Submitted:
12 June 2023
Posted:
12 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
Kombucha culture and media
Experimental design
Preparation of tea extracts, inoculation, and fermentation
Analysis
Kinetic parameters
Kinetic modeling
Statistical analysis
3. Results and discussion
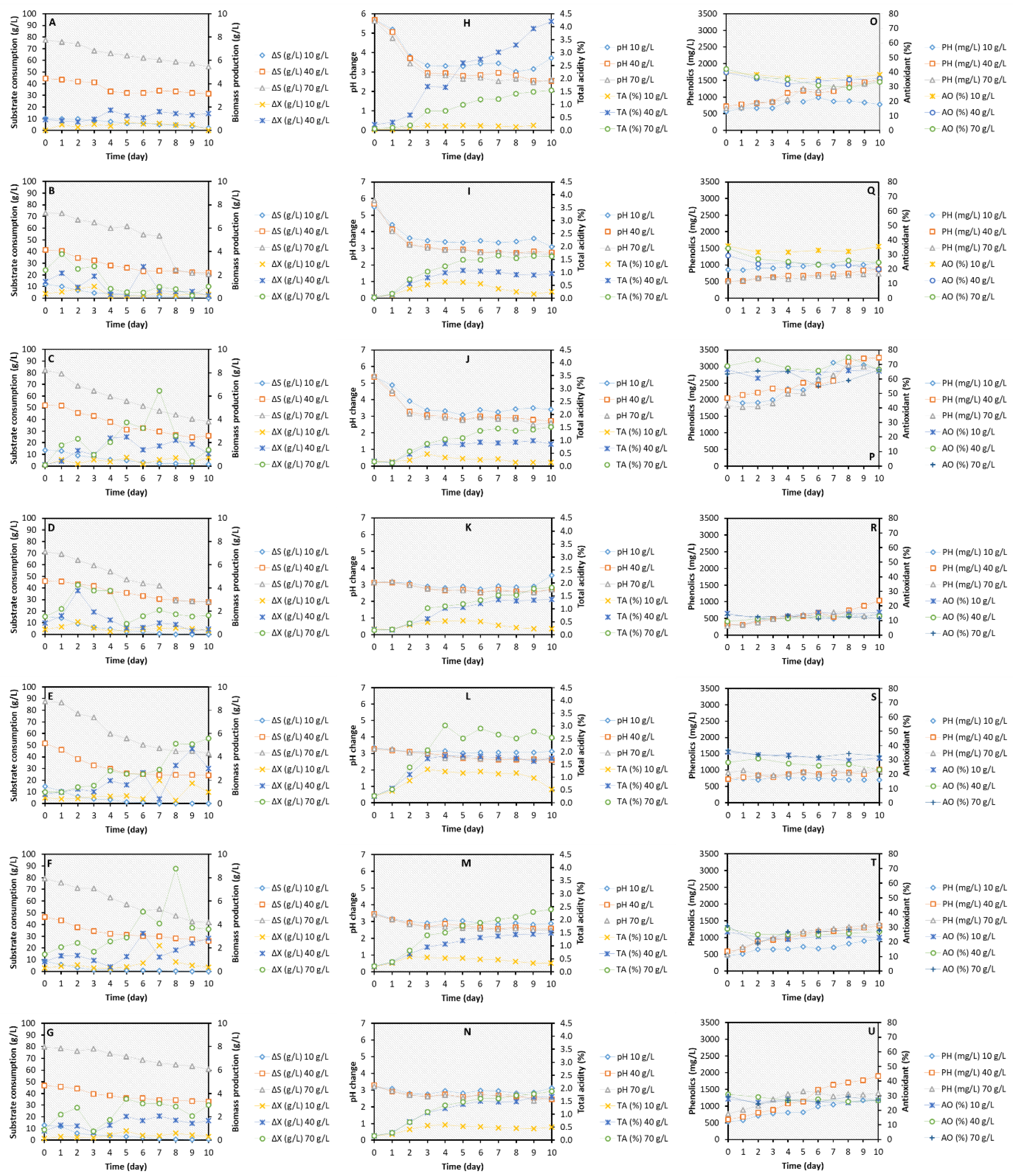
Sugar consumption and biomass production
pH and total acidity
Total phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity
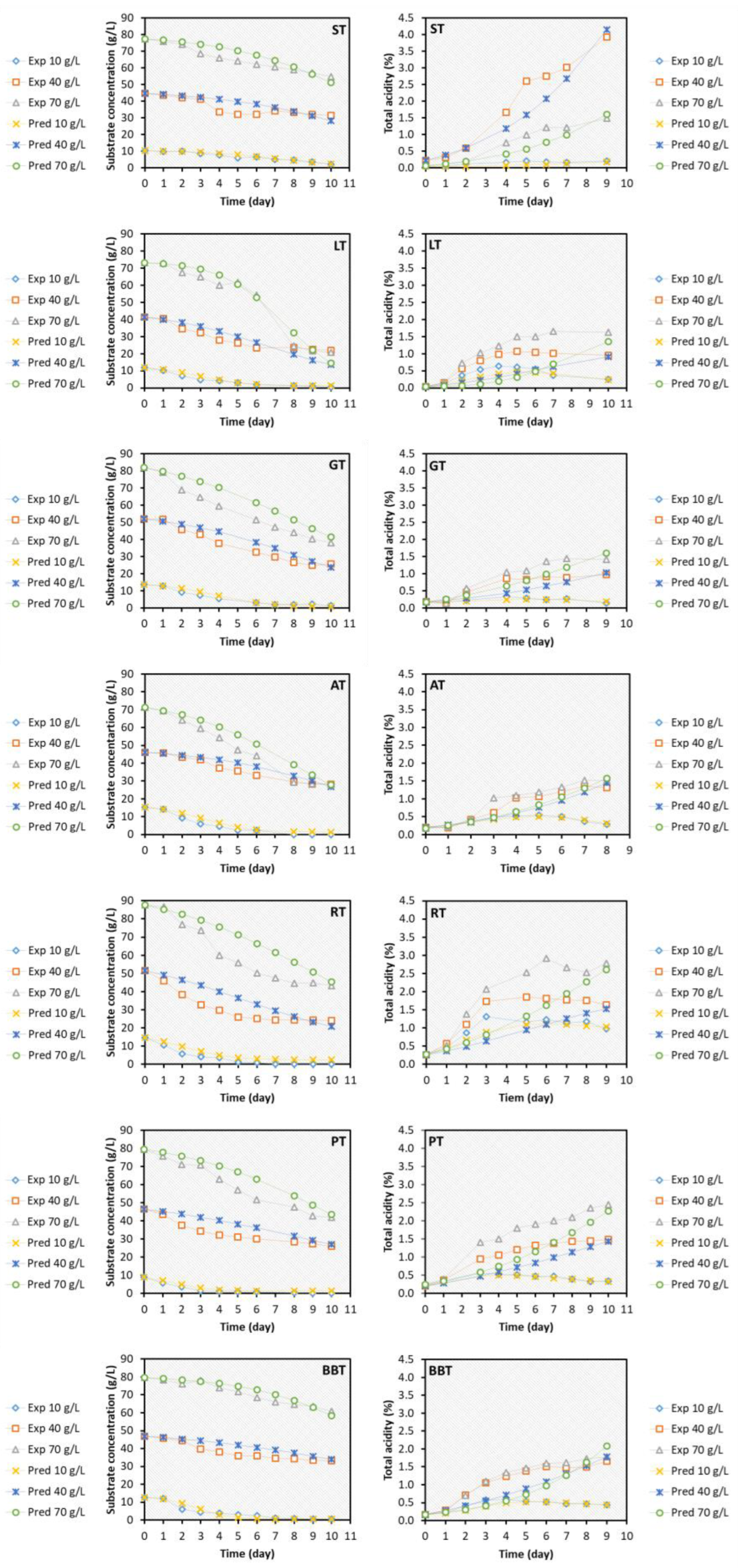
Kinetic characterization
Kinetic modeling
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviations | Full name |
| ISC | Initial sucrose concentration |
| R2 | Determination of coefficient |
| α and β | Empirical constants |
| N | Normal |
| HCl | Hydrochloric acid |
| LPM | Luedeking-Piret model |
| LM | Logistic model |
| GT | Green tea |
| ST | Sage tea |
| LT | Linden tea |
| BT | Black tea |
| BBT | Bilberry tea |
| RT | Rosehip tea |
| AT | Apple tea |
| PT | Pomegranate tea |
| NaOH | Sodium hydroxide |
| GAE | Gallic acid equivalents |
| DPPH | α, α-diphenyl-β-picrylhydrazyl |
| ∆S | Substrate consumption, g/L |
| QS | Maximum substrate consumption rate, g/L/d |
| η | Substrate utilization yield, % |
| ∆X | Biomass production, g/L |
| QX | Maximum biomass production rate, g/L/d |
| YX/S | Biomass yield, g biomass/g substrate |
| TA | Total acidity, % |
| QTA | Maximum total acidity production rate, %/d |
| ∆PH | Phenolics production, mg/L |
| QPH | Maximum phenolics production rate, mg/L/d |
| YPH/S | Phenolics yield, mg phenolics/g substrate |
| −dS/dt | Substrate consumption rate, g/L/d |
| µm,S | specific sugar consumption rate, 1/d |
| S | residual substrate concentration at the time “t”, g/L |
| Sm | maximum substrate concentration, g/L |
| dP/dt | total acidity rate, %/d |
| SAS | Statistical Analysis System |
References
- Dutta, H.; Paul, S.K. Kombucha drink: Production, quality, and safety aspects. In Production and Management of Beverages; Elsevier, 2019; pp. 259–288. [Google Scholar]
- Jayabalan, R.; Malbasa, R.V.; Loncar, E.S.; Vitas, J.S.; Sathishkumar, M. A review on kombucha tea: Microbiology, composition, fermentation, beneficial effects, toxicity, and tea fungus. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety 2014, 13, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, A.L.; Heard, G.; Cox, J. Yeast ecology of Kombucha fermentation. International Journal of Food Microbiology 2004, 95, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malbaša, R.; Lončar, E.; Djurić, M. Comparison of the products of Kombucha fermentation on sucrose and molasses. Food Chemistry 2008, 106, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şafak, S.; Mercan, N.; Aslim, B.; Beyatli, Y. A study on the production of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate by some eukaryotic microorganisms. Turkish Electronic Journal of Biotechnology 2002, 1, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Mayser, P.; Fromme, S.; Leitzmann, G.; Gründer, K. The yeast spectrum of the ‘tea fungus Kombucha’. Mycoses 1995, 38, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsilo, P.H.; Basson, A.K.; Ntombela, Z.G.; Maliehe, T.S.; Pullabhotla, R.V. Isolation and optimization of culture conditions of a bioflocculant-producing fungi from Kombucha tea SCOBY. Microbiology Research 2021, 12, 950–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwalt, C.; Steinkraus, K.; Ledford, R. Kombucha, the fermented tea: microbiology, composition, and claimed health effects. Journal of Food Protection 2000, 63, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtzman, C.P.; Robnett, C.J.; Basehoar-Powers, E. Zygosaccharomyces kombuchaensis, a new ascosporogenous yeast from ‘Kombucha tea’. FEMS Yeast Research 2001, 1, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-H.; Hsu, W.-H.; Lee, F.-L.; Liao, C.-C. The isolation and identification of microbes from a fermented tea beverage, Haipao, and their interactions during Haipao fermentation. Food Microbiology 1996, 13, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravorty, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Chatzinotas, A.; Chakraborty, W.; Bhattacharya, D.; Gachhui, R. Kombucha tea fermentation: Microbial and biochemical dynamics. International Journal of Food Microbiology 2016, 220, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, S.-C.; Chen, C. Effects of origins and fermentation time on the antioxidant activities of kombucha. Food Chemistry 2006, 98, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nummer, B.A. Kombucha brewing under the Food and Drug Administration Model Food Code: Risk analysis and processing guidance. Journal of Environmental Health 2013, 76, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Villarreal-Soto, S.A.; Beaufort, S.; Bouajila, J.; Souchard, J.P.; Taillandier, P. Understanding kombucha tea