1. Introduction
Many organs are composed of epithelial cells polarized along their apico-basal axis. The apical membrane faces the lumen of a tube or the external environment and the basolateral membrane (BM) binds to the neighboring cells and basal extracellular matrix (ECM). Generation of this polarized architecture and lumen formation is critical for the proper development of many organs and for adult mammalian tissue homeostasis (Roignot, Peng, and Mostov 2013). Loss of polarity, the orientation of apico-basal axis, leads to changes in plasticity, Epithelial-Mesenchymal-Transition (EMT) and usually occurs early in tumorigenesis. Although the molecular mechanisms that control polarity and EMT need further investigation (Chatterjee and Deng 2019; Royer and Lu 2011).
The cytoskeleton dependent membrane shaping processes control organelles positioning and endosomal sorting to the specific membrane domains that drive apico-basal polarity and lumen formation in epithelia (Bryant and Mostov 2008; Shewan et al. 2015). The polarization process of epithelial cells is often accompanied by the formation of primary cilia protruding in the lumen which formation is controlled by polarity components (Bossinger and Bachmann 2004; Hamze-Komaiha et al. 2016; Torkko et al. 2008). The roles of microtubules and actin in these dynamic processes were intensively described although the role of other cytoskeletal elements (Mostowy and Cossart 2012) such as septins are just emerging (Gurel, Hatch, and Higgs 2014; Spiliotis 2018). Septins are guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-binding proteins that are evolutionally conserved among all eukaryotes except plants and certain protists (Nishihama, Onishi, and Pringle 2011; Pan, Malmberg, and Momany 2007). Septins are involved in infection by pathogens, including bacteria, fungi and viruses (Akil et al. 2016:9; Bridges and Gladfelter 2014; Mostowy and Cossart 2012). Deregulation of the expression of septins has been linked to severe diseases, including cancers and neurological diseases (Dolat, Hu, and Spiliotis 2014; Fung, Dai, and Trimble 2014; Ivanov et al. 2021).
The septin family is composed of 13 members in mammals, and the complexity of this gene family is increased by the existence of alternate splicing, which dramatically increases the number of isoforms (Fung et al. 2014). Septins form hetero-oligomeric complexes through binding to membrane and may form high order structures such as filaments and rings. These structures acts a diffusion barrier and play a scaffold role in different cellular processes by recruiting cytosolic proteins and cytoskeletal elements such as microtubules or actin during membrane remodeling processes (Dolat et al. 2014; Fung et al. 2014). Septin 9 regulates cell polarity and cilium organization and assembly (Mirvis, Stearns, and James Nelson 2018), The role of septins in cell-cell junctions was also reported (Kim and Cooper 2018; Wang et al. 2021). Nevertheless, the role of septins and particularly septin 9 in epithelial cell morphogenesis and plasticity and its role on lumen and cilia formations and ECM assembly was not investigated in a same study.
The association of septins to membrane is mediated by their binding to PIs via a characterized PB1 domain (Akil et al. 2016; Tanaka-Takiguchi, Kinoshita, and Takiguchi 2009; Zhang et al. 1999). Recently we identified in septin 9, a second polybasic domain (PB2) within the GTP-binding domain and conserved among the family of septins. Furthermore, we showed that PB1 and PB2 are required for septin 9 assembly in filament with septin 2, 6, 7 and for the assembly and functionality of the Golgi apparatus (Omrane et al. 2019a). Thus, suggesting a crucial role of these PB domains in septin functions and apico-basal polarity.
In this study we investigated the role of septin 9 in the establishment of apico-basal polarity and EMT using MDCK (Madin Darby Canine Kidney) cells grown in 2D on transwell filters and in 3D culture in Matrigel. We also assessed the involved mechanisms and the contribution of the PB domains.
2. Material and methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
MDCK (Madin Darby Canine Kidney) cells were maintained in minimal essential medium (MEM; Invitrogen) containing Earle’s balanced salt solution supplemented with 5% fetal bovine serum and 1% of Penicillin/Streptomycin solution. For 2D culture, about 200,000 MDCK cells were plated on 0.4-µm polycarbonate Transwell Filter (12-mm diameter, Corning) for 3 days to polarize. For 3D culture MDCK cells were trypsinized as 10,000 single cells/ml in 2% Matrigel (BD Biosciences), 500 μl of cells were plated in each well of 8-well Lab-Tek II chamber slides (Thermo Fisher Scientific) pre-covered with Matrigel and grown for 1 day, 2 days 4 days or 6 days as the cysts with lumen formed as described previously For transfection, MDCK cells seeded at density (2.5-3 x104 cells/cm2) in 12 well cell culture microplate, were transfected with 1 µg cDNA or 110 pmol siRNA per well using jet PRIMETM (Ozyme) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. For 3D culture, 24 h after transfection, cells were detached with trypsin and plated on Matrigel for 4 days as indicated above.
The specific septin 9 duplexes small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) used were:
5´-GCCAUGAAGCAGGGCUUCGAGUUCA-3´and
5´-UGAACUCGAAGCCCUGCUUCAUGGC-3´.
2.2. Antibodies
Anti-Septin 9 Cat#ab114099 (WB:1/500, IF:1/25), anti-septin 2 Cat# ab88657 (IF:1/100), mouse and rabbit anti-V5 tag Cat#ab27671 (WB:1/1,000, IF:1/400), Cat#ab9116 (WB:1/1,000, IF:1/400), were obtained from Abcam; anti β-tubulin Cat# T4026 (IF:1/100) came from Sigma-Aldrich; anti-E-cadherin Cat#610181 (WB:1/1000, IF:1/100), anti-GM130 Cat#610822 (IF:1/50) were sourced from BD Biosciences. Anti-Na+/K+ATPase Cat#33-9100 (WB:1/1000, IF:1/100), ZO-1 Cat#33-9100 (WB:1/1000, IF:1/100), came from Invitrogen. Anti-cortactin Cat#3503 (WB:1/1000, IF:1/100), anti-p-cortactin Cat#4569s (WB:1/1000, IF:1/100), anti-src Cat#2109s (WB:1/1000, IF:1/100) and anti-p-src Cat#2101s (WB:1/1000, IF:1/100) were from Cell Signaling Technology. Anti-septin 7 Cat# sc-20620 (IF:1/100), anti-β-catenin sc-7199 (IF:1/100), anti-actin Cat#sc-1616 (WB:1/1,000), anti-fibronectin Cat#sc-6952 (WB:1/1,000), anti-Integrin β1 Cat#sc-18887(WB:1/1,000) were from Santa Cruz. GP135 antibody (1:1000) was from George Ojakian (University of New York Downstate Medical Center), USA. Anti-laminin Cat# L9393 (WB:1/1,000) from Sigma. Anti- Vimentin Cat# CBL202 (WB:1/1,000) from Millipore. Alexa Fluor™ 568 Phalloidin Cat#A12380 (IF:1/100), Hoechst Cat#34580 (1:50) from Life Technology. Secondary antibodies: Alexa Fluor® 633, 546 and 488-conjugated were purchased from Life Technology, Hoechst was purchased from Molecular Probes.
2.3. Stable cell lines
The cells were stably transfected with pcDNA V5-septin 9_i1, pcDNA V5-septin 9_del1, pcDNA V5-septin 9_del2 or pcDNA V5-septin 9_del1/del2 plasmids. For MDCK cells, 700μg/mL neomycin (Invivogen) was used for 2 weeks. Stably transfected pools were seeded at 0.5–1 cell/well in 96-well plates for limiting dilution. After another 3–4 weeks, the colonies were generated and analyzed using Immunoblot and Immuno-fluorescence for protein expression and localization (IF). Only those colonies positive under assessment by both methods were selected for further investigation.
2.4. Immunofluorescence staining
Cells were grown on coverslips, fixed for 15 min with paraformaldehyde 4% and permeabilized for 30 min with PFS Buffer (PBS+ containing 0.025% m/v saponin and 0.7% gelatin) at 37°C. The cells were then incubated with primary antibody for 2 h and with appropriate secondary antibodies for 90 min. The coverslips were mounted using Prolong Gold (Invitrogen). For the 3D culture, samples were incubated in primary antibodies at 4°C overnight, followed by incubation for 90 min at 37°C, and treated as described for the 2D culture.
2.5. Image acquisition and analysis
Images were acquired with a Leica TCS SP5 AOBS tandem confocal microscope. 3D images were obtained using Icy bioimage analysis software (
http://icy.bioimageanalysis.org). To quantify the intensities and the distribution of the fluorescence signals, confocal Z stack images were processed by the Image J background subtraction tool.
2.6. Immunoblot
Cells were washed with ice cold Dulbecco’s Phosphate Buffered Saline (DPBS) and lysed on ice in the following buffer: 20 mM Tris, HCl, 100mM NaCl, 1% Triton X100 and 10mM EDTA at PH 7.4 containing a protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (Complete™ ULTRA Cat#05892970001 Roche). The proteins were separated on SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate) polyacrylamide gel and electro-transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes. After transfer, the membranes were saturated in DPBS containing 0.1% Tween 20 and 5% milk. Primary antibodies were added overnight at 4°C or for 2 h at room temperature, depending on the antibody. The membranes were then washed with DPBS and incubated for 1 h at room temperature with appropriate secondary antibodies coupled with peroxidase. The ECL plus kit (Cat#32132) and SuperSignal™ West Femto Maximum Sensitivity Substrate (Cat#34095) from Thermo Scientific were used for protein detection. Chemiluminescent signals were detected by the G: BOX Chemi Fluorescent & Chemiluminescent Imaging System from SYNGENE. The blots were quantified using Image J software.
2.7. Cell fractionation assay
Confluent monolayers of cells were placed on ice and washed twice with ice-cold PBS at pH 7.4, before the addition of 10 mM Tris/HCl (pH 7.4) buffer for 1 min. The cells were scraped into a homogenization buffer comprising 10 mM Tris/HCl, 1 mM EGTA, 0.5 mM EDTA and 0.25 M sucrose, at pH 7.4, which also contained completeTM protease inhibitors. All centrifugation processes were performed at 4°C and the samples were kept on ice throughout the procedure. The combination was centrifuged first at 720g for 5 min. The supernatant was then transferred into a fresh tube and ultracentrifuged at 100,000 g for 1 h, the supernatant being the cytoplasm and the pellet the membrane. The solution was then resuspended in an appropriate TBS with 0.1% SDS for immunoblot.
2.8. Quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR) assay
Total RNA was isolated using an RNeasy Mini Kit 50 (Qiagen). Reverse transcription was performed using the Reverted First Stand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Fermentas). cDNA was amplified with the Quanti Tect SYBR Green PCR Kit (QIAGEN) and the 7500 Fast Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems). The reaction program was 95°C for 10 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 15 s, 55°C for 30 s and 72°C for 30 s. The mRNA level was normalized to GAPDH expression. The primers are listed in
Table S1.
2.9. Statistical analysis
The statistical significances of immunofluorescence, immunoblotting and RT-qPCR findings were determined by Student’s t-test using Microsoft Office Excel software (Microsoft Corporation). The results showed the means and standard deviations, and those with p values lower than 0.05 were considered to be statistically significant (* p<0.05, ** p<0.01, ***p<0.001). All tests are two-tailed.
