Submitted:
11 June 2023
Posted:
13 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
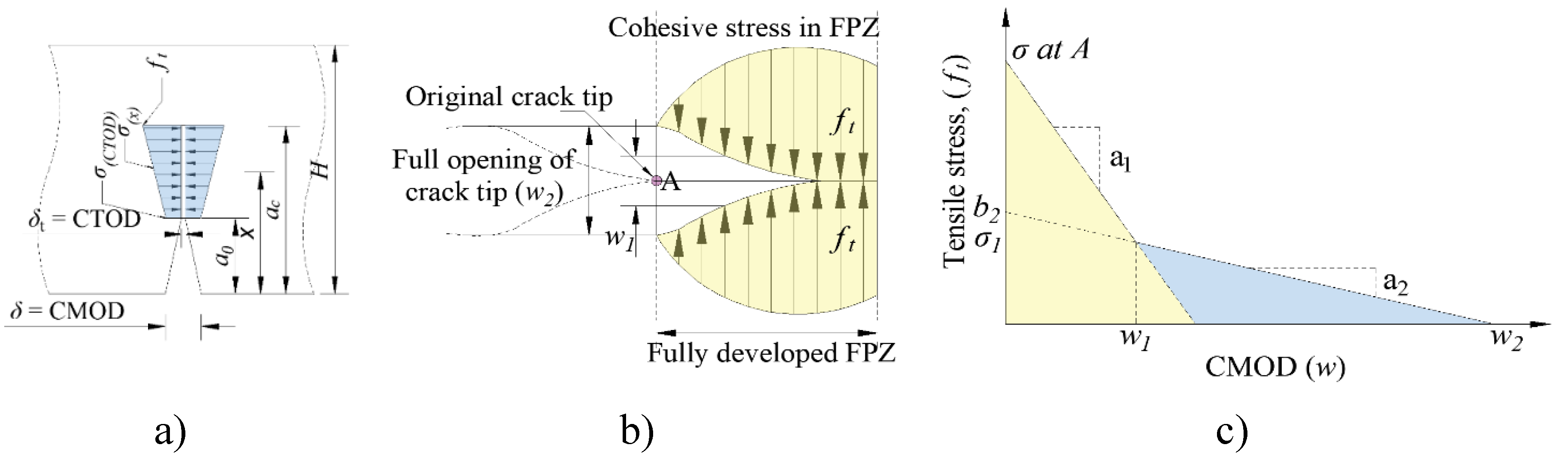
1.1. Bilinear Softening Law
1.2. Fracture Toughness
2. Experimental Investigations
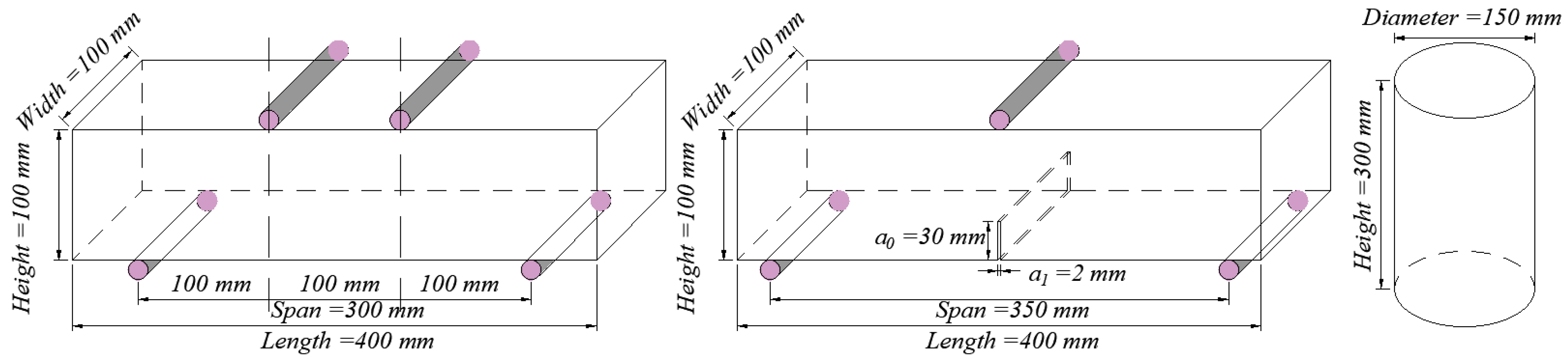
2.1. Experimental Testing
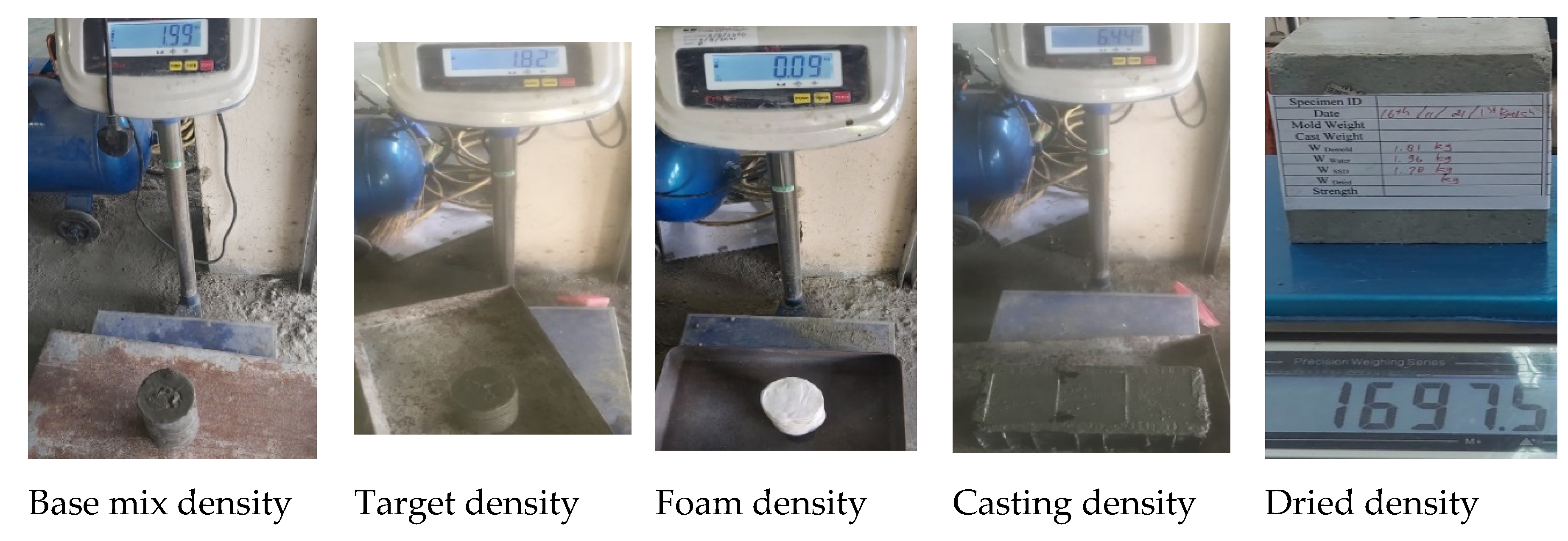

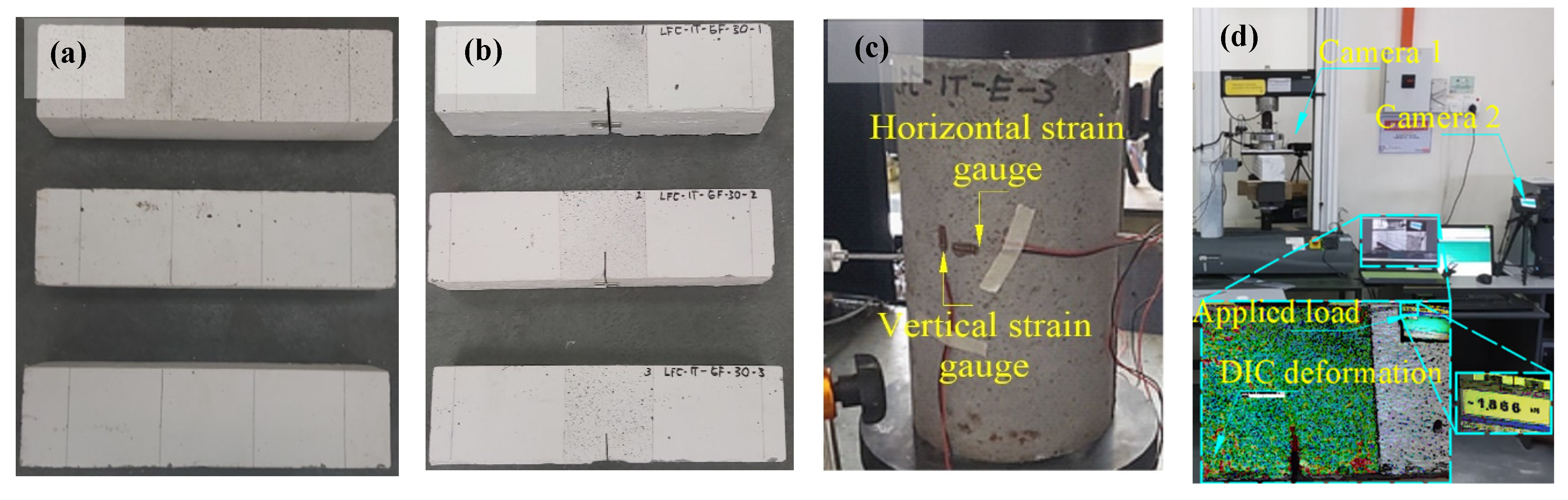
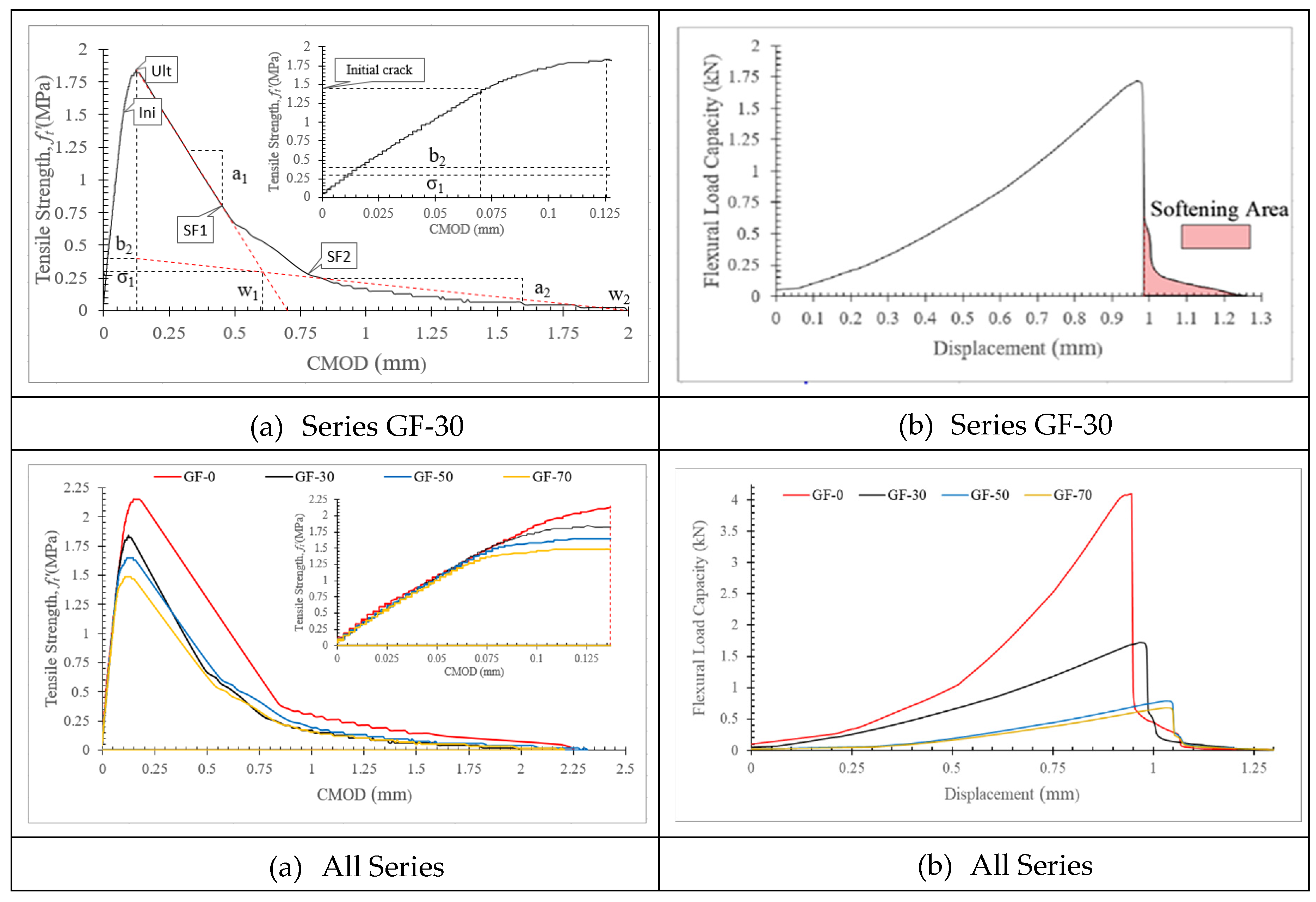
2.2. Experimental Output
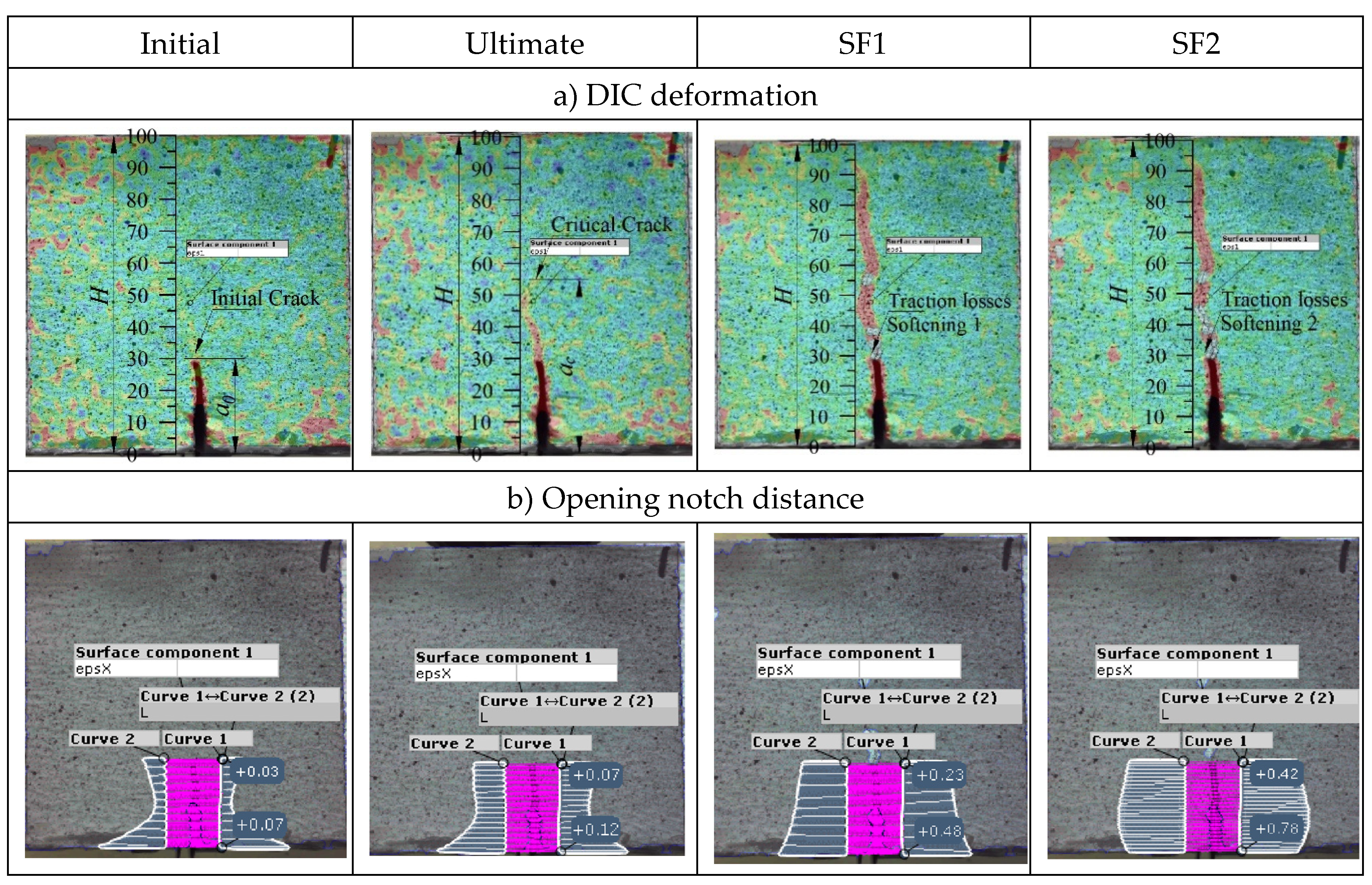
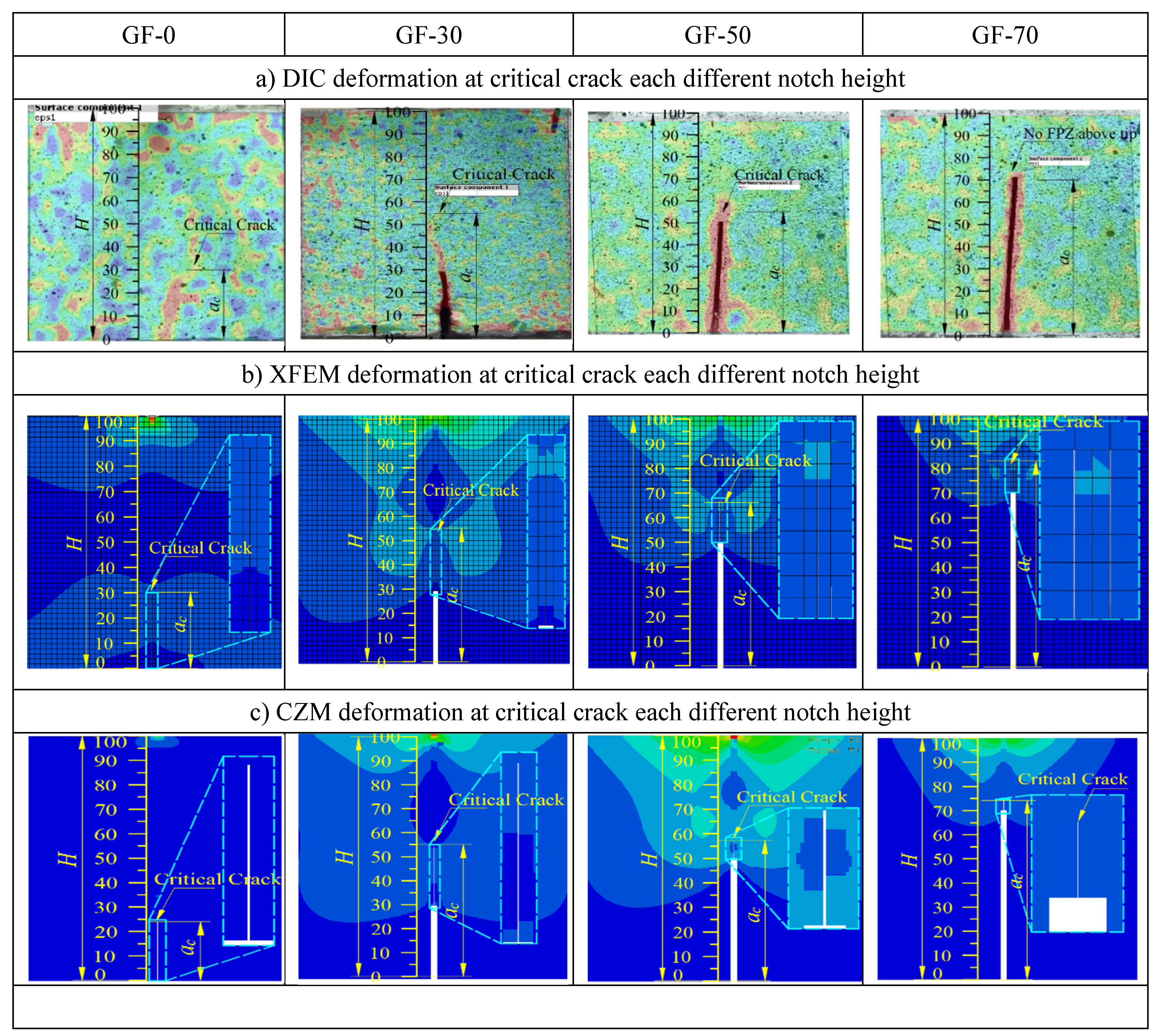
2.3. Digital Image Correlation
3. Finite Element Works
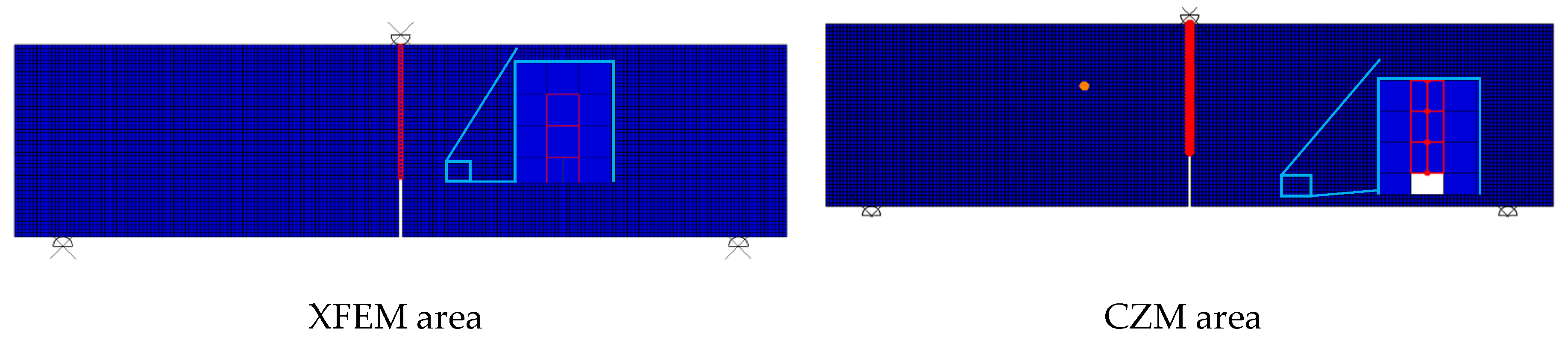
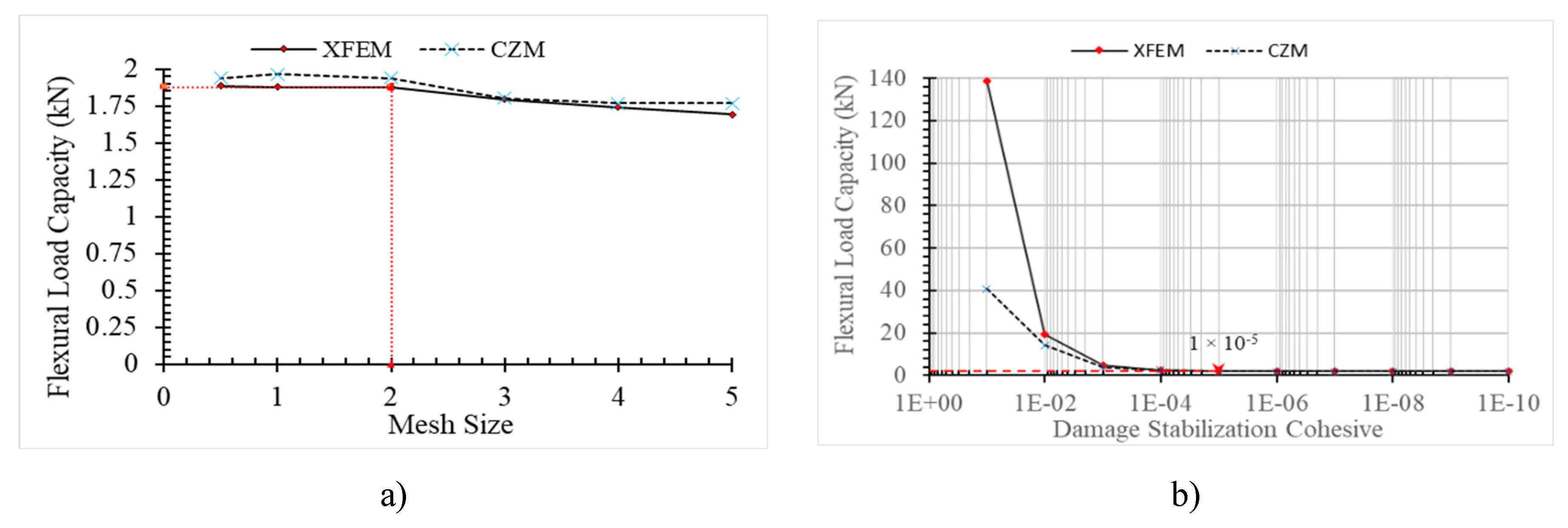
3.1. Sensitivity Study
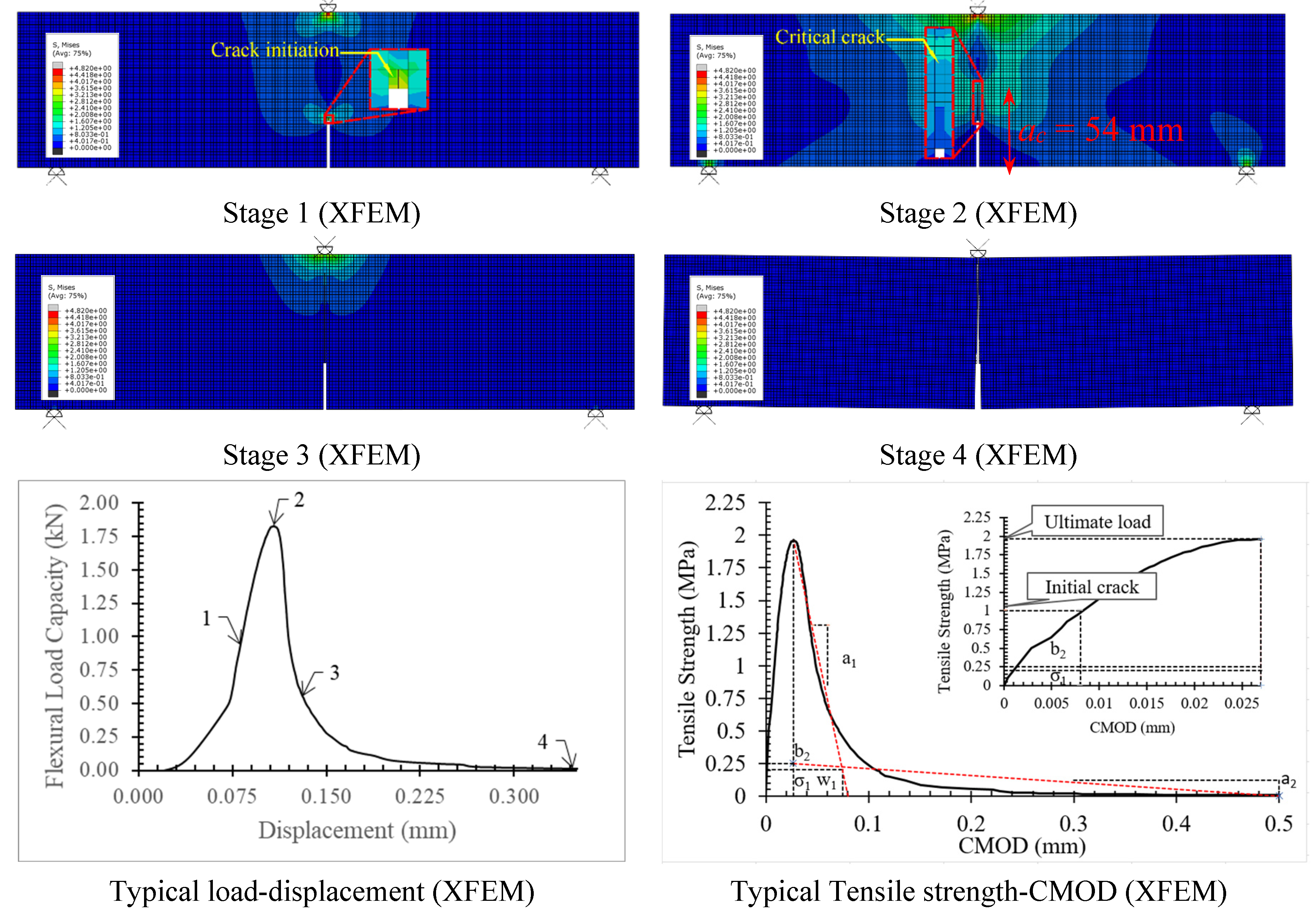
3.2. Damage Plot
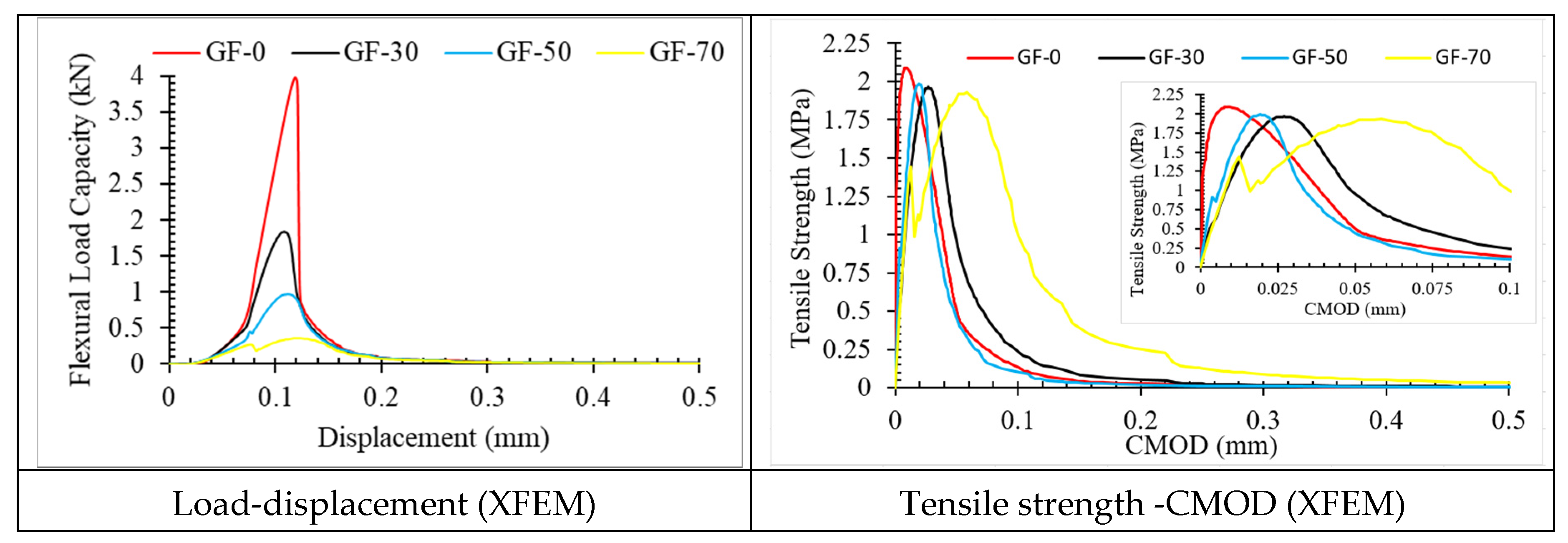
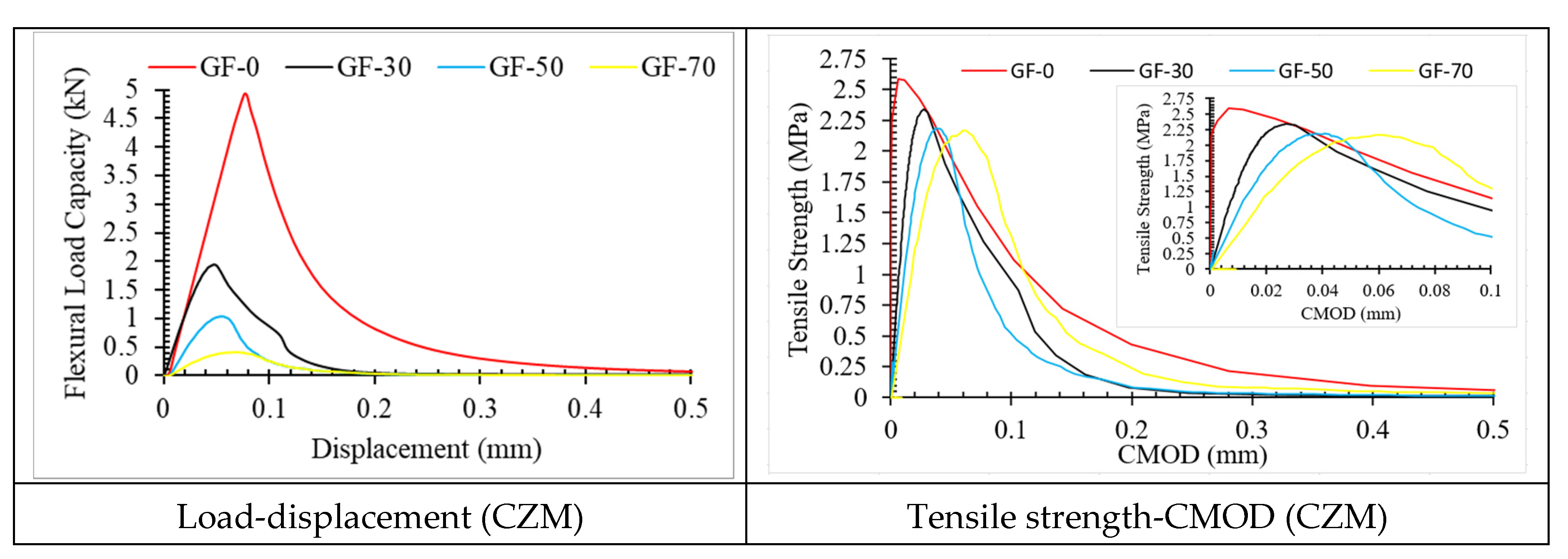
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, Y. L. ; Tan, C. S. ; Lim, S. K., Mohammad, S.; Lim, J. H. Strength Performance on Different Mix of Cement-Sand Ratio and Sand Condition for Lightweight Foamed Concrete. E3S Web of Conferences. 2018; 65, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Gökçe, H. S.; Hatungimana, D.; Ramyar, K. Effect of Fly Ash and Silica Fume on Hardened Properties of Foam Concrete. Construction and Building Materials. 2019, 194(8), 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M. R.; Chen, B.; Farasat Ali Shah, S. Ahmad, M. R.; Chen, B.; Farasat Ali Shah, S. Investigate the Influence of Expanded Clay Aggregate and Silica Fume on the Properties of Lightweight Concrete. Construction and Building Materials. 