1. Introduction
MRSA refers to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, a bacterium resistant to many available antibiotics, including β-lactam. MRSA is the predominant pathogen contributing to antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in both community and health care settings. Studies have shown that 33% of people carry S. aureus in their nose without harm, and two out of every hundred are MRSA carriers [
1]. The consequences of the MRSA infection continue to upsurge, because of elevation in transmission rates, intense colonization, and rapid bacterial activation of virulence factors that increase the infection’s pathogenicity. The population expanding of the bacteria is subjected to a chemical signaling mechanism named as quorum sensing (QS), which allow a cell-to-cell communication. In S. aureus, quorum-sensing accessory gene regulator (agr) system controls the virulence factors production. Therefore, at high cell density, agr is activated leading to the secretion of an auto-inducing peptide (AIP), that is detected by the trans-membrane receptors leading to activation of the bacterial virulence factors that cause the infection. S. aureus pathogenicity is highly dependent on the virulence factors such as toxins (Hemolysins), immune-evasive surface factors (capsule and protein A), and biofilm formation [
3]. S. aureus has two QS systems produced by agr locus; RNAII that originates from the P2 promoter, and RNAIII that originates from the P3 promoter. The RNAIII segment of agr is generated from four genes agr A, B, C and D, which encode all the main components of the QS system. The trans-membrane protein agr B is involved in AIP signal secretion, modification and agr D processing. Whereas, the agr A encodes the cytosolic response regulator (RR), and the agr C encodes membrane-bound histidine kinase (HK), however, they both form the two components regulatory system (AgrAC TCS) [
4]. A Previous study has reported that synthetic molecules of meta-bromo-thiolactone (mBTL) have inhibited virulent bacterial QS, and provided the uppermost activity for QS system inhibition [
5]. Using mBTL molecules, quorum sensing system can be regulated, thus it can be a potential alternative for antibiotic therapy and an approach to reduce the MDR issue. The therapeutic index of pharmacological activity of agents can be increased due to the prolonged release of drugs via polymeric nanoparticles [
6]. Chitosan refers to a class of polymers derived from chitin; a natural polysaccharide comprised of-(1,4)-linked N-acetyl glucosamine units. Fungi and the exoskeletons of crustaceans and insects are the most prevalent sources of chitin [
7]. Chitosan-based nanoparticles can be utilized to deliver active components, such as pharmaceuticals or natural products, via a variety of modes of administration. Chitosan nanoparticles combine the unique characteristics of the polymer with tunable size and the capacity to modify the surface to meet specific demands, making them a very promising and diverse solution for overcoming the bioavailability and stability difficulties that affect most active ingredients [
7]. The aim of this work is to formulate mBTL in chitosan nanoparticles, and test their effect on S. aureus, MRSA and QS various mutants mostly biofilm effect.
