Submitted:
06 June 2023
Posted:
07 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction and Epidemiology: Atrial Fibrillation in Cancer Patients
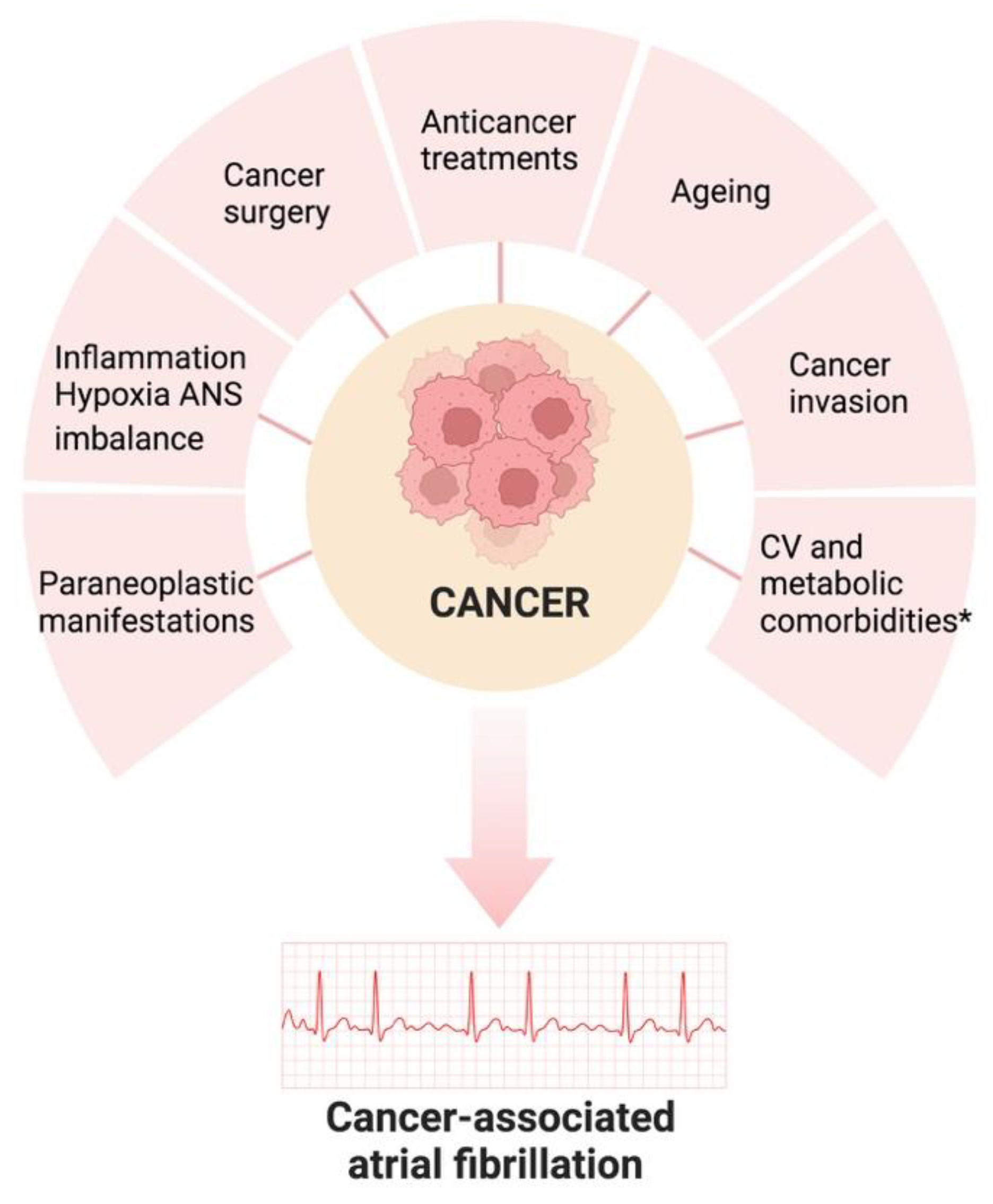
2. Risk Factors and Pathogenesis of Atrial Fibrillation in Cancer Patients
3. Management of Atrial Fibrillation in the Setting of Cancer (Rate and Rhythm Control)
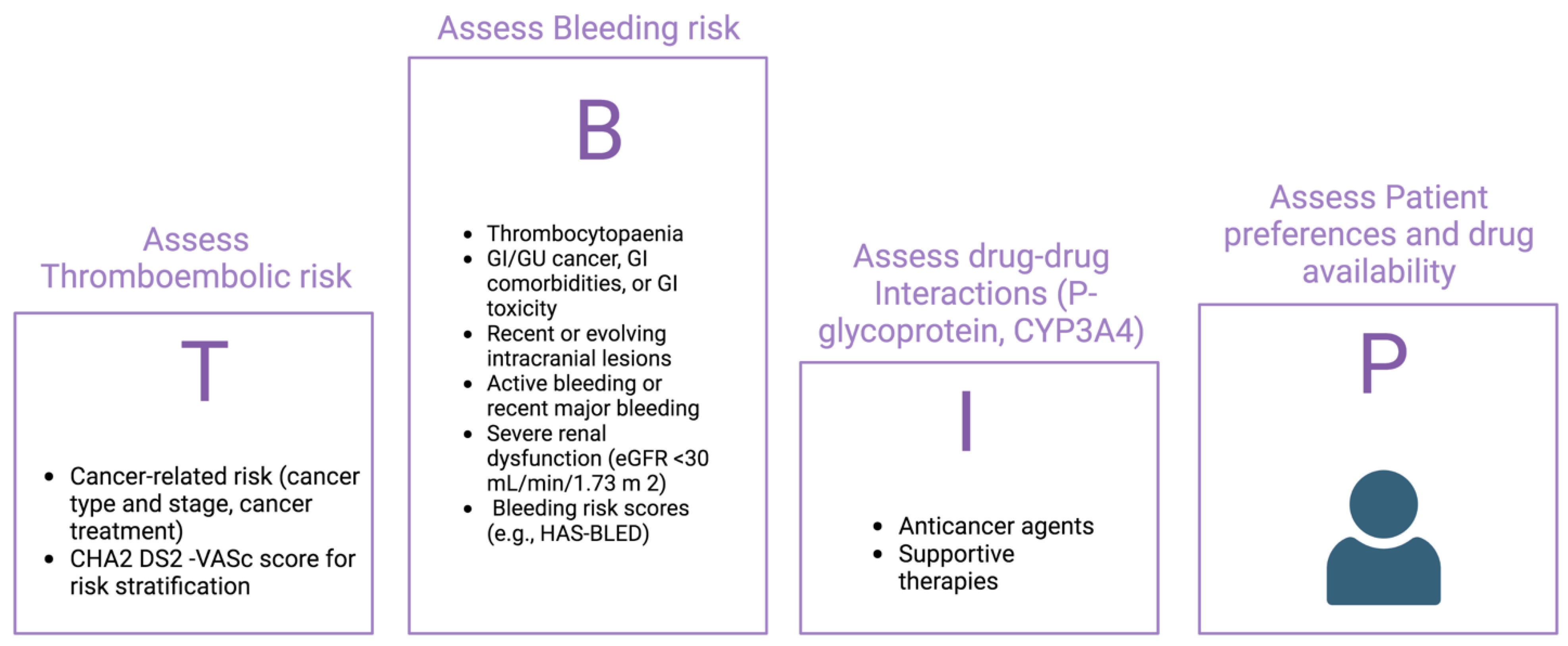
4. Anticoagulant Treatment: What to Do?
Risk Benefit Decision about Anticoagulation: Ischaemic and Bleeding Risck
5. Choice of Anticoagulant Therapy
6. Conclusions
References
- Lyon, A.R.; Lyon, A.R.; López-Fernández, T.; López-Fernández, T.; Couch, L.S.; Couch, L.S.; Asteggiano, R.; Asteggiano, R.; Aznar, M.C.; Aznar, M.C.; et al. 2022 ESC Guidelines on cardio-oncology developed in collaboration with the European Hematology Association (EHA), the European Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (ESTRO) and the International Cardio-Oncology Society (IC-OS). Eur. Hear. J. 2022, 43, 4229–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madnick, D.L.; Fradley, M.G. Atrial Fibrillation and Cancer Patients: Mechanisms and Management. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2022, 24, 1517–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boriani, G.; Menna, P.; Morgagni, R.; Minotti, G.; Vitolo, M. Ibrutinib and Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Focus on Atrial Fibrillation and Ventricular Tachyarrhythmias/Sudden Cardiac Death. Chemotherapy 2022, 68, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Neal, W.T.; Lakoski, S.G.; Qureshi, W.; Judd, S.E.; Howard, G.; Howard, V.J.; Cushman, M.; Soliman, E.Z. Relation Between Cancer and Atrial Fibrillation (from the REasons for Geographic And Racial Differences in Stroke Study). Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 115, 1090–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ay, C.; Grilz, E.; Nopp, S.; Moik, F.; Königsbrügge, O.; Klimek, P.; Thurner, S.; Posch, F.; Pabinger, I. Atrial fibrillation and cancer: prevalence and relative risk from a nationwide study. Res. Pr. Thromb. Haemost. 2023, 7, 100026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Chen, L.; Lin, Z.; Wei, X.; Guo, W.; Yu, Y.; Wu, C.; Cao, Y.; He, J. Prevalence, trends, and outcomes of atrial fibrillation in hospitalized patients with metastatic cancer: findings from a national sample. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 5661–5670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guha, A.; Fradley, M.G.; Dent, S.F.; Weintraub, N.L.; Lustberg, M.B.; Alonso, A.; Addison, D. Incidence, risk factors, and mortality of atrial fibrillation in breast cancer: a SEER-Medicare analysis. Eur. Hear. J. 2021, 43, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.P.; Choi, E.-K.; Han, K.-D.; Jung, J.-H.; Park, S.H.; Ahn, H.-J.; Lim, J.-H.; Lee, S.-R.; Oh, S. Risk of Atrial Fibrillation According to Cancer Type. JACC: CardioOncology 2021, 3, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiani, I.; Colombo, A.; Bacchiani, G.; Cipolla, C.M.; Cardinale, D.M. Incidence, Management, Prevention and Outcome of Post-Operative Atrial Fibrillation in Thoracic Surgical Oncology. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmakis, D.; Parissis, J.; Filippatos, G. Insights Into Onco-Cardiology. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Fernández, T.; Martín-García, A.; Rabadán, I.R.; Mitroi, C.; Ramos, P.M.; Díez-Villanueva, P.; Cervantes, C.E.; Martín, C.A.; Salinas, G.L.A.; Arenas, M.; et al. Atrial Fibrillation in Active Cancer Patients: Expert Position Paper and Recommendations. 72. [CrossRef]