2019, 220(6), 253-266. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, J.; Dai, S.; Ma, B.; Jiang, Q. Investigation of Silica Fume as Foam Cell Stabilizer for Foamed Concrete. Construction and Building Materials. 2020, 237(10), 117514. [CrossRef]
- Hillerborg, A.; Modéer, M.; Petersson, P. E. Analysis of Crack Formation and Crack Growth in Concrete by Means of Fracture Mechanics and Finite Elements. Cement and Concrete Research. 1976, 6(6), 773-781. [CrossRef]
- Bažant, Z. P. Size Effect in Blunt Fracture: Concrete, Rock, Metal. Journal of Engineering Mechanics. 1984 110(4), 518-53. [CrossRef]
- Bažant, Z. P.; Oh, B. H. Crack Band Theory for Fracture of Concrete. Matériaux et Constructions. 1983 16(3), 155-177. [CrossRef]
- Nallathambi, P.; Karihaloo, B. L. Determination of Specimen-Size Independent Fracture Toughness of Plain Concrete. Magazine of Concrete Research. 1986, 38((135)), 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazant, Z. P.; Kazemi, M. T. Determination of fracture energy, process zone longth and brittleness number from size effect, with application to rock and conerete. International Journal of Fracture. 1990, 44((2)), 111–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Reinhardt, H. W. Determination of Double-K Criterion for Crack Propagation in Quasi-brittle fracture, Part II: Experimental investigation of crack propagation. International Journal of Fracture. 1999, 98((2)), 111–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, N. A.; Jaini, Z. M. An Experimental Study on the Fracture Energy of Foamed Concrete Using V-Notched Beams. InCIEC 2014. 2015, (3), 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Kozłowski, M; Kadela, M; Kukiełka, A. Fracture Energy of Foamed Concrete Based on Three-Point Bending Test on Notched Beams. Procedia Engineering. 2015, 108(10), 349-354. [CrossRef]
- Falliano, D.; De Domenico, D.; Sciarrone, A.; Ricciardi, G.; Restuccia, L.; Tulliani, J. M. C.; Gugliandolo, E. Fracture Behavior of Lightweight Foamed Concrete: The Crucial Role of Curing Conditions. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics. 2019, 103((4)), 102297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Ma, J.; Zhang, M.; Ding, Y.; Meng, L. Fracture Energy Analysis of Concrete Considering the Boundary Effect of Single-Edge Notched Beams. Advances in Civil Engineering. 2018, 2018(10), 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Bai, Y.; Dai, J.; Shi, C. An Investigation of Softening Laws and Fracture Toughness of Slag-Based Geopolymer Concrete. 2020, 10(10), 1-14. [CrossRef]
