) Its computation time is within reason.
A function for cryptographic hash can be expressed as . A bit string of any length can be compressed to n through function operations. The following are two properties of a secure cryptographic hash function:
1) Collision resistance: Given these functions , the pair of distinct strings x, y that satisfies cannot be found during computation.
Choose a function
H. The strings
x and
y satisfying
cannot be found during the calculation, where strings
x and
y are different. More formally:
where
is an adversary.
2) One-wayness: The calculation process of the function should be simple; Choose a value
h and compute
. If
x cannot be found in the computation, the cryptographic hash function
is defined as a one-way function. More formally:
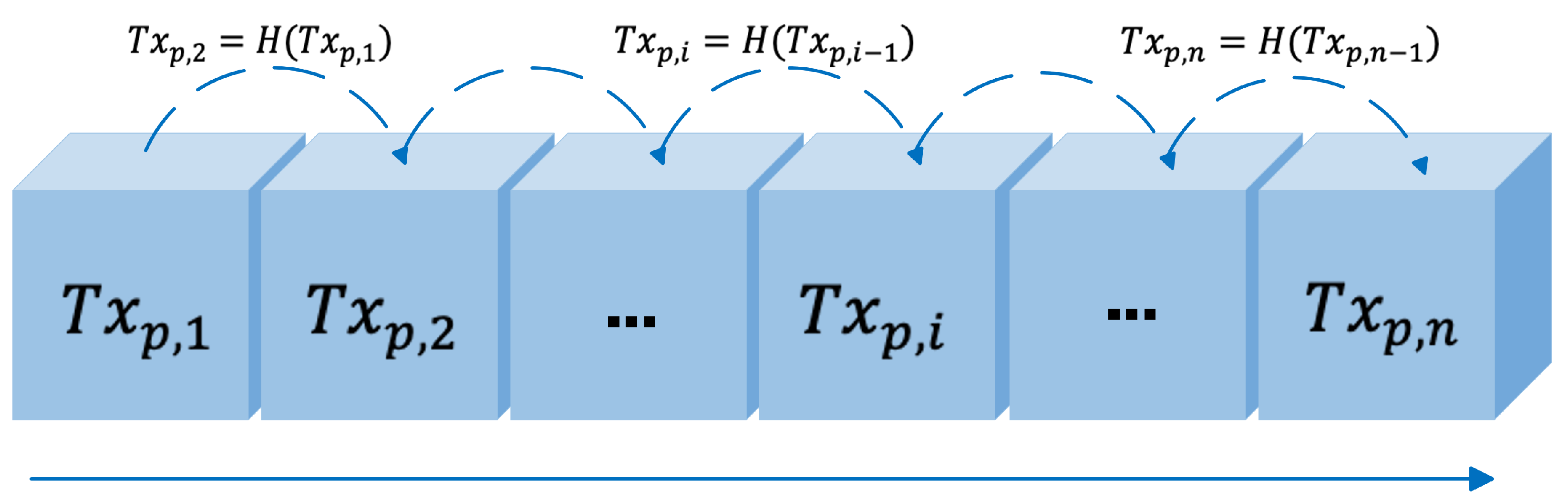
The Hash function can be applied to micropayment schemes to achieve more efficient and faster transactions. The following hash chain is generated in the Pay Word scheme [4].
This approach guarantees that the origin of each transaction is the same. The bank signs the transaction
with its secret key. Subsequent small transactions are associated with
through the hash function. During the transaction, the security of each small transaction depends upon the difficulty of calculating the hash inverse function. The idea of the hash chain is presented in
Figure 1 (see
Figure 1).
2.3. Blockchain
Blockchain can be regarded as a special kind of bookkeeping system. It uses distributed ledger technology to store various kinds of transaction messages in the cloud. Blockchain’s decentralized accounting means that parties have a credible connection without the supervision of a trusted third-party agency. In terms of ensuring the reliability and authenticity of transactions, the big data technology of the blockchain can be achieved by eliminating information asymmetry. The cloud server of the blockchain and the network equipment continuously exchange messages, so that the message can be quickly transmitted to the world.
We assume that there is an ideal function of the blockchain , and can maintain the blockchain. The message on the blockchain is updated according to the transaction process between the clients and the vendors. The client generates a secret key and signs each transaction information with the vendor. And the blockchain can record the transaction messages of the first and the last transactions. We use the symbol to replace the n-th transaction, where () and (). When performing a task, any user C can send a read message to ,and will send the entire transcript of the blockchain to user C. In the main time, We have introduced a time lock interface in the function to set the time point for the last transaction. If the global clock exceeds the expiry point, the transaction is not completed and the transaction amount is withdrawn to the client’s bank account.
2.4. Payment Channel
The payment channel () enables two mutually distrustful parties to transact without uploading every single payment message to blockchain. Two parties broadcast a funding transaction together with their deposits to the blockchain to open a payment channel [36]. The capital capacity to open the payment channel is the total amount of transactions between the two parties, that is, the amount transferred by the bank to the client. The key to the payment channel protocol is that the parties to the transaction can reach a cognitive agreement on the latest fund allocation. If one of the two parties in the transaction wants to close the transaction, they can send a promise to the blockchain regarding the final version of the fund’s distribution. In this way, the payment channel can be closed and the corresponding funds will be returned to the user. Since only the first and the last transactions are uploaded to the blockchain for opening and closing payment channels, the throughput of the blockchain is significantly improved.
Table 1.
Notations in CMS System.
Table 1.
Notations in CMS System.
