1. Introduction
South Africa (population of ~60.6 million people[
1] has one of the highest HIV and TB prevalence rates in the world: 8.45 million people live with HIV (13.9% of the population)[
1] and a TB incident rate of 513/100 000 is reported[
2]. Healthcare is funded through the government for 84 % of the population (public sector) and the remainder is funded privately through individuals, medical schemes, and insurance companies. Laboratory services are provided through networks of private and public sector laboratories, with the latter comprising 256 National Health Laboratory Service (NHLS) facilities positioned centrally and at district level across the nine provinces.
On 5th March 2020, South Africa reported their first case of COVID19 [
3] and both public and private laboratories’ [
4] virology services had to rapidly scaled their SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid amplification technology (NAAT), the primary method of diagnosing infection with SARS-CoV-2 [
5,
6], Within one month, however, the country’s SARS-CoV-2 testing demands required expanding molecular testing to the national priority program (NPP) of the NHLS. The NPP has capacity for 10 million molecular tests/annum, which predominantly support HIV viral load (VL) monitoring [
7] and TB molecular diagnostics[
8]. Testing is performed in 17 VL laboratories (11 also provide HIV early infant diagnostics) equipped with cobas
® [Roche Molecular, Pleasanton, CA, USA] and Alinity m [Abbott Molecular, Des Plains, IL, USA] platforms) and 175 GeneXpert (Cepheid, Sunnyvale, CA, USA) testing laboratories, which service ~3800 primary health care facilities
. Test kit demands for the NPP’s closed platforms, (until 2021) however, could not be met due to the inability of suppliers to ship to South Africa as demands escalated in their countries of manufacture. SARS-CoV-2 testing therefore had to expand to a third network of laboratories. This involved a SARS-CoV-2 surge program initiated by the South African Medical Research Council (SAMRC)[
9] with solidarity funding to support selected academic laboratories, councils, and research institutes to conduct SARS-CoV-2 testing. A rapid laboratory electronic assessment tool was developed to collect information on site location, ISO 15189 status, Health Professions Council of South Africa status of key staff, SARS-CoV-2 readiness (available testing platforms) and implemented quality management systems (trained staff, use of electronic requisition forms, use of barcodes, PPE stock, kit and supply storage and procurement processes, laboratory information (LIS) and IT support on-site). Thirty-two sites were assessed by the NHLS’ Quality Assurance Division and eleven were selected for SARS-CoV-2 surge testing. Testing in these laboratories commenced in June 2020 and continued until January 2021.
Test results (SARS-CoV-2 detected, SARS-CoV-2 not detected and test unsuccessful) from the private laboratories, the surge testing sites and the NHLS (including NPP) were reported as cases by the National Institute of Communicable Diseases (NICD), who provide central COVID-19 epidemiology and surveillance reporting nationally[
10] and regionally[
11]. Overall, the private laboratories performed ~55% of South Africa’s SARS-CoV-2 diagnostics (as reported in week 34 of 2021[
12]). A link was also established to the genomics network with five laboratories identified across South Africa capable of performing SARS-CoV-2 sequencing[
13]. Specimens were shared between the diagnostic laboratories and genomics group, to enable identification of variants of concern (VOC).
In addition to central monitoring of daily test volumes, qualitative test results and indicators to track changes in South Africa’s COVID19 epidemic, the NHLS centrally collected SARS-CoV-2 cycle threshold (Ct) values for each test performed in their laboratories that identified the presence of SARS-CoV-2. A Ct value is intrinsic to PCR assays and is a measure of the amount of target nucleic acid in the specimen[
14]. SARS-CoV-2 test manufacturers provide information on which SARS-CoV-2 gene regions their assays target and provide the Ct values in the test output comma separator value (.csv) files. Through the NHLS’ single national LIS, TrakCare (InterSystems, Cambridge, MA), all SARS-CoV-2 diagnostic systems were interfaced, and Ct values accessed from the central data warehouse (Netezza, IBM, USA-based server in Johannesburg) for analysis.
How the Ct values from the ensemble of closed and open testing platforms and assays in the NHLS laboratories was used for continuous quality monitoring (CQM) of diagnostic assay performance is highlighted.
2. Materials and Methods
Specimens received in the NHLS laboratories for SARS-CoV-2 testing were collected using nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal swabs. These were transported dry during shortages of universal transport medium (UTM) and were cut and placed into phosphate buffered saline upon arrival and processed according to standard operating procedures. Specimens were registered in the LIS and tested across 205 NHLS laboratories using the locally available platforms and testing protocols. Test results, including Ct values (when SARS-CoV-2 was detected) were accessed from the CDW through an extract, transform and load process to generate a .csv file for analysis. Data did not include patient unique identifiers, and hence analyses performed included longitudinal follow-up testing. Ethics approval was obtained from the University of the Witwatersrand Human Research Ethics Committee (number M160978), Johannesburg, South Africa. Data files were analyzed and data visualized using STATA 14 (StataCorp. 2015, Stata Statistical Software: Release 14. College Station, TX: StataCorp LP) and Tableau 2020.3 (Tableau Software. 2020. Seattle, WA: Tableau). Bar charts depicted daily positive test numbers and line graphs represented changes in median Ct values within a 28-day centered moving average.
Ten SARS-CoV-2 molecular assays were recorded in the CDW database, however, 93% of tests were performed on six assays, which form the focus of this analysis. These assays are classified into open laboratory testing platforms: Allplex™ SARS-CoV-2 (SeeGene Inc., Seoul, Korea); TaqPath™ COVID-19 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and closed platforms: cobas
® SARS-CoV-2 (Roche Molecular, Pleasanton, CA, USA); Xpert
® Xpress SARS-CoV-2 (Cepheid, Sunnyvale, CA, USA), RealTime SARS CoV2 (Abbott Molecular, Des Plains, IL, USA) and Alinity m (Abbott Molecular, Des Plains, IL, USA).