3. Results
3.1. Septin 9 is essential to orient apico-basal axis and its knock down inverts polarity
To decipher the role that septin 9 could play in the establishment of apico-basal polarity, we used MDCK cells cultured in 3D in Matrigel as a model system. After 4 days in culture, the control cells form cysts with a monolayer of polarized cells surrounding an open central lumen. Endogenous septin 9 was essentially presented at BM. However, knock down of septin 9 led to the formation of an important proportion of cysts with multiple lumens and inverted polarity (
Figure 1A,B). Furthermore, septin 9 filamentous structure which is required to perform its biological activities. Importantly the filaments are formed by an octameric complex that included septin 2, septin 6, septin 7 (Kim et al. 2011) (
Figure S1A). Subsequently we analyzed septin 7 and septin 2 and we found that the two proteins are located at BM as observed for septin 9 and depletion of septin 9 decreased their expressions as shown by immunofluorescence analysis (
Figure S1B) and by immunoblot (
Figure S1C). Together these data strongly suggested that septin 9 form filament structures at BM in a complex with septin 2 and septin 7.
Figure 1.
Basolateral membrane localized Septin 9 is required for the orientation of apico-basal axis in MDCK cysts. (A). MDCK cells were transfected or not with siRNA of septin 9 for 24 h and then transferred to the Matrigel-covered Lab-Tek. The cells were incubated for 4 days to form cysts. Cells were stained for Septin 9 (green), GP135 (red) and Hoechst (blue). A single confocal section through the middle of a cyst is shown. Scale bar 10 µm. (B). Cysts presented different phenotype, including single open lumen, multiple-lumens and inverted polarity. Color for each phenotype in column is corresponding the color below pictures. (C). For another experiment as in (A), MDCK cysts sections labeled for the Golgi marker GM130 (green), actin (red) and Hoechst (blue). Higher magnifications of the boxed areas are shown. (D). Line profiles showing Golgi distribution from apical to basal area, using Image J. (E). Quantification of Golgi distribution: the ratio of maximal fluorescence intensity at the apical side versus the maximal fluorescence intensity at the basal side. (F). The schematic graph shows that Golgi distributions associated with different cyst phenotypes including cell polarity and lumen formation. Data information: Data are at least two times replicates. n=69 (Control), n=32 (siRNA) (B). n=10 (E). The statistics values are means ±s.e.m. Student’s t-test was used. ***P < 0.001.
Figure 1.
Basolateral membrane localized Septin 9 is required for the orientation of apico-basal axis in MDCK cysts. (A). MDCK cells were transfected or not with siRNA of septin 9 for 24 h and then transferred to the Matrigel-covered Lab-Tek. The cells were incubated for 4 days to form cysts. Cells were stained for Septin 9 (green), GP135 (red) and Hoechst (blue). A single confocal section through the middle of a cyst is shown. Scale bar 10 µm. (B). Cysts presented different phenotype, including single open lumen, multiple-lumens and inverted polarity. Color for each phenotype in column is corresponding the color below pictures. (C). For another experiment as in (A), MDCK cysts sections labeled for the Golgi marker GM130 (green), actin (red) and Hoechst (blue). Higher magnifications of the boxed areas are shown. (D). Line profiles showing Golgi distribution from apical to basal area, using Image J. (E). Quantification of Golgi distribution: the ratio of maximal fluorescence intensity at the apical side versus the maximal fluorescence intensity at the basal side. (F). The schematic graph shows that Golgi distributions associated with different cyst phenotypes including cell polarity and lumen formation. Data information: Data are at least two times replicates. n=69 (Control), n=32 (siRNA) (B). n=10 (E). The statistics values are means ±s.e.m. Student’s t-test was used. ***P < 0.001.
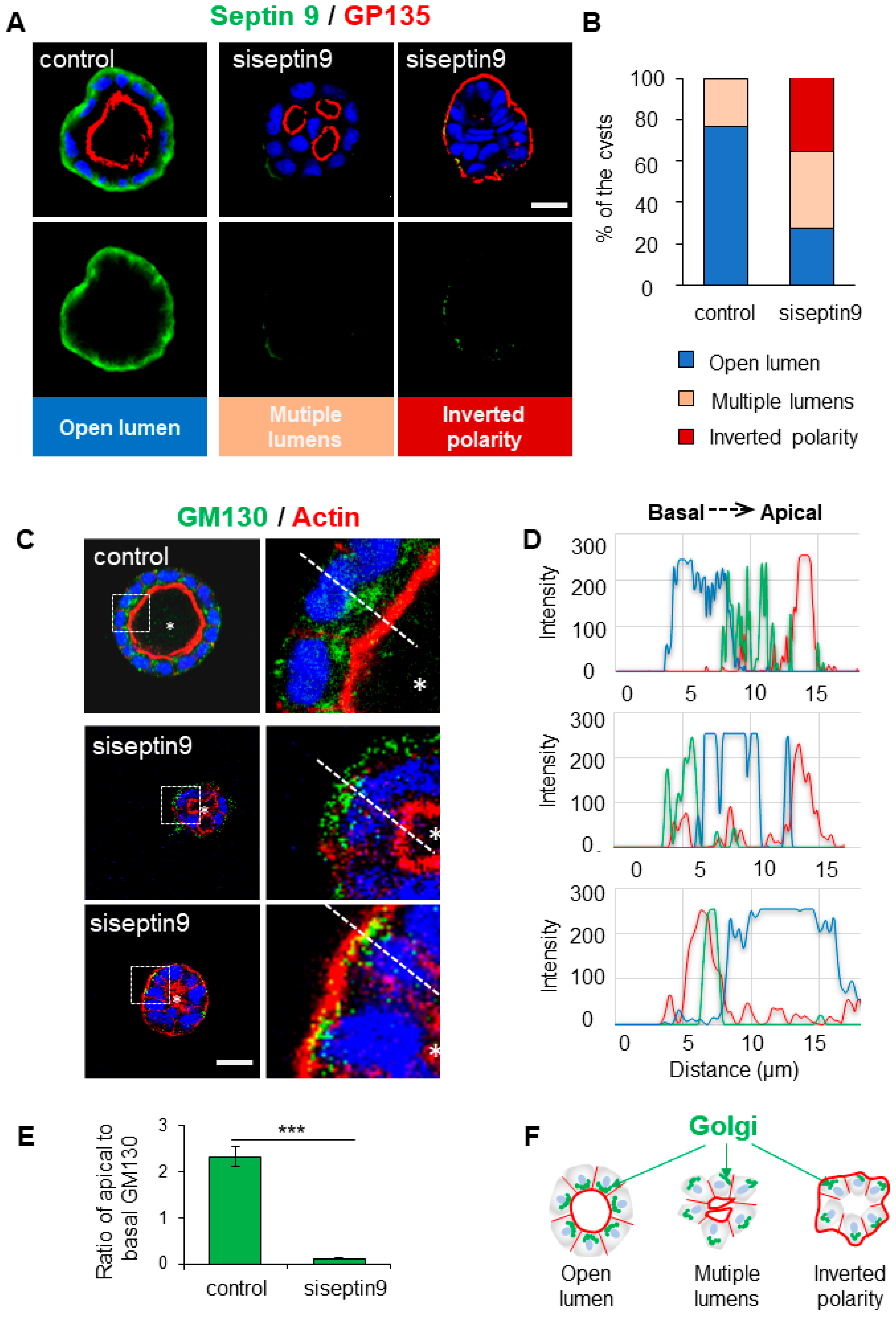
The structure, organization, and positioning of the Golgi apparatus are implicated in the apico-basal polarization process (Omrane et al. 2019b). Given that septin 9 regulates Golgi asymmetrically assembly (Omrane et al. 2019b), we assessed whether the disrupted apical-basal polarization seen in septin 9-depleted cysts also affected Golgi organization. Subsequently we stained for Golgi using an antibody against the Golgi matrix protein GM130. In control cells, the Golgi was localized above the nucleus in the apical part of the cytoplasm toward the cyst lumen as expected (
Figure 1C). By contrast, in inverted polarized cysts formed by cells treated with siRNA septin 9, the Golgi was disorganized and was localized behind the nucleus in the basal part of the cytoplasm beneath the intense actin signal at cell periphery (
Figure 1C–F). Together, these data suggested a specific role of septin 9 in the orientation of Golgi positioning and the orientation of apico-basal polarity axis.
3.2. Septin 9 regulates cell-cell junctions and BM stability
The proper localization and assembly of cell-cell junctions are essential to establishment of apico-basal polarity and the BM stability (
Figure 2A). At the BM, β-catenin links the cytoplasmic domain of E-cadherin with the actin-binding proteins such as cortactin to organize the cortical actin networks and maintain therefore the adherens junctions (Sroka et al. 2016) (
Figure 2A). According to the septin 9 localization at BM membrane and its effects on apico-basal polarity, we investigated the consequences of septin 9 depletion on the cell-cell junctions. We also analyzed the tight junctions protein, Zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) which plays a crucial role in the conversion of AJs to belt-like structures in polarized epithelial cells (Ikenouchi et al. 2007). The results showed that knock-down of septin 9 expression using siRNA decreased the expression of both E-cadherin and β-catenin (
Figure 2B). Loss of cortactin by septin 9 depletion was also validated in 3D culture by immunofluorescence analysis (
Figure 2B). These immunofluorescence data were validated by immunoblots (
Figure 2C).
Figure 2.
Septin 9 regulates impacts cell-cell adhesion and BM stability. (A). The schematic representation of the cell-cell adhesion structure. In the cytoplasm, e-cadherin/catenin complex link to ZO-1 and actin, and actin binding protein cortactin. (B). MDCK cells were transfected or not with siRNA of septin 9 for 24h and plated on Matrigel for 4 days to form cysts, and then stained for E-cadherin (green) and actin (red), β-catenin (green) and ZO-1 (red), and cortactin (green) and actin (red). A single confocal section through the middle of a cyst is shown. Quantification of the fluorescence intensity of each protein expression, E-cadherin (green), and β-catenin (green) and ZO-1 (red). Scale bar 10 µm. (C). MDCK cells transfected or not with siRNA of septin9 for 24 h then grown on plates for 3 days. Cells were lysed and analyzed by western blot for septin 9, E-cadherin, β-catenin, and cortactin proteins expressions. (D). For another experiment as in (C), qRT-PCR analysis of the expression of mRNA encoding septin 9, vimentin, N-cadherin and ZEB1 in cells with Control and septin 9 knock down in 2D condition. Data information: Data are at least two times replicates and cysts (n>10) for 3D staining, three replicates for immunoblot and qRT-PCR. The statistics values are means ±s.e.m. Student’s t-test was used. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P < 0.001.
Figure 2.
Septin 9 regulates impacts cell-cell adhesion and BM stability. (A). The schematic representation of the cell-cell adhesion structure. In the cytoplasm, e-cadherin/catenin complex link to ZO-1 and actin, and actin binding protein cortactin. (B). MDCK cells were transfected or not with siRNA of septin 9 for 24h and plated on Matrigel for 4 days to form cysts, and then stained for E-cadherin (green) and actin (red), β-catenin (green) and ZO-1 (red), and cortactin (green) and actin (red). A single confocal section through the middle of a cyst is shown. Quantification of the fluorescence intensity of each protein expression, E-cadherin (green), and β-catenin (green) and ZO-1 (red). Scale bar 10 µm. (C). MDCK cells transfected or not with siRNA of septin9 for 24 h then grown on plates for 3 days. Cells were lysed and analyzed by western blot for septin 9, E-cadherin, β-catenin, and cortactin proteins expressions. (D). For another experiment as in (C), qRT-PCR analysis of the expression of mRNA encoding septin 9, vimentin, N-cadherin and ZEB1 in cells with Control and septin 9 knock down in 2D condition. Data information: Data are at least two times replicates and cysts (n>10) for 3D staining, three replicates for immunoblot and qRT-PCR. The statistics values are means ±s.e.m. Student’s t-test was used. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P < 0.001.