3. Discussion
A MRSA can cause either a skin infection or a blood infection. First is methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (H-MRSA), which is spread through contact with medical personnel and can result in a variety of unpleasant complications such pneumonia, bacteremia, and surgical site infections. In contrast, community-associated MRSA (C-MRA) causes skin and soft tissue infections in people who have never had contact with a healthcare setting. Despite this, MRSA infections continue to be a leading cause of increased mortality, healthcare expenses, and lengthened hospital stays [
14]. Anti-QS molecules such as mBTL, is one of the approaches used for targeting microbial virulence as reported previously. Previous study performed in our lab revealed antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity of mBTL-calcium alginate NPs against different pseudomonal isolates. Therefore, this study aimed to formulate mBTL in CNPs and evaluate their antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity.
In agreements with previous studies [
15,
16], plain nanoparticles, and mBTL loaded chitosan nanoparticles were synthesized and showed particle size of 158
+1.3 nm and 283.9
+13.55 nm, respectively with positive surface charge making these nanoparticles easily up taken by
S. aureus and other strains due to the negative charge of the organisms.
Microbiological examination and a comparison to free mBTL were performed on mBTL-loaded CNPs. The antagonist activity of the AIP can be obtained by substitutions, truncations or combinations of these modifications for the native AIP. The mBTL is a synthetic analogue
of Acyl-
HSL, other synthetic analogues have been tested for quorum sensing inhibition in
S. aureus. these compounds exert their action by noncompetitive inhibition of the AIP by alteration the activation efficacy of the AIP, they may act as an allosteric inhibitor of AgrC [
17,
18].
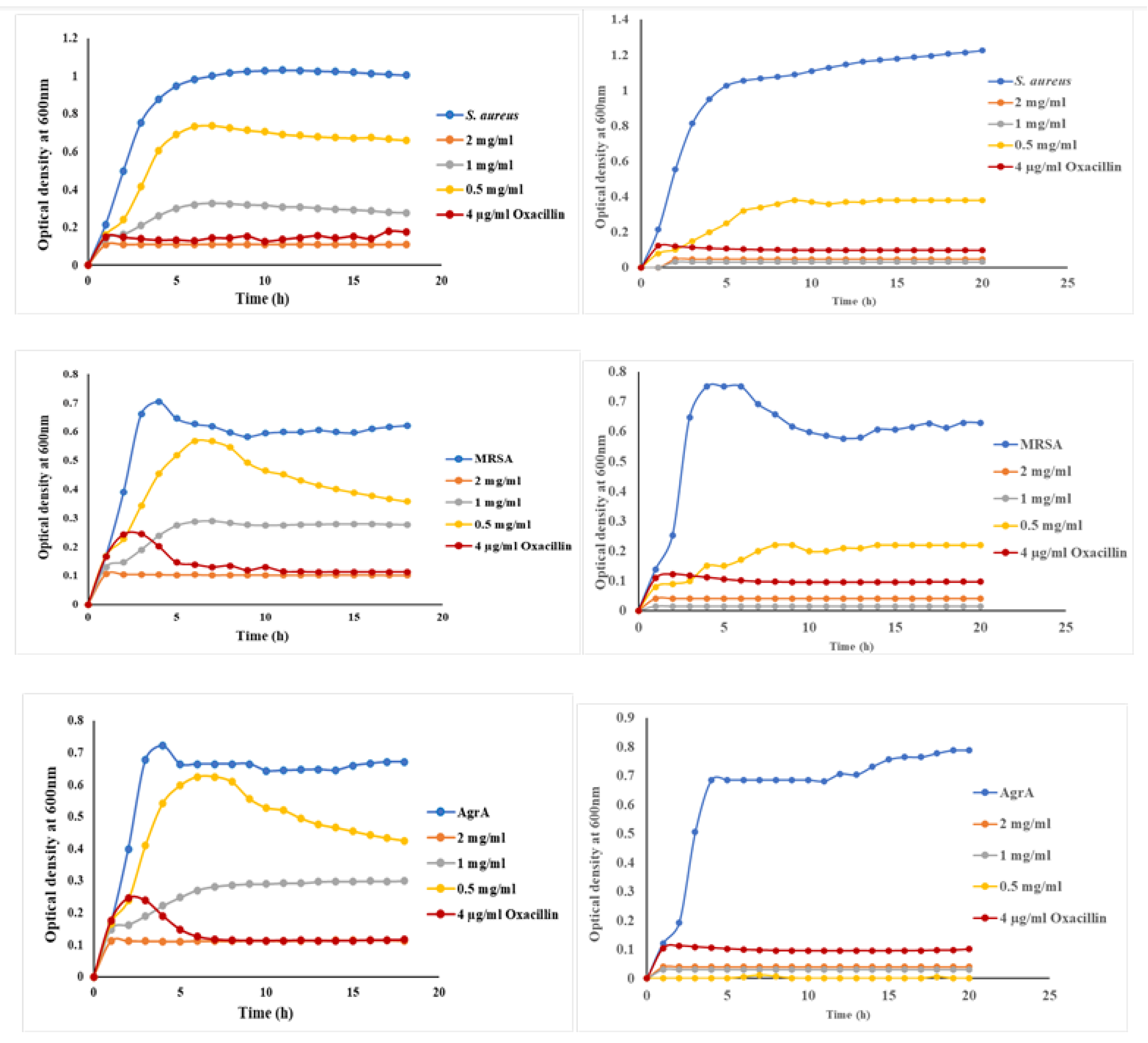
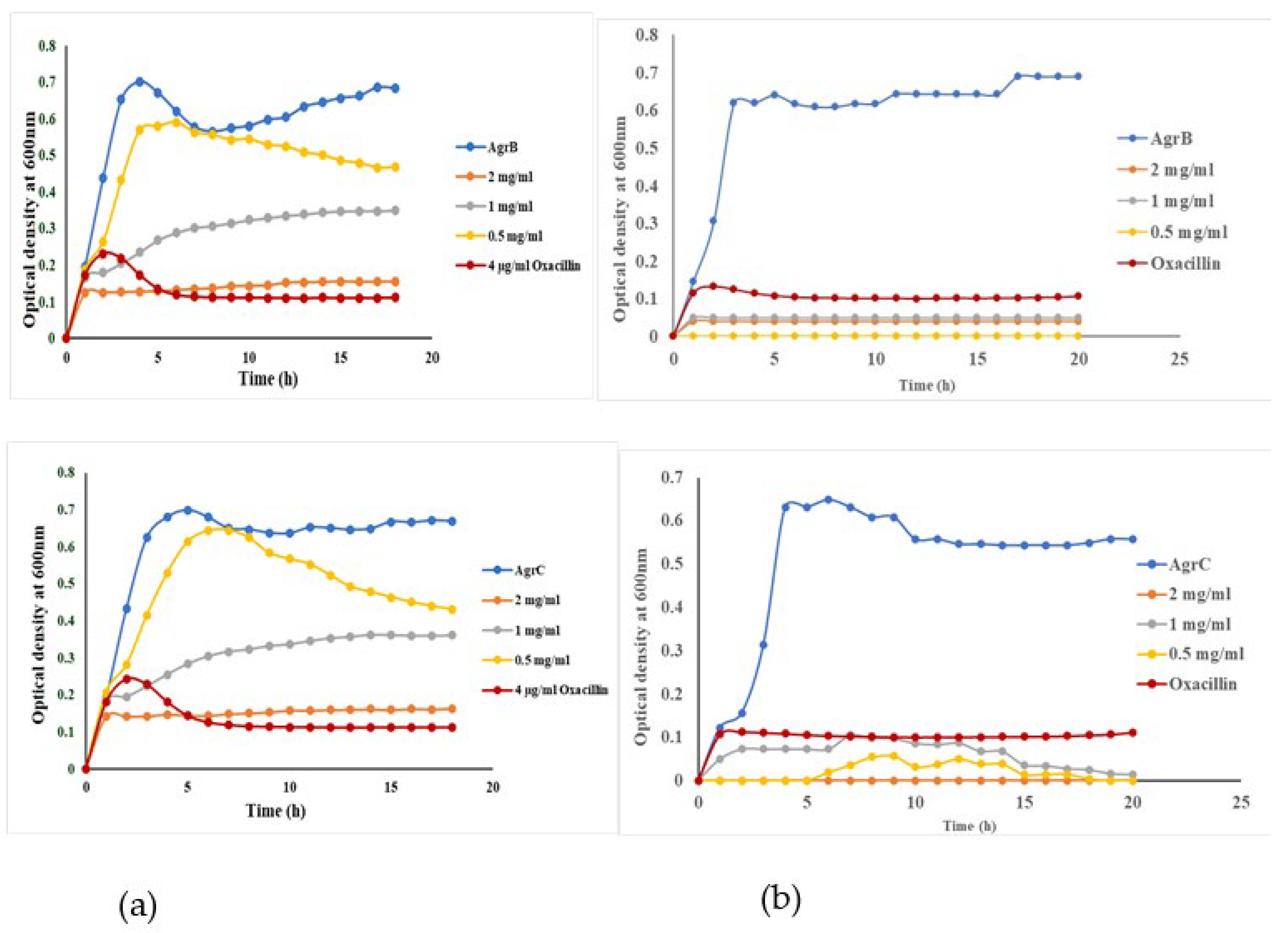
The selected concentrations of mBTL were 2 mg/ml, 1 mg/ml and 0.5 mg/ml. The concentration (2mg/ml) of mBTL has the greater effect on the different strains of
S. aureus. Furthermore, the findings of this study revealed that mBTL inhibited bacterial growth of
S. aureus wild type,
MRSA, and other QS mutants. Interestingly, this antimicrobial activity was enhanced upon loading of mBTL in ChNPs as observed from the growth curve results. The obtained superiority of loaded mBTL over free mBTL in inhibiting bacterial growth were in agreements with other studies [
19].
Biofilms are a type of microbial community that has adapted to living in various habitats, such as on human skin and other medical equipment. They are responsible for two-thirds of all infections and pose a significant risk in medical (and industrial) settings. Microorganisms that form biofilms are notoriously difficult to treat because they exhibit a form of multidrug resistance called adaptive multidrug resistance [
20]. Conventional antibiotics' failure to eradicate biofilms has been traced to several causes. Antibiotic resistance is multifaceted, encompassing biofilm formation, adaptive stress responses, and metabolic inactivation caused by nutrition and gas constraint [
21].