| Notations |
Descriptions |
| B |
Bank |
| C |
Clients |
| V |
Vendors |
| F |
The total amount sent by bank to clients |
|
Partially identifiable information of clients
and vendors |
|
Bank’s signature on transaction information sent to clients |
|
The security parameter |
|
The master public key |
|
The master secret key |
|
An attribute set |
|
The i-th transaction |
|
The time of the i-th transaction |
|
The client’s signature on the i-th transaction information |
|
The lock of the i-th transaction |
3. System Model
3.1. System Model
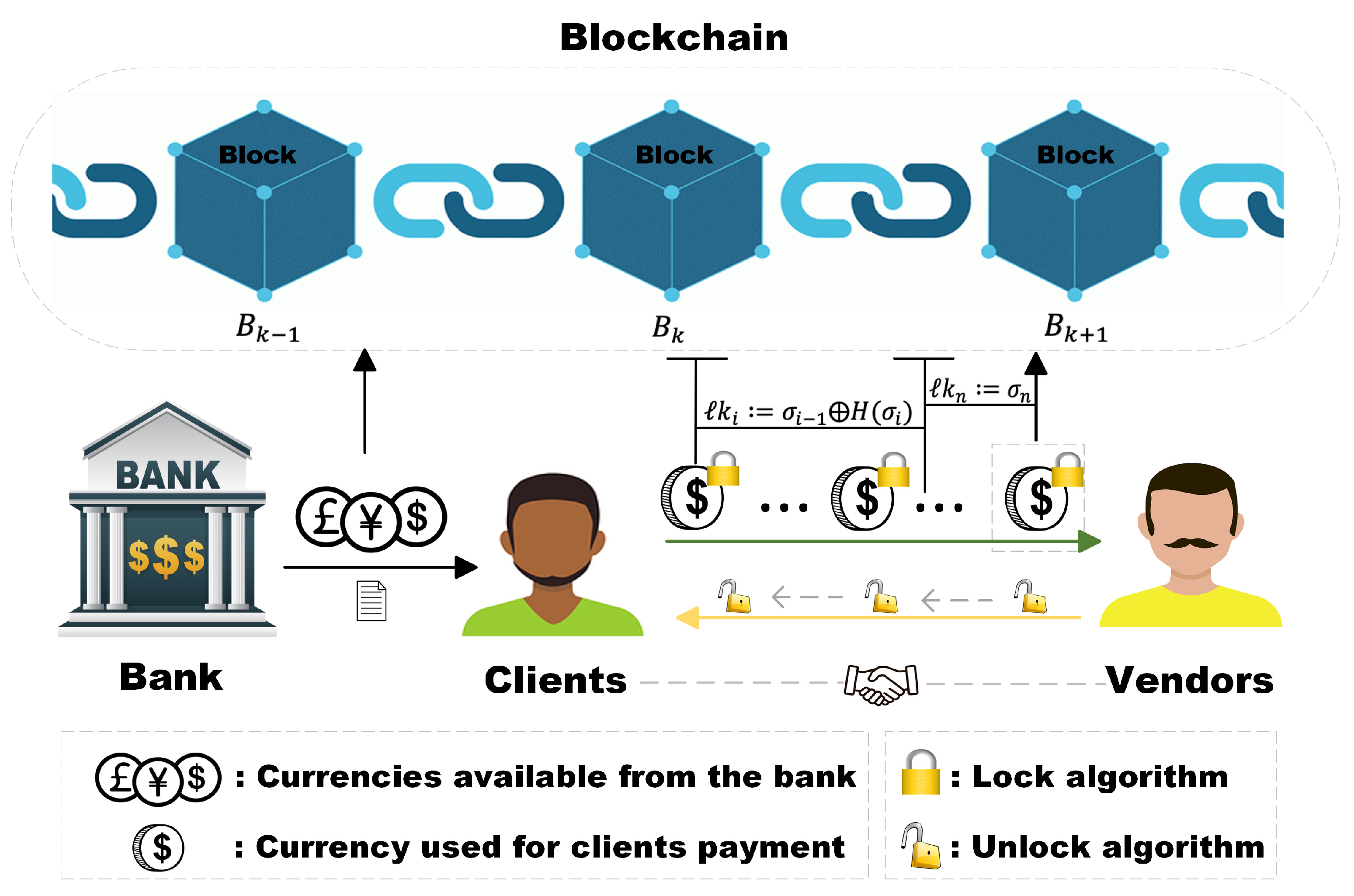
The system model of CMS is presented in Figure2 (see
Figure 2). We briefly describe he function of each entity.
1) Bank B plays the role of transaction supervision, and does not open payment customers for users (clients and vendors) with low reputation value. After the transaction is opened, the bank will send the total transaction amount and the signature of the transaction messages (transaction amount, part of the identity information of both parties, sending time) to clients.
2) Clients C are the initiator of the transaction. Clients with a reputation value higher than 50 on their bank account can successfully initiate transactions. If a client commits a fraudulent transaction during the continual micropayment, the reputation value of the bank account will be deducted according to the severity.
3) Vendors V are the recipient of the transaction. Vendors with a credit score above 50 on their bank account can successfully accept transactions. If a vendor commits a fraudulent transaction during the continual micropayment, the reputation value of the bank account will be deducted according to the severity.
4) Blockchain is used to record transactions between two parties. Only when the transaction is successfully completed, the first and last transaction information will be successfully uploaded and recorded.
3.2. Definitions of lockable signatures
Lockable signature scheme () is defined in terms of public key system signature schemes, as defined below.
: The key generation algorithm takes as input the security parameter and generates a pair of public–private keys
: The key generation algorithm takes as input the security parameter and generates a pair of public–private keys.
: The lock algorithm takes as input two pairs of secret key and message and and returns a lock .
: The unlock algorithm takes as input two pairs of public key and message and , a locking signature , and a lock and outputs a locked signature .
: A lockable signature scheme is correct if for all , all pairs of messages , for all key pairs and in the image of .
3.3. Definitions of micropayment algorithms
We list the notations of CMS in Table 2. The system consists of the following algorithms:
: The setup algorithm takes no input other than the security parameter . It outputs the public key and the master secret key .
: The key generation algorithm takes as input the master secret key and a set of attributes and generates the public key and the secret key .
: The signature algorithm takes as input the transaction , the credibility of both parties to transaction and the timestep of transaction . It outputs the first signature of the transaction , which is the signature sent by the bank to A.
: The signature algorithm takes as input the transaction and the timestep of transaction . It outputs A’s signature for each transaction .
: The lock algorithm takes as input a locked signature and a locking signature and returns a lock .
: The unlock algorithm takes as input a locking signature , public key and a lock , and returns a locked signature .
: The verification algorithm outputs 1 if the individual transaction signatures and transaction messages are obtained gradually by the unlocking algorithm, otherwise it outputs 0.
3.4. Threat Model
In this section, we define the security assumptions and threat model that the scheme will face. We make the following security assumptions:
Neither party is trustworthy, and both have the potential to act maliciously.
We assume that communication between users is synchronous.
The underlying blockchain is secure and cannot be controlled by a malicious party. The blockchain has ideal functionality, updates based on transactions between parties, and has a time-locked interface that cancels the impact of transactions on user balances if they expire after a duration of time t.
In addition, we also provide the threat types that may be encountered in our solution:
Customer’s fraudulent payment. A malicious customer attempts to make a fraudulent payment, without actually making the payment and falsifying the payment information. They sign the payment information, construct a signature lock, and send it to the supplier through a local channel.
