Submitted:
12 June 2023
Posted:
12 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
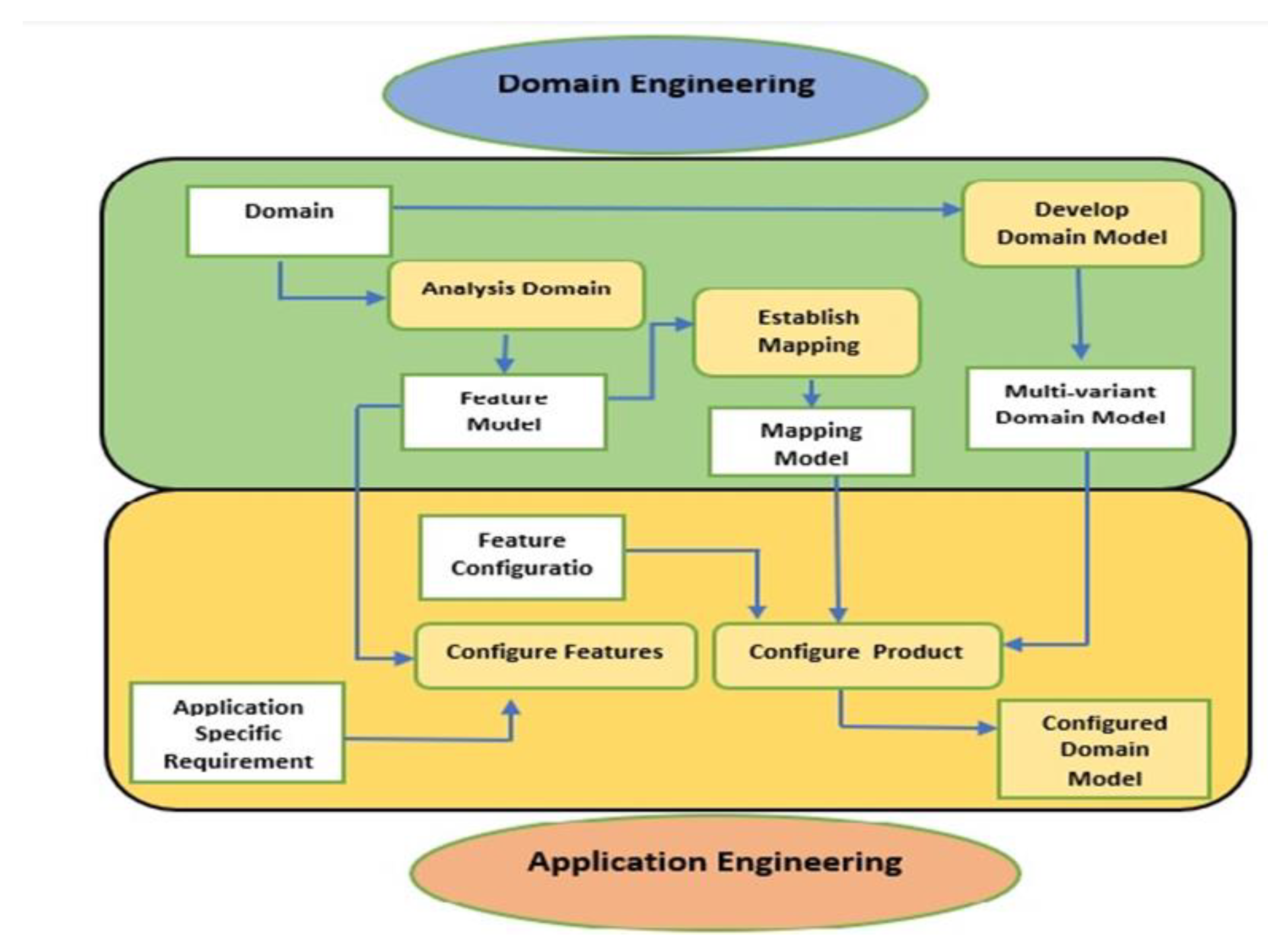
2. Software product Line Engineering
3. Related Work
4. Optimization for SPL Testing using Multiobjective Evolutionary Algorithms
4.1. Method Description
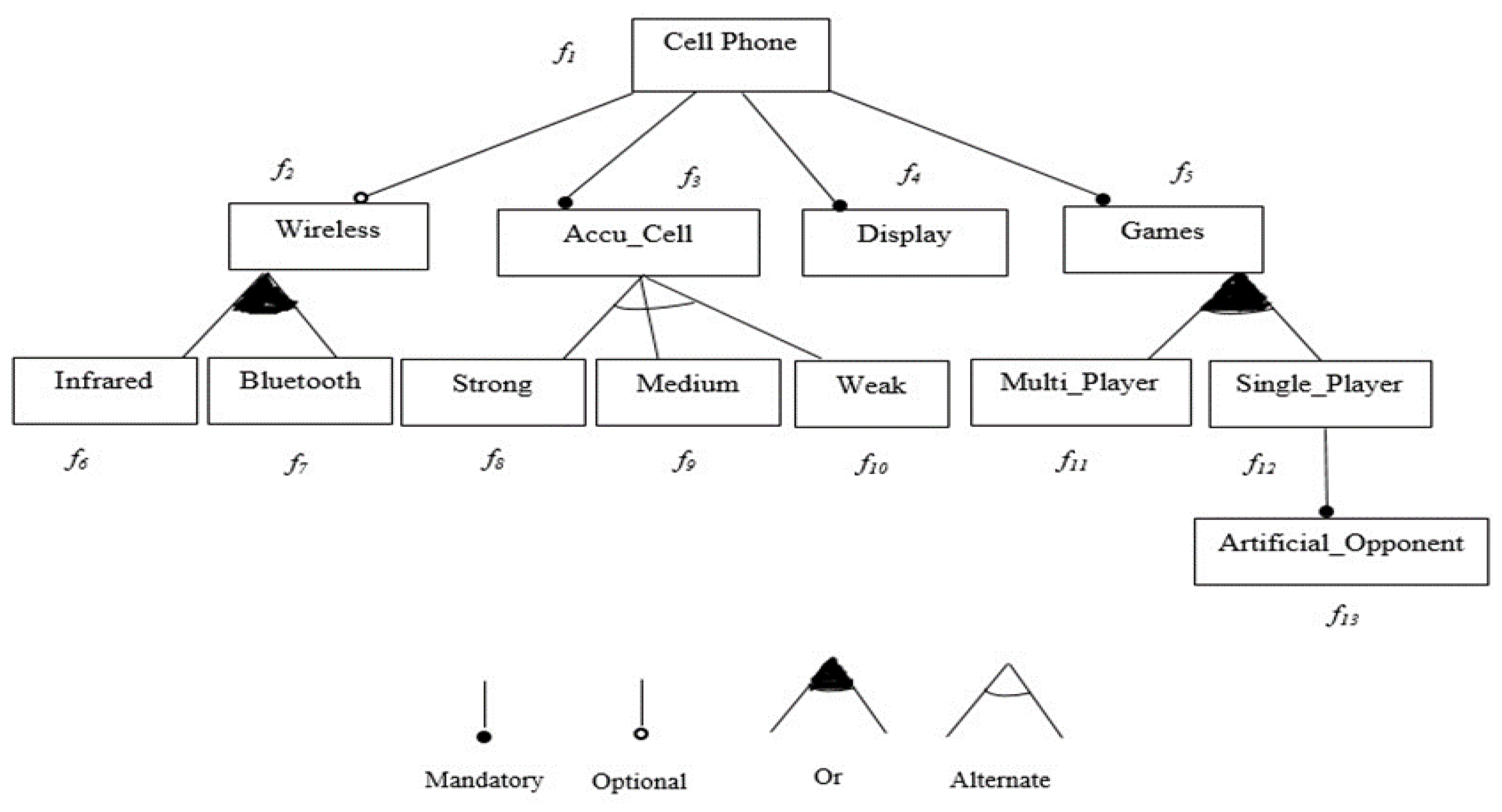
4.1.1. Definition 1 (Feature Model)
4.1.2. Definition 2 (Configuration)
4.1.3. Definition 3 (Configuration Suite)
4.1.4. Definition 3 (Coverage Criteria)
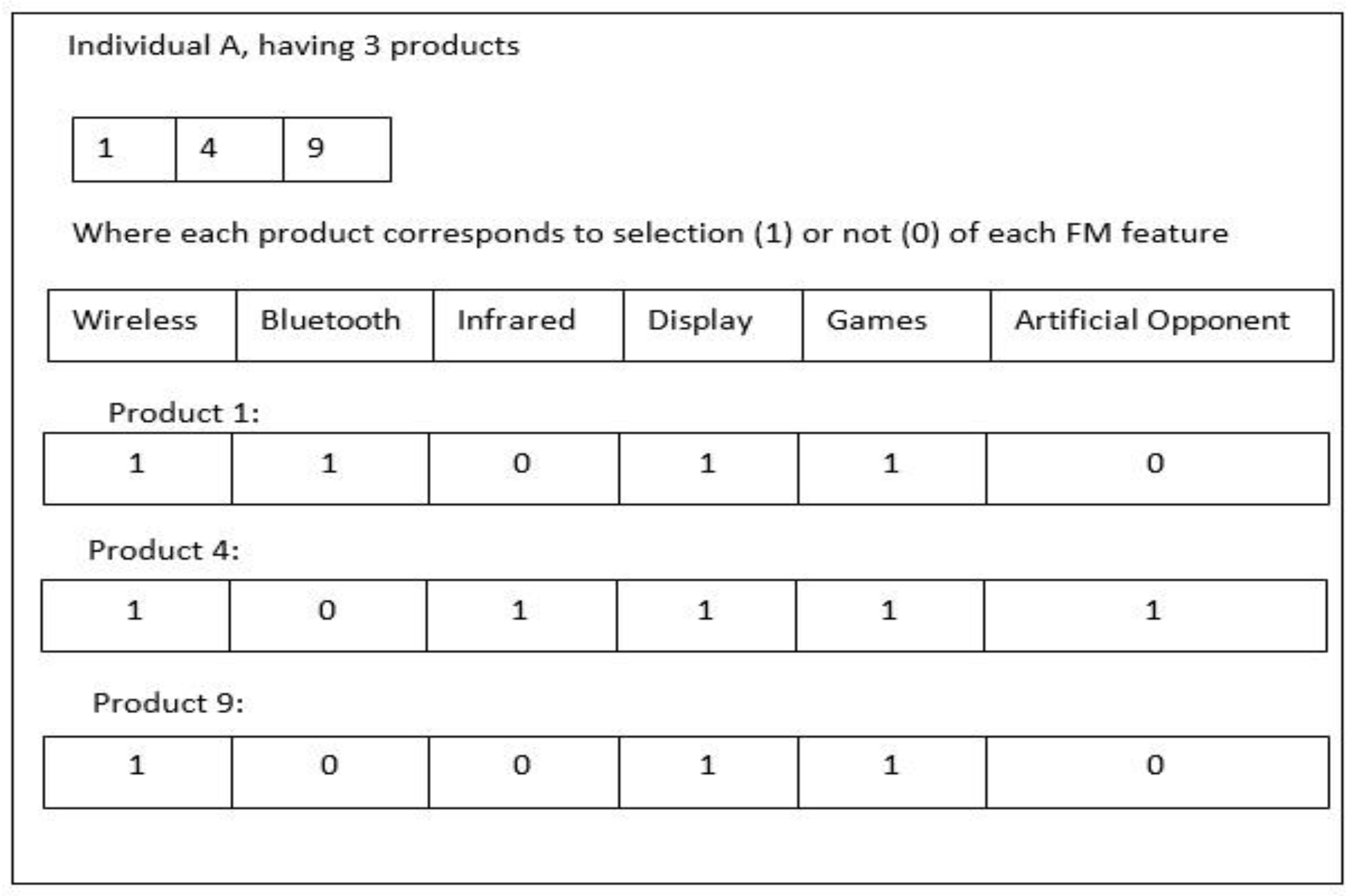
4.1.5. Definition 5 (Individual)
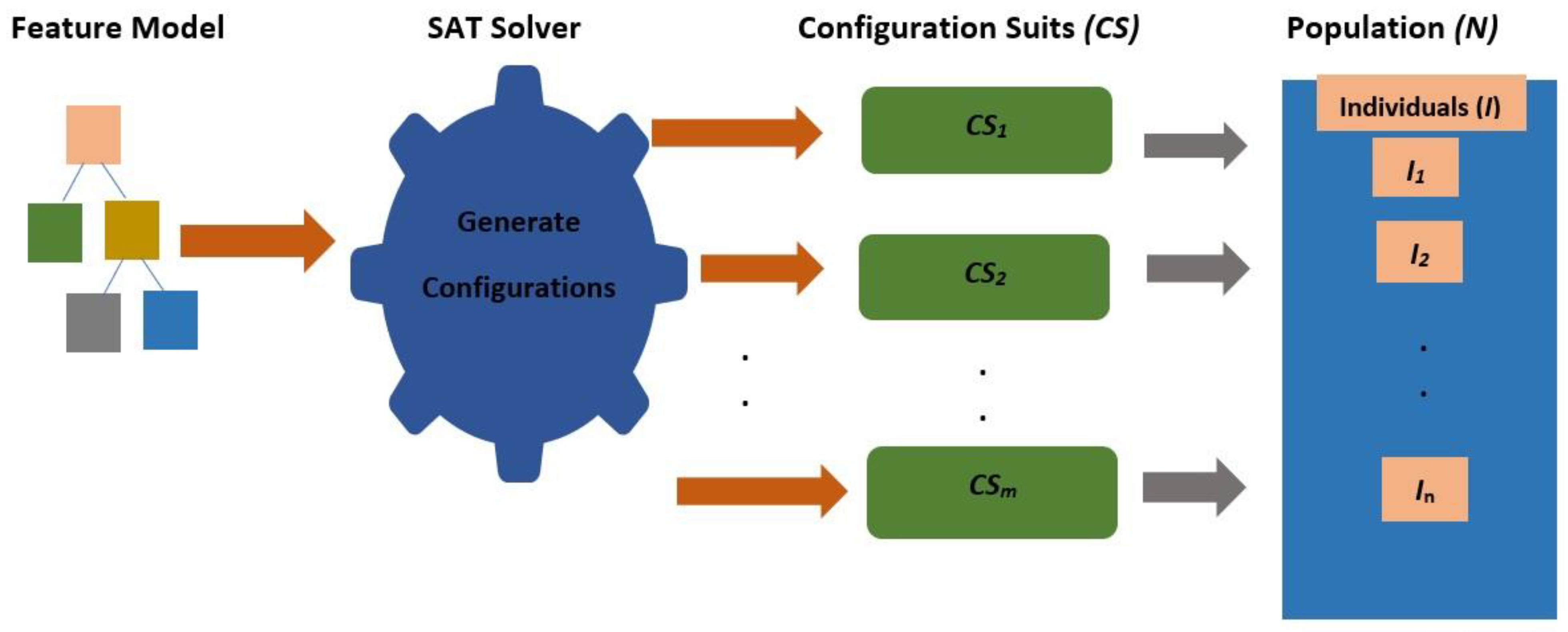
4.1.6. Definition 5 (Population)
4.2. Objectives Definition
4.2.1. Maximize the Pairwise Coverage
4.2.2. Minimize the Number of Products
4.2.3. Testing Cost
4.2.4. Maximizing Number of Features
5. Experiments
5.1. Framework Adopted
5.2. Data Collection
5.3. Parameters Selection
6. Results and Discussion
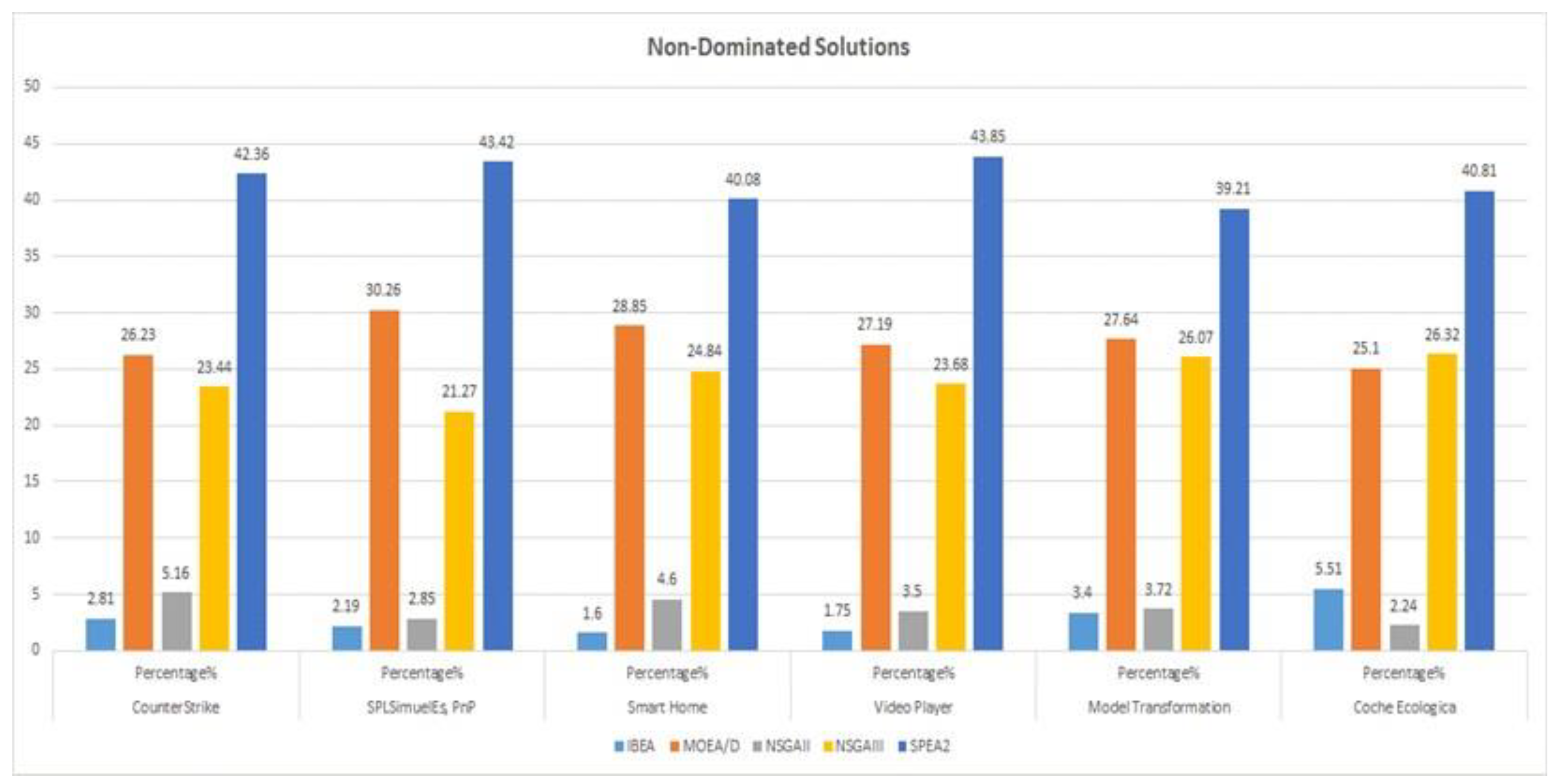
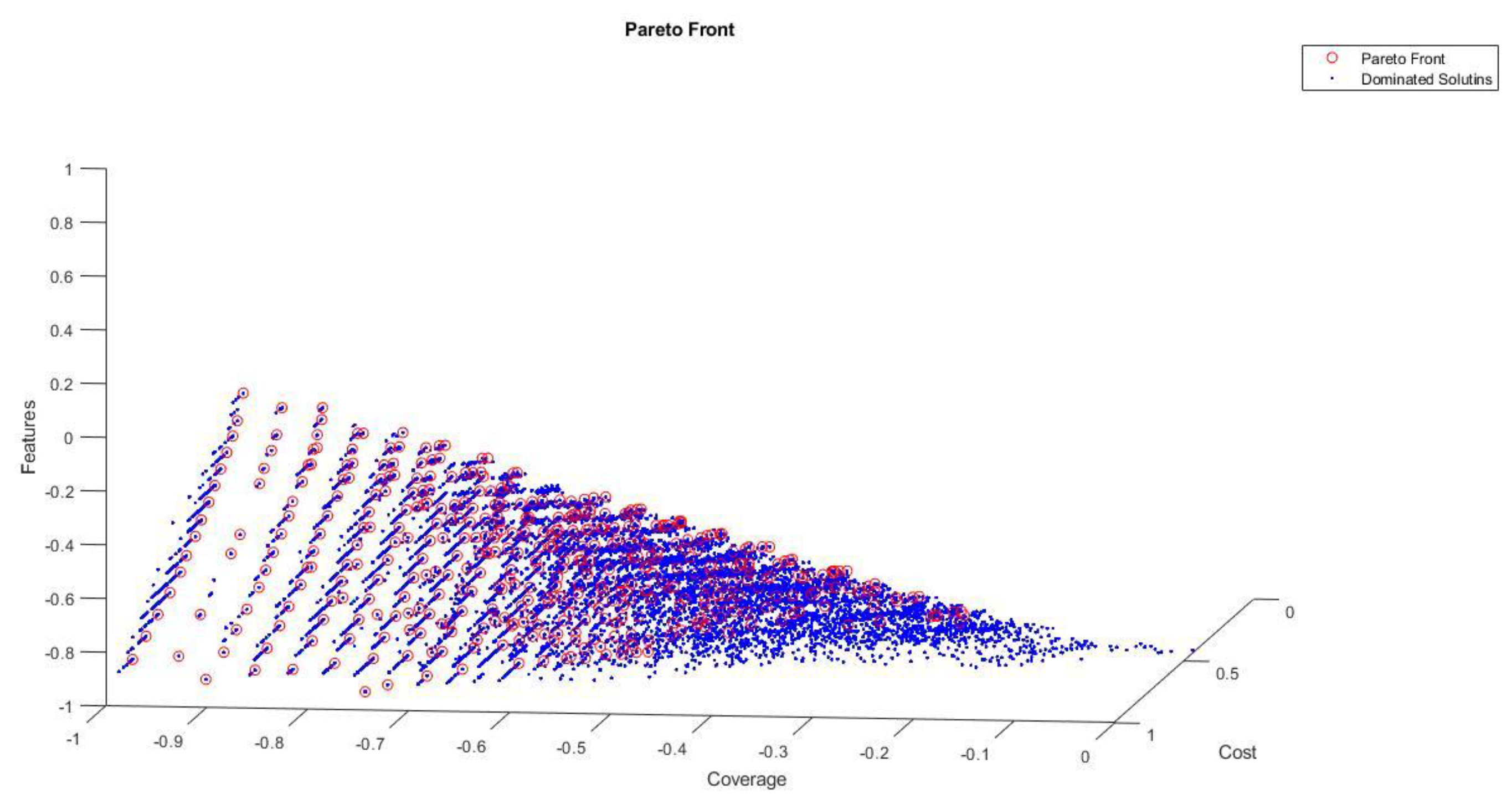
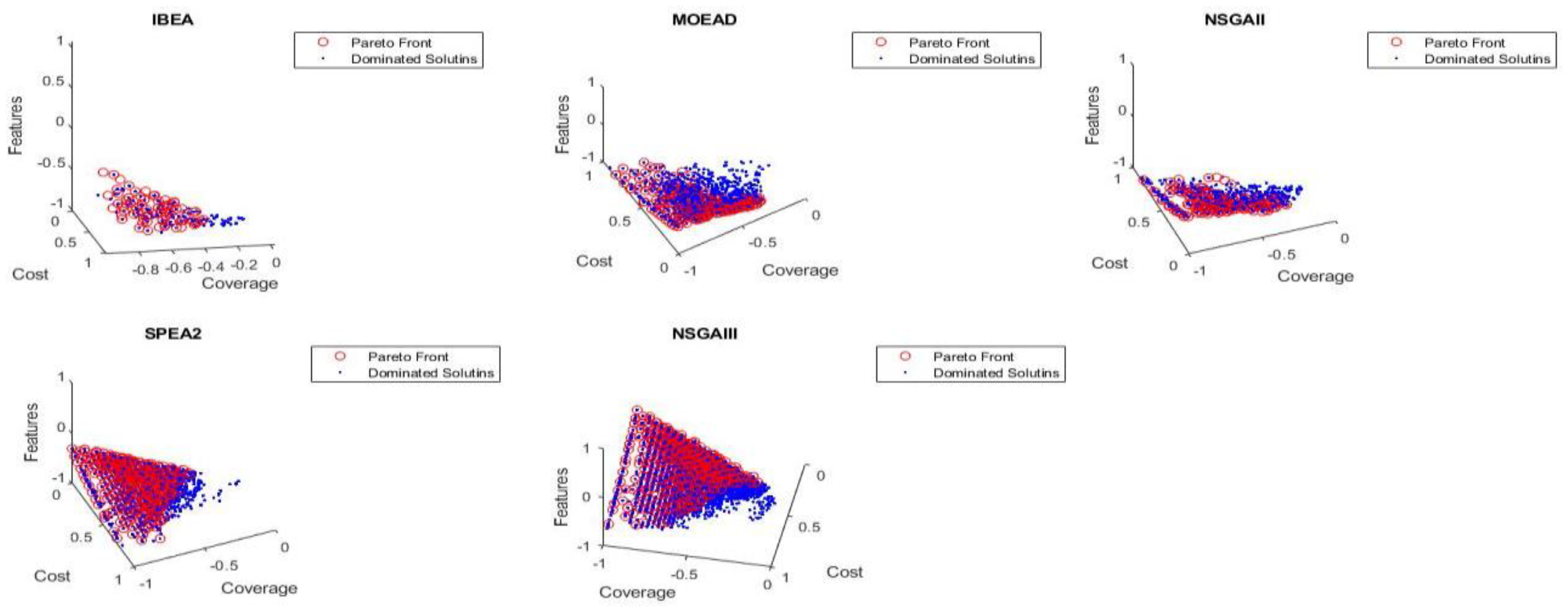
6.1. Pareto Front Solutions
6.2. Results Generated By Quality Indicators
6.3. Fitness Values for Four Objectives Optimization
6.4. Discussion of Results and Answers to Research Questions
7. Results
7.1. Practical Implications
7.2. Threats to Validity
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harman, M.; Mansouri, S.A.; Zhang, Y. Search-based software engineering: Trends, techniques and applications. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR) 2012, 45, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khari, M.; Kumar, P. An extensive evaluation of search-based software testing: a review. Soft Computing 2019, 23, 1933–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engström, E.; Runeson, P. Software product line testing–a systematic mapping study. Information and Software Technology 2011, 53, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshosaz, M.; Al-Hajjaji, M.; Thüm, T.; Runge, T.; Mousavi, M.R.; Schaefer, I. A classification of product sampling for software product lines. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Systems and Software Product Line Conference, Gothenburg, Sweden, 10–14 September 2018; Volume 1, pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Buchmann, T.; Schwägerl, F. Advancing negative variability in model-driven software product line engineering. In International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Cawley, C.; Botterweck, G.; Healy, P.; Abid, S.B.; Thiel, S. A 3d visualisation to enhance cognition in software product line engineering. In International Symposium on Visual Computing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 857–868. [Google Scholar]
- Hotz, L.; Wolter, K.; Krebs, T. Configuration in Industrial Product Families: The ConIPF Methodology; Ios Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cawley, C.; Thiel, S.; Botterweck, G.; Nestor, D. Visualising Inter-Model Relationships in Software Product Lines. In VaMoS; 2009; pp. 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Runeson, P.; Engström, E. Regression testing in software product line engineering. In Advances in Computers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 86, pp. 223–263. [Google Scholar]
- Mendonca, M.; Branco, M.; Cowan, D. SPLOT: software product lines online tools. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGPLAN conference companion on Object oriented programming systems languages and applications; 2009; pp. 761–762. [Google Scholar]
- Pohl, K.; Böckle, G.; Van Der Linden, F. Software product line engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; Volume 10, pp. 3–540. [Google Scholar]
- McGregor, J.D.; Northrop, L.M.; Jarrad, S.; Pohl, K. Initiating software product lines. IEEE Software 2002, 19, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigaux, J.C.; Heymans, P. Software product lines: State of the art. In Product Line ENgineering of food TraceabilitY software FUNDP-Equipe LIEL; 2003; pp. 9–39. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hajjaji, M.; Lity, S.; Lachmann, R.; Thüm, T.; Schaefer, I.; Saake, G. Delta-oriented product prioritization for similarity-based product-line testing. In 2017 IEEE/ACM 2nd International Workshop on Variability and Complexity in Software Design (VACE); IEEE, 2017; pp. 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hajjaji, M.; Thüm, T.; Lochau, M.; Meinicke, J.; Saake, G. Effective product-line testing using similarity-based product prioritization. Software & Systems Modeling 2019, 18, 499–521. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wong, W.E.; Gao, R.; Hu, L.; Hosono, S. Genetic algorithm-based test generation for software product line with the integration of fault localization techniques. Empirical Software Engineering 2018, 23, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, J.; Al-Hajjaji, M.; Leich, T.; Saake, G. Mutation operators for feature-oriented software product lines. Software Testing, Verification and Reliability 2019, 29, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lity, S.; Nieke, M.; Thüm, T.; Schaefer, I. Retest test selection for product-line regression testing of variants and versions of variants. Journal of Systems and Software 2019, 147, 46–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Liang, J.H.; Shi, K.; Yang, D.; Zhang, J.; Czarnecki, K.; Ganesh, V.; Yu, H. SMTIBEA: a hybrid multi-objective optimization algorithm for configuring large constrained software product lines. Software & Systems Modeling 2019, 18, 1447–1466. [Google Scholar]
- Alsewari, A.A.; Kabir, M.N.; Zamli, K.Z.; Alaofi, K.S. Software product line test list generation based on harmony search algorithm with constraints support. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications 2019, 10, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hajjaji, M.; Ryssel, U.; Schulze, M. Validating Partial Configurations of Product Lines. In Proceedings of the 13th International Workshop on Variability Modelling of Software-Intensive Systems; 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ali, S.; Gotlieb, A. Minimizing test suites in software product lines using weight-based genetic algorithms. In Proceedings of the 15th annual conference on Genetic and evolutionary computation; 2013; pp. 1493–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Buchmann, D.; Ali, S.; Gotlieb, A.; Pradhan, D.; Liaaen, M. Multi-objective test prioritization in software product line testing: an industrial case study. In Proceedings of the 18th International Software Product Line Conference; 2014; Volume 1, pp. 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensan, F.; Bagheri, E.; Gašević, D. Evolutionary search-based test generation for software product line feature models. In Advanced Information Systems Engineering: 24th International Conference, CAiSE 2012, Gdansk, Poland, 25–29 June 2012. Proceedings 24; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 613–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henard, C.; Papadakis, M.; Perrouin, G.; Klein, J.; Traon, Y.L. Multi-objective test generation for software product lines. In Proceedings of the 17th International Software Product Line Conference; 2013; pp. 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matnei Filho, R.A.; Vergilio, S.R. A mutation and multi-objective test data generation approach for feature testing of software product lines. In 2015 29th Brazilian Symposium on Software Engineering; IEEE, 2015; pp. 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henard, C. Enabling Testing of Large Scale Highly Configurable Systems with Search-based Software Engineering: The Case of Model-based Software Product Lines. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Luxembourg, Luxembourg, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Olaechea, R.; Rayside, D.; Guo, J.; Czarnecki, K. Comparison of exact and approximate multi-objective optimization for software product lines. In Proceedings of the 18th International Software Product Line Conference; 2014; Volume 1, pp. 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyad, A.S.; Menzies, T.; Ammar, H. On the value of user preferences in search-based software engineering: A case study in software product lines. In 2013 35Th international conference on software engineering (ICSE), 2013; pp. 492–501. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Diaz, J.; Perez, J.; Fernandez-Sanchez, C.; Garbajosa, J. Model-to-code transformation from product-line architecture models to aspectj. In 2013 39th Euromicro Conference on Software Engineering and Advanced Applications, 2013, pp. 98–105. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Karimpour, R.; Ruhe, G. Bi-criteria genetic search for adding new features into an existing product line. In 2013 1st International Workshop on Combining Modelling and Search-Based Software Engineering (CMSBSE), 2013, pp. 34–38. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Cruz, J.; Neto, P.S.; Britto, R.; Rabelo, R.; Ayala, W.; Soares, T.; Mota, M. Toward a hybrid approach to generate software product line portfolios. In 2013 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, 2013, pp. 2229–2236. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; White, J.; Wang, G.; Li, J.; Wang, Y. A genetic algorithm for optimized feature selection with resource constraints in software product lines. Journal of Systems and Software 2011, 84, 2208–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.A.; Figueiredo, E.; Noronha, T. Modelo computacional para apoiar a configuração de produtos em linha de produtos de software. In V Workshop de Engenharia de Software Baseada em Busca (WESB). Congresso Brasileiro de Desenvolvimento de Software (CBSoft), Brasilia, DF, Brazil, 2013, pp. 80–89.