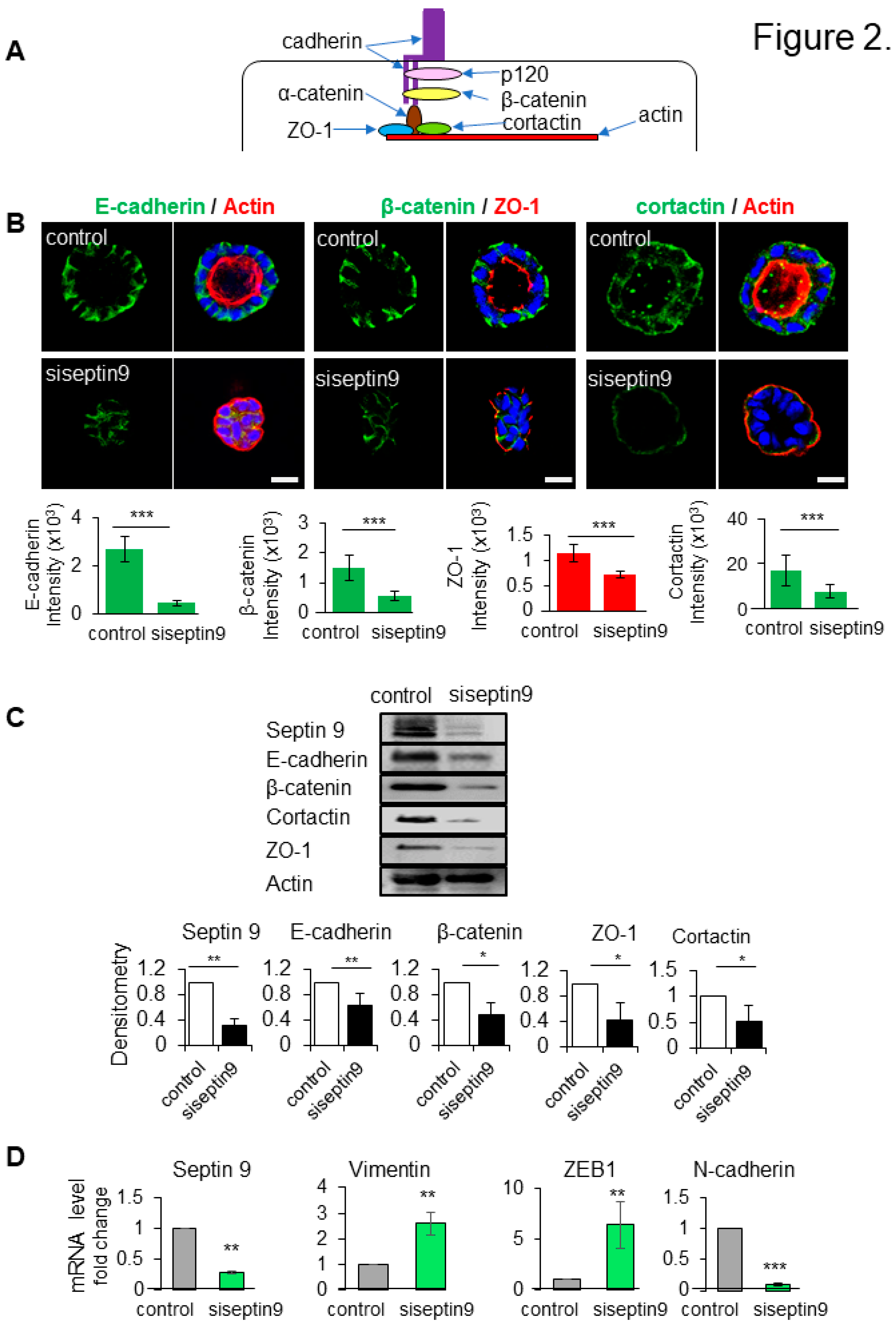
The loss of cell-cell junctions is a fundamental event during the EMT, a process by which epithelial cell loss polarity to acquire mesenchymal and invasive features which characterized cancer cells (Nieto et al. 2016). Thus, using qRT-PCR analysis, we showed that the decrease of septin 9 significantly increased the gene expression of mesenchymal cell markers such as vimentin, EMT-inducing transcriptional factor (ZEB1) and N-cadherin (
Figure 2D). Together, these results suggest a potential function of septins in driving the assembly, maintenance, and remodeling of adhesion junctions, impairing the cells to undergo EMT. Thus septin 9 regulates cell-cell junctions at BM and appeared as a gatekeeper against EMT.
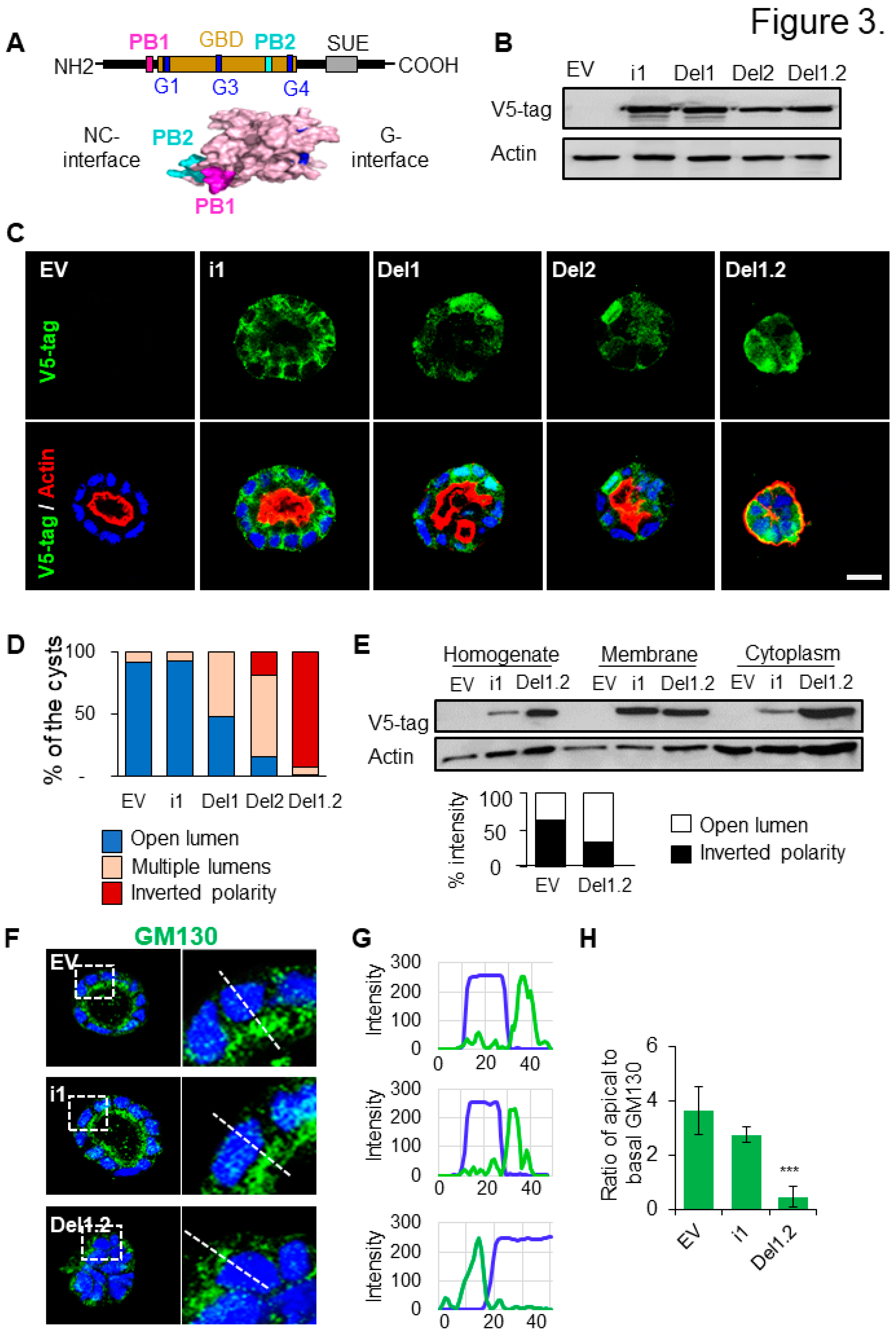
3.3. The two PB domains of septin 9 are required for its basolateral localization and apico-basal polarity
We reported that septins have a second Polybasic Domain (PB2) that forms with PB1 a basic cluster at the NC Interface. In particular, we found that septin 9 PB domains control its filamentous structure formation and assembly and functionality of the Golgi apparatus (Omrane et al. 2019b:9) (
Figure 3A). Accordingly, we sought for the potential requirement of the two PB domains of septin 9 in its role in apico-basal polarity. For that, we established different MDCK cells that stably expressed either empty vector (EV) or the V5 tagged-septin 9_i1 (septin 9_i1) or the mutants deleted from PB1 (septin 9_del1) or the mutants deleted from PB2 (septin 9_del2) or deleted from both PB1 and PB2 (septin 9_del1.2). The expression of the septin 9 protein in these cells was validated first by immunoblot using the V5 tag antibody (
Figure 3B). Then, all the different cell lines were cultured in 3D to form cysts and stained for V5 tag, and actin (
Figure 3C). The EV and septin 9_i1 expressing cells form cysts with an open central lumen and septin 9_i1 was enriched at BM as showed for endogenous septin 9 (
Figure 1A). However, the lumen likely to be filled with septin 9_i1 cells compared to EV cells (
Figure 3C). By contrast the mutants septin 9_del1 and del2 formed multi-lumen cysts while the septin 9_del1.2 cells formed in majority cysts with inverted phenotype (
Figure 3C). The quantification of these different phenotypes was presented in the
Figure 3D. Importantly, we observed a cytoplasmic localization of septin 9_del1, septin 9_del2 and septin 9_del1.2 (
Figure 3C). The increase of septin 9 del1.2 cytoplasm accumulation was confirmed by cell fractionation (
Figure 3E) and thus, confirmed that PB domains are required for septin 9 assembly (Omrane et al. 2019b:9). Together, these data indicated that the PB domains of septin 9 regulated its basolateral localization at the cell cortex, affecting cell shape and single lumen formation. We also validated that the Golgi was localized above the nucleus facing the lumen in EV and septin_i1 cysts whereas, in septin 9_del1.2 cells which formed cysts with an inverted phenotype, the Golgi was localized at the cell periphery as (
Figure 3F–H). Furthermore, deletion of the two PB domains induced the presence of ZO-1 at the periphery of del1.2 cysts with the inverted polarity phenotype (
Figure S2). In conclusion, preventing the assembly of septin 9 by the deletion of its two PB domains inverted apico-basal polarity.
Figure 3.
Deletion of septin 9 PB domains impact different cyst phenotype and septin 9 distribution in the cells. (A). The schematic graph shows the organization of septin 9, in which the two PB domains are highlight in pink and green. And the two PB domains are near the NC interface of the protein. (B). The lysed MDCK stable cells which transfected with septin 9_i1 (I1), septin 9_del1 (Del1), septin 9_del2 (Del2) and septin 9_del1.2 (Del1.2) or empty vector (EV) are tested by western blot with septin 9-v5 tag antibody. (C). The MDCK stable cell lines plated on Matrigel for 4 days to form cysts, and then stained for septin 9-V5 tag (green) and actin (red). Septin 9_del1.2 (Del1.2) MDCK cell lines presented inverted phenotype. A single confocal section through the middle of a cyst is shown. Scale bar 10 µm. (D). Color for each phenotype in column is corresponding the color below pictures. (E). The MDCK stable cell lines were grown overnight before being subjected to a subcellular fractionation assay and analyzed with western blot for septin 9-v5 tag and actin. The graph besides shows septin 9-v5 tag densitometry analysis of the subcellular fractionation assay. (F). As experiment in (C), the cysts from MDCK stable cell lines of EV, i1 and Del1.2 were stained for Golgi (green) and actin (red). A single confocal section through the middle of a cyst is shown. Scale bar 10 µm. (G). Line profiles showing the Golgi distribution from the basal to the apical areas, using Image J. (H). Quantification of Golgi distribution: the ratio of maximal fluorescence intensity at the apical side versus the maximal fluorescence intensity at the basal side. Data information: Data are at least two times replicates and cysts (n>10) for 3D staining, three replicates for immunoblot. For D, n=23 (EV), n=29 (i1), n=38 (Del1), n=20 (Del2), n=44 (Del1.2). The statistics values are means ±s.e.m. Student’s t-test was used. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P < 0.001.