The supplier provides fake goods. A malicious supplier may provide customers with fake or meaningless goods. The transaction is based on the principle of one price for one item. If the supplier engages in fraudulent behavior, the customer can terminate the transaction.
External attack behavior. Malicious adversaries may attempt to alter the transaction process through forged behavior. Adversaries aim to carry out transaction information leakage attacks during a certain stage of off-chain transactions to obtain transaction information and gain undue profits.
4. Our Construction
Firstly, We introduce the framework overview. Then we show the detailed construction of and CMS in this section.
4.1. Framework Overview
The continuous micropayment system can ensure efficient, fast and safe continuous micropayment for both parties. The system is based on blockchain. The use of off-chain payment channels increases the scalability of the blockchain and allows transactions and data to be moved off-chain. The system includes bank, clients and vendors. The bank provides the clients with the total amount of the transaction required. Each user (clients and vendors) has a corresponding reputation value in the bank. After receiving the transaction request, the bank has the right to check the reputation value of both parties to determine whether the transaction can be opened. Continuous small-value transactions between users and suppliers through transaction channels. These consecutive transactions can be micro-coins. Each transaction
is not independent but associated.
The client signs each transaction information, thereby generating a series of signature locks. Every transaction vendors received contains a signature lock. The lock is invisible during the transaction, which can ensure the security of the transaction. After the vendor receives the last transaction, the algorithm is used to unlock the chain of locks one by one. After the unlocking process is completed, each transaction message can be obtained. Finally, the first transaction information and the last transaction information are uploaded to the blockchain.
Table 2.
Notations in LS.
Table 2.
Notations in LS.
| Notations |
Descriptions |
| p |
A prime |
|
The finite field of integers modulo a prime p. |
|
A point on an elliptic curve |
| q |
The order of group
|
|
The client’s signature on the i-th transaction information |
|
The hash function |
|
The instance key |
|
The x-coordinate of the elliptic curve point |
|
The y-coordinate of the elliptic curve point |
|
The locked signature |
|
The locking signature |
4.2. Detailed LS
The algorithm is parameterized by a group of order . The group is generated by a point on an elliptic curve over the finite field of integers modulo a prime . The algorithm makes use of a hash function . Curve coordinates and scalars are represented in bits, which is also the security parameter [16]. The LS algorithms are as follows:
Select the secret key
from the finite field
Compute the public key
as
Select the secret key
from the finite field
Compute the public key
:
Output and
1)
Select
from the finite field
2)
Select the instance key
from the finite field
-
:
-
:
1)
Parse as
2)
Output 1 if for all , all pairs of messages , for all key pairs of and in the image of .
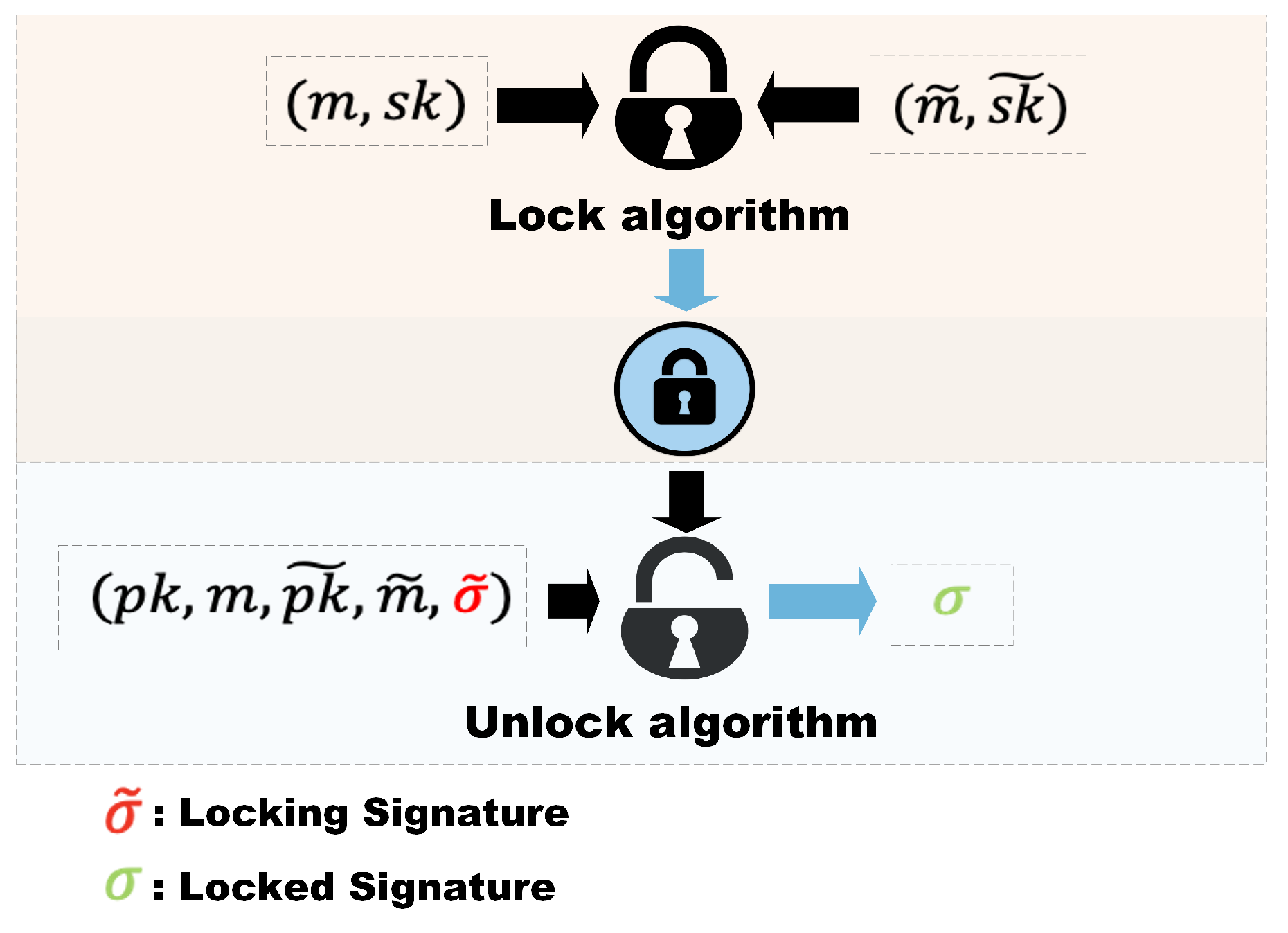
A lockable signature scheme contains two signatures, defined as the locking signature and the locked signature. In the same breath, the lockable signature scheme contains two algorithms, namely the lock algorithm and the unlock algorithm. In the continual micropayment schemes, they sign two different but adjacent transaction messages.