- White, J.; Galindo, J.A.; Saxena, T.; Dougherty, B.; Benavides, D.; Schmidt, D.C. Evolving feature model configurations in software product lines. Journal of Systems and Software 2014, 87, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J. Formalizing feature selection problem in software product lines using 0-1 programming. In Practical Applications of Intelligent Systems: Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Knowledge Engineering, Shanghai, China, Dec 2011 (ISKE2011); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyad, A.S.; Goseva-Popstojanova, K.; Menzies, T.; Ammar, H. On parameter tuning in search based software engineering: A replicated empirical study. In 2013 3rd International Workshop on Replication in Empirical Software Engineering Research, 2013, pp. 84–90. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Sayyad, A.S.; Ingram, J.; Menzies, T.; Ammar, H. Optimum feature selection in software product lines: Let your model and values guide your search. In 2013 1st International Workshop on Combining Modelling and Search-Based Software Engineering (CMSBSE), 2013, pp. 22–27. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Herrejon, R.E.; Chicano, F.; Ferrer, J.; Egyed, A.; Alba, E. Multi-objective optimal test suite computation for software product line pairwise testing. In 2013 IEEE International Conference on Software Maintenance, 2013, pp. 404–407. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Henard, C. , Papadakis, M., Perrouin, G., Klein, J., Heymans, P. and Le Traon, Y. Bypassing the combinatorial explosion: Using similarity to generate and prioritize t-wise test configurations for software product lines. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering 2014, 40, 650–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonca, M.; Wąsowski, A.; Czarnecki, K. SAT-based analysis of feature models is easy. In Proceedings of the 13th International Software Product Line Conference; 2009; pp. 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oster, S.; Markert, F.; Ritter, P. Automated incremental pairwise testing of software product lines. In Software Product Lines: Going Beyond: 14th International Conference, SPLC 2010, Jeju Island, South Korea, September 13-17, 2010. Proceedings 14; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrouin, G.; Oster, S.; Sen, S.; Klein, J.; Baudry, B.; Le Traon, Y. Pairwise testing for software product lines: comparison of two approaches. Software Quality Journal 2012, 20, 605–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, M.F.; Haugen, Ø.; Fleurey, F. Properties of realistic feature models make combinatorial testing of product lines feasible. In Model Driven Engineering Languages and Systems: 14th International Conference, MODELS 2011, Wellington, New Zealand, October 16-21, 2011. Proceedings 14; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 638–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Msie’Deen, R.; Seriai, A.D.; Huchard, M.; Urtado, C.; Vauttier, S.; Salman, H.E. An approach to recover feature models from object-oriented source code. Actes de la Journée Lignes de Produits.
- Jamil, M.A.; Nour, M.K.; Alhindi, A.; Awang Abhubakar, N.S.; Arif, M.; Aljabri, T.F. Towards Software Product Lines Optimization Using Evolutionary Algorithms. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 163, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitzler, E.; Künzli, S. Indicator-based selection in multiobjective search. PPSN 2004, 4, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, H. MOEA/D: A multiobjective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition. IEEE Transactions on evolutionary computation 2007, 11, 712–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Pratap, A.; Agarwal, S.; Meyarivan, T.A.M.T. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE transactions on evolutionary computation 2002, 6, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Jain, H. An evolutionary many-objective optimization algorithm using reference-point-based nondominated sorting approach, part I: solving problems with box constraints. IEEE transactions on evolutionary computation. 2013, 18, 577–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitzler, E.; Laumanns, M.; Thiele, L. SPEA2: Improving the strength Pareto evolutionary algorithm. TIK-report. [CrossRef]
- Hadka, D. MOEA framework user guide, 2014.
- Pareto, V.; Politique, M.D. ; A. Press, “Paris.” Ams Press, 1927.