Table 1 details the assay gene targets and range in Ct values when a specimen is reported positive for the detection of SARS-CoV-2.
3. Results
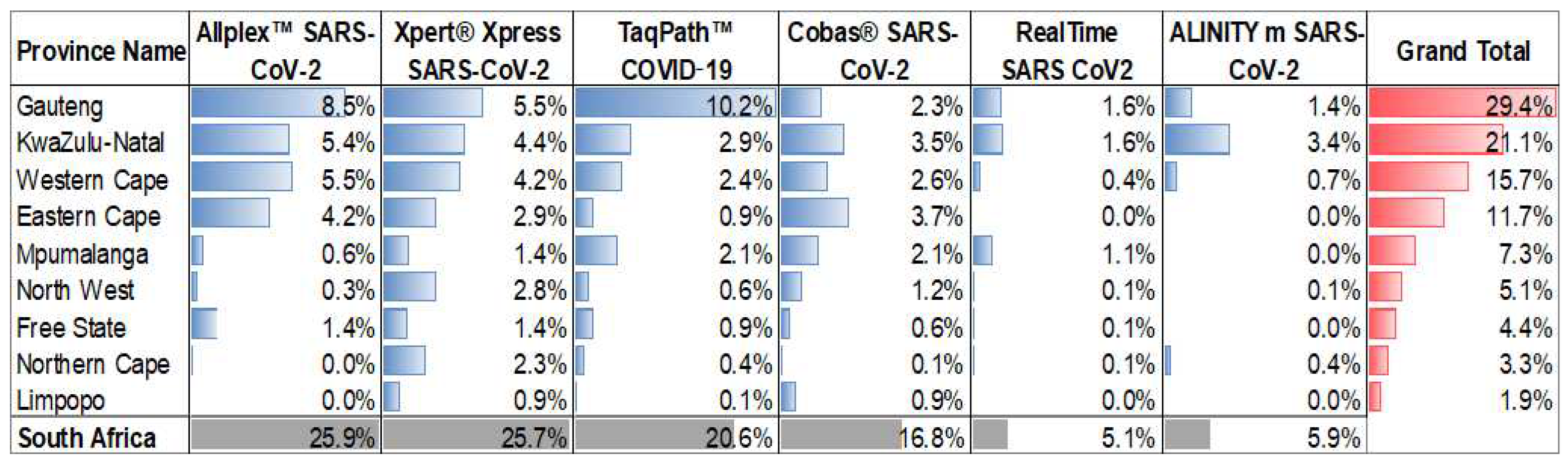
The six SARS-CoV-2 assays utilized by the NHLS were implemented at different times during the pandemic and their uptake at a province level varied as outlined in
Figure 1. Across 36 months of testing (March 2020 – March 2023), the Allplex™ SARS-CoV-2 and the Xpert
® Xpress SARS-CoV-2 contributed 48% of the test results. The Xpert
® Xpress SARS-CoV-2 assay is the only testing platform used in all provinces, which is a consequence of the placement of this platform by the NPP for use in the national TB diagnostic program. In contrast, the TaqPath™ COVID-19 assay was predominantly only used in the Gauteng Province. The RealTime SARS CoV2 and Alinity m assays only contributed ~10% towards testing, despite these platforms used for the HIV diagnostics program of NPP. At least 66% of all testing was reported from the three most densely populated provinces (Gauteng, KwaZulu-Natal and the Western Cape).
A total of 8,573,872 tests were performed by NHLS laboratories during the study time period of which 1,572,098 (18.33%) reported the presence of SARS-CoV-2, and 1,497,669 (95.2%) included Ct values for their gene targets. The daily median Ct for each SARS-CoV-2 gene target for the open and closed platforms is described in the following sections. Common to all assays (and visualized across all plots), is the decrease in median Ct (increase in SARS-CoV-2 viral concentration) followed by an increase in SARS-CoV-2 positivity and vice versa when positivity rates decreased.
3.1. The NHLS SARS-CoV-2 Open Testing Platforms
3.1.1. Allplex™ SARS-CoV-2 (SeeGene)
The Allplex™ SARS-CoV-2 assay was the first test to be implemented by NHLS in March 2020 and contributed a national test count of 2,095,588 million tests (26%) after 36 months. Although this assay was used by all provinces, 91% of the results were generated from the Gauteng, Western Cape, KwaZulu-Natal and Eastern Cape provinces.
Figure 2 highlights that the
E-gene generated the lowest Ct values followed by the
RdRp and
N-gene Ct values. The changes in 28-day centered moving average of the median Ct for all three genes mirror each other except during South Africa’s third COVID19 wave, which peaked in July 2021. The
RdRp median Ct increased above the
N-gene Ct. This increase in Ct (reduced PCR performance) was reported to be a result of the B.1.617.2 (Delta) variant[
15] which had a highly conserved nonsynonymous mutation (G15451A) exclusively within the RdRp gene, and thereby negatively affecting the
RdRp PCR efficiency of the Allplex™ SARS-CoV-2 assay.
This was continuously monitored by calculating the relative change in Ct between RdRp and E and any test result where the Ct of RdRp-E >3.5 indicated the presence of the Delta variant. During the Delta wave, up to 62% of all positive specimens tested using the Allplex™ SARS-CoV-2 assay reported this phenomenon. No changes in this assays’ PCR efficiency were noted beyond the impact from the Delta variant, however, SeeGene introduced a new Allplex™ SARS-CoV-2 assay version that included the S-gene target, but this target is reported in the same PCR fluorescent channel as RdRp and therefore neither target’s PCR efficiency is discernable. Towards the end of the study period (March 2023), the Allplex™ SARS-CoV-2 testing volumes were reduced to ~42/day, making daily monitoring less reliable.