Gram-positive bacterial QS systems have peptide autoinducers that are encoded in the genome, allowing the creation of peptides that are specific to each species. The gram-positive opportunistic bacterium
Staphylococcus aureus is responsible for nosocomial illnesses, such as, sepsis and pneumonia. Methicillin-resistant S. aureus (
MRSA) and other
S. aureus strains with resistance to a variety of B -lactam antibiotics are on the rise. Virulence is regulated by the QS system, which is the accessory gene regulator (Agr). The RNAII and RNAIII transcripts are transcribed by the P2 and P3 promoters. In order to regulate the feed forward loop for quorum-sensing autoinducer peptide expression, a transcript encoding the AgrBDCA locus is required. In
S. aureus the QS systems is required for gene expression, escape from the immunity and establish an infection. The system is encoded by chromosomal locus named the accessory gene regulator (
agr). The locus consists of two operons produced by P2 and P3 promoters. The P2 have
agrBDCA and control the RNAII transcript. While the P3 control the RNAIII transcription, which is consider the effector molecule of the
agr locus. The communication within the cells is managed by AIP, this peptide consists of a thiolactone ring which synthesized by condensation of the carboxyl group in the C-terminus and sulfhydryl group in cysteine. Result in a structure that is necessary for binding of the AIP to its receptor AgrC [
22].
The peptide is translated as AgrD precursor, then a transmembrane protein AgrB convert it to a mature AIP and transport the peptide outside the cell. When there are additional bacteria present, the AIP builds up and binds to the AgrC a membrane-bound histidine-kinase, activating the kinas. This activation led to phosphorylation of the agrA which linked to intergenic DNA between P2 and P3, lead to transcription activation. Increases the transcription cause an increase in the intracellular concentrations of RNAIII which is responsible for the translation of the secreted virulence factor. For example, the
hla which encode the α-toxin and reduce the expression of surface adhesins, such as the protein A and fibronectin-binding protein [
23]. Also, the RNAIII stabilizes
mgrA mRNA and this will increase a global transcriptional regulator called Mgr which serve as intermediate regulator for the
agr to do its function. The Mgr affect gene involved in virulence, such as autolysis, antibiotic resistance, and biofilm formation [
24].
The 4547-residue pro-AIP is synthesized by AgrD, and the 79-residue AIP is then processed and secreted by the AgrB transporter. Through a thiolactone link between the C-terminus and a cysteine residue, the pro-AIP is truncated and cyclized into a five-residue peptide. When there are additional bacteria, the AIP builds up and binds to the Agr C membrane-bound histidine-kinase, activating the QS system. AgrA, the response regulator protein kinase, phosphorylates a conserved histidine and transfers the phosphate group to an aspartate residue. By attaching the upstream of the P2 promotor, AgrA activates the feed-forward the loop and causes the agr operon to be expressed. The hld gene, which codes for the virulence factor -hemolysin, is expressed via the PIII promoter, which is under AgrA's control. On the one hand, RNAIII promotes the expression of -toxin, while on the other, it inhibits the activity of rot factor (a repressor of toxins). Secretion of virulence factors and suppression of factors that control toxin synthesis are both outcomes of this QS regulatory cascade. Additionally, the QS system inhibits biofilm development in the HCD environment while regulating it in the LCD environment. As a result, the biofilm serves as a safe haven for the bacteria to continue multiplying until HCD is attained, after which they can go on to other hosts [
25].
Inactive
agr-system provide an advantage to the
S. aureus to be better adapt and persistence in the host cell. The
agr-system has an important role in biofilm development and the
agr-mutant have a high tendency to form biofilm, cells disseminate from the biofilm showed active
agr-system. Thus, suppression of the
agr-system is required for biofilm formation. In this study the mBTL (0.5 mg/ml) encapsulating ChNPs cause a reduction in the biofilm formation of
S. aureus,
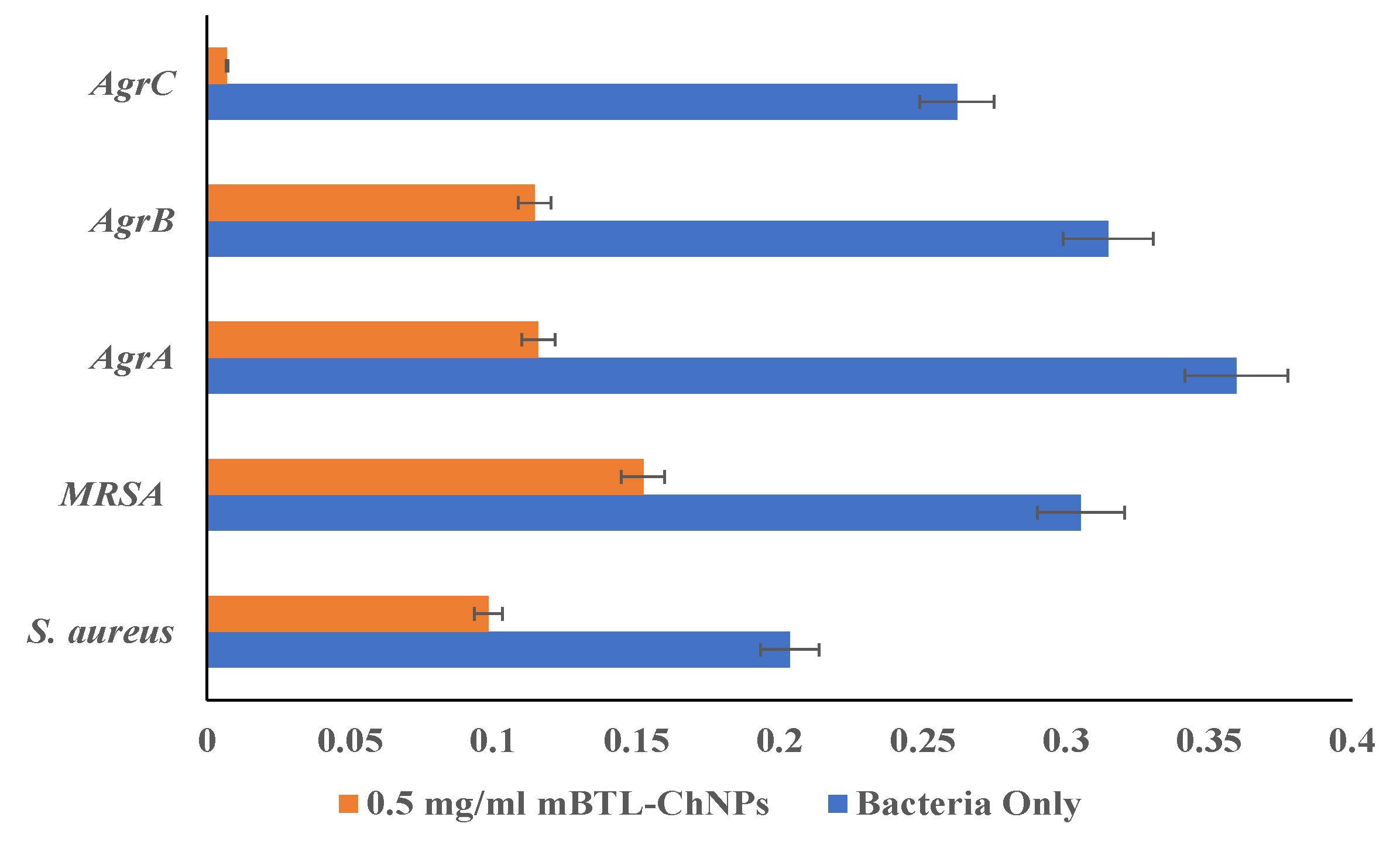
MRSA by 51.7%, 50% respectively. A higher reduction was observed with mutant strains which have a significant ability for biofilm formation compared with wild-type. The biofilm reduced by; 68%, 63.6% for AgrA, AgrB respectively and 97.3% for AgrC suggesting a potent inhibitory activity for the mBTL- ChNPs [
24].
