1. Introduction
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations are common oncogenic alterations in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Activating somatic deletions in exon 19 (del19) and the single amino acid substitution L858R in exon 21 are the “classical” EGFR mutations, accounting for more than 85 % of all EGFR mutations in NSCLC patients (Harrison et al., 2020). The activating mutations of the EGFR genes in NSCLC lead to constitutive tyrosine kinase activity. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) were designed to bind the ATP-binding site of the EGFR kinase domain, thereby inhibiting its activity (da Cunha Santos et al., 2011).
EGFR TKIs of the first- or second generation such as gefitinib, erlotinib, afatinib, icotinib, and dacomitinib demonstrated higher overall response rate (ORR) and longer progression free survival (PFS) compared with chemotherapy and are therefore standard first-line treatments for EGFR-positive NSCLC (Harrison et al., 2020; Remon et al., 2018). Response rates are between 56 % to 74 % with a median progression-free survival of about twelve months (Buder et al., 2018). However, patients treated with first- and second-generation EGFR TKIs often develop acquired resistance and disease progression due to a substitution of threonine with methionine at position 790 in exon 20, also known as T790M mutation (Kobayashi et al., 2005). Several studies demonstrated a T790M-positivity rate between 66 % and 74 % in EGFR-TKI pretreated NSCLC patients, depending on the method used (Buder et al., 2018; Buder et al., 2019; Karlovich et al., 2016; Reungwetwattana T. et al., 2019). A better understanding of the acquired resistance mechanism led to the development of third-generation EGFR-TKIs such as osimertinib, which are active against exon 19 and 21 mutations as well as the T790M mutation.
Osimertinib was the first FDA and EMA approved third-generation EGFR-TKI which received marketing authorization in the first-line for patients with advanced tumors harboring activating EGFR mutations and for patients whose cancer cells show T790M mutations after prior EGFR-TKI treatments (Remon et al., 2018; Schmid et al., 2020). Osimertinib is an irreversible, oral TKI that demonstrated prolonged PFS compared to chemotherapy as a second-line treatment and was associated with higher response rates in patients with NSCLC harboring a T790M mutation (AURA study program: Goss et al., 2016; Jänne et al., 2015; Mok et al., 2017; Yang et al., 2017). These results led to the establishment of osimertinib as standard of care second-line treatment for EGFR T790M mutation-positive NSCLC (Liao et al., 2019; Nagasaka et al., 2021). The correct re-characterization of the tumor is therefore crucial for the initiation of a subsequent therapy for NSCLC patients who progressed under EGFR-TKI therapy. The detection of EGFR mutations in tumor tissue samples is sometimes difficult when insufficient tumor material is available and/or poor patient performance status or other clinical limitations do not allow invasive procedures.
Liquid biopsy is a powerful option for the molecular characterization of the patient´s tumor status by minimal-invasively collecting circulating tumor cells (CTCs) or circulating tumor cellular components from the plasma of patients (Rolfo et al., 2018). Cell-free circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) are highly fragmented genomic pieces resulting from tumor cell apoptosis, necrosis, or the secretion of extracellular vesicles (Jahr et al., 2001). ctDNA forms a tiny fraction (< 1 %) of total cell-free DNA and several technologies have been developed to detect EGFR mutations including amplified refractory mutation system (ARMS), digital droplet polymerase chain reaction (ddPCR), and next-generation sequencing (NGS). Commercially available kits, such as Roche Cobas® EGFR mutation test v1 and v2 (Cobas), use the allele-specific ARMS method to detect up to 1-5 % of mutant DNA. On the other hand, ddPCR and BEAMing (Beads, Emulsions, Amplification, and Magnetics) are a combination of digital PCR and flow cytometry and allow the detection of DNA to a threshold of 0.01-0.03 %. NGS can analyze key genes or screen the entire tumor genome for detecting novel mutations; the sensitivity may vary between NGS platforms, and exceptionally sensitive NGS-based methods have been described able to detect mutant DNA in the presence of 10,000 wild-type DNA molecules (Choo et al., 2018).