3.1.2. TaqPath™ COVID-19 (Thermo Fisher Scientific)
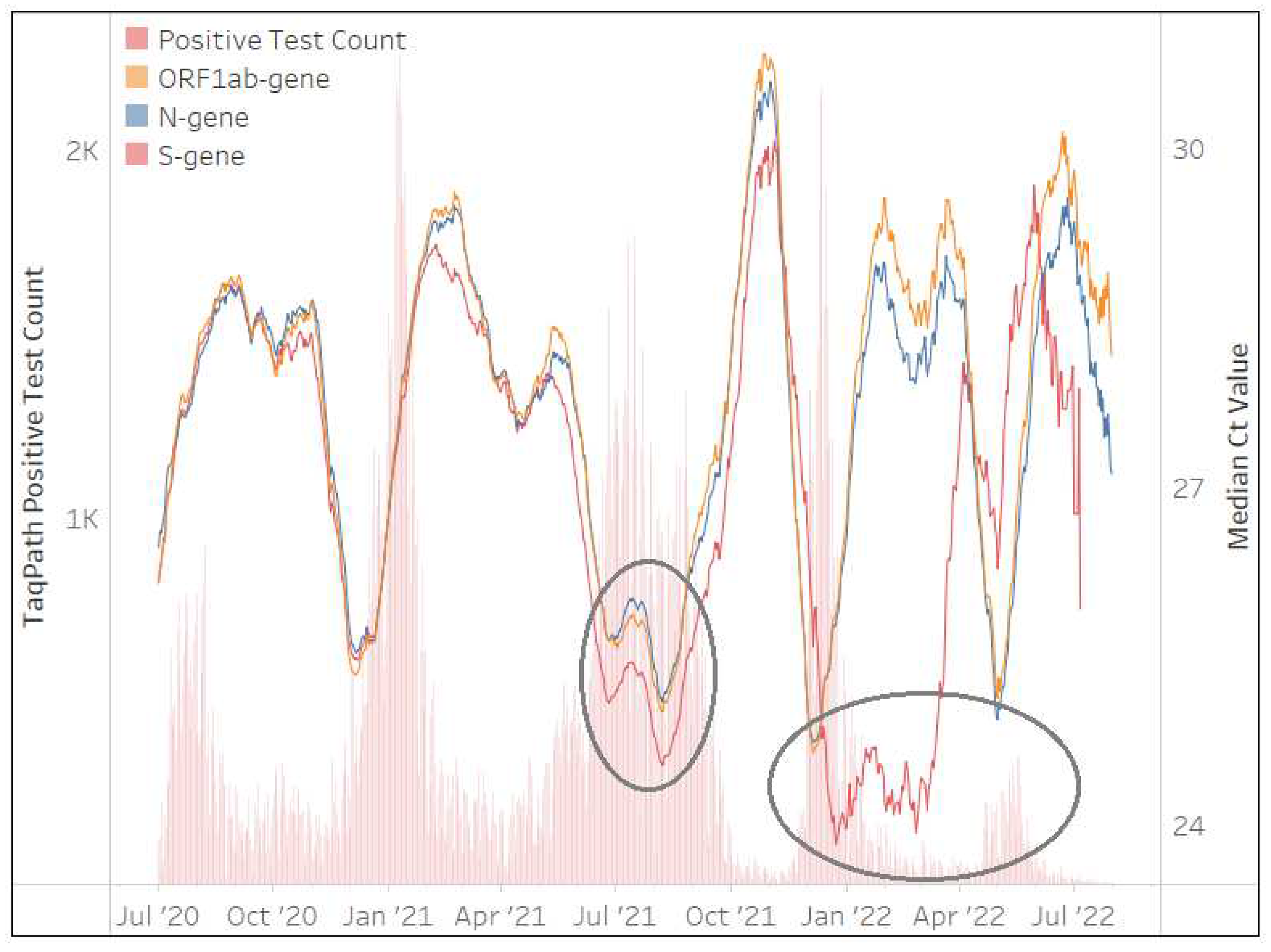
The TaqPath™ COVID-19 assay was implemented in May 2020 and contributed to 1,660,419 million tests (21%) performed by the NHLS. Implementation, however, was not national, and 50% of testing was performed in the Gauteng Province.
Figure 3 shows the Ct values of
ORF1ab,
N and
S-genes generally mirrored each other for the first 2 waves, however, the S-gene pattern changed during the 3rd, 4th and 5th waves, with the median Ct of the
S-gene target much lower than the
ORF1ab and
N-genes. This phenomenon was due to
S-gene target failure (SGTF)[
16], brought about by deletion of amino acids 69 and 70 in B.1.1.7 (Alpha) and B.1.1.529 (Omicron) spike genes. This yielded a distinct absent
S-gene and hence no amplification during PCR and Ct values reported as zero in the TaqPath™ COVID-19 .csv file, which contributed to an overall low median
S-gene Ct value. The TaqPath™ COVID-19 testing rates decreased to <4 tests/day at the end of March 2023, making continuous quality monitoring less reliable.