In the current study, mBTL (0.5 mg/ml) encapsulating ChNPs reduced biofilm formation of S. aureus, MRSA, AgrA, and AgrB by 51.7%, 50%, 68% and 63.6%, respectively, and inhibited biofilm development in AgrC by 97.3%. These results were consistent with previous reports in which chrysin loaded ChNPs exhibited marked anti-biofilm activity against S. aureus when compared with untreated bacteria [
26]. Other study showed that chitosan-coated iron oxide nanoparticles successfully prevented bacterial colonization and reduced the development of biofilm in S. aureus by 53% [
27]. Furthermore, CLSM and SEM were utilized to visualize anti-biofilm activity of mBTL loaded ChNPs towards bacterial isolates tested and the results indicated a decrease in the thickness and density of the biofilm matrix in the presence of NPs.
Chitosan's biodegradability, biocompatibility, and low toxicity have sparked substantial research into its potential uses in a wide variety of sectors. Some of chitosan's many potential applications: as a hydrogel film in the pharmaceutical industry [
28], as a flocking agent in water treatment [
28], as an elicitor to activate plant defenses [
29], as an additive in the food preservation process [
30], and as a drug delivery carrier [
31].[
32,
33,
34,
35]. Many reports have also revealed chitosan's broad antibacterial action against bacteria and fungus. The antibacterial action of chitosan, however, is very microorganism-specific [
36,
37,
38]. Furthermore, chitosan's physicochemical properties are related to the mechanisms of its antibacterial activity. [
39,
40].
Gram-positive bacterium Staphylococcus aureus is an exceptionally adaptable and flexible pathogen. It is a harmless commensal that can reside on the skin and in the mucous membranes.[
41]. However, S. aureus is also one of the top causes of hospital- and community-acquired infections globally due to its ability to grow in the circulation and in numerous tissues, causing significant disease [
42,
43]. It can trigger anything from a simple skin infection to more serious systemic infections that can even be fatal, such pneumonia, osteomyelitis, and endocarditis. S. aureus infections can recur in 8-33% of cases, leading to significant human morbidity and mortality [
30].
O’Loughlin CT, et al, showed that mBTL's effects extended beyond those of an anti-infective agent; it also reduced the development of biofilms and the clogging of microfluidic devices. However, it was suggested that the employing of anti-quorum-sensing molecules might prevent the failure of systems that are susceptible to fouling by biofilms.[
4]. As a result, these molecules may find applications in fields as diverse as industry and the field of medicine. Here, we employed liquid administration of the inhibitor; ultimately, we hope to include mBTL-like molecules into the materials used to manufacture such gadgets, making those goods inherently resistant to biofilms. Together, our results on mBTL provide strong evidence for the efficacy of quorum-sensing modulators in reducing pathogens with quorum-sensing-controlled phenotypes.
Eltayb EK, et al., also agreed with our results in the effectiveness of loaded-mBTL in decreasing minimum inhibitory concentration of mBTL for different Pseudomonal isolates tested [
13].
To our knowledge limited number of studies were conducted to investigate the effect of loaded-mBTL on different bacterial strains, and most of these studies have been conducted on Pseudomonas aeruginosa; this makes our study pioneering in investigating mBTL and loaded-mBTL effect on different Staphylococcus strains. The promising results of loaded-mBTL gives hope for rising new generations of drug that can treat a group of resistant bacteria and decrease the consumption of antibiotics.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial strains, chemicals, and growth conditions
Strains of
Staphylococcus aureus, MRSA, and different QS mutants as described in
Table 1, were grown in tryptic soy broth (TSB) and tryptic soy Agar (TSA) supplemented with is erythromycin and incubated at 37 ºC for 18-24 hr [
8].
4.2. Preparation of chitosan nanoparticles (ChNPs) and mBTL loading
ChNPs were prepared using the ionic gelation method by dissolving 10 ml of 1% v/v acetic acid in 100 ml of deionized water, and then 100 mg of chitosan was added and magnetically stirred for 2-3 hr until it was completely dissolved. The nanoparticles could be affected by the acidic media; accordingly, the solution pH was adjusted using sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to pH of 4.7. mBTL 4% was dissolved in 1200 µl DMSO and 1000 µl of tween 20, the resulted mixture was then added to the prepared chitosan solution. To 10 mL of chitosan solution containing the drug, DMSO, and tween 20, 4 mL of 0.01 % w/v TPP solution was added. This mixture was then continuously magnetically stirred at 500 rpm for 30 min. The nanoparticles were formed. The nanoparticle solution was then centrifuged twice at 14000 rpm for 30 min using a cooling centrifuge. The retrieved nanoparticles were then suspended in deionized water. Finally, the ChNPs were reconstituted in deionized water and stored at 4°C for further characterization.
4.2. Physicochemical analysis of mBTL-loaded ChNPs
The mean particle size, polydispersity index and zeta potential of mBTL-ChNPs was measured at 25 °C using the Zeta sizer Nano ZS (Malvern Instruments, Malvern, UK). The nanoparticle suspension was diluted 5 times with deionized water. All measurements were performed in triplicate.