Liquid biopsy can be used to identify T790M mutations even if the tumor tissue is not available, thereby maximizing the number of patients which may benefit from subsequent treatment with osimertinib in case of T790M-positivity (Hochmair et al., 2019); indeed, analyses of blood samples from 119 patients who had progressed on first- or second-generation EGFR-TKI revealed a plasma T790M-positivity of 71 %. Minimal invasive plasma genotyping represents an attractive alternative for detection of T790M, and cell-free plasma DNA analysis can replace tissue analysis in selected cases (Buder et al., 2018). Previous studies showed that ddPCR detected a substantially higher number of T790M mutations in plasma samples compared to Cobas (Buder et al., 2019). Moreover, in a cross-platform comparison of different technologies for the detection of the T790M mutation, the digital platforms outperformed the non-digital platforms (Thress et al., 2015). It has been shown that digital PCR is clinically useful for the selection of patients who had progressed during first-line EGFR-TKI therapy for the treatment with osimertinib (Buder et al., 2018).
Since no quality standards for detecting EGFR alterations using liquid biopsy exist, different pathological laboratories use their own protocols and platforms of choice depending on individual factors, including turnaround time or cost. Therefore, the sensitivity of the methods can vary greatly among different institutions. However, an accurate testing strategy is needed to identify all patients with T790M correctly, so that patients can receive appropriate subsequent therapy. An inter-laboratory comparison of the individual liquid biopsy test strategies can provide insight into the performance of different methods currently used in a routine clinical practice.
The aim of this collaborative study was to evaluate the clinical routine use of liquid biopsy at different pathological laboratories in Central and Eastern Europe and to describe the possible differences in the sensitivity of the methods used. These results may therefore contribute to the development of a standardization in liquid biopsy testing of EGFR T790M mutations and lead to the identification of more T790M mutation-positive NSCLC patients after progression in need of a targeted subsequent therapy.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Participants
For feasibility reasons, a first testing wave was carried out in selected laboratories between May and July 2020. A second testing wave took place between May and August 2021, involving more laboratories in seven Central and Eastern European countries. All the laboratories remained anonymous. The laboratories used their own in-house methods of choice for the preparation and detection of the T790M mutation in the first testing wave and for the detection of T790M, del19, and L858R in the second testing wave.