fermentation: a review. Journal of Food Science 2018, 83, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malbasa, R.V.; Loncar, E.S.; Vitas, J.S.; Canadanovic-Brunet, J.M. Influence of starter cultures on the antioxidant activity of kombucha beverage. Food Chemistry 2011, 127, 1727–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwalt, C.J.; Ledford, R.A.; Steinkraus, K.H. Determination and characterization of the antimicrobial activity of the fermented tea kombucha. LWT-Food Science and Technology 1998, 31, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battikh, H.; Bakhrouf, A.; Ammar, E. Antimicrobial effect of kombucha analogues. Lwt-Food Science and Technology 2012, 47, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, D.; Bhattacharya, S.; Patra, M.M.; Chakravorty, S.; Sarkar, S.; Chakraborty, W.; Koley, H.; Gachhui, R. Antibacterial activity of polyphenolic fraction of kombucha against enteric bacterial pathogens. Current Microbiology 2016, 73, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.C.; Chen, C.S. Effects of origins and fermentation time on the antioxidant activities of kombucha. Food Chemistry 2006, 98, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malbasa, R.; Loncar, E.; Djuric, M.; Dosenovic, I. Effect of sucrose concentration on the products of kombucha fermentation on molasses. Food Chemistry 2008, 108, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubaidah, E.; Yurista, S.; Rahmadani, N. Characteristic of physical, chemical, and microbiological kombucha from various varieties of apples. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing, 2018; Volume 1, p. 012040. [Google Scholar]
- Tarhan, K. Use of different substrate resources in the production of kombucha tea. 2017. Available online: https://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?recordID=TR2019000120 (accessed on 18 February 2023).
- Tamer, C.E.; Temel, Ş.G.; Suna, S.; Karabacak, A.Ö.; Özcan, T.; Ersan, L.Y.; Kaya, B.T.; Çopur, Ö.U. Evaluation of bioaccessibility and functional properties of kombucha beverages fortified with different medicinal plant extracts. Turkish Journal of Agriculture and Forestry 2021, 45, 13–32. [Google Scholar]