- Bu, J.; Chen, X.; Hu, L.; Yang, H.; Liu, S. Experimental Study on Crack Propagation of Concrete Under Various Loading Rates with Digital Image Correlation Method. International Journal of Concrete Structures and Materials. 2020, 14((1)). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, L.; Su, Y.; Dong, M.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Y. Size effect on double-K fracture parameters of concrete based on fracture extreme theory. Archive of Applied Mechanics. 2021, 91((1)), 427–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarzyński, Kozicki, J.; Tejchman, J. Application of DIC Technique to Concrete-Study on Objectivity of Measured Surface Displacements. Experimental Mechanics. 2013, 53(9), 1545–1559. [CrossRef]
- Ohno, K.; Uji, K.; Ueno, A.; Ohtsu, M. Fracture Process Zone in Notched Concrete Beam under Three-Point Bending by Acoustic Emission. Construction and Building Materials. 2014, 67(PART B), 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S. Y.; Saliba, J.; & Loukili, A. Fracture Examination in Concrete Through Combined Digital Image Correlation and Acoustic Emission Techniques. Construction and Building Materials. 2014, 69, 232–242. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z. M.; Rong, H.; Zheng, J. J.; Xu, F.; Dong, W. An Experimental Investigation on the FPZ Properties in Concrete Using Digital Image Correlation Technique. Engineering Fracture Mechanics. 2011, 78((17)), 2978–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Choi, H.; Paulino, G. H. Assessment of Cohesive Traction-Separation Relationships in ABAQUS: A Comparative Study. Mechanics Research Communications. 