Here, we first determine the transaction information. Then distinguish the information corresponding to the locked signature and the locked signature, and use the signature algorithm to generate the corresponding signature. Then we combine the signature with the hash operation and link the signatures according to the operation method of the hash chain. Finally, the lockable signature calculation process is introduced. The two signatures formed can be verified against different public keys.
The invisible signature lock can be obtained by inputting the locked signature and the locked signature into the locking algorithm. During the transaction process, a series of invisible locks generated by the client, and each node transaction of the hash chain is sent to the vendor through the payment channel. The vendor completes the unlocking process through the unlocking algorithm so that the transaction messages and the amount of each transaction can be obtained.
Our notion of security for lockable signatures is defined as follows. As mentioned earlier, the lockable signature scheme contains two algorithms, namely the lock algorithm and the unlock algorithm. First, we believe that signature algorithms can get deterministic signatures. Then we believe that the lock algorithm is implemented honestly in the security concept.
|
Algorithm 1 Unlockability of lockable signature |
 |
(Unlockability) The unlock ability embodies three features.
1) Correctness: It ensures that lockable signature schemes can be unlocked correctly at the end of a series of transactions;
2) Efficiency: Lockable signature shows higher efficiency during transactions compared to the traditional schemes that use a trusted third party to witness the whole transaction process;
3) Completeness: Lockable signature schemes can prevent the transaction process from being interrupted by an external adversary who might launch a transaction-intercept attack
1.
The adversary obtains the transaction message (time or phase) in the middle of the micropayment transaction using a hash chain. Then can trace back to the first transaction and the account messages of transaction parties are exposed.
There is an adversary in security analysis. He can choose a message pair while accessing the secret key’s signing oracle. In the process of unlockability feature verification, the generated signature lock is obtained by running the lock algorithm honestly. The signature lock is revealed to the adversary . Then the adversary returns a candidate locking signature for unlocking, and obtains the corresponding locked signature through the unlocking process. If the obtained locked signature is an invalid signature for the transaction message m under the public key , the adversary wins.
We say that the lockable signature satisfies the property of unlockability, which means that the adversary has a negligible advantage under the restriction of the given security parameters.
(Invisibility) As mentioned earlier, the signature locks are hidden during transactions [29]. The invisibility feature can ensure that the information of both the locking signature and the locked signature will be invisible within the transaction process. In other words, the transaction information is not exposed when it is not unlocked. In the security analysis,
can query the signature oracle for the secret key
, and then select a message pair
. The lockable signature scheme is reckoned to fit the definition of invisibility, suggesting that the winning probability of the adversary is approximately 1/2.
|
Algorithm 2 Invisibility of lockable signature |
 |
Figure 3.
The idea of Lockable Signature ().
Figure 3.
The idea of Lockable Signature ().
4.3. Detailed CMS
A continuous micropayment system consists of a group of users participating in transactions and a blockchain-based cryptocurrency system for microtransactions. In the case of multiple transactions, it is necessary to ensure that the amount of the previous transaction is deducted. It means that the previous transaction has been completed.
-
Client C confirms the object of the transaction (vendor V) and initiates the transaction request. Upon receipt of the request, the bank B first confirms the reputation value of both parties to the transaction. Bank B will issue a transaction warning or not allow the transaction to start if one party has a reputation value below 50. If the credit value is required, bank will sent client the total amount of the transaction F, some identification information of both parties and a signature to the transaction messages . The transaction messages include time , the reputation value and message .
-
An off-chain payment channel is established between the client and the vendor. The client pays n micro-coins in the amount of (which can be generated via Bitcoin) to the vendor via the payment channel. In the first transactions, the client sends the amount of each transaction , the signature lock (generated by the client’s signature on the transaction via the Lock algorithm) to the vendor.
-
In the n-th transaction, the client sends the transaction amount and the signature lock to the vendor. The difference between the n-th transaction and the first transactions lies in the construction of the signature lock .
The vendor receives each transaction through the payment channel. Through the verification algorithm () and the unlock algorithm (), the client’s signature on each transaction message is gradually obtained, and finally each transaction message is obtained. This allows the vendor to perform verification. Any losses can be compensated at the end of the payment process. Generally speaking, if the client fails to pay in multiple transactions, the total amount received by the vendor will not match the total amount issued by the bank at the end of the transaction.Vendor can provide the voucher to the bank and receive the replenished amount. If one of client or vendor needs to abort the transaction in multiple consecutive transactions, the existence of the signature lock can avoid the loss of both parties after the transaction is interrupted.
The vendor can obtain message about each transaction by progressively unlocking it. After a successful transaction, the first and last transaction is uploaded to the blockchain and used to open and close the blockchain. The blockchain is used as proof of the transaction.
5. Security Analysis
In this section, we have analyzed the security of the scheme. The scheme utilizes the notion of blind signature and some cryptographic tools to defend against the threats defined earlier.
The signature scheme we use is unforgeable and correct. Among them, unforgeability means that the adversary can return a valid signature of a selected message through access to the signature oracle. but the adversary cannot forge a new signature on its newly selected message.
The hash function we use is proven to be efficient and secure. Because the Collision resistance and One-wayness are two properties of the secure hash function.
The customer falsely pays. The supplier receives a series of locks to unlock and obtain signatures for transaction information, thereby obtaining transaction information from the signatures. The supplier fails to verify the transaction information, sends a verification failure flag to the bank, and freezes the funds irreversibly. At the same time, the last transaction information will not be uploaded to the blockchain, and the transaction will not be recorded and confirmed. For example, the scheme is constructed based on ECDSA signature. Alice, as the customer, forges the i-th payment information. Alice randomly selects the private key k, calculates the public key , where G is the base point of the elliptic curve, and then selects a random number r to calculate for information i. When Alice signs the information , she randomly selects d, first calculates , where H is , and then calculates the signature , . Then, the obtained signature is input into the lock algorithm to generate the signature lock , which Bob receives and inputs into the unlock algorithm to obtain Alice’s signature for , verifying that . Therefore, the supplier fails to verify the transaction information, and the transaction will not be recorded and confirmed.
The supplier provides false goods. The transaction is based on the principle of one good, one price, and if the supplier engages in misconduct, the customer can terminate the transaction. A successful transaction means that the customer approves of the goods provided by the supplier. The transaction is unlocked and verified on a transaction-by-transaction basis, and after verification is complete, the last transaction is automatically uploaded to the blockchain.