Determination of mBTL-loaded ChNPs encapsulation efficiency (EE %)
The encapsulation efficiency of mBTL-ChNPs was indirectly determined by measuring the concentration of free mBTL in the aqueous phase. The encapsulation efficiency was estimated using the following equation:
4.2. In vitro release of mBTL-ChNPs
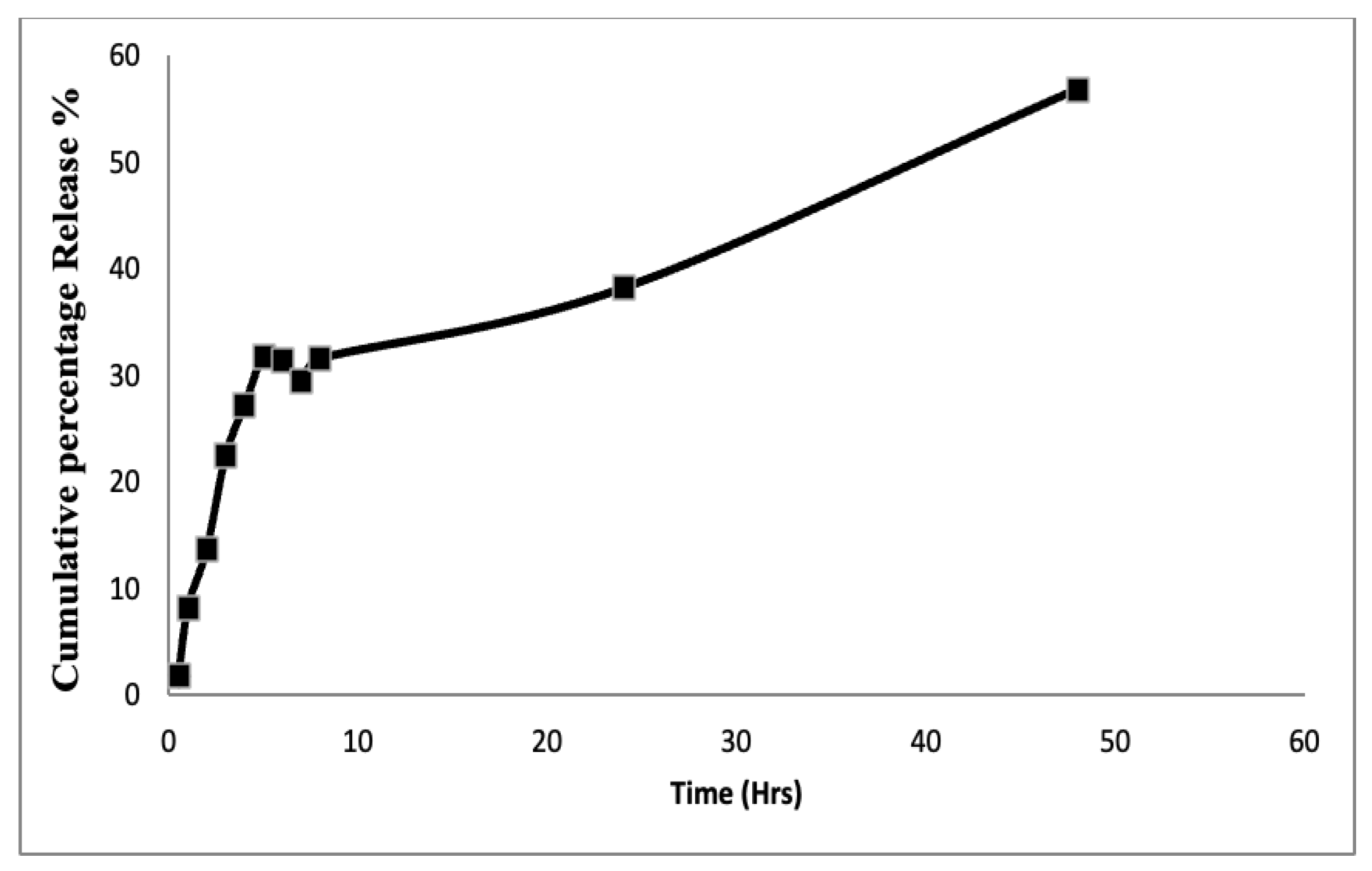
The release profiles of mBTL-ChNPs were evaluated by means of the dialysis method using cellulose dialysis tube sealed at both ends. The membrane was soaked in a release medium overnight before use. One ml of mBTL-ChNPs was placed into dialysis bags, which were then transferred into beakers containing 30 mL of the phosphate buffer pH 7.4. At predetermined time intervals 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and 24, 48 hours, 3 mL of the release medium was withdrawn and instantly replaced by an equal amount of fresh release medium to maintain a sink condition. The amount of released mBTL was determined by measuring the absorbance at 280 nm. The release profile of mBTL was obtained by plotting the cumulative percentage release of the drug versus time.
4.2. Growth Curve Construction
All bacterial strains were grown in 5 ml TS broth with the selected antibiotic marker Erythromycin except for the fourth wild type of strain, then incubated at 37 ºC with continuous overnight shaking at 200 rpm. 200 µl of bacterial broth with optical density of 0.4-0.6 McFarland was added to 96 well plates. All tests were performed in triplicate and controls of media only and untreated bacteria, then the 96 well plates were placed in BioscreenC reader and optical density of bacterial growth was recorded at 600 nm for 24 hr.
4.2. MIC measurements
According to the CLSI guidelines, the MBC is defined as the first dilution that results in three or fewer colonies after 24 hours of incubation at 37 °C.The double-dilution method [
9,
11] is the standard method for determining minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs). The minimal inhibitory concentrations were determined by measuring the concentration of the formula at which no visible growth occurred. The minimal bactericidal concentration (MBC) was also recorded as the lowest concentration of the compound at which no colonies formed after plating the dilutions around the MIC or growing them in fresh TSB media. For all strains MBCs were determined by inoculation of 10 μl from each well that did not show visible bacterial growth on TS plates. After 24 h of incubation at 37 °C, the first dilution yielded three colonies or fewer was scored as the MBC, as described by the CLSI.
4.2. Hemolytic Activity Analysis
For hemolytic activity an overnight culture of all strains was standardized to OD
600of 0.5 and 1:50 diluted in 10 mL TSB with or without antibiotic and tested formula. Strains were streaked on blood agar plates, incubated overnight at 37°C for 24 and 48 hr. The hemolytic activity was observed on plates as transparency around the colonies [
9].
4.2. Biofilm Assay
Modifications were made to the method previously described for detecting biofilms [
10]. Strains were cultivated at 37 °C for 24 hr in TSB broth, diluted to 107 cfu/ml in TSB media, and dispensed in 96-well microliter plates (Thomas science). Then, 100 µL of each antibiotic and compounds at 1 mg/mL FC were added to each well. Biofilm inhibition was evaluated by inoculating 15-well plates with each strain (100 µL of bacterial strain was added to each well) and incubating the plates at 37°C for 24 hr. After removing the cell suspension, the plates were washed twice with a 0.9% NaCl solution and air dried at room temperature for 1 hr. After 15 min, the wells were stained with 150 µl of crystal violet solution (CV; Prolab Diagnostics). Following staining, CV was removed, and 0.9 % NaCl solution was used to wash the wells three times. The attached CV was dissolved in 200 µl of ethanol-acetone (80:20 v/v). Finally, a microplate reader was used to measure the CV absorbance at 595 nm (BioTek). All experiments were carried out in triplicate for three independent times.
4.2. Confocal Microscopy
All isolates were cultured in Tryptic soy agar (TS) or TS agar supplemented with 10 mg/mL erythromycin at 37 ◦C for 18 hr. The culture media were purchased from Oxoid (Basingstoke, Hampshire, UK). 5 samples were treated with 0.5 mg/ml free mBTL. The effect of m-BTL on bacterial cell viability was determined by confocal laser scanning microscope, CLSM, (Leica TCS SP5, UK) with a Live/Dead® BacLight™ viability kit consisting of a universal stain SYTO 9 and propidium iodide (PI). Cells images were acquired using the Leica Application Suite Advanced Fluorescence software 5 (Leica, UK), with an optical magnification of 40× using an oil-immersion objective lens. Images were sized to 1024 × 1024 pixels and recorded by scanning lasers over an area of 25 × 25 µm. An argon-based laser was employed for excitation at 488 nm, and HeNe laser for excitation at 543 nm. The emission was set at 528 nm for SYTO 9 and 645 nm for PI. Via sequential scanning, the images were obtained and processed in Image J software.