Figure 3.
Deletion of septin 9 PB domains impact different cyst phenotype and septin 9 distribution in the cells. (A). The schematic graph shows the organization of septin 9, in which the two PB domains are highlight in pink and green. And the two PB domains are near the NC interface of the protein. (B). The lysed MDCK stable cells which transfected with septin 9_i1 (I1), septin 9_del1 (Del1), septin 9_del2 (Del2) and septin 9_del1.2 (Del1.2) or empty vector (EV) are tested by western blot with septin 9-v5 tag antibody. (C). The MDCK stable cell lines plated on Matrigel for 4 days to form cysts, and then stained for septin 9-V5 tag (green) and actin (red). Septin 9_del1.2 (Del1.2) MDCK cell lines presented inverted phenotype. A single confocal section through the middle of a cyst is shown. Scale bar 10 µm. (D). Color for each phenotype in column is corresponding the color below pictures. (E). The MDCK stable cell lines were grown overnight before being subjected to a subcellular fractionation assay and analyzed with western blot for septin 9-v5 tag and actin. The graph besides shows septin 9-v5 tag densitometry analysis of the subcellular fractionation assay. (F). As experiment in (C), the cysts from MDCK stable cell lines of EV, i1 and Del1.2 were stained for Golgi (green) and actin (red). A single confocal section through the middle of a cyst is shown. Scale bar 10 µm. (G). Line profiles showing the Golgi distribution from the basal to the apical areas, using Image J. (H). Quantification of Golgi distribution: the ratio of maximal fluorescence intensity at the apical side versus the maximal fluorescence intensity at the basal side. Data information: Data are at least two times replicates and cysts (n>10) for 3D staining, three replicates for immunoblot. For D, n=23 (EV), n=29 (i1), n=38 (Del1), n=20 (Del2), n=44 (Del1.2). The statistics values are means ±s.e.m. Student’s t-test was used. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P < 0.001.
3.4. The two PB domains of septin 9 are critical to maintain cell-cell junctions and BM stability
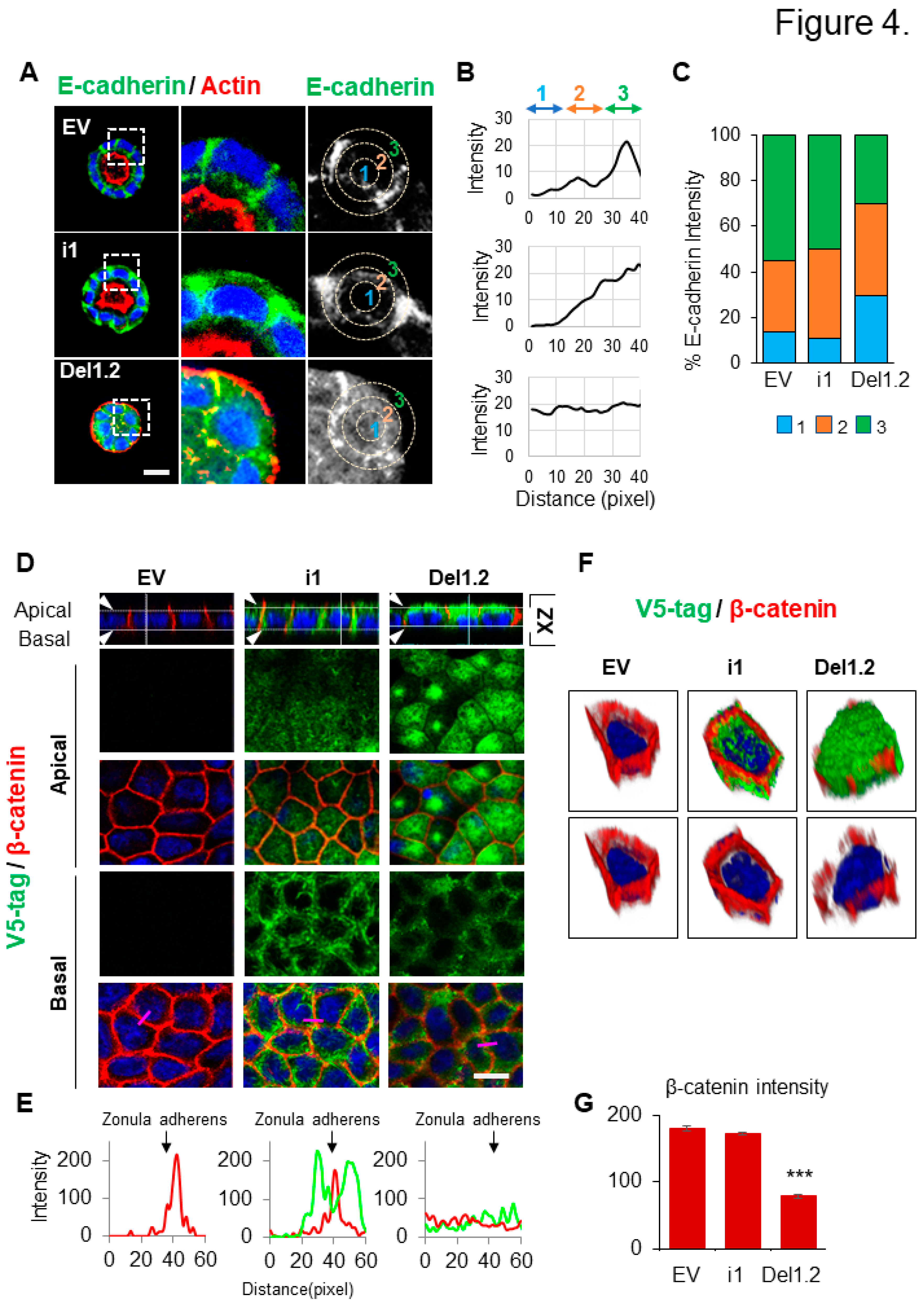
According to data presented above (
Figure 2B,C), we explore the effects of the deletion of the two PB domains on E-cadherin expression (
Figure 4A–C). We didn’t observe a striking decrease of E-cadherin expression rather E-cadherin decreased from the membrane and became more cytoplasmic as highlighted by line plots (
Figure 4B,C). Furthermore, the cells were grown in 2D on semi-permeable filters. Even though this system did not allow lumen formation it permitted a different analysis of apico-basal axis. After 3 days of culture, the EV cells form a monolayer as seen by X-Y and X-Z sections from staining of β-catenin (
Figure 4D). In cells expressing septin 9_i1, the β-catenin was well organized and the septin 9 is enriched in the BM clearly visible on X-Z section and formed filaments mostly at the basal part (
Figure 4D). By contrast the septin 9_del1.2 lost its filamentous structure and was delocalized on the apical domain as better seen on X-Z section (
Figure 4D). Remarkably in septin 9_del1.2 cysts, the signal of β-catenin was diffused and strongly reduced at the zonula adherens (ZAs) as indicated by the line plot and the 3D reconstruction of the septin 9 and β-catenin signals in a single cell from each group (
Figure 4E,F). These results were supported by the quantification of the β-catenin cellular signal (
Figure 4G). Together the data demonstrated that the two PB domains of septin 9 are required for its filaments and basolateral localization and to maintain cell-cell adhesion.
Figure 4.
Deletion of septin 9 PB domains impacts cell-cell adhesion (A). The MDCK stable cell lines plated on Matrigel for 4 days to form cysts, and then stained for E-cadherin (green) and actin (red). A single confocal section through the middle of a cyst is shown. Scale bar 10 µm. (B). The distribution of the E-cadherin signal in cysts presented in (A) was analyzed by ImageJ software in an individual cell from a cyst. A circle was defined at the periphery of each cell and the plugin produced a profile plot of normalized integrated intensities in concentric circles as a function of distance from a point in the image, considered here as the center of the cell. The circle was divided into three bands (1, 2, 3) with an equal radius. (C). Quantification of the fluorescence intensity of E-cadherin from each band is represented as a histogram. (D). The MDCK stable cell lines of EV, i1 and Del1.2 plated on transwell filters for 24h. Cells were fixed and stained for V5 tag (green) and β-catenin (red). Confocal images of XZ sections are presented at the top. A single confocal section of the apical and basal part of the monolayer is shown in the middle. At the bottom of each column, the fluorescence of V5 tag (green) and β catenin (red) signals was scanned along the pink line drawn at a random position and presented in pink squares. Scale bar: 10 µm. (E). Arrowheads indicate the Zonula adherens. Bar graphs in red presents the fluorescence intensity of β-catenin in Zonula adherens. (F). The 3D reconstruction of the septin 9 and β-catenin signals in a single cell from each group. (G). Bar graphs in red present the percentage of β-catenin intensity in the basolateral and apical zones. Data information: Data are at least two times replicates and cysts (n=10) for 3D staining and cysts (n=30) for 2D staining. The statistics values are means ±s.e.m. Student’s t-test was used. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P < 0.001.
Figure 4.
Deletion of septin 9 PB domains impacts cell-cell adhesion (A). The MDCK stable cell lines plated on Matrigel for 4 days to form cysts, and then stained for E-cadherin (green) and actin (red). A single confocal section through the middle of a cyst is shown. Scale bar 10 µm. (B). The distribution of the E-cadherin signal in cysts presented in (A) was analyzed by ImageJ software in an individual cell from a cyst. A circle was defined at the periphery of each cell and the plugin produced a profile plot of normalized integrated intensities in concentric circles as a function of distance from a point in the image, considered here as the center of the cell. The circle was divided into three bands (1, 2, 3) with an equal radius. (C). Quantification of the fluorescence intensity of E-cadherin from each band is represented as a histogram. (D). The MDCK stable cell lines of EV, i1 and Del1.2 plated on transwell filters for 24h. Cells were fixed and stained for V5 tag (green) and β-catenin (red). Confocal images of XZ sections are presented at the top. A single confocal section of the apical and basal part of the monolayer is shown in the middle. At the bottom of each column, the fluorescence of V5 tag (green) and β catenin (red) signals was scanned along the pink line drawn at a random position and presented in pink squares. Scale bar: 10 µm. (E). Arrowheads indicate the Zonula adherens. Bar graphs in red presents the fluorescence intensity of β-catenin in Zonula adherens. (F). The 3D reconstruction of the septin 9 and β-catenin signals in a single cell from each group. (G). Bar graphs in red present the percentage of β-catenin intensity in the basolateral and apical zones. Data information: Data are at least two times replicates and cysts (n=10) for 3D staining and cysts (n=30) for 2D staining. The statistics values are means ±s.e.m. Student’s t-test was used. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P < 0.001.