External attack behavior. Malicious adversaries would like to alter the transaction process through forged behavior. The adversary seeks to carry out transaction information leakage attacks during a certain stage of off-chain transactions, in order to obtain transaction information and illegitimate profits. This scheme uses ECDSA signatures, which are tamper-proof. The digital signature lock in this scheme has concealment. Concealment ensures that the properly generated lock will not expose the locked signature and the signature used to generate the lock. When an adversary chooses to attack, they can choose two messages , randomly generate a b, and if , correctly generates a lock. If , a simulator output a lock. The adversary must solve the elliptic curve discrete logarithm problem to forge a valid signature. The adversary can only run the unlock algorithm using the signature on m.
6. Experiment
Our experiment consists of two stages, one stage is the off-chain transaction process. Another stage is to upload the transaction message to the blockchain, which contains two parts of message. They are the remittance message of the bank to the client at the beginning of the transaction and the last transaction information of the continuous micropayment.
Table 3.
The costs of CMS.
Table 3.
The costs of CMS.
| |
Resources |
| Phase |
Time |
Communication |
| setup |
|
|
| transaction |
|
|
| Release |
|
0 |
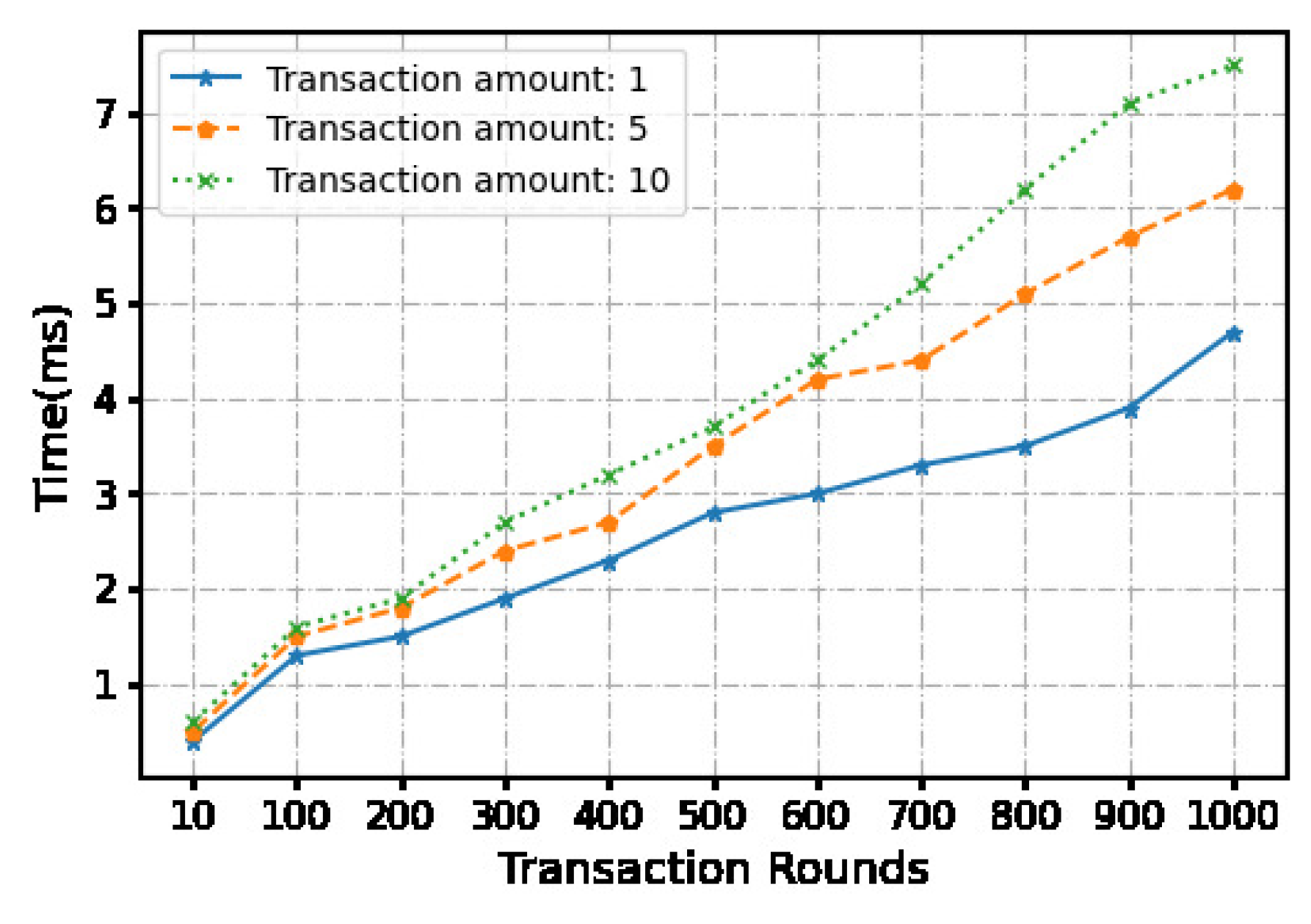
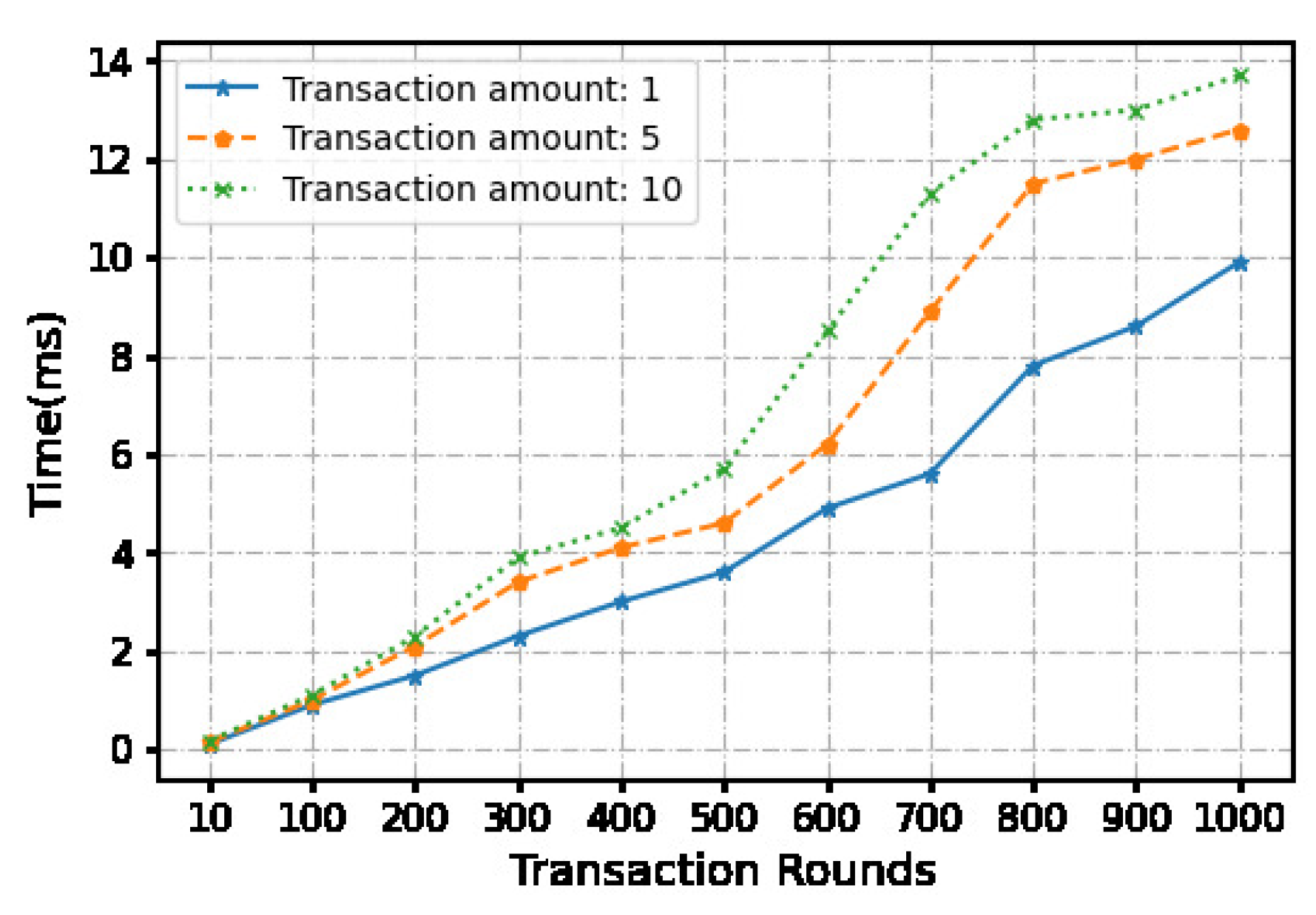
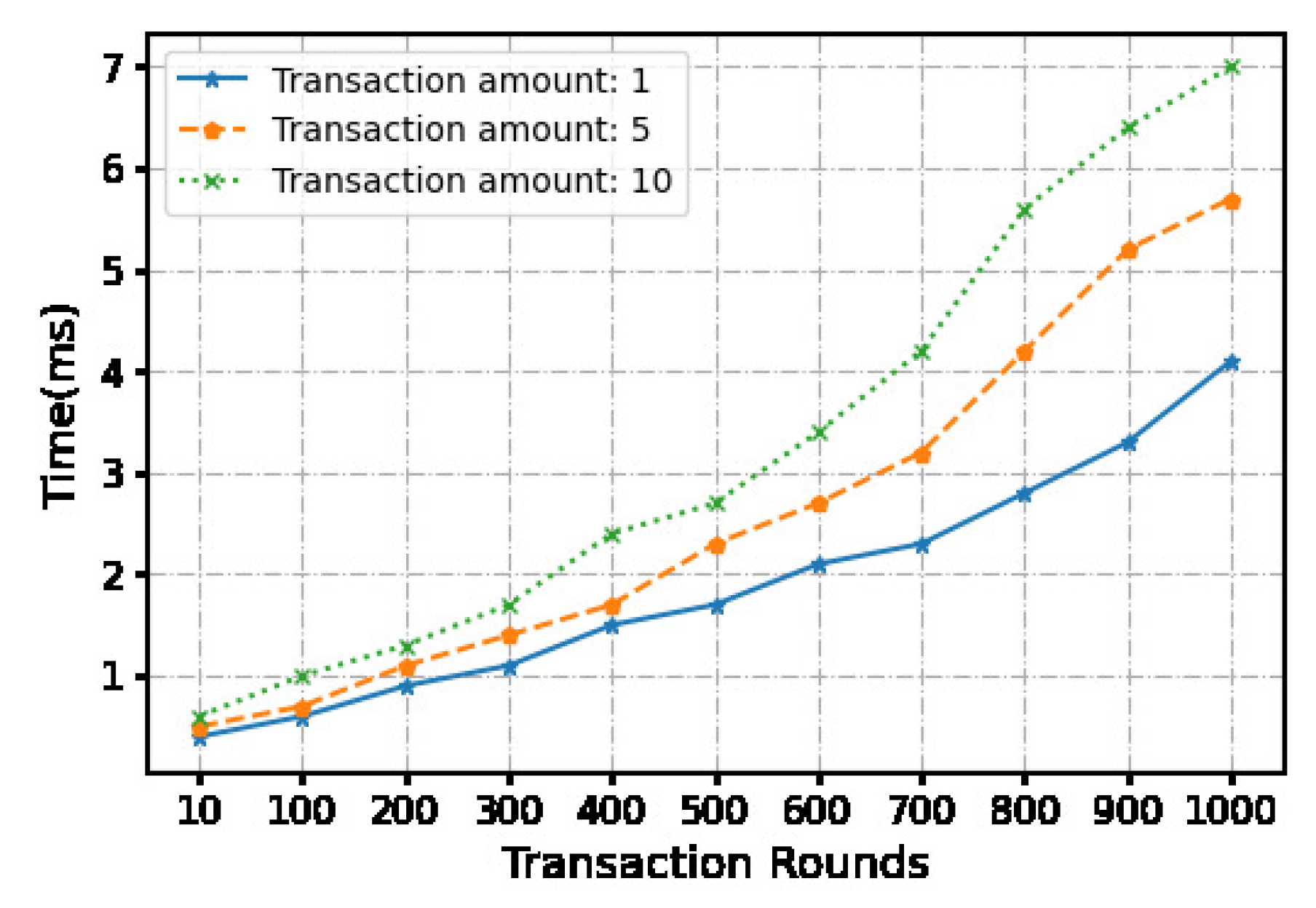
We use a local machine with an apple M1 chip 8-core processor and 16GB memory to conduct experiments, and measure and calculate time and overhead costs. We evaluated the time cost of a continua micropayment scheme using python.Each micropayment is under 10 dollars. In order to compare the impact of the payment amount on the computational cost, we set three payment amounts, namely 1 dollar, 5 dollars, and 10 dollars.