- Jayabalan, R.; Marimuthu, S.; Swaminathan, K. Changes in content of organic acids and tea polyphenols during kombucha tea fermentation. Food Chemistry 2007, 102, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battikh, H.; Chaieb, K.; Bakhrouf, A.; Ammar, E. Antibacterial and antifungal activities of black and green kombucha teas. Journal of Food Biochemistry 2013, 37, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lončar, E.S.; Kanurić, K.G.; Malbaša, R.V.; Đurić, M.S.; Milanović, S.D. Kinetics of saccharose fermentation by Kombucha. Chemical Industry and Chemical Engineering Quarterly 2014, 20, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismaiel, A.A.; Bassyouni, R.H.; Kamel, Z.; Gabr, S.M. Detoxification of patulin by kombucha tea culture. CyTA-Journal of Food 2016, 14, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germec, M.; Karhan, M.; Demirci, A.; Turhan, I. Kinetic modeling, sensitivity analysis, and techno-economic feasibility of ethanol fermentation from non-sterile carob extract-based media in Saccharomyces cerevisiae biofilm reactor under a repeated-batch fermentation process. Fuel 2022, 324, 124729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alboreadi, M.A.; Al-Najdawi, M.M.; Jarrar, Q.B.; Moshawih, S. Evaluation of hair growth properties of topical kombucha tea extracts. Advances in Traditional Medicine 2021, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, M.; Trząskowska, M.; Ścibisz, I.; Pokorski, P. Application of the “SCOBY” and Kombucha tea for the production of fermented milk drinks. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cemeroğlu, B. Gıda analizleri. Gıda Teknolojisi Derneği Yayınları. Bizim Grup Basımevi: Ankara, Turkey, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Germec, M.; Karahalil, E.; Yatmaz, E.; Tari, C.; Turhan, I. Effect of process parameters and microparticle addition on polygalacturonase activity and fungal morphology of Aspergillus sojae. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.L. Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Analytical Chemistry 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škerget, M.; Kotnik, P.; Hadolin, M.; Hraš, A.R.; Simonič, M.; Knez, Ž. Phenols, proanthocyanidins, flavones and flavonols in some plant materials and their antioxidant activities. Food Chemistry 2005, 89, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdinia, E.; Mamouri, S.J.; Puri, V.M.; Demirci, A.; Berenjian, A. Modeling of vitamin K (Menaquinoe-7) fermentation by Bacillus subtilis natto in biofilm reactors. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology 2019, 17, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watawana, M.I.; Jayawardena, N.; Gunawardhana, C.B.; Waisundara, V.Y. Health, wellness, and safety aspects of the consumption of kombucha. Journal of Chemistry 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhialdin, B.; Osman, F.; Muhamad, R.; Che Wan Sapawi, C.; Anzian, A.; Voon, W.; Hussin, A. Effects of sugar sources and fermentation time on the properties of tea fungus (kombucha) beverage. International Food Research Journal 2019, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Kallel, L.; Desseaux, V.; Hamdi, M.; Stocker, P.; Ajandouz, E. Insights into the fermentation biochemistry of kombucha teas and potential impacts of kombucha drinking on starch digestion. Food Research International 2012, 49, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loncar, E.S.; Kanuric, K.G.; Malbasa, R.V.; Duric, M.S.; Milanovic, S.D. Kinetics of saccharose fermentation by kombucha. Chemical Industry & Chemical Engineering Quarterly 2014, 20, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Gachhui, R.; Sil, P.C. Effect of kombucha, a fermented black tea in attenuating oxidative stress mediated tissue damage in alloxan induced diabetic rats. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2013, 60, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emiljanowicz, K.E.; Malinowska-Pańczyk, E. Kombucha from alternative raw materials-the review. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition 2020, 60, 3185–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.L.; Yan, F.; Cao, Z.L.; Xie, F.Y.; Lin, J. Antioxidant activities of kombucha prepared from three different substrates and changes in content of probiotics during storage. Food Science and Technology 2014, 34, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, H.A. Check your confidence: size really does matter. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling 2013, 53, 1837–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilgın, M.; Germec, M.; Turhan, I. Statistical and kinetic modeling of Aspergillus niger inulinase fermentation from carob extract and its partial concentration. Industrial Crops and Products 2020, 156, 112866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germec, M.; Turhan, I. Kinetic modeling and sensitivity analysis of inulinase production in large-scale stirred tank bioreactor with sugar beet molasses-based medium. Biochemical Engineering Journal 2021, 176, 108201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Tea origin | Tea | Initial sugar concentration (g/L) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 40 | 70 | ||