2.2. Sample Panel Composition and Distribution
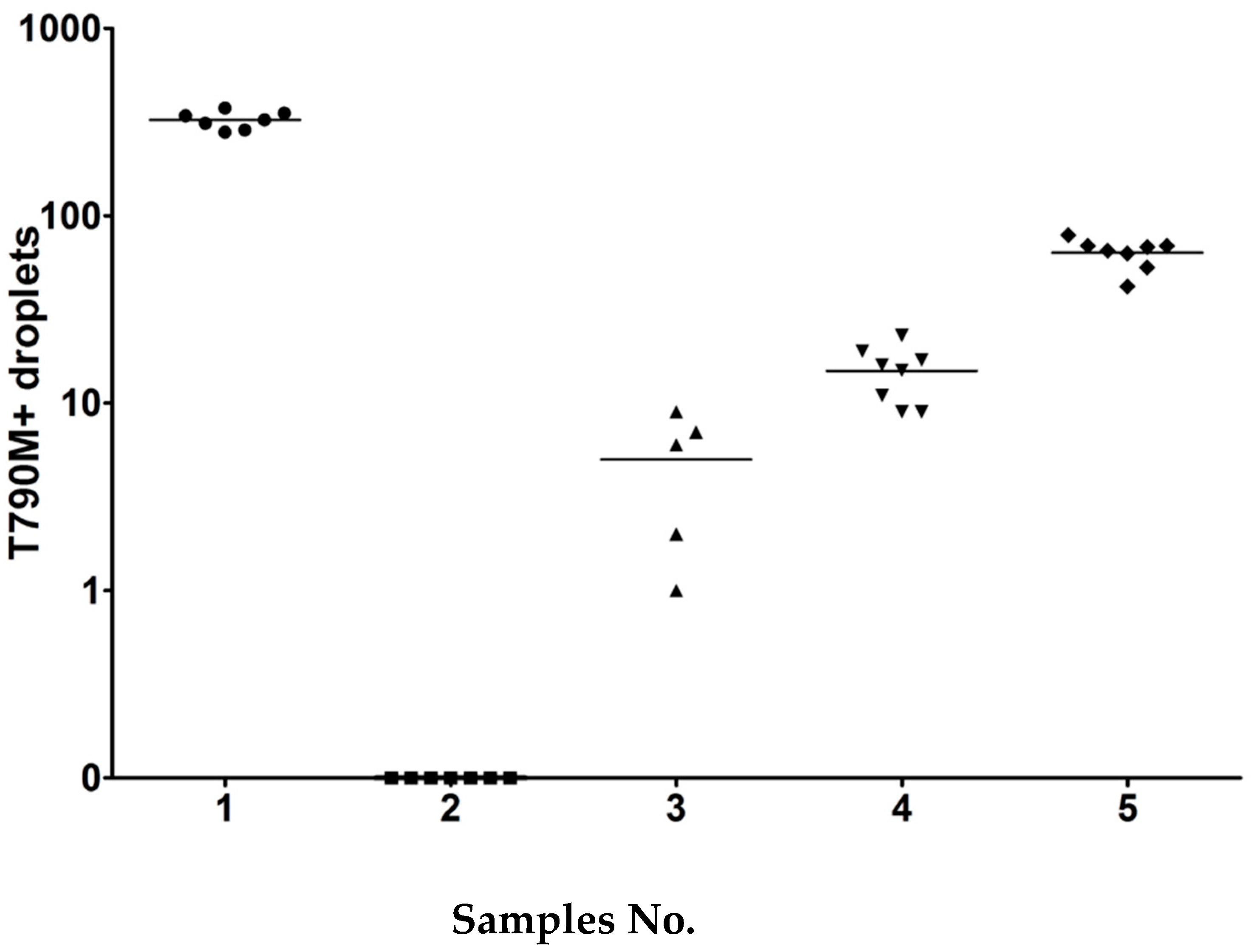
The sample panels were prepared in the Center for Cancer Research, Medical University of Vienna and shipped to each participant laboratories. In the first testing wave of the collaborative study, sets of five cell line DNA samples (0.1 mL) were prepared at different dilutions. Each set consisted of four positive samples and one negative sample. The entire sample should be used only for EGFR T790M testing as requested. Details of sample composition are shown in
Figure 1.
In the second testing wave of this collaborative study, sets of ten plasma samples with a total volume of 1 mL each were sent to each laboratory and should be tested for T790M, del19, and L858R mutations. The cell-lines used for spiking the plasma were HCC-8207 (T790M, del19), CRL-5908 (T790M, L858R), A549 and MCF-7 for EGFR wild-type (wt), respectively (
Table 1). DNA was isolated from HCC-8207 cells using the DNeasy Blood & Tissues kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to manufacturer’s instructions. Each plasma was spiked accordingly and contained various dilutions, except the negative control (sample No 3, 8). The samples No. 1 and 6 contained very high copy numbers of T790M plus del19, and 790M plus L858R, respectively, and should be detectable with any method. Samples No. 3 and 8 served as negative controls, and sample No. 2 was the challenging one with the fewest positive droplets (5 droplets for T790M and 7 for L858R). Three samples (sample No. 4, 7, 9) were at the threshold for Cobas with 25 to 34 copies, and two samples (No. 5, 10) with an intermediate range of droplets.
Information about the collaborative study and specific instructions for using the samples and reporting the results were sent per e-mail to each laboratory 2-3 weeks in advance to allow sufficient time to answer any remaining question about the procedure. All samples were coded to blind the assay, shipped frozen on dry ice to each laboratory and consisted of five (first testing wave) or ten samples (second testing wave) at various dilutions.
3. Results
A first testing wave was carried out to establish the procedure. In this first wave, twelve diagnostic laboratories from Austria (n=5), Bulgaria (n=1), Lithuania (n=1), Poland (n=4) and Switzerland (n=1) participated in the collaborative study (
Table 2A). In the second wave, 21 laboratories from Austria (n=9), Bulgaria (n=1), Croatia (n=1), Hungary (n=3), Lithuania (n=1), Poland (n=2), and Slovakia (n=4) joined the test (
Table 2B).