- Buza, V.; Rajagopalan, B.; Curtis, A.B. Cancer Treatment–Induced Arrhythmias. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.-F.; Chen, Y.-J.; Lin, Y.-J.; Chen, S.-A. Inflammation and the pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2015, 12, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.-L.; Kao, Y.-H.; Chen, S.-A.; Chen, Y.-J. Pathophysiology of cancer therapy-provoked atrial fibrillation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 219, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang X, Li X, Yuan M, et al. Anticancer therapy-induced atrial fibrillation: electrophysiology and related mechanisms. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:1058.
- Alexandre, J. , Moslehi, J. J., Bersell, K. R., Funck-Brentano, C., Roden, D. M., & Salem, J. E. (2018). Anticancer drug-induced cardiac rhythm disorders: Current knowledge and basic underlying mechanisms. Pharmacol Ther, 189, 89–103.
- Onaitis, M.; D'Amico, T.; Zhao, Y.; O'Brien, S.; Harpole, D. Risk Factors for Atrial Fibrillation After Lung Cancer Surgery: Analysis of The Society of Thoracic Surgeons General Thoracic Surgery Database. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2010, 90, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Lopetegui-Lia, N.; Al Malouf, C.; Almnajam, M.; Coll, P.P.; Kim, A.S. Atrial fibrillation in older adults with cancer. 19, 8. [CrossRef]
- Suter, T.M.; Ewer, M.S.; Suter, T.M.; Ewer, M.S. Cancer drugs and the heart: importance and management. Eur. Hear. J. 2012, 34, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butany, J.; Leong, S.W.; Carmichael, K.; Komeda, M. A 30-year analysis of cardiac neoplasms at autopsy. Can. J. Cardiol. 2005, 21, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bussani R, De-Giorgio F, Abbate A, Silvestri F. Cardiac metastases. J Clin Pathol. 2: 2007;60(1), 2007.