| Herbal tea | Sage tea (ST) | ST-10 | ST-40 | ST-70 |
| Linden tea (LT) | LT-10 | LT-40 | LT-70 | |
| Green tea (GT) | GT-10 | GT-40 | GT-70 | |
| Black tea (BT) | BT-10 | BT-40 | BT-70 | |
| Fruit tea | Apple tea (AT) | AT-10 | AT-40 | AT-70 |
| Rosehip tea (RT) | RT-10 | RT-40 | RT-70 | |
| Pomegranate tea (PT) | PT-10 | PT-40 | PT-70 | |
| Bilberry tea (BBT) | BBT-10 | BBT-40 | BBT-70 | |
| Tea | [Substrate] | Kinetic parameters | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ∆S (g/L) | QS (g/L/d) | η (%) | ∆X (g/L) | QX (g/L/d) | YX/S (g/g) | ∆TA (%) | QTA (%/d) | ∆PH (mg/L) | QPH (mg/L/d) | YPH/S (mg/g) | ||
| ST | 10 g/L | 8.52 | 1.29 | 79.48 | 0.72 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 445.96 | 97.18 | 52.34 |
| 40 g/L | 13.10 | 3.71 | 29.39 | 1.74 | 0.51 | 0.13 | 4.10 | 0.60 | 883.17 | 169.75 | 67.42 | |
| 70 g/L | 26.62 | 4.05 | 32.71 | 3.96 | 0.94 | 0.15 | 1.51 | 0.28 | 900.31 | 189.07 | 33.82 | |
| LT | 10 g/L | 11.66 | 2.72 | 97.25 | 1.02 | 0.22 | 0.09 | 0.59 | 0.17 | 242.12 | 26.80 | 20.77 |
| 40 g/L | 19.85 | 4.00 | 47.40 | 2.72 | 1.20 | 0.14 | 1.04 | 0.27 | 399.65 | 49.54 | 20.13 | |
| 70 g/L | 55.40 | 11.28 | 72.78 | 3.80 | 0.14 | 0.07 | 1.63 | 0.31 | 227.06 | 48.14 | 4.10 | |
| GT | 10 g/L | 12.13 | 2.40 | 88.80 | 0.74 | 0.26 | 0.06 | 0.35 | 0.15 | 1217.60 | 410.68 | 100.38 |
| 40 g/L | 32.43 | 4.90 | 56.65 | 2.52 | 0.78 | 0.08 | 0.87 | 0.33 | 1215.90 | 345.69 | 37.49 | |
| 70 g/L | 44.07 | 6.34 | 53.72 | 6.46 | 1.22 | 0.15 | 1.42 | 0.37 | 1268.40 | 264.16 | 28.78 | |
| AT | 10 g/L | 15.75 | 2.82 | 100.00 | 1.09 | 0.34 | 0.07 | 0.34 | 0.15 | 321.98 | 64.14 | 20.44 |
| 40 g/L | 18.61 | 3.07 | 39.89 | 3.76 | 1.39 | 0.20 | 1.18 | 0.27 | 785.45 | 159.90 | 42.21 | |
| 70 g/L | 48.39 | 5.28 | 63.15 | 4.28 | 1.37 | 0.09 | 1.64 | 0.41 | 466.38 | 74.71 | 9.64 | |
| RT | 10 g/L | 15.43 | 3.65 | 100.00 | 2.01 | 0.23 | 0.13 | 1.07 | 0.36 | 130.66 | 21.39 | 8.47 |
| 40 g/L | 28.74 | 6.37 | 54.33 | 4.71 | 2.17 | 0.16 | 1.61 | 0.49 | 295.36 | 76.28 | 10.28 | |
| 70 g/L | 45.66 | 8.32 | 51.38 | 5.60 | 1.31 | 0.12 | 2.77 | 0.82 | 255.86 | 56.83 | 5.60 | |
| PT | 10 g/L | 10.33 | 2.47 | 100.00 | 2.20 | 0.91 | 0.21 | 0.39 | 0.20 | 549.89 | 95.36 | 53.23 |
| 40 g/L | 21.04 | 3.67 | 44.69 | 3.25 | 1.43 | 0.15 | 1.30 | 0.30 | 800.04 | 101.66 | 38.02 | |