3.2. The NHLS SARS-CoV-2 Closed Testing Platforms
3.2.1. Xpert® Xpress SARS-CoV-2 (Cepheid)
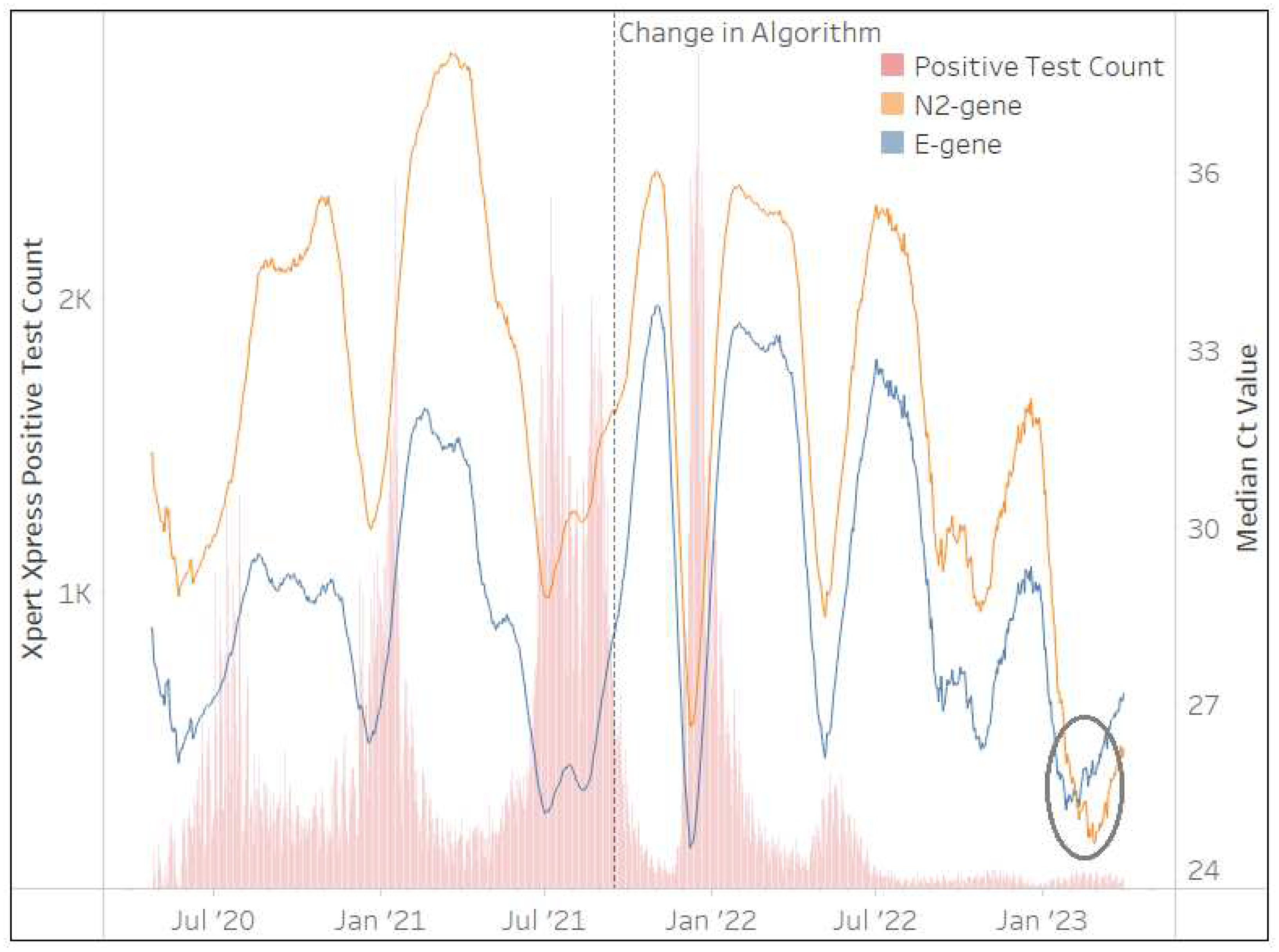
The Xpert
® Xpress SARS-CoV-2 assay was implemented by the NHLS in March 2020 and contributed to 2,073,844 million tests (26%) after 36 months. This assay was used in all provinces across South Africa, however, Gauteng (21%), KwaZulu-Natal (17%), and the Western Cape (16%) accounted for more than half (54%) of the total Xpert
® Xpress SARS-CoV-2 test results.
Figure 4 highlights a change in the NHLS’ testing algorithm implemented by their Xpert
® Xpress SARS-CoV-2 testing sites on 15th September 2021. Concerns were raised by the NHLS virology expert committee on reporting a positive SARS-CoV-2 result when Ct values of either or both gene targets approached the threshold of 45. The following algorithm was therefore implemented within the NHLS LIS: where a single
E or
N2 has a Ct>38 and where both
E and
N2 Ct>40, these specimens are reported as “inconclusive”
(internal memo Dr M.P. da Silva). This change is evident in
Figure 4 with greater mirroring (less variability in the Ct trends) between both gene targets beyond this date.
Figure 4 further shows that the
E-gene generated lower Ct values than the
N2-gene for 33 of the 36 months. Changes in the 28-day centered moving average of the median Ct for both the
E and
N2-genes mirror each other with the exception of the period after January 2023, where the median
E-gene Ct values increase. This phenomenon is due to XBB.1.5. VOC, which affects the
E-gene coverage dropping by 1% due to two mismatches (
personal communication from Cepheid medical affairs) that delay PCR hybridization. As the Xpert
® Xpress SARS-CoV-2 continues to be used in NHLS testing sites (400 tests/day at the end of March 2023), the proportion of specimens with
E-gene Ct>
N2-gene Ct can therefore be used to monitor the circulation of XBB.1.5. This was evident among 92% (28-day moving average) of Xpert
® Xpress SARS-CoV-2 test results at the end of March 2023.