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, J.-A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, A.R.; López-Fernández, T.; Couch, L.S.; Asteggiano, R.; Aznar, M.C.; Bergler-Klein, J.; Boriani, G.; Cardinale, D.; Cordoba, R.; Cosyns, B.; et al. 2022 ESC Guidelines on cardio-oncology developed in collaboration with the European Hematology Association (EHA), the European Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (ESTRO) and the International Cardio-Oncology Society (IC-OS). Eur. Hear. J. - Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 23, e333–e465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heist EK, Mansour M, Ruskin JN. Rate control in atrial fibrillation: targets, methods, resynchronization considerations. Circulation. 2011 Dec 13;124(24):2746-55.
- Echt, D.S.; Ruskin, J.N. Use of Flecainide for the Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2020, 125, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammann, F.; Gotta, V.; Conen, K.; Medinger, M.; Cesana, P.; Rochlitz, C.; Taegtmeyer, A.B. Pharmacokinetic interaction between taxanes and amiodarone leading to severe toxicity. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 83, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su VY, Hu YW, Chou KT, Ou SM, Lee YC, Lin EY, Chen TJ, Tzeng CH, Liu CJ. Amiodarone and the risk of cancer: a nationwide population-based study. Cancer. 2013 ;119(9):1699-705. 1 May.
- Tamargo, J.; Caballero, R.; Delpón, E. Cancer Chemotherapy and Cardiac Arrhythmias: A Review. Drug Saf. 2015, 38, 129–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suter TM, Ewer MS. Cancer drugs and the heart: importance and management. Eur Heart J. 2013 Apr;34(15):1102-11.
- Kanmanthareddy A, Vallakati A, Reddy Yeruva M, Dixit S, DI Biase L, Mansour M, Boolani H, Gunda S, Bunch TJ, Day JD, Ruskin JN, Buddam A, Koripalli S, Bommana S, Natale A, Lakkireddy D. Pulmonary vein isolation for atrial fibrillation in the postpneumonectomy population: a feasibility, safety, and outcomes study. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2015 Apr;26(4):385-389.
- Chatterjee NA, Upadhyay GA, Ellenbogen KA, McAlister FA, Choudhry NK, Singh JP. Atrioventricular nodal ablation in atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2012 Feb;5(1):68-76.
- Patell, R.; Gutierrez, A.; Rybicki, L.; Khorana, A.A. Usefulness of CHADS2 and CHA2DS2-VASc Scores for Stroke Prediction in Patients With Cancer and Atrial Fibrillation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2017, 120, 2182–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastori, D.; Marang, A.; Bisson, A.; Menichelli, D.; Herbert, J.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Fauchier, L. Thromboembolism, mortality, and bleeding in 2,435,541 atrial fibrillation patients with and without cancer: A nationwide cohort study. Cancer 2021, 127, 2122–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’neal, W.T.; Claxton, J.S.; Sandesara, P.B.; MacLehose, R.F.; Chen, L.Y.; Bengtson, L.G.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Norby, F.L.; Lutsey, P.L.; Alonso, A. Provider Specialty, Anticoagulation, and Stroke Risk in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation and Cancer. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 1913–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostolakis S, Lane DA, Guo Y, et al. Performance of the HEMORR 2 HAGES, ATRIA, and HAS-BLED bleeding risk-prediction scores in nonwarfarin anticoagulated atrial fibrillation patients. J Am Coll Cardiol 2013;61:386–7.