3.5. The two PB domains of septin 9 regulates cell-ECM adhesion
To further characterize the inverted polarized cyst formed by del1,2 cells, we stained the Na
+/K
+ ATPase, a key component in the maintenance of the epithelial phenotype which is present at the BM of most epithelial cells (Deborde et al. 2008). Indeed, the Na
+/K
+ ATPase, was found at the BM of the EV cells and the signal was stronger in i1 cells. Surprisingly, Na
+/K
+ ATPase was absent from del1,2 cells, as evidenced by the 3D reconstruction of the confocal data (
Figure S3A). These data recalled our previous report on the absence of integrins and ECM components such as laminin and collagen IV in cysts with inverted polarity phenotype (Peng et al. 2015). Interestingly, Integrin β1 decreased in laminin septin 9_del1.2 cysts compared to septin 9_i1 cysts (
Figure S3B). Besides, laminin was absent from del1,2 cysts (
Figure S3C). Furthermore we tested fibronectin, a main multifunctional protein of the ECM (Cox, Sastry, and Huttenlocher 2001; Engel et al. 1981; Playford and Schaller 2004). Fibronectin increased in septin 9_il cysts compared to EV cysts and formed well-organized structure in the center of the cysts (
Figure S3D) which totally disappeared from the septin 9_del1.2 cysts. However, the signal remained at the periphery of the septin 9_del1.2 cysts and was higher than that of the EV cysts (
Figure S3D). Thus, we concluded that the deletion of the two PB domains of septin 9_i1 impaired ECM assembly and cell-ECM adhesion required to control apico-basal polarity.
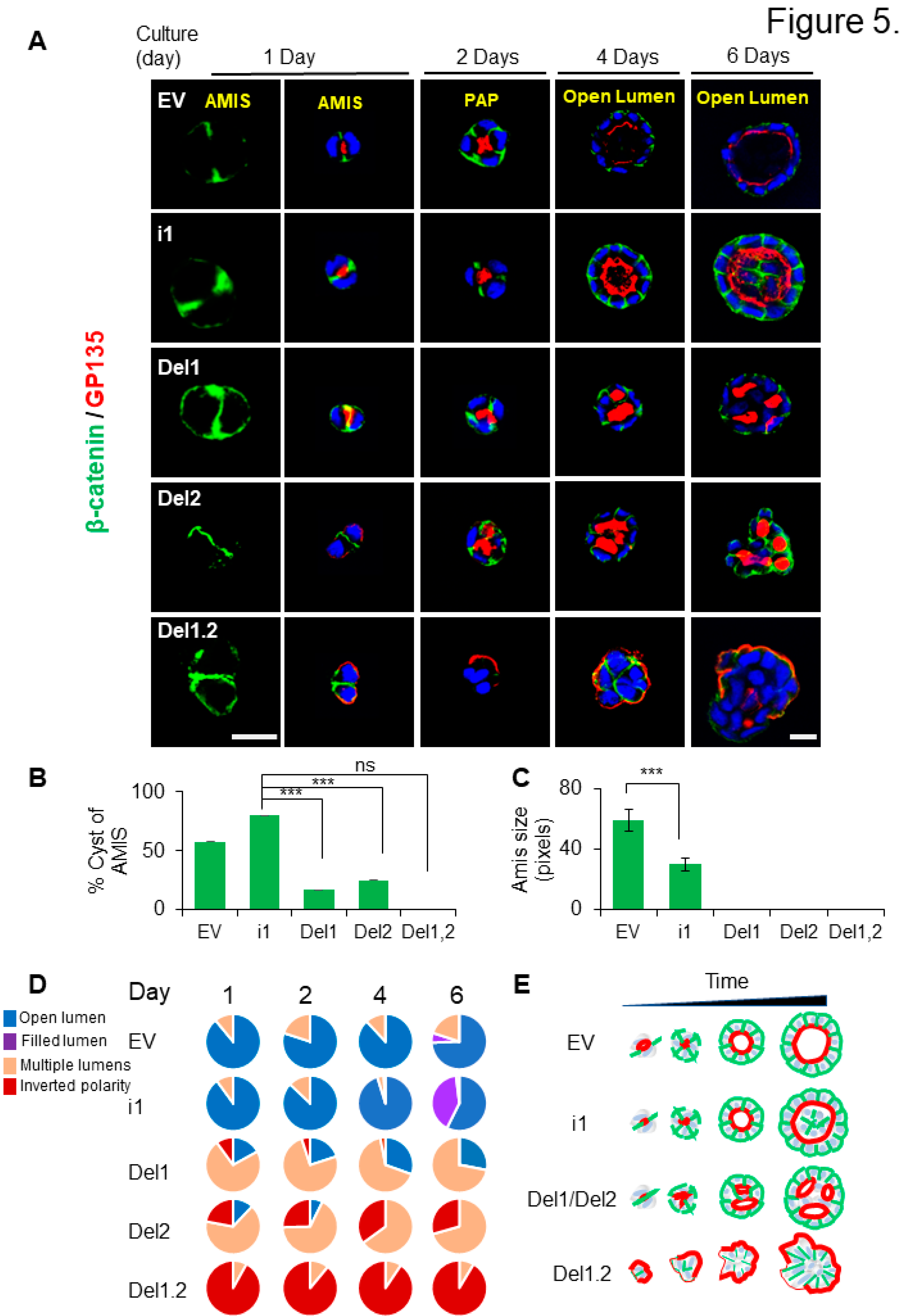
3.6. The PB domains of septin 9 regulate lumen formation at the different stages of the polarization process
To further decipher the importance of PB domains during the polarization process, the different MDCK cell lines were cultured on 3D and analyzed for β-catenin and the apical marker GP135 at different time points, starting from apical membrane initiation site (AMIS) formation after 1 day, the preapical patch (PAP) after 2 days, open lumen formation after 4 days (Bryant et al. 2010) and then we follow the cyst cultured up to 6 days. In EV and septin 9_i1cysts, AMIS was clearly visible, and the PAP was formed, and lumen continued to grow until 6 days (
Figure 5A). Here again as observed in
Figure 3C, the lumen started to fill in septin 9_i1 cysts which suggested overgrowth of the cells. However, no AMIS was presented in the mutant cells and the multiple lumens were already present at the PAP stage. Then at day 4 and day 6 the cysts from both del1 and del2 displayed multiple lumens phenotype. The del1.2 cysts presented the inverted polarity phenotype as expected (
Figure 5A). Although the phenotype was exacerbated at day 6 and the cysts displayed invasive features which are different from the round shape of the cyst at day 4. The apical marker presented asymmetric localization which recalled, the front-rear polarization in migrating cells (Bryant et al. 2014) (
Figure 5A). The quantification of the cyst forming AMIS (
Figure 5B,C) and those with the different phenotype were performed for each condition and at the different time points (
Figure 5D). The schematic representation of the study was presented in
Figure 5E.
Figure 5.
Deletion of septin 9 PB domains impact cyst phenotype from the AMIS formation to the lumen formation. (A). All the MDCK stable cell lines plated on Matrigel for 1 day, 2 days, 4 days and 6 days to form cysts, and then stained for β-catenin (green) and GP135 (red). A single confocal section through the middle of a cyst is shown. For the AMIS stage, β-catenin (green), scale bar is 20 µm, others are all 10 µm. (B). The analysis of AMIS formation of each stable cell lines after 1 days is showed in the histogram. (C). Bars represented the size of AMIS. (D). The phenotype of open lumen, multi-lumen, inverted polarity and filled lumen are counted during the culture times. Color for each phenotype in pie is corresponding the color below pictures. (E). Schematic representation of the septin 9 situation and its effects on the phenotype of the MDCK cell cysts during the different stage. Data information: Data are at least two times replicates and cysts (n>20) for 3D staining. The statistics values are means ±s.e.m. Student’s t-test was used. ***P < 0.001.
Figure 5.
Deletion of septin 9 PB domains impact cyst phenotype from the AMIS formation to the lumen formation. (A). All the MDCK stable cell lines plated on Matrigel for 1 day, 2 days, 4 days and 6 days to form cysts, and then stained for β-catenin (green) and GP135 (red). A single confocal section through the middle of a cyst is shown. For the AMIS stage, β-catenin (green), scale bar is 20 µm, others are all 10 µm. (B). The analysis of AMIS formation of each stable cell lines after 1 days is showed in the histogram. (C). Bars represented the size of AMIS. (D). The phenotype of open lumen, multi-lumen, inverted polarity and filled lumen are counted during the culture times. Color for each phenotype in pie is corresponding the color below pictures. (E). Schematic representation of the septin 9 situation and its effects on the phenotype of the MDCK cell cysts during the different stage. Data information: Data are at least two times replicates and cysts (n>20) for 3D staining. The statistics values are means ±s.e.m. Student’s t-test was used. ***P < 0.001.
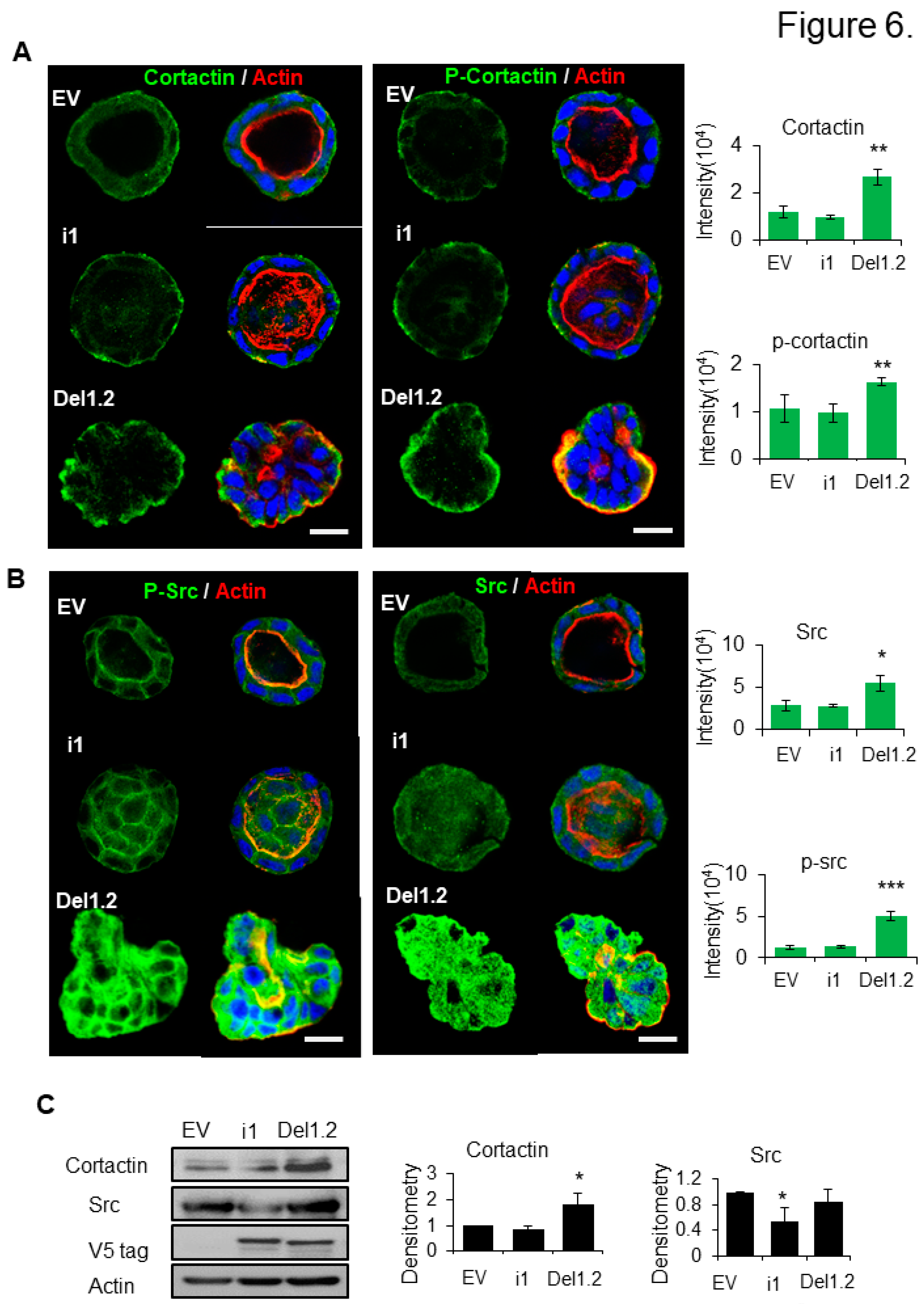
3.7. The deletion of the two PB domains of septin 9 promotes invasive features through the regulation of src and cortactin
To get more mechanistic insights on how deletion of the two PB domains of septin 9 induced the invasive phenotype we studied the cysts formed from EV, septin 9_i1 and septin 9_del1.2 after 6 days of culture in 3D. We found that septin 9 was cytoplasmic at day 6 in each cell cysts (
Figure S4) similarly to data observed at day 4 (
Figure 3C). Interestingly, septin 9 was enriched in the front of cysts with the invasive phenotype (
Figure S4). We analyzed cortactin which was distributed uniformly on the BM membrane and especially on the basal part in EV cysts. A similar staining was observed for septin 9_il cysts. By contrast, cortactin signal strongly increased and colocalized with actin in septin 9_del1.2 cysts (
Figure 6A). Furthermore, the phosphorylation of cortactin (p-cortactin) which reflected its activity showed much more striking signal in septin 9_del1.2 cells (
Figure 6A). As cortactin is the substrate of src (Head et al. 2003; Huang et al. 1998; Patel et al. 1998), and src phosphorylation of cortactin enhances actin assembly (Tehrani et al. 2007), we then analyzed src. Interestingly we found that src and p-src expression increased in septin 9_del1.2 cysts (
Figure 6B). Src and cortactin expressions increased were confirmed by immunoblot (
Figure 6C). Thus, these data indicated that the deletion of two PB domains of septin 9 induces activation and recruitment of the src/cortactin signal allowing the cells to acquire invasive features.