Table 4.
Communication overhead comparison results.
Table 4.
Communication overhead comparison results.
| Scheme |
Client Communication Costs |
Vendor Communication Costs |
| [38] |
|
|
| Our scheme |
|
|
At the same time, we set the number of continuous transactions through the off-chain payment channel between 10-1000 times. And 6 fixed transaction times were selected for statistical time cost. Hash functions are the key components for the blockchain construction, transactions and micropayment. Our system relies on the underlying security of hash functions such as . Using the algorithm as the hash function, the signature is randomly generated during the transaction. We ran 900 operations. The measured transaction time and communication cost averages and are recorded in Table II. While we do not consider the network latency in our measurements, this does not constitute the efficiency bottleneck of our approach.
In the stage, the bank needs to verify the reputation value of both parties to the transaction. The client needs to receive the total transaction amount, signature and partial identity information of both parties sent by the bank. We used 40-bit characters to represent bank-generated signature and measured transaction times to average . During the phase, users use a signature generator to generate signatures for each transaction. Then, the lock is generated through the lock algorithm and sent to the supplier in 10000 consecutive transactions. The average measured transaction time is .The Table III records the time and cost of 10,000 consecutive transactions using the off-chain channel with a transaction amount of 10 dollars.
Figure 4.
The time cost of setup phase.
Figure 4.
The time cost of setup phase.
Figure 5.
The time cost of transaction phase.
Figure 5.
The time cost of transaction phase.
Figure 6.
The time cost of release phase.
Figure 6.
The time cost of release phase.
After the off-chain payment channel is initialized, both parties engage in continuous multiple payment behaviors, including the customer C’s fund expenditure and the supplier B’s receipt process. Our solution can achieve a low-cost payment plan while ensuring secure transactions. Article [33] also uses off-chain transactions, but the difference between their solution and ours is that their off-chain transactions introduce off-chain committees to assist in achieving secure transactions.
To demonstrate the lightweight nature of our scheme in off-chain transactions, we conducted a set of experiments. First, we conducted a comparative experiment using a hash chain to implement continuous transactions in off-chain payment channels, while using an off-chain committee as mentioned in our scheme to ensure the security of these continuous transactions. We compared the results of the comparative experiment with those of our experiment in this paper. For the sake of fairness, we compare these two schemes under the same cryptographic system. Assume that both schemes use the off-chain ECDSA signature scheme, and the length of the generated signature is represented by . We use to represent the length of each transaction amount off the chain, s to represent the length of the off-chain transaction serial number, e to represent the number of off-chain committee members, and h to represent the number of times the hash function is called. We use 10 consecutive transactions as an example.
Experiments have shown that under normal trading conditions without external attacks, our solution has lower costs. If the transaction process is subject to external attacks, the use of off-chain committees will incur additional expenses, while the costs of our solution remain unchanged under both conditions, whether external attacks exist or not.
The second part is to upload the start and end transaction information to the blockchain.
We use a virtual machine to build a blockchain hyperledger framework. During the entire transaction process, the first transaction message (transaction total, transaction number, partial identity information of both parties, bank signature) is uploaded to the blockchain. The last transaction information (single transaction amount, transaction number, customer signature) is also uploaded to the blockchain. Record the time it takes to upload two messages.
7. Related Work
Micropayment first appeared 20 years ago, and the initial micropayment transaction amount ranged from a few cents to a few dollars. Richard J. Liptno [5] proposed a micropayment system specifically for the World Wide Web. The system establishes a coin-tossing protocol to achieve transaction fairness through a third-party organization. Silvio Micali and Ronald L. Rivest [6] proposed three micropayment schemes, namely MR1, MR2, and MR3. They can Improve the efficiency of micropayment schemes and prevent malicious behavior by individual players. Ronald L. Rivest and Adi Shamir [9] proposed micropayment schemes named ’PayWord’ and ’MicroMint’. The author focuses on the use of hash functions to reduce the number of public key operations. Yi et al. [7] proposed three micropayment schemes based on hash chains and hash functions. The author introduces salt into the scheme, which improves the security of payment while eliminating the constraint of the scheme. Quan Son Nguyen [10] proposed the concept of multi-dimensional hash chain and applied it in the micropayment scheme. The author pointed out that the use of multi-dimensional hash chain can improve the security and efficiency of payment. Jie Wu et al. [22] proposed the concept of super nodes to solve the problem of the instant execution capability of Lightning Network applications in micropayment systems. At the same time, it can also reduce the number of small nodes that need to be liquidated in the Lightning Network.
With the development and maturity of blockchain technology, more and more micropayment schemes combined with blockchain have been proposed. Conrad Burchert et al. [8] proposed a micropayment channel network, and at the same time proposed a new layer between the blockchain and the payment channel to solve the scalability problem of the blockchain. Noureddine Boudriga [2] proposed a blockchain-based micropayment scheme, using three trust models for verifying and managing the blockchain network. This scheme can reduce transaction verification costs and reduce network attacks. Fatemeh Rezaeibagha and yi mu [1] proposed a cryptocurrency-based micropayment scheme. The scheme is built on the basis of blockchain, and at the same time uses the chameleon hash function to build a perfect hash chain. Hao Lei et al. [11] proposed a multi-node payment channel method based on the payment channel, which reduces the cost of information transmission and improves the scalability of the blockchain.
8. Conclusions
In this work we introduced an efficient, fast, and secure continuous micropayment system. The micropayment system is based on blockchain and uses off-chain payment channel for transaction. Each transaction is not independent but associated. During the transaction process, we use a lockable signature scheme to generate a signature lock, and the lock is hidden. The system can provide a fast and secure way in the absence of a trading platform and mutual distrust between the trading parties. The micropayment system can improve the scalability of the blockchain, reduce transaction time and storage time, reduce system calculation and transmission overhead, and achieve the purpose of fast transaction.