2016, 78, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elices, M.; Guinea, G. V.; Gómez, J.; Planas, J. The cohesive zone model: Advantages, limitations and challenges. Engineering Fracture Mechanics. 2001, 69((2)), pp.137–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freed, Y.; Banks-Sills, L. A New Cohesive Zone Model for Mixed Mode Interface Fracture in Bimaterials. Engineering Fracture Mechanics. 2008, 75((15)), pp.4583–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarry, J. P.; Ó Máirtín, É.; Parry, G.; Beltz, G. E. Potential-based and non-potential-based cohesive zone formulations under mixed-mode separation and over-closure. Part I: Theoretical analysis. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids. 2014, 63(1), pp.336-362. 2014; 63, pp.336–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faron, A.; Rombach, G. A. Simulation of Crack Growth in Reinforced Concrete Beams Using Extended Finite Element Method. Engineering Failure Analysis. 2020, 116((1)), 104698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campilho, R. D. S. G.; Banea, M. D.; Neto, J. A. B. P.; Da Silva, L. F. M. Modelling adhesive joints with cohesive zone models: Effect of the cohesive law shape of the adhesive layer. International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives. 2013, 44, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Shen, J.; Chen, H. Simulation of Crack Propagation Behavior of Nuclear Graphite by Using XFEM, VCCT and CZM Methods. Nuclear Materials and Energy. 