3.2.2. cobas® SARS-CoV-2 (Roche Molecular)
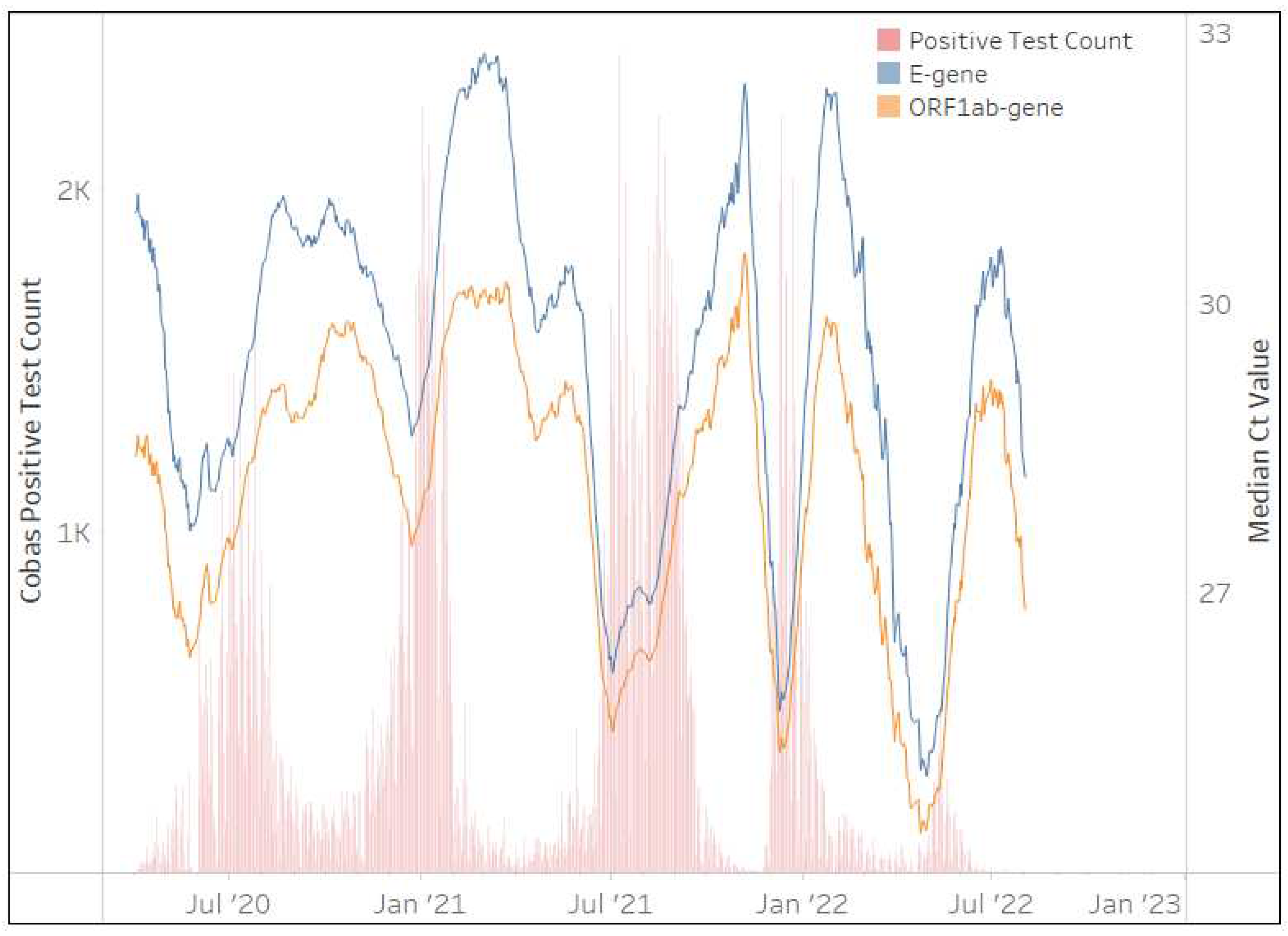
The cobas
® SARS-CoV-2 assay was implemented in April 2020 and contributed 1,357,991 million tests (17%) after 36 months to the NHLS’ test volumes. Although the assay was implemented across all provinces in South Africa; the Eastern Cape (22%), KwaZulu-Natal (21%), and the Western Cape (15%) contributed 60% of the total testing volumes.
Figure 5 clearly shows that changes in the 28-day centered moving average of the median Ct is perfectly aligned for both gene targets (
E and
ORF1ab). Their mirrored pattern remains throughout the 36 months of testing and this assay appears unaffected by any VOCs. SARS-CoV-2 testing on this platform however ceased in the NHLS in July 2022.