4.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
In order to visualize biofilm formation, bacteria were grown overnight in LB at 37 °C. Next day the cultures were diluted in LB to 10
7cfu/ml. Polyvinyl (Fisher Scientific) coverslips were placed in each well of a Thomas 6-well plate before being filled with 2 ml of LB medium and 2 ml of diluted culture. Biofilms were then formed on the coverslips at 37 °C for 24 hr. Biofilm samples were fixed with 3% glutaraldehyde in phosphate buffer pH 7.2 for 24 h. after three washes with phosphate buffer, samples were postfixed for 1 h with 1% osmium tetroxide (in H
2O), and then were applied in to an ethanol dehydration series of 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, and 2 × 100% (v/v) ethanol, for 5 min at each concentration [
12]. All samples were then dried for 1 day and sputter-coated with a palladium-gold thin film. SEM/EDS imaging of the biofilm was performed in a high-vacuum mode at 20 kV using an FEI Quanta 400FEG ESEM/EDAX Genesis X4M (FEI Company, USA).The produced biofilm was viewed with a SEM/EDS system (FEI Quanta 400FEG ESEM/EDAX Genesis X4M, FEI Company, USA) in a high-vacuum mode at 20 kV.
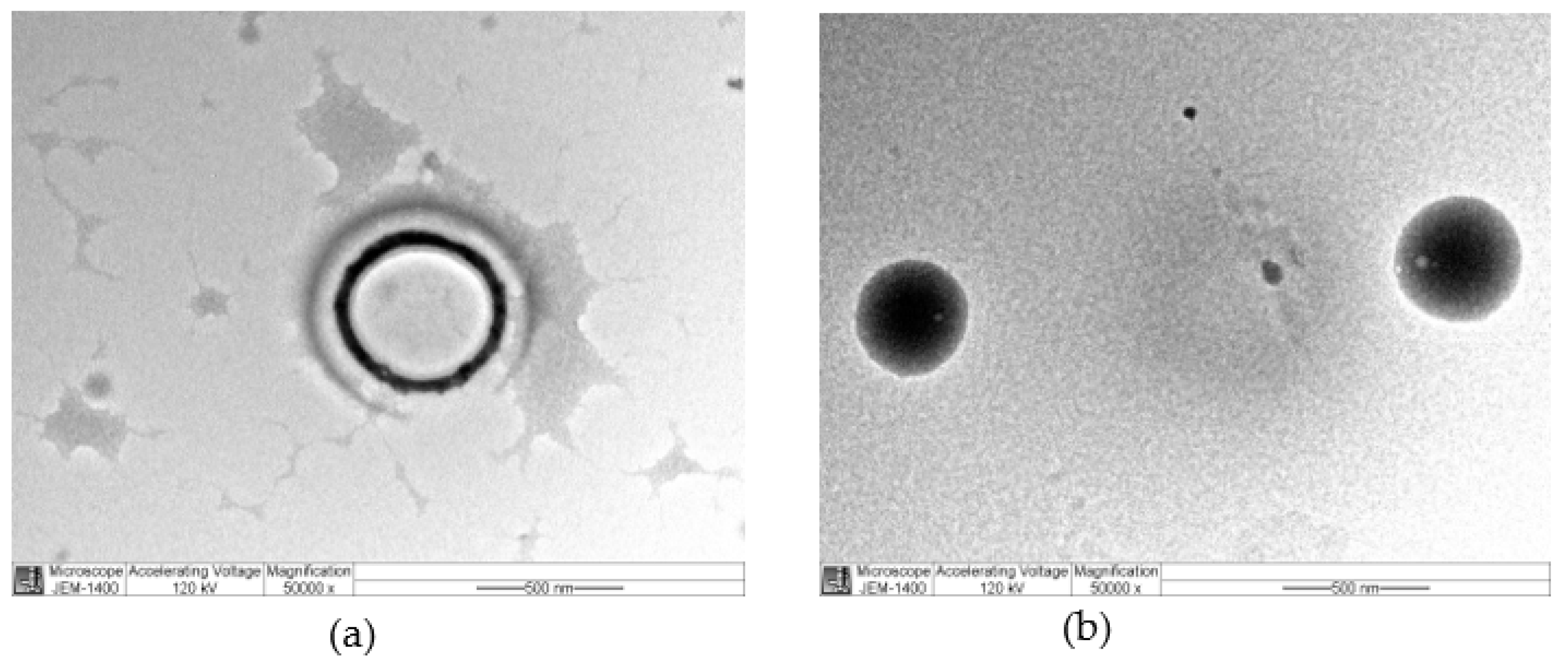
Figure 1.
TEM images: (a) blank ChNPs and; (b) mBTL-loaded ChNPs.
Figure 1.
TEM images: (a) blank ChNPs and; (b) mBTL-loaded ChNPs.
Figure 2.
In-vitro release profile of free mBTL.
Figure 2.
In-vitro release profile of free mBTL.
Figure 3.
The effect of free mBTL (Lane (a)) The effect of mBTL-loaded-ChNPs (Lane (b)) investigated using wild type S. aureus, MRSA, and different staphylococcus QS mutants; NE1532 (AgrA), NE95 (AgrB), NE873 (AgrC). All experiment performed three times in triplicate.
Figure 3.
The effect of free mBTL (Lane (a)) The effect of mBTL-loaded-ChNPs (Lane (b)) investigated using wild type S. aureus, MRSA, and different staphylococcus QS mutants; NE1532 (AgrA), NE95 (AgrB), NE873 (AgrC). All experiment performed three times in triplicate.
Figure 4.
Anti-virulence effect of Loaded-mBTL against Biofilm using wild type Staphylococcus aureus, MRSA and QS mutants, NE1532 (AgrA), NE95 (AgrB) and NE873 (AgrC).
Figure 4.
Anti-virulence effect of Loaded-mBTL against Biofilm using wild type Staphylococcus aureus, MRSA and QS mutants, NE1532 (AgrA), NE95 (AgrB) and NE873 (AgrC).
Figure 5.