A summary of the methods used by the laboratories for DNA analytics is shown in
Table 3 for each wave. The method used was left to the laboratories and test result should be reported as in routine clinical practice. Two main platforms were used in the second testing wave in the collaborative study: PCR based platforms and next generation sequencing (NGS) platforms. The most utilized PCR-based platform in this collaborative study was the Cobas® z480, combined with the quantitative real-time Cobas® EGFR mutation test v2 (Cobas) method in eight laboratories; most of them used the Cobas® cfDNA Sample preparation kit for cfDNA isolation (n=5), other kits used were the Maxwell® RSC ccfDNA Plasma Kit (n=1), the Maxwell® 16 FFPE Plus LEV DNA Purification Kit (n=1) and the QIAsymphony DSP Circulating DNA Kit (n=1). The other PCR platforms used by the remaining laboratories were the following: Idylla
TM platform (n=2), QuantStudio 5 Dx Real-Time PCR System (n=2), EasyPGX® qPCR instrument 96 (n=1), LightCycler® 480 System (n=1), QX200 Droplet Digital PCR System (n=1), Real-time PCR cycler – Rotor -Gene 3000A (n=1) or shaking water bath (n=1). The NGS methods were used by four laboratories and included the following platforms and methods for DNA analytics: Ion S5 system with the Oncomine™ Lung cfDNA Assay (n=2), GeneReader Platform with the QIAamp MinElute ccfDNA Kit (n=1) or Nextseq 500 system with the Avenio ctDNA Targeted kit (n=1).
The results of the liquid biopsy testing from the different participating laboratories were received as expected. In the first wave, almost all laboratories detected sample No. 1 with the highest concentration of T790M. Only laboratory No. 7, which used Cobas/Entrogen for ctDNA-Isolation, reported the sample as negative (false negative). All laboratories correctly reported the negative sample (sample No. 2). The samples No. 3, 4, and 5, which contained different dilutions of HCC-8207 cell line DNA of T790M were recognized by 8, 10 and 11 laboratories for the samples No. 3, 4 and 5 respectively using either ddPCR, GeneReader, NGS, AmoyDx® EGFR 29 Mutations Detection Kit (AmoyDx), or EasyPGX® ready EGFR. Four laboratories using Cobas v2 or Cobas/Entrogen had difficulties to detect T790M, even though there were differences in the sensitivity and specificity between these laboratories: laboratory No. 4 had only problems with one sample (sample No. 3), whereas the other centers had two (lab No. 6) or three (lab No. 9) invalid results (
Table 4).
In the second testing wave of the test, two laboratories (lab No. 10 and 11) identified all samples correctly; most of the laboratories detected the activating mutations but not the T790M mutation (
Table 5A). In general, sample No. 2 was a very challenging one as it contained very low numbers of spiked DNA (5 T790M positive droplets). Sample No. 2 was found only by two centers (lab No. 10 and 11) which used AmoyDx kit as detection method and QX200 Droplet Digital PCR in combination with QIAamp Circulating Nucleic Acid kit as extraction method, respectively. In total, eight centers used the Cobas detection method (lab No. 4, 5, 6, 8, 18, 23, 24 and 25) (
Table 5B). The centers which used additionally the Cobas® extraction method detected all the requested samples as expected except sample No. 2. Laboratory No. 23, that used QIAsymphony DSP Circulating DNA Kit for extraction could also report all samples apart from sample No. 2 correctly. Laboratory No. 18, which used the Maxwell® RSC ccfDNA Plasma Extraction Kit had difficulties to detect the samples No. 4, 7, and 9, with DNA levels at the detection limit of the Cobas® method. Laboratory No. 24 used the Maxwell® 16 FFPE Plus LEV DNA Purification Kit to extract DNA that was not developed for the use in liquid biopsy. This lab was only able to report sample No. 1 correctly, since, obviously, it was not possible to sufficiently extract DNA from the samples.