Figure 6.
Deletion of septin 9 PB domains induces collective migration by regulating src/cortactin signal pathway in day 6. (A). and (B). The MDCK stable cell lines of EV, i1 and Del1.2 plated on Matrigel for 6 days to form cysts, and then stained for cortactin (green) and Actin (red) and p-cortactin (green) and Actin (red), src (green) and Actin (red), p-src (green) and Actin (red). A single confocal section through the middle of a cyst is shown. The scale bar is 10 µm. The quantification of the fluorescence intensity of each marker is showed beside the images. (C)The immunoblotting of the src and cortactin protein and the densitometry analysis. The data are means ±s.e.m. Student’s t-test was used. **P<0.01. Data information: Data are at least two times replicates and cysts (n=10) for 3D staining and immunoblotting three times. The statistics values are means ±s.e.m. Student’s t-test was used. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P < 0.001.
Figure 6.
Deletion of septin 9 PB domains induces collective migration by regulating src/cortactin signal pathway in day 6. (A). and (B). The MDCK stable cell lines of EV, i1 and Del1.2 plated on Matrigel for 6 days to form cysts, and then stained for cortactin (green) and Actin (red) and p-cortactin (green) and Actin (red), src (green) and Actin (red), p-src (green) and Actin (red). A single confocal section through the middle of a cyst is shown. The scale bar is 10 µm. The quantification of the fluorescence intensity of each marker is showed beside the images. (C)The immunoblotting of the src and cortactin protein and the densitometry analysis. The data are means ±s.e.m. Student’s t-test was used. **P<0.01. Data information: Data are at least two times replicates and cysts (n=10) for 3D staining and immunoblotting three times. The statistics values are means ±s.e.m. Student’s t-test was used. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P < 0.001.
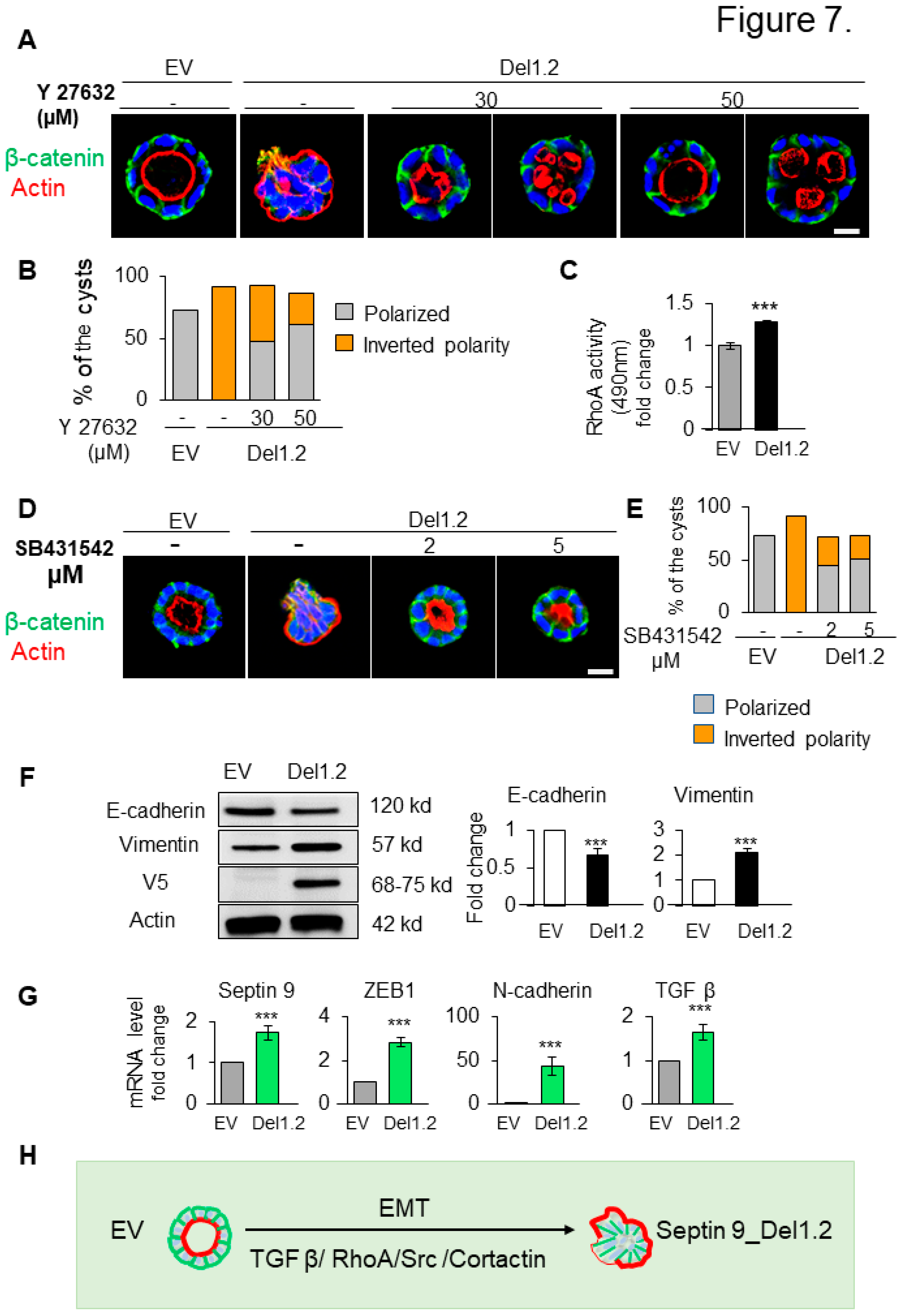
3.8. Inhibition of RhoA and TGF-β type I receptor rescues the polarity of del1,2 cysts
RhoA is the first family member of Rho family of GTPases which control the actin dynamic and is regulated by cortactin (Cox et al. 2001; Liang et al. 2017). Furthermore the activation of RhoA in the cysts with inverted polarity phenotype was reported and inhibition of Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) prevented the inversion (Bryant et al. 2014; Yu et al. 2008). Therefore, we asked whether the inverted polarity and the invasive phenotype of septin 9_del1.2 cysts were dependent on RhoA. We then examined the effect of ROCK inhibitor (Y27632) on control (EV) and septin 9_del1.2 cells (Del1,2) (
Figure S5;
Figure 7A). Interestingly treatment of del1.2 cells with Y27632 at 30 and 50 μM, reverted the polarity and the apical domain was found in the interior either as single or multiple lumens (
Figure 7A,B) and represented 47.7% and 61% of the cysts respectively for the doses of Y27632 at 30 and 50 μM (
Figure 7A,B). Subsequently, we assessed RhoA activity which significantly increased in septin 9_del1.2 cells compared to EV cells as expected (
Figure 7C). Thus, these data indicated that RhoA dependent-actomyosin contractility is involved in the formation of the inverted polarity phenotype of del1,2 cysts.
The transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), is a master regulator of epithelial cell plasticity and a driver of EMT (Nieto et al. 2016:2016). Furthermore, TGF-β mediated activation of RhoA to maintain basal RhoA–ROCK signaling (Fleming et al. 2009; Zhang 2009). Therefore, we analyzed the TGF-β signaling in cysts from depletion of the two PB domains of septin 9 with invasive phenotype. First, we treated the cells with TGF-β type 1 receptor inhibitor (SB431542) at two different concentrations (
Figure 7D). Strikingly, this treatment hampered the inversion of polarity and allowed the formation of single monolayer of cells and a recovery of β-catenin at cell-cell junctions (
Figure 7D,E). Subsequently, we showed a decrease of E-cadherin and the increase of vimentin by immunoblot performed on EV and del1,2 cells (
Figure 7F). Next, using qRT-PCR, we showed the increase of the transcripts of other mesenchymal markers such as ZEB1 and N-Cadherin (
Figure 7G). Interestingly we also observed an increase of the TGF-β (
Figure 7G). Together, these data revealed the role of TGF-β driving plasticity in the invasiveness feature induced by depletion of the two PB domains of septin 9. Thus, it strongly suggested the involvement of the EMT process regulated by the TGFβ/RhoA/cortactin pathway (
Figure 7H).
Figure 7.
Deletion of septin 9 PB domains induces collective migration by regulating src/cortactin signal pathway in day 6. (A). MDCK cells expressing EV and septin 9_del1.2 were plated on Matrigel for 6 days and treated with 30µ M and 50 µM of Y27632. All the cysts were stained with β-catenin (green) for basolateral membrane, actin (red) for apical surface and Hoechst (blue) for nuclei. The representative confocal images are show in merge. (B). Quantification of polarized (lumen inside the cysts) and inverted polarity phenotypes in septin 9_EV and septin 9_del1.2 cysts. (C). RhoA activation fold change in septin 9_EV and septin 9_del1.2 cysts. (D). MDCK cells expressing EV and septin 9_del1.2 were plated on Matrigel for 6 days and treated with 2 µM and 5µM of SB431542. All the cysts were stained with β-catenin (green) actin (red). The representative confocal images for the merge signals are shown. (E). Quantification of cysts with polarized phenotype and the inverted polarity phenotype was represented. (F). Western blot analysis of E-cadherin, vimentin, in cells with EV and septin 9_del1.2 cultured in 3D condition. Actin is shown as a loading control. Quantifications of western blot data of E-cadherin and vimentin protein levels. (G). qRT-PCR analysis of the expression of mRNA encoding septin 9, N-cadherin, ZEB1 and TGFβ in cells with EV and septin 9_del1.2 cultured in 2D condition. (H). Schematic diagram illustrating the inverted polarity phenotype induced upon deletion of the two PB domains of septin 9_i1 in 3D culture. These plastic processes are EMT, and the process is regulated by the TGFβ/RhoA/Src/Cortactin pathway. Data information: Data are at least two times replicates and cysts (n>10) for 3D staining, and three times for RhoA activity test and immunoblotting and qRT-PCR. The statistics values are means ±s.e.m. Student’s t-test was used. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P < 0.001.
Figure 7.