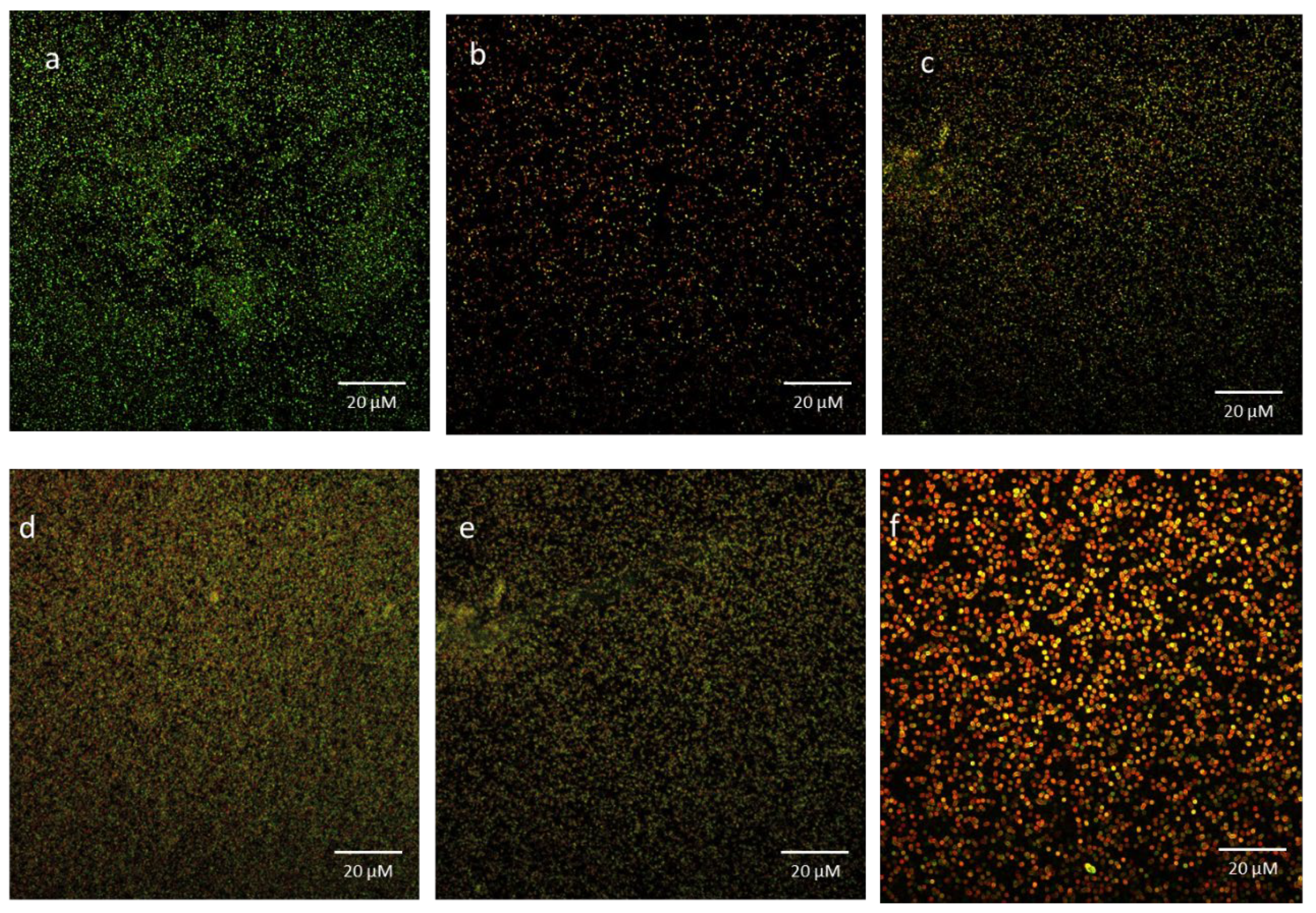
CLSM of Baclight®️ Live/Dead®️ (Syto-9 and PI) stained bacterial cells in absence and presence of m-BTL-ChNPs. The Killing impact of m-BTL in comparison the control group is depicted: (a) shows the control group bacterial cells in absence of m-BTL, the green color indicates 98% living cells.; (b-e) bacterial cells treated with m-BTL-ChNPs demonstrated change in cell viability, as evidenced by the appearance of the red/yellow color that indicate dead cells, as well as a change in the morphology of the bacterial cells; (f) Demonstrates that overtime, 92% of the bacterial cells have died.
Figure 5.
CLSM of Baclight®️ Live/Dead®️ (Syto-9 and PI) stained bacterial cells in absence and presence of m-BTL-ChNPs. The Killing impact of m-BTL in comparison the control group is depicted: (a) shows the control group bacterial cells in absence of m-BTL, the green color indicates 98% living cells.; (b-e) bacterial cells treated with m-BTL-ChNPs demonstrated change in cell viability, as evidenced by the appearance of the red/yellow color that indicate dead cells, as well as a change in the morphology of the bacterial cells; (f) Demonstrates that overtime, 92% of the bacterial cells have died.
Figure 6.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of a) untreated S. aureus, Spherical shaped cells appears in clusters, biofilm is shown as dense extracellular matrix surrounding the cells., b) untreated methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), biofilm matrix appears as a dense network of fibres that surround the MRSA cells and connect them to each other., c) Untreated Agr A mutant, shows alteration in cell morphology, the cells appears irregular with a change in surface structure appeared in capsule like formation., d) Untreated Agr B mutant, the biofilm looks thick (white shadow) and more surrounding bacterial cells., e) Untreated Agr C mutant, biofilm appears more packed over the bacterial cells., f) S. aureus treated with loaded mBTL-CNPs, the bacterial cells are separated from each other, and lack a visible extracellular matrix ., g) MRSA treated with loaded mBTL-CNPs, lacks a visible extracellular matrix., h) Agr A mutant treated with loaded mBTL-CNPs, shows a disorganization of biofilm separating from the cells., i) Agr B mutant treated with loaded mBTL-CNPs, disappearance of the thick biofilm seen in the control (d) with more visibility of bacterial cells., j) Agr C mutant treated with loaded mBTL-CNPs, irregular arrangement of biofilm. .
Figure 6.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of a) untreated S. aureus, Spherical shaped cells appears in clusters, biofilm is shown as dense extracellular matrix surrounding the cells., b) untreated methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), biofilm matrix appears as a dense network of fibres that surround the MRSA cells and connect them to each other., c) Untreated Agr A mutant, shows alteration in cell morphology, the cells appears irregular with a change in surface structure appeared in capsule like formation., d) Untreated Agr B mutant, the biofilm looks thick (white shadow) and more surrounding bacterial cells., e) Untreated Agr C mutant, biofilm appears more packed over the bacterial cells., f) S. aureus treated with loaded mBTL-CNPs, the bacterial cells are separated from each other, and lack a visible extracellular matrix ., g) MRSA treated with loaded mBTL-CNPs, lacks a visible extracellular matrix., h) Agr A mutant treated with loaded mBTL-CNPs, shows a disorganization of biofilm separating from the cells., i) Agr B mutant treated with loaded mBTL-CNPs, disappearance of the thick biofilm seen in the control (d) with more visibility of bacterial cells., j) Agr C mutant treated with loaded mBTL-CNPs, irregular arrangement of biofilm. .