Among the four centers using the AmoyDx kit (lab No. 1, 7, 10, and 22), one laboratory utilized the Cobas® cfDNA extraction sample preparation kit and classified all samples correctly (No. 10). The three other laboratories used AmoyDx® Circulating DNA Kit (lab No. 1), QIAamp Circulating Nucleic Acid kit (lab No. 7) or MagNA Pure 24 Total NA Isolation Kit for DNA extraction and detected all samples but one (sample No. 2) (
Table 5C).
Four laboratories used a NGS platform (No. 16, 17, 19, and 21) (
Table 5D); they interpreted the samples as expected - except for sample No. 2. Only laboratory No. 16, which used the Avenio ctDNA Targeted Kit and the Illumina platform NextSeq 500 System had difficulties in correctly detecting the dilutions and identified only three samples out of 10 (sample Nr. 1, 3, 6, and 8). An explanation might be found in the extraction step, as the DNA fragment size in the samples was bigger than normal ctDNA; this might have influenced the extraction process of these samples. This hypothesis is supported by the fact that the four correctly identified samples were the ones with the higher DNA concentration, as well as the negative samples.
Two centers (No. 3 and 20) used the detection and ctDNA extraction method from Idylla
TM ctEGFR Mutation Assay (Idylla) and showed a worse performance compared with the other methods used, as they detected four and seven samples out of a total of ten respectively (
Table 5E).
4. Discussion
This inter-laboratory comparison of ctDNA detection methods describes the performance of different PCR-based and NGS-based platforms for detecting T790M, del19, and L858R mutations of various laboratories across Central and Eastern Europe.
A first round (first testing wave) was performed to establish the collaborative study procedure. Centers that used the ddPCR detected all samples as expected, as well as centers using the AmoyDx kit, NGS, and EasyPGX® ready EGFR. Centers using Cobas had difficulties to detect various dilutions of T790M. One may consider that the highest dilution (sample No. 3) was below the threshold of this method. However, there were differences between the laboratories which used the Cobas system; laboratory No. 4 had only problems with one sample (sample No. 3), whereas the other centers had two (lab No. 6) or three (lab No. 9) invalid results.
In the second testing wave, most of the participating laboratories obtained the expected results using their in-house methods, despite differences in the platforms and the assay protocols used. Two centers, which used ddPCR and AmoyDx Kit, identified all samples correctly. Centers which used the Cobas extraction method combined with the Cobas ctDNA detection method identified all samples correctly, except the challenging sample No. 2 containing on average only five positive droplets of T790M. This amount was below the threshold of the Cobas method. Interestingly, some centers detected the activating mutation L858R and del19, others not. One laboratory using the Cobas detection method in combination with Maxwell® RSC ccfDNA Plasma Kit additionally did not detect samples No. 4, 7, and 9 containing low numbers of positive T790M/del 19 droplets, which were at the detection limit of the Cobas method. Another laboratory, which used the Cobas detection method in combination with the Maxwell® 16 FFPE Plus LEV DNA Purification Kit only detected sample No. 1 correctly. It is important to consider that the Maxwell® 16 FFPE Plus LEV DNA Purification Kit was developed to extract DNA from tissue samples and not from liquid biopsy. This procedure was chosen by the participating lab that routinely does not utilize liquid biopsy to verify if the extraction method established in-house would have the potential to be used in liquid biopsy. This result emphasizes the importance of using established and specific methods or procedures at any step of the analysis to get reliable results. Most of the laboratories using an NGS platform detected the samples as expected; only one laboratory (No. 16), which used the Avenio ctDNA Targeted Kit after extraction with Maxwell® RSC ccfDNA Plasma Kit and the NextSeq 500 System did not detect samples No. 2, 4, 5, 7, 9 and 10 containing low number of positive T790M/del19 droplets. This might be due to the long DNA fragments, which may interfere with the method. Two laboratories, which used the detection and ctDNA extraction method from Idylla, showed a low performance as the results were not comparable with those obtained with the other detection methods analyzed. For one laboratory using Idylla, the volume of the sample (1 mL) was a problem; this was because Idylla requires 2 mL samples and the laboratory had difficulties in handling the samples. The laboratory divided the sample into two aliquots and tested them with two different methods (Idylla and Cobas). This leads to an underperformance of the methods, because the samples where then under the threshold for these methods; this might explain partly the worse performance of Idylla.