2021, 29((2)). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.; Sugiman, S.; Jaini, Z. M.; Omar, A. Z. Numerical Modelling of Foamed Concrete Beam under Flexural Using Traction-Separation Relationship. 2021, 18(5), 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Paulino, G. H.; Roesler, J. R. Determination of the Kink Point in the Bilinear Softening Model for Concrete. 2008, 75(2), 3806-3818. [CrossRef]
- Petersson, P. E. Crack Growth and Development of Fracture Zones in Plain Concrete and Similar Materials. Ph.D Thesis. Lund University. 1981.
- Wittmann, F. H.; Rokugo, K.; Brühwiler, E.; Mihashi, H.; Simonin, P. Fracture Energy and Strain Softening of Concrete as Determined by Means of Compact Tension Specimens. Materials and Structures. 1988, 21((1)), 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Fan, B. Study on the Bilinear Softening Mode and Fracture Parameters of Concrete in Low Temperature Environments. Engineering Fracture Mechanics. 2019, 211((2)), 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelfstra, P.E.; Wittmann, F. Numerical Method to Link Strain Softening with Failure of Concrete. In Fracture Toughness and Fracture Energy of Concrete. 1986, 163-175.
- Kumar, S.; Barai, S. V. Effect of loading condition, specimen geometry, size-effect and softening function on double-K fracture parameters of concrete. Sadhana - Academy Proceedings in Engineering Sciences. 2012, 37((1)), 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, S.; Zheng, S. Experimental measurement of double-K fracture parameters of concrete with small-size aggregates. Frontiers of Architecture and Civil Engineering in China. 2007, 1((4)), 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Lu, Z. Determining residual double-K fracture toughness of post-fire concrete using analytical and weight function method. Materials and Structures/Materiaux et Constructions. 2014, 47((5)), 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Barai, S. V. Influence of specimen geometry on determination of double-K fracture parameters of concrete: A comparative study. International Journal of Fracture. 2008, 149((1)), 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society Testing and Materials. Standard Test Method for Flexural Strength of Concrete (Using Simple Beam with Third-Point Loading)1. America. ASTM-C78-02. 2002.
- Japan Concrete Institute Standard. Method of Test for Fracture Energy of Concrete by Use of Notched Beam. Tokyo. JCI-S-001.2003.
- >American Society Testing and Materials. Standard Test Method for Static Modulus of Elasticity and Poisson’s Ratio of Concrete in Compression. America. ASTM C469-02.2002.