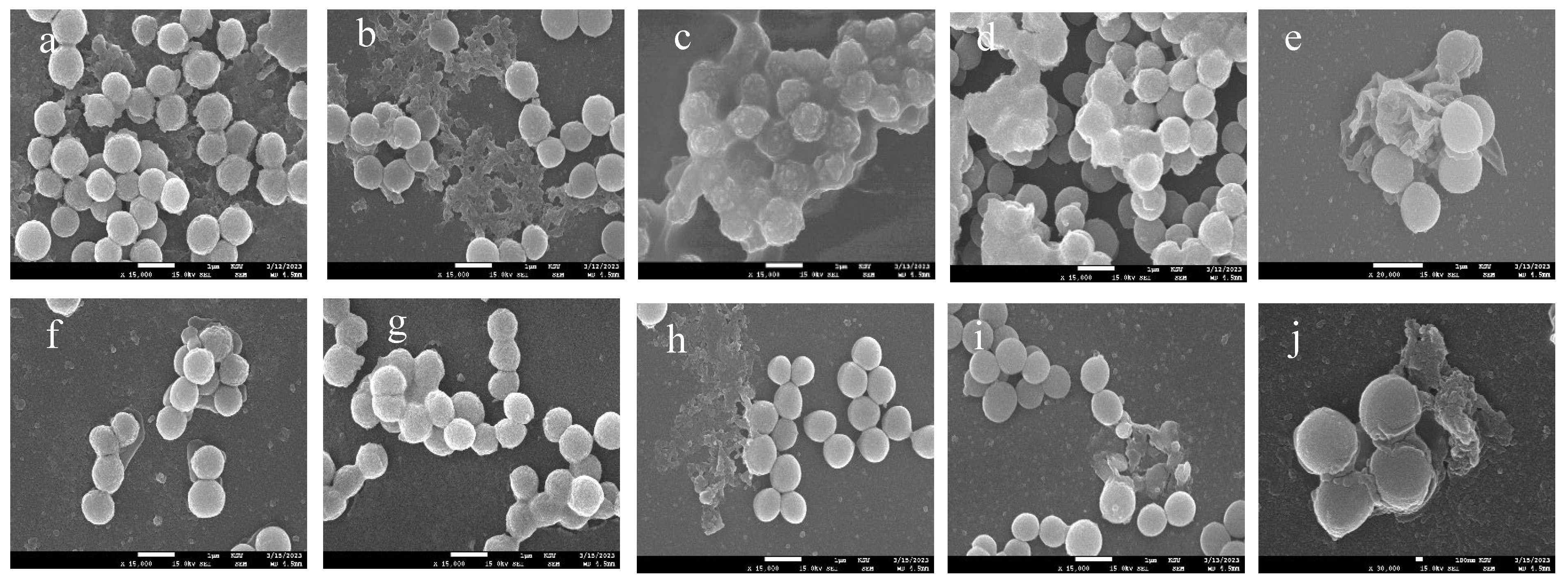

Figure 7.
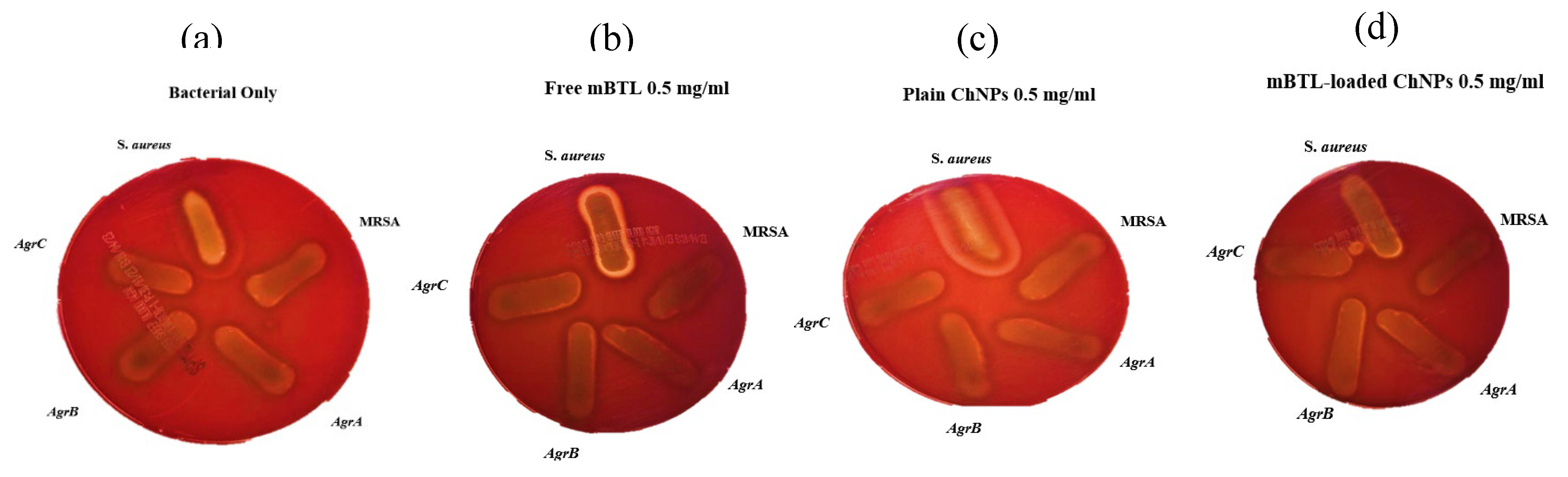
Hemolytic activity of S. aureus, MRSA, Agr A mutant, Agr B mutant, and Agr C mutant: (a) Untreated bacterial strains; (b) Treated with free mBTL, c) treated with plain ChNPs and; (d) Treated with mBTL-loaded ChNPs. No significant differences have been shown.
Figure 7.
Hemolytic activity of S. aureus, MRSA, Agr A mutant, Agr B mutant, and Agr C mutant: (a) Untreated bacterial strains; (b) Treated with free mBTL, c) treated with plain ChNPs and; (d) Treated with mBTL-loaded ChNPs. No significant differences have been shown.
Table 2.
Nanoparticles characteristics all data are presented as mean ±SD.
Table 2.
Nanoparticles characteristics all data are presented as mean ±SD.
| |
Blank ChNPs |
mBTL-ChNPs |
| Particle size |
158.5 ±1.3 |
283.9±13.55 |
| PDI |
0.327 ± 0.016 |
0.253±0.018 |
| Zeta potential |
33.8 ± 0.361 |
19.6±1.25 |
Table 1.
Description of Staphylococcus aureus strains in this study.
Table 1.
Description of Staphylococcus aureus strains in this study.
| Strain Name |
Abbreviation |
Description |
| Staphylococcus aureus |
S. aureus |
wild type |
| Methicillin-Resistance Staphylococcus aureus |
MRSA |
Methicillin-Resistance Staphylococcus aureus
|
| NE1532 |
AgrA |
4 P16 agrA accessory gene regulator protein A SAUSA300_1992 |
| NE95 |
AgrB |
1 O21 agrB accessory gene regulator protein B SAUSA300_1989 |
| NE873 |
AgrC |
3 B17 agrC accessory gene regulator protein C SAUSA300_1991 |