Factors that may influence the accuracy of liquid biopsy are the pre-analytics, DNA analytics, and the biological variability. For the pre-analytics, the type of blood tubes used are important; DNA can be stored at room-temperature for several days by using blood conserving tubes (BCTs), but samples should be processed within one or maximal two hours with EDTA-tubes. Time and temperature between blood collection and processing the plasma (BCTs should not be frozen during transport), centrifugation conditions, methods of quantification and protocols used to isolate ctDNA are other critical factors in successfully performing liquid biopsy. In this collaborative study, we did not control the pre-analytics, except the protocol for ctDNA isolation. Robustness, analytical specificity and sensitivity of the test procedure, intrinsic errors in the PCR methodology, and technological sources of error are critical factors in DNA analytics. Regarding the biological variability, the time point of sampling might as well influence the outcome of liquid biopsy.
Any method, either PCR- or NGS-based, can be used to detect the T790M mutation. However, if a method with lower sensitivity is used, the result should be checked again in case of a negative result, either by repeating the liquid biopsy and/or performing an additional tissue biopsy. If the response to the treatment is no longer given, or the patient’s condition deteriorates, the detection method should be repeated as soon as possible. If time is not a critical factor, the liquid biopsy can be repeated in an interval of two to three weeks.
In this collaborative study, ddPCR and AmoyDx detected all samples. Only these two methods identified the challenging sample No. 2 containing very low concentration of spiked DNA with the T790M mutation (average number of five positive droplets). Laboratories using Cobas performed within the detection limit of the Cobas method; only sample No. 2 was below 25 copies/mL, which is under the detection limit of Cobas. Therefore, it was expected that most Cobas® using laboratories should identify 90 % of the samples, which was mainly the case. However, most of the samples in the clinical routine are under the threshold of 10 copies/mL, and this is possibly the reason why so many patients are not correctly identified and therefore cannot benefit from a subsequent therapy in a timely manner. Previous data have shown a response rate of 61 % in T790M positive patients with ddPCR (Buder et al., 2019). The response to osimertinib is independent of the copy number of the resistance mutations. However, recent data indicate that the copy number of the original activating mutation is important for a response to osimertinib (Buder et al., 2021).
The test had several limitations: we did not control the pre-analytics (except ctDNA extraction); moreover, DNA was not crushed into small fragments (< 150 bp size), which might be a problem for some of the methods. There was only one sample with low copy number (< 10 copies/ml) available for testing.
The emergence of the acquired EGFR T790M resistance mutation after first- or second-generation EGFR-TKIs in EGFR-positive NSCLC has led to the development of third-generation TKIs. Liquid biopsy is a powerful tool and useful in identifying T790M mutations (Hochmair et al., 2019). The correct re-characterization of patients, who have progressed on first- or second-generation TKIs and a reliable method to detect the T790M mutation, is key for the initiation of the subsequent second-line therapy and a favorable outcome for the patient.
5. Conclusions
EGFR testing using liquid biopsy may provide more therapy options for patients with EGFR-positive NSCLC. This is particularly important with respect to the sequential management of EGFR TKIs. The detection of T790M resistance mutations has crucial consequences on the subsequent second-line therapy with a third-generation EGFR-TKI such as osimertinib. As no global standards for testing T790M mutations in liquid biopsy currently exist, the present collaborative study describes the in-house liquid biopsy methods and their sensitivity against T790M, del19 and the L858R mutation. The results might offer an essential contribution to ensure high quality standards and contribute to the development of a standard EGFR T790M testing in liquid biopsy.