- García, S.; Molina, D.; Lozano, M.; Herrera, F. A study on the use of non-parametric tests for analyzing the evolutionary algorithms’ behaviour: a case study on the CEC’2005 special session on real parameter optimization. Journal of Heuristics 2009, 15, 617–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitzler, E.; Thiele, L.; Laumanns, M.; Fonseca, C.M.; Da Fonseca, V.G. Performance assessment of multiobjective optimizers: An analysis and review. IEEE Transactions on evolutionary computation 2003, 7, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitzler, E.; Brockhoff, D.; Thiele, L. The hypervolume indicator revisited: On the design of Pareto-compliant indicators via weighted integration. In Evolutionary Multi-Criterion Optimization: 4th International Conference, EMO 2007, Matsushima, Japan, March 5-8, 2007. Proceedings 4; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 862–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schott, J.R. Fault tolerant design using single and multicriteria genetic algorithm optimization. Air force inst of tech Wright-Patterson afb OH, 1995. http://hdl.handle.net/1721. 1158. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, S.; Harman, M. Pareto efficient multi-objective test case selection. In Proceedings of the 2007 international symposium on Software testing and analysis; 2007; pp. 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcuri, A.; Briand, L. A practical guide for using statistical tests to assess randomized algorithms in software engineering. In Proceedings of the 33rd international conference on software engineering; 2011; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kader, M.A.; Zamli, K.Z.; Alkazemi, B.Y. An Experimental Study of a Fuzzy Adaptive Emperor Penguin Optimizer for Global Optimization Problem. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 116344–116374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odili, J.B.; Noraziah, A.; Alkazemi, B.; Zarina, M. Stochastic process and tutorial of the African buffalo optimization. Scientific Reports 2022, 12, 17319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsewari, A.A.; Zamli, K.Z.; Al-Kazemi, B. Generating t-way test suite in the presence of constraints. Journal of Engineering and Technology (JET) 2015, 6, 52–66. [Google Scholar]
- Zamli, K.Z.; Alsewari, A.R.; Al-Kazemi, B. Comparative benchmarking of constraints t-way test generation strategy based on late acceptance hill climbing algorithm. International Journal of Software Engineering & Computer Sciences (IJSECS) 2015, 1, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamli, K.Z.; Mohd Hassin, M.H.; Al-Kazemi, B. tReductSA–Test Redundancy Reduction Strategy Based on Simulated Annealing. In Intelligent Software Methodologies, Tools and Techniques: 13th International Conference, SoMeT 2014, Langkawi, Malaysia, September 22-24, 2014. Revised Selected Papers 13; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wazirali, R.; Alasmary, W.; Mahmoud, M.M.; Alhindi, A. An optimized steganography hiding capacity and imperceptibly using genetic algorithms. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 133496–133508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhindi, Ahmad. Optimizing Training Data Selection for Decision Trees using Genetic Algorithms. International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security (IJCSNS) 2020, 20. [Google Scholar]
| Feature Model | Features | Configurations | Number of Pairs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Counter Strike | 24 | 18176 | 833 |
| SPL SimulES, PnP | 41 | 6912 | 2592 |
| Smart Homev2.2 | 60 | 3.87×109 | 6189 |
| Video Player | 71 | 4.5×1013 | 7528 |
| Model Transformation | 88 | 1.65×1013 | 13139 |
| Coche Ecologico | 94 | 2.32×107 | 11075 |
| Parameter | Values |
|---|---|
| Population Size | 200 |
| Number of Generations | 500 |
| Crossover Rate | 60% |
| Mutation Rate | 30% |
| Feature Models | Algorithms | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFtrue | IBEA | MOEAD | NSGAII | NSGAIII | SPEA2 | |
| PFcontribution | ||||||
| Counter Strike | 465 | 13 (2.81%) | 122 (26.23%) | 24 (5.16%) | 109 (23.44%) | 197 (42.36%) |
| SPL SimulES, PnP | 456 | 10 (2.19%) | 138 (30.26%) | 13 (2.85%) | 97 (21.27%) | 198 (43.42%) |
| Smart Home v2.2 | 499 | 8 (1.60%) | 144 (28.85%) | 23 (4.60%) | 124 (24.84%) | 200 (40.08%) |
| Video Player | 456 | 8(1.75%) | 124 (27.19%) | 16 (3.5%) | 108 (23.68%) | 200 (43.85%) |
| Model Transformation | 510 | 17 (3.4%) | 141 (27.64%) | 19 (3.72%) | 133 (26.07%) | 200 (39.21%) |
| Coche Ecologico | 490 | 27 (5.51%) | 123 (25.10%) | 11 (2.24%) | 129 (26.32%) | 200 (40.81%) |
| Indicator | Feature Models | IBEA | MOEAD | NSGAII | NSGAIII | SPEA2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | St. D | Average | St. D | Average | St. D | Average | St. D | Average | St. D | ||
| HV | Counter Strike | 0.2826 | 0.1162 | 0.7094 | 0.0129 | 0.6029 | 0.0234 | 0.6498 | 0.0113 | 0.7022 | 0.0165 |