References
- Rezaeibagha, F.; Mu, Y. Efficient micropayment of cryptocurrency from blockchains. The Computer Journal, 2019, 62, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudriga, N. A resilient micro-payment infrastructure: an approach based on blockchain technology. Kuwait Journal of Science 2022, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Pass, R.; Shelat, A. Micropayments for decentralized currencies[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. 2015, 207–218. [Google Scholar]
- Decker, C.; Wattenhofer, R. A fast and scalable payment network with bitcoin duplex micropayment channels[C]//Symposium on Self-Stabilizing Systems; Springer: Cham, 2015; pp. 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Lipton, R. J.; Ostrovsky, R. Micro-payments via efficient coin-flipping[C]//International Conference on Financial Cryptography; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 1998; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Micali, S.; Rivest R, L. Micropayments revisited[C]//Cryptographer Track at the RSA Conference; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2002; pp. 149–163. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, Y.; Varadharajan, V.; Lin Y, X. New micropayment schemes based on Pay Words[C]//Australasian Conference on Information Security and Privacy; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 1997; pp. 283–293. [Google Scholar]
- Burchert, C.; Decker, C.; Wattenhofer, R. Scalable funding of bitcoin micropayment channel networks. Royal Society open science, 2018, 5, 180089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivest, R. L.; Shamir, A. PayWord and MicroMint: Two simple micropayment schemes[C]//International workshop on security protocols; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 1996; pp. 69–87. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, Q. S. Multi-dimensional hash chains and application to micropayment schemes[C]//International Workshop on Coding and Cryptography; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2005; Volume 218, p. 228. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, H.; Huang, L.; Wang, L.; et al. MPC: Multi-node Payment Channel for Off-chain Transactions[C]//ICC 2022-IEEE International Conference on Communications; IEEE, 2022; pp. 4733–4738. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Liu, J.; Tang, Z.; et al. Agentchain: A decentralized cross-chain exchange system[C]//2019 18th IEEE International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications/13th IEEE International Conference on Big Data Science and Engineering (Trustcom/BigdataSE); IEEE, 2019; pp. 491–498. [Google Scholar]
- Buldas, A.; Laanoja, R.; Truu, A. A blockchain-assisted hash-based signature scheme[C]//Nordic Conference on Secure IT Systems; Springer: Cham, 2018; pp. 138–153. [Google Scholar]
- Erdin, E.; Mercan, S.; Akkaya, K. An evaluation of cryptocurrency payment channel networks and their privacy implications. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.02659. [Google Scholar]
- Avarikioti, Z.; Thyfronitis Litos, O. S.; Wattenhofer, R. Cerberus channels: Incentivizing watchtowers for bitcoin[C]//International Conference on Financial Cryptography and Data Security; Springer: Cham, 2020; pp. 346–366. [Google Scholar]
- Doerner, J.; Kondi, Y.; Lee, E.; et al. Secure two-party threshold ECDSA from ECDSA assumptions[C]//2018 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP); IEEE, 2018; pp. 980–997. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Deng, R. H.; Liu, X.; et al. Blockchain based efficient and robust fair payment for outsourcing services in cloud computing. Information Sciences 2018, 462, 262–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, T. A.; Alzahrani, A.; Jan, S.; et al. A comparative analysis of blockchain architecture and its applications: Problems and recommendations. IEEE access 2019, 7, 176838–176869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H. N.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Y. Blockchain for Internet of Things: A survey. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6, 8076–8094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinidis, I.; Siaminos, G.; Timplalexis, C.; et al. Blockchain for business applications: A systematic literature review[C]//International conference on business information systems; Springer: Cham, 2018; pp. 384–399. [Google Scholar]
- Malavolta, G.; Moreno-Sanchez, P.; Schneidewind, C.; et al. Anonymous multi-hop locks for blockchain scalability and interoperability. Cryptology ePrint Archive 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Jiang, S. On Increasing Scalability and Liquidation of Lightning Networks for Blockchains. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A. A.; Fernandez, T. F.; Bansal, R.; et al. Maintaining Scalability in Blockchain[C]//International Conference on Intelligent Systems Design and Applications; Springer: Cham, 2022; pp. 34–45. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, T.; Otsuka, A. Probabilistic micropayments with transferability[C]//European Symposium on Research in Computer Security; Springer: Cham, 2021; pp. 390–406. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, N.; Wu, T W. xlumi: Payment channel protocol and off-chain payment in blockchain contract systems. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.10621. [Google Scholar]
- Fazli, M. A.; Nehzati, S. M.; Salarkia, M. A. Building Stable Off-chain Payment Networks. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.03367. [Google Scholar]
- Nofer, M.; Gomber, P.; Hinz, O.; et al. Blockchain. Business and Information Systems Engineering, 2017, 59, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepa, N.; Pham, Q. V.; Nguyen, D. C.; et al. A survey on blockchain for big data: approaches, opportunities, and future directions. Future Generation Computer Systems 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thyagarajan, S. A. K.; Malavolta, G. Lockable signatures for blockchains: Scriptless scripts for all signatures[C]//2021 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP); IEEE, 2021; pp. 937–954. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Deng, R. H.; Liu, X.; et al. Blockchain based efficient and robust fair payment for outsourcing services in cloud computing. Information Sciences, 2018, 462, 262–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Deng, R. H.; Liu, X.; et al. Blockchain based efficient and robust fair payment for outsourcing services in cloud computing. Information Sciences, 2018, 462, 262–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCorry, P.; Möser, M.; Shahandasti, S. F.; Hao, F. Towards bitcoin payment networks[C]//Australasian Conference on Information Security and Privacy; Springer: Cham, 2016; pp. 57–76. [Google Scholar]
- Delmolino, K.; Arnett, M.; Kosba, A.; et al. Step by step towards creating a safe smart contract: Lessons and insights from a cryptocurrency lab[C]//International conference on financial cryptography and data security; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2016; pp. 79–94. [Google Scholar]
- Boneh, D.; Lynn, B.; Shacham, H. Short signatures from the Weil pairing[C]//International conference on the theory and application of cryptology and information security; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2001; pp. 514–532. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, H.; Huang, L.; Wang, L.; et al. MPC: Multi-node Payment Channel for Off-chain Transactions[C]//ICC 2022-IEEE International Conference on Communications; IEEE, 2022; pp. 4733–4738. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Ye, Y.; Wu, W.; et al. Boros: Secure and Efficient Off-Blockchain Transactions via Payment Channel Hub. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonneau, J.; Preibusch, S.; Anderson, R. Financial cryptography and data security; Springer International Publishing, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Yang, A.; Weng, J.; et al. Concurrent and efficient IoT data trading based on probabilistic micropayments; Wireless Networks, 2022; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
| 1 |
The adversary obtains the transaction message (time or phase) in the middle of the micropayment transaction using a hash chain. Then can trace back to the first transaction and the account messages of transaction parties are exposed. |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).