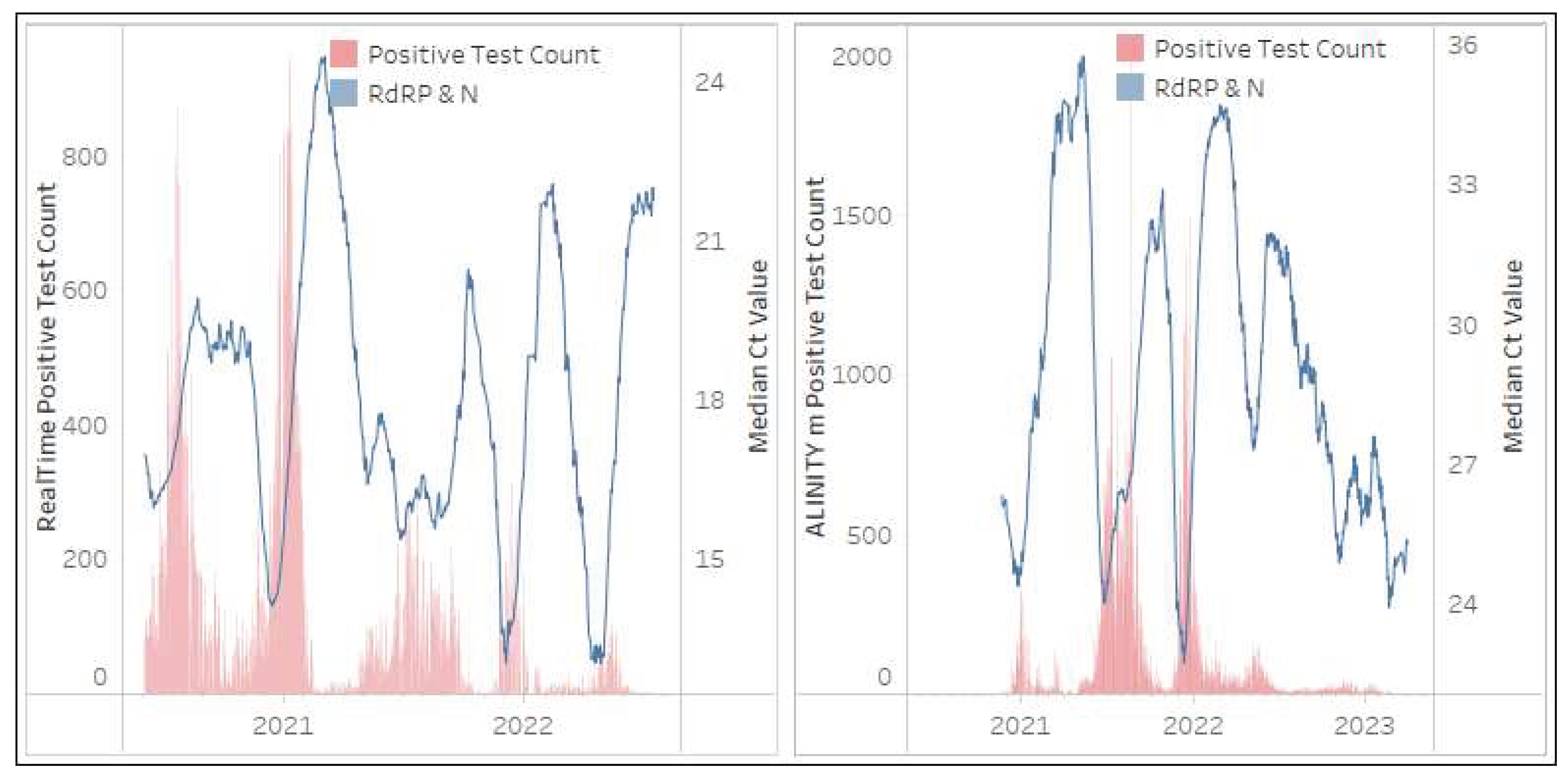
3.2.3. RealTime SARS CoV2 and ALINITY m SARS-CoV-2 (Abbott Molecular)
The RealTime SARS CoV2 and ALINITY m SARS-CoV-2 assays, from a single supplier, were implemented by the NHLS in May 2020 and November 2020 respectively. The RealTime SARS CoV2 assay contributed 409,654 tests (5%) while the ALINITY m SARS-CoV-2 assay contributed 479,536 tests (6%) to the NHLS’ national testing volumes during the 36 months. A significant portion (62% of RealTime SARS CoV2 tests and 81% of ALINITY m SARS-CoV-2) of these tests were conducted by two provinces (KwaZulu-Natal and Gauteng). Both these assays target the
RdRP and
N gene regions, however neither region can be distinguished by a Ct value as both targets fluoresce in a single channel as outlined in
Figure 6. SARS-CoV-2 testing continues to be reported on the ALINITY m SARS-CoV-2 platform (65 tests/day at the end of March 2023), however, testing was discontinued on the RealTime SARS CoV2 in July 2022.
4. Discussion
Laboratories are required to participate in external proficiency testing to monitor pre-analytical, analytical and post-analytical performance, however, after decades of quality indicators, a paradigm shift should be towards indicators of total quality[
17]. During large scale pandemic testing, such as during COVID19, external quality assessment programs were implemented [
18,
19,
20], however, these would not easily identify quality issues timeously. The South African NHLS approached this challenge by including the Ct values for each gene target of the SARS-CoV-2 tests employed for the diagnosis of COVID19 in their LIS interface. The Ct is a variable that correlates with the amount of target RNA in a specimen[
21], and during COVID19 the SARS-CoV-2 viral load in the respiratory tract was reported to align with an individual’s disease progression[
5,
22,
23,
24]. In this analysis, we showed that continuous quality monitoring of median Ct’s of SARS-CoV-2 gene targets at a national (population) level could rapidly identify changes in assay PCR gene target performance, due to genetic mutations of SARS-CoV-2 and assist in changing laboratory reporting algorithms. Analyses of the changes in Ct values over time could therefore be an additional parameter included in good laboratory practices’ quality management systems, and especially within the context of gene mutations that could impact molecular assay performance.
Although the CQM of Ct values across the gene targets and across assays was limited to only the NHLS testing laboratories (<50% of South Africa’s SARS-CoV-2 testing), 1,497,669 Ct values were analyzed over 36 months. This “big” data also reduced the impact of variables (central limit theorem) such as specimen quality, PCR inhibitory substances, variable transport media, variable front-end extraction or extraction-free technologies and NAAT reaction volume, to name a few, that is reported as complexities in SARS-CoV-2 laboratory testing[
25].