- Angelini, D.E.; Radivoyevitch, T.; McCrae, K.R.; Khorana, A.A. Bleeding incidence and risk factors among cancer patients treated with anticoagulation. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, A.R.; Lyon, A.R.; López-Fernández, T.; López-Fernández, T.; Couch, L.S.; Couch, L.S.; Asteggiano, R.; Asteggiano, R.; Aznar, M.C.; Aznar, M.C.; et al. 2022 ESC Guidelines on cardio-oncology developed in collaboration with the European Hematology Association (EHA), the European Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (ESTRO) and the International Cardio-Oncology Society (IC-OS). Eur. Hear. J. 2022, 43, 4229–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.T.; Hellkamp, A.S.; Becker, R.C.; Berkowitz, S.D.; Breithardt, G.; A A Fox, K.; Hacke, W.; Halperin, J.L.; Hankey, G.J.; Mahaffey, K.W.; et al. Efficacy and safety of rivaroxaban vs. warfarin in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation and a history of cancer: observations from ROCKET AF. Eur. Hear. J. - Qual. Care Clin. Outcomes 2018, 5, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melloni, C.; Dunning, A.; Granger, C.B.; Thomas, L.; Khouri, M.G.; Garcia, D.A.; Hylek, E.M.; Hanna, M.; Wallentin, L.; Gersh, B.J.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Apixaban Versus Warfarin in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and a History of Cancer: Insights from the ARISTOTLE Trial. Am. J. Med. 2017, 130, 1440–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanola, C.L.; Ruff, C.T.; Murphy, S.A.; Jin, J.; Duggal, A.; Babilonia, N.A.; Sritara, P.; Mercuri, M.F.; Kamphuisen, P.W.; Antman, E.M.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Edoxaban in Patients With Active Malignancy and Atrial Fibrillation: Analysis of the ENGAGE AF-TIMI 48 Trial. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2018, 7, e008987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, A.C.; Kumar, A.; Mccray, W.; Tetewsky, S.; Parone, L.; Sridhara, S.; Prakash, M.P.H.; Tse, G.; Liu, T.; Kanwar, N.; et al. Superior safety of direct oral anticoagulants compared to Warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation and underlying cancer: a national veterans affairs database study. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 706–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Norby, F.L.; Datta, Y.H.; Lutsey, P.L.; MacLehose, R.F.; Chen, L.Y.; Alonso, A. Comparative effectiveness of direct oral anticoagulants and warfarin in patients with cancer and atrial fibrillation. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deitelzweig, S.; Keshishian, A.V.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, A.; Dhamane, A.D.; Luo, X.; Klem, C.; Ferri, M.; Jiang, J.; Yuce, H.; et al. Effectiveness and Safety of Oral Anticoagulants Among Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation Patients With Active Cancer. JACC: CardioOncology 2021, 3, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariani, M.V.; Magnocavallo, M.; Straito, M.; Piro, A.; Severino, P.; Iannucci, G.; Chimenti, C.; Mancone, M.; Della Rocca, D.G.; Forleo, G.B.; et al. Direct oral anticoagulants versus vitamin K antagonists in patients with atrial fibrillation and cancer a meta-analysis. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2020, 51, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Zhu, D.; Xu, X.; Shen, W.; Wang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, G.; Wu, Q. Efficacy and safety of oral anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation patients with cancer—a network meta-analysis. Hear. Fail. Rev. 2019, 25, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, A.S.; Patel, A.; Khawaja, M.; Chen, C.; Zheng, H.; Kaczmarek, J.; Gao, F.; Karimzad, K.; Song, J.; Koutroumpakis, E.; et al. Outcomes by Class of Anticoagulant Use for Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation in Patients With Active Cancer. JACC: CardioOncology 2022, 4, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, H.B.; An, H.; Ardeshirrouhanifard, S.; Raji, M.A.; Alexander, G.C.; Segal, J.B. Comparative Effectiveness and Safety of Direct Oral Anticoagulants Versus Warfarin Among Adults With Cancer and Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardeshirrouhanifard, S.; An, H.; Goyal, R.K.; Raji, M.A.; Segal, J.B.; Alexander, G.C.; Mehta, H.B. Use of oral anticoagulants among individuals with cancer and atrial fibrillation in the United States, 2010–2016. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2022, 42, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delluc, A.A.; Wang, T.; Yap, E.; Ay, C.; Schaefer, J.; Carrier, M.; Noble, S. Anticoagulation of cancer patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation receiving chemotherapy: Guidance from the SSC of the ISTH. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 17, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boriani, G.; Lee, G.; Parrini, I.; Lopez-Fernandez, T.; Lyon, A.R.; Suter, T.; Van der Meer, P.; Cardinale, D.; Lancellotti, P.; Zamorano, J.L.; et al. Anticoagulation in patients with atrial fibrillation and active cancer: an international survey on patient management. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2020, 28, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, A.; Bottino, R.; D’andrea, A.; Russo, V. Direct Oral Anticoagulants for Stroke Prevention in Special Populations: Beyond the Clinical Trials. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosarla, R.C.; Vaduganathan, M.; Qamar, A.; Moslehi, J.; Piazza, G.; Giugliano, R.P. Anticoagulation Strategies in Patients With Cancer. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 1336–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Miranda. J.F.P.; Takahashi, T.; Iwamoto, F.; Yamashiro, S.; Samano, E.; Macedo, A.V.S.; Ramacciotti, E. Drug–Drug Interactions of 257 Antineoplastic and Supportive Care Agents With 7 Anticoagulants: A Comprehensive Review of Interactions and Mechanisms. Clin. Appl. Thromb. 2020, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study design | Efficacy outcomes | Safety outcomes | Participants | AF patients with cancer on NOAC, n (%) | NOAC prescribed (n) | Type of cancer | Follow-up, y or m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Post hoc analysis from ARISTOTLE trial (39) | Stroke, systemic embolism. Secondary endpoints included myocardial infarction and death |
Major bleeding, (ISTH criteria) | 18,183 patients with AF, a total of 615 patients had a history of cancer at baseline | 615 (49.8) | Apixaban | Prostate (29) Breast (16) Colon (11) Bladder (7) Gastric (2) Lung (3) Melanoma (6) Others (26) |
1.8 |
| Post hoc analysis from ROCKET-AF trial (38) | Stroke, Systemic Embolism | Composite of major and NMCR bleeding events. | 14 264 patients with AF, a total of 640 patients (4.5%) had a history of cancer at baseline | 640 | Rivaroxaban | Prostate cancer (28.6) Colorectal cancer (16.1) Breast cancer (14.7) Genitourinary cancer (12.2) Others (34.4) |
1.9 |
| Post hoc analysis from ENGAGE- AF TIMI 48 (40) | composite of stroke (ischemic or hemorrhagic) or SEE | major bleeding, (ISTH criteria) | 21 105 patients with atrial fibrillation, of which 1153 patients (5.5%) had also cancer | 1153 (5.5) | Edoxaban | Gastrointestinal (20.6%), prostate (13.6%), lung (11.1%), bladder (7.7%), breast (6.7%) |
2.8 |
| Retrospective observational study performed utilizing the national VA* Healthcare data (41) | all-cause mortality, ischemic stroke | hemorrhagic stroke | 654,732 patients who received care at the VA from 2010 to 2015 and were diagnosed with active cancer and AF | 196,521 (30) | Not specified | Not specified | 1.0 |
| Retrospective analysis of a large health care claims database (42) | Not severe bleeding events, ischemic stroke, and VTE (secondary outcomes) | severe bleeding events (primary outcome) | 532 743 AF patients with cancer | 41 036 (7) | Rivaroxaban, Apixaban, Dabigatran | Genitourinary (29.7) Breast (20.9) Lung (11.1) Gastrointestinal (11.6) Gyneco-oncological (2.4) Hematological (9.4) Other (14.9) |
|
| retrospective cohort study (46) | Cerebrovascular accident | Gastrointestinal bleeding, intracranial hemorrhage | 1,133 patients with active cancer and NVAF |
842 (74.3%) | Apixaban, Rivaroxaban, Dabigatran, Edoxaban | Breast Genitourinary Gastrointestinal Hematologic Lung Skin |
4.4 |
| retrospective cohort study (47) | ischemic stroke or systemic embolism | major bleeding | 7675 patients with active cancer and NVAF |
4244 (55.3%) | Apixaban, Rivaroxaban, Dabigatran |
Prostate (22.2) Breast (19.6) Lung (19.3) Colorectal (14.5) |
7.7 (months) |
| A retrospective observational subgroup analysis of the ARISTOPHAS (43) | time to first stroke/SE | time to first major bleeding | 466,991 of which 9% (40271) had also active cancer | 24900 | Apixaban, Rivaroxaban, Dabigatran |
prostate (29%), female breast (17%), genitourinary (14%), lung (13%) |
6-8 months |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