Deletion of septin 9 PB domains induces collective migration by regulating src/cortactin signal pathway in day 6. (A). MDCK cells expressing EV and septin 9_del1.2 were plated on Matrigel for 6 days and treated with 30µ M and 50 µM of Y27632. All the cysts were stained with β-catenin (green) for basolateral membrane, actin (red) for apical surface and Hoechst (blue) for nuclei. The representative confocal images are show in merge. (B). Quantification of polarized (lumen inside the cysts) and inverted polarity phenotypes in septin 9_EV and septin 9_del1.2 cysts. (C). RhoA activation fold change in septin 9_EV and septin 9_del1.2 cysts. (D). MDCK cells expressing EV and septin 9_del1.2 were plated on Matrigel for 6 days and treated with 2 µM and 5µM of SB431542. All the cysts were stained with β-catenin (green) actin (red). The representative confocal images for the merge signals are shown. (E). Quantification of cysts with polarized phenotype and the inverted polarity phenotype was represented. (F). Western blot analysis of E-cadherin, vimentin, in cells with EV and septin 9_del1.2 cultured in 3D condition. Actin is shown as a loading control. Quantifications of western blot data of E-cadherin and vimentin protein levels. (G). qRT-PCR analysis of the expression of mRNA encoding septin 9, N-cadherin, ZEB1 and TGFβ in cells with EV and septin 9_del1.2 cultured in 2D condition. (H). Schematic diagram illustrating the inverted polarity phenotype induced upon deletion of the two PB domains of septin 9_i1 in 3D culture. These plastic processes are EMT, and the process is regulated by the TGFβ/RhoA/Src/Cortactin pathway. Data information: Data are at least two times replicates and cysts (n>10) for 3D staining, and three times for RhoA activity test and immunoblotting and qRT-PCR. The statistics values are means ±s.e.m. Student’s t-test was used. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P < 0.001.
4. Discussion
In this study, we showed that septin 9 is required to orient apico-basal polarity axis and this function was controlled by its two PB domains, which are required for the septin 9 assembly.
Septins are considered as a fourth cytoskeleton element and most of the multiple biological functions they performed are dependent on their membrane binding and their filamentous structure formation (Mostowy and Cossart 2012). Despite the evidence regarding the crucial role of the PB domains for septin filament formation and their binding to phospholipids on membranes, their role in septin functions was under-investigated. Septin 9 in particular form a filament structure by assembly with septin 2, septin 6 and septin 7 (Kim et al. 2011). Interestingly, in our study, we showed that septin 2 and septin 7 were localized at BM in polarized MDCK cysts (
Figure S1B) and their expressions were decrease by knock-down of septin 9 using siRNA. The cell-cell junctions at BM including adherens junctions and tight junctions are required for polarization of epithelial cell and the integrity of epithelium. Interestingly we also showed that septin 9 regulated E-cadherin and β-catenin expressions at BM as well as the tight junction protein ZO-1. These data were also supported by two recent works (Kim and Cooper 2021; Wang et al. 2021). One reported that septin 2 was localized at cell-cell junctions in human microvascular endothelial monolayers and was necessary for organization of cell-cell adhesion (Kim and Cooper 2021). The other showed that the septin complex, containing septin 2, septin 6 and septin 7, acts as a scaffold to recruit β-catenin to synergize with E-cadherin, therefore links the catenin complex to the actin cytoskeleton for establishing epithelial cell polarity (Wang et al. 2021). Furthermore, deletion or disruption of septins liberated the adherens junction and polarity components to the cytoplasm, and induced deformation of apical lumen in cysts in 3D (Wang et al. 2021).
Importantly, we found that depletion of septin 9 or deletion of the two PB domains induced the formation of cysts with inverted polarity phenotype. Interestingly we demonstrated that the septin 9 mutants, deleted from their PB domains were then accumulated in the cytoplasm above the nuclei in the apical region. However, overexpression of the full length septin 9_i1 increased the cell height. Subsequently, we proposed that septin 9 assembled with septin 2 and septin 7 to form filament acting as a scaffold to link the plasma membrane to actin cytoskeleton through the two PB domains and therefore stabilized adherens junctions to maintain apico-basal polarity. The inverted polarity phenotype has been related to the collective cell migration and invasion (Debnath and Brugge 2005). The collective migration behavior was also associated to disruption of cell-cell junctions, whereby allowing the protrusion in vivo and in vitro (Nabeshima et al. 1998; Yu et al. 2003). Furthermore, we found that cortactin and src were activated in the inverted phenotype cysts with septin 9_del1.2 expression. Cortactin is a regulator of actin polymerization at membrane cortex and regulates late endosomes trafficking by inducting branched actin assembly, which subsequently impacts on Golgi homeostasis (Kirkbride et al. 2012). Cortactin is required for the assembly of protrusion in the cancer cell, and it is important for invasion and cell migration (Kirkbride et al. 2011; Yamaguchi and Condeelis 2007; Yin, Ma, and An 2015). Furthermore cortactin was identified as a target of E-cadherin-activated Src family kinase signaling to support cadherin adhesion and the integrity of cell-cell contacts (Ren et al. 2009). Moreover, it was shown that septin 6 cooperated with septin 7 to coordinate actin remodeling and microtubule to promote the formation of filopodia by increasing cortactin recruitment (Head et al. 2003). Thus, activation of cortactin and src in the inverted polarized cysts revealed that the balance of septin 9 expression is required to maintain epithelium homeostasis. Indeed, overexpression induced the proliferative tumor phenotype with lumen filling of MDCK cysts, and loss of expression or deletion of two PB domains of septin 9 induced the invasive tumor phenotype representing by inverted polarized phenotype. Overall, our results demonstrated a central role of the newly identified PB2 domain (Omrane et al. 2019b) in septin 9 biological function. Septin 9 appeared as a central regulator of apico-basal polarity of epithelial cells, a guardian against cancer cell migration and invasion. Thus septin 9 remained therefore an important target in the study of aggressive carcinoma.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
TC: J.P. performed the experimental work and contributed to the writing and editing of the manuscript M.O. and N.B. participated in the experimental procedures and prepared the Fig.s. D.S. discussed the data; A.G.-D. conceived and supervised the project, designed experiments and wrote the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets supporting the current study have not been deposited in a public repository but are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants from INSERM and Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer (ARC) to A.G.-D. and T.C. receive financial support from China Scholarship Council.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Akil, Abdellah, Juan Peng, Mohyeddine Omrane, Claire Gondeau, Christophe Desterke, Mickaël Marin, Hélène Tronchère, Cyntia Taveneau, Sokhavuth Sar, Philippe Briolotti, Soumaya Benjelloun, Abdelaziz Benjouad, Patrick Maurel, Valérie Thiers, Stéphane Bressanelli, Didier Samuel, Christian Bréchot, and Ama Gassama-Diagne. 2016. “Septin 9 Induces Lipid Droplets Growth by a Phosphatidylinositol-5-Phosphate and Microtubule-Dependent Mechanism Hijacked by HCV.” Nature Communications 7:12203. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12203. [CrossRef]
- Bossinger, Olaf, and André Bachmann. 2004. “Ciliogenesis: Polarity Proteins on the Move.” Current Biology: CB 14(19):R844-846. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.09.039. [CrossRef]
- Bridges, Andrew A., and Amy S. Gladfelter. 2014. “Fungal Pathogens Are Platforms for Discovering Novel and Conserved Septin Properties.” Current Opinion in Microbiology 20:42–48. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2014.04.004. [CrossRef]
- Bryant, David M., Anirban Datta, Alejo E. Rodríguez-Fraticelli, Johan Peränen, Fernando Martín-Belmonte, and Keith E. Mostov. 2010. “A Molecular Network for de Novo Generation of the Apical Surface and Lumen.” Nature Cell Biology 12(11):1035–45. doi: 10.1038/ncb2106. [CrossRef]
- Bryant, David M., and Keith E. Mostov. 2008. “From Cells to Organs: Building Polarized Tissue.” Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology 9(11):887–901. doi: 10.1038/nrm2523. [CrossRef]
- Bryant, David M., Julie Roignot, Anirban Datta, Arend W. Overeem, Minji Kim, Wei Yu, Xiao Peng, Dennis J. Eastburn, Andrew J. Ewald, Zena Werb, and Keith E. Mostov. 2014. “A Molecular Switch for the Orientation of Epithelial Cell Polarization.” Developmental Cell 31(2):171–87. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2014.08.027. [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, Deeptiman, and Wu-Min Deng. 2019. “Drosophila Model in Cancer: An Introduction.” Pp. 1–14 in The Drosophila Model in Cancer, Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, edited by W.-M. Deng. Cham: Springer International Publishing.