- Bažant, Z. P. Concrete Fracture Models : Testing and Practice. 2002, 69(3), 165-205. [CrossRef]
- Hillerborg. The Theoretical Basis of a Method to Determine the Fracture Energy GF of Concrete. Mater. Struct. 1985, 21(4), pp.162. [CrossRef]
- Munjiza, A.; John, N. W. M. Mesh Size Sensitivity of the Combined FEM/DEM Fracture and Fragmentation Algorithms. Engineering Fracture Mechanics. 2001, 69(2), pp.281-295. [CrossRef]
- More, S. T., & Bindu, R. S. (2015). Effect of Mesh Size on Finite Element Analysis of Plate Structure. International Journal of Engineering Science and Innovative Technology, 4(3), pp.181-185.
- Maulana, M. R.; Sugiman, S.; Ahmad, H.; Jaini, Z. M.; Mansor, H. XFEM Modelling and Experimental Observations of Foam Concrete Beam Externally-Bonded with KFRP Sheet. Latin American Journal of Solids and Structures. 2022, 19(6), 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Liang, G.; Lei, J.; Li, C. Thin-Walled Structures Singular Intensity Factor Method to Estimate Notch Stress and N-SIF in Double Edge V-Notched Plate. Thin-Walled Structures, 2021, 169((9)), 108387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Gong, Y.; Tao, J.; Cao, T.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Hu, N. Efficiently Determining the R-Curve and Bridging Traction-Separation Relation of Mode I Delamination in a Simple Way. Composite Structures. 2022, 288((1)), 115388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koslan, M. F. S.; Zaidi, A. M. A.; Othman, M. Z.; Abdullah, S.; Thanakodi, S. The Effect of Mesh Sizing Toward Deformation Result in Computational Dynamic Simulation for Blast Loading Application. Modern Applied Science. 2013, 7((7)), 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supar, K.; Ahmad, H. Multi-Holes Configurations of Woven Fabric Kenaf Composite Plates: Experimental Works and 2-D Modelling. Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Sciences. 2018, 12((2)), 3539–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.; Crocombe, A. D.; & Smith, P. A. Strength prediction in CFRP woven laminate bolted double-lap joints under quasi-static loading using XFEM. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing. 2014, 56, 192–202. [CrossRef]
| Binder (kg/m3) | Sand (kg/m3) | SP (kg/m3) |
Water (kg/m3) |
Foam (liter/m3) |
f'c (MPa) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | SF | |||||
| 1043.91 | 54.94 | 366.28 | 10.99 | 461.52 | 105 | 42.3 |
| Testing Series | Dimension (mm) (l × b × h) |
Notch height (mm) | Standard | Speed rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 400 × 100 × 100 | Un-notched | ASTM-C78-02 [39] | 0.5 mm/min |
| GF-0 | 400 × 100 × 100 | 0 | JCI-S-001[40] | 0.1 mm/min |
| GF-30 | 30 | |||
| GF-50 | 50 | |||
| GF-70 | 70 | |||
| E | D150 × 300 | - | ASTM C469-02 [41] | 3 kN/sec |
| Testing Series |
Pini (kN) |
Pult (kN) |
ft (MPa) |
σ1 (MPa) |
w1 (mm) |
w2 (mm) |
a1 (mm-1) |
a2 (mm-1) |
b2 (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GF-0 | 3.333 | 4.101 | 2.153 | 0.380 | 0.820 | 2.250 | 2.623 | 0.214 | 0.550 |
| ± 0.075 | ± 0.089 | ± 0.105 | ± 0.034 | ± 0.098 | ± 0.052 | ± 0.398 | ± 0.025 | ± 0.104 | |
| GF-30 | 1.384 | 1.752 | 1.877 | 0.317 | 0.650 | 2.000 | 2.612 | 0.240 | 0.433 |
| ± 0.135 | ± 0.142 | ± 0.159 | ± 0.057 | ± 0.153 | ± 0.288 | ± 0.398 | ± 0.038 | ± 0.088 | |
| GF-50 | 0.595 | 0.786 | 1.650 | 0.270 | 0.700 | 2.310 | 2.118 | 0.187 | 0.350 |
| ± 0.075 | ± 0.052 | ± 0.095 | ± 0.045 | ± 0.115 | ± 0.288 | ± 0.086 | ± 0.045 | ± 0.093 | |
| GF-70 | 0.244 | 0.254 | 1.303 | 0.270 | 0.670 | 2.203 | 2.082 | 0.200 | 0.345 |
| ± 0.021 | ± 0.015 | ± 0.058 | ± 0.031 | ± 0.124 | ± 0.288 | ± 0.152 | ± 0.018 | ± 0.101 |
|
E (GPa) |
v |
σ0 (MPa) |
GI (N/mm) |
TSL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13.0 | 0.28 | 1.652 | 0.015 | MaxPS |
| TSL |
Pini (kN) |
Pult (kN) |
ft (MPa) |
σ1 (MPa) |
w1 (mm) |
w2 (mm) |
a1 (mm-1) |
a2 (mm-1) |
b2 (MPa) |
|
| GF-0 | XFEM | 2.563 | 3.974 | 2.086 | 0.230 | 0.070 | 2.217 | 33.030 | 0.424 | 0.250 |
| CZM | 2.985 | 4.928 | 2.587 | 0.350 | 0.150 | 2.274 | 15.830 | 0.467 | 0.500 | |
| GF-30 | XFEM | 0.938 | 1.832 | 1.963 | 0.220 | 0.080 | 2.215 | 22.956 | 0.350 | 0.241 |
| CZM | 1.125 | 2.455 | 2.338 | 0.250 | 0.140 | 2.341 | 33.973 | 0.452 | 0.300 | |
| GF-50 | XFEM | 0.552 | 0.945 | 1.985 | 0.210 | 0.090 | 1.659 | 21.562 | 0.325 | 0.236 |
| CZM | 0.589 | 1.040 | 2.185 | 0.240 | 0.130 | 2.547 | 22.867 | 0.441 | 0.280 | |
| GF-70 | XFEM | 0.215 | 0.330 | 1.928 | 0.200 | 0.190 | 1.348 | 21.795 | 0.375 | 0.268 |
| CZM | 0.258 | 0.340 | 2.166 | 0.235 | 0.160 | 2.942 | 22.207 | 0.410 | 0.410 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