Our findings show that of the six SARS-CoV-2 molecular assays implemented at scale across the NHLS, the Ct value analysis by gene target rapidly identified three assays’ targets affected by VOCs: (i) the B.1.617.2 (Delta) variant affected the Allplex™ SARS-CoV-2 assay in the
RdRp target region[
15]; (ii) the B.1.1.7 (Alpha) and the B.1.1.529 (Omicron) affected the TaqPath™ COVID-19 assay in the
S-gene target region[
26]; and (iii) the XBB.1.5 affected the Xpert
® Xpress SARS-CoV-2 in the
E-gene target region. The cobas
® SARS-CoV-2 assay appeared not to be affected by circulating VOCs based on no changes identified in their gene target Ct value trends. The inability to distinguish the Ct values for the multiple gene targets in the RealTime SARS CoV2 and ALINITY m SARS-CoV-2 made the CQM less helpful in identifying changes in the assay quality potentially due to VOC but was a stable marker outlining the expected patterns in Ct change over the course of COVID19 that other assays could be compared. Despite several assays' gene target performance being affected by VOCs, their multiplex nature [
27] (at least two viral genes targeted to increase the probability to identify the virus at low viral load and in the presence of viral mutations), enabled the assays to continue being used as the primary diagnostic for patient care[
28,
29].
Through the Ct CQM, the loss or change in target performance was, however, also quickly identified as an advantage in monitoring the spread of VOC[
16,
26] in “near” real-time with only a two-day lag period between specimen receipt and authorization. This also included monitoring the recovery of Ct values of affected gene targets, with the best example shown by the TaqPath™ COVID-19 where the B.1.1.7 (Alpha) caused the SGTF during wave 3, which was however, rapidly replaced by the B.1.617.2 (Delta) variant and hence the TaqPath™ COVID-19
S-gene target performance could inform changes in circulating variants.
Although the NHLS’ multi-assay implementation approach was governed by test demands and availability of platforms and reagents, it did prove possible to monitor such a multi-assay program through the unique centralized LIS. This in turn also highlighted some limitations, such as the TaqPath™ COVID-19 assay not being implemented nationally, and >50% of test results reported from only the Gauteng Province. Findings such as the SGTF therefore could not be extrapolated to regions where this assay was not being used.
Overall, this study is the first, to our knowledge, that highlights CQM using national program laboratory Ct values from multiple SARS-CoV-2 assays. The data strongly shows that variables of molecular test results can be a key part of laboratory quality management. It also highlights the multidisciplinary approach to CQM with the need to understand molecular technology, the need to understand the role of diagnostics in clinical and laboratory practices and the need to understand big data analytics and visualization. This study also highlights the value molecular diagnostics “near-real-time” analysis has in informing the need for sequencing. The introduction of rapid SARS-CoV-2 antigen tests, and self-tests however severely limits this value and ongoing molecular surveillance should be maintained. This system’s approach to quality management and program performance monitoring therefore should also be investigated for other disease use cases, such as TB and HIV, where molecular technology is the primary diagnostic test.
Author Contributions
Authors contributed in the following ways: LS, NH and GD contributed to conceptualization. LS, GD and JT performed the formal analyses, methodology and data visualization. HV and KM was responsible for data curation. LH, PM, PdS, WP and KM validated the data findings. LS and WS oversaw funding acquisition and project administration. LS prepared the original manuscript draft. NH, GD, WP, KM and WS reviewed the manuscript and contributed to the writing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Research reported in this publication was supported by the South African Medical Research Council with funds received from the Department of Science and Innovation. The content and findings reported are the sole deduction, view and responsibility of the researcher and do not reflect the official position and sentiments of the SAMRC or the Department of Science and Innovation. Research reported in this publication was also supported by the National Institute Of Allergy And Infectious Diseases of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number R01AI152126. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and those accessing the data were approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of The Human Research Ethics Committee of the University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa (protocol code M160978 9th October 2020) under the program ILDAC (Integrated Laboratory Data Analysis for Care) coordinated by PdS and WS.
Data Availability Statement
The National Health Laboratory Service data analyzed in this study is unavailable due to patient privacy and data restrictions. Data resides on the CDW for pathology services. Aggregated data may be accessible through the AARQA (Academic Affairs Research Office and Quality Assurance) division of the NHLS under leadership of KM.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the many NHLS laboratories who performed the SARS-CoV-2 tests analyzed in this study, the Virology Expert Committee of the NHLS and the SAMRC supported South African SARS-CoV-2 Variant Group whose technical, scientific and clinical insights in molecular diagnostics enabled this study to continue and add value to patient care in South Africa during the pandemic.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- https://www.statssa.gov.za/publications/P0302/P03022022.pdf. Mid-year population estimates, 2022. 2022.
- https://www.who.int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/data#profiles. Global Tuberculosis Programme. 2022.
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med 2020, 382, 727-733. [CrossRef]
- Baxter, C.; Abdool Karim, Q.; Abdool Karim, S.S. Identifying SARS-CoV-2 infections in South Africa: Balancing public health imperatives with saving lives. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2021, 538, 221-225. [CrossRef]
- Sethuraman, N.; Jeremiah, S.S.; Ryo, A. Interpreting Diagnostic Tests for SARS-CoV-2. JAMA 2020, 323, 2249-2251. [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.W.; Schmitz, J.E.; Persing, D.H.; Stratton, C.W. Laboratory Diagnosis of COVID-19: Current Issues and Challenges. J Clin Microbiol 2020, 58. [CrossRef]
- Bor, J.; Gage, A.; Onoya, D.; Maskew, M.; Tripodis, Y.; Fox, M.P.; Puren, A.; Carmona, S.; Mlisana, K.; MacLeod, W. Variation in HIV care and treatment outcomes by facility in South Africa, 2011-2015: A cohort study. PLoS Med 2021, 18, e1003479. [CrossRef]
- Stevens, W.S.; Scott, L.; Noble, L.; Gous, N.; Dheda, K. Impact of the GeneXpert MTB/RIF Technology on Tuberculosis Control. Microbiol Spectr 2017, 5. [CrossRef]
- https://www.samrc.ac.za/press-releases/south-africa-strengthens-its-fight-against-covid-19-through-international-solidarity. South Africa strengthens its fight against COVID-19 through international solidarity and the BRICS cooperation. 2020.