| 70 g/L | 42.92 | 6.36 | 50.61 | 8.77 | 1.66 | 0.20 | 2.18 | 0.34 | 930.94 | 166.20 | 21.69 | |
| BBT | 10 g/L | 12.67 | 2.54 | 95.62 | 0.81 | 0.31 | 0.06 | 0.44 | 0.18 | 655.20 | 95.51 | 51.71 |
| 40 g/L | 16.05 | 3.07 | 32.56 | 2.07 | 0.70 | 0.13 | 1.52 | 0.39 | 1311.92 | 187.92 | 81.74 | |
| 70 g/L | 21.41 | 3.24 | 26.02 | 3.55 | 1.40 | 0.17 | 1.73 | 0.41 | 782.90 | 178.13 | 36.57 | |
| Tea | [Substrate] | Kinetics for substrate consumption | Kinetics for acidity | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| µm,S (1/d) | Sm (g/L) | Sf (g/L) | R2 | β (%/gS·d) | α (%/gS) | α > β Fold | R2 | ||
| ST | 10 (g/L) | 0.4738 | 10.24 | 0.34 | 0.9438 | 0.0001 | 0.0201 | 360.19 | 0.5675 |
| 40 (g/L) | 0.2752 | 44.58 | 1.87 | 0.6038 | 0.0076 | 0.2584 | 34.00 | 0.9064 | |
| 70 (g/L) | 0.2864 | 77.45 | 2.54 | 0.8572 | 0.0013 | 0.0662 | 49.85 | 0.8481 | |
| LT | 10 (g/L) | 0.7821 | 11.99 | 1.19 | 0.9672 | -0.0058 | 0.0631 | 10.91 | 0.8060 |
| 40 (g/L) | 0.3462 | 41.42 | 3.89 | 0.8055 | -0.0006 | 0.0343 | 60.27 | 0.5337 | |
| 70 (g/L) | 0.5947 | 73.16 | 0.83 | 0.9655 | 0.0004 | 0.0211 | 55.41 | 0.4809 | |
| GT | 10 (g/L) | 0.7168 | 13.62 | 0.84 | 0.9487 | -0.0024 | 0.0142 | 5.87 | 0.7586 |
| 40 (g/L) | 0.2909 | 52.03 | 4.44 | 0.9185 | 0.0005 | 0.0315 | 63.17 | 0.7220 | |
| 70 (g/L) | 0.2503 | 82.03 | 9.18 | 0.9413 | 0.0001 | 0.0394 | 282.80 | 0.8259 | |
| AT | 10 (g/L) | 0.7798 | 15.34 | 1.24 | 0.9636 | -0.0075 | 0.0468 | 6.24 | 0.9228 |
| 40 (g/L) | 0.2757 | 46.12 | 2.46 | 0.9012 | 0.0019 | 0.0863 | 45.75 | 0.8479 | |
| 70 (g/L) | 0.3324 | 71.27 | 5.07 | 0.9563 | 0.0015 | 0.0365 | 23.65 | 0.8251 | |
| RT | 10 (g/L) | 0.7978 | 14.64 | 2.49 | 0.9671 | -0.0030 | 0.0876 | 29.15 | 0.8465 |
| 40 (g/L) | 0.2765 | 51.46 | 9.47 | 0.7731 | -0.0003 | 0.0475 | 145.00 | 0.6153 | |
| 70 (g/L) | 0.2459 | 87.58 | 9.64 | 0.8645 | -0.0006 | 0.0671 | 110.88 | 0.7225 | |
| PT | 10 (g/L) | 1.0969 | 8.94 | 1.39 | 0.9750 | -0.0039 | 0.0554 | 14.30 | 0.9526 |
| 40 (g/L) | 0.2011 | 46.40 | 6.97 | 0.8137 | 0.0008 | 0.0568 | 75.30 | 0.8141 | |
| 70 (g/L) | 0.2589 | 79.37 | 6.13 | 0.9332 | 0.0013 | 0.0493 | 39.13 | 0.8193 | |
| BBT | 10 (g/L) | 1.1422 | 12.71 | 0.52 | 0.9166 | -0.0023 | 0.0371 | 16.34 | 0.7676 |
| 40 (g/L) | 0.1671 | 46.97 | 4.90 | 0.8257 | 0.0010 | 0.1349 | 129.31 | 0.7937 | |
| 70 (g/L) | 0.3043 | 79.67 | 1.49 | 0.9088 | 0.0008 | 0.1122 | 135.44 | 0.6790 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