- Cox, Elisabeth A., Sarita K. Sastry, and Anna Huttenlocher. 2001. “Integrin-Mediated Adhesion Regulates Cell Polarity and Membrane Protrusion through the Rho Family of GTPases.” Molecular Biology of the Cell 12(2):265–77. [CrossRef]
- Debnath, Jayanta, and Joan S. Brugge. 2005. “Modelling Glandular Epithelial Cancers in Three-Dimensional Cultures.” Nature Reviews. Cancer 5(9):675–88. doi: 10.1038/nrc1695. [CrossRef]
- Deborde, Sylvie, Emilie Perret, Diego Gravotta, Ami Deora, Susana Salvarezza, Ryan Schreiner, and Enrique Rodriguez-Boulan. 2008. “Clathrin Is a Key Regulator of Basolateral Polarity.” Nature 452(7188):719–23. doi: 10.1038/nature06828. [CrossRef]
- Dolat, Lee, Qicong Hu, and Elias T. Spiliotis. 2014. “Septin Functions in Organ System Physiology and Pathology.” Biological Chemistry 395(2):123–41. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2013-0233. [CrossRef]
- Engel, J., E. Odermatt, A. Engel, J. A. Madri, H. Furthmayr, H. Rohde, and R. Timpl. 1981. “Shapes, Domain Organizations and Flexibility of Laminin and Fibronectin, Two Multifunctional Proteins of the Extracellular Matrix.” Journal of Molecular Biology 150(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90326-0. [CrossRef]
- Fleming, Y. M., G. J. Ferguson, L. C. Spender, J. Larsson, S. Karlsson, B. W. Ozanne, R. Grosse, and G. J. Inman. 2009. “TGF-β-Mediated Activation of RhoA Signalling Is Required for Efficient V12 HaRas and V600E BRAF Transformation.” Oncogene 28(7):983–93. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.449. [CrossRef]
- Fung, Karen Y. Y., Lu Dai, and William S. Trimble. 2014. “Cell and Molecular Biology of Septins.” International Review of Cell and Molecular Biology 310:289–339. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800180-6.00007-4. [CrossRef]
- Gurel, Pinar S., Anna L. Hatch, and Henry N. Higgs. 2014. “Connecting the Cytoskeleton to the Endoplasmic Reticulum and Golgi.” Current Biology: CB 24(14):R660–72. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.05.033. [CrossRef]
- Hamze-Komaiha, Ola, Sokavuth Sarr, Yannick Arlot-Bonnemains, Didier Samuel, and Ama Gassama-Diagne. 2016. “SHIP2 Regulates Lumen Generation, Cell Division, and Ciliogenesis through the Control of Basolateral to Apical Lumen Localization of Aurora A and HEF 1.” Cell Reports 17(10):2738–52. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.11.033. [CrossRef]
- Head, Julie A., Dongyan Jiang, Min Li, Lynda J. Zorn, Erik M. Schaefer, J. Thomas Parsons, and Scott A. Weed. 2003. “Cortactin Tyrosine Phosphorylation Requires Rac1 Activity and Association with the Cortical Actin Cytoskeleton.” Molecular Biology of the Cell 14(8):3216–29. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e02-11-0753. [CrossRef]
- Huang, C., J. Liu, C. C. Haudenschild, and X. Zhan. 1998. “The Role of Tyrosine Phosphorylation of Cortactin in the Locomotion of Endothelial Cells.” The Journal of Biological Chemistry 273(40):25770–76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.40.25770. [CrossRef]
- Ikenouchi, Junichi, Kazuaki Umeda, Sachiko Tsukita, Mikio Furuse, and Shoichiro Tsukita. 2007. “Requirement of ZO-1 for the Formation of Belt-like Adherens Junctions during Epithelial Cell Polarization.” The Journal of Cell Biology 176(6):779–86. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200612080. [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, Andrei I., Hongnga T. Le, Nayden G. Naydenov, and Florian Rieder. 2021. “Novel Functions of the Septin Cytoskeleton: Shaping Up Tissue Inflammation and Fibrosis.” The American Journal of Pathology 191(1):40–51. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.09.007. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Joanna, and John A. Cooper. 2018. “Septins Regulate Junctional Integrity of Endothelial Monolayers.” Molecular Biology of the Cell 29(13):1693–1703. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E18-02-0136. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Joanna, and John A. Cooper. 2021. “Junctional Localization of Septin 2 Is Required for Organization of Junctional Proteins in Static Endothelial Monolayers.” Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 41(1):346–59. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.315472. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Moshe S., Carol D. Froese, Mathew P. Estey, and William S. Trimble. 2011. “SEPT9 Occupies the Terminal Positions in Septin Octamers and Mediates Polymerization-Dependent Functions in Abscission.” The Journal of Cell Biology 195(5):815–26. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201106131. [CrossRef]
- Kirkbride, Kellye C., Nan Hyung Hong, Christi L. French, Emily S. Clark, W. Gray Jerome, and Alissa M. Weaver. 2012. “Regulation of Late Endosomal/Lysosomal Maturation and Trafficking by Cortactin Affects Golgi Morphology.” Cytoskeleton (Hoboken, N.J.) 69(9):625–43. doi: 10.1002/cm.21051. [CrossRef]
- Kirkbride, Kellye C., Bong Hwan Sung, Seema Sinha, and Alissa M. Weaver. 2011. “Cortactin.” Cell Adhesion & Migration 5(2):187–98. doi: 10.4161/cam.5.2.14773. [CrossRef]
- Kremer, Brandon E., Timothy Haystead, and Ian G. Macara. 2005. “Mammalian Septins Regulate Microtubule Stability through Interaction with the Microtubule-Binding Protein MAP4.” Molecular Biology of the Cell 16(10):4648–59. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-03-0267. [CrossRef]
- Liang, Xuan, Srikanth Budnar, Shafali Gupta, Suzie Verma, Siew-Ping Han, Michelle M. Hill, Roger J. Daly, Robert G. Parton, Nicholas A. Hamilton, Guillermo A. Gomez, and Alpha S. Yap. 2017. “Tyrosine Dephosphorylated Cortactin Downregulates Contractility at the Epithelial Zonula Adherens through SRGAP1.” Nature Communications 8(1):790. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00797-w. [CrossRef]
- Mirvis, Mary, Tim Stearns, and W. James Nelson. 2018. “Cilium Structure, Assembly, and Disassembly Regulated by the Cytoskeleton.” Biochemical Journal 475(14):2329–53. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170453. [CrossRef]
- Mostowy, Serge, and Pascale Cossart. 2012. “Septins: The Fourth Component of the Cytoskeleton.” Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology 13(3):183–94. doi: 10.1038/nrm3284. [CrossRef]
- Nabeshima, K., Y. Shimao, T. Inoue, H. Itoh, H. Kataoka, and M. Koono. 1998. “Hepatocyte Growth Factor/Scatter Factor Induces Not Only Scattering but Also Cohort Migration of Human Colorectal-Adenocarcinoma Cells.” International Journal of Cancer 78(6):750–59. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0215(19981209)78:6<750::aid-ijc13>3.0.co;2-#. [CrossRef]
- Nieto, M. Angela, Ruby Yun-Ju Huang, Rebecca A. Jackson, and Jean Paul Thiery. 2016. “EMT: 2016.” Cell 166(1):21–45. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.06.028. [CrossRef]
- Nishihama, Ryuichi, Masayuki Onishi, and John R. Pringle. 2011. “New Insights into the Phylogenetic Distribution and Evolutionary Origins of the Septins.” Biological Chemistry 392(8–9):681–87. doi: 10.1515/BC.2011.086. [CrossRef]
- Omrane, Mohyeddine, Amanda Souza Camara, Cyntia Taveneau, Nassima Benzoubir, Thibault Tubiana, Jinchao Yu, Raphaël Guérois, Didier Samuel, Bruno Goud, Christian Poüs, Stéphane Bressanelli, Richard Charles Garratt, Abdou Rachid Thiam, and Ama Gassama-Diagne. 2019a. “Septin 9 Has Two Polybasic Domains Critical to Septin Filament Assembly and Golgi Integrity.” IScience 13:138–53. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2019.02.015. [CrossRef]
- Omrane, Mohyeddine, Amanda Souza Camara, Cyntia Taveneau, Nassima Benzoubir, Thibault Tubiana, Jinchao Yu, Raphaël Guérois, Didier Samuel, Bruno Goud, Christian Poüs, Stéphane Bressanelli, Richard Charles Garratt, Abdou Rachid Thiam, and Ama Gassama-Diagne. 2019b. “Septin 9 Has Two Polybasic Domains Critical to Septin Filament Assembly and Golgi Integrity.” IScience 13:138–53. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2019.02.015. [CrossRef]
- Pan, Fangfang, Russell L. Malmberg, and Michelle Momany. 2007. “Analysis of Septins across Kingdoms Reveals Orthology and New Motifs.” BMC Evolutionary Biology 7:103. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-7-103. [CrossRef]
- Patel, A. S., G. L. Schechter, W. J. Wasilenko, and K. D. Somers. 1998. “Overexpression of EMS1/Cortactin in NIH3T3 Fibroblasts Causes Increased Cell Motility and Invasion in Vitro.” Oncogene 16(25):3227–32. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201850. [CrossRef]
- Peng, Juan, Aline Awad, Sokhavuth Sar, Ola Hamze Komaiha, Romina Moyano, Amel Rayal, Didier Samuel, Annette Shewan, Bart Vanhaesebroeck, Keith Mostov, and Ama Gassama-Diagne. 2015. “Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase P110δ Promotes Lumen Formation through the Enhancement of Apico-Basal Polarity and Basal Membrane Organization.” Nature Communications 6(1):5937. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6937. [CrossRef]
- Playford, Martin P., and Michael D. Schaller. 2004. “The Interplay between Src and Integrins in Normal and Tumor Biology.” Oncogene 23(48):7928–46. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208080. [CrossRef]
- Ren, Gang, Falak M. Helwani, Suzie Verma, Robert W. McLachlan, Scott A. Weed, and Alpha S. Yap. 2009. “Cortactin Is a Functional Target of E-Cadherin-Activated Src Family Kinases in MCF7 Epithelial Monolayers.” The Journal of Biological Chemistry 284(28):18913–22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.000307. [CrossRef]
- Roignot, Julie, Xiao Peng, and Keith Mostov. 2013. “Polarity in Mammalian Epithelial Morphogenesis.” Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology 5(2). doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a013789. [CrossRef]
- Royer, C., and X. Lu. 2011. “Epithelial Cell Polarity: A Major Gatekeeper against Cancer?” Cell Death and Differentiation 18(9):1470–77. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2011.60. [CrossRef]
- Shewan, Annette M., Aline Awad, Juan Peng, and Ama Gassama-Diagne. 2015. “Phosphoinositides as Determinants of Membrane Identity, Apicobasal Polarity, and Lumen Formation.” Pp. 221–44 in Cell Polarity 1: Biological Role and Basic Mechanisms, edited by K. Ebnet. Cham: Springer International Publishing.
- Spiliotis, Elias T. 2018. “Spatial Effects - Site-Specific Regulation of Actin and Microtubule Organization by Septin GTPases.” Journal of Cell Science 131(1). doi: 10.1242/jcs.207555. [CrossRef]
- Spiliotis, Elias T., Stephen J. Hunt, Qicong Hu, Makoto Kinoshita, and W. James Nelson. 2008. “Epithelial Polarity Requires Septin Coupling of Vesicle Transport to Polyglutamylated Microtubules.” The Journal of Cell Biology 180(2):295–303. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200710039. [CrossRef]
- Sroka, Robert, Johan Van Lint, Sarah-Fee Katz, Marlon R. Schneider, Alexander Kleger, Stephan Paschke, Thomas Seufferlein, and Tim Eiseler. 2016. “Cortactin Is a Scaffolding Platform for the E-Cadherin Adhesion Complex and Is Regulated by Protein Kinase D1 Phosphorylation.” Journal of Cell Science 129(12):2416–29. doi: 10.1242/jcs.184721. [CrossRef]
- Tanaka-Takiguchi, Yohko, Makato Kinoshita, and Kingo Takiguchi. 2009. “Septin-Mediated Uniform Bracing of Phospholipid Membranes.” Current Biology: CB 19(2):140–45. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.12.030. [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, Shandiz, Nenad Tomasevic, Scott Weed, Roman Sakowicz, and John A. Cooper. 2007. “Src Phosphorylation of Cortactin Enhances Actin Assembly.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 104(29):11933–38. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0701077104. [CrossRef]
- Torkko, Juha M., Aki Manninen, Sebastian Schuck, and Kai Simons. 2008. “Depletion of Apical Transport Proteins Perturbs Epithelial Cyst Formation and Ciliogenesis.” Journal of Cell Science 121(Pt 8):1193–1203. doi: 10.1242/jcs.015495. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Xueying, Wenwen Wang, Xiwei Wang, Ming Wang, Lijuan Zhu, Fatima Garba, Chuanhai Fu, Barbara Zieger, Xu Liu, Xing Liu, and Xuebiao Yao. 2021. “The Septin Complex Links the Catenin Complex to the Actin Cytoskeleton for Establishing Epithelial Cell Polarity.” Journal of Molecular Cell Biology 13(6):395–408. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjab036. [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Hideki, and John Condeelis. 2007. “Regulation of the Actin Cytoskeleton in Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion.” Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research 1773(5):642–52. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.07.001. [CrossRef]
- Yin, Miao, Wenqing Ma, and Liguo An. 2015. “Cortactin in Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion.” Oncotarget 8. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21088. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Wei, Lucy E. O’Brien, Fei Wang, Henry Bourne, Keith E. Mostov, and Mirjam M. P. Zegers. 2003. “Hepatocyte Growth Factor Switches Orientation of Polarity and Mode of Movement during Morphogenesis of Multicellular Epithelial Structures.” Molecular Biology of the Cell 14(2):748–63. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e02-06-0350. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Wei, Annette M. Shewan, Paul Brakeman, Dennis J. Eastburn, Anirban Datta, David M. Bryant, Qi-Wen Fan, William A. Weiss, Mirjam M. P. Zegers, and Keith E. Mostov. 2008. “Involvement of RhoA, ROCK I and Myosin II in Inverted Orientation of Epithelial Polarity.” EMBO Reports 9(9):923–29. doi: 10.1038/embor.2008.135. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J., C. Kong, H. Xie, P. S. McPherson, S. Grinstein, and W. S. Trimble. 1999. “Phosphatidylinositol Polyphosphate Binding to the Mammalian Septin H5 Is Modulated by GTP.” Current Biology: CB 9(24):1458–67. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)80115-3. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Ying E. 2009. “Non-Smad Pathways in TGF-β Signaling.” Cell Research 19(1):128–39. doi: 10.1038/cr.2008.328. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).