- https://www.nicd.ac.za/diseases-a-z-index/disease-index-covid-19/surveillance-reports/covid-19-special-reports/. COVID-19 SPECIAL REPORTS. 2020.
- Salyer, S.J.; Maeda, J.; Sembuche, S.; Kebede, Y.; Tshangela, A.; Moussif, M.; Ihekweazu, C.; Mayet, N.; Abate, E.; Ouma, A.O.; et al. The first and second waves of the COVID-19 pandemic in Africa: a cross-sectional study. Lancet 2021, 397, 1265-1275. [CrossRef]
- https://www.nicd.ac.za/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/COVID-19-Testing-Summary-Week-34-2021.pdf. COVID19 testing Summary South Africa: Week 34 2021. 2021.
- Msomi, N.; Mlisana, K.; de Oliveira, T.; Network for Genomic Surveillance in South Africa writing, g. A genomics network established to respond rapidly to public health threats in South Africa. Lancet Microbe 2020, 1, e229-e230. [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S.A.; Mueller, R. Real-time reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) and its potential use in clinical diagnosis. Clin Sci (Lond) 2005, 109, 365-379. [CrossRef]
- Valley-Omar, Z.e.a. Reduced amplification efficiency of the RNA-dependent-RNA-polymerase (RdRp) target enables tracking of the Delta SARS-CoV-2 variant using routine diagnostic tests. Under submission 2021.
- Scott, L.; Hsiao, N.Y.; Moyo, S.; Singh, L.; Tegally, H.; Dor, G.; Maes, P.; Pybus, O.G.; Kraemer, M.U.G.; Semenova, E.; et al. Track Omicron's spread with molecular data. Science 2021, 374, 1454-1455. [CrossRef]
- Plebani, M. Quality in laboratory medicine: 50years on. Clin Biochem 2017, 50, 101-104. [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Han, M.G.; Yoo, C.K.; Lee, S.W.; Chung, Y.S.; Park, J.S.; Kim, M.N.; Lee, H.; Hong, K.H.; Seong, M.W.; et al. Nationwide External Quality Assessment of SARS-CoV-2 Molecular Testing, South Korea. Emerg Infect Dis 2020, 26, 2353-2360. [CrossRef]
- Matheeussen, V.; Corman, V.M.; Donoso Mantke, O.; McCulloch, E.; Lammens, C.; Goossens, H.; Niemeyer, D.; Wallace, P.S.; Klapper, P.; Niesters, H.G.; et al. International external quality assessment for SARS-CoV-2 molecular detection and survey on clinical laboratory preparedness during the COVID-19 pandemic, April/May 2020. Euro Surveill 2020, 25. [CrossRef]
- Gorzer, I.; Buchta, C.; Chiba, P.; Benka, B.; Camp, J.V.; Holzmann, H.; Puchhammer-Stockl, E.; Aberle, S.W. First results of a national external quality assessment scheme for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 genome sequences. J Clin Virol 2020, 129, 104537. [CrossRef]
- Hughes, K.; Rao, S.N.; Manissero, D. The Role of Cycle Threshold values in Infectious Disease Diagnostics. 2021. https://www.mlo-online.com/continuing-education/article/21206319/the-role-of-cycle-threshold-values-in-infectious-disease-diagnostics.
- Salvatore, P.P.; Dawson, P.; Wadhwa, A.; Rabold, E.M.; Buono, S.; Dietrich, E.A.; Reses, H.E.; Vuong, J.; Pawloski, L.; Dasu, T.; et al. Epidemiological Correlates of PCR Cycle Threshold Values in the Detection of SARS-CoV-2. Clin Infect Dis 2020. [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.N.; Manissero, D.; Steele, V.R.; Pareja, J. A Systematic Review of the Clinical Utility of Cycle Threshold Values in the Context of COVID-19. Infect Dis Ther 2020, 9, 573-586. [CrossRef]
- Tom, M.R.; Mina, M.J. To Interpret the SARS-CoV-2 Test, Consider the Cycle Threshold Value. Clin Infect Dis 2020, 71, 2252-2254. [CrossRef]
- Scott, L.E.; Noble, L.D.; Singh-Moodley, A.; Kahamba, T.; Hardie, D.R.; Preiser, W.; Stevens, W.S. Challenges and complexities in evaluating severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 molecular diagnostics during the COVID-19 pandemic. Afr J Lab Med 2022, 11, 1429. [CrossRef]
- Tegally, H.; Moir, M.; Everatt, J.; Giovanetti, M.; Scheepers, C.; Wilkinson, E.; Subramoney, K.; Makatini, Z.; Moyo, S.; Amoako, D.G.; et al. Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron lineages BA.4 and BA.5 in South Africa. Nat Med 2022, 28, 1785-1790. [CrossRef]
- Elnifro, E.M.; Ashshi, A.M.; Cooper, R.J.; Klapper, P.E. Multiplex PCR: optimization and application in diagnostic virology. Clin Microbiol Rev 2000, 13, 559-570. [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.K.C.; Lam, W. Laboratory testing for the diagnosis of COVID-19. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2021, 538, 226-230. [CrossRef]
- https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/331329. Laboratory testing for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in suspected human cases: interim guidance, 2 March 2020. 2020.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).