| SPL SimulES, PnP | 0.2698 | 0.0954 | 0.6524 | 0.0150 | 0.4659 | 0.0314 | 0.5413 | 0.0176 | 0.6390 | 0.0155 | |
| Smart Home v2.2 | 0.3460 | 0.1105 | 0.6885 | 0.0160 | 0.5742 | 0.0353 | 0.6052 | 0.0300 | 0.6843 | 0.0198 | |
| Video Player | .0.3659 | 0.0969 | 0.6961 | 0.0155 | 0.5795 | 0.0108 | 0.6085 | 0.0262 | 0.6864 | 0.0193 | |
| Model Transformation | 0.3600 | 0.0771 | 0.6009 | 0.0146 | 0.4677 | 0.0256 | 0.5276 | 0.0210 | 0.6136 | 0.0210 | |
| Coche Ecologico | 0.3257 | 0.0802 | 0.4868 | 0.0048 | 0.3227 | 0.0107 | 0.4541 | 0.0329 | 0.5025 | 0.0013 | |
| Spacing | Counter Strike | 0.1138 | 0.0543 | 0.0329 | 0.0033 | 0.0496 | 0.0115 | 0.0316 | 0.0026 | 0.0157 | 0.0017 |
| SPL SimulES, PnP | 0.0713 | 0.0364 | 0.0208 | 0.0019 | 0.0521 | 0.0121 | 0.0295 | 0.0026 | 0.0113 | 0.0011 | |
| Smart Home v2.2 | 0.0753 | 0.0330 | 0.0302 | 0.0024 | 0.0474 | 0.0102 | 0.0342 | 0.0037 | 0.0126 | 0.0086 | |
| Video Player | 0.0855 | 0.0430 | 0.0296 | 0.0028 | 0.0502 | 0.0108 | 0.0328 | 0.0046 | 0.0127 | 0.0015 | |
| Model Transformation | 0.0527 | 0.0112 | 0.0262 | 0.0021 | 0.0412 | 0.0081 | 0.0292 | 0.0024 | 0.0102 | 0.0008 | |
| Coche Ecologico | 0.0417 | 0.0173 | 0.0217 | 0.0016 | 0.0720 | 0.0218 | 0.0179 | 0.0030 | 0.0095 | 0.0013 | |
| Feature Models | Algorithms | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IBEA | MOEAD | NSGAII | NSGAIII | SPEA2 | |
| Counter Strike | O1(1,0.010,0.086,0.291) O2(1,0.010,0.086,0.291) O3(1,0.010,0.086,0.291) O4(0.274, 0.030,0.365,1) |
O1(1,0.010,0.623,0.666) O2((1,0.010,0.623,0.666)) O3(1,0.010, 0.107, 0.291) O4(0.271, 0.071, 0.136, 1) |
O1(1,0.010,0.666, 0.75) O2(1,0.010,0.666, 0.75) O3(1,0.010, 0.107, .291) O4(0.228, 0.051, .276,1) |
O1(1,0.010,0.537,0.666) O2(1,0.010,0.537,0.666) O3(1,0.010,0.0107,0.291) O4(0.238, 0.051, 0.219,1) |
O1(1,0.010,0.709,0.791) O2(1,0.010, 0.709,0.791) O3(1,0.010,0.0107,0.291) O4(0.260, 0.051, 0.198,1) |
| SPL SimulES, PnP | O1(1,0.010,0.358,0.593) O2(1,0.010, 0.358,0.593) O3(1,0.010,0.305,0.05) O4(0.625, 0.030,0.419,1) |
O1(1,0.010,0.312,0.468) O2(1,0.010, 0.312,0.468) O3(1,0.010,0.229,0.50) O4(0.638, 0.122,0.279,1) |
O1(1,0.010,0.343,0.562) O2(1,0.010, 0.343,0.562) O3(1,0.010,0.236,0.50) O4(0.654, 0.030,0.358,1) |
O1(1,0.010,0.458,0.625) O2(1,0.010, 0.458,0.625) O3(1,0.010,0.244,0.468) O4(0.669, 0.408,0.328,1) |
O1(1,0.010,0.664,0.656) O2(1,0.010, 0.664,0.656) O3(1,0.010,0.236,0.50) O4(0.647, 0.071,0.312,1) |
| Smart Home v2.2 | O1(1,0.010,0.419,0.045) O2(1,0.010, 0.419,0.045) O3(1,0.010,0.257,0.366) O4(0.264, 0.306,0.395,1) |
O1(1,0.010,0.389,0.483) O2(1,0.010, 0.389,0.483) O3(1,0.010,0.069,0.20) O4(0.161, 0.061,0.354,1) |
O1(1,0.010,0.551,0.583) O2(1,0.010, 0.551,0.583) O3(1,0.010,0.077,0.216) O4(0.178, 0.071,0.302,1) |
O1(1,0.010,0.507,0.583) O2(1,0.010, 0.507,0.583) O3(1,0.010,0.036,0.133) O4(0.190, 0.071,0.334,1) |
O1(1,0.010,0.441,0.466) O2(1,0.010, 0.441,0.466) O3(1,0.010,0.106,0.216) O4(0.239, 0.071,0.248,1) |
| Video Player | O1(1,0.010,0.437,0.605) O2(1,0.010, 0.437,0.605) O3(1,0.010,0.234,0.450) O4(0.128, 0.061,0.412,1) |
O1(1,0.010,0.427,0.619) O2(1,0.010, 0.427,0.619) O3(1,0.010,0.128,0.352) O4(0.174, 0.051,0.323,1) |
O1(1,0.010,0.558,0.690) O2(1,0.010, 0.558,0.690) O3(0.801,0,0.156,0.521) O4(0.206, 0.040,0.330,1) |
O1(1,0.010,0.540,0.633) O2(1,0.010, 0.540,0.633) O3(0.772,0.010,0.161,0.535) O4(0.279, 0.036,0.335,1) |
O1(1,0.010,0.601,0.676) O2(1,0.010, 0.601,0.676) O3(1,0.010,0.163,0.380) O4(0.214, 0.040,0.301,1) |
| Model Transformation | O1(1,0.010,0.534,0.579) O2(1,0.010, 0.534,0.579) O3(1,0.010,0.193,0.363) O4(0.211, 0.051,0.393,1) |
O1(1,0.010,0.327,0.454) O2(1,0.010, 0.327,0.454) O3(1,0.010,0.161,0.318) O4(0.021, 0.256,0.404,1) |
O1(1,0.010,0.415,0.50) O2(1,0.010, 0.415,0.50) O3(1,0.010,0.170,0.340) O4(0.165, 0.071,0.371,1) |
O1(1,0.010,0.372,0.477) O2(1,0.010, 0.372,0.477) O3(1,0.010,0.170,0.284) O4(0.224, 0.051,0.342,1) |
O1(1,0.010,0.461,0.534) O2(1,0.010, 0.461,0.534) O3(1,0.010,0.179,0.284) O4(0.158, 0.081,0.319,1) |
| Coche Ecologico | O1(1,0.010,0.251,0.563) O2(1,0.010, 0.251,0.563) O3(1,0.010,0.202,0.563) O4(0.143, 0.112,0.268,1) |
O1(1,0.010,0.398,0.659) O2(1,0.010, 0.398,0.659) O3(1,0.010,0.156,0.510) O4(0.180, 0.816,0.251,1) |
O1(1,0.010,0.310,0.574) O2(1,0.010, 0.310,0.574) O3(1,0.010,0.156,0.521) O4(0.094, 0.173,0.275,1) |
O1(1,0.010,0.310,0.574) O2(1,0.010, 0.310,0.574) O3(1,0.010,0.156,0.521) O4(0.094, 0.173,0.275,1) |
O1(1,0.010,0.316,0.617) O2(1,0.010, 0.316,0.617) O3(1,0.010,0.156,0.50) O4(0.149, 0.102,0.255,1) |
| Feature Models | Quality Indicators | |
|---|---|---|
| Hyper Volume | Spacing | |
| Counter Strike | MOEA/D, SPEA2, NSGAIII | MOEA/D, SPEA2, NSGAIII |
| SPL SimulES, PnP | MOEA/D, SPEA2 | MOEA/D, SPEA2, NSGAIII |
| Smart Home v2.2 | MOEA/D, SPEA2, NSGAIII | MOEA/D, SPEA2, NSGAIII |
| Video Player | MOEA/D, SPEA2, NSGAIII | MOEA/D, SPEA2 |
| Model Transformation | MOEA/D, SPEA2, NSGAIII | MOEA/D, SPEA2, NSGAIII |
| Coche Ecologico | MOEA/D, SPEA2, NSGAIII | SPEA2, NSGAIII, |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