Supplementary Materials
Liquid biopsy collaborative study group – names and affiliations: Austria: Maximilian Prinz-Wohlgenannt, Gabriele Benetka, Institute for Clinical Pathology and Molecular Pathology, Hospital Horn, Austria; Martin Hyden, Elisabeth Schintler, Institute for Pathology, Hospital Klagenfurt/Wörthersee, Austria; Christian Paar, Christa Kubasta, Institute of Laboratory Medicine, Kepler University Hospital Linz, Austria; Christina Schuster, Elisabeth Muckenschnabel, Institute for Clinical Pathology and Molecular Pathology, Hospital Mistelbach, Austria; Selma Hönigschnabl, Edith Perkovits, Institute for Pathology and Bacteriology, Hospital Donaustadt, Vienna, Austria; Ulrike Setinek, Cornelia Aigner, Institute for Pathology and Microbiology, Hospital Ottakring, Vienna, Austria; Leonhard Müllauer, Felicitas Oberndorfer, Department of Pathology, Medical University of Vienna, Austria; Wolfgang Hulla, Tamara Kalchbrenner, Institute for Clinical Pathology and Molecular Pathology Thermenregion, Wiener Neustadt, Austria; Peter Obrist, Jasmin Mustedanagic, Tyrolpath Obrist Brunhuber GmbH, Molecular Pathology, Zams, Austria. Bulgaria: Alexey Savov, Stoyan Bichev, University Hospital "Maichin Dom", National Genetics Laboratory, Sofia, Bulgaria. Croatia: Lovorka Batelja-Vuletic, Department of Pathology, University of Zagreb School of Medicine, Croatia and University Hospital Centre Zagreb, Croatia; Gordana Bubanovic, Laboratory for Molecular Pathology, Department of Pathology, University of Zagreb School of Medicine, Croatia and University Hospital Centre Zagreb, Croatia. Hungary: Erzsébet Csernák, Erika Tóth, National Institute of Oncology, Department of Surgical and Molecular Pathology, Budapest, Hungary; Csaba Bödör, Gergő Papp, Molecular Diagnostic Division, Department of Pathology and Experimental Cancer Research, Semmelweis University, Budapest, Hungary; Attila Mokánszki, Gábor Méhes, Department of Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Debrecen, Hungary. Lithuania: Vaida Kutkienė, Dovilė Kalikauskienė Vabalienė, Hospital of Lithuanian University of Health Sciences Kauno Klinikos, Lithuania. Poland: Bartłomiej Budny, Elżbieta Wrotkowska, E.J. Zeyland Wielkopolska Center of Pulmonology and Thoracic Surgery, 60-569 Poznań and Department of Endocrinology, Metabolism and Internal Medicine, Poznan University of Medical Sciences, 60-355 Poznań, Poland; Andrzej Tysarowski, Cancer Molecular and Genetic Diagnostics Department and Department of Molecular and Translational Oncology, Maria Sklodowska-Curie National Research Institute of Oncology, Warsaw, Poland; Katarzyna Seliga, Department of Molecular and Translational Oncology, Maria Sklodowska-Curie National Research Institute of Oncology, Warsaw, Poland. Slovakia: Ľuboslav Mihók, Imrich Hikkel, National Cancer Institute, Department of Medical Genetics, Bratislava, Slovakia; František Gmitter, Lucia Fröhlichová, Luis Pasteur University Hospital Košice, Department of Pathology, Kosice, Slovakia; Jana Verebová, Slavka Kormaniková, Unilabs Slovakia s. r. o., Laboratory of Medical Genetics, Kosice, Slovakia; Anna Farkašová, Lukáš Plank, Martin´s Biopsy Center, Ltd., Martin, Slovakia.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: Martin Filipits, Viktor Sebek, Herwig Zach; Data curation: all authors; Formal analysis: all authors; Funding acquisition: Martin Filipits, Herwig Zach; Investigation: all authors; Methodology: all authors; Project administration: Martin Filipits, Viktor Sebek, Herwig Zach; Resources: Martin Filipits, Viktor Sebek, Herwig Zach; Supervision: Martin Filipits, Viktor Sebek, Herwig Zach; Roles/Writing - original draft: all authors; Writing - review & editing: all authors.
Funding
The conduct of the reported collaborative study and medical writing assistance were supported by Boehringer Ingelheim RCV GmbH & Co KG.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Eva Eckelhart, PhD, and Florence Boulmé, PhD, for writing assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
Martin Filipits reports personal fees from AstraZeneca, Biomedica, Biorad, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Merck, Novartis, and Pfizer. Verena Kainz declares no conflict of interest. Viktor Sebek was a former employee of Boehringer Ingelheim RCV GmbH & Co KG company during the conduct and first analysis of the results presented in this study. Herwig Zach is employee of Boehringer Ingelheim RCV GmbH & Co KG.
References
- SMPC Tagrisso. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/tagrisso.
- Buder, A., et al., 2021. The Allele Frequency of EGFR Mutations Predicts Survival in Advanced EGFR T790M-Positive Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Osimertinib. Target Oncol. 16, 77-84. [CrossRef]
- Buder, A., et al., 2018. Cell-Free Plasma DNA-Guided Treatment With Osimertinib in Patients With Advanced EGFR-Mutated NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol. 13, 821-830. [CrossRef]
- Buder, A., et al., 2019. EGFR Mutations in Cell-free Plasma DNA from Patients with Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma: Improved Detection by Droplet Digital PCR. Target Oncol. 14, 197-203. [CrossRef]
- Choo, J. R., et al., 2018. Treatment of EGFR T790M-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Target Oncol. 13, 141-156. [CrossRef]
- da Cunha Santos, G., et al., 2011. EGFR mutations and lung cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 6, 49-69. [CrossRef]
- Goss, G., et al., 2016. Osimertinib for pretreated EGFR Thr790Met-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (AURA2): a multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 17, 1643-1652. [CrossRef]
- Harrison, P. T., et al., 2020. Rare epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 61, 167-179. [CrossRef]
- Hochmair, M. J., et al., 2019. Liquid-Biopsy-Based Identification of EGFR T790M Mutation-Mediated Resistance to Afatinib Treatment in Patients with Advanced EGFR Mutation-Positive NSCLC, and Subsequent Response to Osimertinib. Targeted oncology. 14, 75-83. [CrossRef]
- Jahr, S., et al., 2001. DNA fragments in the blood plasma of cancer patients: quantitations and evidence for their origin from apoptotic and necrotic cells. Cancer Res. 61, 1659-65.
- Jänne, P. A., et al., 2015. AZD9291 in EGFR inhibitor-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 372, 1689-99. [CrossRef]
- Karlovich, C., et al., 2016. Assessment of EGFR Mutation Status in Matched Plasma and Tumor Tissue of NSCLC Patients from a Phase I Study of Rociletinib (CO-1686). Clin Cancer Res. 22, 2386-95. [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S., et al., 2005. EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 352, 786-92. [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.-C., et al., 2019. Second-line treatment of EGFR T790M-negative non-small cell lung cancer patients. Therapeutic advances in medical oncology. 11, 1758835919890286-1758835919890286. [CrossRef]
- Mok, T. S., et al., 2017. Osimertinib or Platinum-Pemetrexed in EGFR T790M-Positive Lung Cancer. N Engl J Med. 376, 629-640. [CrossRef]
- Nagasaka, M., et al., 2021. Beyond Osimertinib: The Development of Third-Generation EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors For Advanced EGFR+ NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol. 16, 740-763. [CrossRef]
- Remon, J., et al., 2018. Osimertinib and other third-generation EGFR TKI in EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients. Ann Oncol. 29, i20-i27. [CrossRef]
- Reungwetwattana T., et al., 2019. Longitudinal circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) monitoring for early detection of disease progression and resistance in advanced NSCLC in FLAURA. Annals of Oncology. 30 (suppl_9).
- Rolfo, C., et al., 2018. Liquid Biopsy for Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): A Statement Paper from the IASLC. J Thorac Oncol. 13, 1248-1268. [CrossRef]
- Schmid, S., et al., 2020. Mechanisms of osimertinib resistance and emerging treatment options. Lung Cancer. 147, 123-129. [CrossRef]
- Thress, K. S., et al., 2015. EGFR mutation detection in ctDNA from NSCLC patient plasma: A cross-platform comparison of leading technologies to support the clinical development of AZD9291. Lung Cancer. 90, 509-15. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J. C., et al., 2017. Osimertinib in Pretreated T790M-Positive Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: AURA Study Phase II Extension Component. J Clin Oncol. 35, 1288-1296. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).